Research on the Spatial–Temporal Synthetic Measurement of the Coordinated Development of Population-Economy-Society-Resource-Environment (PESRE) Systems in China Based on Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methods and Collected Data
2.1. Research Index and Data
2.1.1. The Index System and Data Sources
2.1.2. Data Standardization
2.2. The Coupling Coordination Degree Measurement
2.2.1. Coupling Coordination Models
- 1)
- Calculate the comprehensive evaluation index of each subsystem using the following formula:where is the weighted value of the ith index; rij is the standardized value of the ith index within the jth research area; m is the number of index in subsystem; and is the synthetic assessment index of the gth subsystem.
- 2)
- Calculate the coupling degree of the five major systems, namely, population, economy, society, resources, and environment systems using the following formula:where is the coupling degree, with its value in the range of 0 and 1; and represent the synthetic assessment index of the population, economy, society, resources, and environment subsystems, respectively.
- 3)
- Calculate the coupling coordination degree in order to evaluate the level of the coupling coordinated development between systems using the following formula:where D is the coupling coordination degree; T is the synthetic assessment index of the five systems; and a, b, c, d, and e represent the undetermined coefficients. Given that the factors of population, economy, society, resources, and environment are equally important, and based on information provided by the relevant references [3,31,32], the undetermined coefficients are defined as .
2.2.2. Weight Determination
2.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis Models
2.3.1. The Global Moran’s I
2.3.2. The Local Moran’s I
3. Results and Discussion
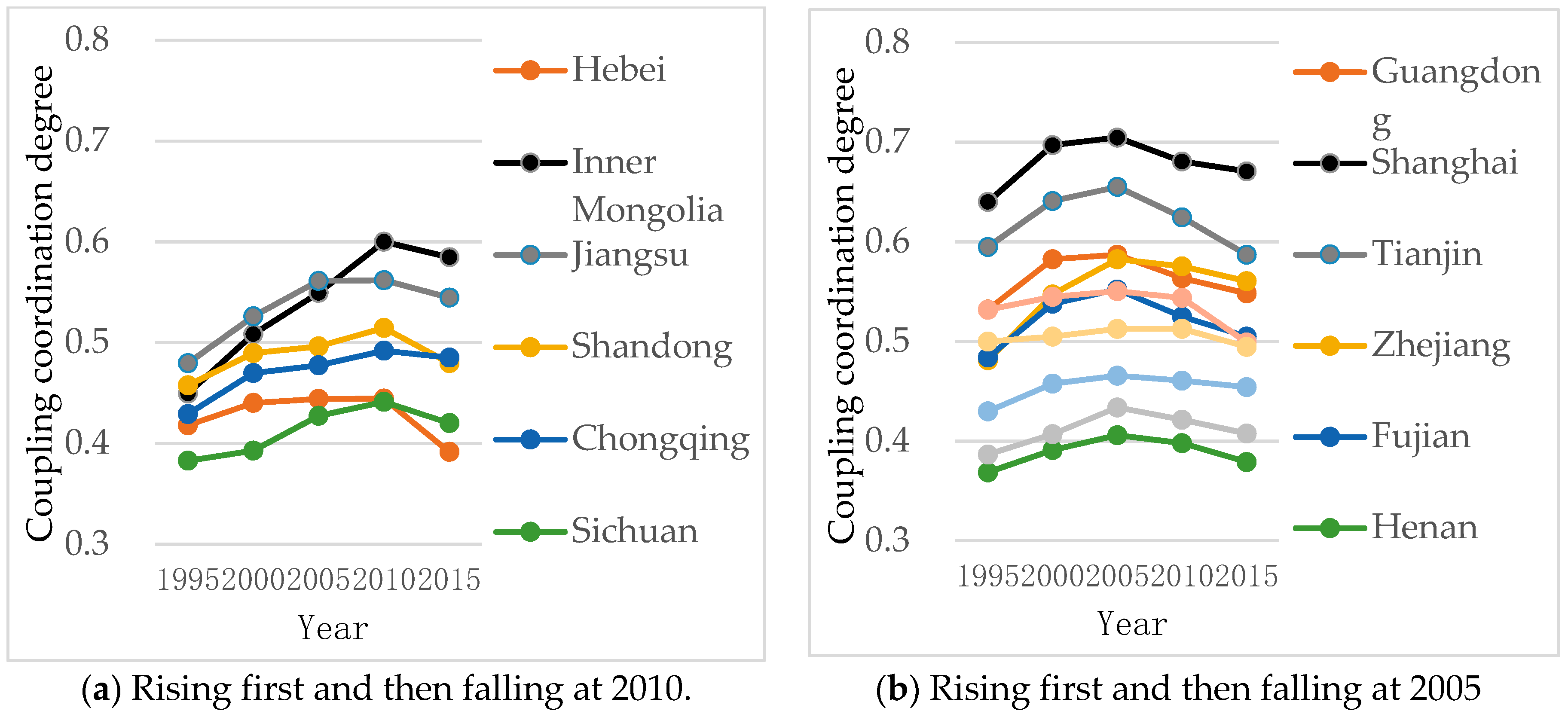
3.1. The Analysis of the Coupling Coordinated Development
3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
3.2.1. Global Spatial Autocorrelation
3.2.2. Local Spatial Autocorrelation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Economic Growth and the Environment. NBER Work. Pap. 1994, 110, 353–377. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, H.E. Beyond Growth: The Economics of Sustainable Environment; Beacon Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; Volume 29, p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, H.Y. Study on Coordinating Development of Economic, Social Growth with Population, Resources and Environment at County Level. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1991, 4, 385–395. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Hu, H.; Li, M.S.; Zhang, Y.J.; Song, J.P.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, F.Y. Ecological civilization evaluation and coordinated development between environment, economy and society. Resour. Sci. 2015, 37, 1444–1454. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.J.; Yang, Y.F.; Wu, Y.F. The Coordinated-evaluation model of urban sustainable development based on a compound system. Stat. Decis. 2010, 14, 36–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.G.; Dietz, T.; Carpenter, S.R.; Folke, C.; Alberti, M.; Redman, C.L.; Schneider, S.H.; Ostrom, E.; Pell, A.N.; Lubchenco, J.; et al. Coupled human and natural systems. AMBIO J. Hum. Environ. 2008, 36, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Victor, P.A. Pollution: Economy and Environment. Economica 1974, 41, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joselow, M.M.; Tobias, E.; Koehler, R.; Coleman, S.; Bogden, J.; Gause, D. Manganese Pollution in the City Environment and Its Relationship to Traffic Density. Am. J. Public Health 1978, 68, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culbertson, J.M. Economic growth population, and the environment. Popul. Environ. 1990, 11, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretariat, A. The Impact of Expanding Population and Economic Growth on Food, Energy, and the Environment; APEC Economic Committee: Singapore, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Newlyn, W.T. Population Growth and Economic Development: Policy Questions. Popul. Resour. Chang. World Curr. Read. 1989, 82, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Commission on Environment and Development. Our Common Future; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Norgaard, R.B. Economic indicators of resource scarcity: A critical essay. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 1990, 19, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.; Morse, S. (Eds.) Routledge Handbook of Sustainability Indicators; Routledge Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Frugoli, P.A.; Almeida, C.M.V.B.; Agostinho, F.; Giannetti, B.F.; Huisingh, D. Can measures of well-being and progress help societies to achieve sustainable development? J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 90, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.; Morse, S. Sustainability Indicators Past and Present: What Next? Sustainability 2018, 10, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Xue, M.G.; Hu, M.S. Dynamic simulation and assessment of the coupling coordination degree of the economy–resource–environment system: Case of Wuhan City in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 230, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiyetan, I.R.; Olomola, P.A. Environmental degradation, energy consumption, population growth and economic growth: Does Environmental Kuznets curve matter for Nigeria? Econ. Policy Rev. 2017, 16, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bastianoni, S.; Coscieme, L.; Pulselli, F.M. The input-state-output model and related indicators to investigate the relationships among environment, society and economy. Ecol. Model. 2016, 325, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, G.; José, A.; Ionides, E.L. Population health and the economy: Mortality and the Great Recession in Europe. Health Econ. 2017, 26, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahoo, M.; Othman, J. Employing a CGE model in analysing the environmental and economy-wide impacts of CO2 emission abatement policies in Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raborar, K.J.F. Sustainable development, education for sustainable development and Philippine community. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 8, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šipilova, V.; Ostrovska, I.; Jermolajeva, E. Evaluation of Sustainable Development in Rural Territories in Latgale Region (Latvia) by Using the Conception of Smart Specialization. J. Teach. Educ. Sustain. 2017, 19, 82–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.T.; Yang, J.; Yan, J.Y. A holistic low carbon city indicator framework for sustainable development. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 1919–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development. Indicators of Sustainable Development: Framework and Methodologies; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- The Administrative Center for China’s Agenda 21. Theory and Practice of Indicators Systems for Sustainable Development; Social Sciences Academic Press: Beijing, China, 2004; p. 150. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hillman, M. Department of the Environment. Indicators of Sustainable Development for the United Kingdom. Policy Stud. 1996, 17, 248–249. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, J. The Roots Index: Exploring Indices as Measures of Local Sustainable Development, New York City: 1990–95. Soc. Indic. Res. 2000, 52, 95–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leukhardt, F.; Allen, S. How environmentally focused is the German sustainability strategy? A critical discussion of the indicators used to measure sustainable development in Germany. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2013, 15, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Wei, Y.M.; Fan, Y.; Li, Z.J.; Xu, W.X. System Analysis of Harmonization Development among Population, Resource, Environment and Economy. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2000, 20, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.R.; Zhao, M. Research on Chinese Different Regional Sustainable Development Capacity and its Spatial Differentiation. Shanghai J. Econ. 2016, 10, 84–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Hao, Z.Y.; Chen, P.A. A Case Study on Shandong Province: Temporal-Spatial Difference of Sustainable Development. Resour. Ind. 2013, 15, 13–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xue, B.; Zhang, Z.L.; Guo, X.J.; Chen, X.P.; Geng, Y. A study on the coupling relationships between regional economic growth and environmental pressure: Case of Ningxia Autonomous Region. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 19, 1125–1131. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, F.F.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.R.; Lu, Z.H. Assessment on coordinative ability of sustainable development of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region based on set pair analysis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 11, 3090–3098. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.H.; Zhong, D.S.; Lu, X.L. Comparative study of the application of PCA and AHP to the analysis and evaluation of the regional sustainable development. J. Saf. Environ. 2016, 16, 359–365. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chou, F.D. On Comprehensive Evaluation of county sustainable Development. Econ. Geogr. 2003, 3, 319–322. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.J.; Yan, Z.Q.; Yang, Q.L. A Case Study on Nanning City: Regional PRED Comprehensive Coordination Based on Entropy and Comprehensive Evaluation. Resour. Ind. 2015, 17, 82–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Ye, G.H. PRED analysis and scenario simulation study of North Guangxi Gulf Economic Zone on the basis of SD. Rural Econ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 29, 148–151. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W.; Ren, L.; Wang, S.J.; Liu, Y.F. Spatial and temporal evolution of the ecological environment and economy coordinated development in Hebei Province, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 2941–2949. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.Y.; Zhu, W.L.; Li, H.J.; Xue, B.; Zhang, Z.L. Study on Comprehensive Measurement of Regional Sustainable Development in the Loess Plateau of East Gansu Province—A Case Study of Qingyang City. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 22, 210–217. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; Daly, L.; Fioramonti, L.; Giovannini, E.; Kubiszewski, I.; Mortensen, L.F.; Pickett, K.E.; Ragnarsdottir, K.V.; Vogli, R.D.; Wilkinson, R. Modelling and measuring sustainable wellbeing in connection with the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 130, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parris, T.M.; Kates, R.W. Characterizing and measuring sustainable development. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2003, 28, 559–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, B.S.; Datta, S.K. Revisiting the link between socio-economic development and environmental status indicators—Focus on panel data. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2015, 17, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.G.; Duan, H.M.; Li, Z.J. Study on Coordinated Development of Population, Economy and Environment in Resource: Taking Karamay City as an Example. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 32, 93–97. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.Y.; Li, W.L.; Li, H.J.; Lu, C.P.; Zhang, Z.L. Study on Comprehensive Measurement of Coordinated Development of Economy-Society-Resource-Environment—A Case Study of Qingyang City, Gansu Province. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2017, 33, 916–921. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese)
- National Bureau of Statistics; Ministry of Environment Protection. China Statistical Yearbook on Environment; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese)
- Department of Comprehensive Statistics of National Bureau of Statistics. China Compendium of Statistics 1949–2008; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese)
- Ding, Y.; de Vries, B.; Han, Q. Measuring Regional Sustainability by a Coordinated Development Model of Economy, Society, and Environment: A Case Study of Hubei Province. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2014, 22, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, D.L.; Peng, B.F.; Xiong, J.X. The Coupling Characteristics of Eco-economic System in Dongting Lake Area. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2013, 33, 1338–1346. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.J. Coupling Coordination Degree Analysis of Population—Regional economy—Environment Development. Stat. Decis. 2017, 15, 101–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.P. The Research on the Evaluation System of Economic Development Based on the Method of Entropy and AHP. Master’s Degree, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2007. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.X.; Wang, X.F.; Chang, Y.M. Study on the coordination of population and economic system based on Moran’s I and LISA. Stat. Decis. 2014, 6, 90–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, P.; Wu, T.; Zhou, J.M. Analysis of spatial distribution pattern and evolutionary characteristics of cultivated lands based on spatial autocorrelation model and GIS platform—A case study of Longquanyi District, Chengdu, China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2016, 24, 325–334. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tiefelsdorf, M.; Boots, B. A Note on the Extremities of Local Moran’s Iis and Their Impact on Global Moran’s I. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 29, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.R.; Huan, X.X.; Sun, Q. Quantitative Evaluation and Comparative Analysis for Coordinated Development of Resource, Environment, Economy and Society in Central China. Econ. Geogr. 2013, 33, 16–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, M.; Ren, J.L.; Liu, K. Coupling Between Subsystems and the Spatial Pattern of China’s Sustainable Development. J. Ludong Univ. 2017, 33, 55–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.X.; Wang, J.Y.; Chen, K. Coordinated development analysis of the “resources-environment-ecology-economy-society” complex system in China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Chen, Z.F.; Wu, H.R.; Sun, X.; Yao, N. Spatial-temporal Differentiation of Urban Sustainable Development in China based on ESDA. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2016, 26, 144–151. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Bai, L.; Wu, Y.M. Coupling and Coordinating Degrees of Provincial Economy, Resources and Environment in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2017, 32, 788–799. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shaker, R.R.; Sirodoev, I.G. Assessing sustainable development across Moldova using household and property composition indicators. Habitat Int. 2016, 55, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, Z.Q.; Lan, X.; Zhang, H.W.; Meng, J.F. The Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Dilemmas of Sustainable Urbanization in China: A New Perspective Based on the Concept of Five-in-One. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| The Target Layer | The System Layer | The Criteria Layer | The Index Layer | Index Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The coordinated development of population, economy, society, resource, and the environment | Population system | Population size | Population count | − |
| Population density | − | |||
| Natural rate of population growth | − | |||
| Population structure | Proportion of nonagricultural population | + | ||
| Overall dependency ratio | − | |||
| Aging coefficient | − | |||
| Population quality | Average life expectancy | + | ||
| Years of education per capita | + | |||
| Proportion of those with a college degree and above | + | |||
| Economic system | Economic size | GDP per capita | + | |
| Fiscal revenue per capita | + | |||
| Social investment in fixed assets per capita | + | |||
| Total retail sales of consumer goods per capita | + | |||
| Economic structure | Percentage of primary industry output values to GDP | − | ||
| Percentage of tertiary industry output values to GDP | + | |||
| Foreign trade dependence | + | |||
| Economic benefit | Input–output ratio | + | ||
| Social system | People’s quality of life | Disposable income of urban residents per capita | + | |
| Net income of rural residents per capita | + | |||
| Engel coefficient of urban residents | − | |||
| Engel coefficient of rural residents | − | |||
| Floor area of residential building per capita | + | |||
| Social development level | Urban employment rate | + | ||
| Road transport mileage per capita | + | |||
| Volume of postal and telecommunication services per capita | + | |||
| Number of health technicians per 10,000 people | + | |||
| Number of public libraries per 10,000 people | + | |||
| Percentage of social security expenditure to GDP | + | |||
| Resource system | Resource conditions | Cultivated area per capita | + | |
| Energy production per capita | + | |||
| Water resources per capita | + | |||
| Forest stock per capita | + | |||
| Resource utilization | Water consumption per 10 thousand Yuan GDP | − | ||
| Energy consumption per 10 thousand Yuan GDP | − | |||
| Grain yield per unit area | + | |||
| Industrial water reuse efficiency | + | |||
| Environmental system | Environmental pollution | Total wastewater discharge | − | |
| Total industrial gas emissions | − | |||
| Total industrial solid waste discharge | − | |||
| Domestic waste discharge in China | − | |||
| Fertilizer application intensity | − | |||
| Environment protection and management | Industrial wastewater discharge compliance rate | + | ||
| Urban sewage treatment rate | + | |||
| Industrial gas purification treatment rate | + | |||
| Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste | + | |||
| Harmless treatment rate of domestic garbage in China | + | |||
| Ecological environment construction | Forest cover rate | + | ||
| Public green area per capita | + | |||
| Green coverage rate in built-up areas | + | |||
| The percentage of environmental protection investment to GDP | + |
| Coupling Coordination Degree | (0, 0.4) | (0.4, 0.5) | (0.5, 0.6) | (0.6, 0.8) | (0.8, 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | Uncoordinated development status | On the verge of uncoordinated development status | Weakly coordinated development status | Well-coordinated development status | Perfectly coordinated development status |
| Province | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.6908 | 0.7255 | 0.7137 | 0.7066 | 0.7084 |
| Tianjin | 0.5948 | 0.6409 | 0.6551 | 0.6246 | 0.5870 |
| Hebei | 0.4180 | 0.4401 | 0.4442 | 0.4444 | 0.3916 |
| Shanxi | 0.5074 | 0.5014 | 0.5442 | 0.5484 | 0.5168 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.4496 | 0.5084 | 0.5494 | 0.6000 | 0.5846 |
| Liaoning | 0.5319 | 0.5448 | 0.5505 | 0.5438 | 0.4990 |
| Jilin | 0.4969 | 0.4853 | 0.5228 | 0.5081 | 0.4579 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.5254 | 0.5272 | 0.5263 | 0.5119 | 0.4865 |
| Shanghai | 0.6401 | 0.6970 | 0.7046 | 0.6806 | 0.6707 |
| Jiangsu | 0.4796 | 0.5260 | 0.5613 | 0.5619 | 0.5447 |
| Zhejiang | 0.4811 | 0.5472 | 0.5825 | 0.5755 | 0.5605 |
| Anhui | 0.3753 | 0.4056 | 0.4024 | 0.4217 | 0.4030 |
| Fujian | 0.4841 | 0.5379 | 0.5522 | 0.5250 | 0.5050 |
| Jiangxi | 0.4203 | 0.4468 | 0.4258 | 0.4458 | 0.4234 |
| Shandong | 0.4577 | 0.4897 | 0.4962 | 0.5146 | 0.4797 |
| Henan | 0.3687 | 0.3911 | 0.4060 | 0.3979 | 0.3789 |
| Hubei | 0.4299 | 0.4577 | 0.4657 | 0.4608 | 0.4542 |
| Hunan | 0.4242 | 0.4583 | 0.4535 | 0.4393 | 0.4159 |
| Guangdong | 0.5321 | 0.5826 | 0.5871 | 0.5635 | 0.5482 |
| Guangxi | 0.4184 | 0.4371 | 0.4263 | 0.4132 | 0.3835 |
| Hainan | 0.4795 | 0.4915 | 0.4703 | 0.4928 | 0.4731 |
| Chongqing | 0.4292 | 0.4698 | 0.4775 | 0.4920 | 0.4852 |
| Sichuan | 0.3829 | 0.3930 | 0.4274 | 0.4413 | 0.4201 |
| Guizhou | 0.3628 | 0.3604 | 0.3936 | 0.4220 | 0.4035 |
| Yunnan | 0.4072 | 0.4429 | 0.4412 | 0.4362 | 0.4194 |
| Tibet | 0.4946 | 0.4958 | 0.4992 | 0.4726 | 0.5227 |
| Shanxi | 0.4171 | 0.4517 | 0.4507 | 0.4728 | 0.4573 |
| Gansu | 0.3866 | 0.4070 | 0.4338 | 0.4214 | 0.4078 |
| Qinghai | 0.4500 | 0.4795 | 0.4788 | 0.4739 | 0.4499 |
| Ningxia | 0.4433 | 0.4748 | 0.4735 | 0.5089 | 0.4998 |
| Xinjiang | 0.4999 | 0.5050 | 0.5127 | 0.5126 | 0.4947 |
| Average | 0.4671 | 0.4943 | 0.5041 | 0.5043 | 0.4849 |
| Year | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.2886 | 0.3208 | 0.3364 | 0.3037 | 0.1953 |
| Z | 2.8284 | 3.1167 | 3.2027 | 2.9150 | 1.9924 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, C.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Jin, S.; Pang, M.; Lu, C. Research on the Spatial–Temporal Synthetic Measurement of the Coordinated Development of Population-Economy-Society-Resource-Environment (PESRE) Systems in China Based on Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Sustainability 2019, 11, 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102877
Lu C, Yang J, Li H, Jin S, Pang M, Lu C. Research on the Spatial–Temporal Synthetic Measurement of the Coordinated Development of Population-Economy-Society-Resource-Environment (PESRE) Systems in China Based on Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Sustainability. 2019; 11(10):2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102877
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Chenyu, Jiaqi Yang, Hengji Li, Shulei Jin, Min Pang, and Chengpeng Lu. 2019. "Research on the Spatial–Temporal Synthetic Measurement of the Coordinated Development of Population-Economy-Society-Resource-Environment (PESRE) Systems in China Based on Geographic Information Systems (GIS)" Sustainability 11, no. 10: 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102877
APA StyleLu, C., Yang, J., Li, H., Jin, S., Pang, M., & Lu, C. (2019). Research on the Spatial–Temporal Synthetic Measurement of the Coordinated Development of Population-Economy-Society-Resource-Environment (PESRE) Systems in China Based on Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Sustainability, 11(10), 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102877






