Abstract
Past years have witnessed the transformation of land use at a high frequency and a warmer and drier climate in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau region. To fully understand the spatial-temporal variation of ecosystem services against the changing global backdrop and to provide scientific ecosystem management measures for decision-making, a study was conducted to investigate the major ecosystem services: water yield, soil conservation and crop production from 1990 to 2015 in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau region. Three scenarios—climate change only, land use change only and both land use and climate change—were included in this study to analyze the response of ES to the above-mentioned global changes. The results show that (1) the total quantity of ES reduced in all the three scenarios, the annual ES change was scenarioII < scenarioIII < scenarioI and the periodical characteristics are present in this region; (2) the ES change in spatial distribution varied with different climate change patterns and land use transfer directions; (3) the ES composition of each ecosystem varied with different driving scenarios and different responses of the forest and wetland on climate change and land use changes were observed. Moreover, the trade-off under land use change and climate change respectively was observed in this study. Based on the results, we recommend that the local government take this trade-off and climate change into account when making decisions, continue with desertification control and improve the quality of grassland as well as forests—these efforts should enable us to achieve sustainable development of human beings and the natural ecosystem.
1. Introduction
Ecosystem service (ES) refers to the benefits people obtain from the ecosystem, including provisioning services, regulating services, cultural services and supporting services [1], which constitute the basis of human survival and are closely related to the well-being of humans [2]. As an important link between human beings and the natural ecosystem, ecosystem services open up a new perspective of ecosystem management and sustainable development [3]. First proposed in the 1970s, ecosystem service studies have been enriched and promoted in terms of conception, classification system and evaluation methods [4,5,6,7,8,9]. In 2005, the Nations Millennium Ecosystem Assessment reviewed changes to the global ecosystem service for the first time and came to the conclusion that 15 ecosystem services out of the 24 services (over 60% of the total) assessed had degraded globally, especially services providing fish, freshwater and erosion control, etc. [1,10,11,12]. The decline in ecosystem service has attracted extensive attention from multiple disciplines [13,14,15,16]. At present, global changes, such as climate change, population growth and urbanization have directly or indirectly altered the pattern and dynamics of material circulation and energy flow on the earth, which greatly impacts the ecosystem and the well-being of humans [17,18]. As the importance of ecosystem service is increasingly acknowledged, a wide range of research has been carried out on the driving factors and management measures [19,20,21,22,23].
Land use change is a pivotal factor that has enduring and widespread influence on ecosystem services [1,12]. It contains a sea of information related to human activities, which mainly affect the ecosystem service in three ways [24,25]: (1) land use type change, which affects the supply of ES through ecological processes such as energy exchange, water cycle, soil erosion and accumulation. For example, conversion of forests to croplands reduced carbon sequestration and storage [26,27,28]; (2) Land use patterns change, land use change will affect the ES through the corresponding ecological processes changes produced by the land use patterns changes. For instance, the landscape fragmentation caused by built-up expansion have an adverse effect on ecosystem service value in four Chinese cities [29]; (3) Land use intensity change, In general, the impact of land use intensity change on ecosystem services is noticeable, compared with the less disturbed land, land more disturbed by human beings has stronger supply function but weaker adjustment and support function [30]. Besides, climate change is also considered to be one of the significant driving factors [31,32,33], which affects ecosystem services through changing the hydrological process, moisture-energy distribution and carbon dioxide concentrations directly or indirectly. Many studies have been conducted to explore the impacts of climate change exerted on ecosystem services, such as rising temperature, decreasing precipitation and greenhouse gases emissions [34,35,36,37,38]. For example, Seidl [38] found that climate change may make the future supply services uncertain due to increased occurrences of fire and droughts in the Rocky Mountains. As well as studies of the Sancha River Basin, China, Lang [35] found that climate change accounted for 97.44% of the change in water yield. In recent years, global climate changes have been ongoing, many regions are experiencing the drying and warming trends, which increase the probability of desertification, water shortage and has placed considerable stress on the sustainable development of ecosystem service [39].
As the two main driving factors, the land use change and climate change jointly shape ecosystem service internally and externally respectively. To fully understand the driving process and the impacts of these two factors to the regional ecosystem service, it is essential to have a reasonable approach to quantify these impacts. In some research, correlation analysis method is widely used [40,41,42,43], calculating the most influential driving factors but ignoring the impact of the spatial heterogeneity and ecosystem processes. Because of that, it is not conducive to fully understanding the dynamics of ecosystem service [44]. Compared with the correlation analysis methods, the biophysical model has its inherent advantage, which quantifies the changes through the simulation of ecosystem process and physical changes [44,45,46,47,48].
The Eastern Tibetan Plateau (ETP region), as the ecological barrier of the Yangtze River and the upper reaches of the Yellow River in China, is a typical ecologically vulnerable area [49]. Just like many other places in the world, this region has experienced overgrazing, over-cultivation, deforestation and the natural ecosystem is seriously damaged [50,51,52,53]. With growing awareness of environmental protection, confronted with the deteriorating environmental conditions, a series of environmental protection projects have been carried out in the region, such as “Natural Forest Protection Project” and “Grain for Green Project” by the government after 2000 [50,54,55]. Land use change in this region is fairly frequent and the climate change tendency is apparent in this area [56]. In addition to the ES total amount estimated by Ouyang [2], we know little about the ecosystem service composition of different ecosystems and their characteristics in response to such changes. To provide a comprehensive perspective for ecosystem adaptive management and scientific research, the temporal and spatial variations of ecosystem service from 1990 to 2015 and their composition characteristics were studied on a regional scale. Besides, scenario simulations were made in this study to reveal the response of ecosystem service to the land use change and climate changes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Studied Area
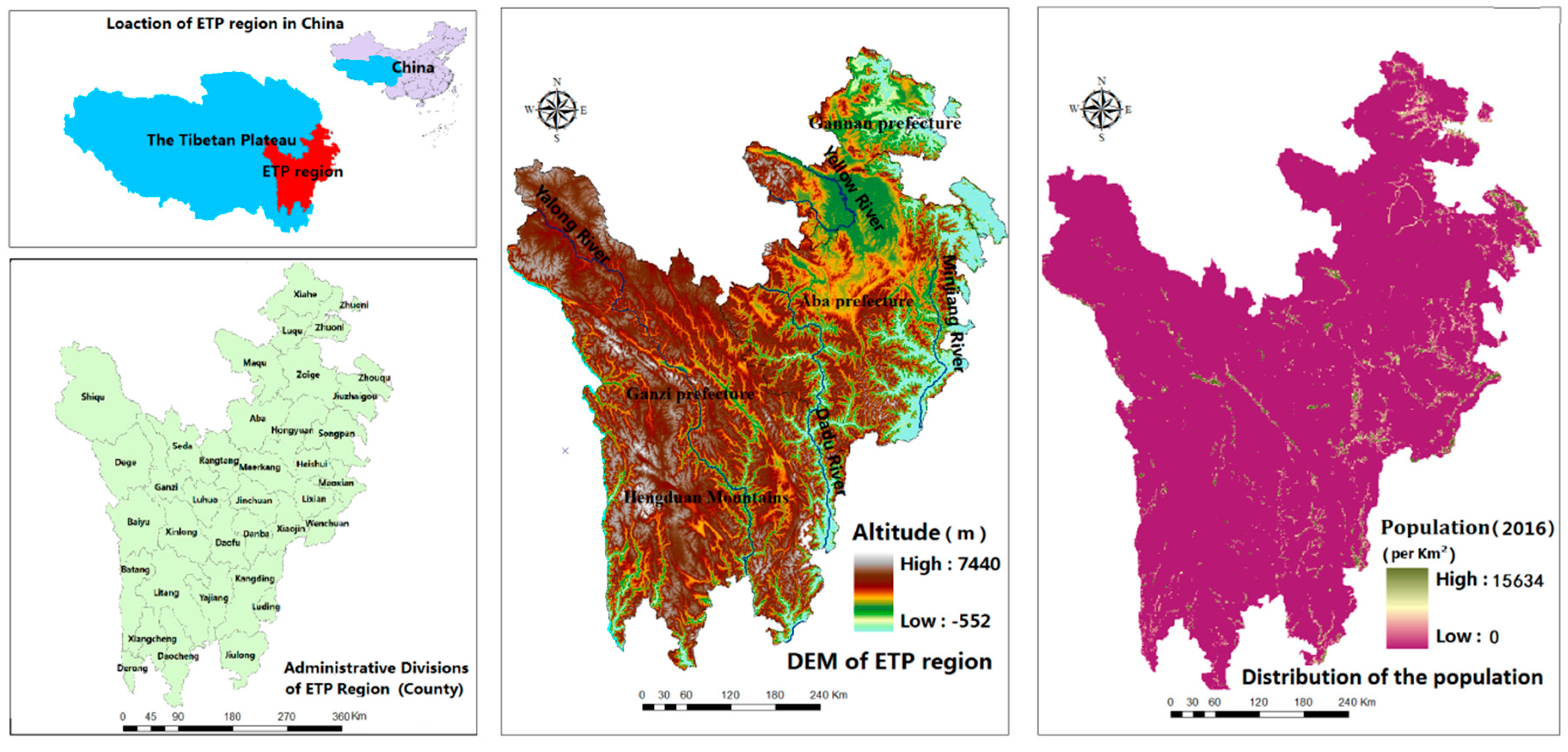
The Eastern Tibetan Plateau (27°59′27″~35°41′39″ N, 97°21′26″~104°42′07″ E)—the ETP region (Figure 1)—in this study consists of three prefectures (Aba and Ganzi prefectures in Sichuan Province and Gannan prefecture in Gansu Province). It covers a total area of 247,729 km2 and the total population is approximately 2.53 × 106 (http://www.sc.stats.gov.cn/, www.gstj.gov.cn/, 2016). The region features diverse terrain ranging from 2500~7500 m and it has a typical continental alpine climate, whose annual average temperature is 0~6 °C, while the average precipitation is 650 mm.
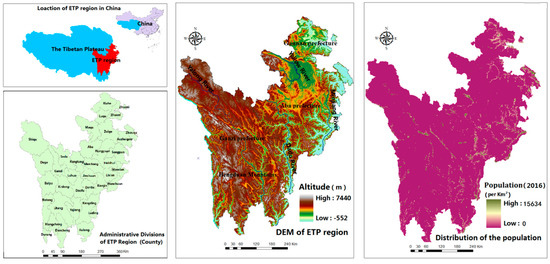
Figure 1.
Location, altitude and population distribution of the ETP region.
ETP region, as the ecological barrier of the Yangtze River and the upper reaches of the Yellow River, is one of the five major grasslands in China (also the best grassland in HKH area) and one of the three major forest areas in China. It plays an important role in the national ecological security strategy. Besides, as an important part of “alpine vegetation zone” in “China Global Change transect,” the ETP region is sensitive to global climate change and is dubbed “a barometer of global climate change in the future” [57]. In the national ecosystem assessment conducted by Ouyang, the importance level of the studied area was rated as “very high” [2]. However, the studied area is a typical ecological fragile and sensitive area in China [58,59]. In recent years, with global warming, population increasing, overgrazing and city expansion, the ecosystem in the area is confronted with a series of severe challenges, such as land desertification, wetland reduction and soil erosion. It faces with the trade-off between economic development and environmental protection [60,61,62].
2.2. Ecosystem Services Assessment
In recent decades, human activities have greatly affected the structure and spatial distribution of regional ecosystems, especially grasslands and forest ecosystems, which provide a wide range of critical regulatory and production services in the ETP region. Meantime, natural disasters such as debris flow and landslides occurred frequently [63,64,65]. Therefore, taking the ecological characteristics of the ETP region and its role in the national ecological security pattern of China into consideration [17], three representative and important ecosystem services including water yield, crop production, soil conservation were studied [2]. In this study, InVEST and CASA models were used to assess the ecosystem services of the ETP region.
2.2.1. Soil Conservation (SC)
The model of soil conservation in InVEST is mainly based on USLE (universal soil loss equation, USLE) model. The model represents soil conservation ability by using the difference between potential soil erosion and actual soil erosion. The soil quantity is calculated with the following model [44]:
U = Uf − Ux
Uf = Rx·Kx·LSx
Ux = Rx·Kx·LSx·Cx·Px
U, Uf, Ux—the amount of soil conservation (t·hm−2·a−1), the actual amount of soil erosion (t·hm−2·a−1), potential amount of soil erosion in the grid x (t·hm−2·a−1), respectively. Factors affecting soil erosion include Rx—rainfall erosion factor (MJ·mm·hm−2·h−1); Kx—soil erodibility factor (t·hm2·h·hm−2·MJ−1·mm−1); LSx—the factor of slope and slope length (dimensionless); Cx—vegetation cover factor (dimensionless); Px—management factor (dimensionless). The rainfall erosivity factor is first established by using the method of Wischmeier to calculate the precipitation of the site, then calculated with the Kriging interpolation method on the Arc-GIS9.3 platform; the soil erodibility factor is calculated by using the Schowalter equations with the soil distribution map; other model inputs are collected from other related data, converted into units in accordance with the model requirements and categorized into appropriate formats.
2.2.2. Water Yield (WY)
The model of Water Yield in InVEST is mainly based on a simplified hydrological cycle model. Mapped by the grid, it calculates the amount of water used for hydropower production from each sub-watershed. The model ignores the influence of groundwater and the more the surface water yield in the given area, the more water supply and the service resource supply. In recent years, this model has been widely used. Water yield is calculated by the following model [44]:
Yxj = (1 − AETxj/Pxj)·Pxj
AETxj/Pxj = (1 + ωxRxj)/(1 + ωxRxj) + 1/Rxj)
Rxj = Kxj·ET0/Pxj
ωx = Z·AWCx/Pxj
AWC = Min(Soil Depth, Root Depth)·PAWC
Yxj—water yield of land use type j and the raster grid X (m3); AETxj—the annual actual evapotranspiration of land use type j and the raster grid x (mm); Pxj—the annual precipitation of land use type j and the raster grid x (mm); ωx—the ratio characterizing the natural climate and soil properties (dimensionless); Rxj—the Budyko aridity index of grid x and type j (dimensionless); Kxj—the plant (vegetation) evapotranspiration coefficient of grid x and type j; ET0—the reference evapotranspiration from grid x (mm); AWCx—the volumetric plant available water content (mm); PAWC—the plant available water capacity (0–1) [44]. Data needed in this model includes annual precipitation, potential evapotranspiration, land use maps, soil depth, root depth, available water content and evapotranspiration coefficients etc. The annual precipitation data is calculated with Kriging interpolation method by annual original data of each Meteorological observation station in the Arc-GIS9.3 platform; the calculation of potential evapotranspiration is based on potential evapotranspiration estimation obtained via the method of Modified-Hargreaves with each meteorological station data, then interpolated by the “Tyson polygon method” in the Arc-GIS9.3 platform; other model input is collected from catchment related data, converted into units in accordance with the model requirements and categorized into appropriate formats.
2.2.3. Crop Production (CP)
The model of Crop Production is mainly based on CASA (Carnegie-Ames-Stanford, Approach, CASA) model, which estimates the CP (Net primary productivity, CP) by the product of absorbed photo synthetically active radiation (APAR) and the actual energy utilization as well as (ε). Crop Production is calculated with the following model [66]:
CP(x,t) = APAR(x,t)·ε(x,t)
APAR(x,t) = SOL(x,t)·FPAR(x,t)·0.5
FPAR(x,t) = [(NDVI(x,t) − NDVImin)/(NDVImax − NDVImin)]·(FPARmax − FPARmin) + FPARmin
ε(x,t) = Tε1(x,t)·Tε2(x,t)·Wε(x,t)·εmax
Wε(x,t) = 0.5 + 0.5·E(x,t)/EP(x,t)
CP(x t)—net primary productivity of grid x in time t (g); APAR(x,t)—photo synthetically active radiation absorbed by the grid x in time t (MJ·m−2); ε(x,t)—actual utilization of the pixel x in time t (gC·MJ−1); SOL(x,t)—the total amount of solar radiation of grid x in time t (MJ·m−2); FPAR (x,t)—the fraction of photosynthetic active radiation absorbed by vegetation (0–1); NDVImax, NDVImin—the maximum and minimum values of NDVI, respectively(0–1); FPARmax, FPARmin—set as fixed values of 0.001 and 0.95, respectively; Tε1(x,t), Tε2(x,t)—the stress coefficient of low and high temperature on the utilization rate of light energy, respectively; Wε(x,t)—Water stress coefficient; εmax—maximum potential utilization efficiency of sun light (gC·MJ−1). The input parameters include the average temperature, the evapotranspiration, sunshine duration, vegetation index, albedo, vegetation type, pixel latitude and longitude information, etc.
2.3. Driving Scenario Settings
There are many factors affecting ecosystem services. In the conceptual framework of IPBES (Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, IPBES), the driving forces can be divided into direct and indirect ones [67]. The direct driving factors include natural driving mechanism and human driving mechanism, such as earthquake, tsunami, volcano and pollution, land degradation, habitat restoration, etc. Indirect driving factors include land policy, legislation, international mechanism, etc. In most cases, land use change and climate change are widely studied in the ecosystem service change, which is closely related to the temporal and spatial changes of ecosystem services [68,69,70]. In this study, without considering other driving forces, land use change and climate change, as two important driving scenarios, were applied to the study on the temporal and spatial change of ecosystem services. The scenarios were as follows: ScenarioI, climate change only, in which the impact of land use was filtered, reflecting the impact of climate change during 1990–2015 on the changes of ecosystem services; ScenarioII, only the land use change was allowed and the climate factors remain in 1990. This scenario filtered the impact of climate change, reflecting the impact of land use change during 1990–2015 on the changes of ecosystem services; ScenarioIII, for the interactions of land use and climate change, which reflect the actual changes of the ecosystem services in the studied area during the period of 1990–2015.
2.4. Data Preparation
The 30 m × 30 m land use data were provided by the Resources and Environmental Sciences at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (RESDC), which is the most accurate land use remote sensing monitoring data product in China, interpreted from the Landsat series remote sensing images from multiple periods (http://www.resdc.cn). Soil data classified by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) classification system is used in this study. Climate data was mainly derived from the daily climatologically dataset of Chinese ground international exchange point on the Chinese meteorological science data sharing service system (cdc.cma.gov.cn), which includes site monitoring data such as Air temperature, precipitation, evaporation, relative humidity, wind direction and wind speed, etc. The temperature and precipitation data from 1990 to 2015 is extracted in this study and the topography factors were considered into the climate data interpolation algorithm to reduce the interpolation error. And the biophysical factors, such as the plant evapotranspiration coefficient and support practice factors used in similar natural conditions [2] were adopted in this study [71,72,73,74,75].
3. Result
3.1. Land Use and Climate Changes
3.1.1. Land Use Change
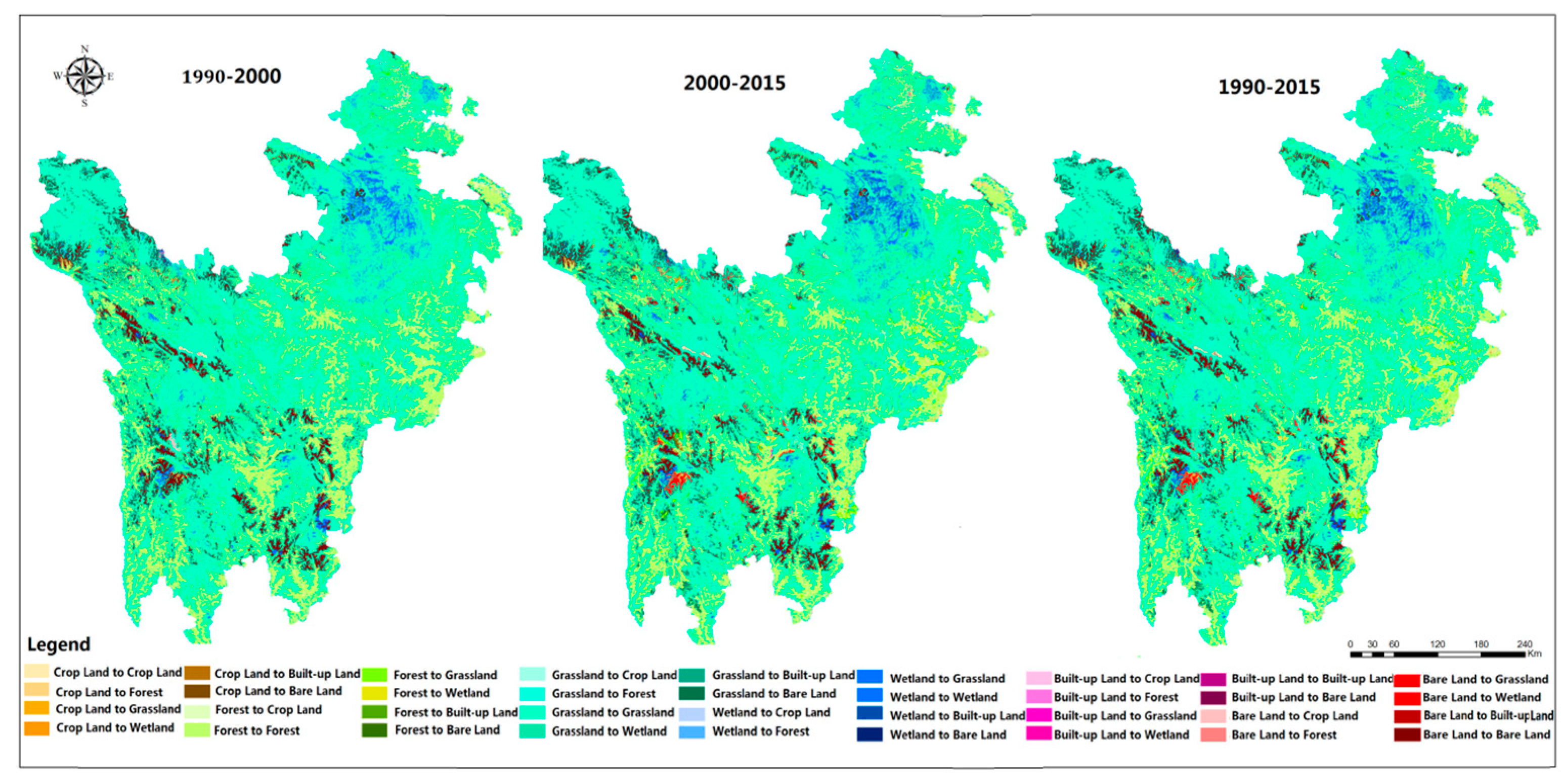
The transition matrix of land use can describe the structure of regional land use change characteristics in a certain period of time comprehensively and specifically [76,77,78,79]. Based on the regional land use maps from 1990 to 2015, the spatial distribution of land use change was shown in Figure 2 and the land use transition matrix of 1990–2015 was calculated by the raster calculation of different land use maps of ETP region (shown in Table 1) [76]. The data xij (i, j are the land use types in row and column, respectively) in the transition matrix of Table 1 represents the land use area transferred from type i to type j.
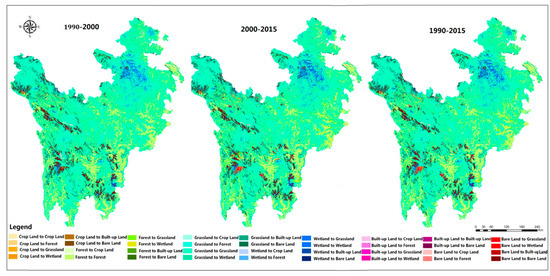
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of land use change during 1990–2015.

Table 1.
Transition matrix of land use change during 1990–2015 (km2) (The value of the table was calculated by the raster calculation of land use maps from 1990 to 2015 in Arcgis9.3 platform).
From 1990 to 2015, on the whole, except for the built-up lands and wetlands, the conversion frequency of forest, grassland, bare land and cultivated land was high. The area of cultivated land decreased on the whole but it can be divided into two stages. During the period from 1990–2000, the area of cultivated land increased by 408 km2, which was mainly transferred from forests and grasslands—especially in the east ETP region—such as Aba Prefecture, including Wenchuan, Lixian, Xiaojin County. The cultivated land increased by 277 km2, the forests and grasslands decreased significantly in this period due to the more intense human interference than in other areas. While after 2000, with the implementation of “Grain for Green Project” and “Returning Grazing to Pasture Project” [79], the cultivated land area takes on a descending trend, with308 km2 decreased in total. Except for the decrease from 1990 to 1995, the forest showed an increasing trend from 1990 to 2015 on the whole, about 3.57% area are added. According to the second classification of land use data, it is not difficult to find that the low coverage forest such as orchard, shrub canopy occupied the most amount of transferred-in forest before 2005, which was mainly transferred from grasslands, cultivated land, etc. Besides, the spatial change of forest is obvious and the change in the east region is much more frequent than the west region. The area change of grassland can also be divided into two stages based on the conversion directions in the past 25 years, Prior to 2000, the grassland area decreased, mainly transferred out to the bare land, cultivated land and forest due to the overgrazing and grasslands degradation, during which the livestock number increased 8.12% in studied area. After 2000, the conversions of grassland were mainly to wetlands and forests with the implementation of Wetland protection and desertification control from 2000. The wetland showed a slight upward trend, in which the marsh wetlands occupied the most increasing area, 32% wetland increased from 2000 to 2015. Meanwhile, the area of bare land showed a slight downward trend especially after 2000, 612 km2 bare land were transferred out. In addition, judging from spatial distribution, the land use type varied drastically especially in some typical ecotone such as the grassland-wetland ecological interface of the Zoige Plateau, subalpine forest-grassland ecological interface of the upper reaches of the Minjiang River, woodland -grassland ecological interface of Eastern Hengduan Mountains.
3.1.2. Climate Change
To reflect the climate change of the ETP region comprehensively and accurately, the daily observation data of 35 local meteorological stations was extracted and analyzed. The two primary climate changing factors, including precipitation and temperature data over the past 25 years, were selected and adopted for this study.
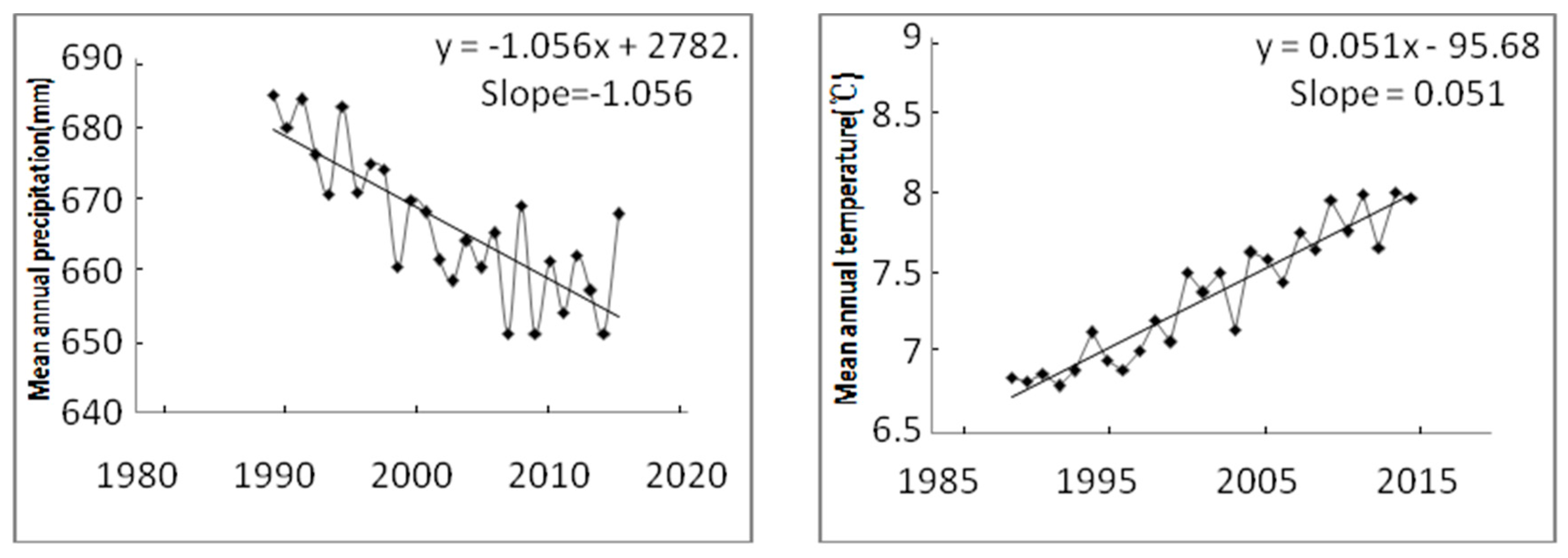
As shown in the Figure 3, the temporal and spatial variation of temperature in ETP region was obvious. In the past 25 years, the average annual temperature was 8.2 °C, the maximum temperature 15.5 °C and the lowest temperature −1.1 °C. During the past 25 years, the annual average temperature of the whole regions showed an upward trend and the inter-annual variation rate of temperature was 0.05.
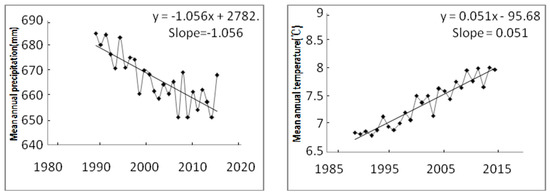
Figure 3.
Temporal variation in the mean precipitation and temperature in ETP region.
In the past 30 years, the annual maximum rainfall was 910 mm, the minimum value 340 mm, the average annual rainfall 650 mm. Regional precipitation showed a downward trend, of which, during1990 to 2000, a larger decline was observed (Figure 3), it was much higher than the average variance ratio of recent 25 years.
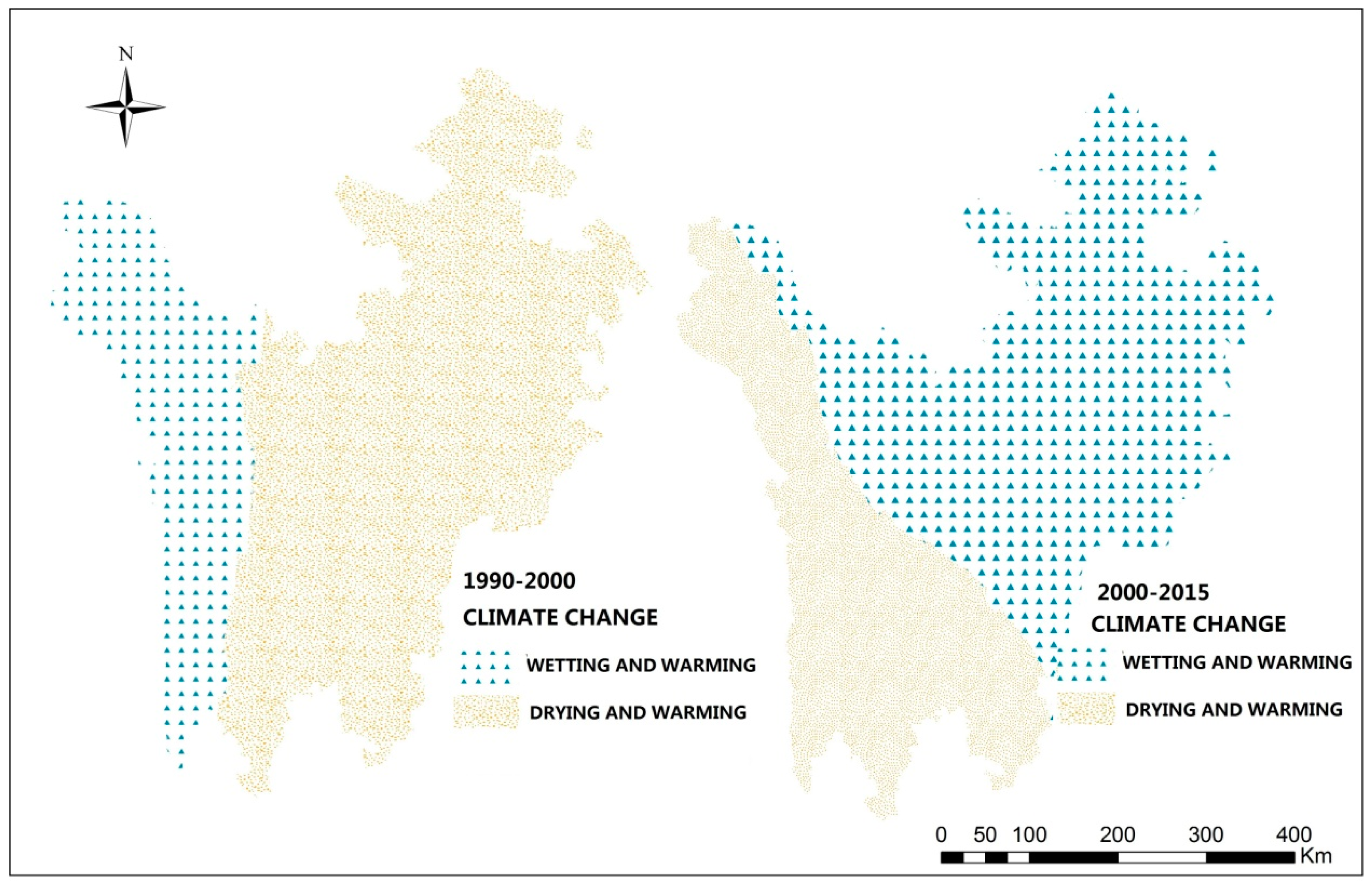
Viewed from spatial distribution, an obvious spatial heterogeneity was observed between 1990 to 2000 and 2000 to 2015 (Figure 4), especially in terms of precipitation, two different changing trends were observed. From 1990 to 2000, the wetting and warming area and drying and warming area accounts for 30% and 70% of the total, respectively, while from 2000 to 2015, the wetting and warming area increased by 30%. This may have an impact on the spatial distribution of ETP ES change, According to the study of Altay Prefecture [44], the climate change spatial heterogeneity was proved have a huge influence on Altay ES distribution, including soil conservation, water yield. Besides, it is noteworthy that in these two stages, land use change tendency is also apparent (Table 1).
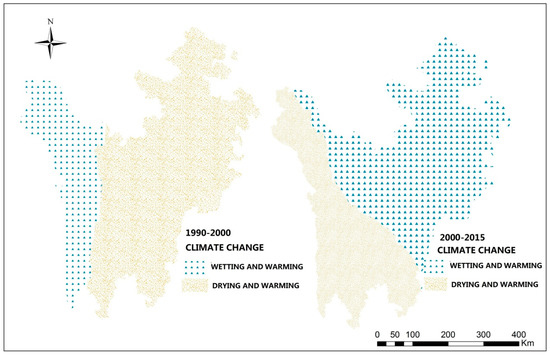
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of climate change relative quantity in the ETP region.
3.2. The Ecosystem Service Change in Different Scenarios
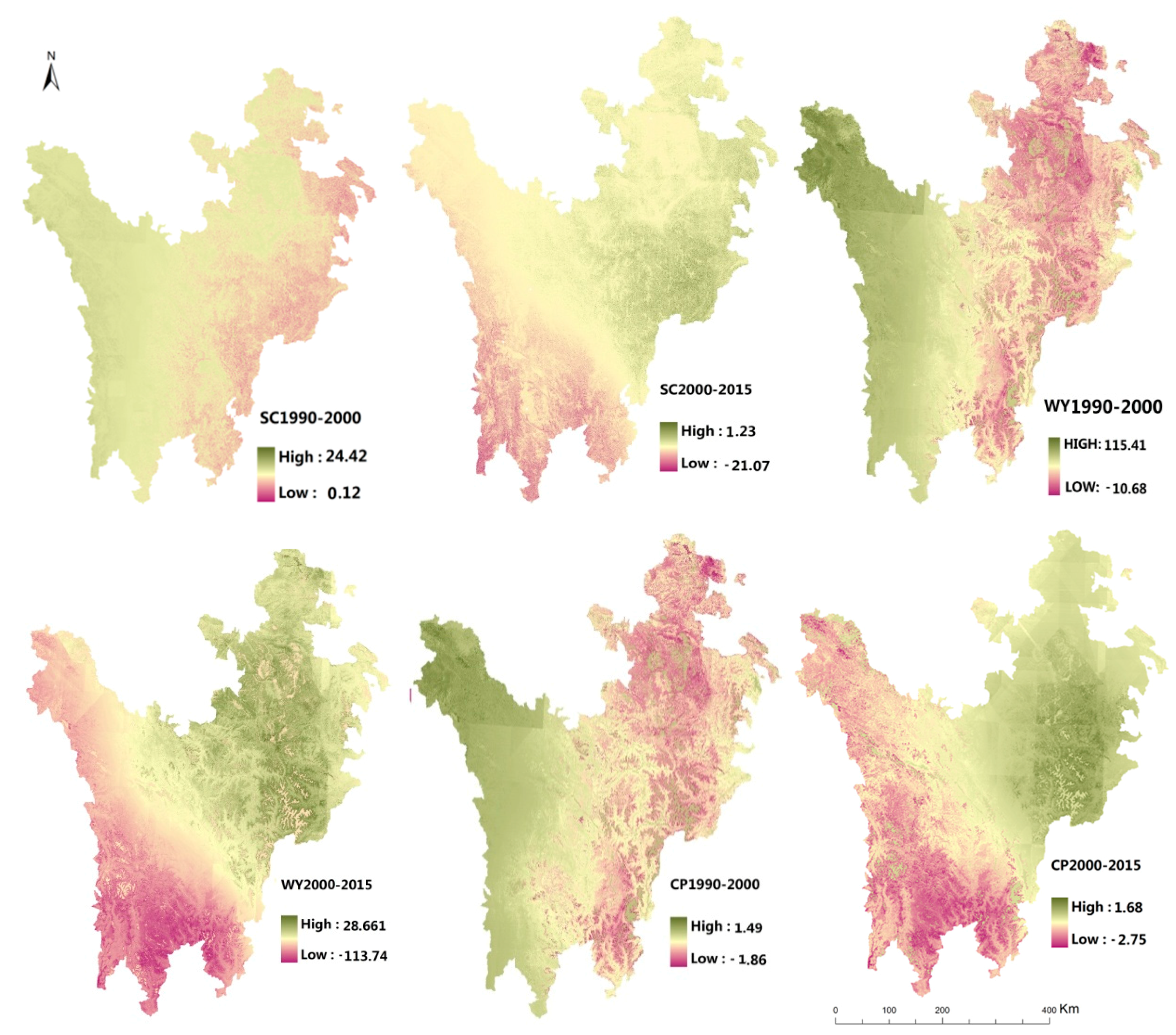
3.2.1. ScenarioI: Climate Change
Scenario I considered the impacts of climate change on ecosystem services only and ignored land use changes. In general, the selected ecosystem service showed a downward trend and was much lower than other two scenarios in quantity. Besides, the changing spatial distribution is similar with the climate change pattern in both three ES types studied (Table 2, Figure 5): (1) Soil Conservation: Soil conservation in the regional scale showed a decreasing trend, down by 0.38% per year. Soil conservation of forests, grasslands and bare land decreased by 4.3 × 106 t, 3.88 × 106 t, 0.52 × 106 t, respectively. While wetlands showed a rising trend, with 0.3 × 106 t increased. This tendency also can be observed from Figure 5, from 1990 to 2000, when the soil conservation of each ecosystem type except the wetland located in the eastern region decreased with the warming and drying climate change. The ES change tendency could also be observed in the next period. While as the main wetland distribution area, the soil conservation of Zoige plateau increased in both two periods in this scenario. (2) Water Yield: water yield in the ETP region dropped 8.59 × 109 m3 in the past 25 years, in which, the water yield of forest and grassland decreased by 3.08 × 109 m3, 5.24 × 109 m3, while the water yield of wetland had a slightly increasing, 0.34 × 109 m3 increased. In terms of spatial distributions, the ES changing pattern was similar to the climate change trend, especially precipitation change in the studied area, with the lower precipitation, the water yield of each ecosystem types reduced. While it is worth noting that the river valley located in the eastern region, mainly the Dadu River, has a stable water yield under the climate change background, this is largely due to the high altitude and it is a snow-fed river. Correspondingly, the much less negative impact of climate change can be observed on Dadu River than the Minjiang River in the eastern region, which is a precipitation recharge river. (3) Crop production: The crop production has few quantitative changes in the regional scale and the crop production of grassland, cultivated land, bare land showed a decreasing trend, with 0.67 × 106 t, 0.04 × 106 t, 0.14 × 106 t reduced for each type, while the forest had a different changing tendency, with 0.27 × 106 t increased. The spatial distribution pattern of crop production is similar to the soil conservation and water yield, varied with the climate change. In addition, the crop production of forest increased with the climate change in this scenario were observed, from 1990 to 2000, the eastern suffered from the warming and drying, the crop production of each ecosystem types decreased but the forest, mainly located in Jiuzhaigou County, Maoxian County, etc. while from 2000 to 2015, the forest in the western region, which suffered warming and drying climate change, increased in crop production—such as the forest in Shiqu County, Batang County.

Table 2.
ES composition of main ecosystem types under ScenarioI: Climate change (SC, WY, CP refer to soil conservation, water yield and crop production, respectively. the unit for WY is m3 and the unit for SC, CP is t/km2. These units are the same in Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 and Table 3 and Table 4).
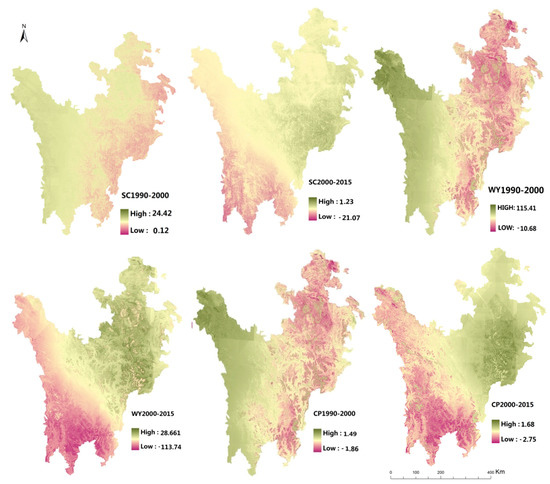
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution of the ES changes under ScenarioI: Climate change.
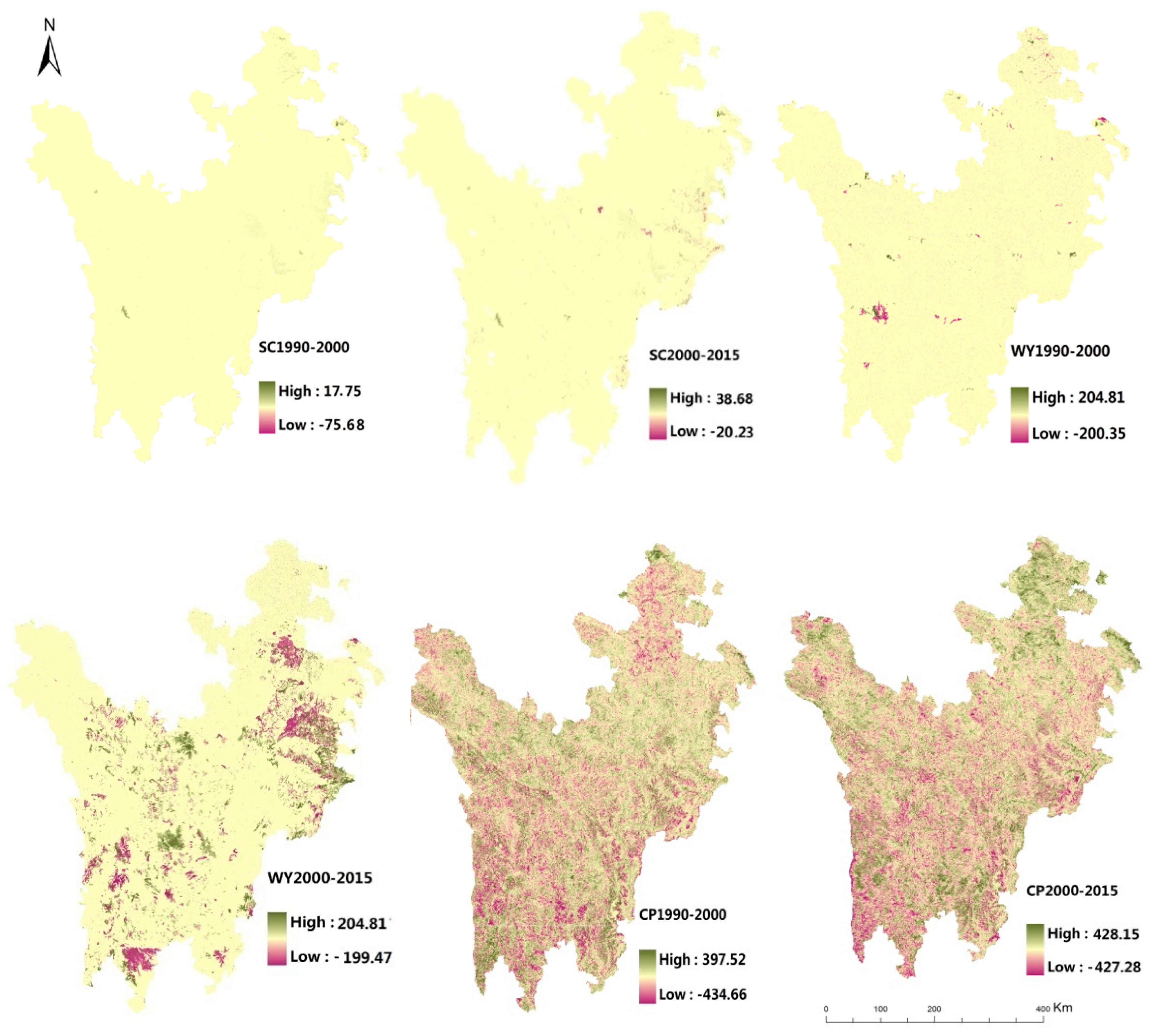
3.2.2. Land Use Change
ScenarioII (Table 3, Figure 6), the total amount of ES was much higher the other two scenarios. (1) Soil Conservation: compared with realistic change scenario (ScenarioIII), the relative contribution of cultivated land and bare land to the regional soil conversation decreased by 2% and 1%, respectively. From 1990 to 2015, soil conservation of forest increased by 3.02 × 106 t, which maintain an average annual amount of 66.59 × 106 t, close to the annual amount of grassland (74.49 × 106 t). From 1990 to 2015, the grassland area and soil conservation reduced by 2527 km2 and 0.25 × 106 t, respectively. Of which, about 1500 km2 of grassland were converted into wetland, soil conservation of wetland increased to 0.24 × 106 t, while the soil conservation of the forest increased 3.02 × 106 t and the transferred grassland was nearly 1000 km2. This indicated that the forest can fix more soil than other ecosystem types. Besides, the periodic characteristic is obvious in this scenario, from 1990 to 2000 and 2000 to 2015, the soil conservation of each ecosystem type showed a different changing trend. For example, soil conservation of cultivated land increased from 1990 to 2000, due to the area increase of farmlands in this period, while the cultivated land reduced from 1999, the soil conservation of cultivated land reduced with the area decrease. moreover, viewed from the spatial distribution, the spatial distribution is much more dispersed than the scenarioI, the soil conservation increase of forest in two periods is mainly located in the Baiyu County, Lixian County, Songpan County, etc., which were the main implementation area of “the natural forest protection project”. (2) Water yield: the regional water yield was between 129.58 × 109 m3 and 129.32 × 109 m3, 0.26 × 109 m3 reduced from 1990 to 2015, much lower than scenarioI. The average annual water yield of grassland was 74.50 × 109 m3, accounting for almost 50% of the total water yield in this region, mainly distributed in the Zoige Plateau and northwest area. In the past 25 years, the amount of water yield of grassland decreased but the annual variation was 0.01%, which was far lower than other two scenarios, the forest had a similar trend with grassland in water yield, the annual variation was 0.15%, far lower than other scenarios. But It is noteworthy that water yield of forest decreased continuously from 2000, dropped from 41.87 × 106 t to 41.34 × 106 t, opposite to the area growth of forest ecosystem. The spatial distribution of water yield is more concentrated and has a higher maximum patch index after 2000. Besides, the conversion of grassland to forest reduced the water yield was observed in this scenario, especially in the north and south Zoige Plateau and south Daocheng county, in which the forest area increased. (3) Crop Production: The average crop production of forest reached 16.96 × 106 t, much higher than other two scenarios, increased from 16.86 to 17.27 under ScenarioII. With the area growth, the crop production of wetland and cultivated land increased by 0.07 × 106 t, 0.22 × 106 t from 1990, respectively. The grassland dropped from 30.35 × 106 t to 30.03 × 106 t with the area reduced. From 1990 to 2015, the spatial heterogeneity of the crop production change is much higher than water yield and soil conservation and the crop production in scenarioI, the hotspots of the crop production change were mainly located in the northeast region, such as Xiahe County, Zoige County, which were the main implementation area of the Ecological protection project such as natural forest protection project and returning farmland to forest project, the periodical characteristics was obvious due to the different human activities from 1990 to 2015.

Table 3.
ES composition of main ecosystem types under ScenarioII: Land use change (SC, WY, CP refer to soil conservation, water yield and crop production, respectively).
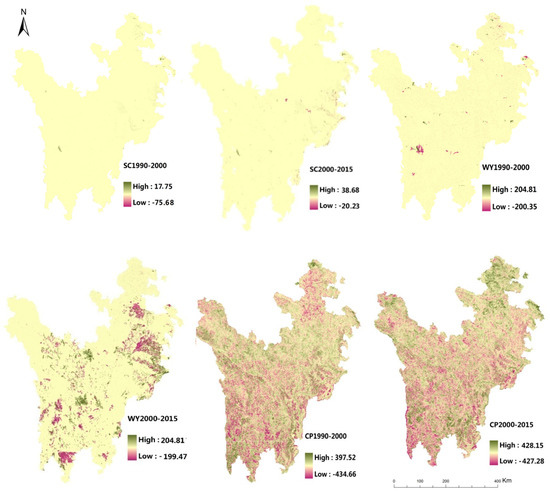
Figure 6.
Spatial distribution of the ES changes under ScenarioII: Land use change.
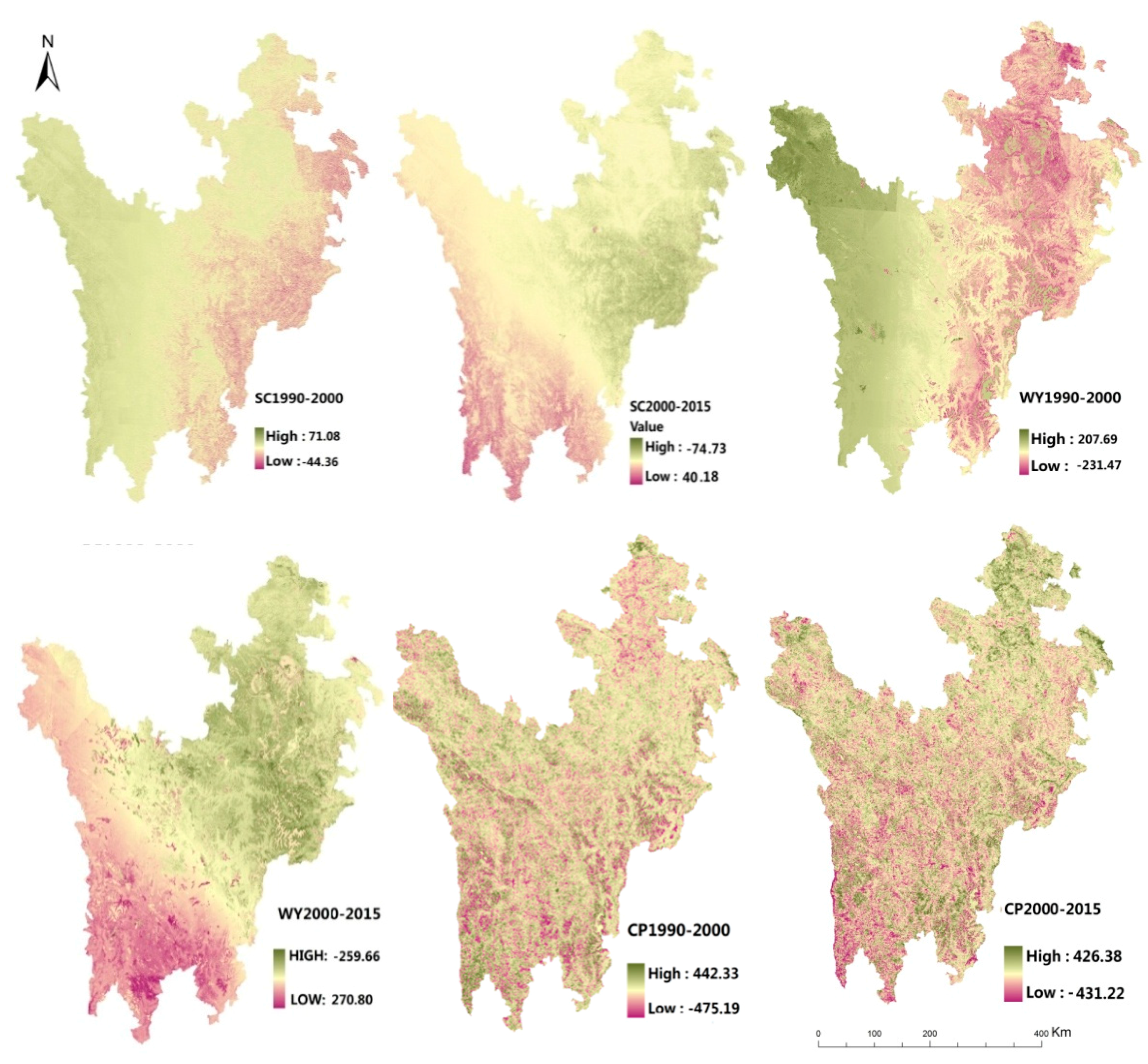
3.2.3. ScenarioIII: Land Use and Climate Change
ScenarioIII, with the change of land use and climate, the regional ecosystem service changed remarkably (Table 4, Figure 7). (1) Soil conservation: From 1990 to 2000, the total amount of soil conservation decreased by 5.76 × 106 t. While after 2000, the total amount of soil conservation began to show an upward trend, increased from 141.5 × 106 t to 143.27 × 106 t. Soil conservation of forest and grassland changed both in the amount and spatial distribution, from 1990 to 2000, the increase of soil conservation mainly occurred in the western region, similar with the climate change and the less human disturbance. While from 2000 to 2015, soil conservation of forest increased almost 2.52 × 106 t, mainly in the southeast mountain area which was the wetting and warming area and the main implementation area of “the natural forest protection project” in China. Soil conservation of grassland showed a decreased trend, 1.4 × 106 t reduced from 1990 to 2015, reduced areas were mainly concentrated in scattered grassland in the south region, which were mainly transferred to cultivated land and wetland. Besides, the soil conservation of wetland showed a similar tendency with the scenarioI. The central region had a stable change due to the transition zone of climate change in this region. (2) Water Yield: During the period of 1990–2015, the total amount of water yield showed a downward trend, which has been reduced 7.06%, especially from 1990 and 2000, the water yield dropped from 129.46 × 109 m3 to 119.19 × 109 m3. While after 2000, the water yield had a slow-growth trend. Contrary to the area growth, water yield of forest and cultivated land ecosystem decreased 3.03 × 109 m3, 0.04 × 109 m3, respectively. While as the main transposition object of grassland, the water yield of wetland increased continuously from 2000 to 2015, 0.4 × 109 m3 increased and the swamp wetlands located in Zoige Plateau and Seda Grassland contributed the most due to the human interference and climate change in this area. (3) Crop production, the crop production showed different trend before and after 2000, the forest and grassland were the two main sources of the crop production, accounting for 33.83% and 58.98% respectively, however, the forest area was just 1/2 of the grassland. In terms of spatial distribution, the crop production changing distribution was similar with the spatial change of scenarioII, changed mainly due to the land use change.

Table 4.
ES composition of main ecosystem types under ScenarioIII: Land use and climate change (SC, WY, CP refer to soil conservation, water yield and crop production, respectively).
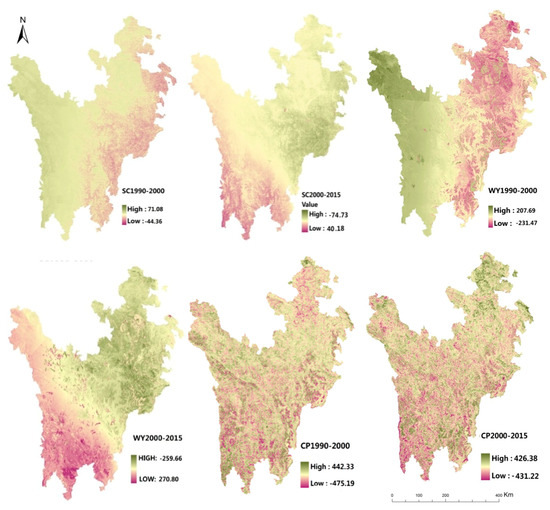
Figure 7.
Spatial distribution of the ES changes under ScenarioIII: Land use and climate change.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effect of Land Use and Climate Change on Regional ES
In recent years, land use change and climate change have had a significant impact on ecosystem services in the studied area. From 1990 to 2015, the basic tendency of land use in the studied area was as follows (Table 1): cultivated land, forest, wetland and built-up land increased and the grassland, bare land decreased. The periodical characteristics of land use change were obvious in the studied area, from 1990 to 2000, with the increase of human disturbance to the natural ecosystem, over-cutting, reclamation and overgrazing have resulted in the increase of cultivated land and bare land and the reduction of grassland and wetland directly or indirectly. After 2000, especially after 2005, with the implementation of various environmental protection policies, such as “Grain for Green project”, “Desertification Control Project”, “Natural Forest Protection Project”. The growth of built-up land, bare land and cultivated land slowed down, the wetland and forest increased. Viewed from the spatial transfer of land type, during this period, cultivated land and bare land continued to be transferred to grassland, while the grassland was mainly converted to forests and wetland so that the forests and wetland ecosystems expanded rapidly at this stage.
With the transfer of land use, ecosystem services of each ecosystem type changed accordingly.
- (1)
- Soil conservation: under the different land use transfer directions, the soil conversation shows different quantity and structure response characteristics correspondingly. It is worth pointing out that from 2000 to 2015, with the conversion of bare land and cultivated land to forest, grassland, the sediment output decreased and the soil conservation increased on the whole with the area increase of the forest. While the forest is only 1/2 of the grassland area but it contributes 46% of the soil conservation capacity, the area increase of the forest also promotes the overall increase of the regional soil conservation.
- (2)
- Water yield: seen from ES composition from 1990 to 2015, the forest ecosystems transferred out more water yield than transferred-in, which was mainly transferred to built-up land and bare land due to the forest loss during 1990–2000. While after 2000, water yield of forest decreased although the area increased 1392 km2, especially in scenarioII. This is largely because of the higher evapotranspiration coefficient of the forest than other ecosystem types. This conclusion is similar with the research conducted by Li in Miyun, who pointed out that the expansion of forest land will significantly reduce the water yield of the basin [80]. The water yield of grassland decreased slightly with the land use change and climate change in three scenarios but it is still the biggest water yield pool in the studied area and the conservation of grassland to wetland increased the water yield of wetland rapidly from 2000–2015, especially the Zoige wetland. Therefore, as an important water conservation area in the source of the Yangtze River and the Yellow River, grassland and wetland are important ecological land, which is of great value for water conservation.
- (3)
- Crop production: the impact of land use change to the crop production is obvious, according to Figure 3, the crop production varied dramatically. With the increase of grassland coverage, low coverage grassland gradually changed to middle and high coverage grassland from 2000 to 2015, the grassland in Shiqu, Dege County located in the northwest not only have an improvement in water yield but also the crop production obviously. Besides, the crop production of forest in the south and east of the region, such as Xiahe County, Zoige County promoted significantly due to the less disturbance after 2000, in where the giant panda protection project and natural forest protection project were widely implemented.
Climate change has had a dramatic impact on ES spatial distribution and its composition structure, especially the water yield and soil conservation. In general, the climate change in the studied area is warming and drying, the periodical changing characteristics exist in this region, ES spatial distribution varied with the climate change. From 1990 to 2000, the area of wetting and warming and drying and warming area accounts for 30% and 70% of the total, respectively. The spatial distribution of water yield and soil conservation also showed a similar changing tendency, with about 35% area increasing in water yield and soil conservation, 65% reducing [44]. Besides, in terms of the composition structure, the response of forest ecosystems to climate change is more intense than that of grassland ecosystems and wetland in water yield and soil conservation, this is largely due to the forest has higher evapotranspiration coefficient than other ecosystem types. While the water yield and soil conservation of wetland appear an upward trend significantly under the climate changing scenario. Besides, our research noticed that the crop production of forest increased under the climate changing situation, this is similar with the observation in the forest under the climate change by Wu and Balthazar [81,82], which reveal that the climate change will make a contribution to an increase in the forest crop production.
By means of scenario simulation, trade-offs between ecosystems in ecosystem services were also found in our study, for example, the conversion of grassland to forest, the soil conservation and water yield increased, the transferred grassland possess higher biological yield and stronger soil fixation but its water yield reduced. The crop production would decrease while the water yield and soil conservation increased when the cultivated land is transformed into grassland and wetland. Meanwhile, the trade-offs of ecosystem services under climate change conditions are also observed, for example, the soil conservation and water yield are reduced, while crop production is increased under ScenarioI. This demonstrates that we must have a definite management goal when managing ecosystems and taking ecosystem services trade-offs into decision-making [83].
4.2. Strategies to Sustainable Use the Regional ES
The impact of land use and climate change on ecosystem services in the ETP region were studied through three scenarios. The influence is not only reflected in the total amount but also in the highly frequent conversion of ecosystem services between different ecosystems. There are two different changing progresses from 1990 to 2015. In the first 10 years, the transformation of land use mainly occurred in the increase of cultivated land, built-up land and bare land, the crop production and water yield has reduced in this period, Meanwhile, natural disasters such as landslides, debris flow, soil erosion occurred frequently and decertified land has been spreading rapidly. Land use conversion in the next 15 years was opposite to the first stage, with the implementation of Ecological Protection Project, the total amount of water yield, crop production and soil conservation increased in total amount but water yield of forest reduced despite the growth of area.
The land use and climate change have had a significant influence on the regional ES, the trade-off and the responses of each ecosystem types of ETP region were observed and analyzed firstly, this provided a new view to the sustainable use the regional ES. It is also of great significance for the comprehensive management of ecosystems to adopt reasonable management measures and optimize the structure of ecosystem services. Bennett [83] argues that the common driving forces are the key to effectively promoting the coordinated development of multiple service functions. In terms of this study, land use and climate change are the common driving force. Therefore, strategies for the optimization of regional ecosystem service should be designed from a comprehensive perspective. (1) Controlling the land desertification. Desertification is a typical degradation phenomenon, which not only endangers grassland and wetland but also brings loss to bio-diversity and residents’ production and living. The ETP region is a typical fragile ecosystem, the risk of low coverage and highly grazing grassland transferring to desertification land is high, especially under the background of climate change. Therefore, we recommend the local government continue to take measures such as reducing the destruction of natural grassland and popularizing artificial grassland on low coverage grassland and livestock grazing controlling to control the land desertification. (2) Protecting the forest and reducing soil erosion. The natural disasters, such as debris flow and landslide frequently occurred in the ETP region, the soil erosion is serious. While our study show that forest not only provided a high crop production but also 46% of the soil conservation capacity in ETP region and a high conservation efficiency than other ecosystem types. For that reason, protecting the existing forest, developing scientific afforestation and improving the forest quantify is very important for reducing the damages caused by soil erosion and improving the crop production of this region. (3) Regulating and controlling the spatial distribution of forest, grassland and wetland scientifically. The trade-off of each ecosystem and ecosystem service function are observed in this study, the increase of forest area will lead to the increase of CP and SC but the negative effect of water yield reduction is also obvious, particularly faced with global warming and drying, water resources contradiction will be further intensified in the forest area. Therefore, we recommend that the local government attach importance to the ES trade-off relationship, rationally plan the spatial layout of the ecological protection project and optimize the planting strategy, especially in the ecologically sensitive area and the important watersheds. (4) Protecting the grassland and wetland, grassland and wetland are not only important pastoral areas for local people but significant water conservation areas of the main rivers in China. Our study show that the grassland and wetland are the main ecosystem to conserve water in ETP region and the water yield of grassland reduced with the area reduction and climate change. Therefore, we recommend the government to reduce grazing intensity, control the number of livestock grazing and optimize the stock breeding structure to minimize the damages to the grassland, simultaneously establish protecting zone and strictly control land uses to protect the wetland.
In general, there are still some uncertainties and limitations in this study. (1) Ecosystem services involved in this study only contain three main types, which cannot reflect the impact of land use and climate change on regional ecosystem services entirely. (2) The spatial heterogeneity could not be well clarified due to the data acquisition, such as the climate data, which is derived from the spatial interpolation of site data, losing the spatial distribution details of a smaller scale. (3) Uncertainties of model applications. Although we collected as much research as possible and selected the appropriate biophysical parameters about this region, the difference with the truly ecosystem service is inevitable [3,44]. In the meantime, details of the ecosystem services in different spatial structures are usually ignored by use of InVest and CASA, such as the surface and underground water yield are not separated in InVest. In addition, it is worth mentioning that due to the different evaluation bases in this study. The ES spatial changes showed in Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 reflect the change of relative quantity, the ES absolute quantity (Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4) should be taken into account in the ES spatial change combined with the relative quantity.
5. Conclusions
In the past 25 years, the ecosystem services have been greatly influenced by climate and land use changes. Through different scenarios set, this study quantifies the inter-annual variability of ecosystem services and the corresponding response characteristics of each ecosystem types. In general, the periodic characteristics of ecosystem services were obvious and the ecosystem service assessed in this study showed a different tendency before and after 2000. Different land use patterns and transfer directions will not only affect the total amount of ecosystem services but also the distribution and functions transfer. The results show that (1): the total quantity of ES reduced in all the three scenarios, the annual ES change was scenarioII < scenarioIII < scenarioI and the periodical characteristics are present in this region; (2) the ES change spatial distribution varied with different climate change patterns and land use transfer directions; (3) the ES composition of each ecosystem varied with different driving scenarios and different responses of forest and wetland on climate change and land use changes were observed. Moreover, the trade-off under land use change and climate change respectively was observed in this study.
Via scenarios set in this study, the quantitative changes of ecosystem services and internal responses of the regional ecosystem to global changes are explored in this study. Based on the results, we recommend that the local government take the trade-off and climate change into account when making decisions, continue with desertification control and improve the quality of grassland as well as forests. These efforts should enable us to achieve sustainable development of human beings and the natural ecosystem.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0501803), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31570517, 31500346, 31350110328), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KFJ-SW-STS-177, KFJ-STS-ZDTP-022-4), Western Light Program, Sichuan Science & Technology Bureau (2015HH0025, 2016HH0082, 2017SZ0080, 2017HH0084) and Chengdu Institute of Biology Youth Professor Program.
Author Contributions
Zhonglin Tang and Geng Sun conceived and designed the experiments; Zhonglin Tang performed the experiments; Zhonglin Tang and Geng Sun analyzed the data; Nannan Zhang, Jing He and Ning Wu contributed materials/analysis tools; Zhonglin Tang wrote the paper, Geng Sun, Nannan Zhang, Jing He and Ning Wu reviewed drafts of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- MEA. Ecosystems and Human well-being: Biodiversity synthesis. World Resour. Inst. 2005, 42, 77–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.Y.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Dietz, T.; Kramer, D.B.; Ouyang, Z.; Liu, J. An integrated approach to understanding the linkages between ecosystem services and human well-being. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2016, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, R.S.D.; Alkemade, R.; Braat, L.; Hein, L.; Willemen, L. Challenges in integrating the concept of ecosystem services and values in landscape planning, management and decision making. Ecol. Complex. 2010, 7, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröter, M.; Zanden, E.H.; Oudenhoven, A.P.E.; Remme, R.P.; Serna-Chavez, H.M.; Groot, R.S.; Opdam, P. Ecosystem Services as a Contested Concept: A Synthesis of Critique and Counter-Arguments. Conserv. Lett. 2015, 7, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, G.C.; Polasky, S.; Goldstein, J.; Kareiva, P.M.; Mooney, H.A.; Pejchar, L.; Ricketts, T.H.; Salzman, J.; Shallenberger, R. Ecosystem Services in Decision Making: Time to Deliver. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargo, S.L.; Wieland, H.; Akaka, M.A. Innovation through institutionalization: A service ecosystems perspective. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2015, 44, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvigy, D.; Wofsy, S.C.; Munger, J.W.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Moorcroft, P.R. Mechanistic scaling of ecosystem function and dynamics in space and time: Ecosystem Demography model version 2. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2015, 114, 270–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, L.; Koppen, C.S.A.V.; Ierland, E.C.V.; Leidekker, J. Temporal scales, ecosystem dynamics, stakeholders and the valuation of ecosystems services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 21, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPOC. Climate Change 2014 Synthesis Report. Environ. Policy Collect. 2014, 27, 408. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, B.; Turner, R.K.; Morling, P. Defining and classifying ecosystem services for decision making. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, M.; Cruz, R.D.; Davidson, N.; Alder, J.; Cork, S.; Groot, R.S.; Lévêque, C.; Milton, G.R.; Peterson, G. Millennium Ecosystem Assessment: Ecosystems and human well-being: Wetlands and water synthesis. Data Fusion Concepts Ideas 2005, 656, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Chazdon, R.L. Beyond deforestation: Restoring forests and ecosystem services on degraded lands. Science 2008, 320, 1458–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Mumby, P.J.; Hooten, A.J.; Steneck, R.S.; Greenfield, P.; Gomez, E.; Harvell, C.D.; Sale, P.F.; Edwards, A.J.; Caldeira, K. Coral Reefs under Rapid Climate Change and Ocean Acidification. Science 2007, 318, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómezbaggethun, E.; Groot, R.D.; Lomas, P.L.; Montes, C.; Pascual, U.; Corbera, E.; Muradian, R.; Kosoy, N. The history of ecosystem services in economic theory and practice: From early notions to markets and payment schemes. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Mooney, H.A.; Agard, J.; Capistrano, D.; Defries, R.S.; Díaz, S.; Dietz, T.; Duraiappah, A.K.; Otengyeboah, A.; Pereira, H.M. Science for managing ecosystem services: Beyond the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Wang, J. Evaluation on effect of land consolidation on habitat quality based on InVEST model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 250–255. [Google Scholar]
- Kueppers, L.M.; Snyder, M.A. Influence of irrigated agriculture on diurnal surface energy and water fluxes, surface climate, and atmospheric circulation in California. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 38, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünewald, C.; Schleuning, M.; Böhning-Gaese, K. Biodiversity, scenery and infrastructure: Factors driving wildlife tourism in an African savannah national park. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 201, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Fu, B.; Ding, J.; Wang, S. Ecosystem service trade-offs and their influencing factors: A case study in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 1250–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Deng, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z. Impacts of land-use change on valued ecosystem service in rapidly urbanized North China Plain. Ecol. Model. 2015, 318, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, I.; Martín-López, B.; Alcorlo, P.; Montes, C. Limitations of Protected Areas Zoning in Mediterranean Cultural Landscapes Under the Ecosystem Services Approach. Ecosystems 2014, 17, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdowell, N.G.; Bowling, D.R.; Bond, B.J.; Irvine, J.; Law, B.E.; Anthoni, P.M.; Ehleringer, J.R. Response of the carbon isotopic content of ecosystem, leaf, and soil respiration to meteorological driving factors in a Pinus ponderosa ecosystem. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18, GB1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; He, L.Y. Major Research Progresses on the Ecosystem Service and Ecological Safety of Main Terrestrial Ecosystems in China. Chin. J. Nat. 2012, 34, 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.H.; Fu, B.J.; He, C.S.; Lü, Y.H. Variation of ecosystem services and human activities. Acta Oecol. 2012, 44, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurance, W.F.; Fearnside, P.M.; Vasconcelos, H.L.; Ferreira, L.V. Deforestation in Amazonia. Science 2004, 304, 1109–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurance, W.F.; Nascimento, H.E.M.; Laurance, S.G.; Andrade, A.C.; Fearnside, P.M.; Ribeiro, J.E.L.; Capretz, R.L. Rain Forest Fragmentation and The Proliferation of Successional Trees. Ecology 2006, 87, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fish, R.; Turner, R.K.; Fish, R.; Turner, R.K. Routledge Handbook of Ecosystem Services; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.; Xiao, R.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Characterizing landscape pattern and ecosystem service value changes for urbanization impacts at an eco-regional scale. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braat, L.C.; Brink; Klok, T.C. The Cost of Policy Inaction. The Case of Not Meeting the 2010 Biodiversity Target. Available online: http://www.globio.info/downloads/85/Report%20-%20Braat%20&%20ten%20Brink%20eds%20%282008%29%20The%20Cost%20of%20Policy%20Ina.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Nelson, E.J.; Kareiva, P.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Arkema, K.; Geller, G.; Girvetz, E.; Goodrich, D.; Matzek, V.; Pinsky, M.; Reid, W. Climate change’s impact on key ecosystem services and the human well-being they support in the US. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.R.; Pendleton, L.; Cameron, D.R.; Morris, B.; Bachelet, D.; Klausmeyer, K.; Mackenzie, J.; Conklin, D.R.; Bratman, G.N.; Lenihan, J. The impact of climate change on California’s ecosystem services. Clim. Chang. 2012, 110, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarque, P.; Lavorel, S.; Mouchet, M.; Quétier, F. Plant trait-based models identify direct and indirect effects of climate change on bundles of grassland ecosystem services. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13751–13756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangash, R.F.; Passuello, A.; Sanchez-Canales, M.; Terrado, M.; Lopez, A.; Elorza, F.J.; Ziv, G.; Acuna, V.; Schuhmacher, M. Ecosystem services in Mediterranean river basin: Climate change impact on water provisioning and erosion control. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, Y.Q.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y. Responses of the water-yield ecosystem service to climate and land use change in Sancha River Basin, China. Phys. Chem. Earth 2017, 101, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, M.E.; Brown, P.M.; MacDonald, L.H.; Carrico, C.M. Climate change impacts on fire regimes and key ecosystem services in Rocky Mountain forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 327, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirpke, U.; Kohler, M.; Leitinger, G.; Fontana, V.; Tasser, E.; Tappeiner, U. Future impacts of changing land-use and climate on ecosystem services of mountain grassland and their resilience. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, R.; Spies, T.A.; Peterson, D.L.; Stephens, S.L.; Hicke, J.A. Searching for resilience: Addressing the impacts of changing disturbance regimes on forest ecosystem services. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 53, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröter, D.; Cramer, W.; Leemans, R.; Prentice, I.C.; Araújo, M.B.; Arnell, N.W.; Bondeau, A.; Bugmann, H.; Carter, T.R.; Gracia, C.A. Ecosystem Service Supply and Vulnerability to Global Change in Europe. Science 2005, 310, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y. Examining the potential impact of land use/cover changes on the ecosystem services of Baguio city, the Philippines: A scenario-based analysis. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 35, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Chi, D.; Xu, K. The influence of climate change and human activities on ecosystem service value. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 87, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendozagonzález, G.; Martínez, M.L.; Lithgow, D.; Pérezmaqueo, O.; Simonin, P. Land use change and its effects on the value of ecosystem services along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 82, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño, L.; Frank, F.C.; Viglizzo, E.F. Tradeoffs between economic and ecosystem services in Argentina during 50 years of land-use change. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 154, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Li, B.; Hou, Y.; Bi, X.; Zhang, X. Effects of land use and climate change on ecosystem services in Central Asia's arid regions: A case study in Altay Prefecture, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, P.C.; Anderson, S.J.; Costanza, R.; Kubiszewski, I. The ecological economics of land degradation: Impacts on ecosystem service values. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 129, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Whitehead, P.; Wolf, J.; Rahman, M.; Salehin, M. The Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna delta system: Biophysical models to support analysis of ecosystem services and poverty alleviation. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2015, 17, 1016–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagstad, K.J.; Reed, J.M.; Semmens, D.J.; Sherrouse, B.C.; Troy, A. Linking biophysical models and public preferences for ecosystem service assessments: A case study for the Southern Rocky Mountains. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2016, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavorel, S.; Bayer, A.; Bondeau, A.; Lautenbach, S.; Ruiz-Frau, A.; Schulp, N.; Seppelt, R.; Verburg, P.; Teeffelen, A.V.; Vannier, C. Pathways to bridge the biophysical realism gap in ecosystem services mapping approaches. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 74, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Yin, L.C.; Zhang, Y. Discussion on Some Issues of Ecological Barrier. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 25, 2035–2040. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.R.; Wang, J.X.; Chen, L.W. Ecology and restoration of sub-alpine ecosystem in western Sichuan, China. Inf. Bot. Ital. 2003, 35, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, L.J.; Zhao, L.; Tang, X.J.; Fu-Hua, L.I.; Wang, S.Y. Evaluation of Economic Losses from Damage of Grassland Ecosystem in Sichuan Province. Sichuan Environ. 2012, 6, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.X.; Hong, C.S.; Quan, C.Y.; Sheng, G.W.; Yue Cun, M.A.; Li, M.A. Evaluation of the multi-cropping ecosystem services under conservation tillage paddy field in Sichuan basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 3782–3788. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, G.W.; Shi, C.C.; Qiu, P.F. Remote sensing monitoring of sand expansion at fragile grassland ecosystem in Ruoergai Plateau, Sichuan, China. Southwest China J. Agric. 1998, 2, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.F.; Ming, X.U. Estimating the Values of Forest Ecosystems in Conserving Rare and Endangered Animals in Sichuan Province. J. Nat. Resour. 2016, 31, 789–799. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.; Liang, X.Y.; Yi, J. Review on Protection of Zoigê Grassland Ecosystem. China Herbiv. Sci. 2012, 6, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.S.; Ran, B.; He, G. Study on the causes and Countermeasures of ecological problems in the high mountain areas of Northwest Sichuan. Tour. Overv. 2014, 24, 220–224. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, W.Z.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Choices of Environmental Strategy and Policy on the Fragile Ecological Areas of Northwest Sichuan Province. Soft Sci. 2012, 26, 45. [Google Scholar]
- MEPC. China’s National Ecological Fragile Zone Protection Plan; Ministry of Environment Protection of the People’s Republic of China (MEPC): Beijing, China, 2008; Volume 92.
- Liu, J.H.; Gao, J.X.; Ma, S.; Wang, W.J.; Zou, C.X. Evaluation of Ecological Sensitivity in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Su, C.J.; Peng, L.; Wang, H.E.; Wang, H.M.; Liu, W.; Li, P.; Fang, Y. Ecological suitability assessment and introduction experiment on Rosa damascena trigintipetala in Sichuan Province, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2014, 11, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Zhao, K.; Yuan, X.; Sun, R. Evaluation of Ecological Sensitivity in Mountain Area Based on Spatial Analysis—A Case Study of Wanyuan City in Sichuan Province. J. Mt. Sci. 2008, 5, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Study on Evaluation of Rural Ecological Environment and Its Influencing Factors in Sichuan Province. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.C.; Liu, S.H. Characteristics of Geologic Hazards and Causes Analysis of Ebian Yi Autonomous County of Sichuan Province. Jilin Water Resour. 2015, 1, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, T.B. The features and mechanism of geologic hazards and control measures in DongXing district of NeiJiang, Sichuan Province. J. Geol. Hazards Environ. Preserv. 2007, 1, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.P.; Zheng, W.M.; Li, M.H.; Deng, G.S.; Yang, G.H. Geologic hazards on the western Sichuan plateau and their controls. Sediment. Geol. Tethyan Geol. 2005, 25, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Potter, C.S.; Randerson, J.T.; Field, C.B. Terrestrial ecosystem production: A process modelbased on global satellite and surface data. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1993, 7, 811–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Demissew, S.; Joly, C.; Lonsdale, W.; Ash, N. The IPBES Conceptual Framework-232 connecting nature and people. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2015, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaman, R.; Lyver, P.; Mpande, R.; Perez, E.; Cariño, J.; Takeuchi, K. The contribution of indigenous and local knowledge systems to IPBES: Building synergies with Science. Eur. Psychiatry 2013, 13, 246s. [Google Scholar]
- Covich, A.P. On Frank Golley’s International and Interdisciplinary Insights for a Twenty-First Century Earth Stewardship Based on Environmental Ethics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 431–450. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.J.; Yu, D.D. Trade-off analyses and synthetic integrated method of multiple ecosystem services. Resour. Sci. 2016, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, Z.F.; Bai, W.Q. Changes of Wetland Ecosystem Service Value in the LhasaRiver Basin of Tibetan Plateau. Resour. Sci. 2010, 32, 2038–2044. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, G. Land use/land cover change induced impacts on water supply service in the upper reach of Heihe River Basin. Sustainability 2014, 7, 366–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.K.; Fu, B.; Xu, P. Evaluation the impact of earthquake on ecosystem services. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H. Ecosystem Services Evaluation Based on the InVEST Model: Case Studies in Baoxing County, Sichuan and Mentougou District; Beijing Forestry University: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.F. Dynamics Evaluation of Ecosystem Services Based on InVEST Model in Baoxing County, Sichuan Province, China; Hunan University of Science and Technology: Hunan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, W.; Sheng, Y.; Fang, B. Land use change information mining in highly urbanized area based on transfer matrix: A case study of Suzhou, Jiangsu Province. Geogr. Res. 2013, 32, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, N.; Tiyip, T.; Nurmemet, I.; Gao, Y. Remote Sensing Monitoring for Assessing Vegetation Coverage in East Juggar Desert of Xinjiang. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 4, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Jia, H. Simulating the spatial dynamics of urban growth with an integrated modeling approach: A case study of Foshan, China. Ecol. Model. 2016, 353, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J. Utilization of Returning Farmland to Forest in Resettlement of Shuangjiangkou Hydropower Station Project in Aba Prefecture. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2012, 19, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Aijm, V.D.; Keenan, R.J. Planted forests and water in perspective. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 251, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Balthazar, V.; Vanacker, V.; Molina, A.; Lambin, E.F. Impacts of forest cover change on ecosystem services in high Andean mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Dai, E.F.; Ge, Q.S.; Min, X.W.; Wang, X.F. Modelling the integrated effects of land use and climate change scenarios on forest aboveground biomass:A case study in Taihe County of China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, E.M.; Peterson, G.D.; Gordon, L.J. Understanding relationships among multiple ecosystem services. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).