Abstract
During the last three decades, human behavior has been becoming energy alarming towards environmental sustainability. One of the most influential initiatives towards environmental protection and increased environmental consciousness is the solidification of primary and secondary environmental education. The purpose of this paper is to investigate different environmental profiles amongst secondary education students, in light of a multi-parametric analysis that involved the contributive role of school and family towards environmental awareness and participation. By reviewing relevant studies, the benefits offered by environmental education are presented. Accordingly, a questionnaire survey was deployed using a sample of 270 secondary education students, from schools situated in the prefecture of Larissa, central Greece. The statistical methods included factor analysis and cluster analysis. Particularly, four groups of different environmental characteristics are identified and interviewed. Results suggest that most students are environmental affectionate, although there is a need for more solidified environmental education and motivation from out-of-school societal opportunities, such as in the contexts of family and public socialization. The deployed research method and analysis can be proven supportive in adopting and scheduling school environmental programs after an initial identification of the various environmental attitudes among the student population.
1. Introduction
In recent years, severe environmental problems are associated with rising energy consumption due to economic development and population growth, while a simultaneous imperative need for a sustainable environment for humans necessitates the scientific and technological research to be concentrated on energy preservation and the abiding role of renewable energy sources (RES) [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. In the Brundtland Report (1987), issued under the World Commission on Environment and Development, the need to value the obligations for future generations in balance to the needs of present generations was introduced, setting the foundations for “sustainable development” [8]. In the environment-based literature production, the need for a safe, environmentally sound and economically viable energy pathway that supports human progress into future generations was recognized, in line with efficient energy use and the development of renewables [9,10,11]. Implementing the context of sustainability in the real world, the EU set a target of increasing RES share up to 20% upon total energy consumption by the year 2020, while Greece has committed to achieving RES penetration up to 18% of its total national energy consumption [12]. European countries, China and Greece have set additional national targets for achieving sustainable development under national strategies for sustainable development [13,14,15,16].
In response to global alarm for current environmental depletion, many studies have been published, especially during the last decade. Several studies focus on the effective production, distribution, and exploitation of biomass energy, especially within residential areas, where diverse RES exists [17,18,19,20]. These studies also signify an increasing awareness of energy-focused education programs. It is reported that shifts in energy consumption and energy behavior can be achieved by changing cultural beliefs that are also abiding to the need of continuing and life-long education.
In a normal societal context, energy behavior is promptly instilled inside the family environment and is subsequently developed by the citizens’ cultural and societal behavior out of the core-household environment. The existing research production on energy behavior is mainly focused on energy consumption in residential areas, attempting to determine the factors that simultaneously define human behavior and energy use [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. Households consume energy not only to satisfy subsistence needs of their members, but also towards a wider spectrum of societal activities, such as transport, work, leisure, and entertainment [41]. In residential areas, domestic energy consumption can widely vary within households, since it is directly associated with households’ behavior and sociodemographic characteristics [42,43]. Relevant studies highlight the impact of individuals’ energy behavior and conclude that around 1/3 of the residential energy consumption is attributed to diversified variations that are prevailing in each household [44,45].
An essential step towards changing energy behavior is the notional development of an “environmental culture”. In the relevant literature production, the concept of environment in sustainable development (ESD) is not new, dating over a decade ago, both for North Europe and for countries worldwide [46,47]. Environmental education aims at formulating an ecological awareness from early ages [48]. In this respect, programs implemented as early as in preschool age constitute a much different educational approach in comparison to the traditional educational methods, which have been implemented in past educational curricula. Such programs are characterized by their student-centered nature, the active role attributed to the person undergoing education and, among others, the mutual collaboration between the children and the educator for the desired outcome to be achieved for children of preschool age [48].
In the context of energy education, there is a growing interest for research in the dynamic linkage between energy-based issues and their educational context of applicability. The pronounced role of science education adaptation to the taught educational curriculum in primary schools is highlighted [49]. Such educational reforms enable students to be scientifically and technologically literate citizens and shapes their thinking and behavior towards the importance of sustainable development.
Therefore, it can be noted that environmental behavior change is a dynamic but low-pace process that can be proven achievable through proper education.
Within the above theoretical framework, the sampling methodology suggested in this study is pooled from secondary education students, taking as its premise that, if properly educated, they are vital and effective stakeholders and future decision makers in promoting environmentally responsible behavior at their family and socializing environment [50,51]. According to the proposed methodology, the profile of secondary education students concerning environmental awareness and environmental behavior is captured and used to classify them into clusters, to facilitate decision makers for the application of efficient environmental education programs. Furthermore, a theoretical review on the benefits that environmental education offers, with implications for secondary education, are presented in the theoretical section.
2. Benefits of Environmental Education
Several studies manipulate the interdisciplinary issues of Environmental education/environmental issues/energy behavior, in an integrated manner [52,53,54]. Energy-oriented curricula of environmental education must be an integral and inseparable part of contemporary education for all citizens. The key-entity of “sustainability” can develop environmentally conscious citizens from their early phases of education. The purpose of a “sustainable school” is not only to help children acquire environmental literacy and understand the dimensions of sustainability. The main goal of such an educational reform is to change the school itself for promoting sustainability and helping today students to follow sustainable practices in their everyday life. Indeed, this educational reform is the tool for achieving sustainable development and instilling energy behavior into all levels of educational operation: teaching, social/organizational, and technical/financial [55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66]. Educational activities play a dominant role to educate students on how to take initiatives, set goals, make decisions, handle information data, and be engaged in creative argumentation and productive criticism [67]. Energy-educated children can stand on an equal footing to the adult members of the family, participate, take initiatives, and rationalize their argumentation in taking household decisions and priorities concerning energy consumption. Environmental education in schools can also promote the agenda of energy wastes reduction in households [68,69].
A cognitive gap between attitudes and behavior has been attributed to a contradiction between a generalized interest for the environment and a feeling of hopelessness and incapability in applying this interest to specific actions [70]. Under this framework, environmental education can play a determining role, enabling students to develop sustainability-conscious behavior and make decisions in favor of a sustainable environment. Students are vital contributors to the development of environmental consciousness and the promotion of environmentally responsible behavior [50]. Furthermore, it has been reported that secondary school students are prone to rapid intellectual development, with the ability of abstracted thinking. This period of students’ psychosomatic development is significant because students of this group-age develop their personality values of socialization and shape their attitudes towards environment protection [71].
Teaching about climate change in environmental secondary education curricula is considered crucial for developed countries [72]. Particularly, teachers in the US are willing to teach climate change topics with their students, taking this as an opportunity to teach them the nature of sciences and strengthen their skills upon data analysis, systematic thinking, and critical argumentation [72]. Such a climate-driven curriculum offers the opportunity to make climate change topic familiar to local communities, by enriching the knowledge upon local ecosystem impacts and opening policies’ argumentation upon the relevant taught curricula.
In the case of developing countries, environmental education is crucial for primary education because in many countries this educational level is the only formal education that children may receive throughout their life-span. In this respect, energy-related school courses may facilitate students and parents with energy-oriented information, especially in those countries in which there is a cultural trait for parents to be actively involved in their children’s schoolwork [73]. In a relevant study, it has been pointed out that many secondary education students in Turkey were introduced to the renewable energy entity during their secondary school education [74]. The contribution of greenhouse gas emissions to environmental degradation, as well as the pronounced role of education driven public awareness upon environment pollution and petroleum exploration has been pointed out in a study for Uganda [54].
In the Greek context, environmental sustainability in higher education students has been investigated in a study on Aegean University [75]. The authors reported important constraints concerning the promotion of environmental sustainability. Particularly, according to the interviewed students, the most important constraint is lack of environmental knowledge among the academic community members. Another critical issue is lack of environmental projects funding from private-based ownership, since Greek university funding is mainly state-dependent [75]. Furthermore, a study for Greek elementary students in the Prefecture of Evros reveals that students are sensitive to energy management issues and recycling [76].
Conclusively, a successful adaptation and implementation of an environmental education to current curricula of secondary education worldwide should reflect the accomplishment of:
- Critical thinking skills [72]: Creative thinking in environmental education remains a greatly under-researched topic, thus connections must be opened to broader approaches that are currently narrowing creativity of the relevant researches undertaken to handle environmental problems [77]. Developing contextual thinking in students seems to be a key-parameter for the perspectives of educational reforms [78]. Under an environmental education context, the need for active engagement with environmental topics and the active participation in monitoring and problem-solving activities should prevail over the need for obtaining individual knowledge [78]. Educational activities play a dominant role to educate students how to take initiatives, set goals, make decisions, handle information data, and be engaged to creative argumentation and productive criticism [67].
- The entities of “sustainability” and “environmental clubs” that reflect how these notions can help both teachers and learners to develop all skills and positive attitudes’ needed towards the environmental sustainability [79]. In a relevant study, it was pointed out that biodiversity loss has encouraged scientists to begin promoting the idea of ecosystem services that can be offered to humans to be active supporters of conservation policies. To this end, the concept of ecosystem services can be designed to communicate societal needs. This societal viewpoint is perfectly served by the school system because it plays a key role in educating students to be active and responsible citizens [80]. In another study, the link between the “sustainable development” concept and development was investigated [81]. This author proposed some examples of sustainability integration in new textbooks for primary education. Under this research framework, it was illustrated the extent of curricular materials that could contribute to developing skills, values, and attitudes aligned with sustainable development perspectives [81].
- The elevation of the environment as a vital natural asset that strengthens the proactive and active inquiry to promote problem-based learning approaches in real environment-degradation issues. Under this framework, technology can also be used as a supportive tool that induces a new educational approach, not just to be used in reproducing traditional teaching roles that are based in conservative repetition of environmental concepts [82]. Students and citizens familiar with the methodological tools of web-repositories and web-quests for environmental education can assist in promoting environmental affection [83].
- Key-project stakeholders to explore the challenges of project sustainability and promote participation. Applying the principles of interdisciplinary learning theory, the contradictions that emerge from the interaction between different project stakeholders can be rationalized and taught within the school environment, as powerful sources for learning [84].
3. Materials and Methods
The purpose of this study was the classification of students according to their profile on environmental awareness. Data collection was performed using a structured questionnaire including various dichotomous type questions and Likert type questions on the topics of school and family role toward environmental behavior, students’ environmental consciousness and environmental knowledge.
The statistical methods used in this study included descriptive statistics, reliability analysis, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and cluster analysis by using the K-means algorithm. K-means clustering is applicable because of the large sample size [85]. This statistical process initiates by assigning temporary k-centroids. If the distance of an observation from the center is higher than the shortest distance between that center and all other centers, this observation replaces the nearest cluster center. The centers are continually re-evaluated, based on the above criteria through a loop process. The process is repeated until there is no change in the centers or the convergence criterion has been achieved [85,86,87].
In the Results Section, the socio-demographic profile and respondents’ opinion on environmental questions are presented. Affirmative responses to the dichotomous (yes/no) variables are expressed as percentages of the total sample, whereas responses to Likert-type questions are presented by using the mean and standard deviation. Subsequently, reliability analysis by using Cronbach’s alpha is deployed. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) method is afterwards used to identify factors (components). The same methodology was applied in an analogous study for the energy behavior of secondary education Greek students in Grevena [88]. In this method, each one of the identified factors (components) interprets a percentage of the variance that has not been captured by previous factors (components). The final number of factors (components) is determined according to the Kaiser criterion, where a factor is created when the calculated eigenvalue is greater than 1. Finally, by using the variables created from the PCA method, k-mean analysis estimated the number of students included in each cluster, sustaining common environmental characteristics.
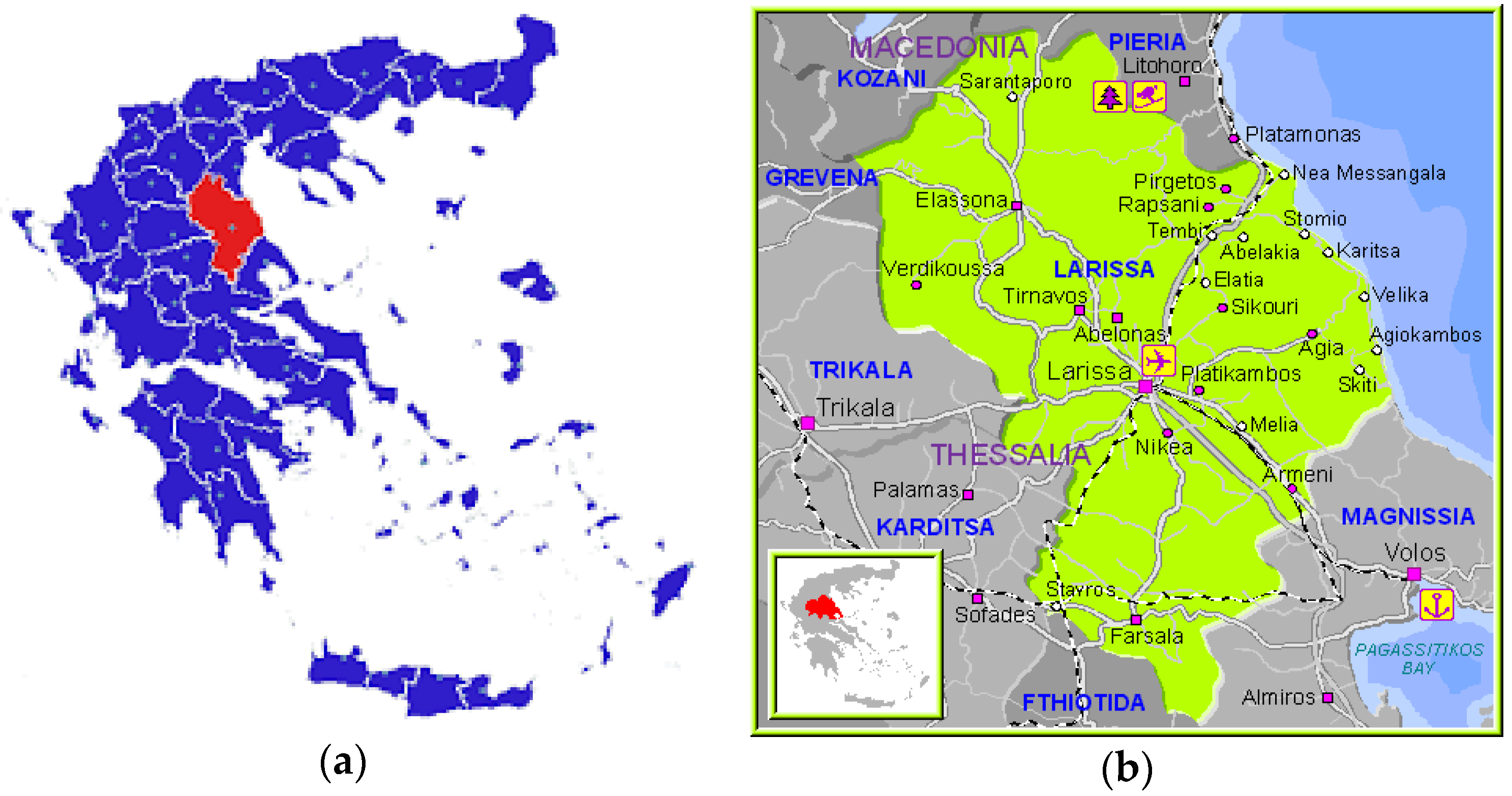
This research was conducted during 2014 within Larissa Regional Unit (Figure 1). The research area is in the northeastern part of Thessaly, where Larissa is largest regional unit at about 5381 km2 occupying 38.3% of the total area of the Region [89]. The population is 284,420 inhabitants according to the 2011 National Statistical Service census. The economic character of Larissa Regional Unit is outlined under the three main economic sectors (primary, secondary and tertiary). The primary sector is a key activity for the area and is characterized by: (a) low field resting rate; (b) the dominance of arable crops; and (c) minor contribution of forestry and fishery products. The secondary economic sector is focused on processing of agricultural products. There are also activities such as wood processing, textiles, garment production, food, paper, engineering and machining. The tertiary economic sector is mainly dominated by commercial activity and industry services owing to the area’s strategic geographical position on the county map.
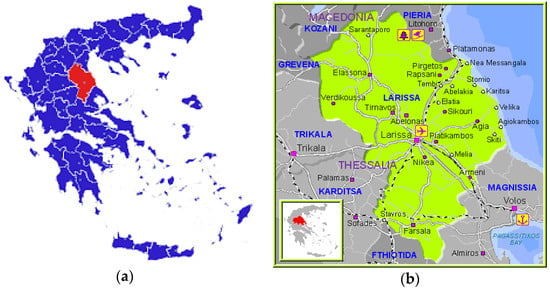
Figure 1.
(a) Map of Greece depicting the regional unit of Larissa citation upon the map [90]; and (b) detailed research area map [91].
Under the research framework of this study, students attending the third grade of Secondary education schools constituted the research population. The total number of students (15 year old) attending the third grade, at the Regional Unit of Larissa at the time of the survey, was 2589 [92]. The sample of this research consisted of 270 students, accounting for 10.4% of the total student population attending the third Grade of secondary education (Table 1). Concerning sample size calculation, according a formula provided by the CheckMarket survey company [93], for a confidence level of 95%, we expected an error margin of 5.65% for our analysis. The sample was taken from four representative schools of the research area: the 1st Secondary school of Larissa, the 1st High School of Elassona, the 1st Secondary School of Farsala, and the 2nd Secondary school of Tyrnavos (Table 1). The selection of those specific school units was undertaken under the basis that they capture the characteristics of the typical school units operating in the region. The research area included urban areas (Larissa and Tyrnavos), semi-mountainous areas with large livestock activities (Elassona) and suburban areas (Farsala). These four sampled cities are the largest ones throughout the research, while the selected school units gather students from all their surrounding areas. Another fundamental precondition for the sampling stratification was the representation of all social strata and all occupational professions of the local inhabitants. The sample selection of students in the third grade of Secondary school was considered appropriate since there exist taught courses upon environmental education. This approach matches the scopes of the conducted research, since under the educational curricula and the deliverable learning outcomes, students have already engaged in energy issues under the taught courses of Science and Technology. Therefore, in the context of the interdisciplinary teaching of courses and consequently of the wider acquisition of knowledge and skills, it is argued that students sustain appropriate cognitive capacities and knowledge background to be familiarized with the set of the surveyed questions. Indeed, students at the age of 15 years who have undertaken the formal educational curriculum, have already developed formal thinking which enables them to theoretically deepen their thought and manipulate information in such way that they can clearly and accurately express their personal views and worldview experiences [71].

Table 1.
Socio-geographic features of the schools and corresponding number of students who participated in the survey.
We cannot overlook that people in a survey do not only represent theories, words, and numbers. Every participant in a survey must be “treated” with respect and courtesy, especially in the case of underaged participants. The ethics of research with children needs to balance between different conditions. On the one hand, it is necessary to avoid or minimize damage caused by research and to ensure the protection of children and young people and, on the other hand, research needs to be alert to the dangers and harm caused by the concealment of children’s opinions and experiences by excluding them. Consensus, confidentiality and anonymity were the three ethical parameters of this research. In addition, this study was about human emotions. Following the suggestion of Seale and Filmer [94], there is a moral “obligation” not to take advantage of the time and confidence of the participants. In this research we followed articles 3 and 12 on the Rights of the Child of the United Nations [95] (UNCRC), which also applies to the Greek legal context. Article 3 provides that the child’s interests are a fundamental prerequisite for all actions relating to the child. Article 12 requires that children have, depending on their age and maturity, the ability to form opinions, the right to freely express themselves and their views on all matters concerning them. Permission to conduct the survey was initially granted by the School Directors, as proposed by relevant literature for research in education [96,97]. A visit to the students’ classroom was afterwards carried out with the escort of the teacher, briefly informing the students about the process of conducting the research. Students were informed by the researcher about the purpose of the visit and the process of completing the questionnaire. The participants in the survey were asked to complete the questionnaire as reliably as possible by honestly answering the questions in an anonymous manner, without the physical presence of their educators. The completion of the process required one teaching hour for each class. Research conditions could be characterized as excellent since there was a climate of collaboration between students, teachers and researchers.
The questionnaire was written in a way to be understandable, to be complemented by all participants, to minimize potential errors and not be boring or tiring. It consists of four sections: Section A is divided into two subsections. Subsection A1 includes the socio-demographics, such as place of residence, parents’ occupation and personal details. Under Subsection A2, there are questions about students’ level of knowledge related to ecological awareness, information on ecological and environmental terms and student habits towards environment. Section B includes questions concerning the role of school and family towards environmental motivation, as well as some conceptual questions about students’ environmental sensitivity. Section C consists of questions on students’ self-evaluation concerning environmental knowledge, environmental education and willingness to participate in ecological activities. In conclusion, the content of the questionnaire included information and data related to actions concerning energy use and “green” behavior taken inside and outside the classroom.
4. Results
The sample consists of 270 students attending the third grade of secondary education, with an average age of 15 years, while the students’ place of residence is the same as the place of the school (Table 1). Regarding gender, 49.6% of the students are boys and 50.4% are girls. About the overall school performance of the sample, 40.4% of students have an average score of 18.1 to 20 (with a maximum of 20), while 35.6% achieved a performance from 16.1 to 18. The remaining 24% of the sample achieved a graduation grade lower than 16. In response to family statues, 13.7% live in a three-member family, 53% live in a four-member (two parents and two children), 25% live in five-member family and 9% live in large families of six or more members. Regarding type of residence, 55% of students live in detached houses while the remaining 45% reside in apartment blocks. The educational level of the parents is high, since the parents of 40% of the students surveyed are higher education graduates, with the parents of 27.4% and 12% of the students surveyed being high school and secondary high school graduates, respectively. Concerning the professional occupation of the father, the predominant profession is “freelancer” with 27%, followed by “private employee” with 22.6%. Moreover, 21.9% are civil servants and 21.5% are farmers. Regarding the mother’s professional situation, the highest percentage of 27.4% are unemployed/households followed by 25.2% and 18.5% who are civil servants and private employees, respectively.
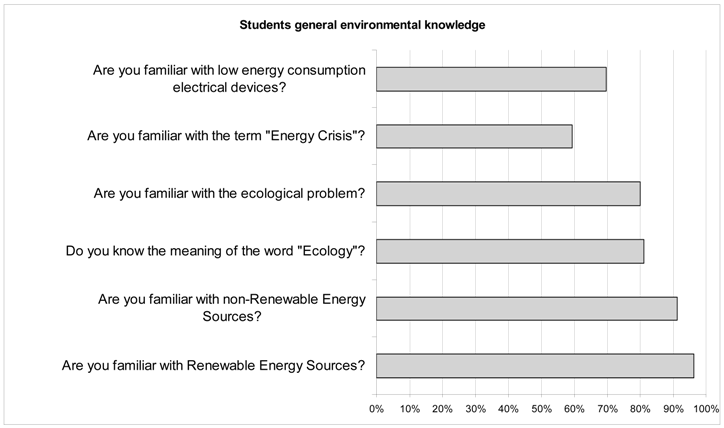
The overall responses of students to the three environmental-driven sections of the survey are outlined in Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4. In Table 2, Section A focuses on students’ self-reported knowledge on general environmental subjects and the various energy sources (see Appendix A).

Table 2.
Questionnaire Section A: Answers Synopsis.

Table 3.
Questionnaire Section B: Answers Synopsis.

Table 4.
Questionnaire Section C: Answers Synopsis.
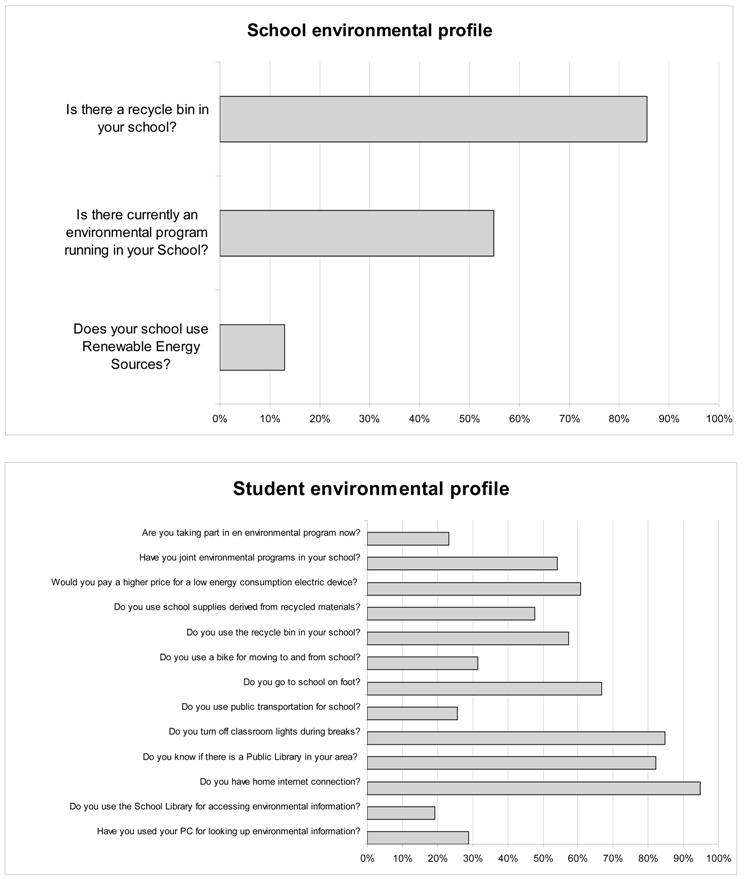
Most students report that they are informed about diverse types of energy sources as well as energy use and consumption. According to Table 2, the descriptive statistics revealed that around 96% of the students are familiar with the term “renewable energy sources” and around 80% are familiar with the word “ecology”. On the contrary, only 60% are familiar with the word “energy crisis” and only 13% of the students answered positively regarding the use of renewable energy technologies at school. Around half of the students responded positively concerning their current or previous participation in environmental programs/actions. A lower percentage of the students of about 30% responded positively concerning Internet use for retrieving environmental information and around 20% answered positively about using the school library for environmental information.
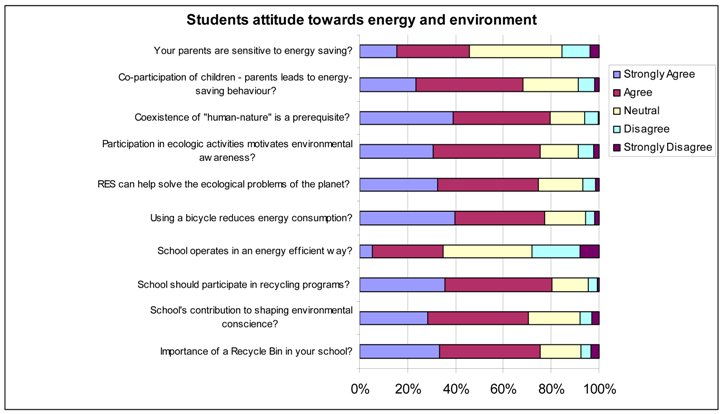
In Table 3, Section B includes questions on students’ attitudes concerning school and the role of the family towards environmentalism, as well as general ecological sensitivity questions (see Appendix A).
Concerning schools’ role, results reveal that around 70% students agree or strongly agree on schools’ contribution to shaping environmental conscience. Around 80% of the students believe that their school should participate in recycling programs and 75% of the students believe that participation in ecological activities motivates environmental awareness. On the contrary, only 35% of the students agree that their school operates in an energy efficient way while 30% of the students disagree or totally disagree. By examining students attitude concerning the role of the family, around 45% of the students agree or totally agree with the content of the question concerning their parents’ environmental sensitivity while 70% of the students agree that the co-operation of children and parents leads to energy-saving behavior. There were also three general ecological sensitivity questions concerning the role of RES towards solving the ecological problem, participation in ecological activities and a question about the harmonious coexistence of humankind with nature. Students agreed or strongly agreed with these broad questions, with rates of above 75%.
In Table 4, Section C refers to student environmental knowledge, environmental education and willingness to participate in environmental actions.
Environmental self-reported knowledge of students is moderate. Only 5% of the students believe that they have very strong environmental knowledge and 19% believe that they have good knowledge. On the other hand, around 25% of the students evaluate their environmental knowledge level as low or very low while 50% of the students have moderate knowledge. Concerning students’ opinion on environmental education in school, around 30% of the sample yielded a positive answer. Around 45% believe they receive moderate environmental education at schools and 6% believe they receive no environmental education at all. Concerning the question on students’ beliefs whether participation in ecological activities leads to environmental awareness, around 68% agree or totally agree while 8% disagree or totally disagree. A graphical representation of students’ answers can be found in the Appendix (students’ attitude towards energy and environment).
Reliability analysis is performed using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient. The coefficient equals 0.757 and is considered acceptable, according to the empirical scale provided by Darren and Mallery [98]. However, by looking at the last column of Table 5 (Cronbach’s Alpha if Item Deleted), it was noticed that questions marked in italics seem to reduce overall reliability, i.e., a higher overall alpha index was reported if these questions were not used at all. Therefore, for reasons of analysis simplification and increased reliability, a decision to drop variables QB4, QB10 and QC10 was taken.

Table 5.
Cronbach’s Alpha reliability analysis.
After removing the three variables marked in bold in Table 5, running a corrected trial revealed that Cronbach’s Alpha index is higher (0.771).
By calculating the correlation matrix, we noticed that statistically significant correlation exists between most of the variables, thus several tests to check the appropriateness of data for factor analysis were deployed. KMO measure of sampling adequacy and Bartlett’s test of sphericity were used to test data appropriateness for factor analysis. KMO measure for our data equals 0.822, indicative that the correlations between the variables are satisfactory for factor analysis to be performed. Ideally, the KMO index should take values >0.8, although values >0.55 are considered acceptable. Another test of appropriateness for factor analysis is Bartlett’s test of sphericity. It tests the null hypothesis that the sample comes from a normal multivariate population, by using the x2 distribution. The value of the x2 test function is 602.912 with 66 degrees of freedom, indicating statistical significance at the 0.001 level, which satisfies the assumption that the data are suitable for factor analysis.
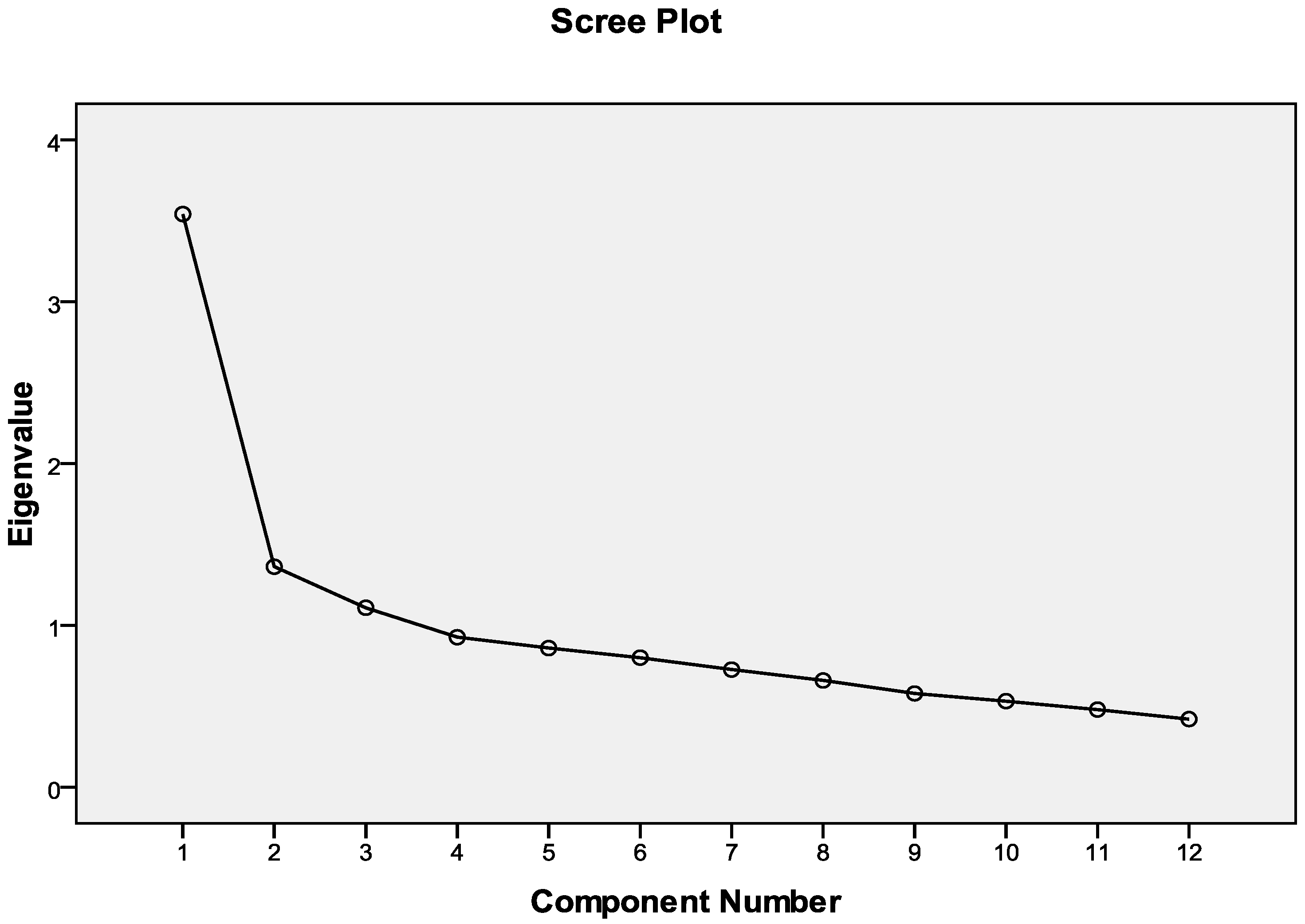
The number of factors to be used for the analysis was estimated using the scree plot and confirmed with the Kaiser criterion (Figure 2).
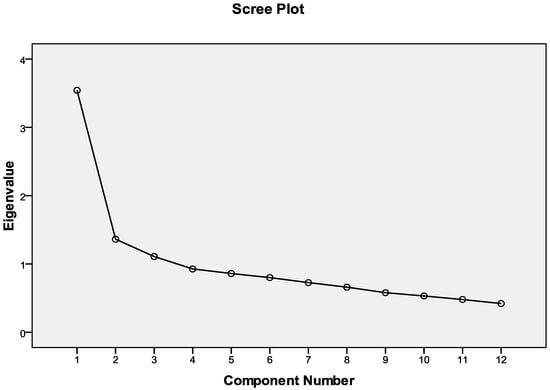
Figure 2.
Components with eigenvalue greater than 1.
By looking at the scree plot and using Kaiser’s empirical criterion, which suggests setting the number of components equal to the components having eigenvalue > 1, we concluded that three factors are appropriate for this analysis.
By using Principal Component Method (PCA), loadings were calculated for the three factors (components), as presented in Table 6.

Table 6.
Initial component matrix.
In Table 6, high factor loadings do not support the identification of the factors, so an orthogonal rotation of the initial matrix is required. The total variance explained by the factors is presented in Table 7 under “Extraction of Sums of Squared Loadings”.

Table 7.
Total variance explained.
According to Table 7, the first component explains 29.5% of the total variance, and in total all three components explain 50.11% of the variance. This outcome remarked that all three factors seem to explain a relative low percentage of the total variance, but it has been reported that in social sciences information collected usually by questionnaires includes less precision, so a solution that accounts for 60% of the total variance (and in some instances even less) is commonly considered satisfactory [99].
Since the questionnaires were filled by secondary education students and the questions included their opinion on vague topics, it was decided to keep the proposed factor number according to Kaiser’s criterion of an eigenvalue greater than 1.
By using the Varimax method and removing scores <0.5, the Rotated Component Matrix and factor loadings were calculated, and the corresponding outcomes are presented in Table 8.

Table 8.
Rotated Component Matrix: Varimax method.
The questions assigned to each component to reflect students’ perceptions fall into three distinct categories. In the first component of the rotated component matrix, there are questions emphasizing student perception concerning school and family role towards environmental conscience. Variables included in the second component refer to “Student’s Environmental conscience”. Variables in the third component represent “Student’s perception on Environmental Education”. The first component of the rotated matrix explains 19.1% of the variance while the second component explains 16.8% and the third component explains 14.2% (see Table 7). The three components are presented on Table 9, and are referred to as such in the next sections of the analysis.

Table 9.
Factors (Components) identification.
Our main aim was to divide student population into groups with common characteristics according to their environmental behavior. To identify the appropriate number of clusters, K-Means method in SPSS was applied, by inputting all three components that were saved as standardized scale variables during the factor analysis stage. According to the algorithm, the user must input the initial number of cluster centers, and observations are assigned to each center with the criterion of the closer distance so that a cluster is formed. The algorithm continues locating new data centers and stops if there is no noticeable difference between two consecutive iterations. For our data, the initial number of cluster centers was set to four.
K-Means method provides a reliability test via the produced ANOVA. Table 10 depicts the initial cluster centers for the three factors, in standardized z values (mean = 0, St. dev. = 1).

Table 10.
Initial cluster centers: k-means method.
After 10 iterations, the algorithm stopped by locating no further difference between iterations. In Table 11, final cluster centers, which were used for the analysis, are located.

Table 11.
Final cluster centers, k-means method (highest score is in bold).
By using the ANOVA method, it is observed that the differences in the mean between the clusters are statistically significant at the 99.9% confidence level (sig. < 0.001) (Table 12).

Table 12.
Statistical significance of identified clusters, ANOVA method.
Concerning the 1st factor, “School and family role towards environment”, Cluster 4 yielded the highest positive normalized score, as can be seen in Table 10, which presents the final cluster centers. Clusters 1–3, on the contrary, yielded a below average score. Cluster 3, which includes 25 students, has the lowest score.
Concerning the second factor, “Students’ Environmental Awareness”, Clusters 1 and 2 have an above average normalized score. Clusters 3 and 4 sustain scores lower than average. Furthermore, around 2/3 of the students (Clusters 3 and 4 include 62% of the students) scored above average in the factor “environmental awareness”, thus it seems most secondary level students are currently environmentally active.
In Table 13, the total number of students, as calculated by the K-means, is presented.

Table 13.
Cluster size.
Concerning the third factor, “Students’ Environmental Education”, Cluster 2 revealed an above average normalized score (see Table 11). Clusters 1, 3 and 4 yielded a negative normalized average score and Cluster 1 sustained the lowest score on this factor. These important findings revealed that most students considered their environmental knowledge and education to be inadequate.
By looking at the four identified student groups from cluster analysis, Cluster 1 seems to experience low environmental education, is environmentally active, and has a low expectation for school and family contribution towards environmental awareness. This student group seems to disregard school and family role towards the environment, exhibits environmental awareness and yielded a low score in evaluating their environmental education level. They can be characterized as “the ecologists, need education”. Cluster 2 is the biggest student cluster, representing around 1/3 of the sample. Secondary education students belonging to Cluster 2 seem to have an appropriate level of environmental education, are environmentally sensitive and take the role of school and family into account towards environmental activation. These students are characterized as the “environmentally activated”. Cluster 3 represents the minority of the student sample (9.2%), disregards school and family role towards the environment, exhibits low environmental awareness and yielded a low score in evaluating their environmental education level. They can be characterized as “environmentally indifferent”. Cluster 4 represents 28.1% of the sample, considers school and family role towards environmental motivation to be very significant and sustained low scores on environmental awareness and environmental education. Cluster 4 is the most challenging student cluster, as it seems that those students depend on school role and are willing to become environmentally active in the future within the “green” school environment. This student minority seems to be interested in forming an environmentally focused behavior and can be characterized as the “school motivated and potentially active”.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
This study investigated the accumulated knowledge, the prevailing attitudes, and the energy habits of students at secondary education in the prefecture of Larissa. The study focused on determining the students’ environmental behavior and their attitudes towards environmental sustainability. Specifically, the key-areas examined are: (a) the familiarity of students with the concept of energy; (b) their accumulated knowledge and their assimilation of the topics of renewable and conventional energy; (c) students’ attitudes towards energy saving and integrated/multifaceted environmental protection; (d) their habits concerning efficient energy use; and (e) the applicability of environment-driven knowledge to students’ attitudes and habits.
Concerning students’ wider knowledge on various environmental issues and energy sources, the results of the study were noteworthy, since 96.30% of students self-reported to be extensively knowledgeable about the diverse types of energy sources while, on the other hand, only 60% reported to be aware of the term of “energy crisis”. Students’ awareness towards environment was evident in their daily habits. A proportion of 85% turns off the lights during breaks, 54% have joined voluntary environmental programs organized by their schools, 78% believe that it is important for the school to have recycle bins and around 60% would buy a low energy consumption electric device with higher price. Concerning school role, around 80% of the students believe their schools should participate in recycling, 2/3 of the students consider that the school environment can contribute and support their environmentally-based initiative and 75% of them find participation in ecological activities to be equally important in improving awareness. In parallel, the role of family is of utmost importance since 70% of the students believe that the family environment in collaboration with their teachers’ creativity can encourage them in environmental-oriented educational activities, even though 45% of students believe that they have received modest environmental education, while only 30% state that they have received adequate environmental education. In a methodological overview, for several Likert scale questions, factor analysis under the PCA approach was used. This method extracted three factors, interpreting students’ behavior. Consequently, according to the identified factors, priority should be given to three dimensions: “School and family role towards environmental conscience”, “Student’s Degree of Environmental conscience and “Student’s Degree of Environmental Education”.
Concerning the factor of “School and family role”, it has been reported that individual-oriented energy behavior is an extremely complex issue that is determined by many parameters, such as the intrinsic socio-economic status [100]. Thus, adult family members should be aware that the energy behavior within the household greatly influences the energy behavior of their children. Furthermore, the purpose of a “sustainable school” is not only to help children acquire environmental literacy and understand the dimensions of sustainability. The main goal of such an educational reform is to change the school itself in promoting sustainability and helping today students to follow sustainable practices in their everyday life. Such schools have managed to raise students’ environmental consciousness [101]. Concerning the factor named as “Student’s Degree of Environmental conscience”, emphasis should be placed even at primary education level, for the availability of resource material and information—such as renewable energy educational software or laboratory applications—which should be available to students, in the form of educational games and activities. Concerning student’s environmental education, it is reported that the extent of curricular materials on environmental and energy subjects could contribute to developing skills, values, and attitudes aligned with sustainable development perspectives [81].
Grouping the sample into clusters by using the K-means method enabled the identification of four different student clusters. These clusters reflected differences of environmental attitudes that were reported among students. More specifically, the clusters segmented the student sample under the following sub-groups: (1) the ecologists, need education; (2) the environmentally activated, which is the largest group; (3) the environmentally indifferent, which is the smallest group; and (4) the school motivated and potentially active. Except for Cluster 2 (environmentally activated), all other clusters require more environmental education. Furthermore Clusters 1 and 2 need more support from family and school towards environmental issues. Custer 4, representing 28% of the sample, has adequate support from family but needs more motivation and education to become active. Finally, there is a minority of students (9.2%) that seem completely indifferent to the environmental issues.
It is noteworthy that students require a more solid environmental education than current taught courses offer. By looking at students’ responses, it becomes evident that school and family background are expected to play a key role in assisting students overcome the future challenges in the energy sector. In this respect, younger and senior family members must be soundly educated and collaborate with each other. Moreover, initiatives taken by the formal educational system must be encouraged, enabling students to become aware of energy and inspire changes from conservative perspectives of energy behavior. Energy education taught courses can be further incorporated into humanitarian, social, and natural sciences, respectively. Education is an interdisciplinary area of a wide consortium of sciences where decisions about taught content, resources’ allocation, and learning deliverables/outcomes are made at regional and national level. Cultural and national aspects are also directly affecting the learning environment and the abiding public-driven policies. However, energy issues are prevailing across Europe and their inclusion in the school curricula should be a European-level priority, too. Furthermore, the core of learning process is still focusing on local action and it must be adaptable to each student cognitive background. To this end, focusing environmental topics on energy education, the abiding energy-based policies should bring together energy, environment, and economics, giving a rational basis for decision-making. Many educational courses on environmental issues also incorporate energy studies—but usually only towards the viewpoint of sustainable development.
However, there is still an imperative need of specific energy education programs to be developed that could formulate the basis of cultivating the behavioral consciousness of current and future energy consumers. These programs should not only focus on environmental deterioration but also on the advantages abided to RES, since the expansion of RES usage can positively contribute to life quality [102]. The main policies concerned must increase all students’ awareness by educating them on the capabilities, pricing, and multifaceted impact of the various energy sources (both renewable and conventional). Such policies should further consider local energy availability/backup technologies and requirements, together with localized climatic and cultural characteristics. In parallel, the content of educational curricula should remain consistent with national and international priorities, reflecting the values of “thinking globally, acting locally”. By understanding the measures established through currently applied energy policies, students should become capable of being creatively involved in shaping a viable RES-driven future.
Author Contributions
V.P. designed the experimental framework and collected the data. V.P., S.N. and M.C. carried out the implementation, performed the calculations and the computer programming. G.L.K. and G.A. gathered and implemented all the theoretical background of the paper, having the input from the experimental development. G.A., G.L.K., and S.N. reviewed and discussed the results of the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
References
- Van Gent, H.A.; Rietveld, P. Road transport and the environment in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 1993, 129, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.A.; Srinivasan, T.N. Long-term consequences of population growth: Technological change, natural resources, and the environment. In Handbook of Population and Family Economics; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 1997; Volume 1, pp. 1175–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, C.W.; Lim, S.; Schoenung, J.M. Environmental and risk screening for prioritizing pollution prevention opportunities in the U.S. printed wiring board manufacturing industry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockenden, M.C.; Deasy, C.; Quinton, J.N.; Bailey, A.P.; Surridge, B.; Stoate, C. Evaluation of field wetlands for mitigation of diffuse pollution from agriculture: Sediment retention, cost and effectiveness. Environ. Sci. Policy 2012, 24, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Rashid, M. Energy consumption to environmental degradation, the growth appetite in SAARC nations. Renew. Energy 2017, 111, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M. Does environmental degradation shackle economic growth? A panel data investigation on 11 Asian countries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 65, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, R.; Salar, L.; Awan, U.; Zaman, K.; Shahbaz, M. Causal links between renewable energy, environmental degradation and economic growth in selected SAARC countries: Progress towards green economy. Renew. Energy 2014, 71, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundtland, G.H. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Mantzava, G. Climate Change. Master’s Thesis, National Technical University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2003. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Tatsidjodoung, P.; Dabat, M.H.; Blin, J. Insights into biofuel development in Burkina Faso: Potential and strategies for sustainable energy policies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 5319–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Mancl, K. Biogas as a sustainable energy source in China: Regional development strategy application and decision making. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 35, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive 2001/77/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 September 2001 on the Promotion of Electricity Produced from Renewable Energy Sources in the Internal Electricity Market. European Commission: Luxembourg, 2001. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:32001L0077&from=EN (accessed on 10 May 2018).
- NDDS Greece. National Strategy for Sustainable Development Greece—Executive Summary, Hellenic Republic Ministry for the Environment, Physical Planning and Public Works. 2002. Available online: http://www.minenv.gr/4/41/000/nssd-english-final.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2015).
- Xu, L.J.; Fan, X.C.; Wang, W.Q.; Xu, L.; Duan, Y.L.; Shi, R.J. Renewable and sustainable energy of Xinjiang and development strategy of node areas in the “Silk Road Economic Belt”. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaigalis, V.; Skema, R. Analysis of the fuel and energy transition in Lithuanian industry and its sustainable development in 2005–2013 in compliance with the EU policy and strategy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaigalis, V.; Markevicius, A.; Skema, R.; Savickas, J. Sustainable energy strategy of Lithuanian Ignalina Nuclear Power Plant region for 2012–2035 as a chance for regional development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1680–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulos, G.; Chalikias, M. The Investigation of Woodfuels’ Involvement in Green Energy Supply Schemes at Northern Greece: The Model Case of the Thrace Prefecture. Procedia Technol. 2013, 8, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolovos, K.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Chalikias, M. Co-evaluation of basic woodfuel types used as alternative heating sources to existing energy network. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2011, 12, 733–742. [Google Scholar]
- Chalikias, M.; Christopoulou, O. Factors affecting the forest plantations establishment in the frame of the common Agricultural policy. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2011, 12, 305–316. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakopoulos, G.; Kolovos, Κ.; Chalikias, Μ. Woodfuels Prosperity towards a More Sustainable Energy Production. In Track I: Social & Humanistic Computing for the Knowledge Society: Emerging Technologies and Systems for the Society and the Humanity, Proceedings of the 3rd World Summit on the Knowledge Society (WSKS 2010), Corfu, Greece, 22–24 September 2010; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamse, W.; Steg, L.; Vlek, C.; Rothengatter, T. The effect of tailored information: Goal setting, and tailored feedback on household energy use, energy-related behaviors and behavioral antecedents. J. Environ. Psychol. 2007, 27, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamse, W.; Steg, L. How do socio-demographic and psychological factors relate to households’ direct and indirect energy use and savings? J. Econ. Psychol. 2009, 30, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, T.; Nye, M.; Burgess, J. Making energy visible: Aqualitative field study of how householders interact with feedback from smart energy monitors. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 6111–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiskainen, M.; Coburn, J. The role of information and communication technologies (ICTs) in household energy consumption—Prospects for the UK. Energy Effic. 2011, 4, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCalley, L.T.; Midden, C.J.H. Energy conservation through product-integrated feedback: The roles of goal-setting and social orientation. J. Econ. Psychol. 2002, 23, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, T.; Sano, F.; Saeki, O.; Tsuji, K. Effectiveness of an energy-consumption information system on energy savings in residential houses based on monitored data. Appl. Energy 2006, 83, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, S.S.; Bakker, C.A.; van Hal, J.D.M. Home energy monitors: Impact over the medium-term. Build. Res. Inf. 2010, 38, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, R.; Stewart, R.; Panuwatwanich, K.; Jones, S.; Kyriakides, A. Alarming visual display monitors affecting shower end use water and energy conservation. Australian residential households. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galis, V.; Gyberg, P. Energy behaviour as a collective. Energy Effic. 2011, 4, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighty, W.; Meier, A. Accelerated electricity conservation in Juneau, Alaska: A study of household activities that reduced demand 25%. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 2299–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosbie, T. Household energy consumption and consumer electronics: The case of television. Energy Policy 2008, 36, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, R.; Crosbie, T. Potential for reducing electricity demand for lighting in households: An exploratory socio-technical study. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, S.; Gilg, A.W.; Ford, N. The household energy gap: Examining the divide between habitual- and purchase-related conservation behaviours. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 1425–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek, K.; Sfderholm, P. The devil is in the details: Household electricity saving behavior and the role of information. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maréchal, K. Not irrational but habitual: The importance of behavioural lock-in in energy consumption. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsson, J.; Lundqvist, L.J.; Sundström, A. Energy saving in Swedish households. The (relative) importance of environmental attitudes. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 5182–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, G.; Gustavsson, L.; Mahapatra, K. Factors influencing energy efficiency investments in existing Swedish residential buildings. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 2956–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naassen, J.; Holmberg, J. Quantifying the rebound effects of energy efficiency improvements and energy conserving behaviour in Sweden. Energy Effic. 2009, 2, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Yin, J.; Zhang, Y. Determinants and policy implications for household electricity-saving behaviour: Evidence from Beijing, China. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 3550–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntanos, S.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Chalikias, M.; Arabatzis, G.; Skordoulis, M. Public Perceptions and Willingness to Pay for Renewable Energy: A Case Study from Greece. Sustainability 2018, 10, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayla, J.M.; Maizi, N.; Marchand, C. The role of income in energy consumption behaviour: Evidence from French households data. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 7874–7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussaoui, I. De la société de consommation à la société de modération. Ce que les Français disent, pensent et font en matière de maîtrise de l’énergie. Ann. Rech. Urbaine 2007, 103, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabatzis, G.; Malesios, C. Pro-Environmental attitudes of users and not users of fuelwood in a rural area of Greece. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 22, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillman, D.A.; Rosa, E.A.; Dillman, J.J. Lifestyle and home energy conservation in the United States: The poor accept lifestyle cutbacks while the wealthy invest in conservation. J. Econ. Psychol. 1983, 3, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.S.; Stern, P.C.; Elsworth, J.T. Personal and contextual influences on household energy adaptations. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 1985, 70, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, C. Education for sustainable development and the secondary curriculum in English schools: Rhetoric or reality? Camb. J. Educ. 2007, 37, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, C.; Firth, R. Knowledge about Education for Sustainable Development: Four case studies of student teachers in English secondary schools. J. Educ. Teach. 2007, 33, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsekos, C.A.; Christoforidou, E.I.; Tsekos, E.A. Planning an environmental education project for kindergarten under the theme of “The Forest”. Rev. Eur. Stud. 2012, 4, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, S.Z.S. Science education in primary school towards environmental sustainability. Res. J. Appl. Sci. 2011, 6, 330–334. [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne, R.; Fien, J.; Packer, J. Program effectiveness in facilitating intergenerational influence in environmental education: Lessons from the field. J. Environ. Educ. 2001, 32, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillemo, S.C. Measuring the effect of procrastination and environmental awareness on households’ energy-saving behaviours: An empirical approach. Energy Policy 2014, 66, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. Professional development of energy education teachers in rural areas from the perspective of environmental factors. Energy Educ. Sci. Technol. Part A Energy Sci. Res. 2014, 32, 2657–2664. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, C.K.; Chen, Y.W.; Kao, T.S.; Chien, S.C. The environmental education strategy of integration of universities, NGOs and elementary schools to develop Taiwan’s energy education program. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 167, 165–175. [Google Scholar]
- Nabalegwa, M.; Buyinza, M. Prospects of petroleum exploration and local community environmental education in the Albertine Graben, Western Uganda. Res. J. Appl. Sci. 2012, 7, 409–412. [Google Scholar]
- Flogaiti, E. Environmental Education; Pedio Publications: Athens, Greece, 2011. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A. A vision of a 21st-century community learning centre. In Education for Sustainability; Huckle, J., Sterling, S., Eds.; Earthscan: London, UK, 1996; pp. 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Posch, P. The ecologisation of schools and its implications for educational policy. Camb. J. Educ. 1999, 29, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.; Cottrell, R.; Dierkes, P. Fostering changes in attitude, knowledge and behavior: Demographic variation in environmental education effects. Environ. Educ. Res. 2017, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.R.; Selby, S.T.; Durham, W.H. Place-based education for environmental behavior: A ‘funds of knowledge’ and social capital approach. Environ. Educ. Res. 2017, 24, 627–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chankrajang, T.; Muttarak, R. Green Returns to Education: Does Schooling Contribute to Pro-Environmental Behaviours? Evidence from Thailand. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 131, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullenbach, L.E.; Green, G.T. Can environmental education increase student-athletes’ environmental behaviors? Environ. Educ. Res. 2018, 24, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, R.; Castro, P.; Martins-Loução, M.A. How to promote conservation behaviours: The combined role of environmental education and commitment. Environ. Educ. Res. 2017, 23, 1322–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A. Does education increase pro-environmental behavior? Evidence from Europe. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 116, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Manzanal, R.; Serra, L.M.; Morales, M.J.; Carrasquer, J.; Rodríguez-Barreiro, L.M.; Del Valle, J.; Murillo, M.B. Environmental behaviours in initial professional development and their relationship with university education. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsóka, Á.; Szerényi, Z.M.; Széchy, A.; Kocsis, T. Greening due to environmental education? Environmental knowledge, attitudes, consumer behavior and everyday pro-environmental activities of Hungarian high school and university students. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 48, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damerell, P.; Howe, C.; Milner-Gulland, E.J. Child-orientated environmental education influences adult knowledge and household behaviour. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 015016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repka, P.; Švecová, M. Environmental education in conditions of National Parks of Slovak Republic. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 55, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzigeorgiou, E.; Haralambopoulos, H. CO2 emissions, GDP and energy intensity: A multivariate cointegration and causality analysis for Greece, 1977–2007. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandpal, T.; Broman, L. Renewable energy education: A global status review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 300–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez Suárez, P.; Vega Marcote, P. Developing sustainable environmental behavior in secondary education students (12–16): Analysis of a didactic strategy. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2010, 2, 3568–3574. [Google Scholar]
- Marcinkowski, T.J.; Volk, T.J.; Hungerford, H.R. An Environmental Education Approach to the Training of Middle Level Teachers a Teacher Education Program Specialization; UNESCO/UNEP: Paris, France, 1990; Available online: http://www.unesco.org/education/information/pdf/333_52.pdf (accessed on 27 November 2013).
- Monroe, M.C.; Oxarart, A.; Plate, R.R. A Role for Environmental Education in Climate Change for Secondary Science Educators. Appl. Environ. Educ. Commun. 2013, 12, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acikgoz, C. Renewable energy education in Turkey. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelikler, D.; Aksan, Z. The opinions of secondary school students in Turkey regarding renewable energy. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelinos, K.; Jones, N.; Panoriou, E. Challenges and opportunities for sustainability in regional universities: A case study in Mytilene, Greece. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkeli, S.; Manolas, E.; Ioannou, K.; Tsantopoulos, G. Socio-cultural impact of energy saving: Studying the behaviour of elementary school students in Greece. Sustainability 2018, 10, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskolia, M.; Dimos, A.; Kampylis, P.G. Secondary teachers’ conceptions of creative thinking within the context of environmental education. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2012, 7, 269–290. [Google Scholar]
- Macko, J.; Blahútová, D.; Stollárová, N. Space for the environmental education in the system of secondary education in Slovakia. Informatologia 2013, 46, 256–260. [Google Scholar]
- Bokhoree, C.; Jheengut, A.; Bholah, R. Environmental clubs as vehicles for promoting education for environmental sustainability in Mauritian secondary schools. Int. J. Environ. Cult. Econ. Soc. Sustain. 2012, 7, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkar, G. Secondary school students’ environmental concerns and attitudes toward forest ecosystem services: Implications for biodiversity education. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2016, 11, 11019–11031. [Google Scholar]
- Capelo, A. Integration of education for sustainable development into formal secondary curricula of East Timor. In Handbook of Research on Pedagogical Innovations for Sustainable Development; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 54–66. [Google Scholar]
- Sorgo, A.; Kamensek, A. Implementation of a curriculum for environmental education as education for sustainable development in Slovenian upper secondary schools. Energy Educ. Sci. Technol. Part B Soc. Educ. Stud. 2012, 4, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Lamas, J.G.; Cuadrado, V.A. Argumentative skills in the design of webquests in environmental education for secondary students. Int. J. Learn. 2012, 18, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ongevalle, J.; van Petegem, P.; Deprezc, S.; Chimbodza, I.J.M. Participatory planning for project sustainability of environmental education projects: A case study of the secondary teacher training environmental education project (St2eep) in Zimbabwe. Environ. Educ. Res. 2011, 17, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siardos, G. Multivariate Statistical Analysis Methods. Part One; Ziti Publications: Thessaloniki, Greece, 1999. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- SPSS. The SPSS Two-Step Cluster Component—A Scalable Component Enabling More Efficient Customer Segmentation; White Paper-Technical Report; SPSS Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Statistics Solutions. Conduct and Interpret a Cluster Analysis. 2015. Available online: http://www.statisticssolutions.com/cluster-analysis-2/ (accessed on 20 November 2017).
- Ntona, E.; Arabatzis, G.; Kyriakopoulos, G. Energy saving: Views and attitudes of students in secondary education. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 46, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Local Union of Municipalities and Communities of Prefecture of Larissa. Prefecture of Larissa, Nature-History-Development; Local Union of Municipalities and Communities of Prefecture of Larissa: Larissa, Greece, 2002. (In Greek)
- Locator Map of Larisa Prefecture in Greece. Greece, 2017. Available online: http://www.mykosmos.gr/loc_mk/images/maps/map_greece_larissa.gif (accessed on 21 June 2017).
- Larissa Prefecture Depicting Main Cities. 2017. Available online: https://pirgetoslarisas.files.wordpress.com/2011/02/map.png?w=300&h=300 (accessed on 20 June 2017).
- Directorate of Secondary Education of Larissa. Statistical Data of Schools of Prefecture of Larissa; Directorate of Secondary Education of Larissa: Larissa, Greece, 2014. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- CheckMarket. Sample Size Calculator. 2018. Available online: https://www.checkmarket.com/sample-size-calculator/ (accessed on 20 April 2018).
- Seale, C.; Filmer, P. doing social research. In Researching Society and Culture; Seale, C., Ed.; Sage Publications: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child. 1990. Available online: https://www.unicef.org.uk/what-we-do/un-convention-child-rights/ (accessed on 10 April 2018).
- Cohen, L.; Lawrence, M.; Morrison, K. Research Methods in Education; Routledge: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Denscombe, M. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects, 4th ed.; Volume: Open UP Study Skills; McGraw-Hill Open University Press: Maidenhead, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Darren, G.; Mallery, P. SPSS for Windows Step by Step: A Simple Guide and Reference. 11.0 Update, 4th ed.; Allyn & Bacon: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Explanatory Factor Analysis. Chapter 3. In Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Prentice Hall International, Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 89–150. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, J.; Barton, B.; Carrington, G.; Gnoth Lawson, R.; Thorsnes, P. Energy cultures: A framework for understanding energy behaviours. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 6120–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, T.; Gericke, N.; Chang Rundgren, S.N. The implementation of education for sustainable development in Sweden: Investigating the sustainability consciousness among upper secondary students. Res. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2014, 32, 318–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntanos, S.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Chalikias, M.; Arabatzis, G.; Skordoulis, M.; Galatsidas, S.; Drosos, D. A Social Assessment of the Usage of Renewable Energy Sources and Its Contribution to Life Quality: The Case of an Attica Urban Area in Greece. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).