Technical Feasibility and Comprehensive Sustainability Assessment of Sweet Sorghum for Bioethanol Production in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Agricultural Zones
2.2. Evaluation of Technical Feasibility of Sweet Sorghum Production
2.3. Comprehensive Sustainability Assessment of Sweet Sorghum Production
2.4. Economic Profitability Assessment of Sweet Sorghum Bioethanol Production
2.4.1. Theoretical Bioethanol Production Potential for Selected Sites
grain, L/t) × grain yield (t/ha)
2.4.2. Prospective Economic Profitability of ASSF for Selected Sites
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Technical Feasibility of Sweet Sorghum Production in China
3.2. Comprehensive Sustainability Assessment of Sweet Sorghum Production
3.3. Analysis of Theoretical Bioethanol Productive Potential
3.4. Prospective Economic Profitability of Sweet Sorghum Bioethanol
3.5. Sensitive Analysis of the Theoretical Net Economic Output under the Current Biomass Conversion Technology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, L.T.; Cafferty, K.; Roni, M.; Jacobson, J.; Xie, G.H.; Ovard, L.; Wright, C. Analyzing and comparing biomass feedstock supply systems in China: Corn stover and sweet sorghum case studies. Energies 2015, 8, 5577–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. Sustainable Production of Second-Generation Biofuels: Potential and Perspectives in Major Economies and Developing Countries; IEA: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Xie, G.; Li, S.; Ge, L.; He, T. The productive potentials of sweet sorghum ethanol in China. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 2360–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, A.E.; Plevin, R.J.; Turner, B.T.; Jones, A.D.; O’Hare, M.; Kammen, D.M. Ethanol can contribute to energy and environmental goals. Science 2006, 311, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J. A handful of carbon. Nature 2207, 447, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Huang, J.; Keyzer, M.; Van, V.W.; Rozelle, S.; Fisher, G.; Ermolieva, T. Biofuel development, food security and the use of marginal land in China. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fargione, J.E.; Cooper, T.R.; Flaspohler, D.J.; Hill, J.; Lehman, C.; Tilman, D.; Mccoy, T.; Mcleod, S.; Nelson, E.J.; Oberhauser, K.S. Bioenergy and Wildlife: Threats and Opportunities for Grassland Conservation. BioScience 2009, 59, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonin, C.; Lal, R. Agronomic and ecological implications of biofuels. Adv. Agron. 2012, 117, 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J. The present situation of soil fertility, organic and inorganic fertilizer application and suggestion of fertilizer application. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci. 2005, 4, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.J.; Pitman, W.D.; Misook, K.; Day, D.F.; Alison, M.W.; Mccormick, M.E.; Aita, G. Ethanol production potential of sweet sorghum assessed using forage fiber analysis procedures. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakoglou, I.; Dhima, K.; Karagiannidis, N.; Gatsis, T. Sweet sorghum productivity for biofuels under increased soil salinity and reduced irrigation. Field Crop. Res. 2011, 120, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Y.; Zhao, W.J.; Ping, J.A. Macroergic Crop—Sweet Sorghum. Rev. China Agric. Sci. Technol. 2006, 1, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Xi, Z. The prospect of sweet sorghum in bioenergy industry. Curr. Biotechnol. 2012, 2, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Dolat, A.; Steinberger, Y.; Wang, X.; Osman, A.; Xie, G.H. Biomass yield and changes in chemical composition of sweet sorghum cultivars grown for biofuel. Field Crop. Res. 2009, 111, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Steinberger, Y.; Shi, M.; Han, L.P.; Xie, G.H. Changes in stem composition and harvested produce of sweet sorghum during the period from maturity to a sequence of delayed harvest dates. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 39, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnavathi, C.V.; Suresh, K.; Kumar, B.S.V.; Pallavi, M.; Komala, V.V.; Seetharama, N. Study on genotypic variation for ethanol production from sweet sorghum juice. Biomass Bioenergy 2010, 34, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.Y.; Ma, Z.; Vanitha, J.; Ramachandran, S. Genetic variation and expression diversity between grain and sweet sorghum lines. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.P.; Guo, X.Q.; Yu, Y.J.; Duan, L.S.; Rao, M.S.; Xie, G.H. Effect of prohexadione-calcium, maleic hydrazide and glyphosine on lodging rate and sugar content of sweet sorghum. Res. Crops 2011, 12, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Han, D.Q.; Yu, Y.J.; Steinberger, Y.; Han, L.P.; Xie, G.H. Dynamics in elongation and dry weight of internodes in sweet sorghum plants. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 126, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.J.; Pitman, W.D.; Alison, M.W.; Harrell, D.L.; Viator, H.P.; Mccormick, M.E.; Gravois, K.A.; Kim, M.; Day, D.F. Agronomic Considerations for Sweet Sorghum Biofuel Production in the South-Central USA. Bioenergy Res. 2012, 5, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegada-Lizarazu, W.; Monti, A. Are we ready to cultivate sweet sorghum as a bioenergy feedstock? A review on field management practices. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, J.E.; Woodard, K.R.; Sollenberger, L.E. Optimizing sweet sorghum production for biofuel in the southeastern USA through nitrogen fertilization and top removal. Bioenergy Res. 2012, 5, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holou, R.A.Y.; Stevens, G. Juice, sugar, and bagasse response of sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench cv. M81E) to N fertilization and soil type. GCB Bioenergy 2012, 4, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.P.; Steinberger, Y.; Zhao, Y.L.; Xie, G.H. Accumulation and partitioning of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in different varieties of sweet sorghum. Field Crop. Res. 2011, 120, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tew, T.L.; Cobill, R.M.; Richard, E.P.J. Evaluation of sweet sorghum and sorghum × sudangrass hybrids as feedstocks for ethanol production. Bioenergy Res. 2008, 1, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Wang, M.L.; Spiertz, J.H.J.; Liu, Z.X.; Han, L.P.; Xie, G.H. Genetic variation in yield and chemical composition of wide range of sorghum accessions grown in north-west China. Res. Crops 2013, 14, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C. Improved varieties sweet sorghum for feedstock, sugar and energy production. Bull. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2003, 2, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Luo, F.; Li, X.; Pei, Z.; Gao, J.; Sun, S. Responsiveness of Sweet Sorghum in Yield and Quality Related Traits to Environmental Factors. Acta Agron. Sin. 2015, 41, 1612–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D. Ethanol Fuel from Sweet Sorghum Desiderates development. J. Agric. Sci. Technol.-Iran 2003, 4, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Ou, X.; Chang, S. Life-cycle greenhouse gas emission and energy use of bioethanol produced from corn stover in China: Current perspectives and future prospectives. Energy 2016, 115, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Dai, L.; Tian, Y.S.; Qin, S.P. Analysis of the development status and trends of biomass energy industry in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2007, 23, 276–282. [Google Scholar]
- De Vries, S.C.; Van de Ven, G.W.J.; Van Ittersum, M.K.; Giller, K.E. Resource use efficiency and environmental performance of nine major biofuel crops, processed by first-generation conversion techniques. Biomass Bioenergy 2010, 34, 588–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.T.; Liu, Z.X.; Wei, T.Y.; Xie, G.H. Evaluation of energy input and output of sweet sorghum grown as a bioenergy crop on coastal saline-alkali land. Energy 2012, 47, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giller, K.E. The production-ecological sustainability of cassava, sugarcane and sweet sorghum cultivation for bioethanol in Mozambique. GCB Bioenergy 2011, 4, 20–35. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.H.; Ren, L.T.; Spiertz, H.; Zhu, Y.B.; Xie, G.H. An economic analysis of sweet sorghum cultivation for ethanol production in North China. GCB Bioenergy 2015, 7, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.W.; Liu, G.Q.; Liu, D.Q.; Chen, Y.S.; Feng, R.; Li, M.; Dong, R.J. Survey and analysis on economic benefit of sorgo to fuel ethanol production—with sorgo to fuel ethanol project in Huachuan county, Heilongjiang Province as example. Renew. Energy Resour. 2008, 26, 86–89. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Xie, G.; Li, S.; Ge, L.; Qi, Y. Spatial suitability and its bio-ethanol potential of sweet sorghum in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 4765–4770. [Google Scholar]
- Linton, J.A.; Miller, J.C.; Little, R.D.; Petrolia, D.R.; Coble, K.H. Economic feasibility of producing sweet sorghum as an ethanol feedstock in the southeastern United States. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3050–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee of National Agricultural Regionalization. Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning in China; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Z.; Lang, L. Sweet Sorghum; China Agriculture Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J. Control problems of grey systems. Syst. Control Lett. 1982, 1, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Sun, H. Drought control analysis on Yuelai irrigation area in Huachuan County. J. Heilongjiang Hydraul. Eng. Coll. 2002, 29, 136–137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, S. The main diseases and insect pests occurrence and prevention countermeasures in Morin Dawa artificial grassland of Inner Mongolia. Prat. Sci. 2004, 21, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F. The introduction of soil erosion present situation and the countermeasures in Morin Dawa. Inn. Mong. Water Resour. 2007, 4, 99–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Su, L. The analysis and evaluation of new reservoir land reclamation project in Dawoer community of Morin Dawa autonomous county, Hulunbeier City. Westem Resour. 2014, 1, 113–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Study on the Suitable Applying Amount of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fertilizer on the Tide Soil Cotton Field at Binzhou. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K. The productive cultivation techniques of Wudi gold silk jujube. North. Fruits. 1999, 3, 17–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L. Study on Determination of Canal Water Use Efficiency in Bojili Irrigation District, Binzhou City, Shandong Province. Master’s Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, F.; Luo, W.; Li, L.; Feng, Y. Soil nutrient and microorganism of Pinus thunbergli forest in Weihai. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2008, 17, 1590–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J. The health assessment of the agro-ecosystem in Weihai city of Shandong province. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, E. Effects of different fertilization treatments on soil moisture from 0 to 100 cm in the late growth stage of Maize. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2008, 15, 205–206. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J. Development of Eco-milk and Local Milk Products in TURPAN. Master’s Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Liang, J.; Guo, F. The application of balanced fertilization technology of seedless grape. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. Technol. 2009, 4, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J. Research on country territory agricultural land grade appraise in Hetao region-take the Wuyuan country of Inner Mongolia as the example. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Normal University, Huhehaote, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Q. The study on sunflower production present situation and development countermeasure in Wuyuan county of Bayannur in Inner Mongolian. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Huhehaote, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.; Shi, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, H.; Li, L. Effects of coupling of soil water and fertilizer on the growth of sunflower during its seeding period in saline soil. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2007, 3, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Huang, S. Report of Introduction Demonstration Experiment of Sweet Sorghum. Sugar Crops China 2013, 3, 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T. The research on the development of the grassland vegetation during the course of the improvement and recovery of the grassland in the northern deserts of Gulang County. Pratacult. Sci. 2005, 8, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Effects of different land use patterns on soil structure and properties in yellow Irrigation District of Gulang County. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2009, 21, 222–223. [Google Scholar]
- Baligar, V.; Fageria, N.; He, Z. Nutrient use efficiency in plants. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2001, 32, 921–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Han, B.; Hou, W.; Wang, J.; Li, T. A demonstration study of ethanol production from sweet sorghum stems with advanced solid state fermentation technology. Appl. Energy 2013, 102, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.P. Exploration in superiorities and economic characters of several crops for automobile use alcohol producing. Renew. Energy Resour. 2007, 25, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Hu, S.Y.; Li, Y.R.; Chen, D.J.; Bing, Z. Greenhouse gas emission of sweet sorghum ethanol in life-cycle. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.Q.; Ren, X.; Bei, Z.L. Commercialization analysis of sweet sorghum based bioethanol on salt farm land in China. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2010, 38, 11279–11282. [Google Scholar]
- Rooney, W.L.; Blumenthal, J.; Bean, B.; Mullet, J.E. Designing sorghum as a dedicated bioenergy feedstock. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2007, 1, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnansounou, E.; Dauriat, A.; Wyman, C.E. Refining sweet sorghum to ethanol and sugar: Economic trade-offs in the context of North China. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 985–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Ameen, A.; Tang, C.C.; Du, F.; Yang, X.L.; Xie, G.H. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilization on Soil Nitrogen for Energy Sorghum on Marginal Land in China. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, X.Y.; Han, L.P.; Spiertz, H.; Liao, S.H.; Wei, M.G.; Xie, G.H. A quantitative assessment of crop residue feedstocks for biofuel in North and Northeast China. GCB Bioenergy 2015, 7, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Xia, X.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Energy efficiency and environmental performance of bioethanol production from sweet sorghum stem based on life cycle analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 163, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Pan, X.; Xia, X.; Xi, B.; Wang, L. Environmental sustainability of bioethanol produced from sweet sorghum stem on saline–alkali land. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 187, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Xie, X.; Huang, Z. Life Cycle Water footprints of nonfood biomass fuels in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4137–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Meng, F.; Molatudi, R.L.; Zhang, B. Sorghum and switchgrass as biofuel feedstocks on marginal lands in Northern China. Bioenergy Res. 2016, 9, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Xu, M.; Zhang, T. Unintended consequences of bioethanol feedstock choice in China. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 125, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.C. Jue Sheng Sheng Wu Zhi; China Agricultural University Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Caserta, G.; Bartolelli, V.; Mutinati, G. Herbaceous energy crops: A general survey and a microeconomic analysis. Biomass Bioenergy 1995, 9, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Gao, W.S.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.Q.; Sui, P. Reducing agricultural carbon footprint through diversified crop rotation systems in the North China Plain. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 76, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, K.; Li, K.; Wang, P.; Ma, Y.; Stahr, K. Effect of optimal irrigation, different fertilization, and reduced tillage on soil organic carbon storage and crop yields in the North China Plain. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2013, 176, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Li, S.; Liu, G.; Ji, G.; Hou, S.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, N. Analysis on key factors of sweet sorghum as raw material for bio-fuel production. J. China Agric. Univ. 2012, 17, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Scott, S.; Johathanl, P.; Williaml, R.; Yu, J.; Wang, D. Features of sweet sorghum juice and their performance in ethanol fermentation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2010, 31, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.J.; Wang, F.; Liu, C.Z. Deep-bed solid state fermentation of sweet sorghum stalk to ethanol by thermotolerant Issatchenkia orientalis IPE 100. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 11262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regassa, T.H.; Wortmann, C.S. Sweet sorghum as a bioenergy crop: Literature review. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 64, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zu, X.; Fu, J.; Li, J.; Li, S. A Novel Combined Ethanol and Power Model of Microgrid Driven by Sweet Sorghum Stalks Using ASSF. Energy Procedia 2016, 103, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, C.; Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Peng, L. Genetic modification of plant cell walls to enhance biomass yield and biofuel production in bioenergy crops. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 997–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
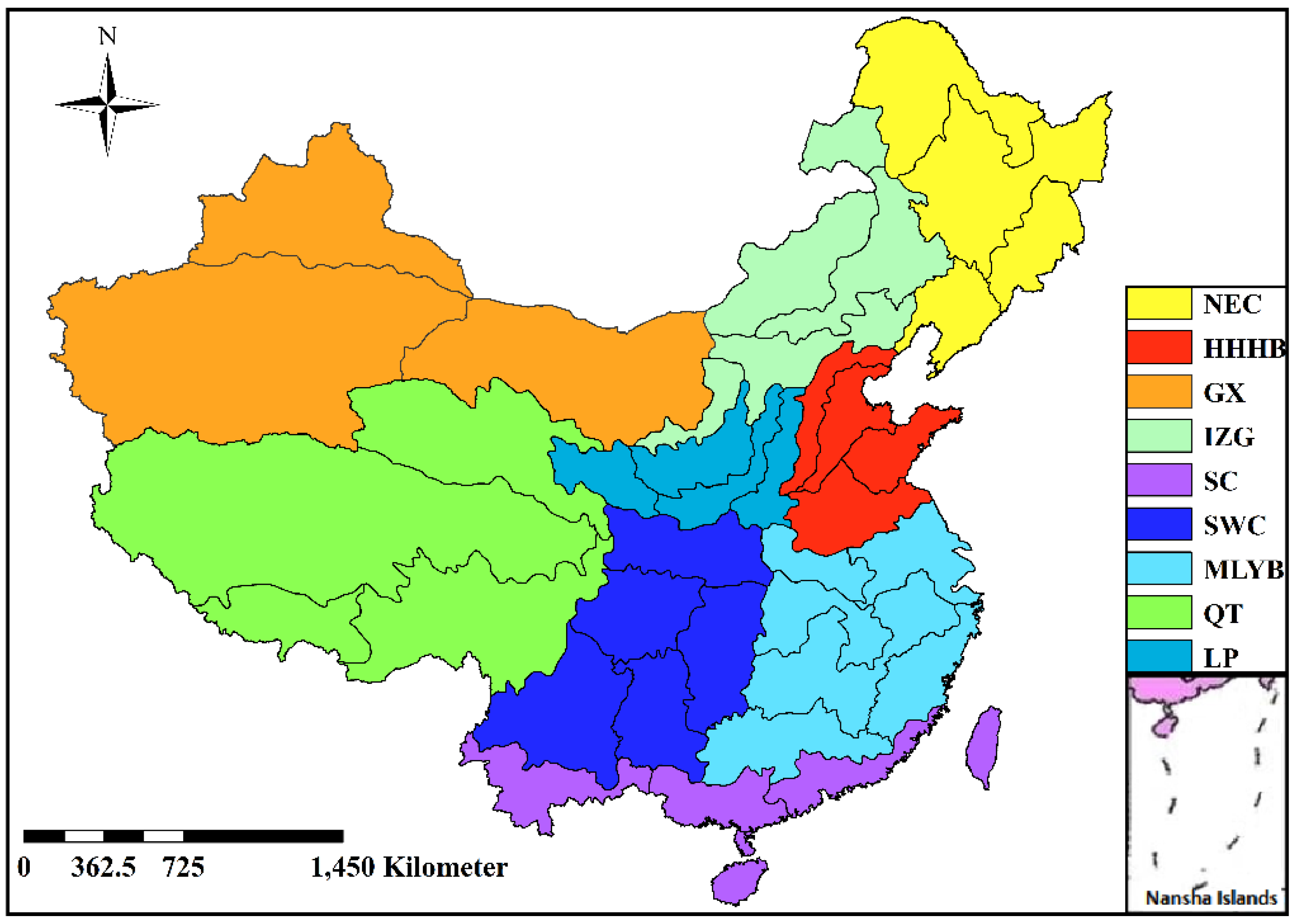
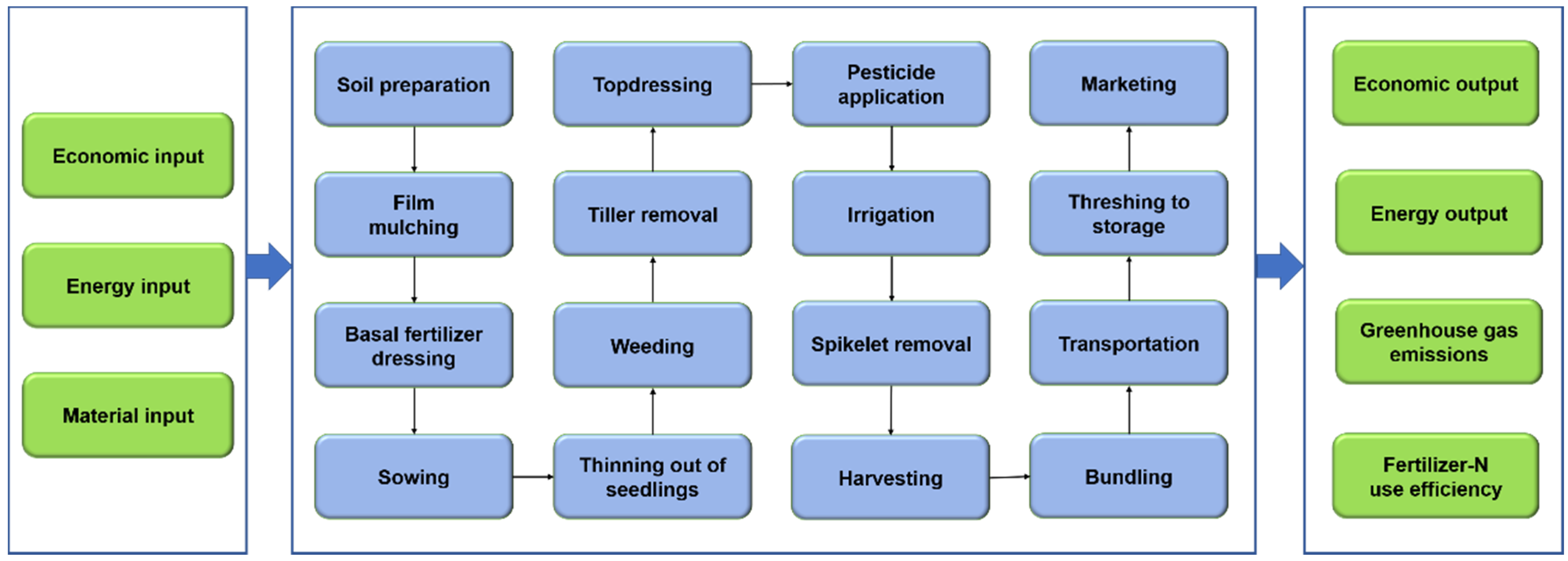
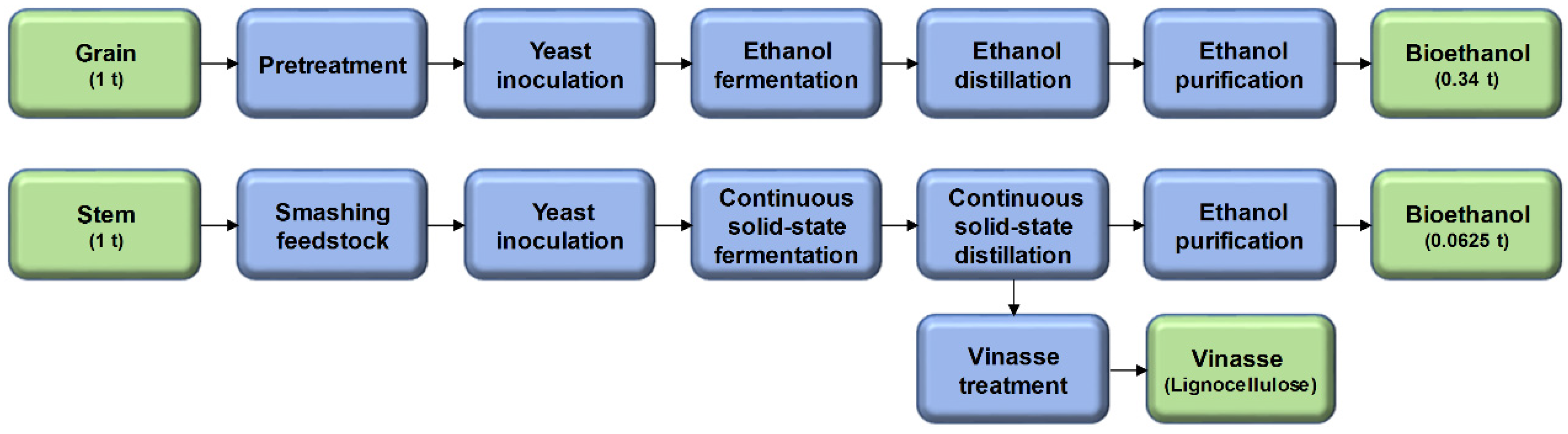
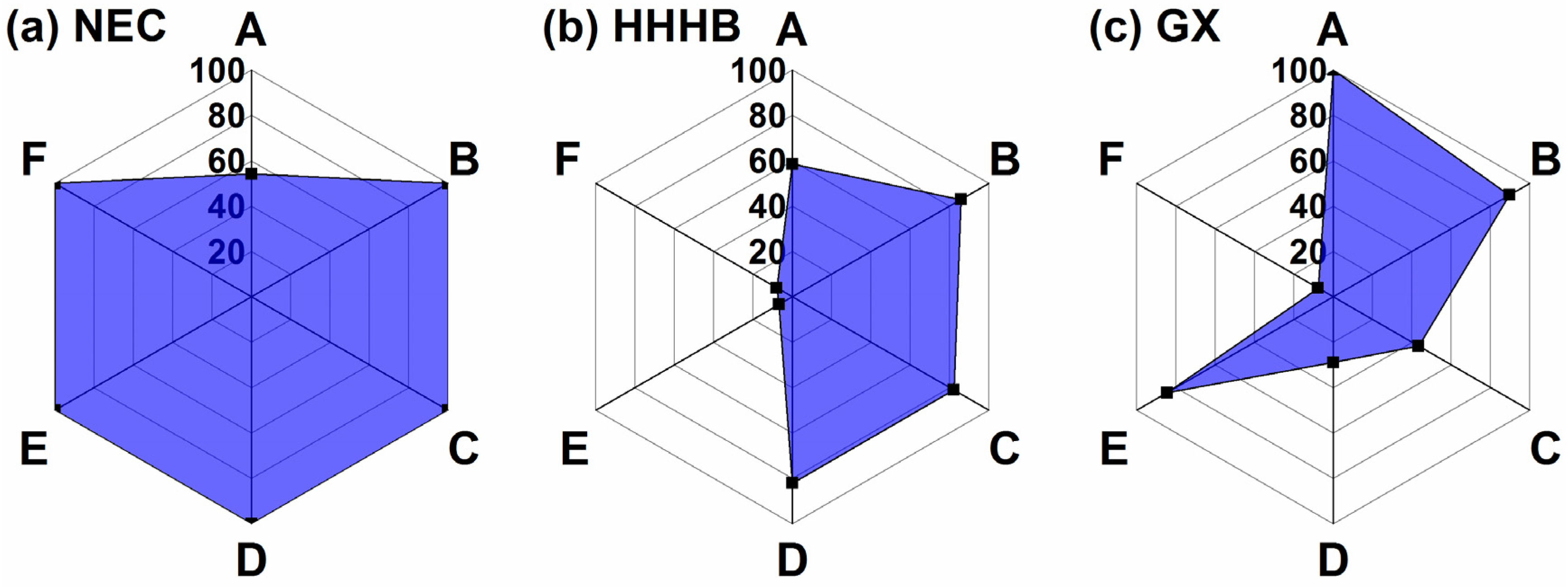
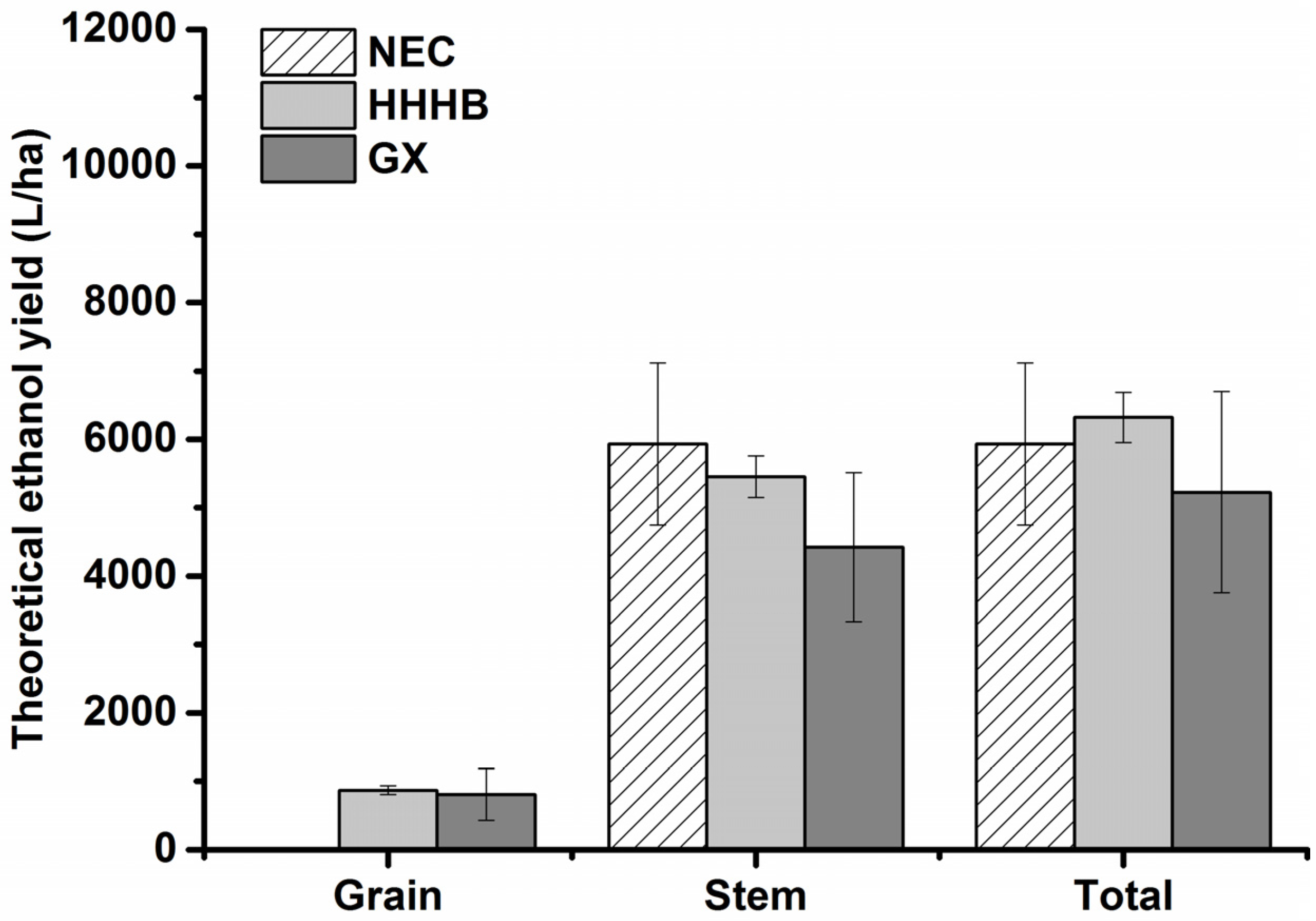
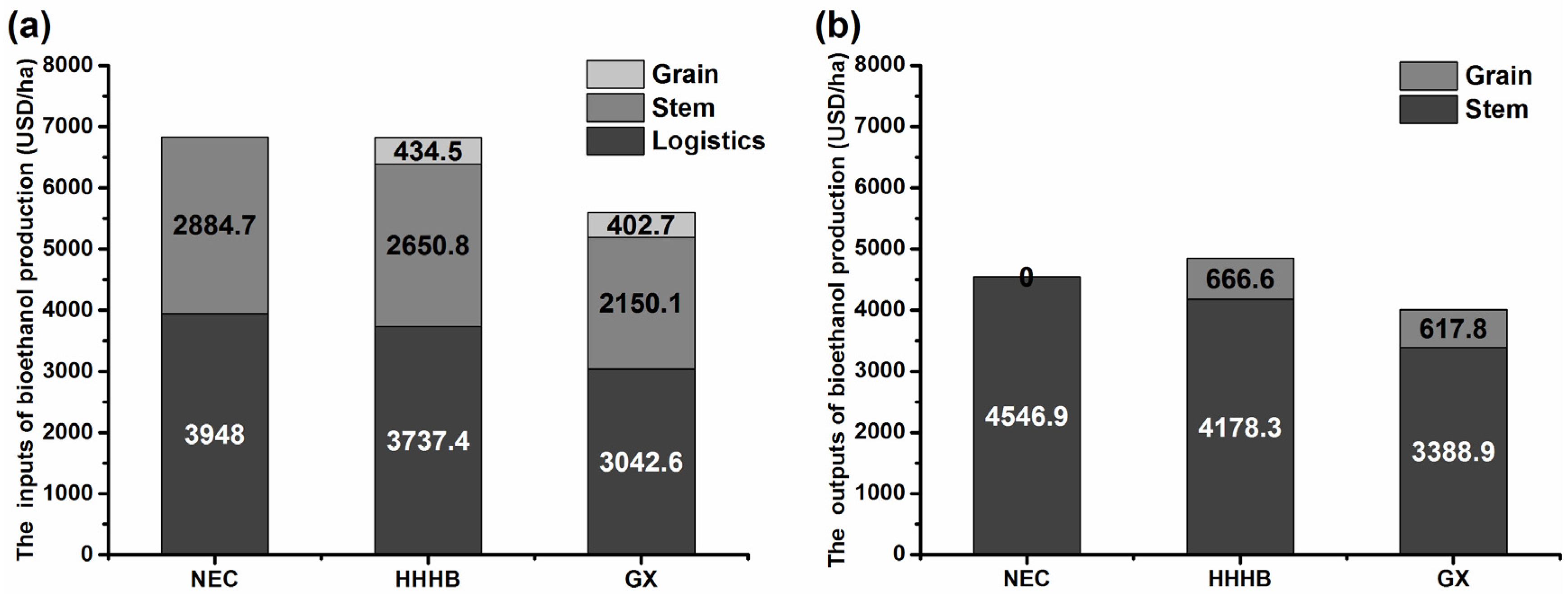

| Item | Unit | Northeast China (NEC) # | Huang-Huai-Hai Basin (HHHB) # | Ganxin Region (GX) # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huachuan * | Morin Dawa * | Wudi * | Wendeng * | Turpan * | Wuyuan * | Gulang * | ||
| Position: | ||||||||
| East-longitude | 130°16′–131°34′ | 123°33′–125°16′ | 117°31′–118°04′ | 121°57′–122°17′ | 87°14′–91°54′ | 107°35′–108°37′ | 102°38′–103°54′ | |
| North latitude | 46°31′–47°14′ | 48°05′–49°55′ | 37°41′–38°16′ | 36°19′–37°55′ | 41°12′–43°35′ | 40°46′–41°16′ | 37°09′–37°54′ | |
| Altitude | m | 60–70 | 173–638.3 | 50 | 257 | −154–4000 | 1019–1035 | 1550–3469 |
| Climate: | ||||||||
| Precipitation | mm | 476.4 | 400–500 | 598.6 | 768.4 | 3.9–25.5 | 177 | 250 |
| Annual average temperature | °C | 2.5 | 3.2 | 12.1 | 11.4 | 13.9 | 6.1 | 5.2 |
| Annual highest temperature | °C | 36.8 | 39.5 | 26 | 24.6 | 32.7 | 22.7 | 37.2 |
| Annual lowest temperature | °C | −39.7 | −45 | −4 | −1.4 | −9.5 | −13.2 | −26.4 |
| accumulated temperature ≥10 °C | °C | 2500–2700 | 1815–2413 | 4339 | 4000 | 5455 | 2896 | 2686 |
| Frost-free season | day | 133 | 100–134 | 206 | 221 | 250–300 | 117–136 | 150 |
| Annual sunshine hours | h | 2500–2600 | 2500–2800 | 2724.5 | 2512 | 3056 | 3231 | 2852 |
| Annual average evaporation | mm | 1275 | 1050–1450 | 1238 | 1500–1700 | 2879–3822 | 2039 | 2807 |
| Soil: | ||||||||
| pH value | 6.62 | 6.8 | 7.0–7.5 | 6.8 | 8.6–9.1 | 8.4 | 8.0 | |
| Organic matter | % | 4.46 | 4.15–10.0 | 1.31 | 1.2 | 4.04 | 1.17 | 1.54 |
| Total nitrogen | % | 0.23 | 0.28–0.67 | 0.47 | 0.71 | 0.22 | 0.54 | 0.096 |
| Available N | mg/kg | 163.7 | N/A | 58.53 | N/A | 63.56 | 52.37 | 75.5 |
| Available P | mg/kg | 27.9 | 18.26 | 15.32 | 26 | 55.03 | 14.17 | 6.05 |
| Available K | mg/kg | 158.3 | 150–200 | 158.45 | 51 | 165.67 | 157.9 | N/A |
| Reference | [9,42] | [43,44,45] | [46,47,48] | [49,50,51] | [52,53] | [54,55,56] | [57,58,59] | |
| Agriculture Region * | Breeding Technique | Cultivation Technique | Storage Technique | Stress-Resistance Physiology | DTM | Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEC | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.5385 | 0.4510 | 0.8066 | 1 |
| GX | 0.4851 | 0.8750 | 1.0000 | 0.4510 | 0.7531 | 2 |
| HHHB | 0.4757 | 1.0000 | 0.3889 | 1.0000 | 0.6594 | 3 |
| MLYB | 0.3379 | 0.3784 | 0.4667 | 0.4182 | 0.3967 | 4 |
| LP | 0.3630 | 0.3415 | 0.3684 | 0.4510 | 0.3670 | 5 |
| SC | 0.4336 | 0.3333 | 0.3333 | 0.3333 | 0.3634 | 6 |
| IZG | 0.3333 | 0.3684 | 0.3684 | 0.3538 | 0.3564 | 7 |
| SWC | 0.3333 | 0.3415 | 0.3333 | 0.3333 | 0.3358 | 8 |
| Indicator | Unit | Northeast China | Huang-Huai-Hai Basin | Ganxin Region | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Site Numbers | Average Value | Sample Site Numbers | Average Value | Sample Site Numbers | Average Value | ||
| Economic input | USD/ha | 2 | 904.8 | 3 | 1282.2 | 2 | 2129.0 |
| Economic output | USD/ha | 2 | 1814.0 | 3 | 2263.5 | 2 | 3806.5 |
| Net economic output | USD/ha | 2 | 909.3 | 3 | 981.4 | 2 | 1677.5 |
| Economic input-output ratio | 2 | 2.28 | 3 | 1.79 | 2 | 1.86 | |
| Energy input | GJ hm−2 | 1 | 27.1 | 2 | 27.9 | 1 | 43.2 |
| Energy output | GJ hm−2 | 1 | 387.3 | 2 | 300.6 | 1 | 204.5 |
| Net energy output | GJ hm−2 | 1 | 360.2 | 2 | 272.7 | 1 | 161.3 |
| Energy input-output ratio | 1 | 14.28 | 2 | 10.8 | 1 | 4.7 | |
| Greenhouse gas emissions | g CO2-eq/kg stalk | 1 | 29.1 | 1 | 53.7 | 1 | 35.6 |
| Amount of Fertilizer-N | kg N ha−1 | 1 | 45.8 | 1 | 211.4 | 1 | 126.9 |
| N fertilizer-use efficiency | GJ kg−1 N | 1 | 7.86 | 1 | 1.29 | 1 | 1.27 |
| Reference | [36,63], survey data | [33,63,64] | [33,57,63] | ||||
| Index | Northeast China | Huang-Huai-Hai Basin | Ganxin Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grain t/ha | 0 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.9 |
| Stem t/ha | 75.0 ± 15.0 | 68.9 ± 3.8 | 55.9 ± 13.9 |
| Biomass t/ha | 75.0 ± 15.0 | 71.0 ± 4.0 | 57.8 ± 14.8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Ren, L.; Xie, G. Technical Feasibility and Comprehensive Sustainability Assessment of Sweet Sorghum for Bioethanol Production in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030731
Yang X, Li M, Liu H, Ren L, Xie G. Technical Feasibility and Comprehensive Sustainability Assessment of Sweet Sorghum for Bioethanol Production in China. Sustainability. 2018; 10(3):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030731
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaolin, Meng Li, Huihui Liu, Lantian Ren, and Guanghui Xie. 2018. "Technical Feasibility and Comprehensive Sustainability Assessment of Sweet Sorghum for Bioethanol Production in China" Sustainability 10, no. 3: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030731
APA StyleYang, X., Li, M., Liu, H., Ren, L., & Xie, G. (2018). Technical Feasibility and Comprehensive Sustainability Assessment of Sweet Sorghum for Bioethanol Production in China. Sustainability, 10(3), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030731





