Measuring Country Sustainability Performance Using Ensembles of Neuro-Fuzzy Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sustainability and Fuzzy Neural Networks
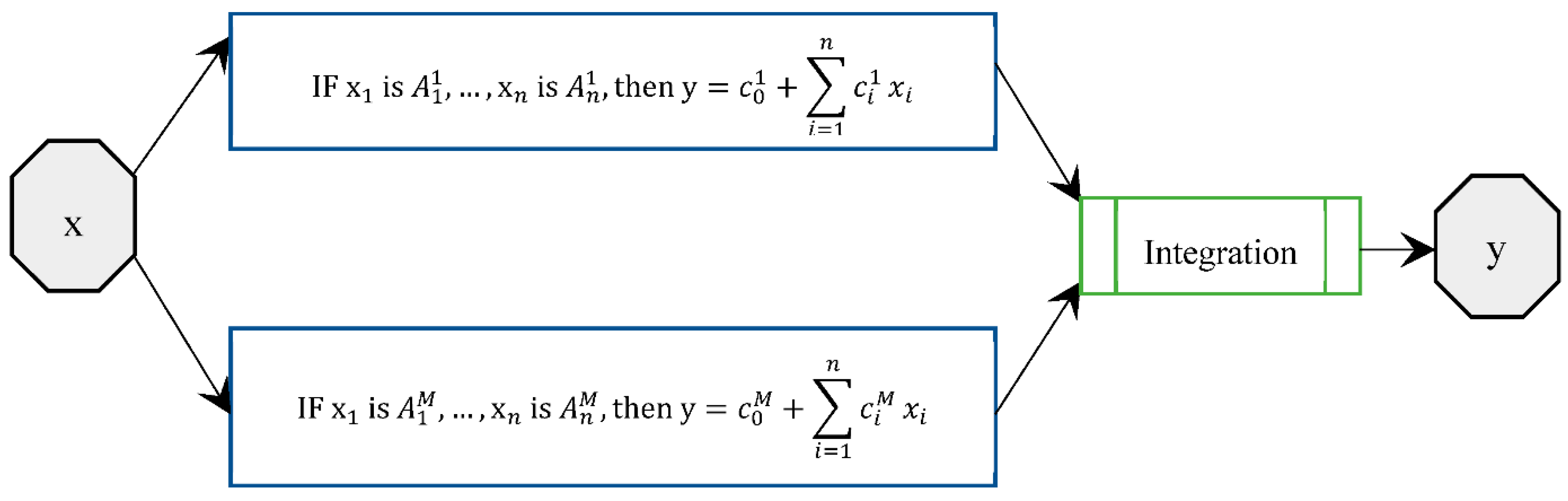
3. ANFIS
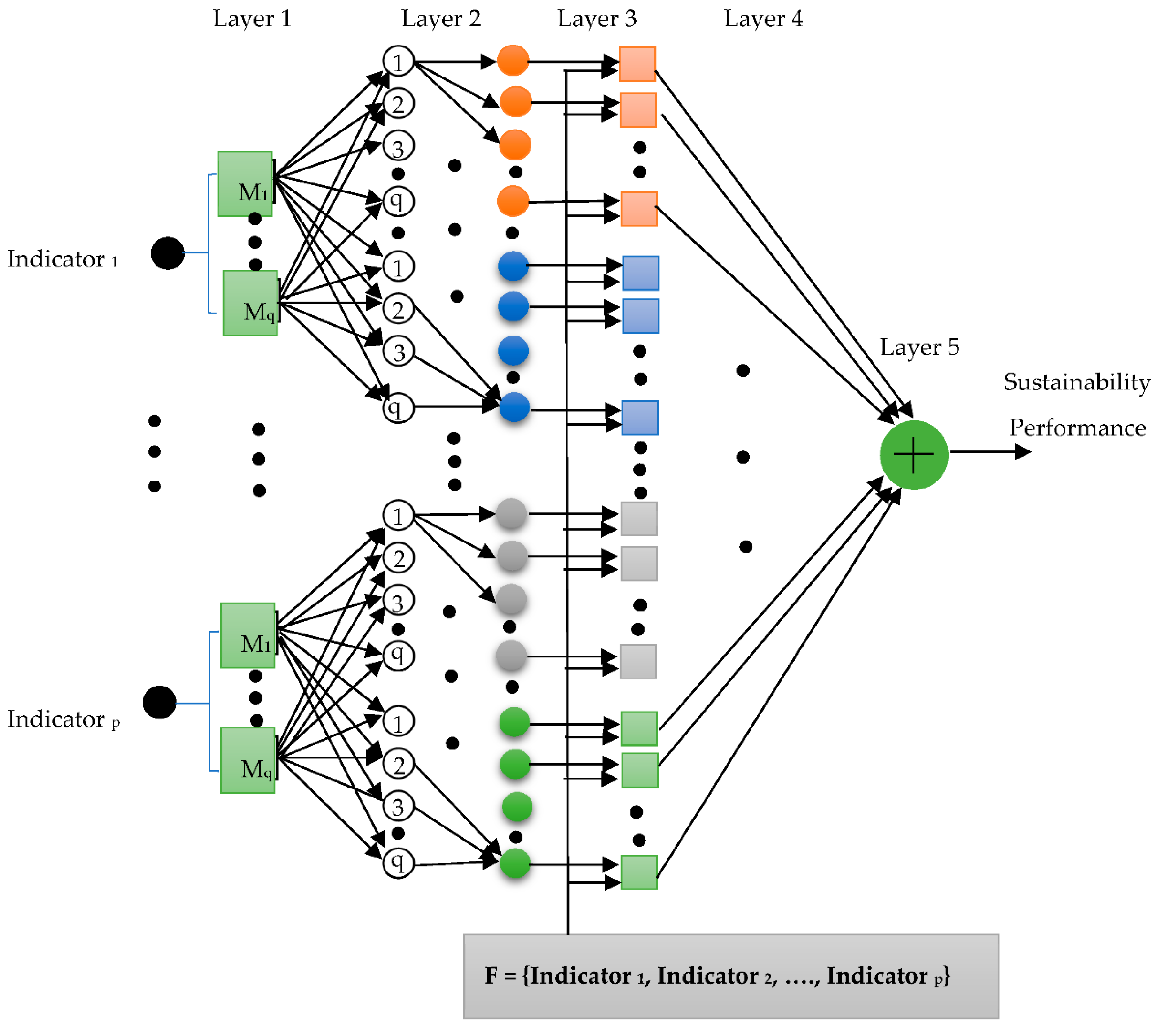
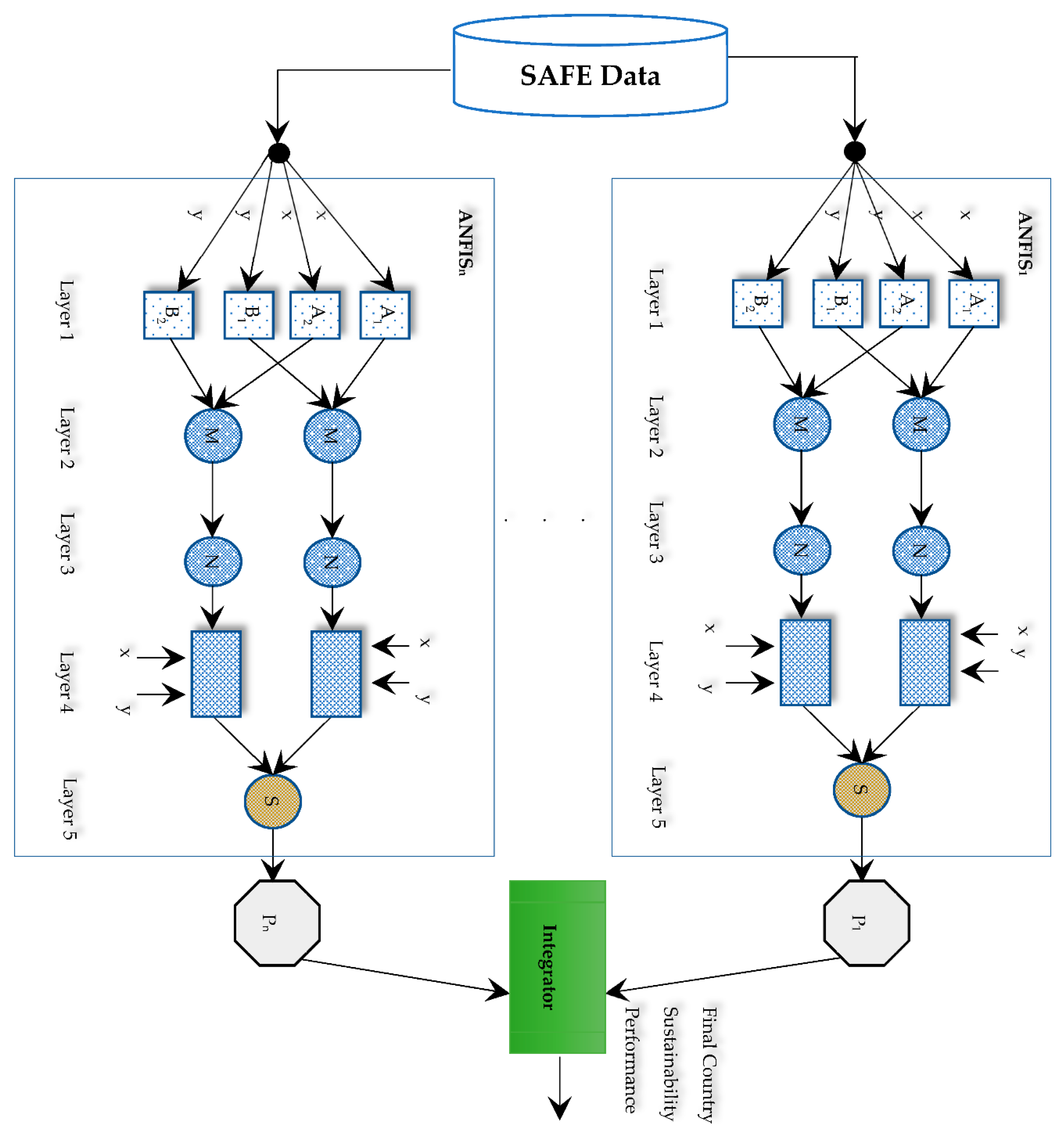
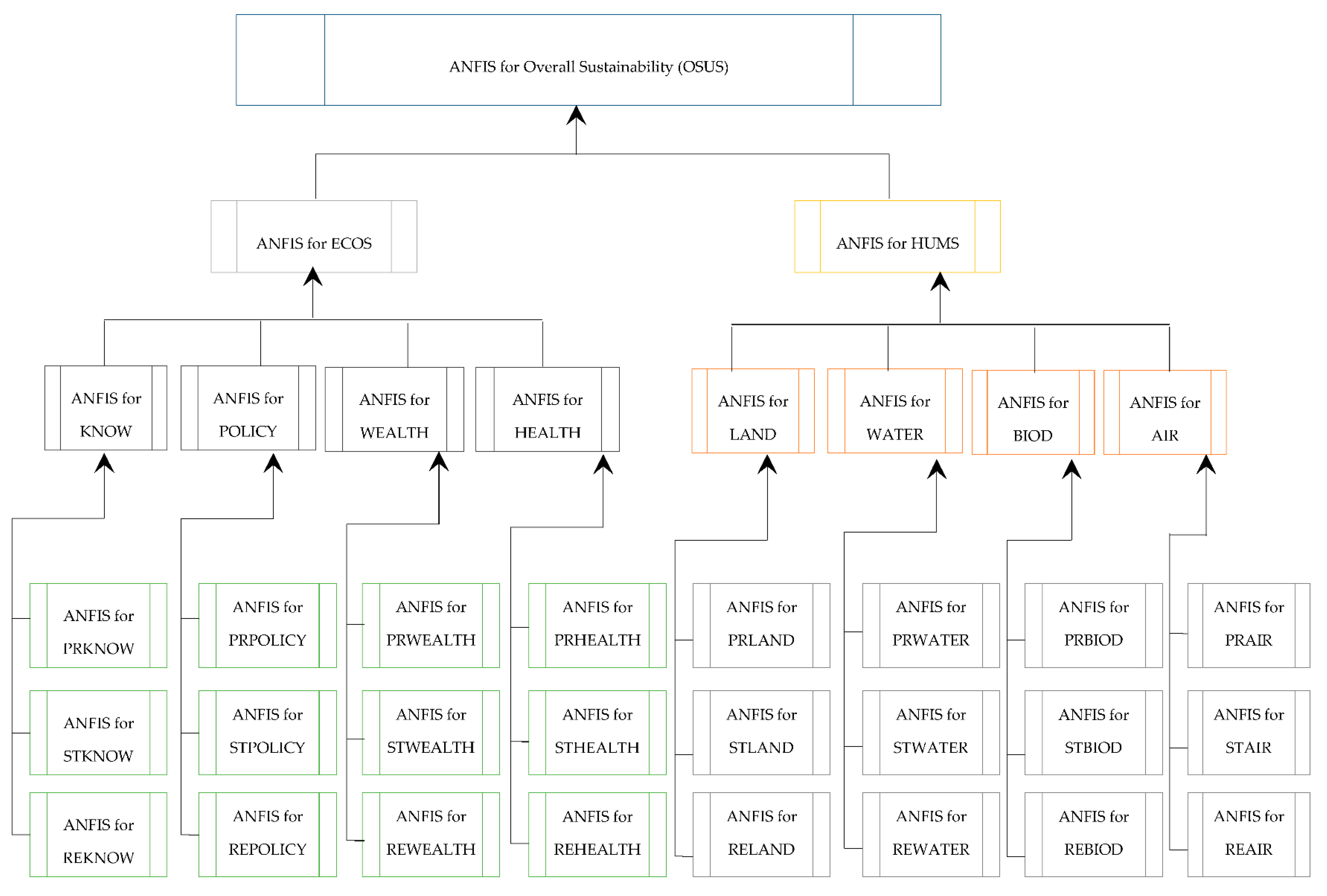
4. ANFIS Ensemble Evaluation
5. Discussion and Recommendations
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Component | Basic Indicator |
|---|---|
| PR(LAND) | “Municipal waste (kg per capita per year)” |
| PR(LAND) | “Nuclear waste (tons per capita per year)” |
| PR(LAND) | “Hazardous waste (tons per capita per year)” |
| PR(LAND) | “Population growth rate (percent)” |
| PR(LAND) | “Pesticide consumption (kg per hectare)” |
| PR(LAND) | “Fertilizer consumption (kg per hectare)” |
| ST(LAND) | “Desertification of land (percent of dryland area)” |
| ST(LAND) | “Forest area (percent of what existed in 2000)” |
| RE(LAND) | “Forest change (annual rate)” |
| RE(LAND) | “Protected area (percent of total land area)” |
| RE(LAND) | “Glass recycling (percent of apparent consumption)” |
| RE(LAND) | “Paper recycling” |
| PR(WATER) | “Pesticide consumption (kg per hectare)” |
| PR(WATER) | “Fertilizer consumption (kg per hectare)” |
| PR(WATER) | “Water withdrawals (percent of internal resources)” |
| ST(WATER) | “Organic water pollutant (BOD) emissions (kg per capita per day)d1” |
| ST(WATER) | “Phosphorous concentration (mg per liter of water)” |
| ST(WATER) | “Metals concentration (micro-Siemens per centimeter)” |
| RE(WATER) | “Public wastewater treatment plants (percent of population connected)” |
| PR(BIOD) | “Threatened mammals (percentage)” |
| PR(BIOD) | “Threatened birds (percentage)” |
| PR(BIOD) | “Threatened plants (percentage)” |
| PR(BIOD) | “Threatened fishes (percentage)” |
| PR(BIOD) | “Threatened amphibians (percentage)” |
| PR(BIOD) | “Threatened reptiles (percentage)” |
| ST(BIOD) | “Desertification of land (percent of dryland area)” |
| ST(BIOD) | “Forest area (percent of what existed in 2000)” |
| RE(BIOD) | “Forest change (annual rate)” |
| RE(BIOD) | “Protected area (percent of total land area)” |
| PR(AIR) | “Ozone depleting substances (metric tons per capita)” |
| PR(AIR) | “Greenhouse gas emissions (tons of CO2 equivalent per capita)” |
| ST(AIR) | “Mortality from poor air quality (deaths per 100,000 population)” |
| ST(AIR) | “Urban NO2 concentration (g/m3 of air)” |
| ST(AIR) | “Urban SO2 concentration (g/m3 of air)” |
| ST(AIR) | “Urban TSP (total suspended particulates) concentration (g/m3 of air)” |
| RE(AIR) | “Renewable energy production (percent of total primary energy supply)” |
| PR(POLICY) | “Military spending (percent of gross domestic product (GDP)d2)” |
| PR(POLICY) | “Refugees per capita (country of origin)” |
| PR(POLICY) | “Poverty (percent of population below national poverty line)” |
| ST(POLICY) | “Political rights (values in [1,7])d3” |
| ST(POLICY) | “Civil liberties (values in [1,7])d3” |
| ST(POLICY) | “Gini indexd4” |
| ST(POLICY) | “Corruption Perceptions Index (values in [0,10])d5” |
| RE(POLICY) | “Environmental laws and enforcement (values in [0,1])d6” |
| RE(POLICY) | “Tax revenue (percent of GDP)” |
| PR(WEALTH) | “GDP implicit deflator (annual percent growth rate)” |
| PR(WEALTH) | “Imports (percent of GDP)” |
| PR(WEALTH) | “Unemployment (percent of total labor force)” |
| PR(WEALTH) | “Unemployment gender gap (percent)” |
| ST(WEALTH) | “Poverty (percent of population below national poverty line)” |
| ST(WEALTH) | “Central government debt (percent of GDP)” |
| ST(WEALTH) | “Gross National Income (GNI) per capita PPPd7” |
| RE(WEALTH) | “Exports (percent of GDP)” |
| RE(WEALTH) | “Foreign direct investment (percent of GDP)” |
| RE(WEALTH) | “Mortality from poor air quality (deaths per 100,000 population)” |
| RE(WEALTH) | “Infant mortality rate (deaths per thousand)” |
| RE(WEALTH) | “Maternal mortality rate (deaths per 100,000 live births)” |
| RE(WEALTH) | “HIV/AIDS prevalence rate (percent of population aged 15–49)” |
| RE(WEALTH) | “Tuberculosis prevalence rate (per 100,000 population)” |
| RE(WEALTH) | “Malaria cases (per thousand people)” |
| ST(HEALTH) | “Life expectancy (years)” |
| ST(HEALTH) | “Immunization against measles (percent of population)” |
| ST(HEALTH) | “Immunization against diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis (DTB) (percent of population)d8” |
| ST(HEALTH) | “Daily per capita calorie supply” |
| RE(HEALTH) | “Number of doctors (per thousand people)” |
| RE(HEALTH) | “Hospital beds (per thousand people)” |
| RE(HEALTH) | “Public health expenditure (percent of GDP)” |
| RE(HEALTH) | “Access to improved water sources (percent of population)” |
| RE(HEALTH) | “Access to improved sanitation (percent of population)” |
| PR(KNOW) | “Primary education ratio of students to teaching staff” |
| PR(KNOW) | “Secondary education ratio of students to teaching staff” |
| PR(KNOW) | “Tertiary education ratio of students to teaching staff” |
| ST(KNOW) | “Male expected years of schooling” |
| ST(KNOW) | “Female expected years of schooling” |
| ST(KNOW) | “Primary net school enrollment (percent of children)” |
| ST(KNOW) | “Secondary net school enrollment (percent of children)” |
| ST(KNOW) | “Literacy rate (percent of population)” |
| ST(KNOW) | “Knowledge Economy Index (KEI; values in [0,10])d9” |
| RE(KNOW) | “Public expenditure on research and development (percent of GDP)” |
| RE(KNOW) | “Public expenditure on education (percent of GDP)” |
| RE(KNOW) | “Personal computers (per thousand people)” |
| RE(KNOW) | “Internet users (per hundred people)” |
| RE(KNOW) | “Expenditure on information and communication (percent of GDP)” |
Appendix B
| Country | SAFE | ANFIS | ANFIS Ensemble | Difference (ANFIS Ensemble and SAFE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germany | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Switzerland | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Sweden | 3 | 2 | 2 | −1 |
| Norway | 4 | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| Finland | 5 | 6 | 5 | 0 |
| Denmark | 6 | 5 | 8 | 2 |
| Austria | 7 | 8 | 6 | −1 |
| Netherlands | 8 | 7 | 7 | −1 |
| Belgium | 9 | 9 | 9 | 0 |
| France | 10 | 11 | 10 | 0 |
| New Zealand | 11 | 10 | 11 | 0 |
| UK | 12 | 12 | 12 | 0 |
| Canada | 13 | 13 | 13 | 0 |
| Australia | 14 | 14 | 14 | 0 |
| Lithuania | 15 | 16 | 15 | 0 |
| Czech Rep. | 16 | 15 | 16 | 0 |
| Italy | 17 | 19 | 17 | 0 |
| Latvia | 18 | 21 | 18 | 0 |
| Slovenia | 19 | 18 | 19 | 0 |
| Slovakia | 20 | 17 | 20 | 0 |
| Spain | 21 | 25 | 21 | 0 |
| Ireland | 22 | 26 | 22 | 0 |
| Poland | 23 | 24 | 23 | 0 |
| Portugal | 24 | 22 | 25 | 1 |
| Estonia | 25 | 23 | 28 | 3 |
| Uruguay | 26 | 20 | 24 | −2 |
| Belarus | 27 | 27 | 26 | −1 |
| Japan | 28 | 31 | 27 | −1 |
| Croatia | 29 | 28 | 29 | 0 |
| Romania | 30 | 29 | 30 | 0 |
| Greece | 31 | 30 | 32 | 1 |
| USA | 32 | 33 | 31 | −1 |
| Hungary | 33 | 32 | 33 | 0 |
| Argentina | 34 | 34 | 34 | 0 |
| Brazil | 35 | 35 | 35 | 0 |
| Bulgaria | 36 | 37 | 36 | 0 |
| Turkey | 37 | 36 | 37 | 0 |
| Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia (FYR) Maced. | 38 | 39 | 38 | 0 |
| Ukraine | 39 | 38 | 39 | 0 |
| Kazakhstan | 40 | 40 | 40 | 0 |
| Russia | 41 | 41 | 42 | 1 |
| Georgia | 42 | 42 | 41 | −1 |
| Panama | 43 | 46 | 43 | 0 |
| Albania | 44 | 43 | 44 | 0 |
| Chile | 45 | 44 | 45 | 0 |
| Ecuador | 46 | 45 | 48 | 2 |
| Morocco | 47 | 47 | 47 | 0 |
| South Korea | 48 | 53 | 46 | −2 |
| Israel | 49 | 48 | 50 | 1 |
| Nicaragua | 50 | 49 | 49 | −1 |
| Venezuela | 51 | 50 | 51 | 0 |
| Armenia | 52 | 51 | 52 | 0 |
| Paraguay | 53 | 52 | 53 | 0 |
| Kyrgyzstan | 54 | 54 | 54 | 0 |
| Tunisia | 55 | 58 | 56 | 1 |
| Bolivia | 56 | 57 | 55 | −1 |
| Malaysia | 57 | 55 | 57 | 0 |
| El Salvador | 58 | 56 | 58 | 0 |
| Kuwait | 59 | 61 | 59 | 0 |
| Mexico | 60 | 60 | 60 | 0 |
| Peru | 61 | 59 | 62 | 1 |
| China | 62 | 63 | 61 | −1 |
| Tajikistan | 63 | 62 | 63 | 0 |
| Thailand | 64 | 64 | 64 | 0 |
| Indonesia | 65 | 66 | 65 | 0 |
| Moldova | 66 | 65 | 66 | 0 |
| Honduras | 67 | 68 | 67 | 0 |
| Azerbaijan | 68 | 67 | 68 | 0 |
| Ghana | 69 | 70 | 69 | 0 |
| Zimbabwe | 70 | 69 | 70 | 0 |
| Botswana | 71 | 72 | 71 | 0 |
| Guatemala | 72 | 71 | 72 | 0 |
| Syria | 73 | 73 | 73 | 0 |
| Philippines | 74 | 74 | 74 | 0 |
| Mongolia | 75 | 77 | 77 | 2 |
| Jordan | 76 | 75 | 75 | −1 |
| Namibia | 77 | 76 | 76 | −1 |
| United Arab Emirates | 78 | 80 | 78 | 0 |
| Saudi Arabia | 79 | 78 | 79 | 0 |
| Uzbekistan | 80 | 79 | 80 | 0 |
| Vietnam | 81 | 82 | 81 | 0 |
| Gabon | 82 | 81 | 82 | 0 |
| Algeria | 83 | 85 | 83 | 0 |
| Kenya | 84 | 84 | 85 | 1 |
| South Africa | 85 | 83 | 84 | −1 |
| Malawi | 86 | 88 | 88 | 2 |
| Sri Lanka | 87 | 89 | 87 | 0 |
| Zambia | 88 | 87 | 86 | −2 |
| Nepal | 89 | 86 | 91 | 2 |
| Gambia | 90 | 90 | 93 | 3 |
| Rwanda | 91 | 95 | 89 | −2 |
| Egypt | 92 | 96 | 90 | −2 |
| Lebanon | 93 | 94 | 92 | −1 |
| Senegal | 94 | 91 | 94 | 0 |
| Congo | 95 | 92 | 97 | 2 |
| Mozambique | 96 | 93 | 95 | −1 |
| Guinea Bissau | 97 | 100 | 96 | −1 |
| Burkina Faso | 98 | 98 | 98 | 0 |
| Cote d’Ivoire | 99 | 97 | 99 | 0 |
| Guinea | 100 | 99 | 100 | 0 |
| Angola | 101 | 104 | 101 | 0 |
| Chad | 102 | 103 | 102 | 0 |
| Iran | 103 | 101 | 104 | 1 |
| Tanzania | 104 | 102 | 103 | −1 |
| Colombia | 105 | 105 | 105 | 0 |
| DR Congo | 106 | 108 | 106 | 0 |
| Burundi | 107 | 106 | 107 | 0 |
| Uganda | 108 | 107 | 108 | 0 |
| Sierra Leone | 109 | 109 | 109 | 0 |
| Nigeria | 110 | 112 | 110 | 0 |
| Togo | 111 | 110 | 111 | 0 |
| Laos | 112 | 111 | 113 | 1 |
| Cameroon | 113 | 113 | 112 | −1 |
| Madagascar | 114 | 114 | 114 | 0 |
| Oman | 115 | 115 | 115 | 0 |
| India | 116 | 116 | 116 | 0 |
| Cambodia | 117 | 117 | 117 | 0 |
| Papua NG | 118 | 118 | 118 | 0 |
| Ethiopia | 119 | 119 | 119 | 0 |
| Benin | 120 | 120 | 121 | 1 |
| Centr. Afr. R | 121 | 123 | 120 | −1 |
| Mali | 122 | 121 | 122 | 0 |
| Bangladesh | 123 | 122 | 123 | 0 |
| Niger | 124 | 124 | 124 | 0 |
| Pakistan | 125 | 126 | 125 | 0 |
| Yemen | 126 | 125 | 126 | 0 |
| Sudan | 127 | 128 | 127 | 0 |
| Mauritania | 128 | 127 | 128 | 0 |
References
- Brundtland Commission. Development, World Commission on Environment and Our Common Future; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Myronidis, D.; Ioannou, K.; Sapountzis, M.; Fotakis, D. Development of a sustainable plan to combat erosion for an island of the Mediterranean region. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2010, 19, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Widya-Hasuti, A.; Mardani, A.; Streimikiene, D.; Sharifara, A.; Cavallaro, F. The Role of Process Innovation between Firm-Specific Capabilities and Sustainable Innovation in SMEs: Empirical Evidence from Indonesia. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devuyst, D.; Hens, L.; De Lannoy, W. How Green Is the City?: Sustainability Assessment and the Management of Urban Environments; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; Shuai, C.; Jiao, L.; Shen, L. An adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) approach for measuring country sustainability performance. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2017, 65, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddings, B.; Hopwood, B.; O’brien, G. Environment, economy and society: Fitting them together into sustainable development. Sustain. Dev. 2002, 10, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hediger, W. Sustainable development and social welfare. Ecol. Econ. 2000, 32, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinos, I.; Georgios, T.; Garyfallos, A.; Zacharoula, A.; Eleni, Z. A Spatial Decision Support System Framework for the Evaluation of Biomass Energy Production Locations: Case Study in the Regional Unit of Drama, Greece. Sustainability 2018, 10, 531. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannou, K.; Birbilis, D.; Lefakis, P. A method for predicting the possibility of ring shake appearance on standing chestnut trees (Castanea sativa MIL L.). J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2011, 12, 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Arushanyan, Y.; Ekener, E.; Moberg, Å. Sustainability assessment framework for scenarios–SAFS. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2017, 63, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houshyar, E.; SheikhDavoodi, M.J.; Almassi, M.; Bahrami, H.; Azadi, H.; Omidi, M.; Sayyad, G.; Witlox, F. Silage corn production in conventional and conservation tillage systems. Part I: Sustainability analysis using combination of GIS/AHP and multi-fuzzy modeling. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 39, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, F. A Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy Inference System for developing a sustainability index of biomass. Sustainability 2015, 7, 12359–12371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, N. Performance evaluation for sustainability of strong smart grid by using stochastic AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS methods. Sustainability 2016, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillis, Y.A.; Grigoroudis, E.; Kouikoglou, V.S. Sustainability ranking and improvement of countries. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillis, Y.A.; Andriantiatsaholiniaina, L.A. Sustainability: An ill-defined concept and its assessment using fuzzy logic. Ecol. Econ. 2001, 37, 435–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, K.; Kegelmeyer, W.P.; Bowyer, K. Combination of multiple classifiers using local accuracy estimates. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1997, 19, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.K.; Salamon, P. Neural network ensembles. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1990, 12, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncheva, L.I. Combining Pattern Classifiers: Methods and Algorithms; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Soto, J.; Melin, P.; Castillo, O. A new approach for time series prediction using ensembles of ANFIS models with interval type-2 and type-1 fuzzy integrators. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence for Financial Engineering & Economics (CIFEr), Singapore, 16–19 April 2013; pp. 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.-S. ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1993, 23, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkijevic, I.; Vukovic, Z.; Vouk, D. Indicators and a Neuro-Fuzzy Based Model for the Evaluation of Water Supply Sustainability. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 3683–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, F. Electric load analysis using an artificial neural network. Int. J. Energy Res. 2005, 29, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruben, R.B.; Asokan, P.; Vinodh, S. Performance evaluation of lean sustainable systems using adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system: A case study. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2017, 10, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pousinho, H.M.I.; Mendes, V.M.F.; Catalão, J.P.S. A hybrid PSO–ANFIS approach for short-term wind power prediction in Portugal. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altin, N.; Sefa, İ. dSPACE based adaptive neuro-fuzzy controller of grid interactive inverter. Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 56, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshirband, S.; Petković, D.; Ćojbašić, Ž.; Nikolić, V.; Anuar, N.B.; Mohd Shuib, N.L.; Mat Kiah, M.L.; Akib, S. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy optimization of wind farm project net profit. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 80, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osório, G.J.; Matias, J.C.O.; Catalão, J.P.S. Electricity prices forecasting by a hybrid evolutionary-adaptive methodology. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 80, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, H.-Q.; Li, Y.-F. Comparison of new hybrid FEEMD-MLP, FEEMD-ANFIS, Wavelet Packet-MLP and Wavelet Packet-ANFIS for wind speed predictions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 89, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, K.; Shamshirband, S.; Tong, C.W.; Alam, K.A.; Petković, D. Potential of adaptive neuro-fuzzy system for prediction of daily global solar radiation by day of the year. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 93, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghandoor, A.; Samhouri, M.; Al-Hinti, I.; Jaber, J.; Al-Rawashdeh, M. Projection of future transport energy demand of Jordan using adaptive neuro-fuzzy technique. Energy 2012, 38, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, G.; Azizi, S.; Bahadori, A.; Elkamel, A.; Wan Alwi, S.R. Electricity demand estimation using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy network: A case study from the Ontario province—Canada. Energy 2013, 49, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, V.; Shamshirband, S.; Petković, D.; Mohammadi, K.; Ćojbašić, Ž.; Altameem, T.A.; Gani, A. Wind wake influence estimation on energy production of wind farm by adaptive neuro-fuzzy methodology. Energy 2015, 80, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, V.; Petković, D.; Shamshirband, S.; Ćojbašić, Ž. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy estimation of diffuser effects on wind turbine performance. Energy 2015, 89, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, S.; Shamshirband, S.; Basser, H.; Keivani, A.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Petković, D. Application of adaptive neuro-fuzzy methodology for estimating building energy consumption. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petković, D.; Shamshirband, S.; Kamsin, A.; Lee, M.; Anicic, O.; Nikolić, V. Survey of the most influential parameters on the wind farm net present value (NPV) by adaptive neuro-fuzzy approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshirband, S.; Keivani, A.; Mohammadi, K.; Lee, M.; Hamid, S.H.A.; Petkovic, D. Assessing the proficiency of adaptive neuro-fuzzy system to estimate wind power density: Case study of Aligoodarz, Iran. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellit, A.; Kalogirou, S.A. ANFIS-based modelling for photovoltaic power supply system: A case study. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, C. Interpolation of missing wind data based on ANFIS. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Jimenez, L.A.; Muñoz-Jimenez, A.; Falces, A.; Mendoza-Villena, M.; Garcia-Garrido, E.; Lara-Santillan, P.M.; Zorzano-Alba, E.; Zorzano-Santamaria, P.J. Short-term power forecasting system for photovoltaic plants. Renew. Energy 2012, 44, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilashi, M.; Ibrahim, O.; Ahani, A. Accuracy improvement for predicting Parkinson’s disease progression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilashi, M.; bin Ibrahim, O.; Ithnin, N. Hybrid recommendation approaches for multi-criteria collaborative filtering. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 3879–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-S.R.; Sun, C.-T.; Mizutani, E. Neuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing—A Computational Approach to Learning and Machine Intelligence, 1997.
- Nilashi, M.; bin Ibrahim, O.; Ithnin, N.; Sarmin, N.H. A multi-criteria collaborative filtering recommender system for the tourism domain using Expectation Maximization (EM) and PCA–ANFIS. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2015, 14, 542–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-Y. RFM-based eco-efficiency analysis using Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy and AHP approach. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2009, 29, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, H.; Gholamzadeh, M.; Shahmoradi, L.; Nilashi, M.; Rashvand, P. Diseases Diagnosis Using Fuzzy Logic Methods: A Systematic and Meta-Analysis Review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 161, 145–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilashi, M.; Dalvi-Esfahani, M.; Ibrahim, O.; Bagherifard, K.; Mardani, A.; Zakuan, N. A soft computing method for the prediction of energy performance of residential buildings. Measurement 2017, 109, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahani, A.; Rahim, N.Z.A.; Nilashi, M. Forecasting social CRM adoption in SMEs: A combined SEM-neural network method. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 75, 560–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilashi, M.; Bagherifard, K.; Rahmani, M.; Rafe, V. A recommender system for tourism industry using cluster ensemble and prediction machine learning techniques. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 109, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilashi, M.; Ibrahim, O.; Ahmadi, H.; Shahmoradi, L.; Farahmand, M. A hybrid intelligent system for the prediction of Parkinson’s Disease progression using machine learning techniques. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, L.M. Peak load forecasting using Bayesian regularization, Resilient and adaptive backpropagation learning based artificial neural networks. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2008, 78, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-H.; Kao, C.-H.; Lee, W.-H. A new interactive model for improving the learning performance of back propagation neural network. Autom. Constr. 2007, 16, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, P.; Bagheri, A. Navigating towards sustainable development: A system dynamics approach. Futures 2006, 38, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoroudis, E.; Kouikoglou, V.S.; Phillis, Y.A. SAFE 2013: Sustainability of countries updated. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 38, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

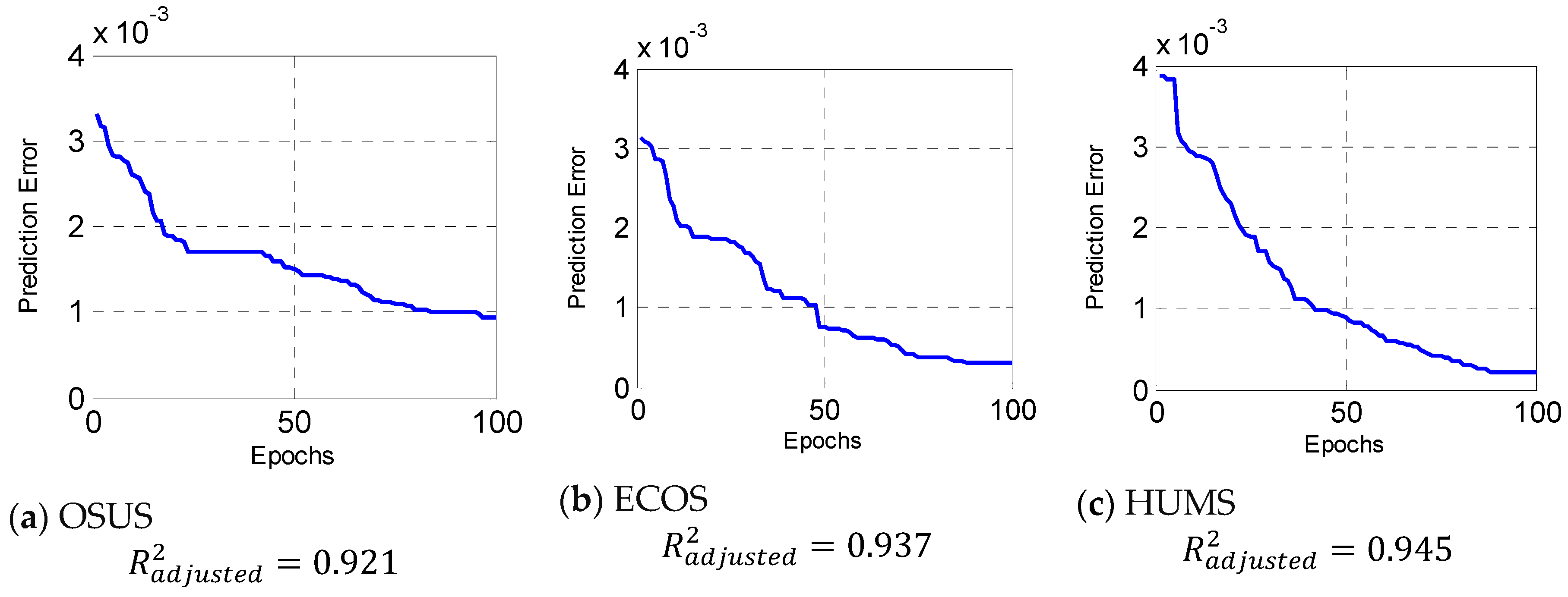
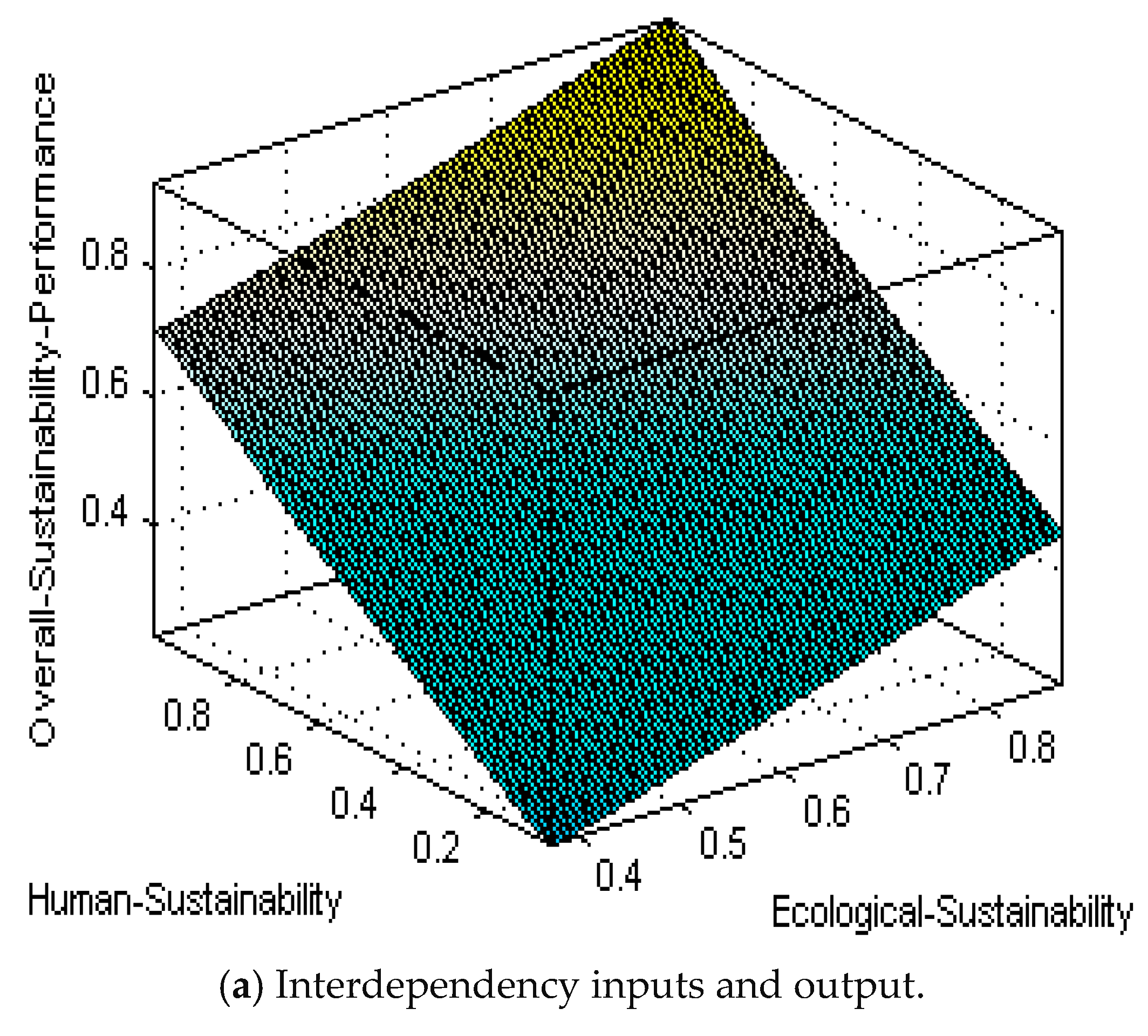
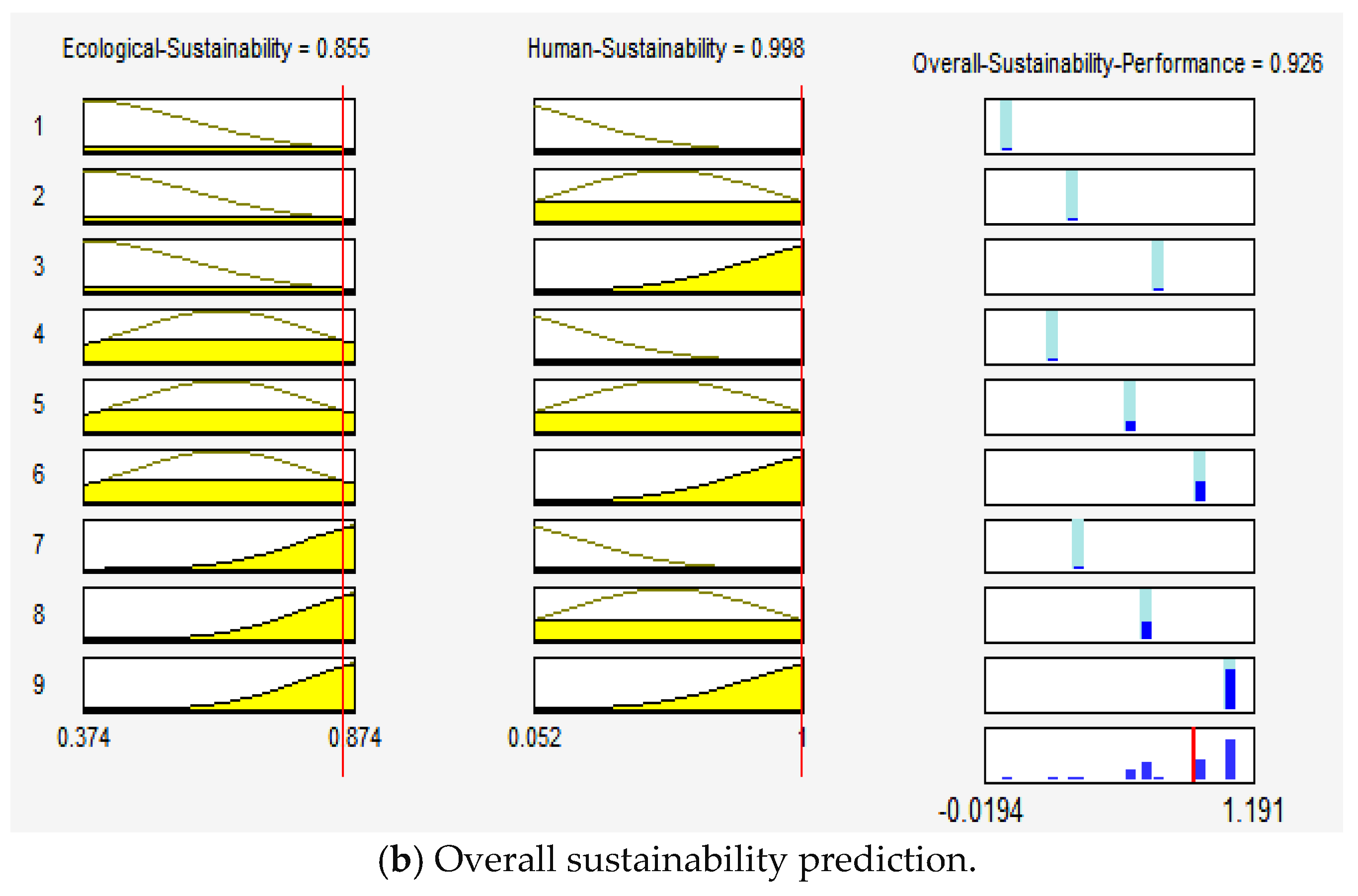
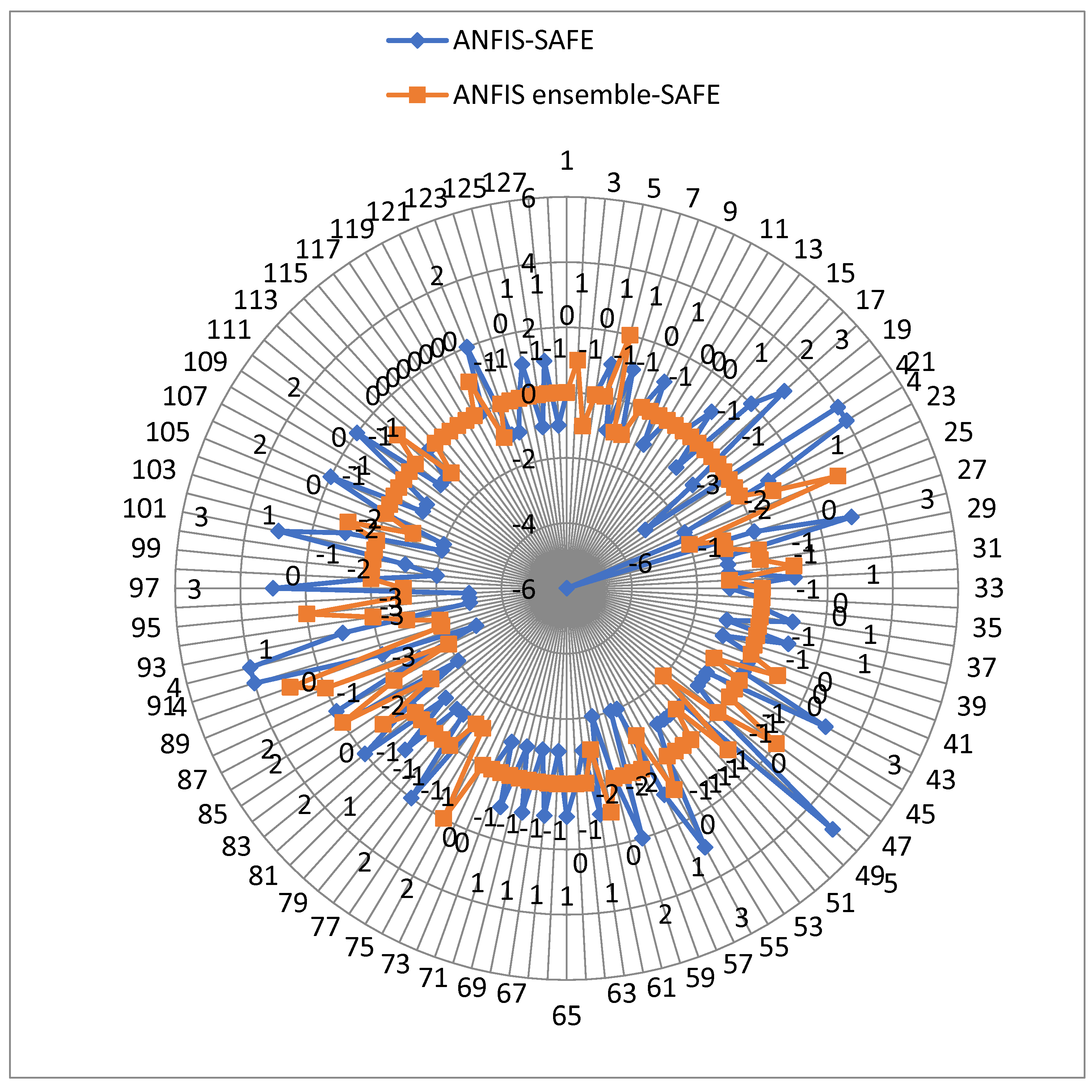
| Method | Membership Function | RMSE |
|---|---|---|
| ANFIS-Ensemble | Triangular, Generalized Bell-Shaped, Gaussian, and Π-Shaped | 0.00086 |
| ANFIS-Ensemble | Gaussian, Π-Shaped, and Generalized Bell-Shaped | 0.00065 |
| ANFIS-Ensemble | Gaussian, Triangular, and Generalized Bell-Shaped | 0.00059 |
| ANFIS-Ensemble | Gaussian, Triangular, and Π-Shaped | 0.00038 |
| NN | - | 0.02649 |
| SVR | - | 0.00916 |
| MLR | - | 0.03438 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nilashi, M.; Cavallaro, F.; Mardani, A.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Samad, S.; Ibrahim, O. Measuring Country Sustainability Performance Using Ensembles of Neuro-Fuzzy Technique. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10082707
Nilashi M, Cavallaro F, Mardani A, Zavadskas EK, Samad S, Ibrahim O. Measuring Country Sustainability Performance Using Ensembles of Neuro-Fuzzy Technique. Sustainability. 2018; 10(8):2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10082707
Chicago/Turabian StyleNilashi, Mehrbakhsh, Fausto Cavallaro, Abbas Mardani, Edmundas Kazimieras Zavadskas, Sarminah Samad, and Othman Ibrahim. 2018. "Measuring Country Sustainability Performance Using Ensembles of Neuro-Fuzzy Technique" Sustainability 10, no. 8: 2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10082707
APA StyleNilashi, M., Cavallaro, F., Mardani, A., Zavadskas, E. K., Samad, S., & Ibrahim, O. (2018). Measuring Country Sustainability Performance Using Ensembles of Neuro-Fuzzy Technique. Sustainability, 10(8), 2707. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10082707








