Comparing Stenting with Medical Therapy Versus Medical Therapy Alone in Patients with Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis: A Current Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
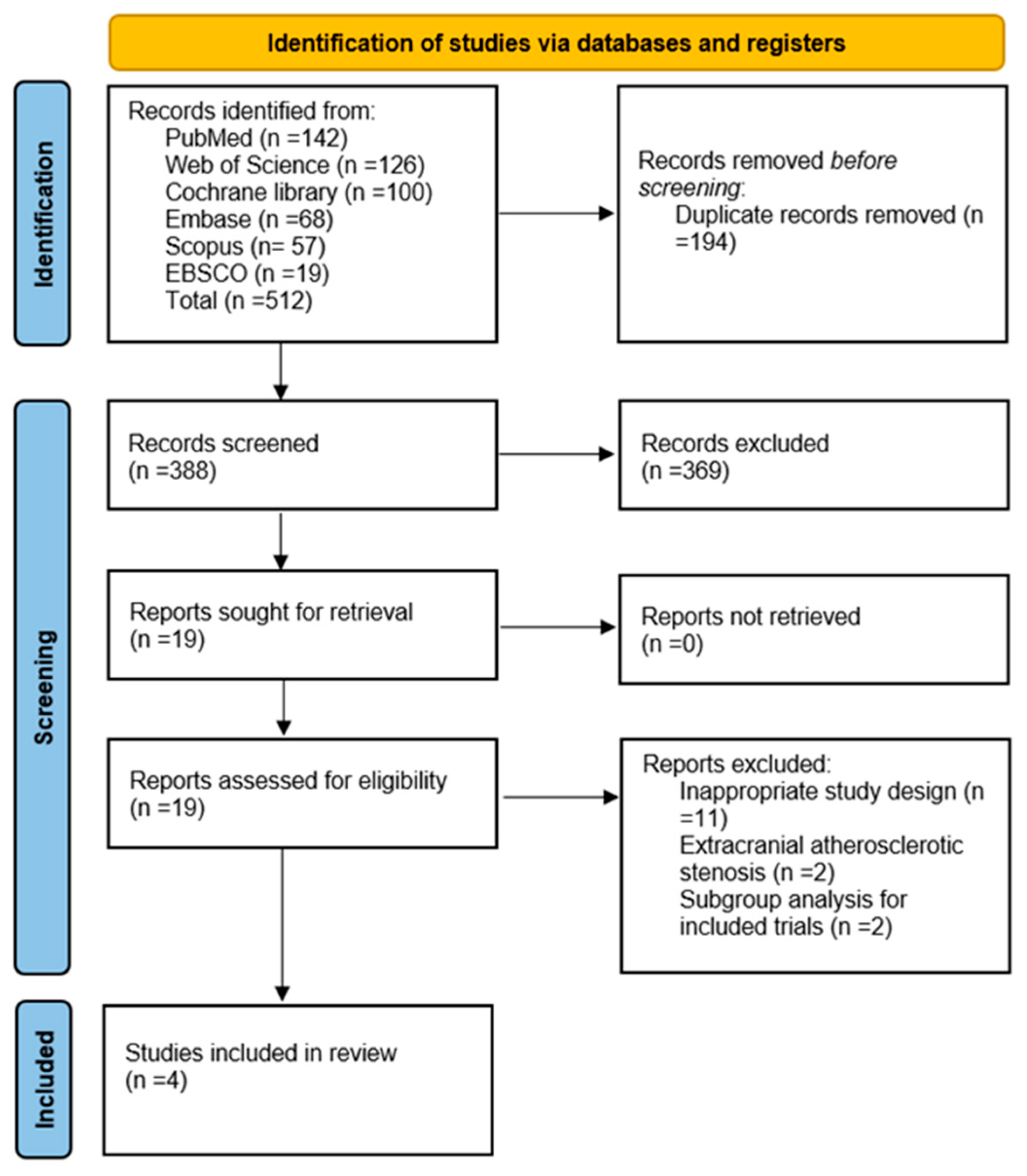
2.3. Screening and Selection of Studies
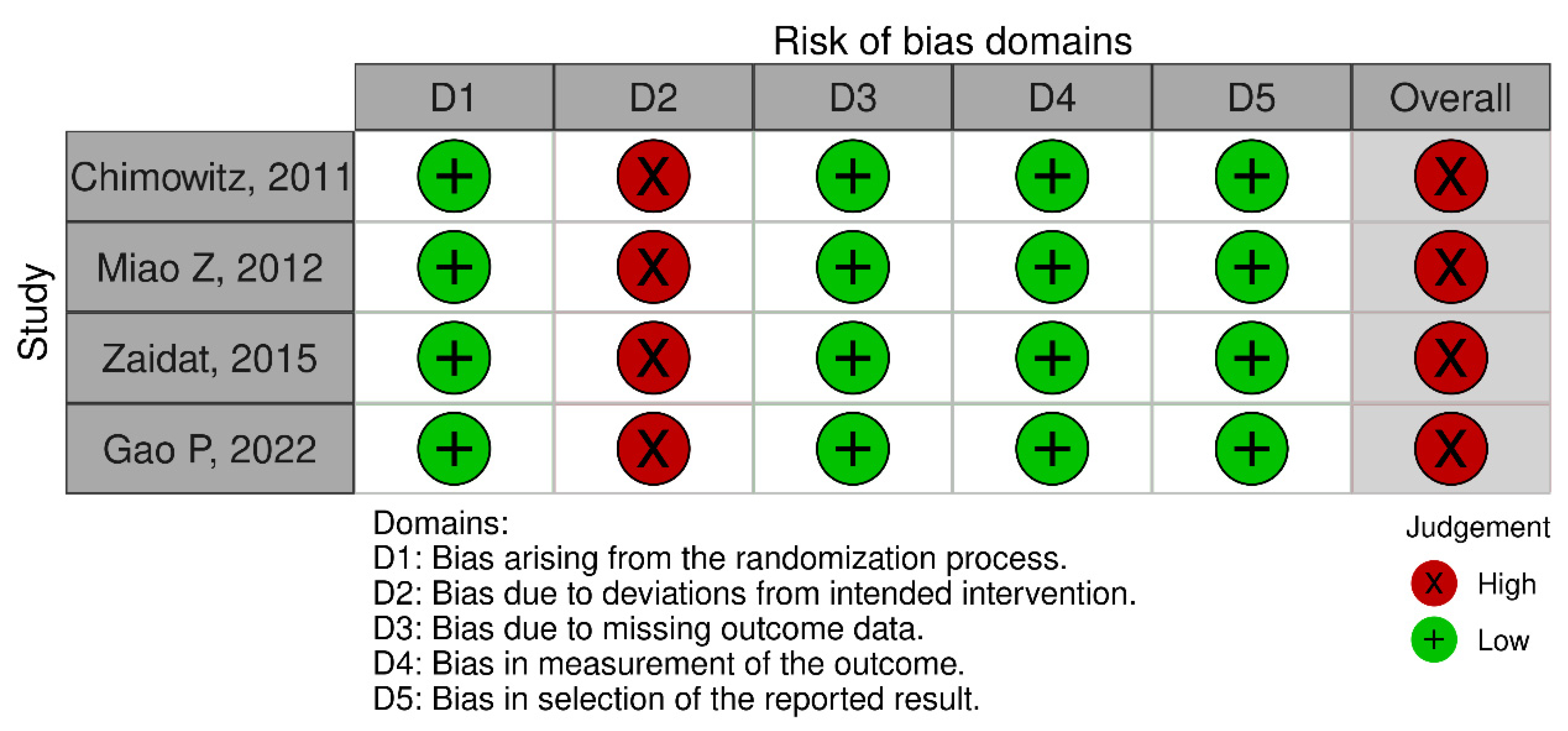
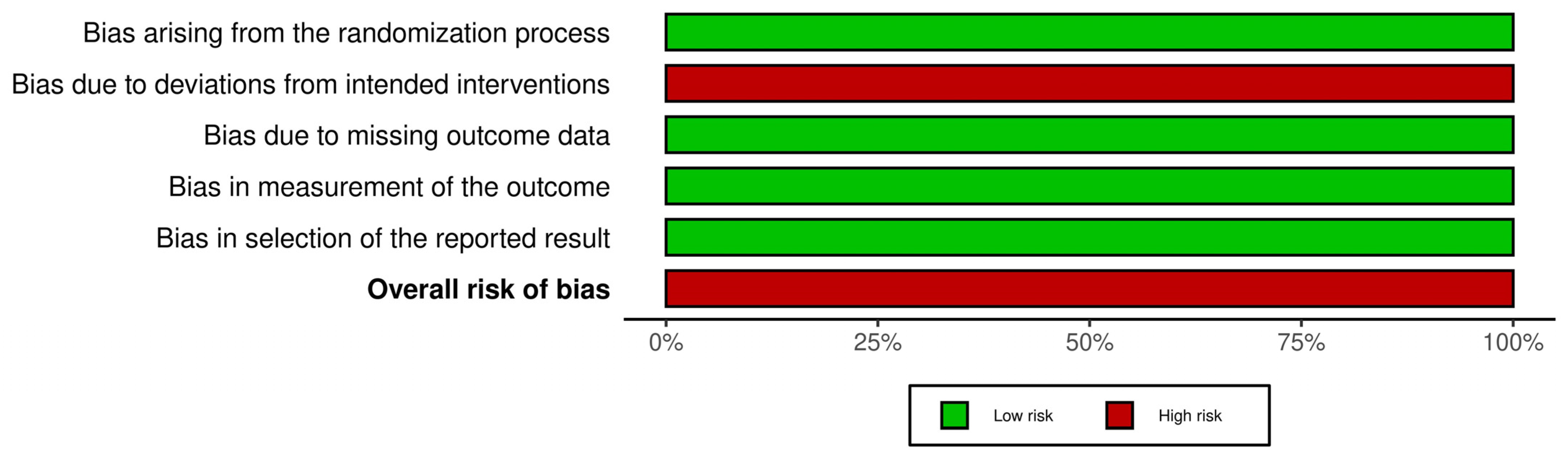
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included Studies and Patients
3.2. Baseline Clinical and Angiographic Characteristics of Participants
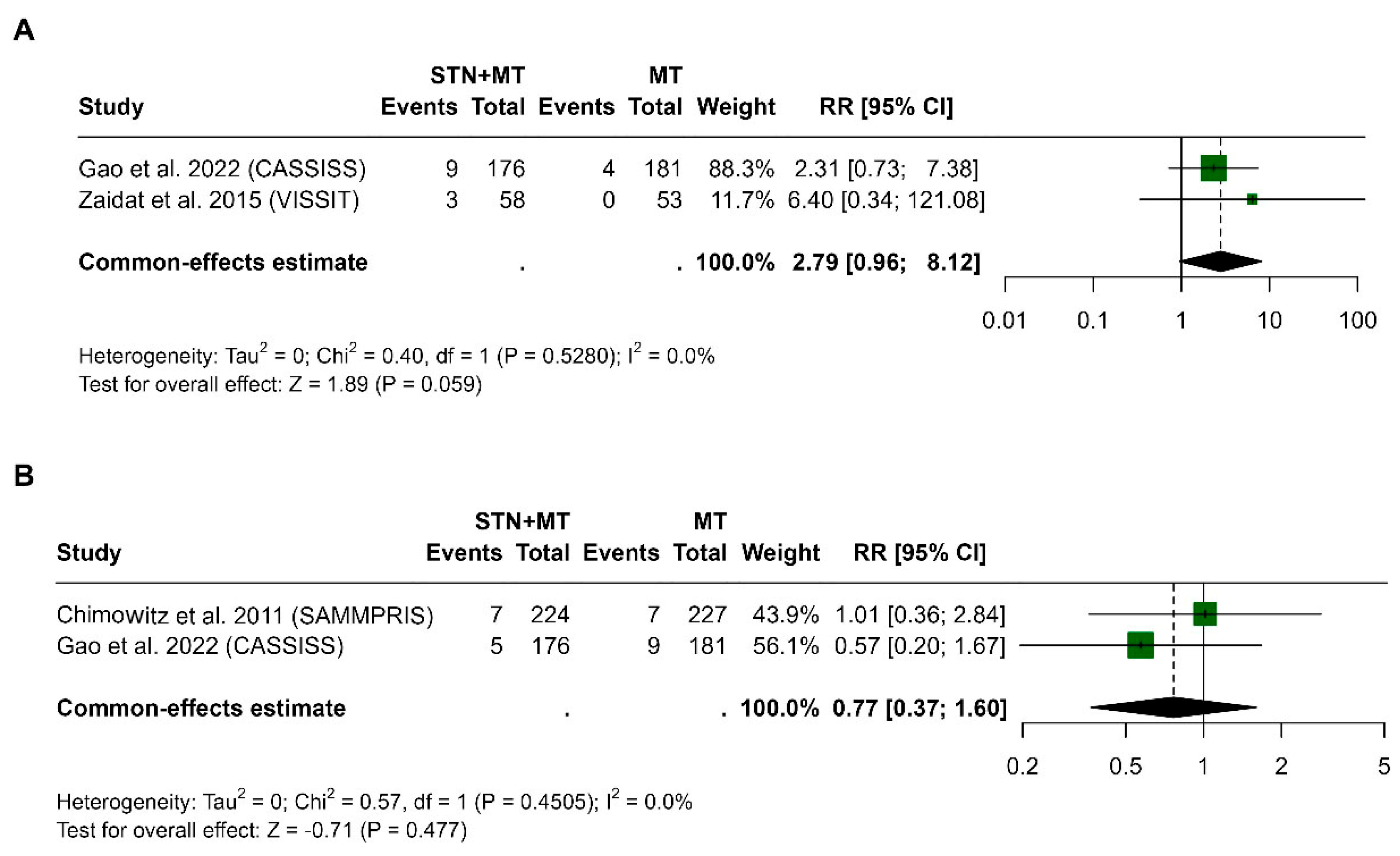
3.3. Death at 30 Days and 1 Year
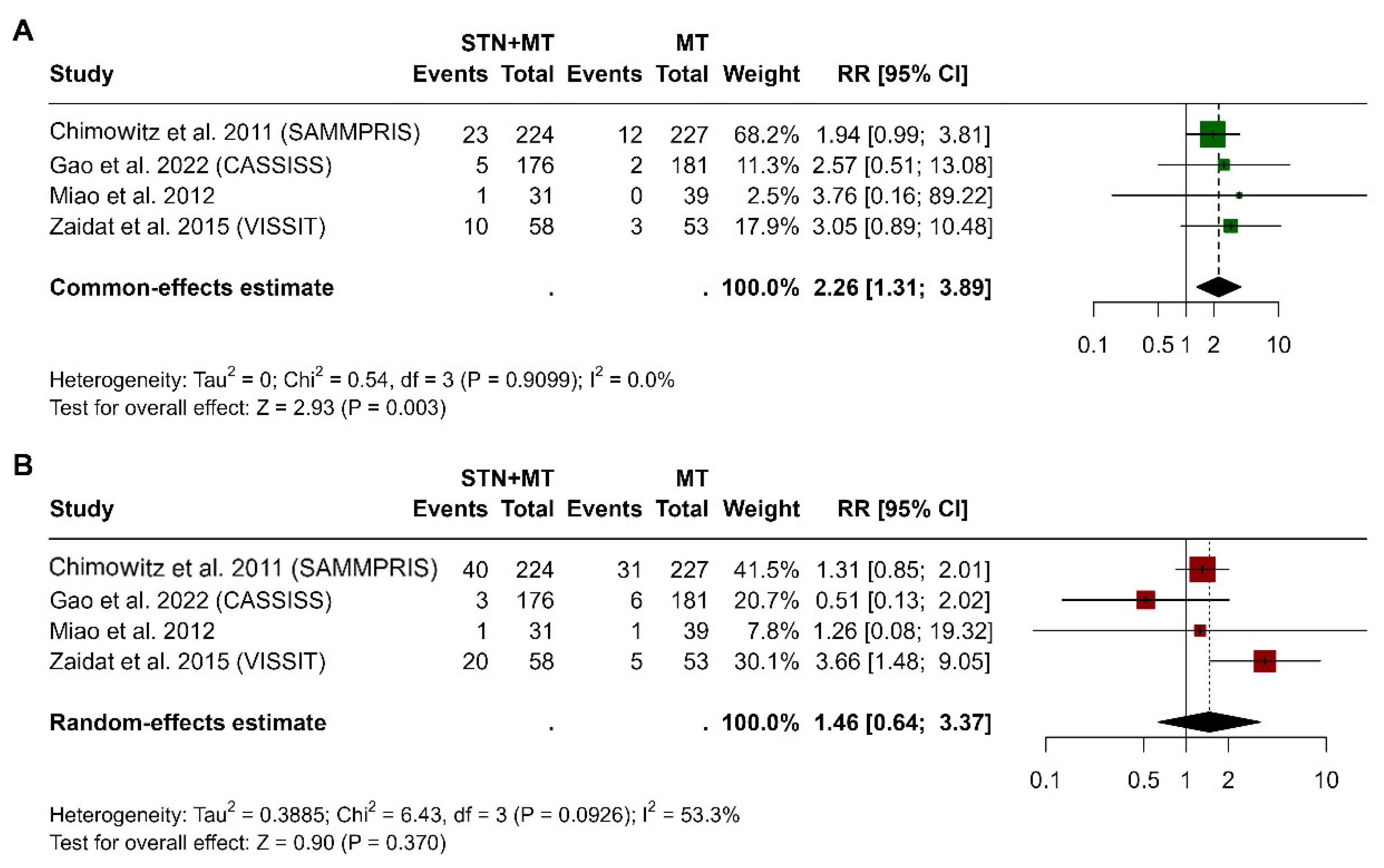
3.4. Stroke at 30 Days and 1 Year
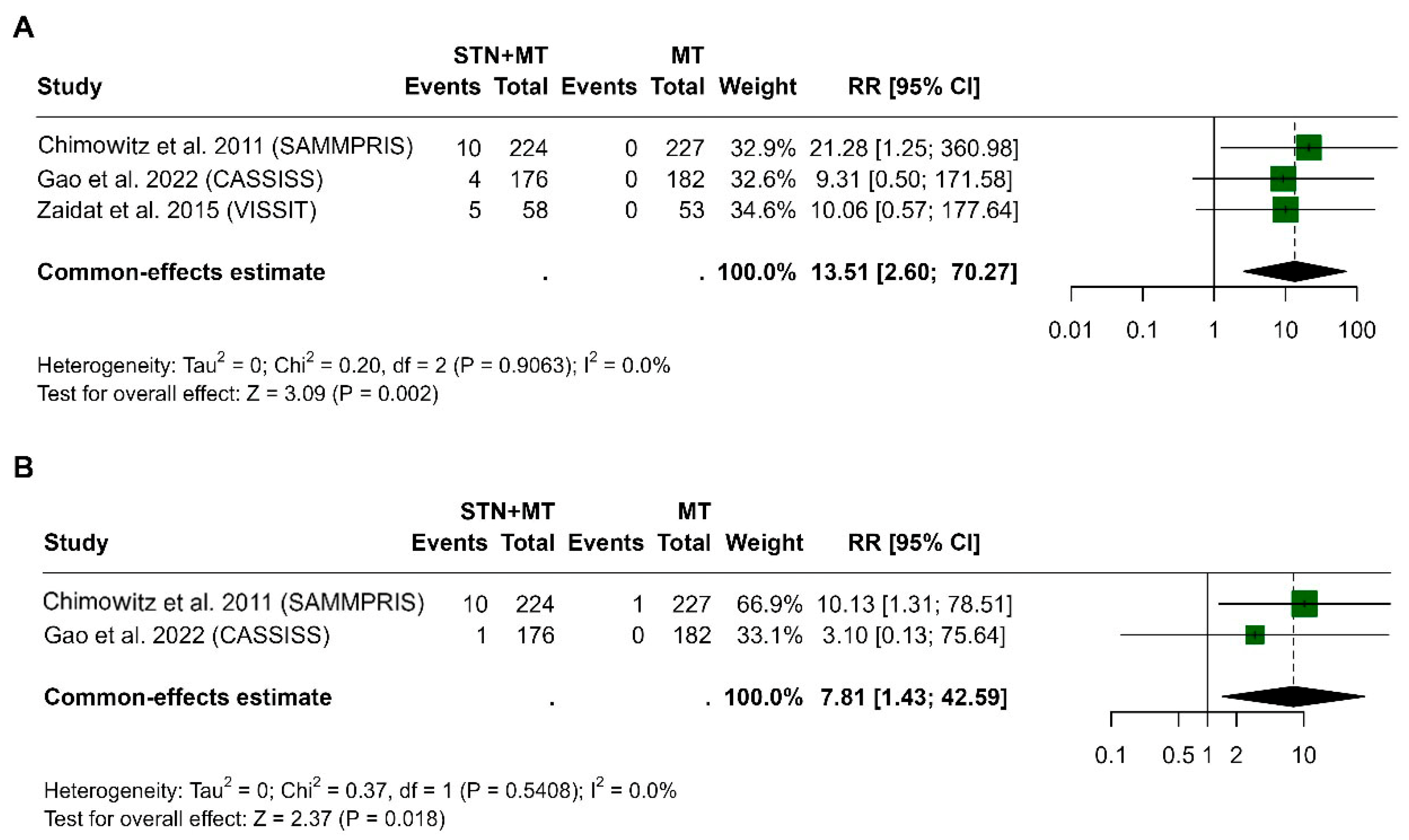
3.5. Intracerebral Hemorrhage at 30 Days and 1 Year
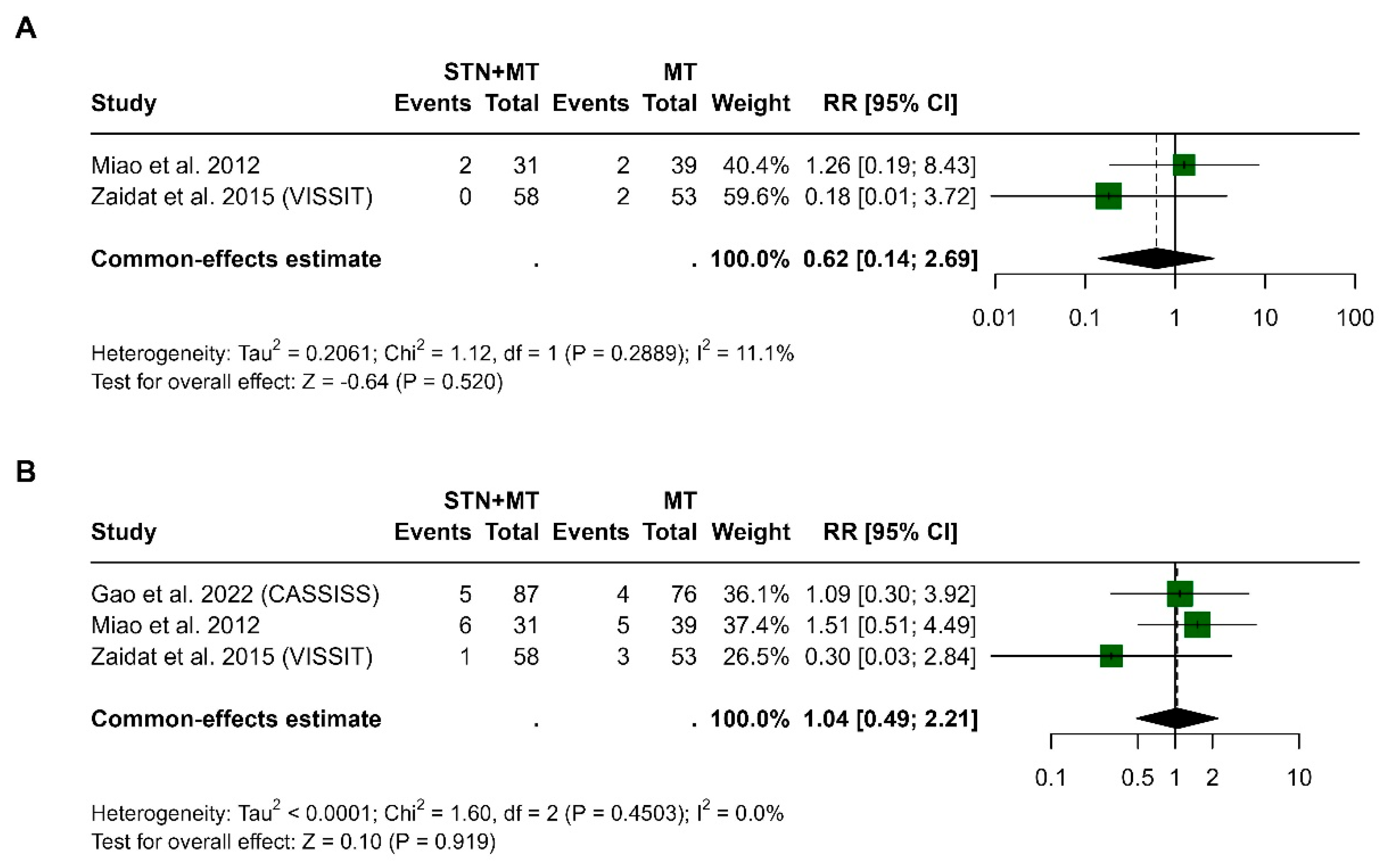
3.6. Transient Ischemic Attack at 30 Days and 1 Year
3.7. Publication Bias
3.8. Meta-Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
Limitations and Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICAS | Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis |
| PTAS | Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty and Stenting |
| STN+MT | Stenting Plus Medical Therapy |
| MT | Medical Therapy |
| TIA | Transient Ischemic Attack |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| SAMMPRIS | Stenting and Aggressive Medical Management for Preventing Recurrent Stroke in Intracranial Stenosis |
| VISSIT | Vitesse Intracranial Stent Study for Ischemic Stroke Therapy |
| CASSISS | Chinese Angioplasty and Stenting for Symptomatic Intracranial Severe Stenosis |
| BASIS | Balloon Angioplasty vs. Best Medical Therapy in Symptomatic ICAS |
| WEAVE | Wingspan Stent System Post Market Surveillance Study |
| ICH | Intracerebral Hemorrhage |
References
- World Health Organization. The Top 10 Causes of Death. World Health Organization. Published 7 August 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Feigin, V.L.; Stark, B.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Roth, G.A.; Bisignano, C.; Abady, G.G.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abedi, V.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suri, M.F.; Johnston, S.C. Epidemiology of intracranial stenosis. J. Neuroimaging 2009, 19, 11S–16S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.H.; Spagnolo-Allende, A.; Yang, D.; Qiao, Y.; Gutierrez, J. Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Imaging of Atherosclerotic Intracranial Disease. Stroke 2024, 55, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- White, H.; Boden-Albala, B.; Wang, C.; Elkind, M.S.; Rundek, T.; Wright, C.B.; Sacco, R.L. Ischemic stroke subtype incidence among whites, blacks, and Hispanics: The Northern Manhattan Study. Circulation 2005, 111, 1327–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J. The Latest Information on Intracranial Atherosclerosis: Diagnosis and Treatment. Interv. Neurol. 2015, 4, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Albakr, A.; Shahid, R.; Alkhamis, F.; Alabdali, M.; Aljaafari, D.; Nazish, S.F.; Ishaque, N.F.; Soltan, N.M.M.; Msmar, A.H.; et al. Prevalence and Clinico-Radiologic Spectrum of Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease-Related Stroke: An Observation from a Single Center in Saudi Arabia. Neurologist 2023, 28, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasteva, M.P.; Lau, K.K.; Mordasini, P.; Tsang, A.C.O.; Heldner, M.R. Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenoses: Pathophysiology, Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Current Therapy Options. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 1829–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Panagiotopoulos, E.; Stefanou, M.I.; Magoufis, G.; Safouris, A.; Kargiotis, O.; Psychogios, K.; Vassilopoulou, S.; Theodorou, A.; Chondrogianni, M.; Bakola, E.; et al. Prevalence, diagnosis and management of intracranial atherosclerosis in White populations: A narrative review. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2024, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballout, A.A.; Liebeskind, D.S. Recurrent stroke risk in intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1001609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Muzio, B. Basilar Artery Stenosis. Case Study, Radiopaedia.org. Available online: https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-30288 (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Luo, J.; Wang, T.; Gao, P.; Krings, T.; Jiao, L. Endovascular Treatment of Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis: Current Debates and Future Prospects. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimowitz, M.I.; Lynn, M.J.; Derdeyn, C.P.; Turan, T.N.; Fiorella, D.; Lane, B.F.; Janis, L.S.; Lutsep, H.L.; Barnwell, S.L.; Waters, M.F.; et al. Stenting versus aggressive medical therapy for intracranial arterial stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 993–1003, Published Correction Appears in N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Fitzsimmons, B.F.; Woodward, B.K.; Wang, Z.; Killer-Oberpfalzer, M.; Wakhloo, A.; Gupta, R.; Kirshner, H.; Megerian, J.T.; Lesko, J.; et al. Effect of a balloon-expandable intracranial stent vs medical therapy on risk of stroke in patients with symptomatic intracranial stenosis: The VISSIT randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2015, 313, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Wang, T.; Wang, D.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Shi, H.; Li, T.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, Y.; Wu, W.; He, W.; et al. Effect of Stenting Plus Medical Therapy vs Medical Therapy Alone on Risk of Stroke and Death in Patients with Symptomatic Intracranial Stenosis: The CASSISS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 328, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wu, H.; Bao, Y.; Jiao, L.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Hua, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of symptomatic middle cerebral artery stenosis: Endovascular versus medical therapy in a Chinese population. Stroke 2012, 43, 3284–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wabnitz, A.; Chimowitz, M. Angioplasty, Stenting and Other Potential Treatments of Atherosclerotic Stenosis of the Intracranial Arteries: Past, Present and Future. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doheim, M.F.; Al-Bayati, A.R.; Bhatt, N.R.; Lang, M.; Starr, M.; Rocha, M.; Gross, B.A.; Nogueira, R.G. Intracranial stenting versus aggressive medical therapy for symptomatic intracranial stenosis: A meta-analysis of multicenter randomized controlled trials and an expert assessment of the current data. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, T.; Yang, K.; Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Gong, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, R.; Gao, P.; et al. Endovascular therapy versus medical treatment for symptomatic intracranial artery stenosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 2, CD013267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Zou, Y.; Tang, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z. Comparative effect of stenting plus medical therapy vs medical therapy alone on the risk of stroke and death in patients with symptomatic intracranial stenosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsivgoulis, G.; Katsanos, A.H.; Magoufis, G.; Kargiotis, O.; Papadimitropoulos, G.; Vadikolias, K.; Karapanayiotides, T.; Ellul, J.; Mitsias, P.D.; Alexandrov, A.V. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty and stenting for symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2016, 9, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.J.; Zauner, A.; Chaloupka, J.C.; Baxter, B.; Callison, R.C.; Gupta, R.; Song, S.S.; Yu, W. WEAVE Trial: Final Results in 152 On-Label Patients. Stroke 2019, 50, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Shuai, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, K.; Liu, L.; Li, B.; Shi, X.; Gao, L.; et al. Balloon-mounted stenting for ICAS in a multicenter registry study in China: A comparison with the WEAVE/WOVEN trial. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2021, 13, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Sun, D.; Nguyen, T.N.; Tong, X.; Peng, G.; Liu, A.; Xu, Y.; et al. Balloon Angioplasty vs Medical Management for Intracranial Artery Stenosis: The BASIS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 332, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
|
|
| Authors | Country | Sample Size/Male/Female | Number of Patients (N) | Active Smokers (N) | Age (Mean ± SD, Years) | Stent Type in the Intervention Group (STN+MT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STN+MT/MT Alone | STN+MT/MT Alone | STN+MT/MT Alone | ||||
| Chimowitz et al., 2011 (SAMMPRIS) [13] | USA | 451 (272/179) | 224/227 | 54/69 | 61 ± 10.7/59.5 ± 11.8 | Wingspan stent |
| Miao et al., 2012 [16] | China | 70 (49/21) | 31/39 | 21/19 | 53.42 ± 13.55/49.18 ± 9.29 | Balloon Angioplasty: 4, Wingspan stent: 7, Coroflex blue: 17, PTA Firebird stent: 1 |
| Zaidat et al., 2015 (VISSIT) [14] | International | 111 (73/38) | 58/53 | 11/12 | 61.8 ± 12.28/61.8 ± 12.28 | Balloon-expanding stent |
| Gao et al., 2022 (CASSISS) [15] | China | 358 (263/95) | 176/182 | 41/50 | 56.7 ± 9.4/55.9 ± 9.8 | Wingspan stent |
| Authors | Stroke as a Cause of the Intervention | TIA as a Cause of the Intervention | Arteries Affected | Time from Event to Randomization (Mean ± SD) | Degree of Arterial Stenosis (Mean ± SD) | Receiving Antithrombotic Before Event | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STN+MT/MT Alone | STN+MT/MT Alone | STN+MT | MT Alone | STN+MT/MT Alone | STN+MT/MT Alone | STN+MT/MT Alone | |
| Chimowitz et al., 2011 (SAMMPRIS) [13] | 142/152 | 82/75 | ICA: 45 (20.1), MCA: 92 (41.1), Vertebral 38 (17), Basilar: 49 (21.9) | ICA: 49 (21.6), MCA: 105 (46.3), Vertebral: 22 (9.7), Basilar: 51 (22.5 | 9.0 ± 9.0/6.7 ± 3.7 | 80.0 ± 7.0/81.0 ± 7.0 | 145/141 |
| Miao et al., 2012 [16] | 7/8 | 29/26 | Left MCA: 12, Right MCA: 24 | Left MCA: 18, Right MCA: 16 | NA | 83.9 ± 8.1/85.0 ± 6.7 | NA |
| Zaidat et al. 2015 (VISSIT) [14] | 36/34 | 24/22 | NA | NA | 12.3 ± 9.6/15.2 ± 10.3 | 78.9 ± 7.3/80.4 ± 7.5 | NA |
| Gao et al., 2022 (CASSISS) [15] | 89/105 | 87/77 | MCA (M1): 65 (36.9), Basilar artery: 50 (28.4), Intracranial vertebral artery: 46 (26.1), Intracranial internal carotid artery 15 (8.5) | MCA (M1): 79 (43.4), Basilar artery: 52 (28.6), Intracranial vertebral artery: 34 (18.7), Intracranial internal carotid artery 17 (9.3) | 42.3 ± 28.8/44.0 ± 29.9 | 78.4 ± 6.4/76.9 ± 5.8 | 49/48 |
| Characteristic | Stroke at 30 Days | Stroke at 1 Year | Intracerebral Hemorrhage at 30 Days | Transient Ischemic Attack at 1 Year | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta | 95% CI | p-Value | Beta | 95% CI | p-Value | Beta | 95% CI | p-Value | Beta | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Age | −0.02 | −0.28, 0.23 | 0.852 | 0.17 | −0.07, 0.40 | 0.161 | 0.05 | −0.67, 0.77 | 0.887 | −0.12 | −0.33, 0.09 | 0.247 |
| Year of publication | 0.03 | −0.12, 0.19 | 0.662 | −0.08 | −0.32, 0.15 | 0.499 | −0.07 | −0.43, 0.30 | 0.713 | −0.01 | −0.27, 0.24 | 0.917 |
| Proportion of males | 0.03 | −0.09, 0.16 | 0.580 | −0.06 | −0.27, 0.14 | 0.531 | −0.06 | −0.37, 0.25 | 0.703 | 0.12 | −0.22, 0.45 | 0.495 |
| Smoking | 0.00 | −0.09, 0.09 | 0.982 | −0.02 | −0.11, 0.07 | 0.665 | 0.09 | −0.51, 0.69 | 0.768 | 0.02 | −0.03, 0.07 | 0.375 |
| Stroke as a cause of intervention | −0.02 | −0.08, 0.05 | 0.656 | 0.02 | −0.06, 0.09 | 0.664 | 0.06 | −0.29, 0.41 | 0.752 | −0.02 | −0.07, 0.02 | 0.345 |
| TIA as a cause of intervention | 0.02 | −0.05, 0.09 | 0.575 | −0.01 | −0.09, 0.07 | 0.834 | −0.08 | −0.44, 0.29 | 0.673 | 0.02 | −0.03, 0.07 | 0.379 |
| Degree of arterial stenosis | −0.03 | −0.49, 0.43 | 0.911 | 0.11 | −0.40, 0.63 | 0.674 | 0.25 | −1.14, 1.64 | 0.725 | 0.08 | −0.22, 0.38 | 0.604 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bin Aziz, K.; Alhathlol, H.; Bin Aziz, F.; Alshammari, M.; Alhefdhi, M.A.; Alrasheed, A.M.; Alfayez, N.; Alhowaish, T.S. Comparing Stenting with Medical Therapy Versus Medical Therapy Alone in Patients with Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis: A Current Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15060113
Bin Aziz K, Alhathlol H, Bin Aziz F, Alshammari M, Alhefdhi MA, Alrasheed AM, Alfayez N, Alhowaish TS. Comparing Stenting with Medical Therapy Versus Medical Therapy Alone in Patients with Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis: A Current Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clinics and Practice. 2025; 15(6):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15060113
Chicago/Turabian StyleBin Aziz, Khalid, Hussam Alhathlol, Fahad Bin Aziz, Mohammed Alshammari, Mohammed Ali Alhefdhi, Abdulrahman M. Alrasheed, Nawwaf Alfayez, and Thamer S. Alhowaish. 2025. "Comparing Stenting with Medical Therapy Versus Medical Therapy Alone in Patients with Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis: A Current Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Clinics and Practice 15, no. 6: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15060113
APA StyleBin Aziz, K., Alhathlol, H., Bin Aziz, F., Alshammari, M., Alhefdhi, M. A., Alrasheed, A. M., Alfayez, N., & Alhowaish, T. S. (2025). Comparing Stenting with Medical Therapy Versus Medical Therapy Alone in Patients with Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis: A Current Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clinics and Practice, 15(6), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15060113





