Estimating the Possibility of Surface Soil Pollution with Atmospheric Lead Deposits Using the ADMER Model
Abstract
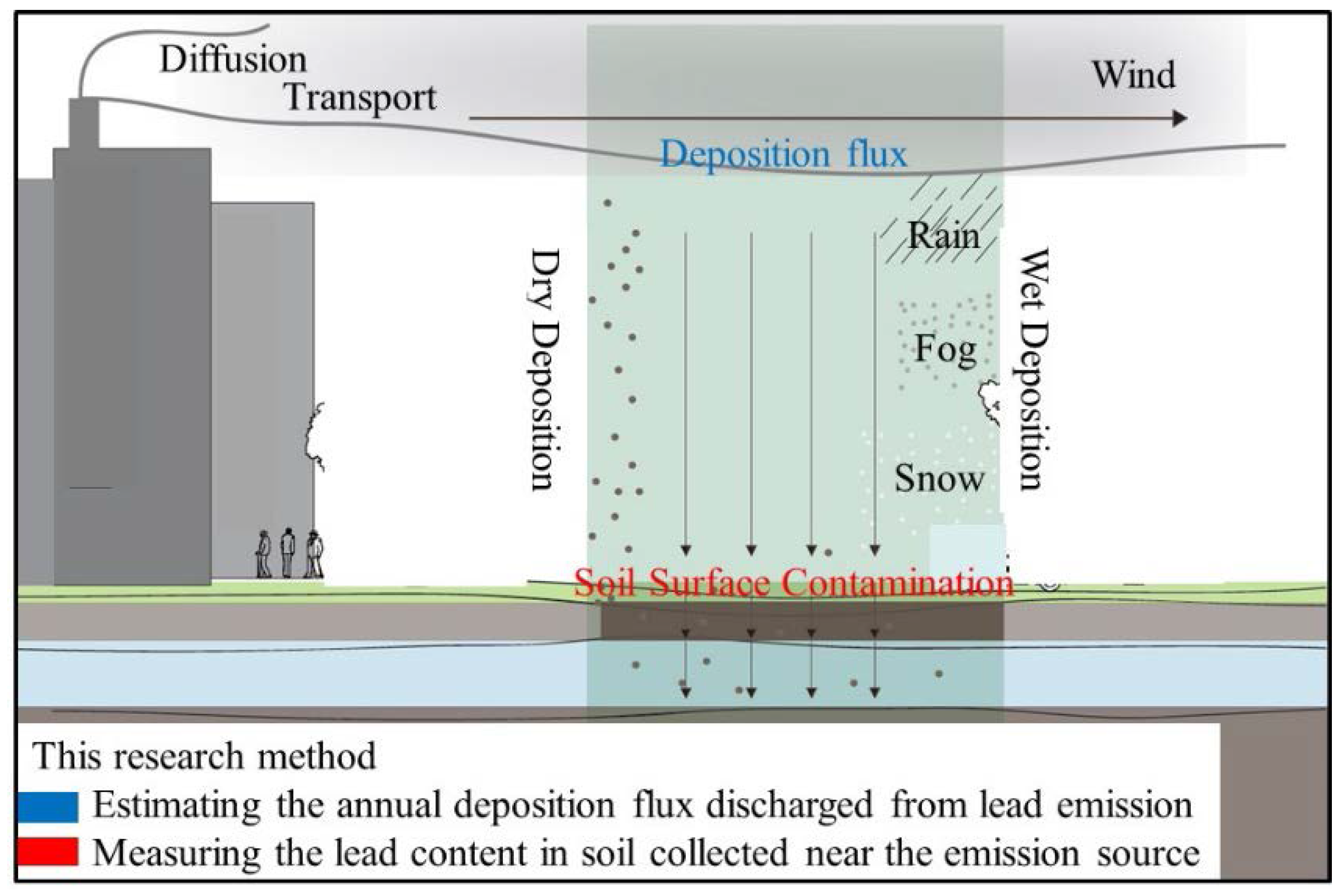
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
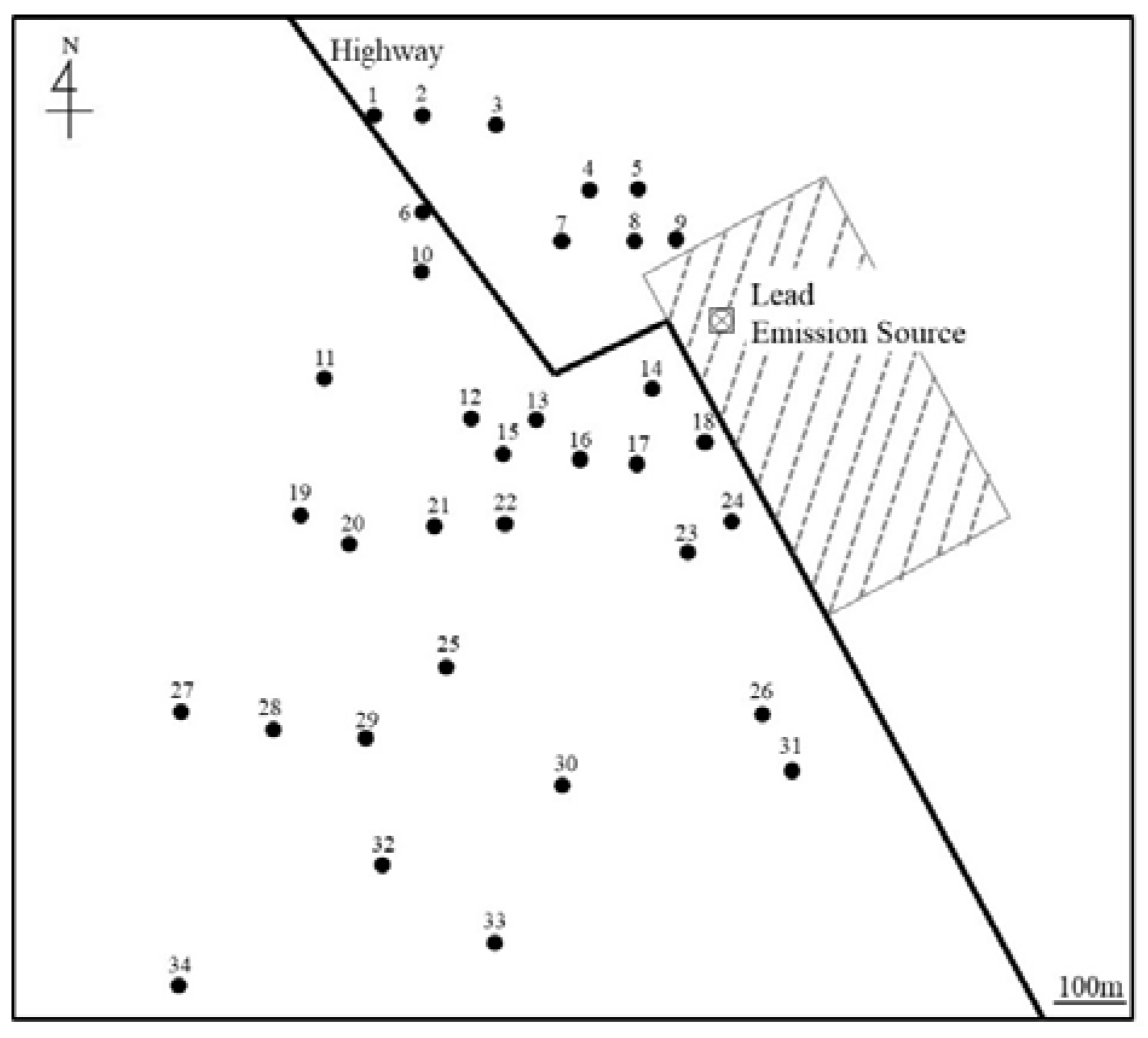
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Techniques
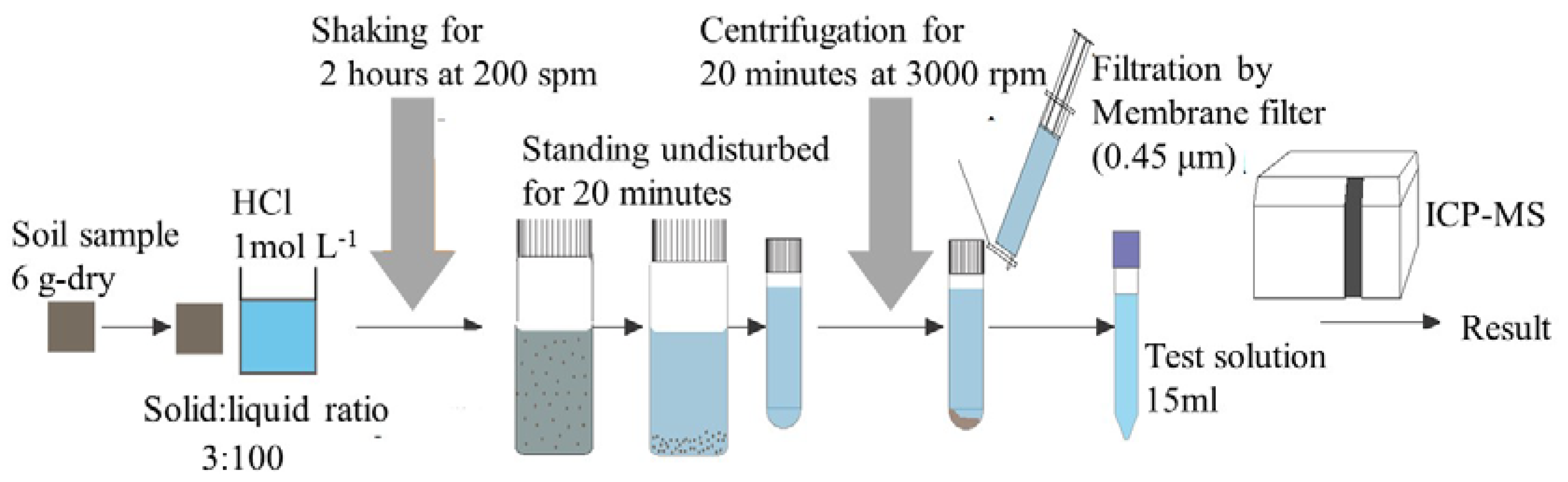
2.2. Measurement of Lead Content in Soil Samples
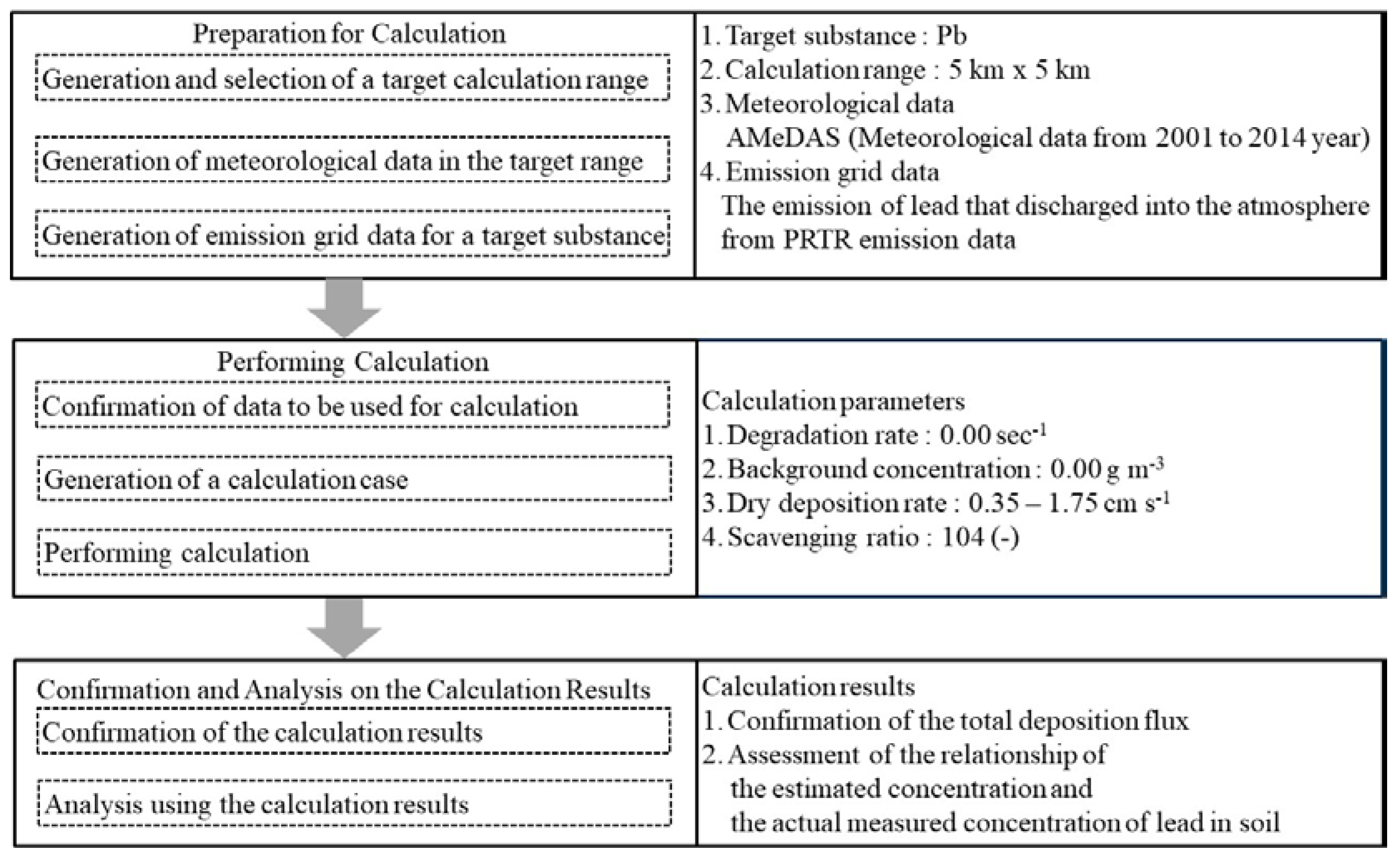
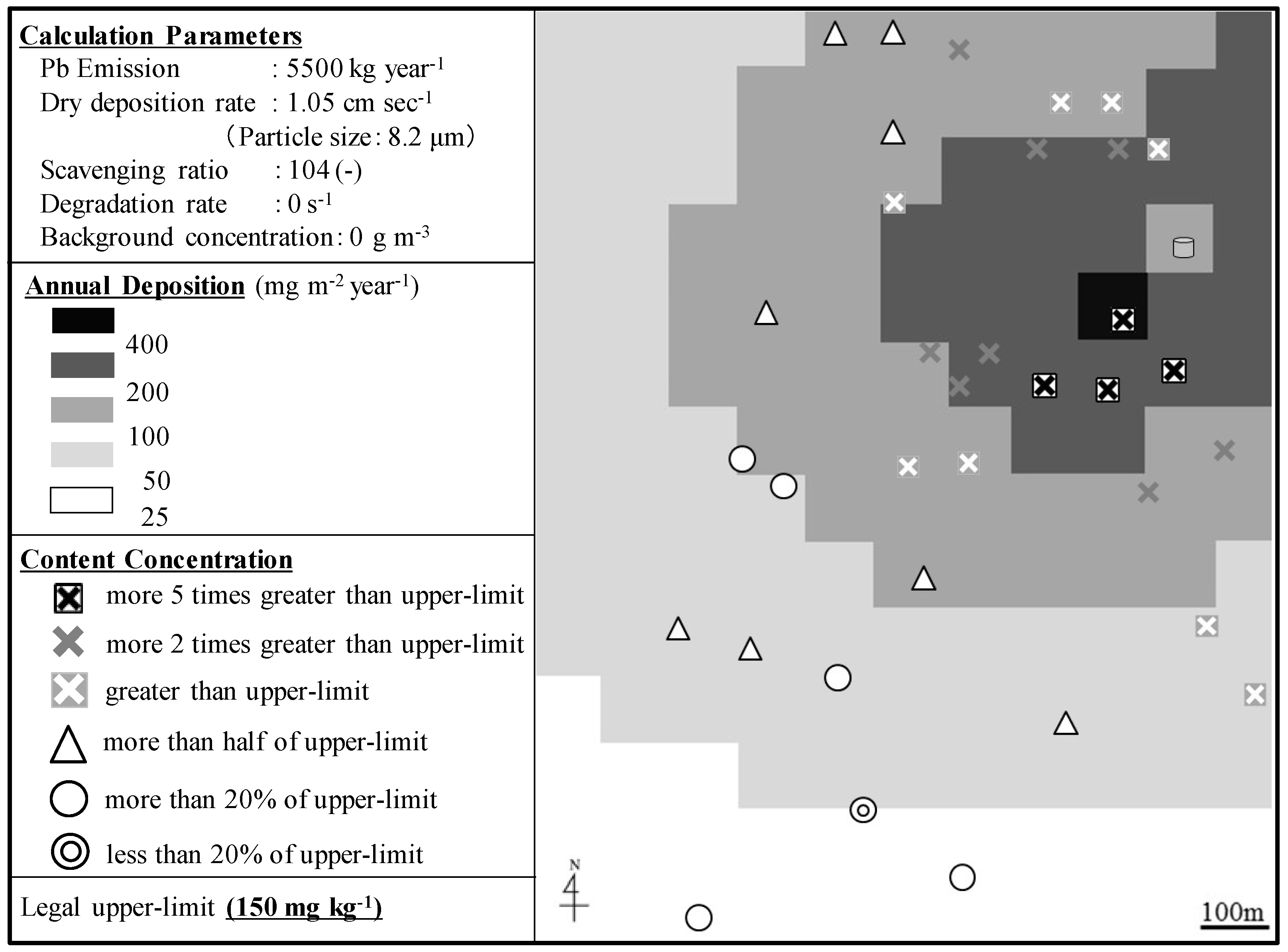
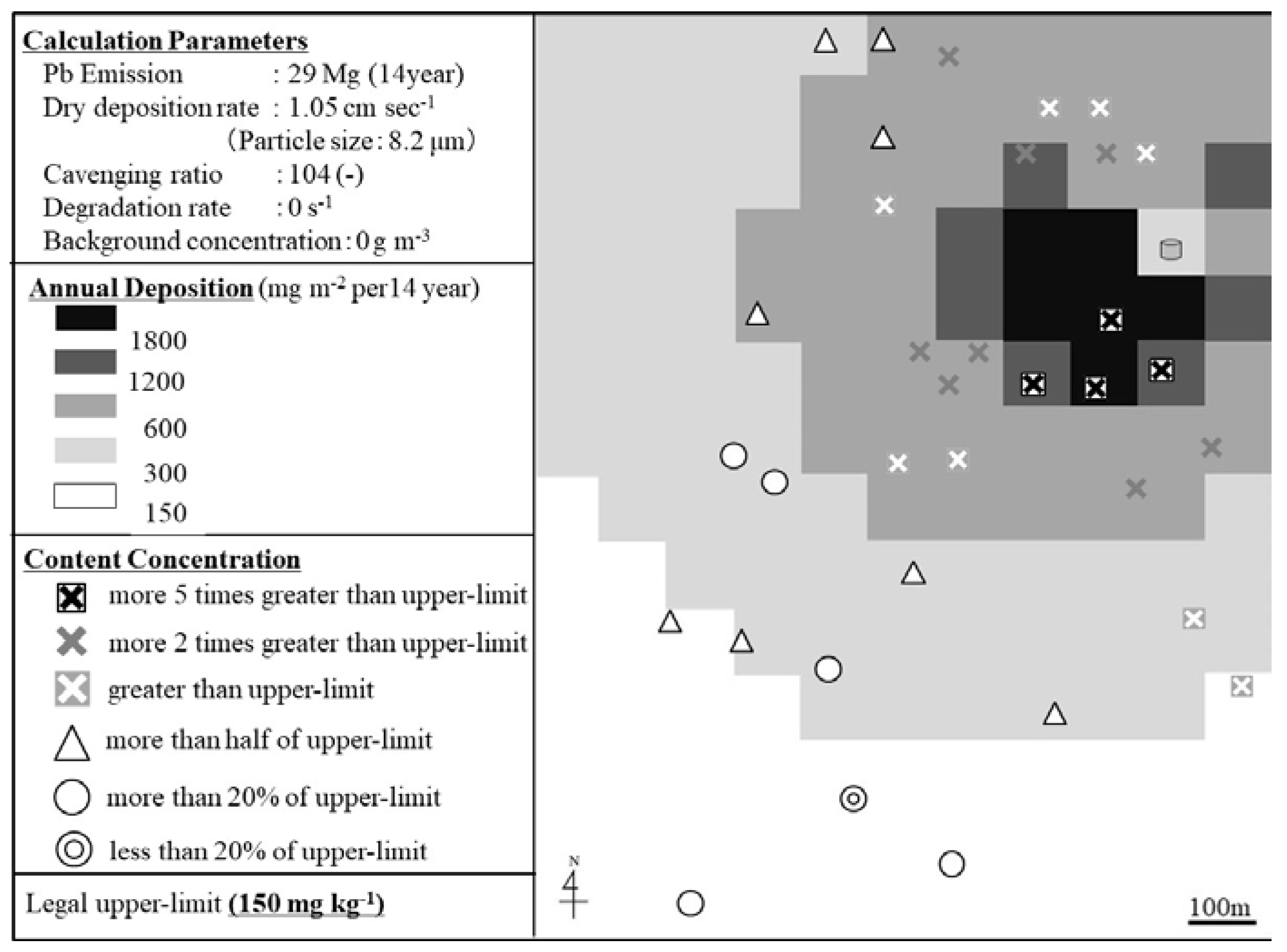
2.3. Estimation of Annual Deposition Flux Using ADMER
3. Results and Discussion
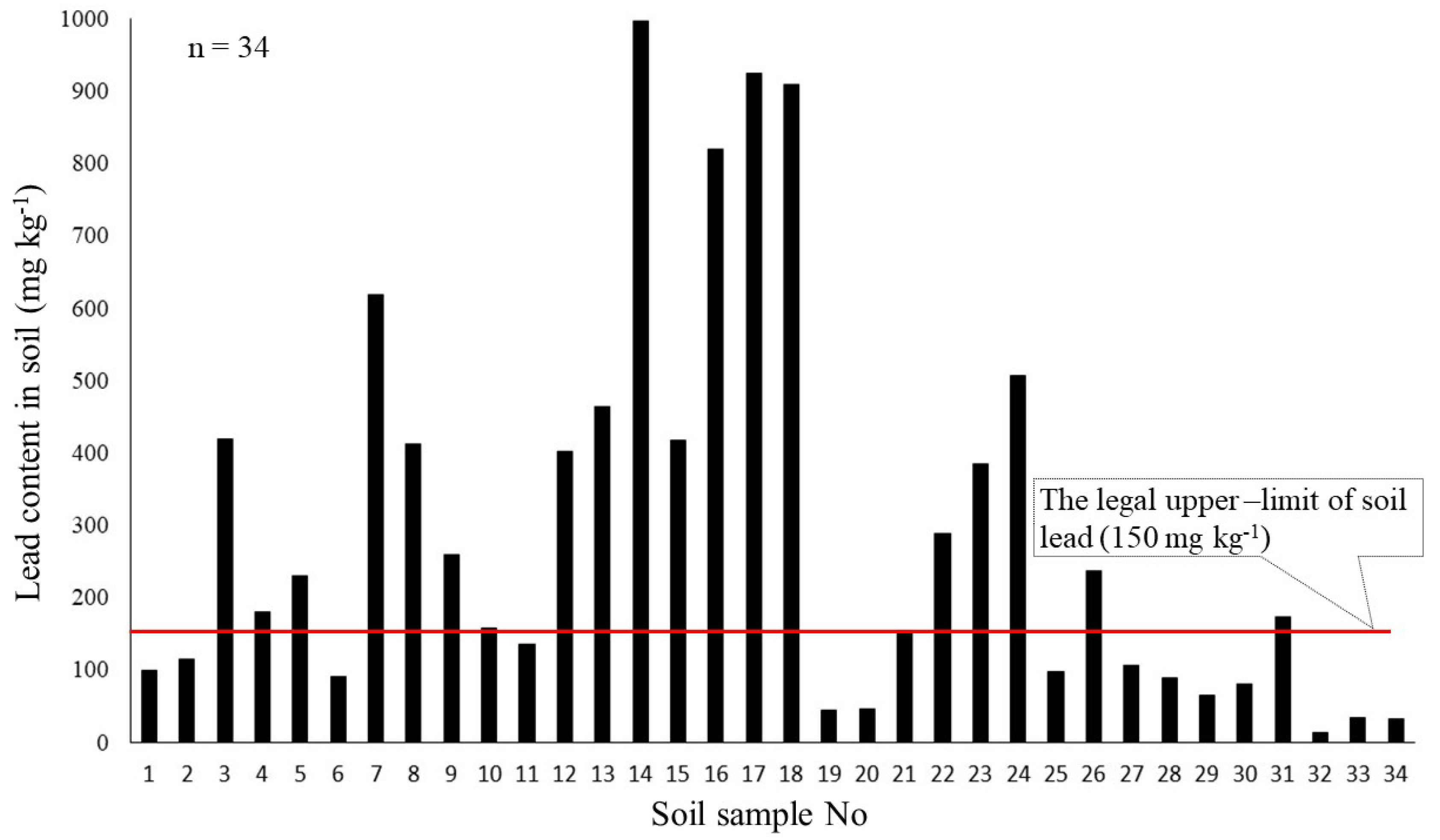
3.1. Lead Content in Soil
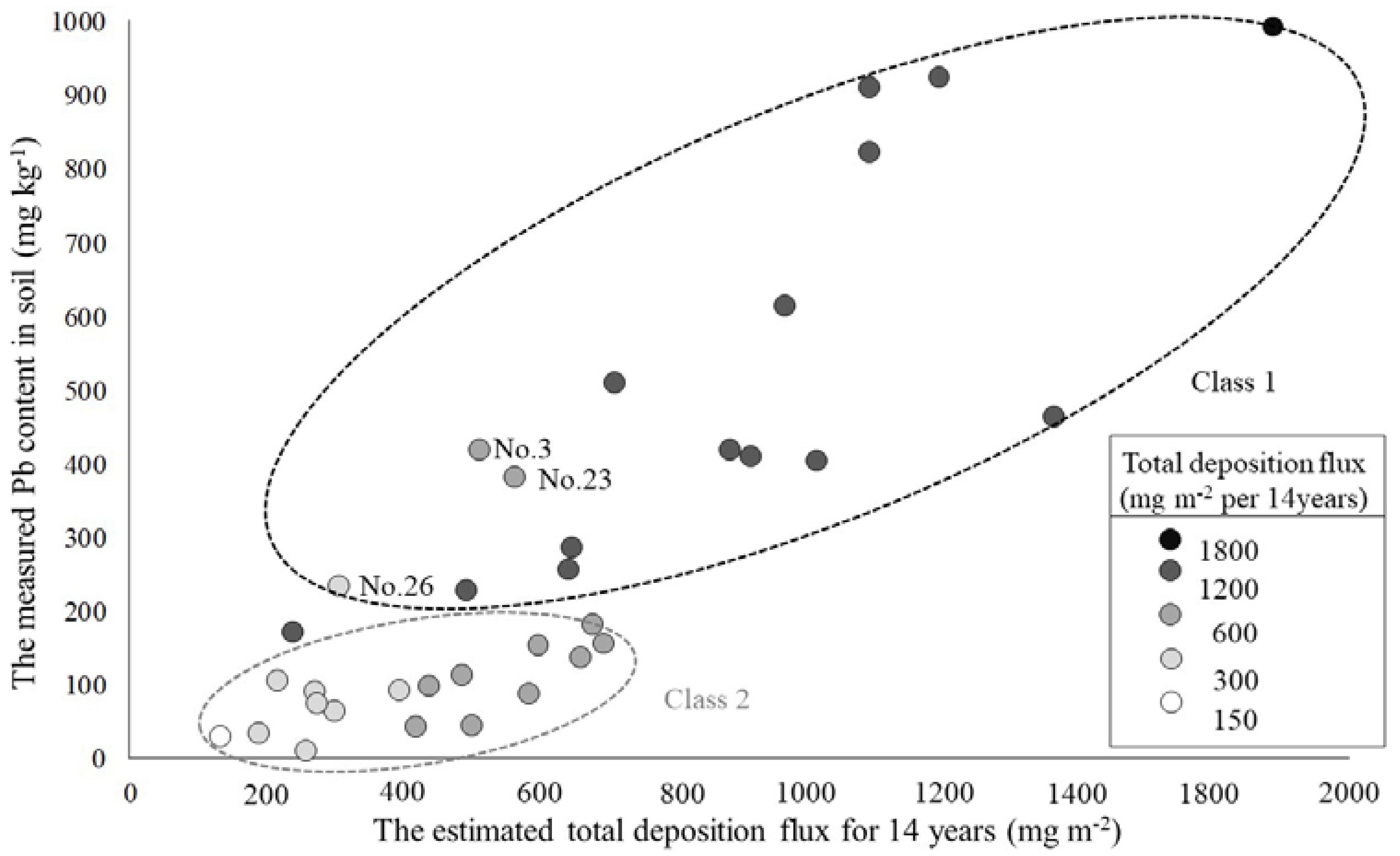
3.2. ADMER and Field Measurement Calculation Results—Comparison & Discussion
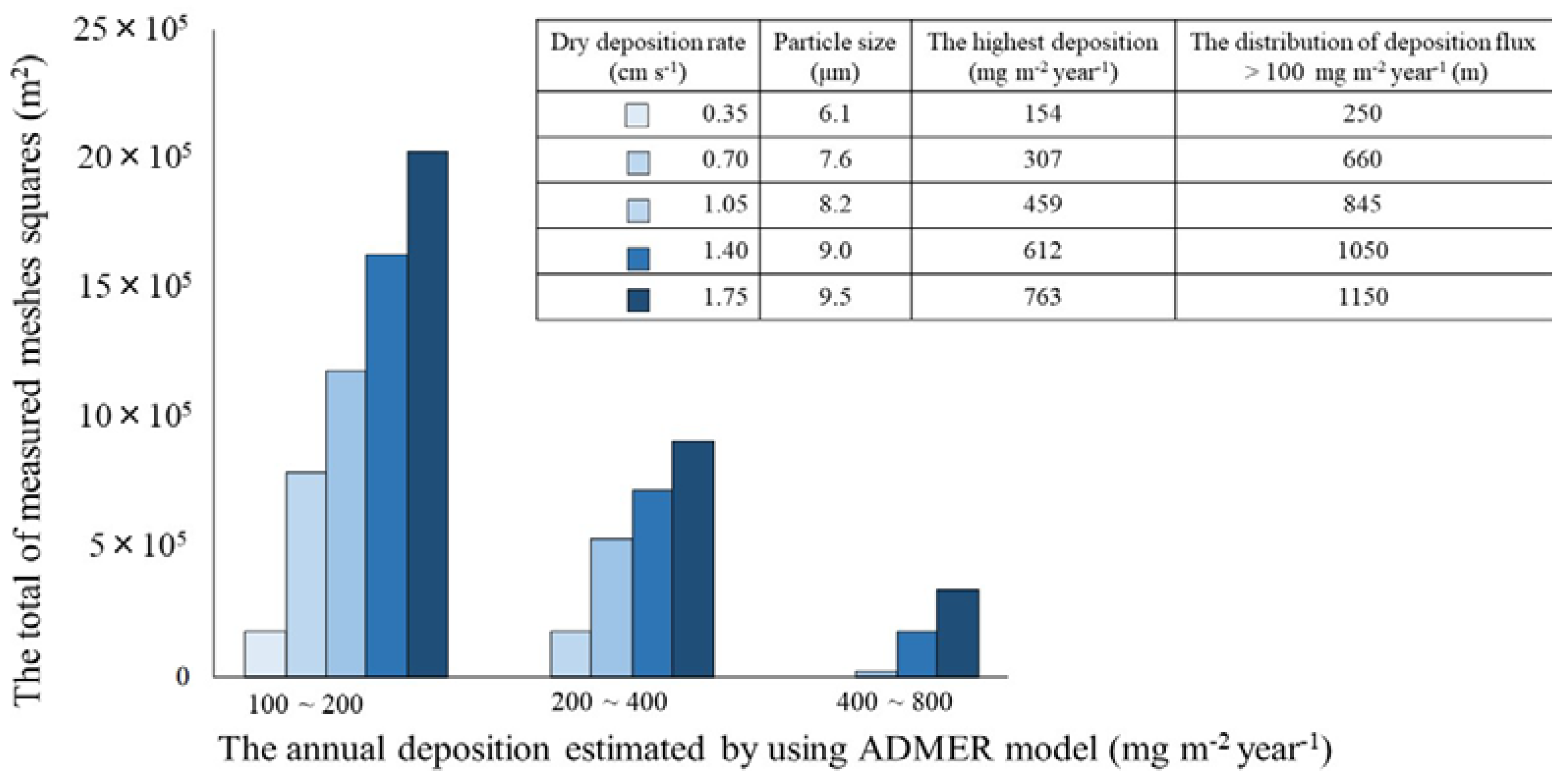
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Estimated Lead Deposition Flux Using Varied Dry Deposition Velocities
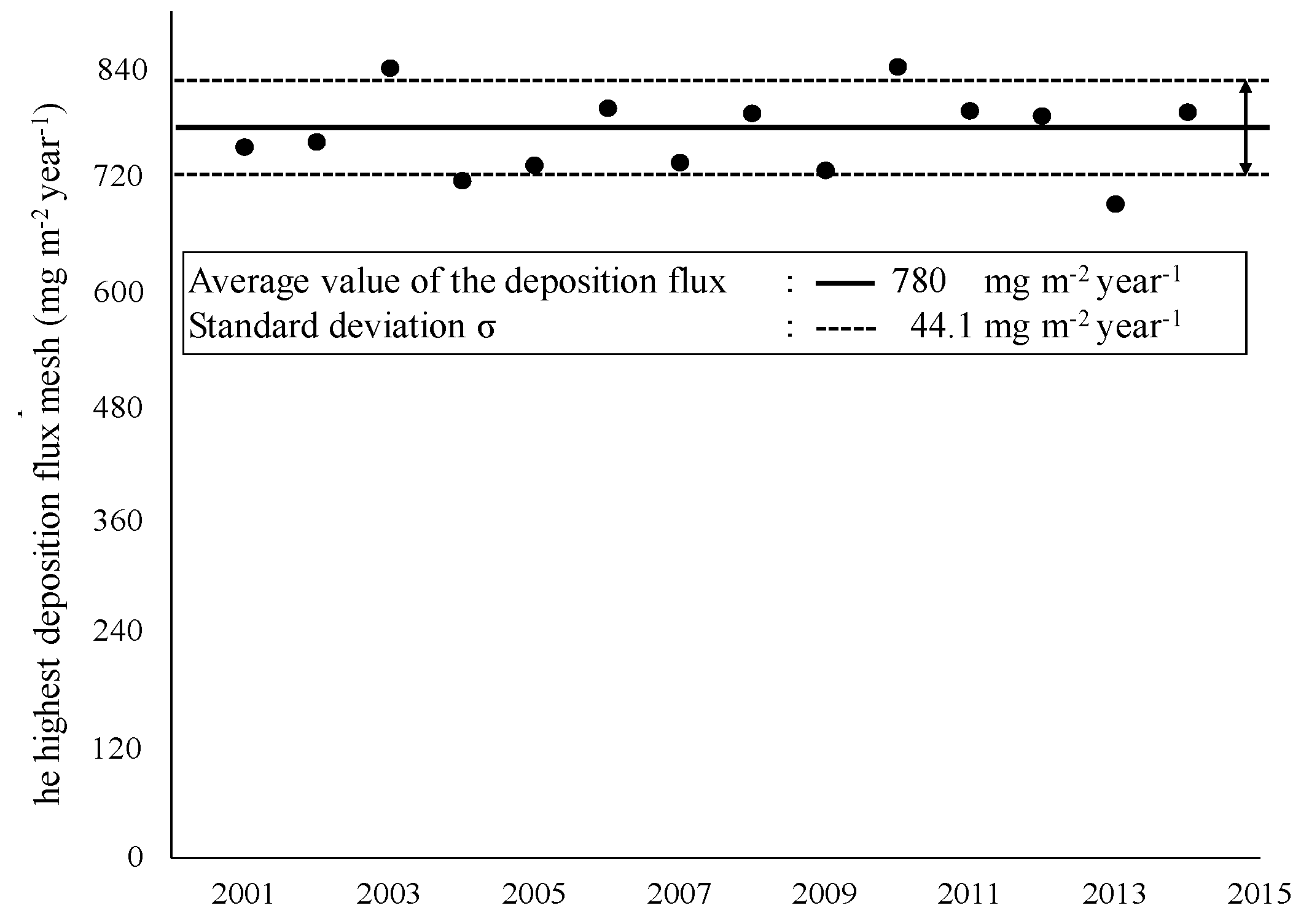
3.4. Differences in Estimated Deposition due to Annual Climate Fluctuations
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Japan Ministry of the Environment. Results of the Survey on the Enforcement Status of the Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act and Soil Contamination Investigations and Countermeasures in FY 2015. Available online: http://www.env.go.jp/en/headline/2331.html (accessed on 2 October 2017).
- Japan Ministry of Economy Trade and Industry. The Result of the Pollutant Release and Transfer Register (PRTR), 2015. Available online: http://www.env.go.jp/en/chemi/prtr/prtr.html (accessed on 2 October 2017).
- Urrutia-Goyes, R.; Argyraki, A.; Ornelas-Soto, N. Assessing Lead, Nickel, and Zinc Pollution in Topsoil from a Historic Shooting Range Rehabilitated into a Public Urban Park. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, C.W.; McLaren, R.G.; Roberts, A.H.C. Atmospheric accessions of heavy metals to some New Zealand pastoral soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 305, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zheng, Y.; Lei, M.; Huang, Z.; Wu, H.; Chen, H.; Fan, K.; Yu, K.; Wu, X.; Tian, Q. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Geological Survey. Lead in the Environment; QE516.P3L4 553′.44 76-7962; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1976.
- European Commission (‘DG Environment’). Science for Environment Policy; Soil Contamination: Impacts on Human Health; European Commission: Bristol, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin, M.M.; Leckie, J.O. Multiple-Site Adsorption of Cd, Cu, Zn, and Pb on Amorphous Iron Oxyhydroxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1981, 79, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khashman, O.A.; Shawabkeh, R.A. Metals distribution in soils around the cement factory in southern Jordan. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 140, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, A.K.; Govil, P.K. Soil contamination due to heavy metals from an industrial area of Surat, Gujarat, Western India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 124, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, A.; Pallarés, S.; Pardo, F.; Vicente, A.B.; Sanfeliu, T.; Bech, J. Deposition of heavy metals from particulate settleable matter in soils of an industrialised area. J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 113, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Lei, M.; Guo, G.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, T. Quantitative Analysis of the Factors Influencing Soil Heavy Metal Lateral Migration in Rainfalls Based on Geographical Detector Software: A Case Study in Huanjiang County, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Liu, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Kameya, T.; Yamada, Y. The Adsorption Equilibrium of Pb and Cd on Several Soils in Various pH Solutions or in the Presence of Dissolved Humic Substances. In Heavy Metal Contamination of Soils; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Godin, P.M.; Feinberg, M.H.; Ducauze, C.J. Modelling of Soil Contamination by Airborne Lead and Cadmium around Several Emission Sources. Environ. Pollut. Ser. B 1985, 10, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinnes, E.; Solberg, W.; Petersen, H.M.; Wren, C.D. Heavy metal pollution by long range atmospheric transport in natural soils of Southern Norway. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1989, 45, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yang, J.; Gong, Z. Historical change of heavy metals in urban soils of Nanjing, China during the past 20 centuries. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Hu, Y. Lead (Pb) isotopic fingerprinting and its applications in lead pollution studies in China: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1134–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Shih, K.; Zeng, E.Y.; Cheng, H. Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 6150–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, P.; Baishiki, R. CALINE3—A Versatile Dispersion Model for Predicting Air Pollutant Levels Near Highways and Arterial Streets; FHWA/CA/TL-79/23, NTIS: PB 220842; California State Department of Transportation: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1979; p. 129.
- Rao, S.T.; Sistla, G.; Keenan, M.T.; Wilson, J.S. An evaluation of some commonly used highway dispersion models. J. Air Pollut. Control 1980, 30, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.T.; Keenan, M.; Sistla, G.; Samson, P. Dispersion of Pollutants near Highways—Data Analysis and Model Evaluation; EPA-600/479-011; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1979.
- Brandt, J.; Christensen, J.H.; Frohn, L.M. Modelling transport and deposition of caesium and iodine from the Chernobyl accident using the DREAM model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2002, 2, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, M.; Nakayama, H.; Nagai, H.; Terada, H.; Katata, G.; Yamazawa, H. Preliminary Estimation of Release Amounts of 131I and 137Cs Accidentally Discharged from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant into the Atmosphere. J. Nuclear Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashino, H.; Inoue, K.; Mita, K.; Shinozaki, H.; Yoshikado, H. Atmospheric Dispersion Model for Exposure and Risk assessment (ADMER) development and verification of nationwide version. Environ. Manag. 2004, 40, 1242–1250. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Higashino, H.; Inoue, K. Development of an Atmospheric Dispersion Model for Exposure and Risk Assessment (ADMER) Ver. 3. Jpn. J. Risk Anal. 2016, 26, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashino, H.; Mita, K.; Yoshikado, H.; Iwata, M.; Nakanishi, J. Exposure and risk assessment of 1,3-butadiene in Japan. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2007, 166, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japan Ministry of Economy Trade and Industry. The Result of the Pollutant Release and Transfer Register (PRTR), 2001–2014. Available online: http://www.env.go.jp/en/chemi/prtr/prtr.html (accessed on 2 October 2017).
- Japan Ministry of the Environment. Environmental Quality Standards for Soil Pollution. Available online: http://www.env.go.jp/en/water/index.html (accessed on 2 October 2017).
- The Lead Content in the Soil Was Measured by the Japan Ministry of the Environment, Notification N.19, 2004. (In Japanese). Available online: http://www.env.go.jp/hourei/06/000029.html (accessed on 2 October 2017).
- Higashino, H.; Kitabayashi, K.; Inoue, K.; Mita, K.; Yonezawa, Y. Development of an atmospheric dispersion model for exposure and risk assessment (AIST–ADMER). J. Jpn. Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 38, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maenhaut, W.; Zoller, W.H.; Duce, R.A.; Hoffman, G.L. Concentration and size distribution of particulate trace elements in the south polar atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 2421–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Monitoring and Evaluation Programme (EMEP). Heavy Metals and POP Measurements, 2004; Norwegian Institute for Air Research: Kjeller, Norway, 2006; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga, J. Lead in the Japanese living environment. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2012, 17, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, M.; Marumoto, K. Dry deposition fluxes and deposition velocities of trace metals in the Tokyo Metropolitan Area Measured with a Water Surface Sampler. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2190–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noll, K.E.; Fang, K.Y.P. Development of a Dry deposition model for atmosphere coarse paticles. Atmos. Environ. 1967, 23, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Ministry of the Environment. Soil Contamination Countermeasures. Available online: http://www.env.go.jp/en/water/soil/contami_cm.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2017).

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen Thi Lan, B.; Kobayashi, T.; Suetsugu, A.; Tian, X.; Kameya, T. Estimating the Possibility of Surface Soil Pollution with Atmospheric Lead Deposits Using the ADMER Model. Sustainability 2018, 10, 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030720
Nguyen Thi Lan B, Kobayashi T, Suetsugu A, Tian X, Kameya T. Estimating the Possibility of Surface Soil Pollution with Atmospheric Lead Deposits Using the ADMER Model. Sustainability. 2018; 10(3):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030720
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen Thi Lan, Binh, Takeshi Kobayashi, Atsushi Suetsugu, Xiaowei Tian, and Takashi Kameya. 2018. "Estimating the Possibility of Surface Soil Pollution with Atmospheric Lead Deposits Using the ADMER Model" Sustainability 10, no. 3: 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030720
APA StyleNguyen Thi Lan, B., Kobayashi, T., Suetsugu, A., Tian, X., & Kameya, T. (2018). Estimating the Possibility of Surface Soil Pollution with Atmospheric Lead Deposits Using the ADMER Model. Sustainability, 10(3), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030720




