Decision Support Model for Evaluating Alternative Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Management Schemes—A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Research Question 1—What is the mathematical formulation of a decision support model for the assessment of alternative WEEE management scenarios under specific criteria?
- Research Question 2—What are recommended performance criteria for the assessment of alternative WEEE management schemes?
- Research Question 3—Which could be a viable WEEE management strategy for the case of Greece?
2. Materials and Methods
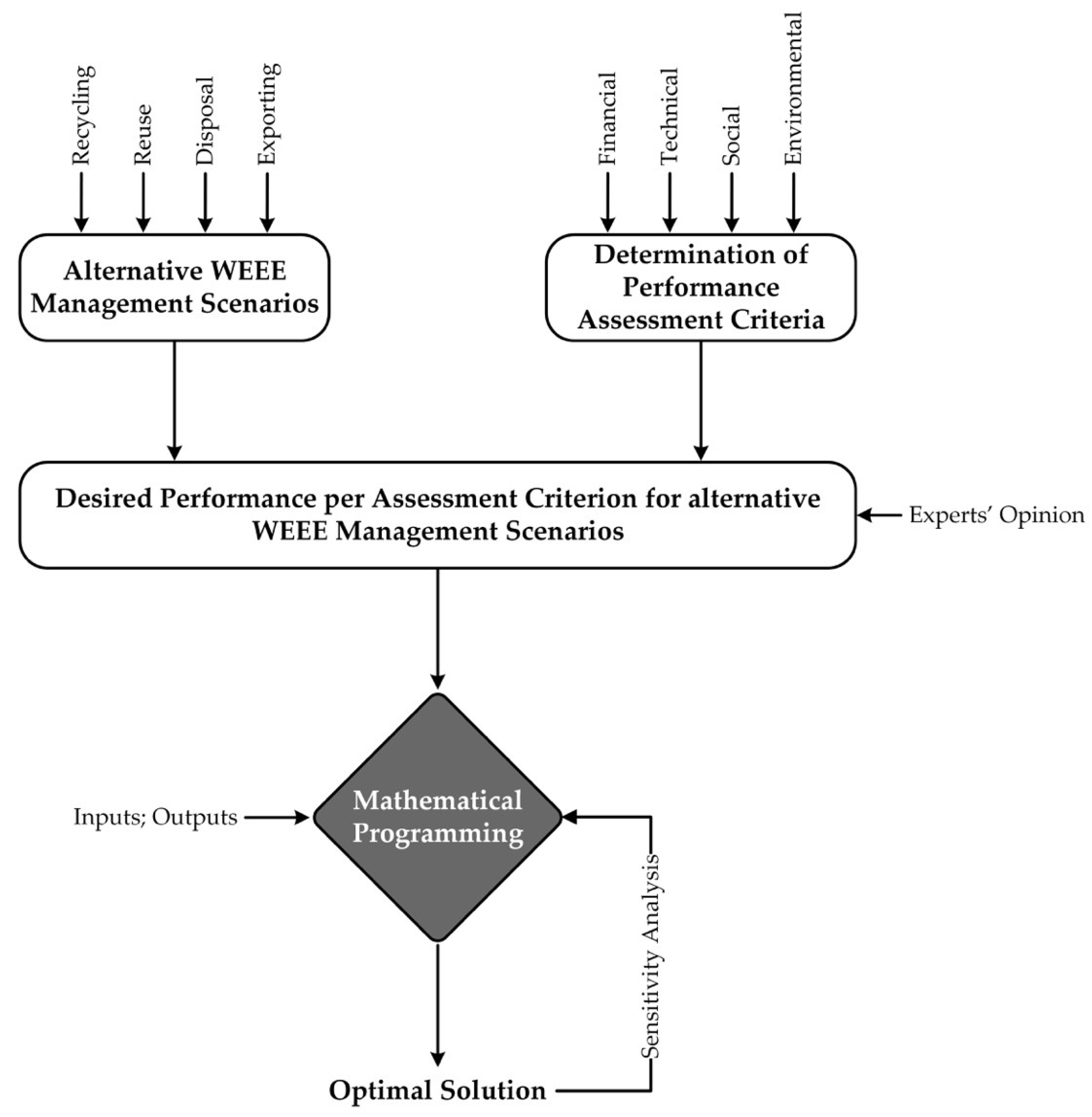
2.1. Methodological Framework
2.2. Decision Support Model
2.3. Application Scenarios
- Recycling (Scenarios Rec1–Rec3)
- Reuse (Scenarios Reu1–Reu2)
- Disposal (Scenarios Disp1–Disp2)
- Exporting (Scenarios Exp1–Exp2).
2.4. Assessment Criteria
3. Results
4. Discussion
- coefficient e2 (second priority level) ranging from 0.10 to 0.95 with an increment step of 0.05;
- coefficient e3 (third priority level) ranging from 0.05 to 0.90 with an increment step of 0.05.
5. Conclusions
5.1. Practical Implications
5.2. Limitations and Future Research Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Achillas, C.; Vlachokostas, C.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Banias, G. Decision support system for the optimal location of electrical and electronic waste treatment plants: A case study in Greece. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongondo, F.O.; Williams, I.D.; Cherrett, T.J. How are WEEE doing? A global review of the management of electrical and electronic wastes. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 714–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Forssberg, E. Mechanical recycling of waste electric and electronic equipment: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 99, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Li, G.; Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Xu, M.; Huang, C. WEEE recovery strategies and the WEEE treatment status in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hischier, R.; Wäger, P.; Gauglhofer, J. Does WEEE recycling make sense from an environmental perspective? The environmental impacts of the Swiss take-back and recycling systems for waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE). Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2005, 25, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiruga, D.; Walther, G.; Gonzalez-Benito, J.; Spengler, T. Evaluation of sites for the location of WEEE recycling plants in Spain. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldé, C.P.; Forti, V.; Gray, V.; Kuehr, R.; Stegmann, P. The Global E-waste Monitor–2017, United Nations University (UNU), International Telecommunication Union (ITU) & International Solid Waste Association (ISWA). Bonn/Geneva/Vienna 2018. Available online: https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-D/Climate-Change/Documents/GEM%202017/Global-E-waste%20Monitor%202017%20.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2019).
- Bahers, J.-B.; Kim, J. Regional approach of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) management in France. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 129, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguchi, M.; Sakanakura, H.; Terazono, A.; Takigami, H. Fate of metals contained in waste electrical and electronic equipment in a municipal waste treatment process. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, K. Producing usable materials from e-waste. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6782–6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakakis, E.; Janz, A.; Bilitewski, B.; Gidarakos, E. Small WEEE: Determining recyclables and hazardous substances in plastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovou, E.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Xanthopoulos, A.; Achillas, C.; Michailidis, N.; Chatzipanagioti, M. Multicriteria Matrix: A methodology for end-of-life management. Resources, Conserv. Recycl. 2009, 53, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnorom, I.C.; Osibanjo, O. Toxicity characterization of waste mobile phone plastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.H. E-waste: An assessment of global production and environmental impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuidwijk, R.; Krikke, H. Strategic response to EEE returns: Product eco-design or new recovery processes? Eur. J. Op. Res. 2008, 191, 1206–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckinger, P.; Glachant, M. The organization of extended producer responsibility in waste policy with product differentiation. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2010, 59, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achillas, C.; Vlachokostas, C.; Aidonis, D.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Iakovou, E.; Banias, G. Optimising reverse logistics network to support policy-making in the case of electrical and electronic equipment. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2592–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, P.; Bernardes, A.M.; Huda, N. Ensuring best E-waste recycling practices in developed countries: An Australian example. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lopez, N.B.N.; Liu, L.; Zhao, N.; Yu, K.; Zheng, L. Regional or global WEEE recycling. Where to go? Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namlis, K.-G.; Komilis, D. Influence of four socioeconomic indices and the impact of economic crisis on solid waste generation in Europe. Waste Manag. 2019, 89, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat. Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE). Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/waste/key-waste-streams/weee (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Islam, M.T.; Huda, N. Reverse logistics and closed-loop supply chain of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)/E-waste: A comprehensive literature review. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 137, 48–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannidis, A.; Perkoulidis, G.; Papadopoulos, A.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Tsatsarelis, T. Characteristics of wastes from electric and electronic equipment in Greece: Results of a field survey. Waste Manag. Res. 2005, 23, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussiopoulos, N.; Karagiannidis, A.; Papadopoulos, A.; Achillas, C.; Antonopoulos, I.S.; Perkoulidis, G.; Vlachos, D.; Vlachokostas, C. Transportation cost analysis of the Hellenic system for alternative management of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2012, 10, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achillas, C.; Vlachokostas, C.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Perkoulidis, G.; Banias, G.; Mastropavlos, M. Electronic waste management cost: A scenario-based analysis for Greece. Waste Manag. Res. 2011, 29, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, T. WEEE, WEEE, WEEE, WEEE, all the way home? An evaluation of proposed electrical and electronic waste legislation. Eur. Environ. 2000, 10, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottberg, A.; Morris, J.; Pollard, S.; Mark-Herbert, C.; Cook, M. Producer responsibility, waste minimisation and the WEEE Directive: Case studies in eco-design from the European lighting sector. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 359, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallawarachchi, H.; Karunasena, G. Electronic and electrical waste management in Sri Lanka: Suggestions for national policy enhancements. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 68, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiruga, D.; González Benito, J.; Lannelongue, G. Evolution of the electronic waste management system in Spain. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 24, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousis, K.; Moustakas, K.; Malamis, S.; Papadopoulos, A.; Loizidou, M. Multi-criteria analysis for the determination of the best WEEE management scenario in Cyprus. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1941–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torretta, V.; Ragazzi, M.; Istrate, I.A.; Rada, E.C. Management of waste electrical and electronic equipment in two EU countries: A comparison. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanskanen, P. Management and recycling of electronic waste. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J. A comparative analysis of DEA as a discrete alternative multiple criteria decision tool. Eur. J. Op. Res. 2000, 123, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achillas, C.; Aidonis, D.; Vlachokostas, C.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Banias, G.; Triantafillou, D. A multi-objective decision-making model to select waste electrical and electronic equipment transportation media. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 66, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.; Metternicht, G. Assessing effectiveness of WEEE management policy in Australia. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Yang, J.; Ijomah, W.; Wu, W.; Zlamparet, G. Perspectives on reuse of WEEE in China: Lessons from the EU. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 135, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dixit, G. Evaluating critical barriers to implementation of WEEE management using DEMATEL approach. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 131, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, K.; Lichrou, M.; Fitzpatrick, C. Treasured trash? A consumer perspective on small Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) divestment in Ireland. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 145, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Hanafiah, M.M. An overview of LCA application in WEEE management: Current practices, progress and challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, O.; Capraz, O.; Gungor, A. Modelling of WEEE recycling operation planning under uncertainty. J. Clean. Prod 2018, 180, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messmann, L.; Helbig, C.; Thorenz, A.; Tuma, A. Economic and environmental benefits of recovery networks for WEEE in Europe. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Definition |
|---|---|
| Binary decision variable that determines the selection or not of solution i: Yi = 0 the solution i is not recommended Yi = 1 the solution i is proposed |
| Parameter | Definition |
| Desired value for input criteria with positive effect (in+) in priority level j | |
| Desired value for input criteria with negative effect (in−) in priority level j | |
| Desired value for output criteria with positive effect (out+) in priority level j | |
| Desired value for output criteria with negative effect (out−) in priority level j | |
| Performance of solution i in input criteria with positive effect (in+) in priority level j | |
| Performance of solution i in input criteria with negative effect (in−) in priority level j | |
| Performance of solution i in output criteria with positive effect (out+) in priority level j | |
| Performance of solution i in output criteria with negative effect (out−) in priority level j | |
| A very large number (compared to the other parameters of the model) | |
| Coefficient with a domain 0 to 1 |
| E-Waste Management Concept | Scenario | Description—Process Flow |
|---|---|---|
| Recycling | Rec1 | Collection of e-waste → Recycling and recovery of useful and precious quantities → Disposal of residues in landfills |
| Rec2 | Collection of e-waste → Recycling and recovery of useful and precious quantities → Incineration of residues | |
| Rec3 | Collection of e-waste → Recycling and recovery of useful and precious quantities → Export of hazardous waste and residues | |
| Reuse | Reu1 | Collection of e-waste → Control of reusability → Recovery of devices or components → Disposal of residues in landfills or incineration |
| Reu2 | Collection of e-waste → Control of reusability → Recovery of devices or components → Recycling-disposal of residues in landfill or incineration | |
| Disposal | Disp1 | Collection of e-waste → Disposal in landfills |
| Disp2 | Collection of e-waste → Incineration | |
| Exporting | Exp1 | Collection of e-waste → Export of collected quantities for further processing |
| Exp2 | Collection of e-waste → Recovery of reusable materials and components → Export of non-reusable material |
| Thematic Area | Criterion | Description of Criterion | Type | Priority Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial | F1 | Investment cost | Input (−) | 1st |
| F2 | Operational cost | Input (−) | 2nd | |
| F3 | Collection cost | Input (−) | 2nd | |
| F4 | Profit from reused products | Output (+) | 2nd | |
| Technical | T1 | Existence of infrastructure | Input (+) | 3rd |
| T2 | Reliability and experience | Input (+) | 3rd | |
| T3 | Flexibility | Output (+) | 3rd | |
| Social | S1 | Social acceptance | Output (+) | 1st |
| S2 | Employment opportunities | Output (+) | 3rd | |
| Environmental | E1 | Air, water and solid waste pollution | Output (−) | 2nd |
| E2 | Noise and aesthetics pollution | Output (−) | 3rd | |
| E3 | Energy and material recovery | Output (−) | 3rd |
| Scenario | Assessment Criterion | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | T1 | T2 | T3 | S1 | S2 | E1 | E2 | E3 | |
| Rec1 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 6.3 | 3.6 | 3.1 | 4.1 | 5.2 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 2.2 |
| Rec2 | 6.7 | 5.8 | 5.1 | 1.0 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 2.8 | 2.2 | 5.4 | 2.7 | 3.1 | 4.8 |
| Rec3 | 1.9 | 1.3 | 4.2 | 1.0 | 6.3 | 2.7 | 3.0 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| Reu1 | 2.8 | 2.2 | 6.1 | 5.3 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 6.7 | 6.4 | 4.2 | 3.6 | 5.4 |
| Reu2 | 5.7 | 5.9 | 6.1 | 5.3 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 6.7 | 6.4 | 3.6 | 3.4 | 6.2 |
| Disp1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 6.8 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 7.0 | 5.2 | 1.0 |
| Disp2 | 5.8 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.7 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 6.4 | 4.9 | 2.2 |
| Exp1 | 3.1 | 2.0 | 5.2 | 1.0 | 6.1 | 3.1 | 3.3 | 2.4 | 1.1 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 1.0 |
| Exp2 | 3.6 | 5.1 | 6.1 | 5.3 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 3.1 | 6.4 | 6.2 | 4.0 | 3.2 | 5.8 |
| Desired value | 5.2 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 1.05 | 2.0 | 2.3 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 4.3 | 4.4 |
| Case | Values for e2, e3 | Recommended Scenario | Objective Function Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | e2 = 0.10 | Reu1 | 8.93 |
| e3 = 0.05 | |||
| 2 | e2 = 0.15 | Reu1 | 8.93 |
| e3 = 0.10 | |||
| 3 | e2 = 0.20 | Reu1 | 8.93 |
| e3 = 0.15 | |||
| 4 | e2 = 0.25 | Reu1 | 8.93 |
| e3 = 0.20 | |||
| 5 | e2 = 0.30 | Reu1 | 8.93 |
| e3 = 0.25 | |||
| 6 | e2 = 0.35 | Reu1 | 8.93 |
| e3 = 0.30 | |||
| 7 | e2 = 0.40 | Reu1 | 8.93 |
| e3 = 0.35 | |||
| 8 | e2 = 0.45 | Reu1 | 8.93 |
| e3 = 0.40 | |||
| 9 | e2 = 0.50 | Reu1 | 8.93 |
| e3 = 0.45 | |||
| 10 | e2 = 0.55 | Reu1 | 8.93 |
| e3 = 0.50 | |||
| 11 | e2 = 0.60 | Reu1 | 8.93 |
| e3 = 0.55 | |||
| 12 | e2 = 0.65 | Reu1 | 8.93 |
| e3 = 0.60 | |||
| 13 | e2 = 0.70 | Rec3 | 6.48 |
| e3 = 0.65 | |||
| 14 | e2 = 0.75 | Rec3 | 6.48 |
| e3 = 0.70 | |||
| 15 | e2 = 0.80 | Rec3 | 6.48 |
| e3 = 0.75 | |||
| 16 | e2 = 0.85 | Rec3 | 6.48 |
| e3 = 0.80 | |||
| 17 | e2 = 0.90 | Rec3 | 6.48 |
| e3 = 0.85 | |||
| 18 | e2 = 0.95 | Rec3 | 6.48 |
| e3 = 0.90 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aidonis, D.; Achillas, C.; Folinas, D.; Keramydas, C.; Tsolakis, N. Decision Support Model for Evaluating Alternative Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Management Schemes—A Case Study. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3364. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123364
Aidonis D, Achillas C, Folinas D, Keramydas C, Tsolakis N. Decision Support Model for Evaluating Alternative Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Management Schemes—A Case Study. Sustainability. 2019; 11(12):3364. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123364
Chicago/Turabian StyleAidonis, Dimitrios, Charisios Achillas, Dimitrios Folinas, Christos Keramydas, and Naoum Tsolakis. 2019. "Decision Support Model for Evaluating Alternative Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Management Schemes—A Case Study" Sustainability 11, no. 12: 3364. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123364
APA StyleAidonis, D., Achillas, C., Folinas, D., Keramydas, C., & Tsolakis, N. (2019). Decision Support Model for Evaluating Alternative Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Management Schemes—A Case Study. Sustainability, 11(12), 3364. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123364








