Eleven-Year Incidence of Salivary Gland Tumors—A Retrospective, Single-Centered Study in Croatia
Abstract
1. Introduction
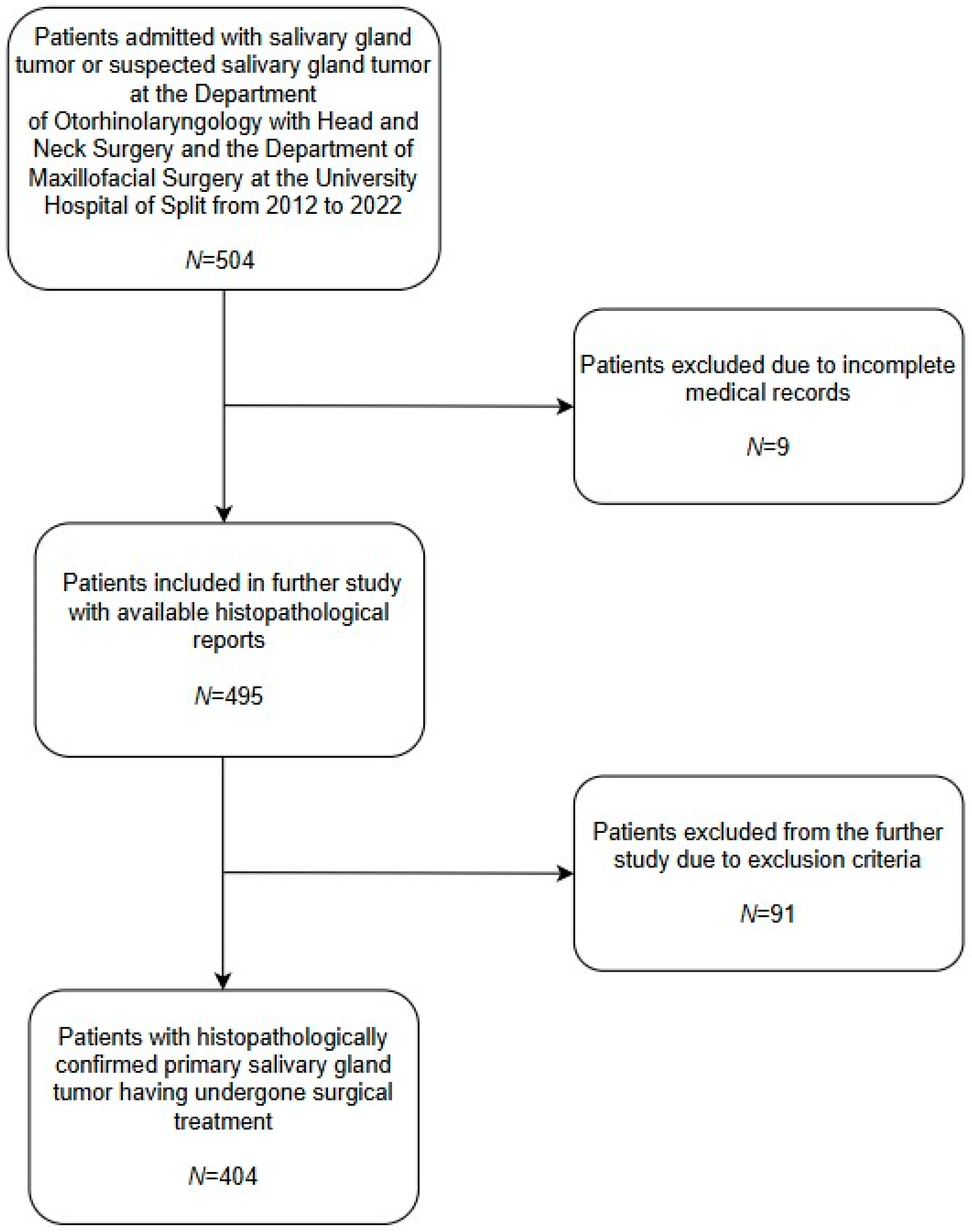
2. Materials and Methods
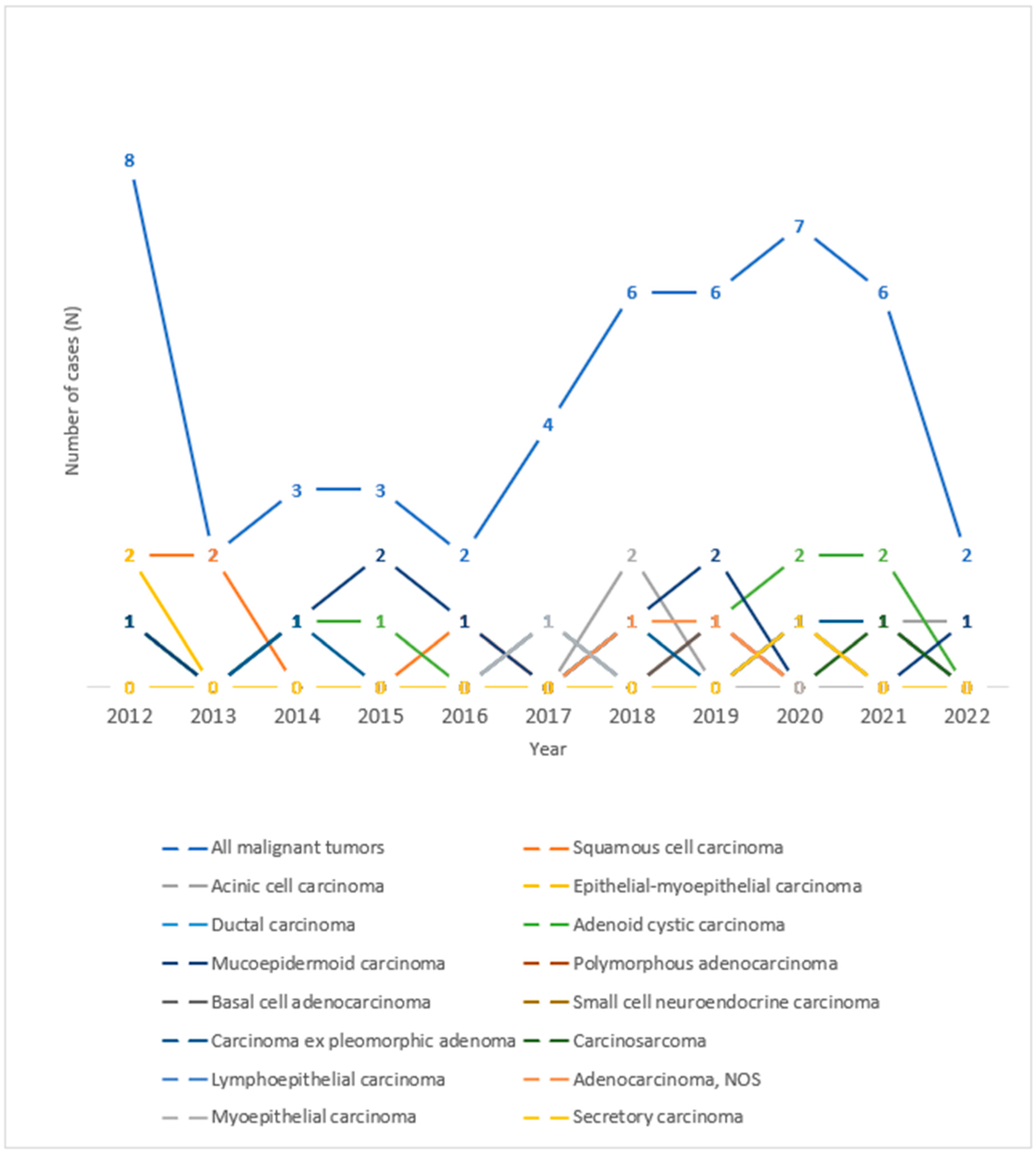
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| SCC | Squamous cell carcinoma |
| BCC | Basal cell carcinoma |
References
- Stryjewska-Makuch, G.; Kolebacz, B.; Janik, M.A.; Wolnik, A. Increase in the incidence of parotid gland tumors in the years 2005-2014. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2017, 71, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.H.; Lee, K.W.; Chiang, F.Y.; Ho, K.Y.; Chai, C.Y.; Kuo, W.R. Features of parotid gland diseases and surgical results in southern Taiwan. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2010, 26, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, F.P.; Carvalho Mde, V.; de Almeida, O.P.; Rangel, A.L.; Takizawa, M.C.; Bueno, A.G.; Vargas, P.A. Clinicopathologic analysis of 493 cases of salivary gland tumors in a Southern Brazilian population. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2012, 114, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, P.A.; Gerhard, R.; Araújo Filho, V.J.; de Castro, I.V. Salivary gland tumors in a Brazilian population: A retrospective study of 124 cases. Rev. Hosp. Clin. 2002, 57, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, L.; Eveson, J.W.; Reichart, P.A.; Sidranskiy, D. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. In Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumours; IARC: Lyon, France, 2005; pp. 211–281. Available online: https://screening.iarc.fr/doc/BB9.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Parkin, D.M.; Whelan, S.L.; Ferlay, J.; Teppo, L.; Thomas, D.B. Cancer Incidence in Five Continents, Vol. VIII. IARC Scientific Publications No.155; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2002; Available online: https://publications.iarc.fr/Book-And-Report-Series/Iarc-Scientific-Publications/Cancer-Incidence-In-Five-Continents-Volume-VIII-2002 (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Kordzińska-Cisek, I.; Grzybowska-Szatkowska, L. Salivary gland cancer —Epidemiology. Nowotw. J. Oncol. 2018, 68, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzo, M.; Locati, L.D.; Prott, F.J.; Gatta, G.; McGurk, M.; Licitra, L. Major and minor salivary gland tumors. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2010, 74, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.K.; Morton, R.P. Demographics of benign parotid tumors: Warthin’s tumor versus other benign salivary tumors. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016, 136, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawabe, M.; Ito, H.; Takahara, T.; Oze, I.; Kawakita, D.; Yatabe, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Murakami, S.; Matsuo, K. Heterogeneous impact of smoking on major salivary gland cancer according to histopathological subtype: A case-control study. Cancer 2018, 124, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, G.; Guzzo, M.; Locati, L.D.; McGurk, M.; Prott, F.J. Major and minor salivary gland tumors. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 152, 102959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantù, G. Adenoid cystic carcinoma. An indolent but aggressive tumor. Part A: From aetiopathogenesis to diagnosis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. Organo Uff. Della Soc. Ital. Otorinolaringol. E Chir. Cerv-Facc. 2021, 41, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, G.M.; Burns, P.B. Cancers of the salivary gland: Workplace risks among women and men. Ann. Epidemiol. 1997, 7, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, J.; Campbell, P.; Kreiger, N.; Sloan, M. Salivary gland cancer: An exploratory analysis of dietary factors. Nutr. Cancer 2008, 60, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn-Ross, P.L.; Ljung, B.M.; Morrow, M. Environmental factors and the risk of salivary gland cancer. Epidemiology 1997, 8, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, E.S.; Ramos, J.C.; Normando, A.G.C.; Mariano, F.V.; Paes Leme, A.F. Epigenetic alterations in salivary gland tumors. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 1610–1618, Erratum in: Oral Dis. 2023, 29, 853. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.13819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walvekar, R.; Phalke, N.P. The Evaluation and Management of Carcinoma of the Minor Salivary Glands. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 54, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Cho, J.; Ryu, J.; Jeong, H.S. Diagnosis and management of malignant sublingual gland tumors: A narrative review. Gland Surg. 2021, 10, 3415–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalgic, A.; Karakoc, O.; Aydin, U.; Hidir, Y.; Gamsizkan, M.; Karahatay, S.; Gerek, M. Minor salivary gland neoplasms. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2014, 25, e289–e291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukšić, I.; Virag, M.; Manojlović, S.; Macan, D. Salivary gland tumors: 25 years of experience from a single institution in Croatia. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 40, e75–e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val-Bernal, J.F.; Mayorga, M.M.; Martín-Soler, P.; Obeso, S.; Alonso-Fernández, E.M.; López-Rasines, G. Synchronous Warthin Tumor and Papillary Oncocytic Cystadenoma in the Ipsilateral Parotid Gland: An Unreported Association. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2019, 60, 993–1002. Available online: https://www.rjme.ro/RJME/resources/files/6003199931002.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Klamminger, G.G.; Issing, C.; Burck, I.; Herr, C.; Endemann, E.; Stöver, T.; Wild, P.J.; Winkelmann, R. Uncommon Coexistence of Pleomorphic Adenoma and Warthin’s Tumor in a Painfully Swollen Left Parotid Gland: A Surgical Case Report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2023, 24, e940985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, Y.; Sakaguchi, R. Synchronous oncocytoma and Warthin’s tumor in the ipsilateral parotid gland. Auris Nasus Larynx 2004, 31, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavrianos, S.D.; McLean, N.R.; Soames, J.V. Synchronous unilateral parotid neoplasms of different histological types. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 1999, 25, 331–332. [Google Scholar]
- Gnepp, D.R.; Schroeder, W.; Heffner, D. Synchronous tumors arising in a single major salivary gland. Cancer 1989, 63, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żurek, M.; Fus, Ł.; Niemczyk, K.; Rzepakowska, A. Salivary gland pathologies: Evolution in classification and association with unique genetic alterations. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 280, 4739–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gontarz, M.; Bargiel, J.; Gąsiorowski, K.; Marecik, T.; Szczurowski, P.; Zapała, J.; Wyszyńska-Pawelec, G. Epidemiology of primary epithelial salivary gland tumors in Southern Poland—A 26-year, clinicopathologic, retrospective analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, J.; Martinez, R.; Niklander, S.; Marshall, M.; Esguep, A. Incidence and prevalence of salivary gland tumors in Valparaiso, Chile. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2015, 20, e532–e539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, S.; Therkildsen, M.H.; Bjørndal, K.; Homøe, P. Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland 1985-2010: A Danish nationwide study of incidence, recurrence rate, and malignant transformation. Head Neck 2016, 38, E1364–E1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Aneja, A.; Ghossein, R.; Katabi, N. Salivary gland epithelial neoplasms in pediatric population: A single-institute experience with a focus on the histologic spectrum and clinical outcome. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 67, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauro, F.; Cianfrone, F.; Ralli, M. Retrospective Study of Salivary Gland Tumor Cases in a Large Italian Public Hospital and Review of the Literature. Clin. Ter. 2021, 172, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.J.; McGurk, M. Incidence of salivary gland neoplasms in a defined UK population. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 51, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, B.W.; Silva, L.P.; Serpa, M.S.; Borges, M.d.A.; Moura, S.; Silveira, M.; Sobral, A. Incidence and profile of benign epithelial tumors of salivary glands from a single center in Northeast of Brazil. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2021, 26, e108–e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westergaard-Nielsen, M.; Godballe, C.; Eriksen, J.G.; Larsen, S.R.; Kiss, K.; Agander, T.; Ulhøi, B.P.; Charabi, B.; Klug, T.E.; Jacobsen, H.; et al. Salivary gland carcinoma in Denmark: A national update and follow-up on incidence, histology, and outcome. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 278, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivunen, P.; Suutala, L.; Schorsch, I.; Jokinen, K.; Alho, O.P. Malignant epithelial salivary gland tumors in northern Finland: Incidence and clinical characteristics. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2002, 259, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Xu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Yang, W. Simultaneous occurrence of benign and malignant tumors in the ipsilateral parotid gland—Retrospective study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafari-Ashkavandi, Z.; Khademi, B.; Malekzadeh, M.; Shahmoradi, Z. Serum Levels of Zinc, Copper and Ferritin in Patients with Salivary Gland Tumors. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubiński, J.; Lener, M.R.; Marciniak, W.; Pietrzak, S.; Derkacz, R.; Cybulski, C.; Gronwald, J.; Dębniak, T.; Jakubowska, A.; Huzarski, T.; et al. Serum Essential Elements and Survival after Cancer Diagnosis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Histological Type | Occurrence † | Gender | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | |||
| Benign tumors | ||||
| Pleomorphic adenoma | 169 (41.2) | 107 (63.3) | 62 (36.7) | <0.001 a* |
| Warthin’s tumor | 156 (38) | 60 (38.5) | 96 (61.5) | <0.001 a* |
| Myoepithelioma | 8 (2) | 5 (62.5) | 3 (37.5) | 0.726 b |
| Basal cell adenoma | 20 (4.9) | 14 (70) | 6 (30) | 0.113 b |
| Oncocytoma | 3 (0.7) | 0 | 3 (100) | 0.108 b |
| Cystadenoma | 4 (1) | 0 | 4 (100) | 0.051 b |
| Canalicular adenoma | 1 (0.2) | 1 (100) | 0 | 1.0 b |
| All benign tumors | 361 | 188 (52.1) | 173 (47.9) | <0.001 a* |
| Malignant tumors | ||||
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 7 (1.7) | 0 | 7 (100) | 0.005 b* |
| Acinic cell carcinoma | 5 (1.2) | 5 (100) | 0 | 0.062 b |
| Epithelial–myoepithelial carcinoma | 3 (0.7) | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | 0.608 b |
| Ductal carcinoma | 3 (0.7) | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.7) | 0.608 b |
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma | 9 (2.2) | 5 (55.6) | 4 (44.4) | 1.0 b |
| Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | 9 (2.2) | 7 (77.8) | 2 (22.2) | 0.179 b |
| Polymorphous adenocarcinoma | 1 (0.2) | 1 (100) | 0 | 1.0 b |
| Basal cell adenocarcinoma | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 1 (100) | 0.478 b |
| Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 1 (100) | 0.478 b |
| Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma | 4 (1) | 1 (25) | 3 (75) | 0.353 b |
| Carcinosarcoma | 1 (0.2) | 1 (100) | 0 | 1.0 b |
| Lymphoepithelial carcinoma | 1 (0.2) | 1 (100) | 0 | 1.0 b |
| Adenocarcinoma, NOS | 2 (0.5) | 2 (100) | 0 | 0.500 b |
| Myoepithelial carcinoma | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 1 (100) | 0.478 b |
| Secretory carcinoma | 1 (0.2) | 1 (100) | 0 | 1.0 b |
| All malignant tumors | 49 | 26 (53.1) | 23 (46.9) | 0.044 b* |
| Histological Type | Occurrence † | Age | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | |||
| Benign tumors | ||||
| Pleomorphic adenoma | 169 (41.2) | 55 (5–84) CI (48.7–55.5) | 53.5 (9–82) CI (47.9–53.5) | 0.965 |
| Warthin’s tumor | 156 (38) | 62 (30–84) CI (59.2–62) | 63 (31–85) CI (59.6–63.4) | 0.857 |
| Myoepithelioma | 8 (2) | 42 (36–84) CI (25.3–74.7) | 49 (37–52) CI (26.2–65.7) | 0.881 |
| Basal cell adenoma | 20 (4.9) | 60 (33–76) CI (52.2–67.4) | 59.5 (33–81) CI (41.8–78.9) | 0.869 |
| Oncocytoma | 3 (0.7) | 0 | 70 (59–73) CI (49–85.6) | Na |
| Cystadenoma | 4 (1) | 0 | 55.5 (49–85) CI (35.2–87.3) | Na |
| Canalicular adenoma | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 0 | Na |
| All benign tumors | 361 | 59 (5–84) CI (53.1–57.7) | 60 (9–85) CI (55.9–61.2) | 0.221 |
| Malignant tumors | ||||
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 7 (1.7) | 0 | 80 (43–82) CI (59.3–85.3) | Na |
| Acinic cell carcinoma | 5 (1.2) | 50 (27–79) CI (20.5–82.7) | 0 | Na |
| Epithelial–myoepithelial carcinoma | 3 (0.7) | 0 | 39.5 (29–50) CI (22.7–43.8) | Na |
| Ductal carcinoma | 3 (0.7) | 0 | 76 (75–77) CI (73.9–86.2) | Na |
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma | 9 (2.2) | 74 (69–79) CI (68.8–78.4) | 55.5 (29–65) CI (26.6–75.9) | 0.016 * |
| Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | 9 (2.2) | 54 (36–79) CI (43.5–67.6) | 70 (65–75) CI (6.5–133.5) | 0.184 |
| Polymorphous adenocarcinoma | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 0 | Na |
| Basal cell adenocarcinoma | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 0 | Na |
| Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 0 | Na |
| Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma | 4 (1) | 0 | 46 (39–82) CI (34.8–50.1) | Na |
| Carcinosarcoma | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 0 | Na |
| Lymphoepithelial carcinoma | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 0 | Na |
| Adenocarcinoma, NOS | 2 (0.5) | 48 (29–67) CI (19.2–56.3) | 0 | Na |
| Myoepithelial carcinoma | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 0 | Na |
| Secretory carcinoma | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 0 | Na |
| All malignant tumors | 49 | 59 (28–85) CI (51.6–66.7) | 70 (29–82) CI (55.5–71.7) | 0.283 |
| Histological Type | Parotid Gland | Submandibular Gland | Sublingual Gland | Minor Salivary Glands |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign tumors | ||||
| Warthin’s tumor | 155 (47.0) | 1 (4.4) | 0 | 0 |
| Pleomorphic adenoma | 144 (43.6) | 20 (86.9) | 0 | 5 (62.5) |
| Basal cell adenoma | 17 (5.7) | 1 (4.4) | 0 | 2 (25) |
| Myoepithelioma | 6 (1.8) | 1 (4.4) | 0 | 1 (12.5) |
| Cystadenoma | 4 (1.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Oncocytoma | 3 (0.9) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Canalicular adenoma | 1 (0.3) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| All benign tumors | 330 | 23 | 0 | 8 |
| Malignant tumors | ||||
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 5 (16.1) | 2 (20) | 0 | 0 |
| Acinic cell carcinoma | 5 (16.1) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | 5 (16.1) | 1 (10) | 0 | 3 (37.5) |
| Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma | 4 (12.9) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ductal carcinoma | 3 (9.7) | 0 | 0 | |
| Epithelial–myoepithelial carcinoma | 1 (3.2) | 2 (20) | 0 | 0 |
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma | 1 (3.2) | 5 (50) | 0 | 3 (37.5) |
| Polymorphous adenocarcinoma | 1 (3.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Basal cell adenocarcinoma | 1 (3.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma | 1 (3.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Carcinosarcoma | 1 (3.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Lymphoepithelial carcinoma | 1 (3.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Adenocarcinoma, NOS | 1 (3.2) | 0 | 0 | 1 (12.5) |
| Secretory carcinoma | 1 (3.2) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Myoepithelial carcinoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (12.5) |
| All malignant tumors | 31 | 10 | 0 | 8 |
| Total | 361 | 33 | 0 | 16 |
| Histological Type | Minor Salivary Glands | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palate | Floor of the Mouth | Buccal Mucosa | Lip | Total | |
| Benign tumors | |||||
| Warthin’s tumor | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pleomorphic adenoma | 5 (71.4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 (62.5) |
| Basal cell adenoma | 1 (14.3) | 0 | 1 (100) | 0 | 2 (25) |
| Myoepithelioma | 1 (14.3) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (12.5) |
| Cystadenoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Oncocytoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Canalicular adenoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| All benign tumors | 7 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 8 |
| Malignant tumors | |||||
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Acinic cell carcinoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | 2 (40) | 1 (100) | 0 | 0 | 3 (37.5) |
| Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ductal carcinoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Epithelial–myoepithelial carcinoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma | 2 (40) | 0 | 1 (100) | 0 | 3 (37.5) |
| Polymorphous adenocarcinoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Basal cell adenocarcinoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Carcinosarcoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Lymphoepithelial carcinoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Adenocarcinoma, NOS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (100) | 1 (12.5) |
| Secretory carcinoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Myoepithelial carcinoma | 1 (20) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (12.5) |
| All malignant tumors | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| Total | 12 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 16 |
| Year | Population Sample | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dalmatian Counties | Republic of Croatia | |||
| Benign Tumors | Malignant Tumors | Benign Tumors | Malignant Tumors | |
| 2012 | 2.80 | 0.94 | 0.56 | 0.19 |
| 2013 | 3.28 | 0.23 | 0.66 | 0.05 |
| 2014 | 2.34 | 0.35 | 0.47 | 0.07 |
| 2015 | 2.82 | 0.35 | 0.57 | 0.07 |
| 2016 | 3.90 | 0.24 | 0.79 | 0.05 |
| 2017 | 5.47 | 0.48 | 1.12 | 0.1 |
| 2018 | 4.18 | 0.72 | 0.86 | 0.15 |
| 2019 | 6.09 | 0.72 | 1.26 | 0.15 |
| 2020 | 4.42 | 0.84 | 0.91 | 0.17 |
| 2021 | 3.77 | 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.15 |
| 2022 | 4.15 | 0.25 | 0.86 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Modrić, A.; Gabelica, M.; Mihovilović, A.; Dumančić, S.; Dunatov Huljev, A.; Medvedec Mikić, I. Eleven-Year Incidence of Salivary Gland Tumors—A Retrospective, Single-Centered Study in Croatia. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15060104
Modrić A, Gabelica M, Mihovilović A, Dumančić S, Dunatov Huljev A, Medvedec Mikić I. Eleven-Year Incidence of Salivary Gland Tumors—A Retrospective, Single-Centered Study in Croatia. Clinics and Practice. 2025; 15(6):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15060104
Chicago/Turabian StyleModrić, Anđela, Mirko Gabelica, Ante Mihovilović, Stipe Dumančić, Ana Dunatov Huljev, and Ivana Medvedec Mikić. 2025. "Eleven-Year Incidence of Salivary Gland Tumors—A Retrospective, Single-Centered Study in Croatia" Clinics and Practice 15, no. 6: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15060104
APA StyleModrić, A., Gabelica, M., Mihovilović, A., Dumančić, S., Dunatov Huljev, A., & Medvedec Mikić, I. (2025). Eleven-Year Incidence of Salivary Gland Tumors—A Retrospective, Single-Centered Study in Croatia. Clinics and Practice, 15(6), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15060104







