Modern Wheat Varieties as a Driver of the Degradation of Spanish Rainfed Mediterranean Agroecosystems throughout the 20th Century
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Trials: Site Description and Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling Method
2.4. Modelling of NPP and Biomass Fluxes According to Their Destiny
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Fields Results
3.1.1. Net Primary Productivity (NPP) and Its Components of Both OV and MV under Organic Managements
3.1.2. Biomass Allocation and Partitioning Indices
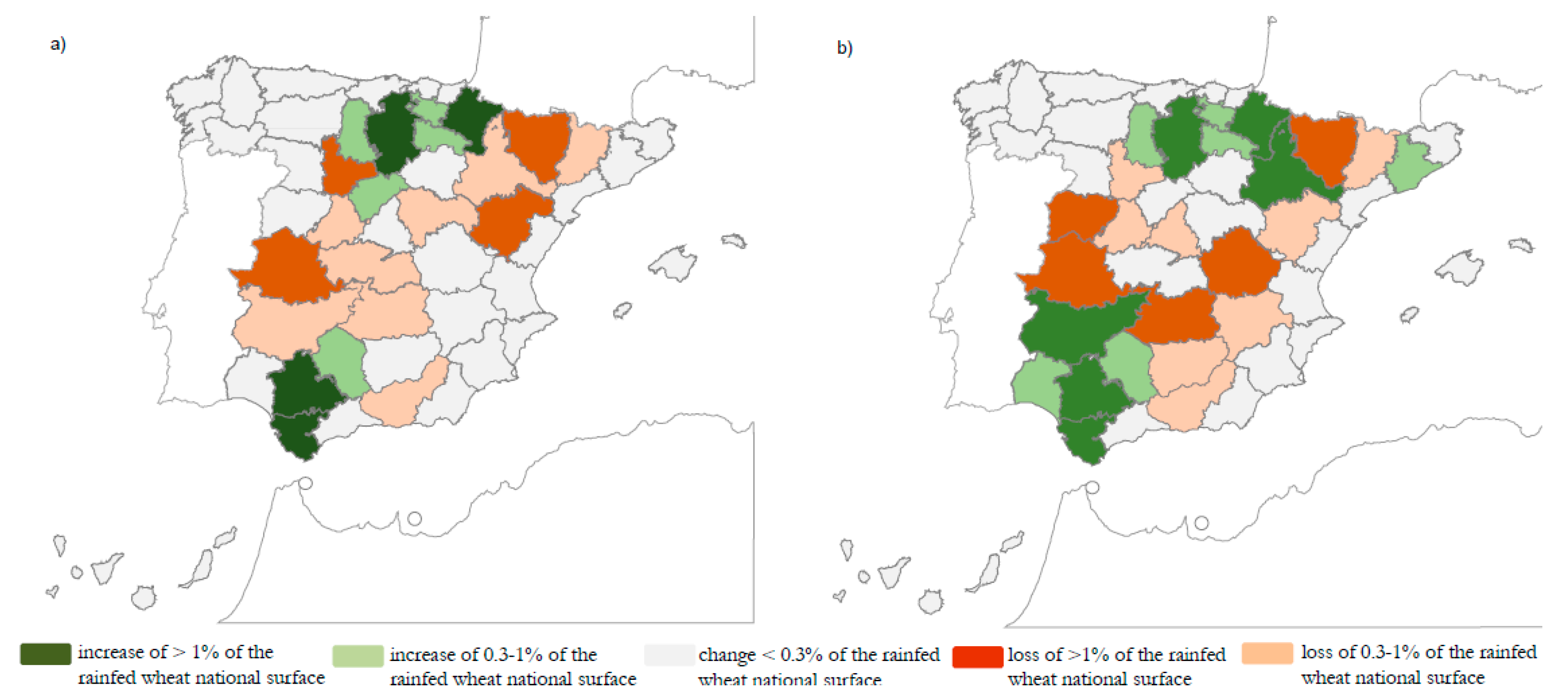
3.2. Total Wheat Production and Cultivated Area for Spanish Wheat Fields in the 20th Century
3.3. Modelling of NPP and Biomass Destinies for Spanish Wheat Fields in the 20th Century
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Old and Modern Varieties Under Two Traditional Organic Managements
4.2. Evolution of NPP of Wheat Fields in Spain throughout the 20th Century
4.3. Impact on the Fund Elements and Environmental Services of Spanish Wheat Fields
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borlaug, N.; Dowsell, C. The green revolution: An unfinished agenda. In Proceedings of the Lecture to Food and Agriculture Organization, Committee on World Food Security, 30th Session, Rome, Italy, 20–23 September 2004; Available online: www.fao.org/docrep/meeting/008/J3205e/j3205e00.html (accessed on 24 August 2018).
- Kloppenburg, J.R. First the Seed: The Political Economy of Plant Biotechnology; University of Wisconsin Press: Madison, WI, USA, 2005; p. 468. ISBN 029919244X. [Google Scholar]
- Pingali, P.; Raney, T. From the green revolution to the gene revolution: How will the poor fare? Mansholt Publ. Ser. 2005, 4, 407. [Google Scholar]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization). FAOSTAT, 2018. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/es/#home (accessed on 29 June 2018).
- Austin, R.B.; Bingham, J.; Blackwell, R.D.; Evans, L.T.; Ford, M.A.; Morgan, C.L.; Taylor, M. Genetic improvements in winter-wheat yields since 1900 and associated physiological-changes. J. Agric. Sci. 1980, 94, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, P.; Nicosia, O.L.D.; Nigro, F.; Platani, C.; Riefolo, C.; Di Fonzo, N.; Cattivelli, L. Breeding progress in morpho-physiological, agronomical and qualitative traits of durum wheat cultivars released in Italy during the 20th century. Eur. J. Agron. 2007, 26, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarda, G.; Padovan, S.; Delogu, G. Grain yield, nitrogen-use efficiency and baking quality of old and modern Italian bread-wheat cultivars grown at different nitrogen levels. Eur. J. Agron. 2004, 21, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Garcia, M. Genetic Gains and Changes in the Pattern of Adaptation of Bread Wheat Varieties Grown in Spain during the 20th Century. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat de Lleida and IRTA, 2013. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10803/109262 (accessed on 15 June 2018).
- Gliessman, S.R. Field and Laboratory Investigations in Agroecology: A Manual to Accompany Agroecology: Ecological Processes in Sustainable Agriculture; Ann Arbor Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1998; p. 330, ISBN-10: 1-56670-445-6. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán, G.I.; González de Molina, M. Energy in Agroecosystems: A Tool for Assessing Sustainability; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guzman, G.I.; Aguilera, E.; Garcia-Ruiz, R.; Torremocha, E.; Soto-Fernandez, D.; Infante-Amate, J.; Gonzalez de Molina, M. The agrarian metabolism as a tool for assessing agrarian sustainability, and its application to Spanish agriculture (1960–2008). Ecol. Soc. 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.-W. Circular thermodynamics of organisms and sustainable systems. Systems 2013, 1, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.-W.; Ulanowicz, R. Sustainable systems as organisms? Biosystems 2005, 82, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Valvo, P.J.; Miralles, D.J.; Serrago, R.A. Genetic progress in Argentine bread wheat varieties released between 1918 and 2011: Changes in physiological and numerical yield components. Field Crops Res. 2017, 221, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Garcia, M.; Alvaro, F.; Peremarti, A.; Trevaskis, B.; Martin-Sanchez, J.A.; Royo, C. Breeding effects on dry matter accumulation and partitioning in Spanish bread wheat during the 20th century. Euphytica 2015, 203, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GEHR. Estadísticas históricas de la producción agraria española, 1859–1935; Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación: Madrid, Spain, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- MAPAMA (Ministerio de Agricultura y Pesca, Alimentación y Medio Ambiente). Anuario de Estadística. 2018. Available online: https://www.mapama.gob.es/es/estadistica/temas/publicaciones/anuario-de-estadistica/ (accessed on 12 July 2018).
- JCA (Junta Consultiva Agronómica). Avance estadístico sobre el cultivo cereal y de leguminosas asociadas en España formado por la Junta Consultiva Agronómica, 1890, quinquenio de 1886 a 1890 ambos inclusive; Dirección General de Agricultura, Industria y Comercio, Tipografía de L. Peant e hijos: Madrid, Spain, 1891. [Google Scholar]
- JCA (Junta Consultiva Agronómica). Noticias estadísticas sobre la producción agrícola española por la Junta Consultiva Agronómica, 1902; Dirección General de Agricultura, Imprenta Alemana: Madrid, Spain, 1903. [Google Scholar]
- JCA (Junta Consultiva Agronómica). Avance estadístico de la riqueza que en España representa la producción media anual en el decenio de 1903 a 1912 de cereales y leguminosas, vid y olivo y aprovechamientos diversos derivados de estos cultivos; Resumen hecho por la Junta Consultiva Agronómica de las memorias de 1913, remitidas por los ingenieros del servicio agronómico provincial, Madrid; Ministerio de Fomento, Dirección General de Agricultura, Minas y Montes: Madrid, Spain, 1913. [Google Scholar]
- JCA (Junta Consultiva Agronómica). Avance estadístico de la producción agrícola en España. Resumen hecho por la Junta Consultiva Agronómica de las memorias de 1922; Remitidas por los ingenieros del servicio agronómico provincial, Madrid; Ministerio de Fomento, Dirección General de Agricultura, Minas y Montes. Imprenta de los hijos de M.G. Hernández: Madrid, Spain, 1923. [Google Scholar]
- Bektas, H.; Hohn, C.E.; Waines, J.G. Root and shoot traits of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) landraces and cultivars. Euphytica 2016, 212, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, K.H.M.; Belford, R.K.; Tennant, D. Root-shoot ratios of old and modern, tall and semidwarf wheats in a mediterranean environment. Plant Soil 1990, 121, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subira, J.; Ammar, K.; Álvaro, F.; Del Moral, L.F.G.; Dreisigacker, S.; Royo, C. Changes in durum wheat root and aerial biomass caused by the introduction of the Rht-B1b dwarfing allele and their effects on yield formation. Plant Soil 2016, 403, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.; Marschner, P.; Rengel, Z. Effect of Internal and External Factors on Root Growth and Development. In Marschner's Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Marschner, H., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 331–346. [Google Scholar]
- Hilbert, D.W.; Canadell, J. Biomass partitioning and resource allocation of plants from Mediterranean-type ecosystems: Possible responses to elevated atmospheric CO2. In Global Change and Mediterranean-Type Ecosystems; Moreno, J.M., Oechel, W.C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 76–101. ISBN 978-1-4612-8690-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Sorensen, P.; Wahlstrom, E.M.; Chirinda, N.; Sharif, B.; Li, X.; Olesen, J.E. Root biomass in cereals, catch crops and weeds can be reliably estimated without considering aboveground biomass. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 251, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, M.; Raven, J.A.; Sprent, J.I. Environmental effects on dry matter partitioning between shoot and root of crop plants: Relations with growth and shoot protein concentration. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2001, 138, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirinda, N.; Olesen, J.E.; Porter, J.R. Root carbon input in organic and inorganic fertilizer-based systems. Plant Soil 2012, 359, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.T.; Campbell, C.A.; Janzen, H.H.; Lemke, R.L.; Basnyat, P.; McDonald, C.L. Carbon input to soil from oilseed and pulse crops on the Canadian prairies. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 132, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Toosi, A.; Christensen, B.T.; Glendining, M.; Olesen, J.E. Consolidating soil carbon turnover models by improved estimates of belowground carbon input. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesmeier, M.; Huebner, R.; Dechow, R.; Maier, H.; Spoerlein, P.; Geuss, U.; Hangen, E.; Reischl, A.; Schilling, B.; von Luetzow, M.; et al. Estimation of past and recent carbon input by crops into agricultural soils of southeast Germany. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 61, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Romero, V.; Benítez-Vega, J.; López-Bellido, R.J.; Fontán, J.M.; López-Bellido, L. Effect of tillage system on the root growth of spring wheat. Plant Soil 2010, 326, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmo, M.; Antonio Alburquerque, J.; Barron, V.; Carmen del Campillo, M.; Gallardo, A.; Fuentes, M.; Villar, R. Wheat growth and yield responses to biochar addition under Mediterranean climate conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Bonilla, D.; Alvaro-Fuentes, J.; Hansen, N.C.; Lampurlanes, J.; Cantero-Martinez, C. Winter cereal root growth and aboveground-belowground biomass ratios as affected by site and tillage system in dryland Mediterranean conditions. Plant Soil 2014, 374, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza-Gallego, G.; Guzmán, G.I.; García-Ruíz, R.; González de Molina, M.; Aguilera, E. Addressing the role of old wheat varieties in the sustainability of Mediterranean rainfed agroecosystems. forthcoming.
- Soto, D.; Infante-Amate, J.; Guzmán, G.I.; Cid, A.; Aguilera, E.; García-Ruiz, R.; González de Molina, M. The social metabolism of biomass in Spain, 1900–2008: From food to feed-oriented changes in the agro-ecosystems. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 128, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, D.B.; Williams, M.; Aragão, L.; Da Costa, A.C.L.; De Almeida, S.S.; Braga, A.P.; Gonçalves, P.H.L.; De Athaydes, J.; Junior, S.; Malhi, Y. A method for extracting plant roots from soil which facilitates rapid sample processing without compromising measurement accuracy. New Phytol. 2007, 174, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol-Andreu, J. Nuevas perspectivas en historia económica: Innovaciones biológicas y cambio técnico en el sector triguero europeo, siglos XIX-XX. Sociedad Española de Historia Agraria-Documento de Trabajo: 11-03. 2011, p. 42. Available online: http://repositori.uji.es/xmlui/bitstream/handle/10234/21036/DT%2011-03.pdf (accessed on 3 July 2018).
- González de Molina, M.; Soto, D.; Infante-Amate, J.; Aguilera, E.; Vila-Traver, J.; Guzmán, G.I. Decoupling food from land: The evolution of Spanish agriculture from 1960 to 2010. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, E.; Guzmán, G.I.; Álvaro-Fuentes, J.; Infante-Amate, J.; García-Ruiz, R.; Carranza-Gallego, G.; Soto, D.; de Molina, M.G. A historical perspective on soil organic carbon in Mediterranean cropland (Spain, 1900–2008). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González de Molina, M.; Guzmán Casado, G.I.; García Ruíz, R.; Soto Fernández, D.; Herrera, A.; Infante Amate, J. Claves del crecimiento agrario: La reposición de la fertilidad en la agricultura andaluza de los siglos XVIII y XIX. In La reposición de la fertilidad en los sistemas agrarios tradicionales; Garrabou Segura, R., González de Molina, M., Eds.; Icaria: Barcelona, Spain, 2010; pp. 127–170. ISBN 978-84-9888-215-5. [Google Scholar]
- Giambalvo, D.; Ruisi, P.; Di Miceli, G.; Frenda, A.S.; Amato, G. Nitrogen use efficiency and nitrogen fertilizer recovery of durum wheat genotypes as affected by interspecific competition. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza-Gallego, G.; Guzman, G.I.; Garcia-Ruiz, R.; Gonzalez de Molina, M.; Aguilera, E. Contribution of old wheat varieties to climate change mitigation under contrasting managements and rainfed Mediterranean conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annicchiarico, P.; Abdellaoui, Z.; Kelkouli, M.; Zerargui, H. Grain yield, straw yield and economic value of tall and semi-dwarf durum wheat cultivars in Algeria. J. Agric. Sci. 2005, 143, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzo, R.; Fois, S.; Giunta, F. Relationship between grain yield and quality of durum wheats from different eras of breeding. Euphytica 2004, 140, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayadi, S.; Karmous, C.; Chamekh, Z.; Hammami, Z.; Baraket, M.; Esposito, S.; Rezgui, S.; Trifa, Y. Effects of nitrogen rates on grain yield and nitrogen agronomic efficiency of durum wheat genotypes under different environments. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2016, 168, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angás, P.; Lampurlanés, J.; Cantero-Martínez, C. Tillage and N fertilization: Effects on N dynamics and barley yield under semiarid Mediterranean conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 87, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacasta, C. Agricultura ecológica en cereales de secano; Conserjería de Agricultura y Pesca, Ed.; Junta de Andalucía: Seville, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante, A.; Cartelle, J.; Savin, R.; Slafer, G.A. Yield determination, interplay between major components and yield stability in a traditional and a contemporary wheat across a wide range of environments. Field Crops Res. 2017, 203, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.S.; El-Basyoni, I.; Baenziger, P.S.; Singh, S.; Royo, C.; Ozbek, K.; Aktas, H.; Ozer, E.; Ozdemir, F.; Manickavelu, A.; et al. Exploiting genetic diversity from landraces in wheat breeding for adaptation to climate change. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 3477–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annicchiarico, P.; Pecetti, L. Developing a tall durum wheat plant type for semi-arid, Mediterranean cereal–livestock farming systems. Field Crops Res. 2003, 80, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baresel, J.P.; Reents, H.J.; Zimmermann, G. Field evaluation criteria for nitrogen uptake and nitrogen use efficiency. In Proceedings of the COST SUSVAR/ECO-PB Workshop on Organic Plant Breeding Strategies and the Use of Molecular Markers, Driebergen, The Netherlands, 17–19 January 2005; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes, M.J.; Sylvester-Bradley, R.; Scott, R.K. Evidence for differences between winter wheat cultivars in acquisition of soil mineral nitrogen and uptake and utilization of applied fertilizer nitrogen. J. Agric. Sci. 1998, 130, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasse, D.P.; Rumpel, C.; Dignac, M.F. Is soil carbon mostly root carbon? Mechanisms for a specific stabilisation. Plant Soil 2005, 269, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kätterer, T.; Bolinder, M.A.; Andrén, O.; Kirchmann, H.; Menichetti, L. Roots contribute more to refractory soil organic matter than above-ground crop residues, as revealed by a long-term field experiment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 141, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacono, M.; Montemurro, F. Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaidi, J.; Kallenbach, C.M.; Byrne, P.F.; Fonte, S.J. Root traits and root biomass allocation impact how wheat genotypes respond to organic amendments and earthworms. PLoS ONE 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, M.P.; Acevedo, E.; Sayre, K.D.; Fischer, R.A. Yield potential in modern wheat varieties: Its association with a less competitive ideotype. Field Crops Res. 1994, 37, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadras, V.O.; Lawson, C. Genetic gain in yield and associated changes in phenotype, trait plasticity and competitive ability of South Australian wheat varieties released between 1958 and 2007. Crop Pasture Sci. 2011, 62, 533–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, S.; Reynolds, M.P.; Lopes, M.S.; Crossa, J. Genome-Wide Association Study for Adaptation to Agronomic Plant Density: A Component of High Yield Potential in Spring Wheat. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 2609–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrol, N.; Carranza-Gallego, G.; Canabal, A.; Guzmán, G.I. Allelopathic ability of old and modern wheat varieties under organic rainfed Mediterranean conditions. A filed and laboratory test. forthcoming.
- Bertholdsson, N.O. Variation in allelopathic activity over 100 years of barley selection and breeding. Weed Res. 2004, 44, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Iglesias, L.; Puig, C.G.; Garabatos, A.; Reigosa, M.J.; Pedrol, N. Vicia faba aqueous extracts and plant material can suppress weeds and enhance crops. Allelopath. J. 2014, 34, 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Borojevic, K.; Borojevic, K. The transfer and history of “reduced height genes” (Rht) in wheat from Japan to Europe. J. Hered. 2005, 96, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MAGRAMA (Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Medio Ambiente). Inventario de emisiones de gases de efecto invernadero de España 1990–2010; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Medio Rural y Marino: Madrid, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- AEMET (Agencia Estatal de Meteorología). Visor del atlas climático de la Península y Baleares. 2018. Available online: http://www.aemet.es/es/serviciosclimaticos/datosclimatologicos/atlas_climatico/visor_atlas_climatico (accessed 14 August 2018).
- Rodriguez Martin, J.A.; Alvaro-Fuentes, J.; Gonzalo, J.; Gil, C.; Ramos-Miras, J.J.; Corbi, J.M.G.; Boluda, R. Assessment of the soil organic carbon stock in Spain. Geoderma 2016, 264, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanyá, J.A.; Rovira, P.; Vallejo, R. Análisis del carbono en los suelos agrícolas de España. Aspectos relevantes en relación a la reconversión a la agricultura ecológica en el ámbito mediterráneo. Rev. Ecosistemas 2007, 16, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Paustian, K.; Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Hunt, H.W. Management options for reducing CO2 emissions from agricultural soils. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, E.; Lassaletta, L.; Gattinger, A.; Gimeno, B.S. Managing soil carbon for climate change mitigation and adaptation in Mediterranean cropping systems: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 168, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, A.; Mougou, R.; Moneo, M.; Quiroga, S. Towards adaptation of agriculture to climate change in the Mediterranean. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, C.; Jimenez, M.N.; Nieto, O.; Navarro, F.B.; Fernandez-Ondono, E. Changes in soil organic carbon over 20 years after afforestation in semiarid SE Spain. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 381, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEME (Evaluación de los Ecosistemas del Milenio de España). La Evaluación de los Ecosistemas del Milenio de España. Síntesis de resultados. Fundación Biodiversidad; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, y Medio Rural y Marino: Madrid, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Consejería de Medio Ambiente. Factores limitantes para las poblaciones. In El cernícalo primilla en Andalucía. Bases ecológicas para su conservación. Manuales de conservación de la naturaleza, nº 2’; Fernández-Palacios, J.M. (Coord), Ed.; Consejería de Medio Ambiente, Junta de Andalucía: Sevilla, Spain, 2004; pp. 56–73. Available online: www.juntadeandalucia.es/medioambiente/web/Bloques_Tematicos/Estado_Y_Calidad_De_Los_Recursos_Naturales/Fauna/Cernicalo_primilla/cap3.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2017).
- Consejería de Medio Ambiente. Actuaciones del proyecto LIFE Esteparias. 2003. Available online: http://www.juntadeandalucia.es/medioambiente/site/portalweb/menuitem.7e1cf46ddf59bb227a9ebe205510e1ca/?vgnextoid=feb3855b92a3a210VgnVCM1000001325e50aRCRD&vgnextchannel=1d6df3378dea5310VgnVCM2000000624e50aRCRD&lr=lang_es&vgnsecondoid=3664855b92a3a210VgnVCM1000001325e50a____¶m1=1 (accessed on 10 October 2017).
- Freemark, K.; Boutin, C. Impacts of agricultural herbicide use on terrestrial wildlife in temperate landscapes—A review with special reference to North-America. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1995, 52, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- José-María, L.; Sans, F.X. Weed seedbanks in arable fields: Effects of management practices and surrounding landscape. Weed Res. 2011, 51, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, E.J.P.; Brown, V.K.; Boatman, N.D.; Lutman, P.J.W.; Squire, G.R.; Ward, L.K. The role of weeds in supporting biological diversity within crop fields. Weed Res. 2003, 43, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Acquay, H.; Biltonen, M.; Rice, P.; Silva, M.; Nelson, J.; Lipner, S.; Giordano, S.; Horowitz, A.; D'amore, M. Environmental and economic costs of pesticide use. BioScience 1992, 42, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittonell, P.; Scopel, E.; Andrieu, N.; Posthumus, H.; Mapfumo, P.; Corbeels, M.; van Halsema, G.E.; Lahmar, R.; Lugandu, S.; Rakotoarisoa, J.; et al. Agroecology-based aggradation-conservation agriculture (ABACO): Targeting innovations to combat soil degradation and food insecurity in semi-arid Africa. Field Crops Res. 2012, 132, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrizio, R.; Todorovic, M.; Matic, T.; Stellacci, A.M. Comparing the interactive effects of water and nitrogen on durum wheat and barley grown in a Mediterranean environment. Field Crops Res. 2010, 115, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghzawi, A.L.A.; Khalaf, Y.B.; Al-Ajlouni, Z.I.; Al-Quraan, N.A.; Musallam, I.; Hani, N.B. The Effect of Supplemental Irrigation on Canopy Temperature Depression, Chlorophyll Content, and Water Use Efficiency in Three Wheat (Triticum aestivum L. and T. durum Desf.) Varieties Grown in Dry Regions of Jordan. Agric.-Basel 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Tedone, L.; Verdini, L.; De Mastro, G. Effect of different crop management systems on rainfed durum wheat greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint under Mediterranean conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apesteguia, M.; Virto, I.; Orcaray, L.; Enrique, A.; Bescansa, P. Effect of the Conversion to Irrigation of Semiarid Mediterranean Dryland Agrosecoystems on Soil Carbon Dynamics and Soil Aggregation. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2015, 29, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, I.; Masoni, A.; Ercoli, L.; Mariotti, M. Grain yield, and dry matter and nitrogen accumulation and remobilization in durum wheat as affected by variety and seeding rate. Eur. J. Agron. 2006, 25, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas-Corraliza, M.G.; López-Díaz, M.L.; Moreno, G. Winter cereal production in a Mediterranean silvoarable walnut system in the face of climate change. Agric. Ecosys. Environ. 2018, 264, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bort, J.; Fraj, M.B.; Latiri, K.; Kehel, Z.; Araus, J.L. Comparative performance of the stable isotope signatures of carbon, nitrogen and oxygen in assessing early vigour and grain yield in durum wheat—CORRIGENDUM. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 152, 408–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouthiba, A.; Debaeke, P.; Hamoudi, S.A. Varietal differences in the response of durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var. durum) to irrigation strategies in a semi-arid region of Algeria. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 26, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campiglia, E.; Mancinelli, R.; De Stefanis, E.; Pucciarmati, S.; Radicetti, E. The long-term effects of conventional and organic cropping systems, tillage managements and weather conditions on yield and grain quality of durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) in the Mediterranean environment of Central Italy. Field Crops Res. 2015, 176, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, S.K.; Madenoglu, S.; Sonmez, B.; Avag, K.; Turker, U.; Cayci, G.; Kutuk, C.; Heng, L. Assessment of effects of different irrigation water regime on winter wheat yield and water use efficiency. Sci. Pap. Ser. E Land Reclam. Earth Observ. Surv. Environ. Eng. 2017, 6, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Dalias, P. Increased yield surplus of vetch-wheat rotations under drought in a mediterranean environment. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 658518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diacono, M.; Castrignano, A.; Troccoli, A.; De Benedetto, D.; Basso, B.; Rubino, P. Spatial and temporal variability of wheat grain yield and quality in a Mediterranean environment: A multivariate geostatistical approach. Field Crops Res. 2012, 131, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercoli, L.; Lulli, L.; Mariotti, M.; Masoni, A.; Arduini, I. Post-anthesis dry matter and nitrogen dynamics in durum wheat as affected by nitrogen supply and soil water availability. Eur. J. Agron. 2008, 28, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercoli, L.; Lulli, L.; Arduini, I.; Mariotti, M.; Masoni, A. Durum wheat grain yield and quality as affected by S rate under Mediterranean conditions. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 35, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagnano, M.; Fiorentino, N.; D’Egidio, M.G.; Quaranta, F.; Ritieni, A.; Ferracane, R.; Raimondi, G. Durum wheat in conventional and organic farming: Yield amount and pasta quality in Southern Italy. Sci. World J. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, R.J.; Schultz, J.E. Water use efficiency of wheat in a Mediterranean-type environment. I. The relation between yield, water use and climate. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1984, 35, 743–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martín, A.; López-Bellido, R.J.; Coleto, J.M. Fertilisation and weed control effects on yield and weeds in durum wheat grown under rain-fed conditions in a Mediterranean climate. Weed Res. 2007, 47, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, P.J.; Tennant, D.; Belford, R.K. Root and shoot growth, and water and light use efficiency of barley and wheat crops grown on a shallow duplex soil in a Mediterranean-type environment. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1992, 43, 555–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangir, K.; Saifullah, K.; Munir Ahmad Khetran, A.; Sadiq, N.; Islam, M.; Hanan, A.; Aziz, A. Tijaban-10 a drought tolerant and high yielding wheat variety for rainfed/sailaba areas of Balochistan. Pak. J. Bot. 2013, 45, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar]
- Karam, F.; Kabalan, R.; Breidi, J.; Rouphael, Y.; Oweis, T. Yield and water-production functions of two durum wheat cultivars grown under different irrigation and nitrogen regimes. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobata, T.; Koç, M.; Barutçular, C.; Tanno, K.-I.; Inagaki, M. Harvest index is a critical factor influencing the grain yield of diverse wheat species under rain-fed conditions in the Mediterranean zone of southeastern Turkey and northern Syria. Plant Prod. Sci. 2018, 21, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, M.; Barutçular, C.; Genç, I. Photosynthesis and productivity of old and modern durum wheats in a Mediterranean environment. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 2089–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bellido, L.; López-Bellido, R.J.; Redondo, R. Nitrogen efficiency in wheat under rainfed Mediterranean conditions as affected by split nitrogen application. Field Crops Res. 2005, 94, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Bellido, L.; López-Bellido, R.J.; Redondo, R.; Benítez, J. Faba bean nitrogen fixation in a wheat-based rotation under rainfed Mediterranean conditions: Effect of tillage system. Field Crops Res. 2006, 98, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, A.; Oudjehih, B.; Benbelkacem, A.; Fellahi, Z.E.A.; Bouzerzour, H. Variation and Relationships among Agronomic Traits in Durum Wheat [Triticum turgidum (L.) Thell. ssp. turgidum conv. durum (Desf.) MacKey] under South Mediterranean Growth Conditions: Stepwise and Path Analyses. Int. J. Agron. 2018, 2018, 8191749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenov, N.; Hristov, N.; Kondic-Spika, A.; Djuric, V.; Jevtic, R.; Mladenov, V. Breeding progress in grain yield of winter wheat cultivars grown at different nitrogen levels in semiarid conditions. Breed. Sci. 2011, 61, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olgun, M.; Aygün, C. Evaluation of yield and yield components by different statistical methods in wheat (T. aestivum L.). CEP 2011, 88, 900. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, M.W.; d’Antuono, M.F. Yield improvement and associated characteristics of some Australian spring wheat cultivars introduced between 1860 and 1982. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1989, 40, 457–472. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, R.A.; Rebetzke, G.J.; Condon, A.G.; Van Herwaarden, A.F. Breeding opportunities for increasing the efficiency of water use and crop yield in temperate cereals. Crop Sci. 2002, 42, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruisi, P.; Frangipane, B.; Amato, G.; Frenda, A.S.; Plaia, A.; Giambalvo, D.; Saia, S. Nitrogen uptake and nitrogen fertilizer recovery in old and modern wheat genotypes grown in the presence or absence of interspecific competition. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, K.H.M.; Kirby, E.J.M.; Perry, M.W. Ear: Stem ratio in old and modern wheat varieties; relationship with improvement in number of grains per ear and yield. Field Crops Res. 1989, 21, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, K.H.M.; Belford, R.K.; Perry, M.W.; Tennant, D. Growth, development and light interception of old and modern wheat cultivars in a Mediterranean-type environment. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1989, 40, 473–487. [Google Scholar]
- Soriano, J.M.; Villegas, D.; Aranzana, M.J.; del Moral, L.F.G.; Royo, C. Genetic structure of modern durum wheat cultivars and mediterranean landraces matches with their agronomic performance. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaeefar, A.; Emamzadeh, H.; Varnamkhasti, M.G.; Rahimizadeh, R.; Karimi, M. Comparison of energy of tillage systems in wheat production. Energy 2009, 34, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taner, A.; Arisoy, R.Z.; Kaya, Y.; Gultekin, I.; Partigoc, F. The effects of various tillage systems on grain yield, quality parameters and energy indices in winter wheat production under the rainfed conditions. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2015, 24, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Tedone, L.; Ali, S.A.; Verdini, L.; De Mastro, G. Nitrogen management strategy for optimizing agronomic and environmental performance of rainfed durum wheat under Mediterranean climate. J. Clean Prod. 2018, 172, 2058–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, S.; Yazar, A.; Barut, H. Comparison of wheat-based rotation systems and monocropping systems under dryland Mediterranean conditions. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2017, 10, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unkovich, M.; Baldock, J.; Forbes, M. Variability in harvest index of grain crops and potential significance for carbon accounting: Examples from Australian agriculture. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 105, pp. 173–219. [Google Scholar]
- van den Boogaard, R.; Veneklaas, E.J.; Peacock, J.M.; Lambers, H. Yield and water use of wheat (Triticum aestivum) in a Mediterranean environment: Cultivar differences and sowing density effects. Plant Soil 1996, 181, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Diaz, O.; Kefauver, S.C.; Elazab, A.; Nieto-Taladriz, M.T.; Araus, J.L. Grain yield losses in yellow-rusted durum wheat estimated using digital and conventional parameters under field conditions. Crop J. 2015, 3, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Oweis, T.Y.; Garabet, S.; Pala, M. Water-use efficiency and transpiration efficiency of wheat under rain-fed conditions and supplemental irrigation in a Mediterranean-type environment. Plant Soil 1998, 201, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borger, C.P.D.; Hashem, A.; Pathan, S. Manipulating crop row orientation to suppress weeds and increase crop yield. Weed Sci. 2010, 58, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campiglia, E.; Radicetti, E.; Mancinelli, R. Floristic composition and species diversity of weed community after 10 years of different cropping systems and soil tillage in a Mediterranean environment. Weed Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, M.T.; Verdú, A.M.C. Tillage system effects on weed communities in a 4-year crop rotation under Mediterranean dryland conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2003, 74, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, G.; Cirujeda, A.; Aibar, J.; Cavero Campo, J.; Zaragoza Larios, C. Weed harrowing in winter cereal under semi-arid conditions. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2008, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togay, N.; Tepe, I.; Togay, Y.; Cig, F. Nitrogen levels and application methods affect weed biomass, yield and yield components in Tir'wheat (Triticum aestivum). N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2009, 37, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
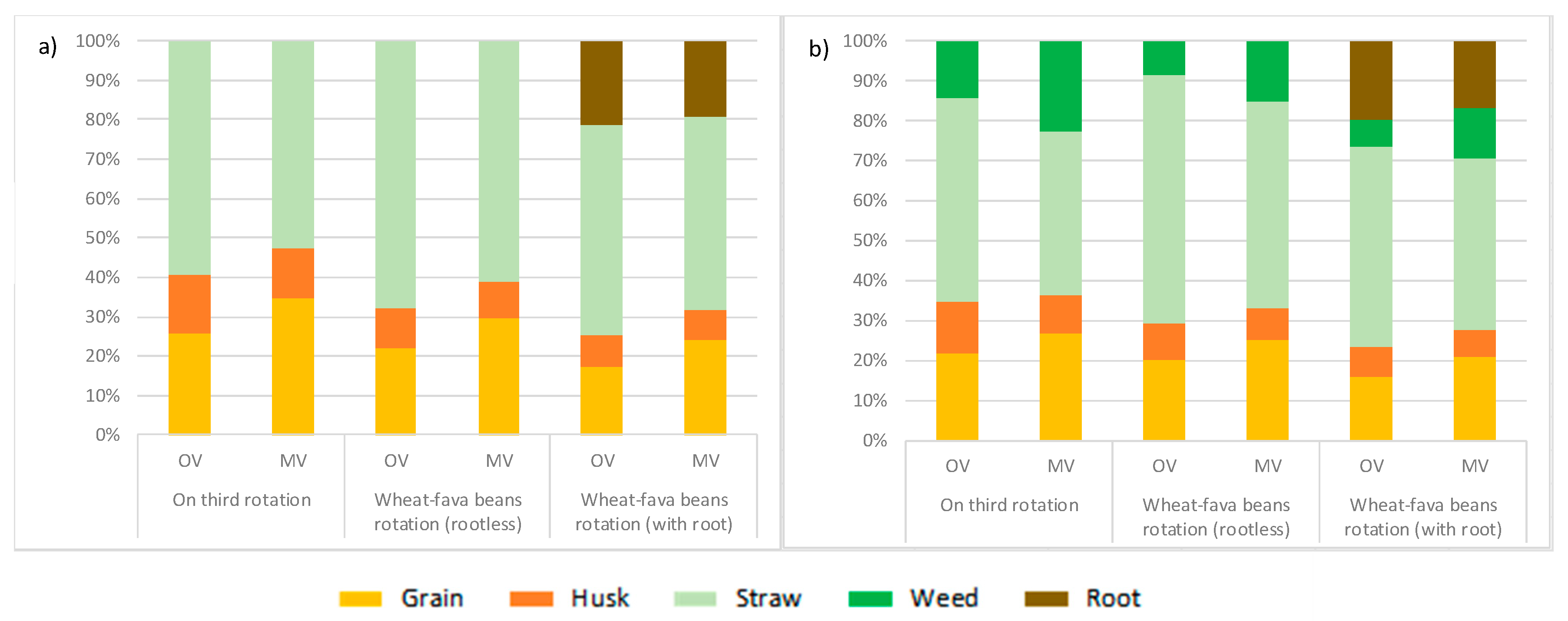
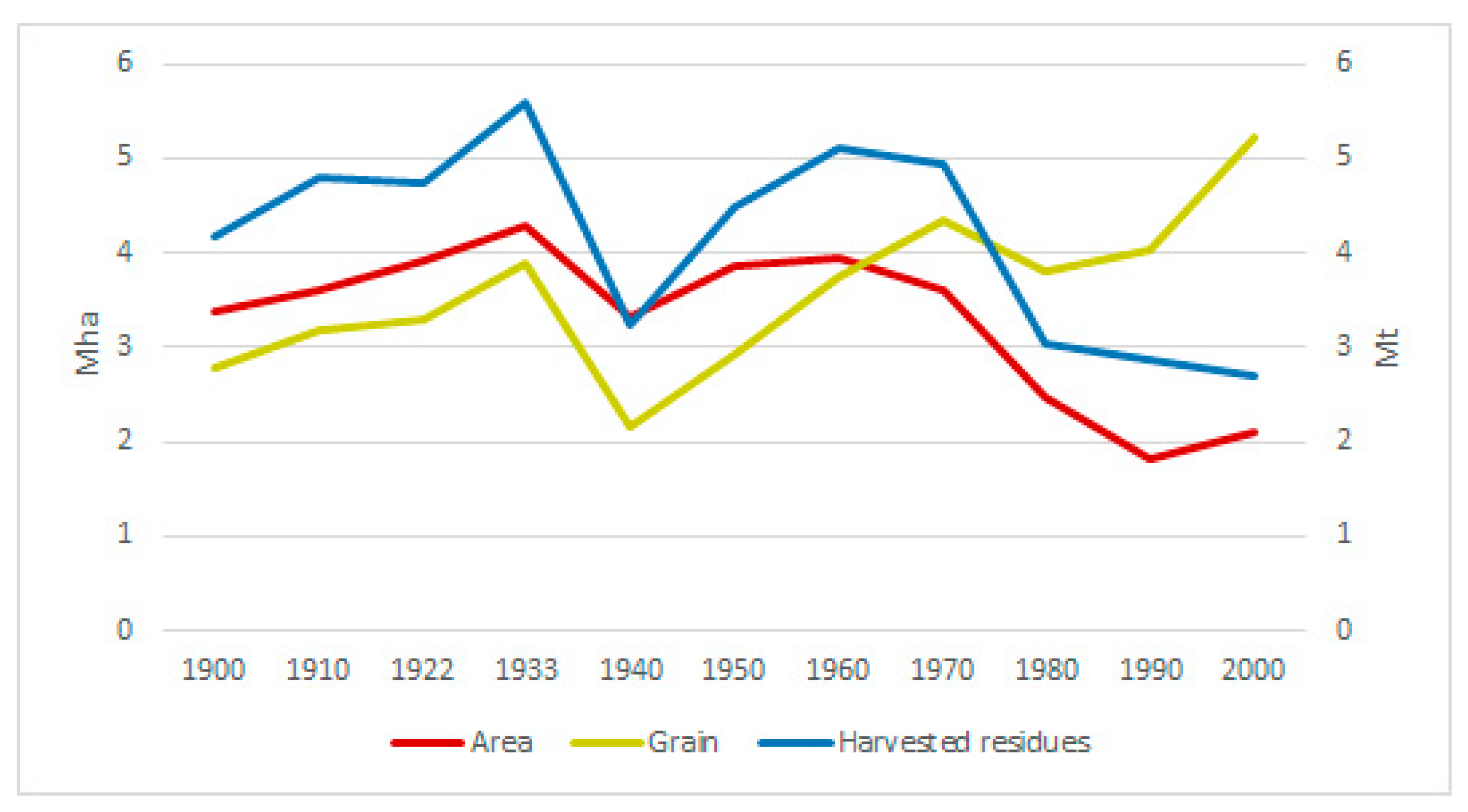
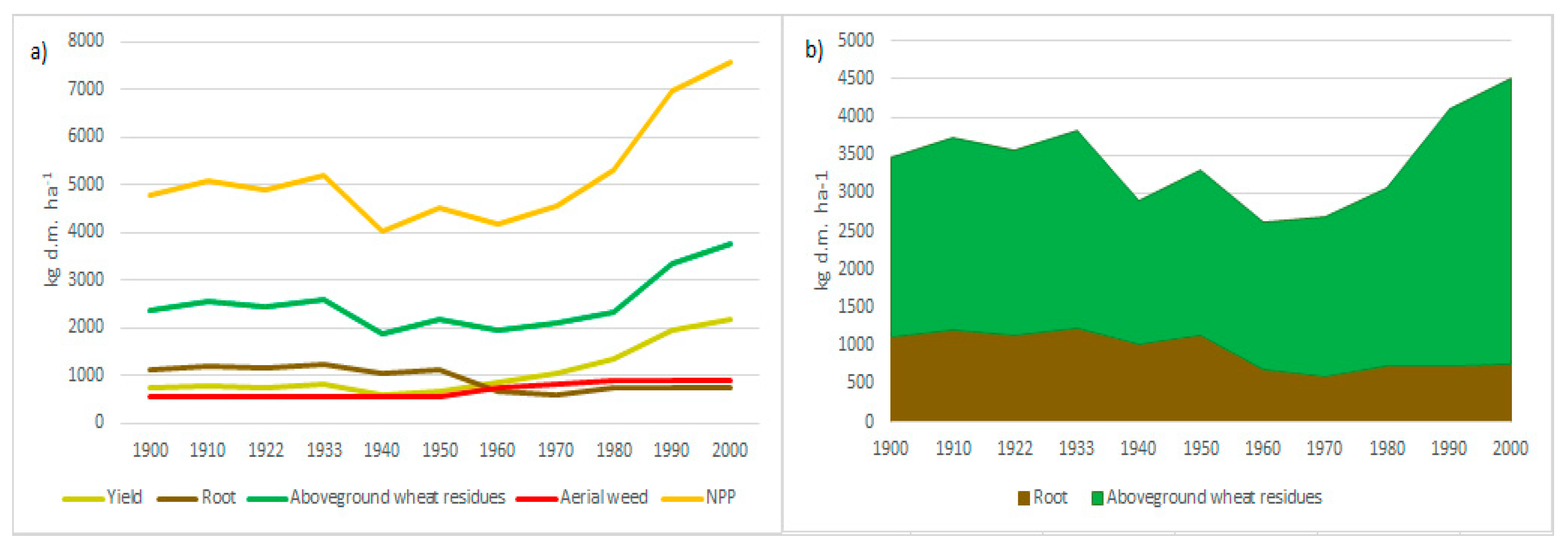
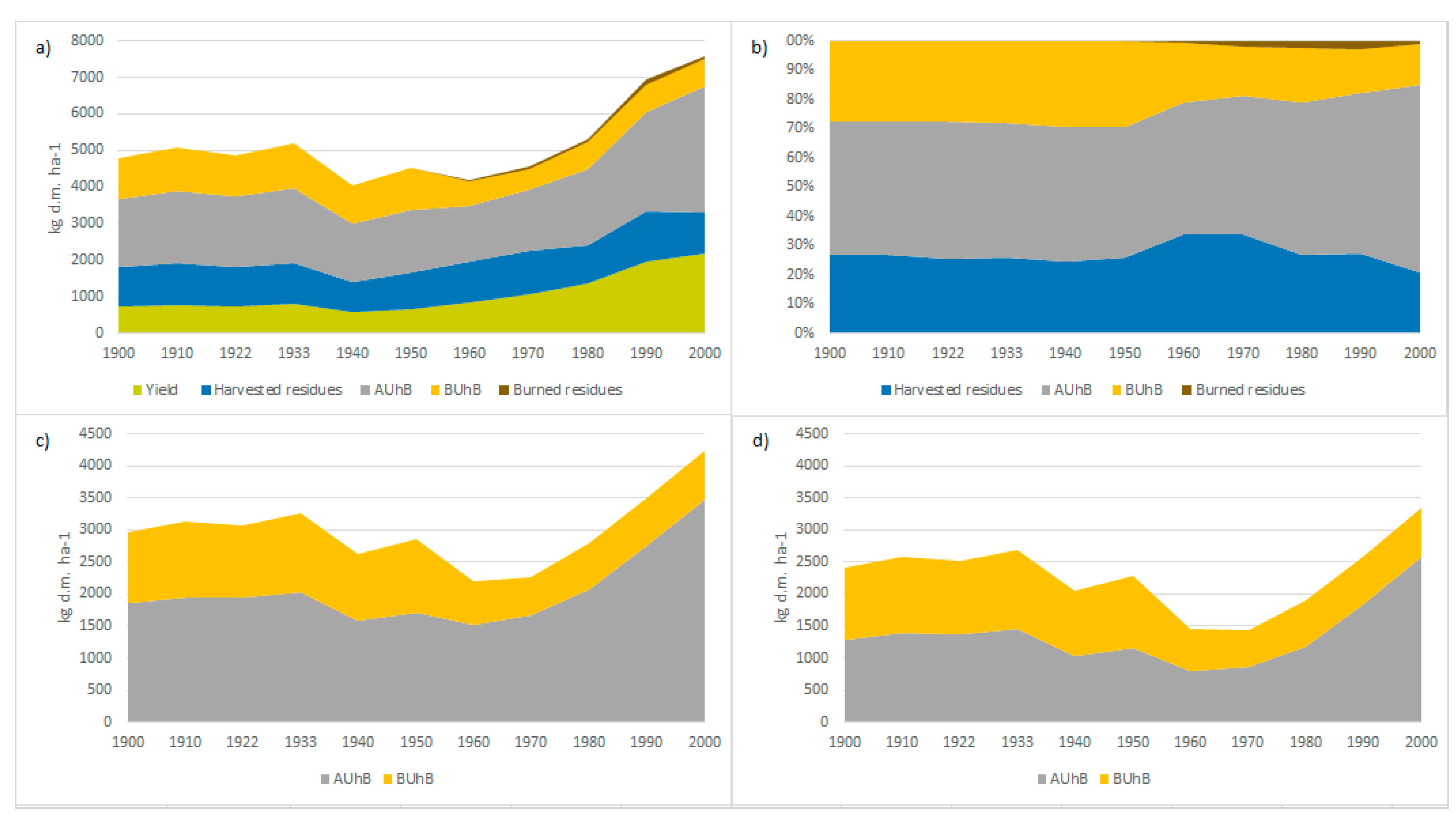
| Sierra de Yeguas (Wheat-Faba Bean Rotation) | Ronda (One-Third Rotation) | |
|---|---|---|
| Rainfall (mm) | ||
| 2013–2014 | 433 | 612 |
| 2014–2015 | 344 | 448 |
| 2015–2016 | 363 | 846 |
| 1982–2012 average | 673 | 775 |
| Rotation | Wheat-faba bean | Wheat-fallow-fallow |
| Fertilization | Manure | - |
| (3.6% N, d.m.) (3.0 Mg ha−1, f.m.) | ||
| Weed control | Manual weeding | - |
| Irrigation | Rainfed | Rainfed |
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | Average | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old | Modern | Old | Modern | Old | Modern | Old | Modern | ||
| W-FB R | NPPa | 11,807a ± 581 | 9292b ± 697 | 11,570a ± 428 | 11,078a ± 483 | 7000a ± 395 | 5957b ± 315 | 10,126 ± 377 | 8776 ± 389 |
| NPP | 9486a ± 395 | 7713b ± 315 | |||||||
| Grain | 2187a ± 240 | 1223b ± 198 | 2523b ± 108 | 3966a ± 198 | 1374a ± 143 | 1414a ± 154 | 2028 ± 114 | 2201 ± 182 | |
| Straw | 6186a ± 492 | 3812b ± 312 | 7767a ± 305 | 5946b ± 288 | 4967a ± 271 | 3831b ± 189 | 6307 ± 250 | 4530 ± 194 | |
| Husk | 1014a ± 120 | 544b ± 43 | 1276a ± 63 | 1126a ± 60 | 532a ± 52 | 458a ± 33 | 941 ± 60 | 709 ± 44 | |
| Root | 2486a ± 252 | 1757b ± 166 | |||||||
| Weed | 2421b ± 417 | 3712a ± 609 | 3b ± 2 | 40a ± 14 | 126b ± 30 | 254a ± 50 | 850 ± 191 | 1335 ± 283 | |
| O-T R | NPPa | 1249a ± 115 | 893b ± 88 | 2553a ± 175 | 1841b ± 110 | 1957a ± 139 | 1611b ± 121 | 1920 ± 104 | 1448 ± 78 |
| Grain | 256a ± 45 | 153b ± 36 | 623a ± 58 | 569a ± 46 | 385a ± 47 | 438a ± 61 | 421 ± 34 | 387 ± 35 | |
| Straw | 597a ± 40 | 374b ± 38 | 1247a ± 73 | 684b ± 53 | 1095a ± 77 | 708b ± 51 | 980 ± 50 | 589 ± 33 | |
| Husk | 139a ± 29 | 66b ± 19 | 342a ± 28 | 201b ± 14 | 251a ± 21 | 162b ± 15 | 244 ± 18 | 143 ± 11 | |
| Weed | 257a ± 35 | 300a ± 36 | 342a ± 41 | 387a ± 44 | 226b ± 24 | 302a ± 33 | 275 ± 20 | 330 ± 22 | |
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | Average | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OV | MV | OV | MV | OV | MV | OV | MV | ||
| Harvest index | W-FB R | 0.235a ± 0.021 | 0.206a ± 0.028 | 0.238b ± 0.006 | 0.393a ± 0.011 | 0.211a ± 0.017 | 0.262a ± 0.020 | 0.228 ± 0.009 | 0.287 ± 0.015 |
| O-T R | 0.209a ± 0.026 | 0.219a ± 0.037 | 0.308b ± 0.013 | 0.389a ± 0.020 | 0.193b ± 0.012 | 0.287a ± 0.023 | 0.237 ± 0.012 | 0.298 ± 0.018 | |
| Weed:NPPa | W-FB R | 0.210b ± 0.038 | 0.371a ± 0.041 | 0.0003b ± 0.000 | 0.004a ± 0.002 | 0.019b ± 0.004 | 0.041a ± 0.006 | 0.076 ± 0.017 | 0.139 ± 0.024 |
| O-T R | 0.195b ± 0.020 | 0.358a ± 0.042 | 0.130b ± 0.011 | 0.212a ± 0.020 | 0.124b ± 0.013 | 0.194a ± 0.022 | 0.150 ± 0.010 | 0.255 ± 0.019 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carranza-Gallego, G.; Guzmán, G.I.; Soto, D.; Aguilera, E.; Villa, I.; Infante-Amate, J.; Herrera, A.; González de Molina, M. Modern Wheat Varieties as a Driver of the Degradation of Spanish Rainfed Mediterranean Agroecosystems throughout the 20th Century. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103724
Carranza-Gallego G, Guzmán GI, Soto D, Aguilera E, Villa I, Infante-Amate J, Herrera A, González de Molina M. Modern Wheat Varieties as a Driver of the Degradation of Spanish Rainfed Mediterranean Agroecosystems throughout the 20th Century. Sustainability. 2018; 10(10):3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103724
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarranza-Gallego, Guiomar, Gloria Isabel Guzmán, David Soto, Eduardo Aguilera, Inma Villa, Juan Infante-Amate, Antonio Herrera, and Manuel González de Molina. 2018. "Modern Wheat Varieties as a Driver of the Degradation of Spanish Rainfed Mediterranean Agroecosystems throughout the 20th Century" Sustainability 10, no. 10: 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103724
APA StyleCarranza-Gallego, G., Guzmán, G. I., Soto, D., Aguilera, E., Villa, I., Infante-Amate, J., Herrera, A., & González de Molina, M. (2018). Modern Wheat Varieties as a Driver of the Degradation of Spanish Rainfed Mediterranean Agroecosystems throughout the 20th Century. Sustainability, 10(10), 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103724






