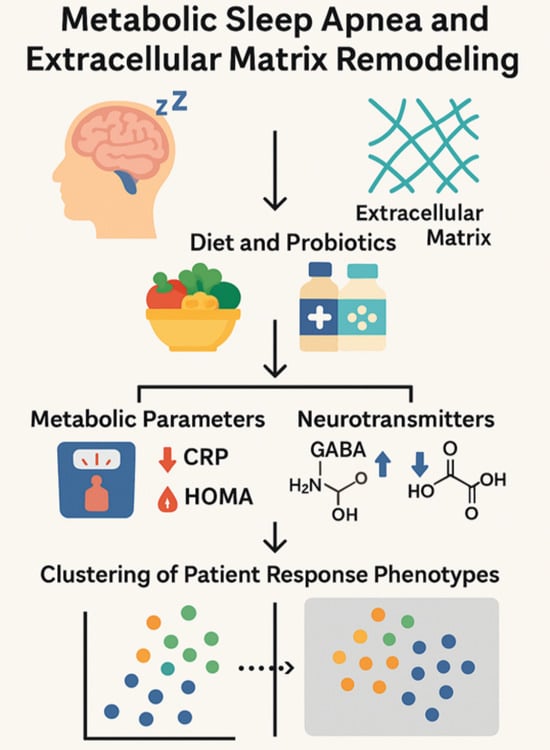
Effects of Dietary and Probiotic Interventions in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome and Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
1. Introduction
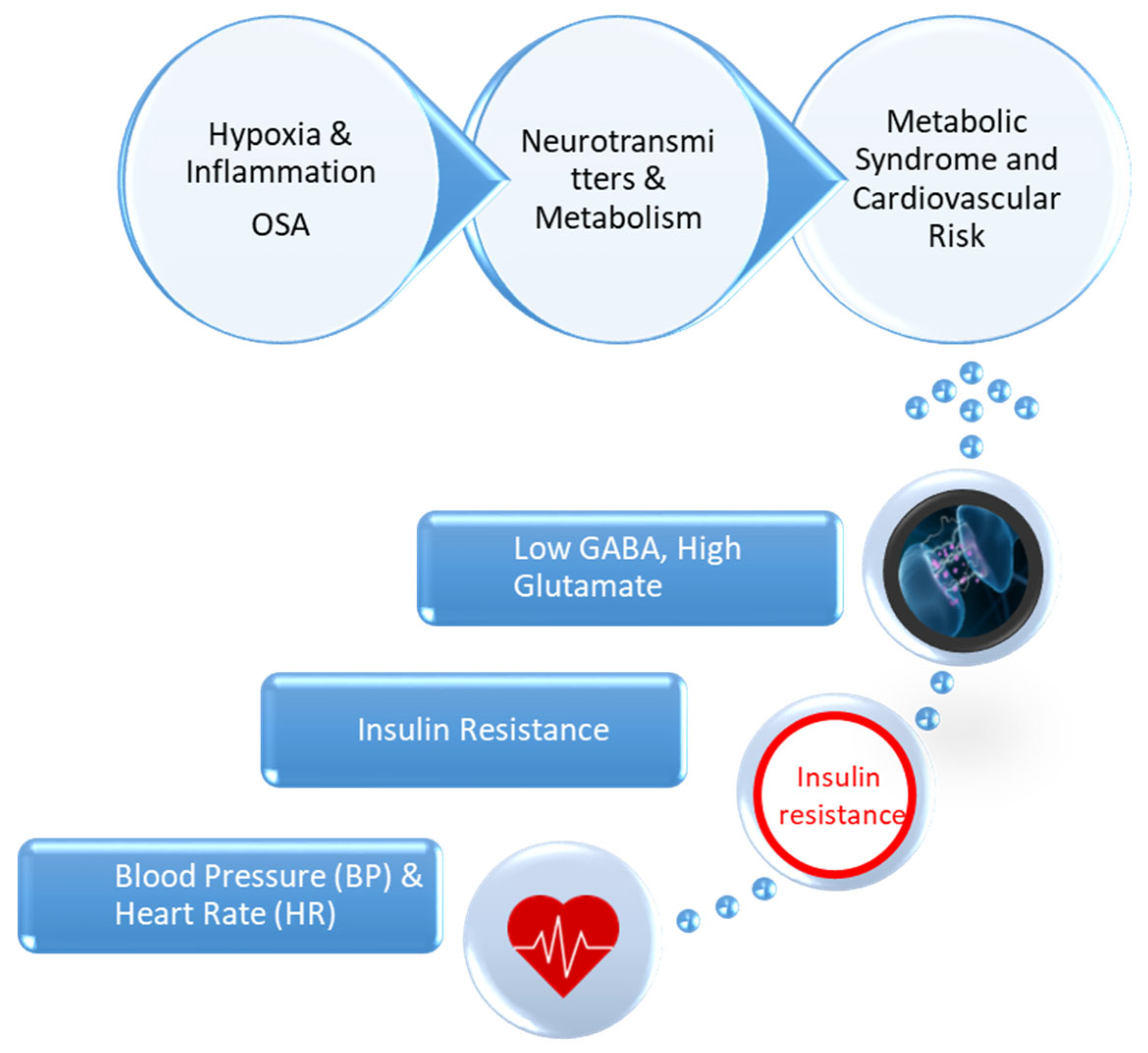
1.1. Pathophysiological Mechanisms Linking Metabolic Syndrome and Obstructive Sleep Apnea
1.2. Rationale and Significance of the Study
2. Materials and Methods
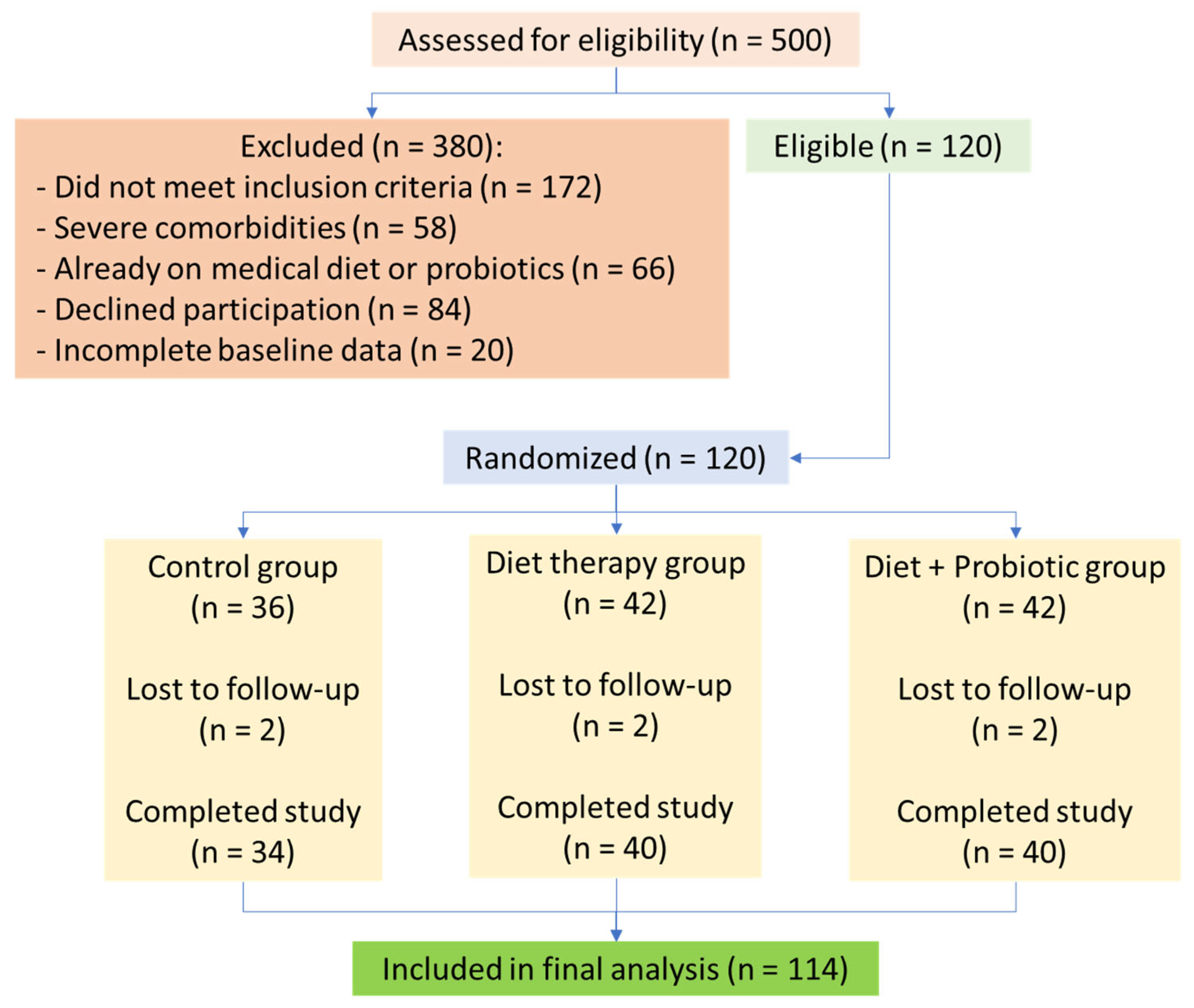
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Participant Selection and Intervention
2.4. Biochemical and Anthropometric Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethics Committee Approval
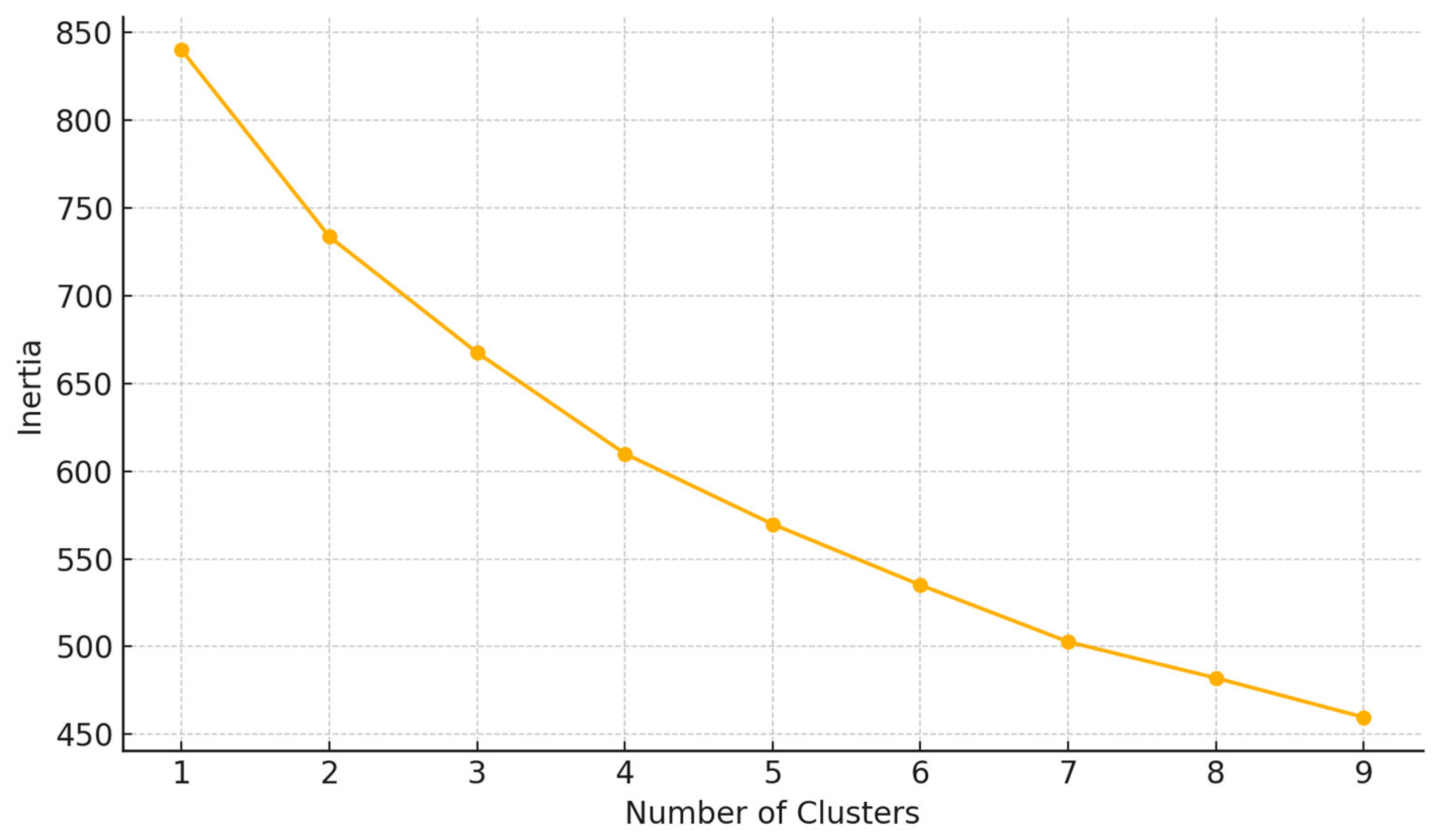
2.7. Clustering Algorithm
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Group Characteristics
3.2. Metabolic Parameters
3.2.1. Body Composition and Metabolic Markers
3.2.2. Glycemic Control and Insulin Resistance
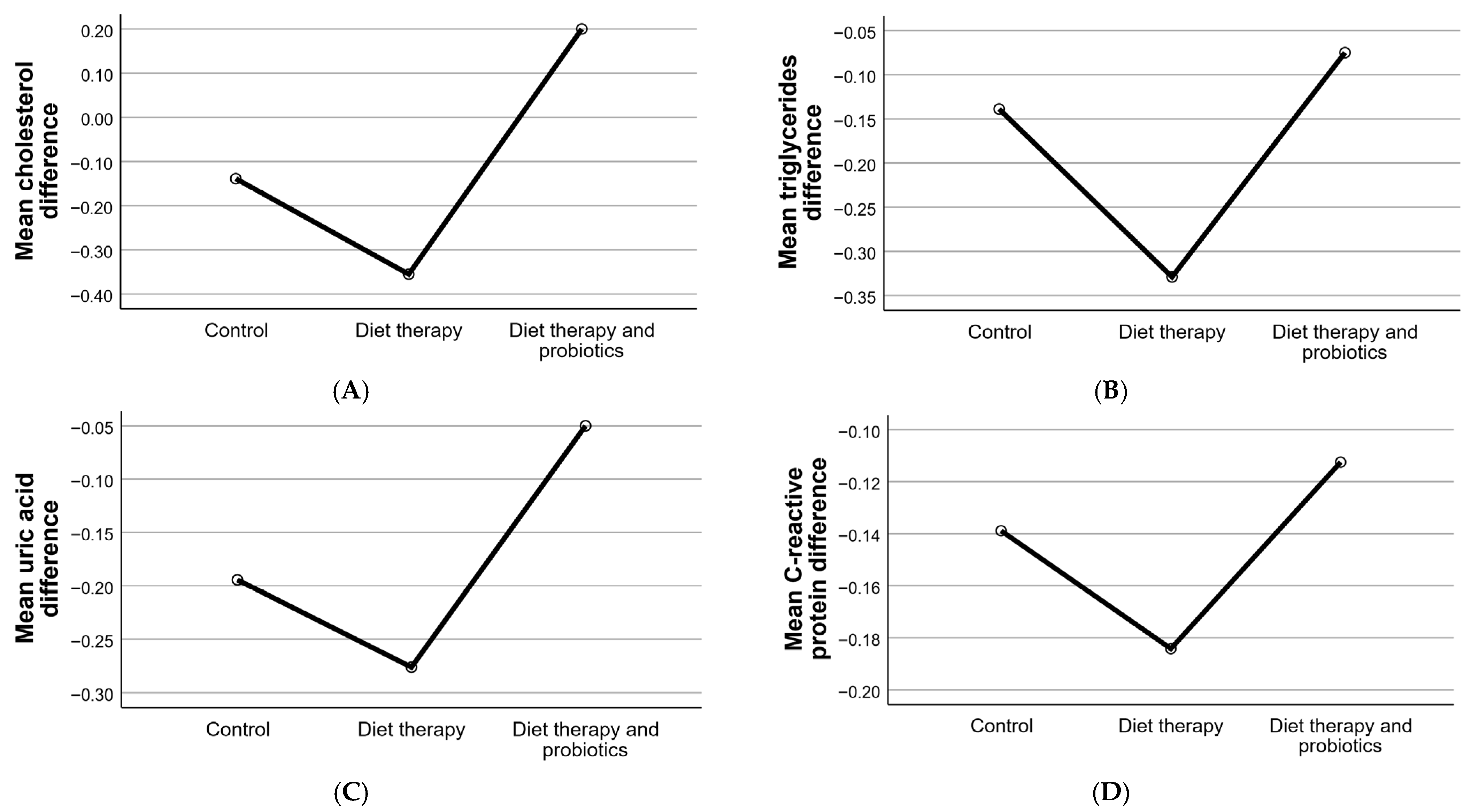
3.2.3. Lipid Profile and Inflammatory Markers
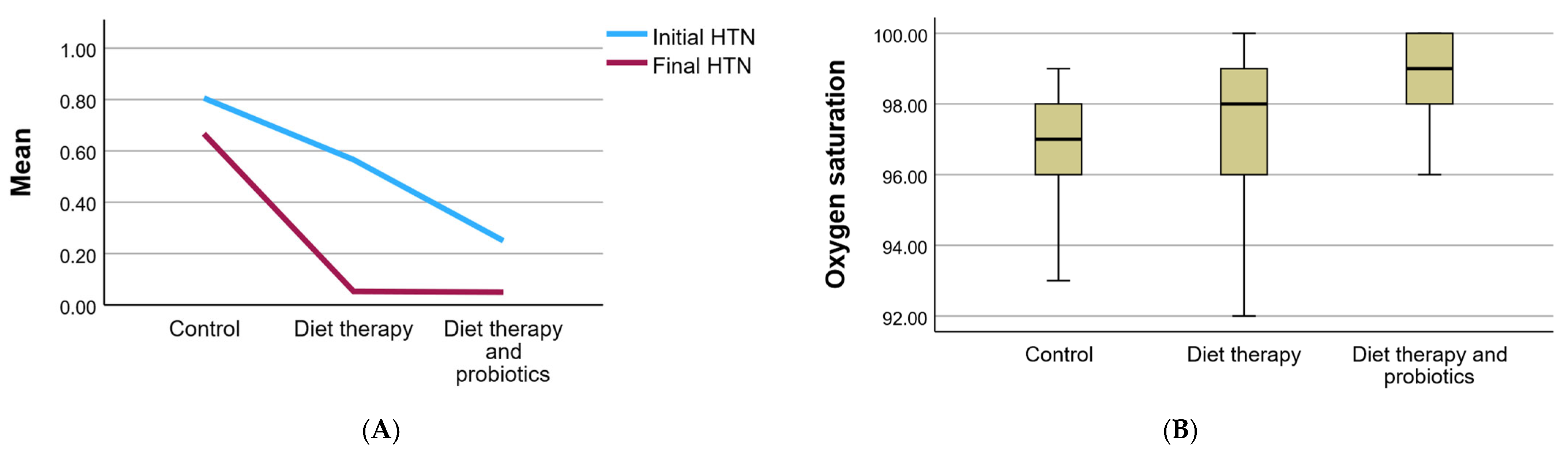
3.2.4. Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Parameters
3.3. Hemodynamic Parameters
3.4. Biochemical Parameters
3.5. Cholesterol, Triglycerides, and Inflammatory Markers
3.6. Response Phenotypes Identified Through Clustering and PCA
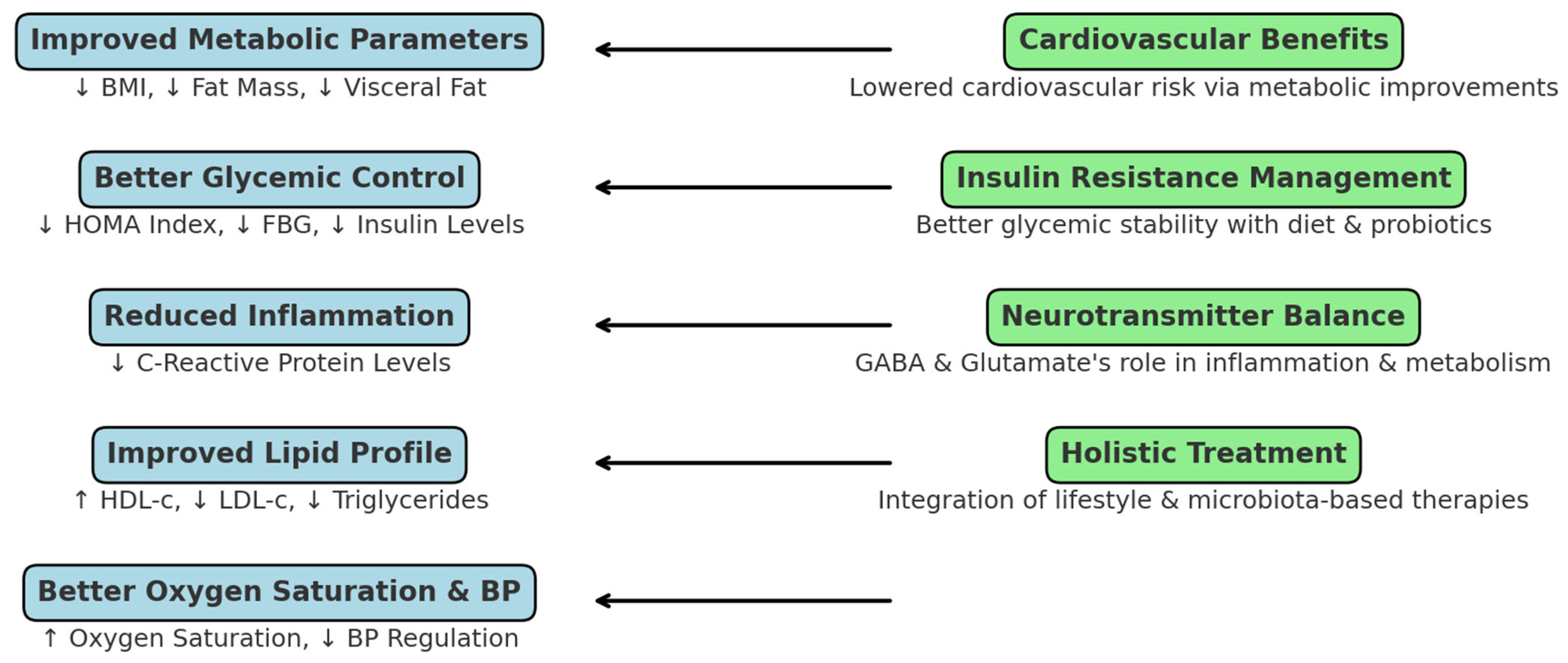
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Diet Therapy on Metabolic Syndrome and Obstructive Sleep Apnea
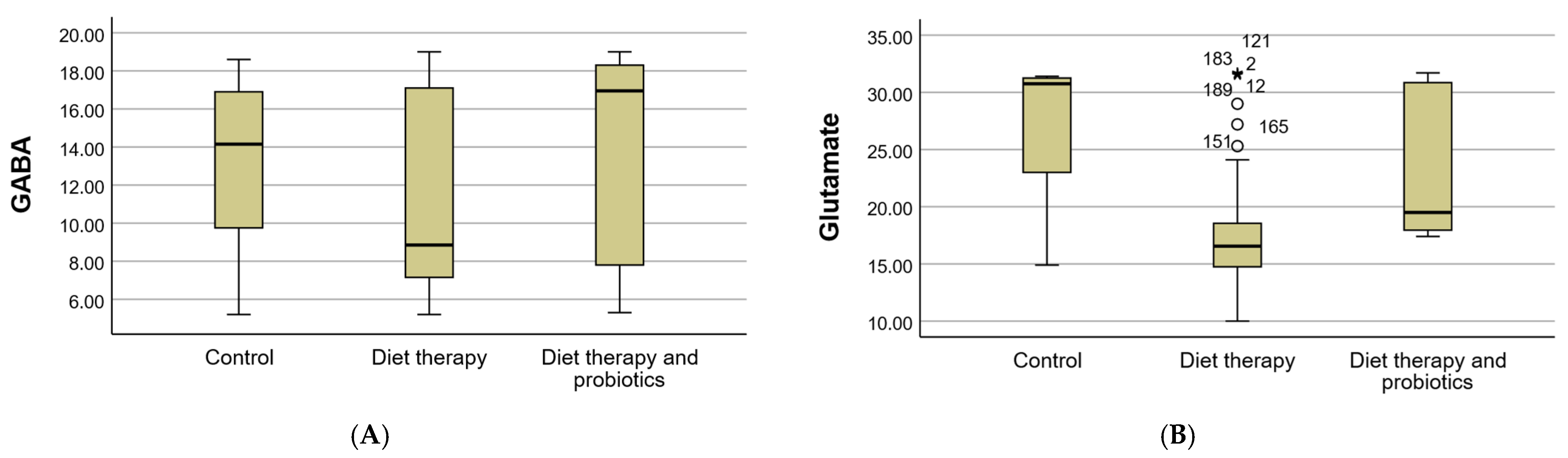
4.2. Impact of Probiotics on Metabolic and Neurophysiological Parameters
4.3. Comparison with Baseline Data
4.4. Phenotypic Stratification via Clustering Analysis
4.5. Toward Predictive Personalization
4.6. Clinical Implications
4.7. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mugnai, G. Pathophysiological links between obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and metabolic syndrome. G. Ital. Cardiol. 2010, 11, 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- Drager, L.F.; Togeiro, S.M.; Polotsky, V.Y.; Lorenzi-Filho, G. Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Cardiometabolic Risk in Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thareja, S.; Mandapalli, R.; Shaik, F.; Rajeev Pillai, A.; Palaniswamy, G.; Sahu, S.; Cherukuri, S.P.; Younas, S. Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Cardiovascular Health: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e71940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sforza, E.; Roche, F. Chronic intermittent hypoxia and obstructive sleep apnea: An experimental and clinical approach. Hypoxia 2016, 4, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A.R.; Patil, S.P.; Laffan, A.M.; Polotsky, V.; Schneider, H.; Smith, P.L. Obesity and obstructive sleep apnea: Pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labarca, G.; Gower, J.; Lamperti, L.; Dreyse, J.; Jorquera, J. Chronic intermittent hypoxia in obstructive sleep apnea: A narrative review from pathophysiological pathways to a precision clinical approach. Sleep. Breath. 2020, 24, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, N.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Yue, H.; Yin, Q. Pathophysiological mechanisms and therapeutic approaches in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, N.R.; Peng, Y.-J.; Nanduri, J. Hypoxia-inducible factors and obstructive sleep apnea. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5042–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarski, P.; Sochal, M.; Strzelecki, D.; Białasiewicz, P.; Gabryelska, A. Influence of glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmission on obstructive sleep apnea. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1213971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czapski, G.A.; Strosznajder, J.B. Glutamate and GABA in Microglia-Neuron Cross-Talk in Alzheimer's Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-G.; Lin, W.-N.; Hsin, L.-J.; Huang, Y.-S.; Chuang, L.-P.; Fang, T.-J.; Li, H.-Y.; Kuo, T.B.J.; Yang, C.C.H.; Lee, C.-C.; et al. Alterations in Gut Microbiota Composition Are Associated with Changes in Emotional Distress in Children with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Navarro-Jiménez, E.; Laborde-Cárdenas, C.C.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. The Role of Adipokines in Health and Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, D.C.L.; Lam, K.S.L.; Ip, M.S.M. Obstructive sleep apnoea, insulin resistance and adipocytokines. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 82, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaines, J.; Vgontzas, A.N.; Fernandez-Mendoza, J.; Bixler, E.O. Obstructive sleep apnea and the metabolic syndrome: The road to clinically-meaningful phenotyping, improved prognosis, and personalized treatment. Sleep. Med. Rev. 2018, 42, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghitea, T.C.; Aleya, L.; Tit, D.M.; Behl, T.; Stoicescu, M.; Sava, C.; Iovan, C.; El-Kharoubi, A.; Uivarosan, D.; Pallag, A.; et al. Influence of diet and sport on the risk of sleep apnea in patients with metabolic syndrome associated with hypothyroidism—A 4-year survey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 23158–23168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumpston, E.; Chen, P. Sleep apnea syndrome. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jean-Louis, G.; Zizi, F.; Clark, L.T.; Brown, C.D.; McFarlane, S.I. Obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease: Role of the metabolic syndrome and its components. J. Clin. Sleep. Med. 2008, 4, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempsey, J.A.; Veasey, S.C.; Morgan, B.J.; O'Donnell, C.P. Pathophysiology of sleep apnea. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 47–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifan, D.F.; Tirla, A.G.; Mos, C.; Danciu, A.; Bodog, F.; Manole, F.; Ghitea, T.C. Involvement of Vitamin D3 in the Aging Process According to Sex. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masenga, S.K.; Kabwe, L.S.; Chakulya, M.; Kirabo, A. Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hassani, I.; Khan, N.A.; Elmenyar, E.; Al-Hassani, A.; Rizoli, S.; Al-Thani, H.; El-Menyar, A. The Interaction and Implication of Stress-Induced Hyperglycemia and Cytokine Release Following Traumatic Injury: A Structured Scoping Review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Maemura, K.; Kanbara, K.; Tamayama, T.; Hayasaki, H. GABA and GABA receptors in the central nervous system and other organs. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2002, 213, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiș, L.; Alexandru, B.A.; Fodor, R.; Daina, L.G.; Ghitea, T.C.; Vlad, S. Effect of Probiotic Therapy on Neuropsychiatric Manifestations in Children with Multiple Neurotransmitter Disorders: A Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicosia, N.; Giovenzana, M.; Misztak, P.; Mingardi, J.; Musazzi, L. Glutamate-Mediated Excitotoxicity in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Neurodevelopmental and Adult Mental Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arm, J.; Oeltzschner, G.; Al-Iedani, O.; Lea, R.; Lechner-Scott, J.; Ramadan, S. Altered in vivo brain GABA and glutamate levels are associated with multiple sclerosis central fatigue. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 137, 109610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier-Santos, D.; Bedani, R.; Lima, E.D.; Saad, S.M.I. Impact of probiotics and prebiotics targeting metabolic syndrome. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienel, S.J.; Enwright, J.F., III; Hoftman, G.D.; Lewis, D.A. Markers of glutamate and GABA neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex of schizophrenia subjects: Disease effects differ across anatomical levels of resolution. Schizophr. Res. 2020, 217, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Wang, K.-Y.; Wang, N.-R.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.-P. Effect of probiotics and paraprobiotics on patients with sleep disorders and sub-healthy sleep conditions: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1477533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Barquero, S.; Ruiz-León, A.M.; Sierra-Pérez, M.; Estruch, R.; Casas, R. Dietary Strategies for Metabolic Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudat, Q.; Okour, A. The Role of Probiotics in Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Health for Weight Management: A Mini Review. Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.; Mallery, P. IBM SPSS Statistics 27 Step by Step: A Simple Guide and Reference; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ghitea, T.C. Correlation of Periodontal Bacteria with Chronic Inflammation Present in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, R.; Yang, L.; Zhou, J.; Sanford, L.D.; Tang, X. The effect of treating obstructive sleep apnea with continuous positive airway pressure on posttraumatic stress disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis with hypothetical model. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 102, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parish, J.M.; Adam, T.; Facchiano, L. Relationship of metabolic syndrome and obstructive sleep apnea. J. Clin. Sleep. Med. 2007, 3, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulek, M.; Frosztega, W.; Wieckiewicz, M.; Szymanska-Chabowska, A.; Gac, P.; Poreba, R.; Mazur, G.; Sciskalska, M.; Kepinska, M.; Martuszewski, A.; et al. The link between sleep bruxism and oxidative stress based on a polysomnographic study. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, J.A. Nutrition, insulin resistance and dysfunctional adipose tissue determine the different components of metabolic syndrome. World J. Diabetes 2016, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, D.L.; McEvoy, R.D.; Sprecher, K.E.; Thomson, K.J.; Ryan, M.K.; Thompson, C.C.; Catcheside, P.G. Abdominal compression increases upper airway collapsibility during sleep in obese male obstructive sleep apnea patients. Sleep 2009, 32, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-Y.; Zhou, D.-D.; Gan, R.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Zhao, C.-N.; Shang, A.; Xu, X.-Y.; Li, H.-B. Effects and mechanisms of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics on metabolic diseases targeting gut microbiota: A narrative review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.A.; Kim, J. Effect of Probiotics on Blood Lipid Concentrations: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicine 2015, 94, e1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reutrakul, S.; Mokhlesi, B. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Diabetes: A State of the Art Review. Chest 2017, 152, 1070–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Leng, S.; Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qie, D.; Yang, F. Pharmacological interventions for pediatric obstructive sleep apnea (OSA): Network meta-analysis. Sleep. Med. 2024, 116, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunta, S.P.; Jakulla, R.S.; Ubaid, A.; Mohamed, K.; Bhat, A.; López-Candales, A.; Norgard, N. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Diseases: Sad Realities and Untold Truths regarding Care of Patients in 2022. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2022, 2022, 6006127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markey, M.; Corsica, J.; Cvengros, J.; Wyatt, J. Impact of a brief dietary self-monitoring intervention on weight change and CPAP adherence in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. J. Psychosom. Res. 2013, 74, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenneth, R. The effect of diet on cardiovascular disease and lipid and lipoprotein levels. In Endotext [Internet] 2000; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Grosso, G.; Laudisio, D.; Frias-Toral, E.; Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A. Anti-Inflammatory Nutrients and Obesity-Associated Metabolic-Inflammation: State of the Art and Future Direction. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Shen, X.; Shi, X.; Sakandar, H.A.; Quan, K.; Li, Y.; Jin, H.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z. Targeting gut microbiota and metabolism as the major probiotic mechanism—An evidence-based review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 178–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofori, F.; Dargenio, V.N.; Dargenio, C.; Miniello, V.L.; Barone, M.; Francavilla, R. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of probiotics in gut inflammation: A door to the body. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 578386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sproston, N.R.; Ashworth, J.J. Role of C-Reactive Protein at Sites of Inflammation and Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchernof, A.; Nolan, A.; Sites, C.; Ades, P.; Poehlman, E. Weight Loss Reduces C-Reactive Protein Levels in Obese Postmenopausal Women. Circulation 2002, 105, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Yuan, M.; Xu, Y.; Xu, H. Gout and Diet: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanisms and Management. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Chen, Q.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Jing, C.; Gong, A.; Zhang, Y. Exploring a novel therapeutic strategy: The interplay between gut microbiota and high-fat diet in the pathogenesis of metabolic disorders. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1291853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.E.; Rosa, P.W.L.; Melo, M.E.; Martins, R.C.R.; Santin, F.G.O.; Moura, A.; Coelho, G.; Sabino, E.C.; Cercato, C.; Mancini, M.C. Differences in the gut microbiota of women according to ultra-processed food consumption. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 33, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.; Borges-Canha, M.; Pimentel-Nunes, P. Microbiota Modulation in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2022, 14, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.; Behl, T.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Bhatia, S.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E.; Bungau, S. Unravelling the involvement of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Life Sci. 2021, 273, 119311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezenabor, E.H.; Adeyemi, A.A.; Adeyemi, O.S. Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Syndrome: Relationships and Opportunities for New Therapeutic Strategies. Scientifica 2024, 2024, 4222083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.X.; Deng, X.R.; Zhang, C.H.; Yuan, H.J. Gut microbiota and metabolic syndrome. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Shi, B. Gut microbiota as a potential target of metabolic syndrome: The role of probiotics and prebiotics. Cell Biosci. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A.; Galiè, S. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Metabolic Syndrome and Sleep Disorders: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.-P.; Wang, L.-J.; Fan, Y.-Q.; Dou, Z.-J.; Han, J.-X.; Wang, B. Analysis of the characteristics of intestinal microbiota in patients with different severity of obstructive sleep apnea. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuvat, N.; Tanriverdi, H.; Armutcu, F. The relationship between obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and obesity: A new perspective on the pathogenesis in terms of organ crosstalk. Clin. Respir. J. 2020, 14, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Count | % | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 38.96 ± 14.63 | 0.330 | ||
| Gender | Male | 152 | 79.2% | 0.001 ** |
| Female | 40 | 20.8% | ||
| Environment | Urban | 84 | 43.8% | 0.830 |
| Rural | 108 | 56.2% | ||
| Group | Control | 36 | 18.8% | 0.001 ** |
| Diet therapy | 76 | 39.6% | ||
| Diet therapy and probiotics | 80 | 41.7% | ||
| Parameter | Group | p | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Diet Therapy | Diet Therapy and Probiotics | |||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Initial | |||||||||
| BMI | 29.29 | 5.60 | 31.03 | 6.28 | 31.42 | 9.89 | 0.092 | 30.87 | 7.89 |
| Fat mass | 32.27 | 7.82 | 34.21 | 7.14 | 25.64 | 10.08 | 0.001 ** | 30.27 | 9.44 |
| Visceral fat | 8.78 | 4.87 | 9.32 | 6.43 | 4.90 | 3.34 | 0.001 ** | 7.38 | 5.44 |
| Insulin | 11.7 | 4.12 | 20.4 | 4.68 | 16.00 | 8.84 | 0.004 ** | 16.03 | 5.88 |
| FBG | 101.5 | 31.12 | 94.1 | 23.81 | 103.68 | 18.98 | 0.031 * | 99.76 | 24.63 |
| HOMA index | 2.97 | 0.66 | 4.76 | 2.50 | 4.10 | 2.75 | 0.001 ** | 4.15 | 2.47 |
| HbA1C | 5.7 | 2.33 | 5.6 | 2.03 | 5.8 | 2.81 | 0.475 | 5.7 | 2.39 |
| HDL-c | 32 | 5.66 | 51 | 5.16 | 46 | 4.81 | 0.007 ** | 43 | 5.21 |
| LDL-c | 123 | 32.2 | 155.4 | 37.2 | 213 | 40.2 | 0.001 ** | 163.8 | 36.53 |
| TG | 103 | 37.41 | 147 | 41.21 | 216 | 37.41 | 0.001 ** | 155.33 | 38.67 |
| CPR mg/dL | 0.46 | 0.25 | 0.51 | 0.34 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 0.067 | 0.49 | 0.28 |
| Systolic blood pressure | 132 | 21 | 141 | 33 | 135 | 22 | 0.047 * | 136 | 25 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | 97 | 11 | 100 | 16 | 91 | 17 | 0.032 * | 96 | 15 |
| Final | |||||||||
| BMI | 29.47 | 5.79 | 24.66 | 2.95 | 24.77 | 3.19 | 0.001 ** | 25.61 | 4.15 |
| Fat mass | 32.32 | 7.82 | 28.07 | 5.23 | 20.75 | 7.86 | 0.001 ** | 25.82 | 8.26 |
| Visceral fat | 8.89 | 5.11 | 7.68 | 5.49 | 3.90 | 2.77 | 0.001 ** | 6.33 | 4.92 |
| Insulin µU/mL | 17.1 | 4.12 | 12.5 | 3.61 | 9.16 | 5.14 | 0.007 ** | 10.4 | 4.85 |
| FBG mg/dL | 74 | 31.12 | 89.00 | 21.67 | 81.80 | 14.98 | 0.009 ** | 89.1 | 22.22 |
| HOMA index | 3.22 | 0.75 | 2.59 | 1.14 | 2.29 | 1.50 | 0.001 ** | 2.58 | 1.33 |
| HbA1C | 6.56 | 2.39 | 5.3 | 2.07 | 5.1 | 2.83 | 0.001 ** | 5.65 | 2.39 |
| HDL-c | 27.20 | 5.65 | 55 | 5.18 | 60 | 4.84 | 0.001 ** | 47.4 | 5.21 |
| LDL-c | 141.45 | 32.7 | 130 | 37.9 | 110 | 40.6 | 0.001 ** | 127.15 | 36.53 |
| TG | 118.45 | 37.48 | 120 | 41.27 | 95 | 37.48 | 0.001 ** | 111.15 | 38.67 |
| CPR | 0.53 | 0.29 | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.012 * | 0.40 | 0.28 |
| Systolic blood pressure | 151 | 23 | 126 | 30 | 121 | 24 | 0.032 * | 132 | 22 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | 107 | 14 | 90 | 15 | 85 | 19 | 0.004 ** | 94 | 14 |
| Parameter | Group | p | Total | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Diet Therapy | Diet Therapy and Probiotics | ||||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |||
| Oxygen saturation (Mean ± SD) | 96.56 ± 1.92 | 97.11 ± 2.04 | 98.80 ± 1.13 | 0.325 | 97.71 ± 1.93 | |||||
| HTN initial | absent | 7 | 3.6 | 33 | 17.2 | 60 | 31.2 | 0.001 ** | 100 | 52.1 |
| present | 29 | 15.1 | 43 | 22.4 | 20 | 10.4 | 0.001 ** | 92 | 47.9 | |
| HTN final | absent | 12 | 6.2 | 72 | 37.5 | 76 | 39.6 | 0.001 ** | 160 | 83.3 |
| present | 24 | 12.5 | 4 | 2.1 | 4 | 2.1 | 0.001 ** | 32 | 16.7 | |
| Parameter | Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Diet Therapy | Diet Therapy and Probiotics | |||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| GABA (Mean ± SD) | 13.18 ± 4.33 | 11.07 ± 5.03 | 13.84 ± 5.31 | ||||
| GABA | <2.25 µmol/g creatinine | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 2.25–12.8 µmol/g creatinine | 9 | 4.7 | 49 | 25.5 | 28 | 14.6 | |
| >12.8 µmol/g creatinine | 27 | 14.1 | 27 | 14.1 | 52 | 27.1 | |
| Glutamate (Mean ± SD) | 27.05 ± 6.87 | 17.64 ± 4.56 | 23.78 ± 6.14 | ||||
| Glutamate | <8 µmol/g creatinine | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 8–30 µmol/g creatinine | 9 | 4.7 | 72 | 37.5 | 52 | 27.1 | |
| >30 µmol/g creatinine | 27 | 14.1 | 4 | 2.1 | 28 | 14.6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venter, A.; El-kharoubi, A.-F.; El-kharoubi, M.; Ghitea, E.C.; Ghitea, M.C.; Ghitea, T.C.; Venter, C.F. Effects of Dietary and Probiotic Interventions in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15090159
Venter A, El-kharoubi A-F, El-kharoubi M, Ghitea EC, Ghitea MC, Ghitea TC, Venter CF. Effects of Dietary and Probiotic Interventions in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Clinics and Practice. 2025; 15(9):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15090159
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenter, Amina, Amin-Florin El-kharoubi, Mousa El-kharoubi, Evelin Claudia Ghitea, Marc Cristian Ghitea, Timea Claudia Ghitea, and Ciprian Florian Venter. 2025. "Effects of Dietary and Probiotic Interventions in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome and Obstructive Sleep Apnea" Clinics and Practice 15, no. 9: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15090159
APA StyleVenter, A., El-kharoubi, A.-F., El-kharoubi, M., Ghitea, E. C., Ghitea, M. C., Ghitea, T. C., & Venter, C. F. (2025). Effects of Dietary and Probiotic Interventions in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Clinics and Practice, 15(9), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15090159