Differential Game Analysis of Scientific Crowdsourcing on Knowledge Transfer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Model Formulation
3.1. Scientific Crowdsourcing Knowledge Transfer Mechanism
3.2. Game Model Construction and Solution
3.2.1. Model Assumption and Parameters Description
3.2.2. The Stackelberg Game Model Led by the Initiator
3.2.3. The Benefit Sharing Model
3.3. Comparison Analysis
3.3.1. Knowledge Transfer Behavior Comparison
3.3.2. Scientific Crowdsourcing Total Revenue Comparison
3.3.3. The Optimal Revenue Distribution Mechanism in Scientific Crowdsourcing
4. Simulation and Discussion
4.1. Generic Simulation
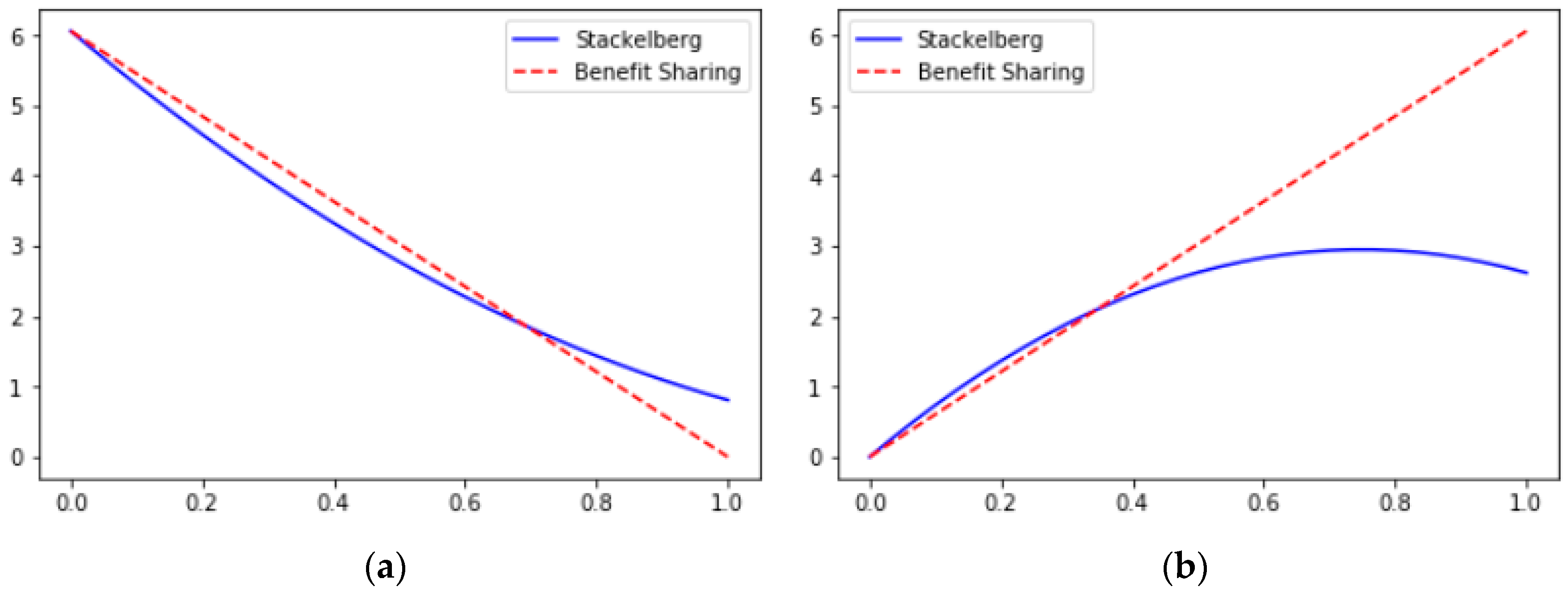
4.2. How Does the Revenue Distribution Coefficient Impact Revenue?
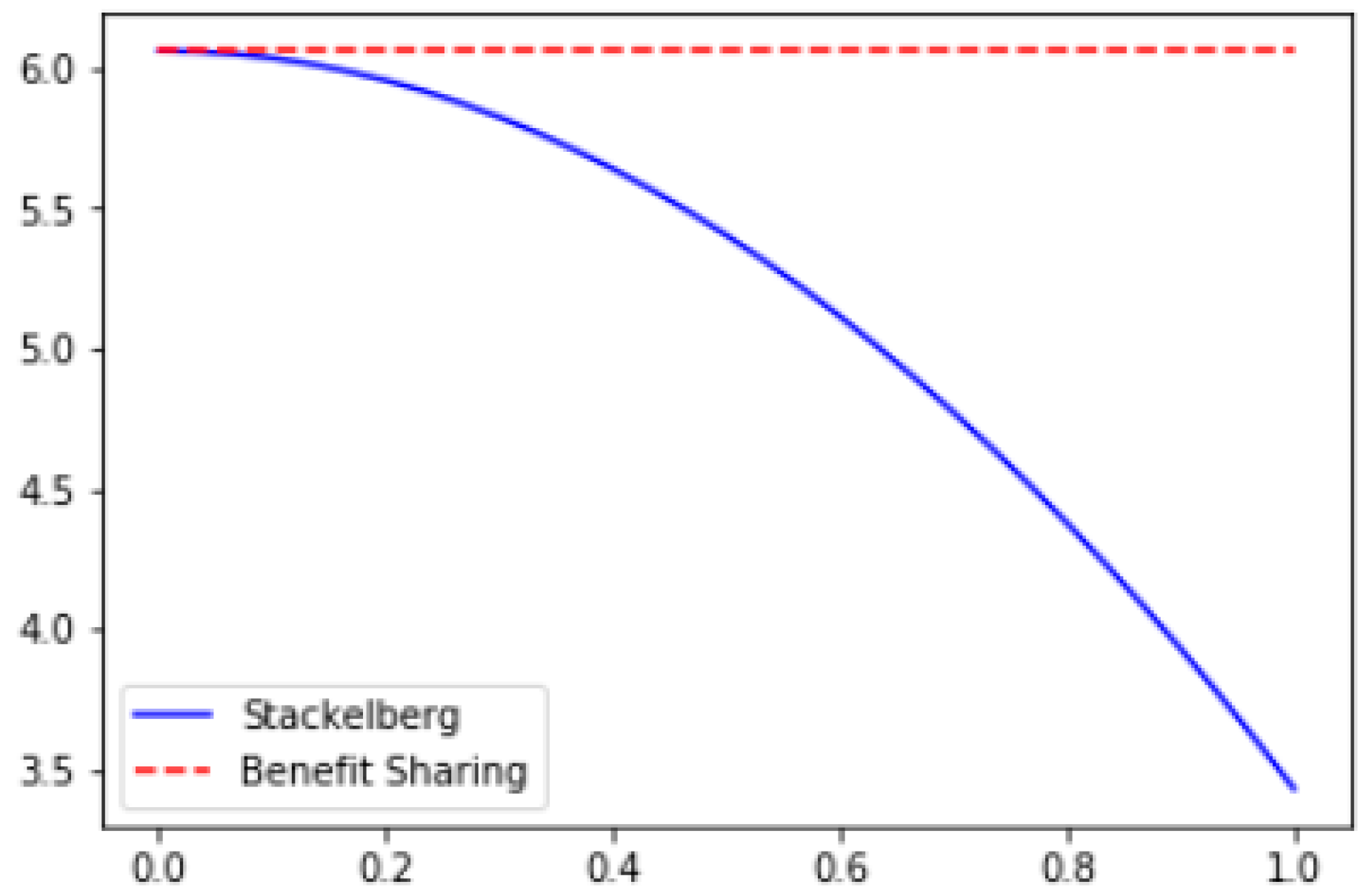
4.3. Does the Knowledge Coupling Degree Play a Key Role in Regulating Knowledge Transfer Behavior and Revenue?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howe, J. The rise of crowdsourcing. Wired Mag. 2006, 14, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.Q.; Jiang, T.; Tao, S.Y.; Xie, G.F.; Tan, Z.Y. Science sourcing—A new model of scientific cooperation. Sci. Manag. Res. 2015, 33, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Q. The impact of scientific crowdsourcing on Chinese scientific research activities. Forum Sci. Technol. China 2015, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Agafonovas, A.; Alonderiene, R. Value creation in innovation crowdsourcing: Example of creative agencies. Organ. Mark. Emerg. Econ. 2013, 2, 72–104. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, P.; Wei, J.; Ying, Y.; Tian, M. International R&D alliances and innovation for emerging market multinationals: Roles of environmental turbulence and knowledge transfer. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkut, B. What Did SAP Change? A Market Shaping Analysis. Mark. Brand. Res. 2018, 5, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollok, P.; Luttgens, D.; Piller, F.T. How firms develop capability for crowdsourcing to increase open innovation performance: The interplay between organizational roles and knowledge processes. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fombrun, G.; Shanley, M. What’s in a name: Reputation building and corporate strategy. Acad. Manag. J. 1990, 33, 233–258. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, B.; Perry, S. Removing the financial performance halo from fortune’s most admired companies. Acad. Manag. J. 1994, 37, 1347–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Sedighi, M.; van Splunter, S.; Brazier, F.; van Beers, C.; Lukosch, S. Exploration of multi-layered knowledge sharing participation: The roles of perceived benefits and costs. J. Knowl. Manag. 2016, 20, 1247–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscotti, A.M.; D’Amico, E.; Monge, F. Do environmental management system affect the knowledge management process? The impact on the learning evolution and the relevance of organizational contect. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2018, 22, 603–620. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Wang, J.R. Game Analysis of Knowledge Transfer of Product Innovation Team in Multinational Corporations. J. Hum. Res. Manag. 2017, 5, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, P.B.; Bandera, C.; Thomas, E. A behavioral game theory perspective on the collaboration between innovative and entrepreneurial firms. Int. J. Work Innocation 2017, 2, 6–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.Y.; He, H.Y.; Fang, J.; Huang, J. Research on Knowledge Sharing Behavior of Employee based on Game Theory and Multi-Agent Situation from the Employee Position Perspective. Bol. Tec. 2017, 55, 262–271. [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka, I.; Takeuchi, H. The Knowledge-Creating Company: How Japanese Companies Create the Dynamic of Innovation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; Cary, NC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka, I.; Toyama, R.; Konno, N. SECI, Ba and leadership: A unified model of dynamic knowledge creation. Long Range Plan. 2000, 33, 5–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.A.; Lakhani, K.R. The contingent effect of absorptive capacity: An open innovation analysis. Harv. Bus. Sch. Work. Paper Ser. 2011, 21, 11–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spithoven, A.; Clarysse, B.; Knockaert, M. Building absorptive capacity to organize inbound open innovation in traditional industries. Technovation 2010, 31, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, A.; Gabelloni, D.; Martini, A.; Natalicchio, A. Crowdsourcing: A Review and Suggestions for Future Research. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2017, 20, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darr, E.; Argote, L.; Epple, D. The acquisition, transfer, and depreciation of knowledge in service organizations: Productivity in franchises. Manag. Sci. 1995, 41, 1750–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Wang, Y.W.; Zuo, Y.; Yang, H.D.; Zhang, M. Internet of Things in product life-cycle energy management. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2016, 1, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkut, B. The Emergence of the ERP Software Market between Product Innovation and Market Shaping. J. Open Innov. Technol. Market Complex. 2018, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H.; Liang, Q.Z. Research on the relationship between technology acquisition methods and enterprise value. Stud. Sci. Sci. 2010, 28, 741–746+776. [Google Scholar]
- Witt, U.; Zellner, C. How firm organizations adapt to secure a sustained knowledge transfer. Econ. Innov. New Technol. 2009, 18, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelbach, A.; Walter, A. Complex technological knowledge and value creation in science-to-industry technology transfer projects: The moderating effect of absorptive capacity. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2015, 47, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Li, K.K. Research on Influencing Factors of Collaborative Innovation Knowledge Transfer of Industry, University and Research Based on Dynamic Capability Theory. Inf. Sci. 2016, 34, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Zou, H.; Qi, G. Knowledge absorptive capacity and innovation performance in high-tech companies: A multi-mediating analysis. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 88, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistella, C.; De Toni, A.F.; Pillon, R. Inter-organisational technology/knowledge transfer: A framework from critical literature review. J. Technol. Transf. 2016, 41, 1195–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Sheng, T.B. Transferring R&D knowledge: The key factors affecting knowledge transfer success. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2003, 20, 39–68. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit-de Vries, E.; Dolfsma, W.A.; van der Windt, H.J. Knowledge transfer in university-industry research partnerships: A review. J. Technol. Transf. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, F.; Bigliardi, B. Redesigning the model of the initiative and evolution of inter-firm knowledge transfer in R&D relationships. J. Knowl. Manag. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yin, F.C. An analysis of knowledge valuation and organization respond of website—Based crowdsourcing. Sci. Res. Manag. 2017, 38, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Helander, N.; Kärkkäinen, H.; Jussila, J. Value Creation in Business-To-Business Crowd Sourcing. Int. J. Knowl. Soc. Res. 2014, 5, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, J.; Helander, N.; Jussila, J.; Kärkkäinen, H. Crowdsourcing in Business-to-Business Markets: A Value Creation and Business Model Perspective. In Encyclopedia of E-Commerce Development, Implementation, and Management; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 933–943. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.T.; Wu, C.H. Embedded or involved, why crowdsourcing individual contribute knowledge? Sci. Res. Manag. 2017, 38, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Howe, J. Crowdsourcing: How the Power of the Crowd is Driving the Future of Business; Random House Business: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Estellés-Arolas, E.; González-Ladrón-de-Guevara, F. Towards an integrated crowdsourcing definition. J. Inf. Sci. 2012, 38, 89–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jussila, J.; Kärkkäinen, H.; Leino, M. Learning from and with customers with social media: A model for social customer learning. Int. J. Manag. Knowl. Learn. 2012, 1, 5–25. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Ding, C.Q.; Yuan, J. The evolutionary game study of knowledge transfer behavior in cooperative crowdsourcing community of innovation. Adv. Model. Anal. A 2016, 53, 164–175. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.S.; Hu, L.Y. Analysis on knowledge transfer decisions in technology innovation alliance based on leader—Followers games. Sci. Res. Manag. 2011, 32, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, X.W.; Zhang, X.Z. Governance Model Construction of Inter-organizational Knowledge Transfer: The Role of Dissemination Capacity and Absorptive Capacity. Inf. Stud. Theory Appl. 2018, 41, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Zeng, S.Q. Research on Differential Countermeasure Model of Vertical Cooperative Advertising. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2007, 27, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.M.; Lin, M.; Lei, Z.H. Enterprise Knowledge Transfer Strategy under Competitive Conditions and Its Impact on Industrial Evolution. Chin. J. Manag. 2014, 11, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.H.; Chen, J.F.; Huang, P. Analysis on Decision-making of Supplier’s R&D Vertical Knowledge Spillover. Ind. Eng. Manag. 2008, 4, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Dockner, E.; Jorgensen, S.; Van, L.; Sorger, G. Differential Games in Economics and Management Science; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. 41–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jeang, A.; Rahim, A. Lot size determination for finite horizon under the effect of productivety and quality learning process. Int. J. Syst. Sci. Oper. Logist. 2018, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| α | Influence coefficient of the solver’s knowledge dissemination ability on final knowledge transfer quality |
| β | Influence coefficient of the initiator’s knowledge absorption ability on final knowledge transfer quality |
| γ | The natural decay rate of knowledge transfer quality when knowledge transfer effort is zero |
| k | Knowledge coupling degree of between initiator and solver |
| θ | Revenue distribution coefficient |
| µ | Discount factor |
| φ | Cost sharing coefficient |
| λ | Influence coefficient of knowledge transfer quality on the final scientific crowdsourcing value |
| η | Constant |
| Q | Knowledge transfer quality |
| ɛup | Solver’s knowledge transfer cost coefficient |
| ɛdown | Initiator’s knowledge transfer cost coefficient |
| Iup | Solver’s knowledge dissemination ability |
| Idown | Initiator’s knowledge absorption ability |
| Cup | Solver’s knowledge dissemination cost |
| Cdown | Initiator’s knowledge absorption cost |
| Vup | Solver’s scientific crowdsourcing revenue objective function |
| Vdown | Initiator’s scientific crowdsourcing revenue objective function |
| Stackelberg Master–Slave Game | Benefit Sharing | Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iup | 0.819 | 1.024 | 20.00% |
| Idown | 0.461 | 0.768 | 40.00% |
| Vup | 0.569 + 0.305Q | 0.577 + 0.305Q | 1.52% |
| Vdown | 0.842 + 0.457Q | 0.866 + 0.457Q | 2.74% |
| V | 1.411 + 0.762Q | 1.444 + 0.762Q | 2.25% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Yu, L. Differential Game Analysis of Scientific Crowdsourcing on Knowledge Transfer. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102735
Wang G, Yu L. Differential Game Analysis of Scientific Crowdsourcing on Knowledge Transfer. Sustainability. 2019; 11(10):2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102735
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Guohao, and Liying Yu. 2019. "Differential Game Analysis of Scientific Crowdsourcing on Knowledge Transfer" Sustainability 11, no. 10: 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102735
APA StyleWang, G., & Yu, L. (2019). Differential Game Analysis of Scientific Crowdsourcing on Knowledge Transfer. Sustainability, 11(10), 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102735





