The Influence of Word of Mouth on Tourism Destination Choice: Tourist–Resident Relationship and Safety Perception among Mainland Chinese Tourists Visiting Macau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Tourist–Resident Relationship
2.2. Safety in a Destination
2.3. Research in Service Quality, Satisfaction, and Word of Mouth (WOM)
3. Research Method
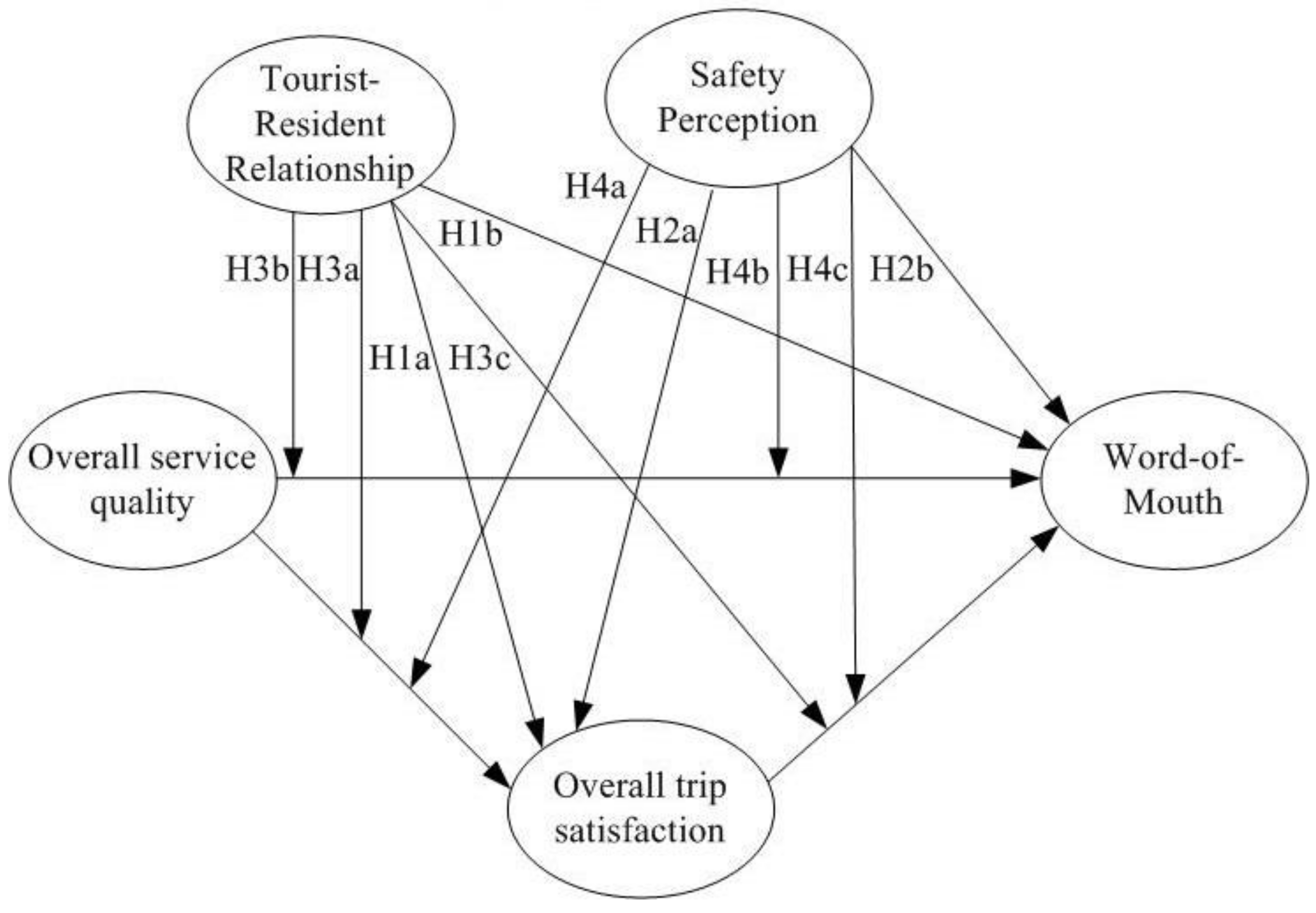
3.1. Research Hypothesis
3.2. Research Instrument
3.3. Questionnaire Design
3.4. Data Collection
3.5. Analysis Method
4. Findings
4.1. Reliability, Validity and Correlation
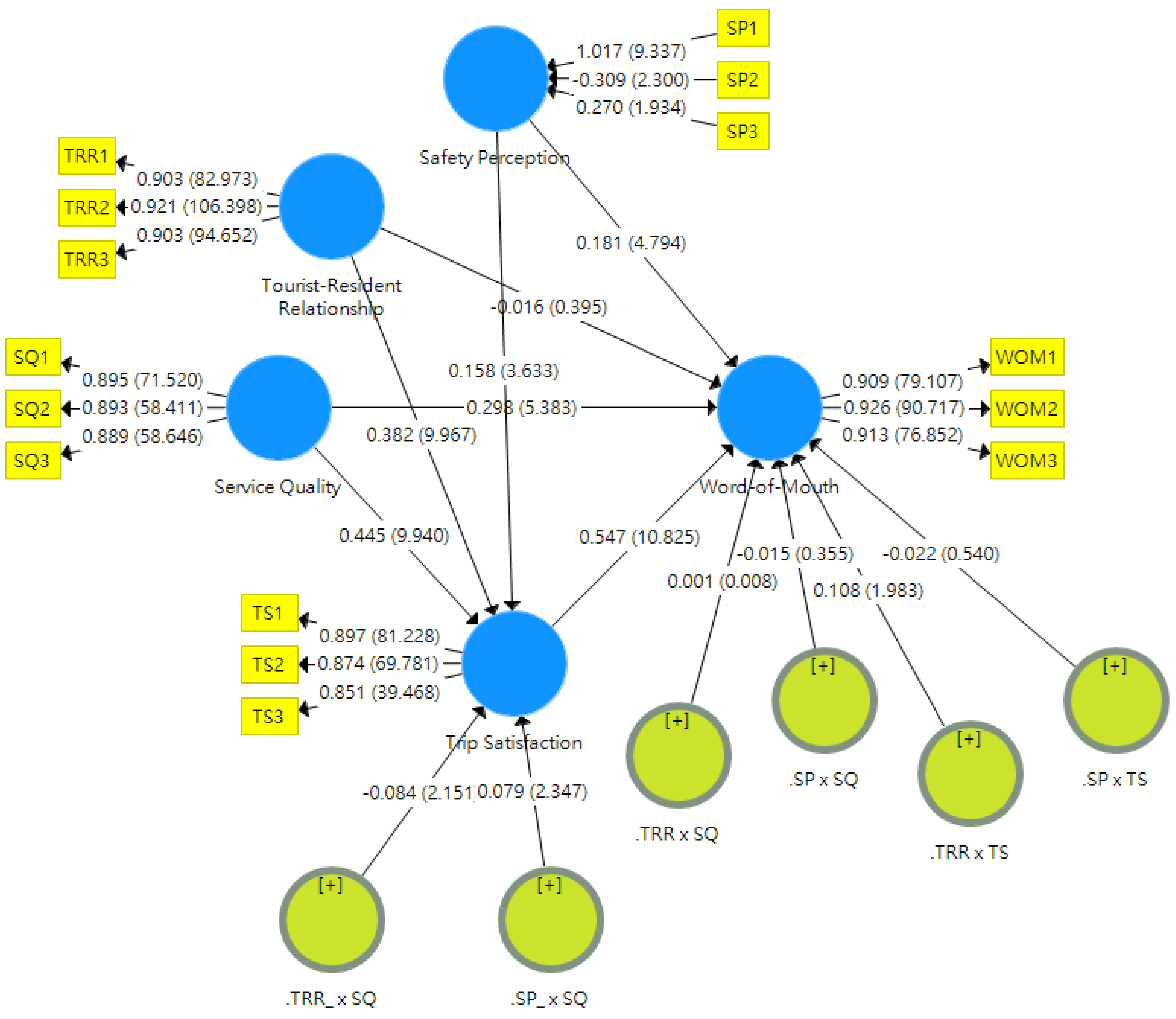
4.2. Results of PLS Analysis
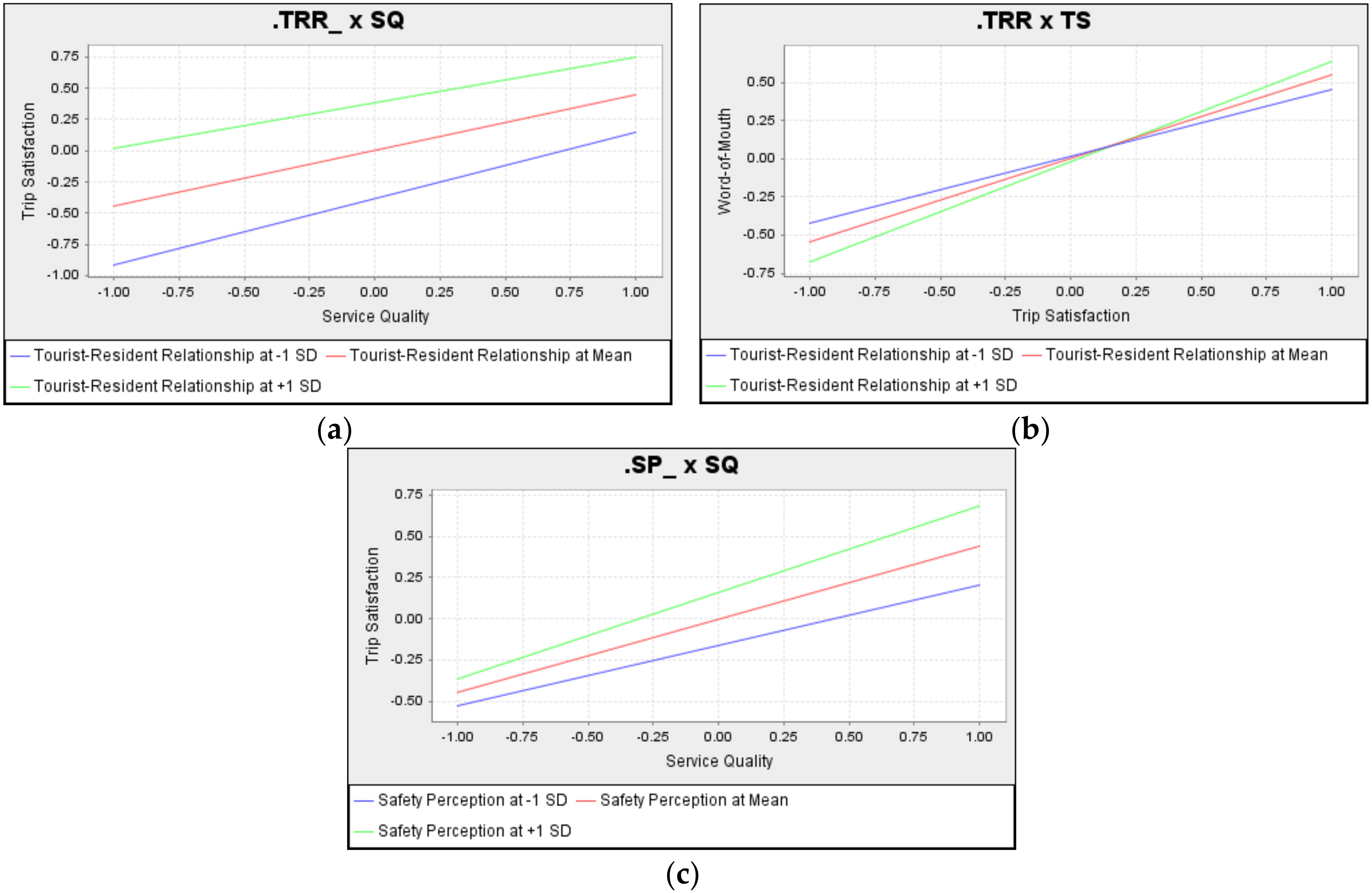
4.3. Further Analysis in Socio-Demographic Characteristics
5. Conclusions and Discussions
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Theoretical Contributions
5.3. Practical Implications
5.4. Limitations and Further Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCartney, G.; Lei, W.W.I. House of Cards—An analysis of Macao’s resident support for tourism and casino development. Tour. Hosp. Res. 2016, 16, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, I.K.W.; Hitchcock, M. Local reactions to mass tourism and community tourism development in Macau. J. Sustain. Tour. 2017, 25, 451–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Yoo, J.J. Travel motivations of Mainland Chinese travelers to the United States. J. China Tour. Res. 2011, 7, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfeld, Y.; Pizam, A. Toward a theory of tourism security. In Tourism, Security and Safety: From Theory to Practice; Mansfeld, Y., Pizam, A., Eds.; Elsevier, Butterworth-Heinemann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Adeloye, D.; Brown, L. Terrorism and domestic tourist risk perceptions. J. Tour. Cult. Chang. 2018, 16, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, A.; Croy, G.; Mair, J. Social media in destination choice: Distinctive electronic word-of-mouth dimensions. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2013, 30, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasci, A.D.A.; Gartner, W.C. Destination image and its functional relationships. J. Travel Res. 2007, 45, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, W.M.J.; Wolfe, K.; Hodur, N.; Leistritz, F.L. Tourist word of mouth and revisit intentions to rural tourism destinations: A case of North Dakota, USA. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2013, 15, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxey, G.V. A causation theory of visitor-resident irritants: Methodology and research inferences. In Proceedings of the Sixth Annual Conference on Travel and Tourism Research Associations, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–11 September 1975; pp. 195–198. [Google Scholar]
- Moyle, B.D.; Weiler, B.; Croy, G. Visitors’ perceptions of tourism impacts: Bruny and Magnetic Islands, Australia. J. Travel Res. 2013, 52, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C. Sustainable tourism as an adaptive paradigm. Ann. Tour. Res. 1997, 24, 850–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snepenger, D.J.; Murphy, L.; O’Connell, R.; Gregg, E. Tourists and residents use of a shopping space. Ann. Tour. Res. 2003, 30, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes-Freeland, F. Packaging dreams: Javanese perceptions of tourism and performance. In Tourism in Southeast Asia; Hitchcock, M., King, V.T., Parnwell, M.J.G., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 1993; pp. 138–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ap, J. Residents’ perceptions on tourism impacts. Ann. Tour. Res. 1992, 19, 665–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekrem, T.F.E.; Huseyin, O.; Sedat, Z. Resident attitudes toward tourism impacts: The case of Kusadasi in Turkey. Int. J. Hosp. Tour. Adm. 2002, 3, 79–100. [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg, K.; Johnson, R.L. Modeling resident attitudes toward tourism. Ann. Tour. Res. 1997, 24, 402–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, S.F.; Martin, S.R. Community attachment and attitudes toward tourism development. J. Travel Res. 1994, 32, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, G.F. Resident perceptions of the impact of tourism on an Australian city. J. Travel Res. 1992, 30, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.C.; Var, T. Resident attitudes toward tourism impacts in Hawaii. Ann. Tour. Res. 1986, 13, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, G.; Lee, L.Y.S.; Leung, D. Residents’ perceptions toward the “Chinese tourists’ wave” in Hong Kong: An exploratory study. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2013, 18, 446–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.M.; Park, S.H.; Huh, C. A Comparison Model of Residents’ and Tourists’ Attitudes toward Sustainable Tourism Development: A Case of Penghu Island in Taiwan. Tourism Travel and Research Association: Advancing Tourism Research Globally. 2016. Available online: http://scholarworks.umass.edu/ttra/2010/Oral/11 (accessed on 29 May 2018).
- United Nations Environment Programme and World Tourism Organization. Making Tourism More Sustainable-A Guide for Policy Makers. 2005. Available online: http://www.unep.fr/shared/publications/pdf/DTIx0592xPA-TourismPolicyEN.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2018).
- Hassan, S.S. Determinants of Market Competitiveness in an Environmentally Sustainable Tourism Industry. J. Travel Res. 2000, 38, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashyanusorn, V.; Kaviya, S.; Yupapin, P. Surveillance system for sustainable tourism with safety and privacy protection. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2010, 2, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, C. Crime, violence, terrorism and tourism: An accidental or intrinsic relationship? Tour. Manag. 1993, 14, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekinc, J.; Cvikl, H. The structure of security and safety crises in tourism. J. Tour. Serv. 2013, 4, 38–50. [Google Scholar]
- Seabra, C.; Dolnicar, S.; Abrantes, J.L.; Kastenholz, E. Heterogeneity in risk and safety perceptions of international tourists. Tour. Manag. 2013, 36, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumayer, E. The impact of political violence on tourism: Dynamic cross-national estimation. J. Confl. Resolut. 2004, 48, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J. Mexico Cartel Clashes Worry Canadian Tourists. CTVNew.ca Published Tuesday, 5 May 2015 10:44AM EDT. 2015. Available online: http://www.ctvnews.ca/canada/mexico-cartel-clashes-worry-canadian-tourists-1.2359460 (accessed on 20 May 2018).
- Pizam, A. A comprehensive approach to classifying acts of crime and violence at tourism destinations. J. Travel Res. 1999, 38, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerva, K. Crime and tourism: Organizational opportunities and social marketing in LA Gang Tours. J. Tour. Cult. Chang. 2013, 11, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, R. Tourist’s perceptions of safety and security while visiting Cape Town. Tour. Manag. 2003, 24, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, P.; Mawby, R.; Hambly, Z. Tourist victimization and the fear of crime on holiday. Tour. Manag. 2000, 21, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Frimpong, N.; Nwankwo, S.; Blankson, C.; Tarnanidis, T. The effect of service quality and satisfaction on destination attractiveness of sub-Saharan African countries: The case of Ghana. Curr. Issues Tour. 2013, 16, 627–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.B.; Qu, H. Is there any gender effect on the relationship between service quality and word-of-mouth? J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2011, 28, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakharyan, M.; Omidvar, S.; Khodadadian, M.R.; Jalilvand, M.R.; Nasrolahi Vosta, L. Examining the effect of customer-to-customer interactions on satisfaction, loyalty, and word-of-mouth behaviors in the hospitality industry: The mediating role of personal interaction quality and service atmospherics. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2014, 31, 610–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.S.; Byun, B.; Shin, S. An Examination of the Relationship between Rural Tourists’ Satisfaction, Revisitation and Information Preferences: A Korean Case Study. Sustainability 2014, 6, 6293–6311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.A.; Crompton, J.L. Quality, satisfaction and behavioral intentions. Ann. Tour. Res. 2000, 27, 785–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.J. The impact of emotions on service quality, satisfaction, and positive word-of-mouth intentions over time. J. Mark. Manag. 2010, 26, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A.; Zeithaml, V.A.; Berry, L.L. A conceptual model of service quality and its implications for future research. J. Mark. 1985, 49, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, I.K.W.; Hitchcock, M.; Yang, T.; Lu, T.W. Literature review on service quality in hospitality and tourism (1984–2014): The future directions and trends. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 20, 114–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouthouris, C.; Alexandris, K. Can service quality predict customer satisfaction and behavioral intentions in the sport tourism industry? An application of the SERVQUAL model in an outdoors setting. J. Sport Tour. 2005, 10, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Lee, H.T.; Chen, S.H.; Huang, T.H. Tourist behavioral intentions in relation to service quality and customer satisfaction in Kinmen National Park, Taiwan. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2011, 13, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Law, R. The influence of hotel price on perceived service quality and value in e-tourism: An empirical investigation based on online traveller reviews. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2014, 38, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, R.M.; Rodríguez, E.T.F.; Díaz, R.R. A model of market positioning based on value creation and service quality in the lodging industry: An empirical application of online customer reviews. Tour. Econom. 2015, 21, 1273–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, I.K.W. The roles of value, satisfaction, and commitment in the effect of service quality on customer loyalty in Hong Kong-style tea restaurants. Cornell Hosp. Quart. 2015, 56, 118–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J.J., Jr.; Brady, M.K.; Hult, G.T.M. Assessing the effects of quality, value, and customer satisfaction on consumer behavioral intentions in service environments. J. Retail. 2000, 76, 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richins, M.L. Negative word-of-mouth by dissatisfied consumers: A pilot study. J. Mark. 1983, 47, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloemer, J.; de Ruyter, K.; Wetzels, M. Linking perceived service quality and service loyalty: A multi-dimensional perspective. Eur. J. Mark. 1999, 33, 1082–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramwell, B.; Lane, B. Sustainable Tourism: An Evolving Global Approach. J. Sustain. Tour. 1993, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappu, R.; Quester, P. Does customer satisfaction lead to improved brand equity? An empirical examination of two categories of retail brands. J. Prod. Brand Manag. 2006, 15, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J.J.; Taylor, S.A. Measuring service quality: A reexamination and extension. J. Mark. 1992, 56, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.W.; Fornell, C.; Lehmann, D.R. Customer satisfaction, market share and profitability. J. Mark. 1994, 58, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.L. Satisfaction: A Behavioral Perspective on the Consumer; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bloemer, J.; Odekerken-Schroder, G. Store satisfaction and store loyalty explained by customer- and store-related factors. J. Cust. Satisf. Dissatisfaction Complain. Behav. 2002, 15, 68–80. [Google Scholar]
- UNWTO. Sustainable Development of Tour. Available online: http://sdt.unwto.org/content/about-us-5 (accessed on 26 October 2017).
- Meng, S.M.; Liang, G.S.; Yang, S.H. The relationships of cruise image, perceived value, satisfaction and post-purchase behavioral intention on Taiwanese tourists. Afr. J. Bus. Manag. 2011, 5, 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Okello, M.M.; Yerian, S. Tourist Satisfaction in Relation to Attractions and Implications for Conservation in the Protected Areas of the Northern Circuit, Tanzania. J. Sustain. Tour. 2009, 17, 605–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Var, T.; Beck, R.A.D.; Loftus, P. Determination of tourism attractiveness of the touristic areas in British Columbia. J. Travel Res. 1997, 15, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hse, C.H.C.; Cai, L.A.; Li, M. Expectation, motivation, and attitude: A tourist behavioral model. J. Travel Res. 2010, 49, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.M.; Long, Y.; Wall, G.; Jin, M. Tourist–community interactions in ethnic tourism: Tuva villages, Kanas Scenic Area, China. J. Tour. Cult. Chang. 2016, 14, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizam, A.; Tarlow, P.E.; Bloom, J. Making tourists feel safe: Whose responsibility is it? J. Travel Res. 1997, 36, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasci, A.D.A.; Boylu, Y. Cultural comparison of tourists’ safety perception in relation to trip satisfaction. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2010, 12, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Uysal, M. An examination of the effects of motivation and satisfaction on destination loyalty: A structural model. Tour. Manag. 2005, 26, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkovics, R.R.; Penz, E. Social distance between residents and international tourists—Implications for international business. Int. Bus. Rev. 2009, 18, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechinda, P.; Serirat, S.; Gulid, N. An examination of tourists’ attitudinal and behavioral loyalty: Comparison between domestic and international tourists. J. Vacat. Mark. 2009, 15, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, S.; Ratchford, B.T.; Talukdar, D. Consumer information search revisited: Theory and empirical analysis. J. Consum. Res. 1997, 23, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitner, M.J. Evaluating service encounters: The effects of physical surroundings and employee responses. J. Mark. 1990, 54, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, B.; Rajendran, C.; Prakash Sai, L. Scales to measure and benchmark service quality in tourism industry. Benchmark. Int. J. 2008, 15, 469–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, M.; Pettinari, J. Personal safety and transit paths, environments, stops and stations. In Final Report Centre for Transportation Studies; Center for Transporation Studies: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Babin, B.J.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, E.J.; Griffin, M. Modeling consumer satisfaction and word-of-mouth: Restaurant patronage in Korea. J. Serv. Mark. 2005, 19, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.J.; van Witteloostuijn, A.; Eden, L. From the editors: Common method variance in international business research. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2010, 41, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DSEC, 2016 Statistics Reports, Statistics and Census Service. Government of Macao Special Administrative Region. 2016. Available online: http://www.dsec.gov.mo/default.aspx?noredirect=true (accessed on 20 May 2018).
- Macao Tourism Data Plus, Tourism Statistics. Government of Macao Special Administrative Region. 2018. Available online: http://mtdplus.macaotourism.gov.mo (accessed on 20 May 2018).
- Wan, Y.K.P.; Li, X. Sustainability of tourism development in Macao, China. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2013, 15, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wan, Y.K.P. Residents’ attitudes toward tourism development in Macao: A path model. Tour. Anal. 2013, 18, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringle, C.M.; Wende, S.; Becker, J.M. SmartPLS 3. Boenningstedt: SmartPLS GmbH, 2015. Available online: http://www.smartpls.com (accessed on 20 May 2018).
- Haenlein, M.; Kaplan, A.M. A beginner’s guide to partial least square analysis. Underst. Stat. 2004, 3, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Choi, S.Y.; Kang, Y.S. Formation of e-satisfaction and repurchase intention: Moderating roles of computer self-efficacy and computer anxiety. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 7848–7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. PLS-SEM: Indeed a silver bullet. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 2011, 19, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Mena, J.A. An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2012, 40, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Valle, P.O.; Assaker, G. Using partial least squares structural equation modeling in tourism research: A review of past research and recommendations for future applications. J. Travel Res. 2016, 55, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulos, A.; Winklhofer, H.M. Index construction with formative indicators: An alternative to scale development. J. Mark. Res. 2001, 38, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), 2nd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Monbiot, G. How Sustainability Became “Sustained Growth”. 2012. Available online: http://www.monbiot.com/2012/06/22/how-sustainability-became-sustained-growth/ (accessed on 20 May 2018).
- Bramwell B, L.B. Sustainable tourism: An evolving global approach. J. Sustain. Tour. 1993, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanja, A.; Dragicevic, V.; Pejović, L. Interaction between tourists and residents: Influence on tourism development. Pol. Sociol. Rev. 2011, 173, 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Wei, C.; Li, W.; Wang, L. Residents’ attitudes towards sustainable tourism development in a historical-cultural village: Influence of perceived impacts, sense of place and tourism development potential. Sustainability 2017, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muresan, I.C.; Oroian, C.F.; Harun, R.; Arion, F.H.; Porutiu, A.; Chiciudean, G.O.; Todea, A.; Lile, R. Local residents’ attitude toward sustainable rural tourism development. Sustainability 2016, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Gursoy, D. An investigation of tourists’ destination loyalty and preferences. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2001, 13, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, R.; Swart, K. Tourists’ perceptions of London, United Kingdom (UK), as a safe host city during the 2012 Olympic Games. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2015, 32, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Frequency | Percent | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 184 | 47.7 |
| Female | 202 | 52.3 | |
| Age | 20 or under 20 | 13 | 3.4 |
| 21–30 | 112 | 29.0 | |
| 31–40 | 129 | 33.4 | |
| 41–50 | 111 | 28.8 | |
| Over 50 | 21 | 5.4 | |
| Education | Secondary school level | 54 | 14.0 |
| Undergraduate level | 281 | 72.8 | |
| Postgraduate level | 51 | 13.2 | |
| Income (personal monthly) | Less than USD1000 | 13 | 3.4 |
| USD1000–2999 | 162 | 42.0 | |
| USD3000 or above | 211 | 54.7 | |
| Main purpose | Business | 38 | 9.8 |
| Visit relatives | 20 | 5.2 | |
| Vacation | 328 | 85.0 |
| Measured Item | Mean | Std. Dev. | Factor Loadings | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SQ | Overall service quality (adapted from Cronin et al. [47]) | |||
| SQ1 | The overall tourism services delivered in Macau is excellent. | 5.891 | 0.978 | 0.895 |
| SQ2 | Overall, the tourism services offerings in Macau are of high quality. | 5.930 | 0.948 | 0.893 |
| SQ3 | Macau maintains superior tourism services in every way. | 5.922 | 0.887 | 0.889 |
| TS | Trip satisfaction (adapted from Bloemer and Odekerken-Schroder [55]) | |||
| TS1 | I am fully satisfied with the trip to Macau. | 5.754 | 1.108 | 0.897 |
| TS2 | The tourism services offered in Macau meet my expectations. | 5.547 | 1.206 | 0.874 |
| TS3 | I am satisfied with my decision to visit Macau. | 5.650 | 1.240 | 0.851 |
| WOM | Word of mouth (adapted from Babin et al. [71]) | |||
| WOM1 | I will encourage friends and relatives to visit Macau. | 5.870 | 1.079 | 0.909 |
| WOM2 | I will recommend Macau to someone who seeks my advice. | 5.870 | 1.128 | 0.926 |
| WOM3 | I will say positive things about Macau to other people. | 5.925 | 1.139 | 0.913 |
| TRR | Tourist–resident relationship | |||
| TRR1 | The residents in Macau are willing to have contact with tourists. | 5.049 | 1.425 | 0.903 |
| TRR2 | The residents in Macau show friendliness to tourists. | 4.951 | 1.519 | 0.921 |
| TRR3 | The residents in Macau are willing to interact with tourists. | 5.026 | 1.477 | 0.903 |
| SP | Safety perception | |||
| SP1 | I don’t feel worried about crime in Macau. | 5.759 | 1.155 | |
| SP2 | I don’t feel worried about violence in Macau. | 5.889 | 1.209 | |
| SP3 | I don’t feel worried about terrorist attacks in Macau. | 5.878 | 1.128 | |
| Cronbach’s Alpha | CR | AVE | SP | SQ | TRR | TS | WOM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SQ | 0.872 | 0.921 | 0.796 | 0.463 | 0.892 | |||
| TRR | 0.895 | 0.934 | 0.826 | 0.348 | 0.443 | 0.909 | ||
| TS | 0.845 | 0.907 | 0.764 | 0.496 | 0.685 | 0.642 | 0.874 | |
| WOM | 0.904 | 0.940 | 0.839 | 0.577 | 0.723 | 0.509 | 0.796 | 0.916 |
| Coefficients | t-Statistic | f-Square | Hypothesis | Result | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SQ → TS | 0.445 *** | 9.940 | 0.306 | ||
| SQ → WOM | 0.298 *** | 5.383 | 0.128 | ||
| TS → WOM | 0.547 *** | 10.825 | 0.364 | ||
| TRR → TS | 0.382 *** | 9.967 | 0.306 | H1a | Accept |
| TRR → WOM | −0.016(ns) | 0.395 | 0.001 | H1b | Reject |
| SP → TS | 0.158 *** | 3.633 | 0.052 | H2a | Accept |
| SP → WOM | 0.181 *** | 4.794 | 0.080 | H2b | Accept |
| SQ × TRR → TS | −0.084 * | 2.151 | 0.013 | H3a | Accept |
| SQ × TRR → WOM | 0.001(ns) | 0.008 | 0.000 | H3b | Reject |
| TS × TRR → WOM | 0.108 * | 1.983 | 0.022 | H3c | Accept |
| SQ × SP → TS | 0.079 * | 2.347 | 0.015 | H4a | Accept |
| SQ × SP → WOM | −0.015(ns) | 0.355 | 0.001 | H4b | Reject |
| TS × SP → WOM | −0.022(ns) | 0.540 | 0.001 | H4c | Reject |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, I.K.W.; Hitchcock, M.; Lu, D.; Liu, Y. The Influence of Word of Mouth on Tourism Destination Choice: Tourist–Resident Relationship and Safety Perception among Mainland Chinese Tourists Visiting Macau. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072114
Lai IKW, Hitchcock M, Lu D, Liu Y. The Influence of Word of Mouth on Tourism Destination Choice: Tourist–Resident Relationship and Safety Perception among Mainland Chinese Tourists Visiting Macau. Sustainability. 2018; 10(7):2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072114
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Ivan Ka Wai, Michael Hitchcock, Dong Lu, and Yide Liu. 2018. "The Influence of Word of Mouth on Tourism Destination Choice: Tourist–Resident Relationship and Safety Perception among Mainland Chinese Tourists Visiting Macau" Sustainability 10, no. 7: 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072114
APA StyleLai, I. K. W., Hitchcock, M., Lu, D., & Liu, Y. (2018). The Influence of Word of Mouth on Tourism Destination Choice: Tourist–Resident Relationship and Safety Perception among Mainland Chinese Tourists Visiting Macau. Sustainability, 10(7), 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072114





