Triggers, Types, and Treatments for Kounis Syndrome: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
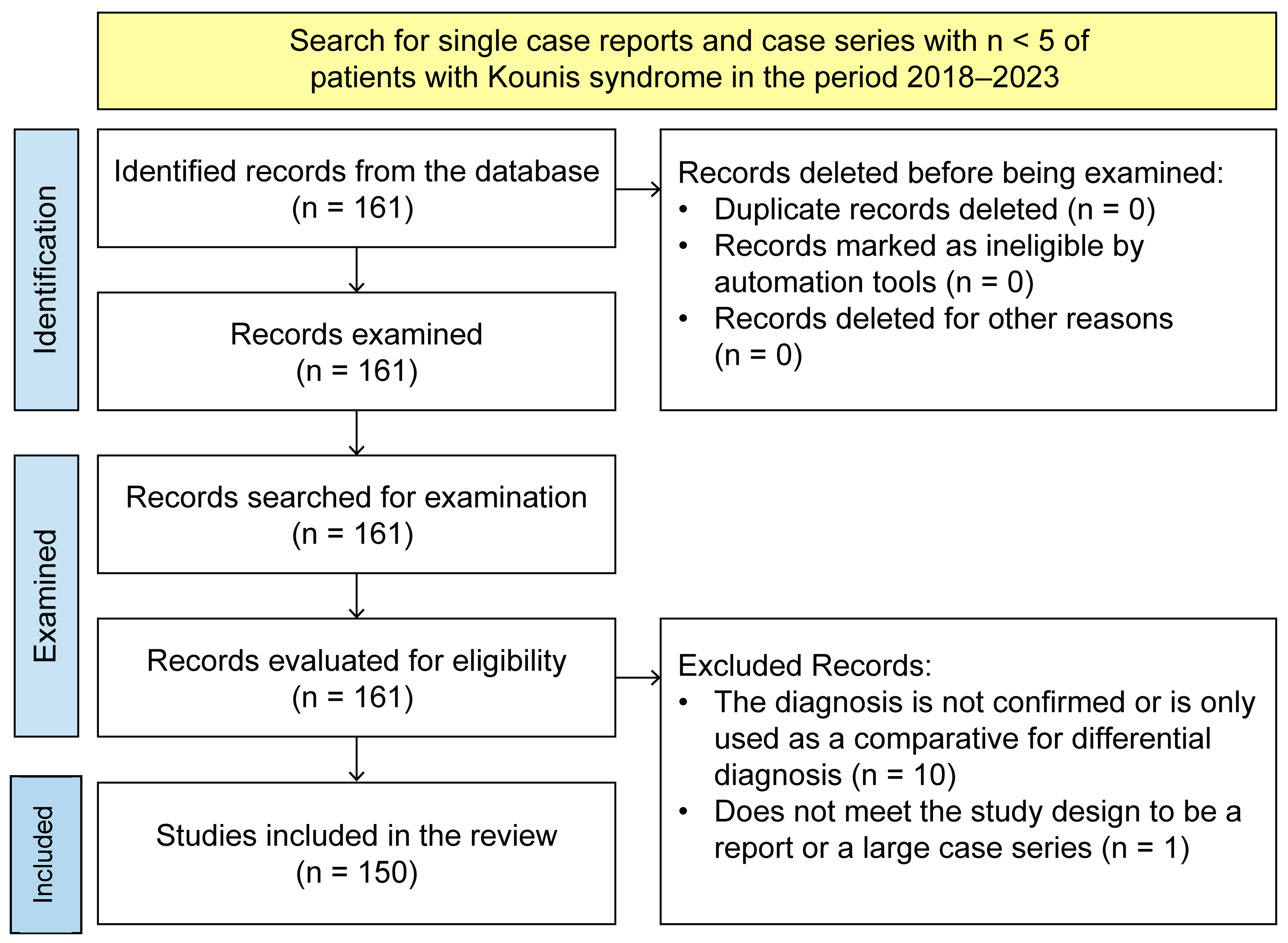
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Data and Variable Extraction
2.4. Clinical Variables
- KS classification: The classification assigned to patients based on the three forms of presentation of the syndrome.
- The causative agent: The etiological agent that causes allergic reactions.
- Therapeutic approach: The treatment they received during the hospital stay.
- Days of hospital stay.
- Electrocardiogram findings: ST-segment elevation, ST-segment depression, T-wave inversion, normal, and other findings (sinus tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, prolonged QT segment, sinus bradycardia, AV block, biphasic T-waves, etc.).
- Laboratory results: These are used to identify cardiac (cardiac enzymes) and immunological involvement (serum tryptase levels, IgE, histamine, or mast cell degranulation).
- Imaging tests: These are performed if angiography and/or a CT scan was performed.
- The presence of acute myocardial infarction: Necrosis of the myocardium caused by an obstruction of the blood supplied to the heart [9].
- The outcome of the emergency.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
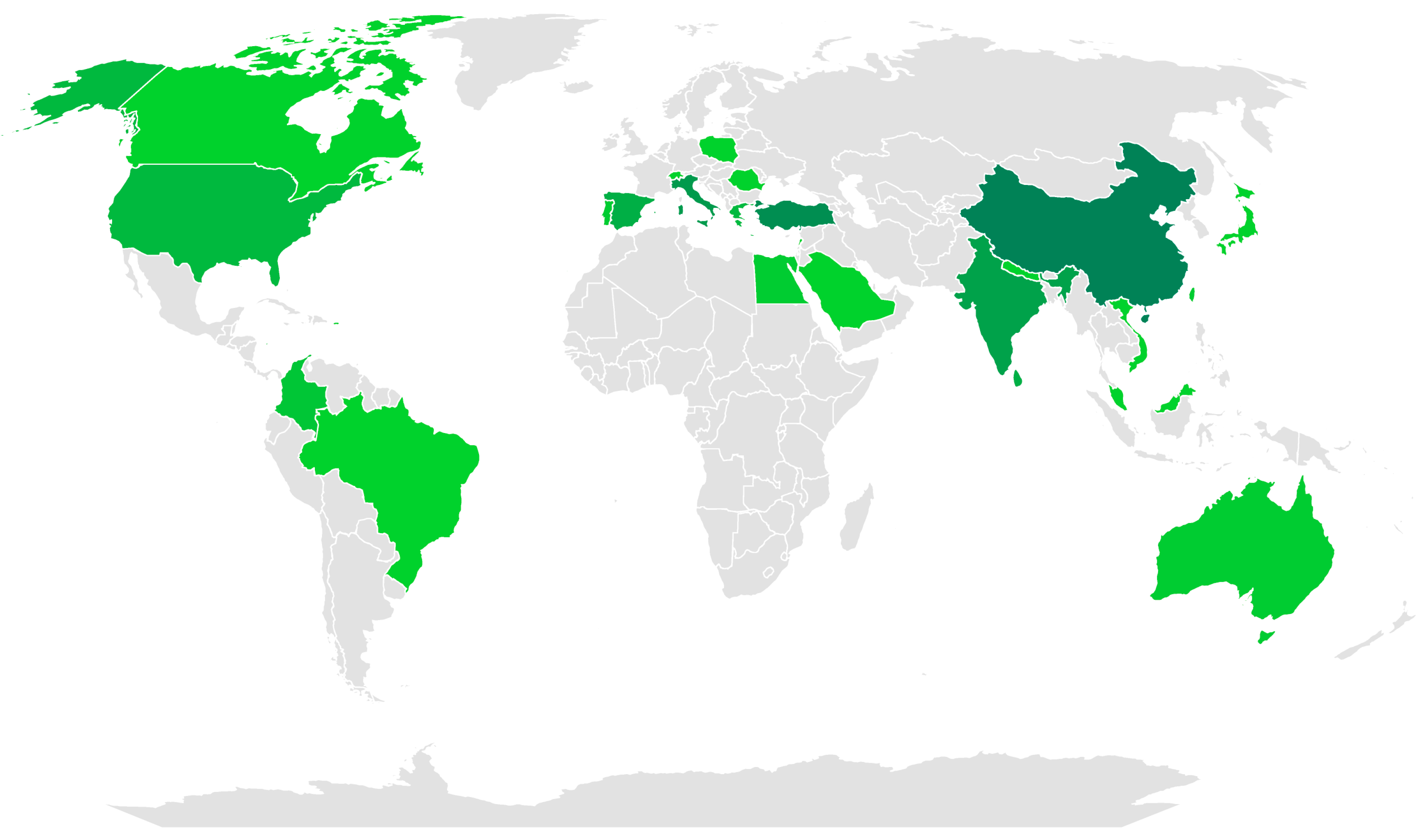
3. Results
3.1. Type I
3.2. Type II
3.3. Type III
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kounis, N.G.; Zavras, G.M. Histamine-induced coronary artery spasm: The concept of allergic angina. Br. J. Clin. Pract. 1991, 45, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejcic, A.V.; Milosavljevic, M.N.; Jankovic, S.; Davidovic, G.; Folic, M.M.; Folic, N.D. Kounis Syndrome Associated With the Use of Diclofenac. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2023, 50, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollo-Morales, P.; Gutierrez-Niso, M.; De-La-Viuda-Camino, E.; Ruiz-De-Galarreta-Beristain, M.; Osaba-Ruiz-De-Alegria, I.; Martel-Martin, C. Drug-Induced Kounis Syndrome: Latest Novelties. Curr. Treat. Options Allergy 2023, 10, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.G. Kounis syndrome: An update on epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapeutic management. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1545–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.-Z.; Zhao, H.; Gao, J.; Cao, C.-F.; Wang, W.-M. Epirubicin-induced Kounis syndrome. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounis, N.G. Coronary Hypersensitivity Disorder: Kounis Syndrome. Clin. Ther. 2013, 35, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Peng, W. Acute coronary syndrome secondary to allergic coronary vasospasm (Kounis Syndrome): A case series, follow-up and literature review. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2018, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Moher, D. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Library of Medicine (U.S.), Myocardial Infarction [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 1979. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68009203 (accessed on 14 July 2024).
- Fletcher, R.H.; Fletcher, S.W.; Fletcher, G.S. Clinical Epidemiology, 6th ed.; Jiménez-González, D., Translator; Wolters Kluwer: Barcelona, Spain, 2020; pp. 407–415. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Boutron, I.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Kirkham, J.J.; Li, T.; Lundh, A.; Mayo-Wilson, E.; McKenzie, J.; Stewart, L.; et al. ROB-ME: A tool for assessing risk of bias due to missing evidence in systematic reviews with meta-analysis. BMJ 2023, 383, e076754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda, P.R.; Herrejón, E.P.; Aguirregabiria, M.R. Síndrome de Kounis. Med. Intensiv. 2012, 36, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahuapaza-Gutierrez, N.L.; Calderon-Hernandez, C.C.; Chambergo-Michilot, D.; De Arruda-Chaves, E.; Zamora, A.; Runzer-Colmenares, F.M. Clinical characteristics, management, diagnostic findings, and various etiologies of patients with Kounis syndrome. A systematic review. Int. J. Cardiol. 2025, 418, 132606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghany, M.; Subedi, R.; Shah, S.; Kozman, H. Kounis syndrome: A review article on epidemiology, diagnostic findings, management and complications of allergic acute coronary syndrome. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 232, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-González, I. Epidemiology of coronary heart disease. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2014, 67, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HEARTS en las Américas: Marco de Evaluación Para la Mejora Continua de la Calidad en los Centros de Atención Primaria de Salud. 2024. 62p. Available online: https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/64210 (accessed on 31 December 2024).
- López-Jaramillo, P.; López-López, J.P. Factores de riesgo y muerte cardiovascular en América del Sur. Clin. Investig. Arter. 2023, 35, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowbar, A.N.; Gitto, M.; Howard, J.P.; Francis, D.P.; Al-Lamee, R. Mortality From Ischemic Heart Disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2019, 12, e005375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Namara, K.; Alzubaidi, H.; Jackson, J.K. Cardiovascular disease as a leading cause of death: How are pharmacists getting involved? Integr. Pharm. Res. Pract. 2019, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghavi, M.; Ong, K.L.; Aali, A.; Ababneh, H.S.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasgholizadeh, R.; Abbasian, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastabar, H.; et al. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2100–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monello, A.; Moderato, L.; Lazzeroni, D.; Benatti, G.; Demola, P.; Binno, S.; Vermi, A.C.; Valenti, G.; Losi, L.; Rusticali, G.; et al. Acute coronary syndrome after insect bite: A systematic literature review. Circulation 2021, 22, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Cavaye, J.; Judd, M.; Beuth, J.; Iswariah, H.; Gurunathan, U. Perioperative Presentations of Kounis Syndrome: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesthesia 2022, 36, 2070–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschi, E.; Affini, L.F.; Antonazzo, I.C.; Diemberger, I.; Poluzzi, E.; De Ponti, F. Drug-induced Kounis syndrome: A matter of pharmacovigilance. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 274, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paratz, E.D.; Khav, N.; Burns, A.T. Systemic Mastocytosis, Kounis Syndrome and Coronary Intervention: Case Report and Systematic Review. Heart Lung Circ. 2017, 26, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.-J.; He, J.-T.; Huang, H.-Y.; Xue, Y.; Xie, X.-L.; Wang, Q. Diagnostic role of serum tryptase in anaphylactic deaths in forensic medicine: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2018, 14, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, I.; Kuschnir, P.; Sciancalepore, A.; Conde, D.; Furmento, J.; Costabel, J.P. Coronary angiotomography in patients with acute coronary syndrome without ST elevation. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannini, M.; Alletto, A.; Koniari, I.; Mori, F.; Favilli, S.; Sarti, L.; Barni, S.; Liccioli, G.; Lodi, L.; Indolfi, G.; et al. Kounis Syndrome: A pediatric perspective. Minerva Pediatr. 2020, 72, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassio, F.; Losappio, L.; Antolin-Amerigo, D.; Peveri, S.; Pala, G.; Preziosi, D.; Massaro, I.; Giuliani, G.; Gasperini, C.; Caminati, M.; et al. Kounis syndrome: A concise review with focus on management. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMAScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Frequency | Mean/Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic Data | ||
| Age (years) | 150 | 54.37 |
| Not reported | 5 | 7.8% |
| Male | 100 | 67.50% |
| Female | 50 | 32.50% |
| Not reported | 5 | 7.8% |
| Type | ||
| Type I | 71 | 46.01% |
| Type II | 41 | 26.38% |
| Type III | 22 | 14.11% |
| Not reported | 21 | 13.49% |
| Trigger | ||
| Prescription drug | 71 | 44.37% |
| Poison | 44 | 27.50% |
| Contrast medium | 16 | 10.00% |
| Food | 11 | 6.87% |
| Vaccine | 9 | 5.62% |
| Object | 4 | 2.50% |
| Unspecified | 4 | 2.50% |
| Other | 2 | 1.25% |
| Tests Performed | ||
| Electrocardiogram | 151 | 97.41% |
| Cardiac enzymes | 136 | 87.74% |
| Tryptase immune response tests | 45 | 29.03% |
| Angiography | 119 | 76.77% |
| Tomography | 19 | 12.25% |
| Outcomes | ||
| Death | 7 | 4.37% |
| Myocardial infarction | 92 | 57.50% |
| Approach and Treatment | ||
| Allergic management | 107 | 69.03% |
| Antihypertensive management | 25 | 12.62% |
| Lipid-lowering management | 24 | 15.00% |
| Cardiovascular management | 96 | 60.00% |
| Corticosteroids | 97 | 60.62% |
| Antibiotic | 7 | 4.37% |
| Antimuscarinic | 7 | 5.00% |
| Non-pharmacological treatment | 77 | 48.12% |
| Other | 15 | 9.37% |
| Variable | Odds Ratio (OR) | Standard Error | p | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type I | |||||
| Sex (male) | 0.41 | 0.14 | 0.011 | 0.20 | 0.81 |
| Age | 0.96 | 0.00 | 0.001 | 0.94 | 0.98 |
| Drug | 1.61 | 0.51 | 0.137 | 0.85 | 3.02 |
| Contrast medium | 0.48 | 0.27 | 0.194 | 0.15 | 1.45 |
| Vaccine | 0.54 | 0.39 | 0.408 | 0.13 | 2.27 |
| Food | 2.08 | 1.35 | 0.257 | 0.58 | 7.42 |
| Poison | 0.71 | 0.25 | 0.353 | 0.35 | 1.44 |
| Object | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.393 | 0.03 | 3.62 |
| Death | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.114 | 0.02 | 1.51 |
| Type II | |||||
| Sex (male) | 3.99 | 1.91 | 0.004 | 1.56 | 10.21 |
| Age | 1.04 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 1.01 | 1.07 |
| Drug | 0.71 | 0.26 | 0.361 | 0.34 | 1.46 |
| Contrast medium | 1.73 | 0.95 | 0.317 | 0.58 | 5.10 |
| Vaccine | 0.76 | 0.63 | 0.746 | 0.15 | 3.84 |
| Food | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.199 | 0.03 | 2.05 |
| Poison | 1.88 | 0.72 | 0.098 | 0.88 | 3.98 |
| Infarct | 1.03 | 0.37 | 0.921 | 0.51 | 2.10 |
| Type III | |||||
| Sex (male) | 1.88 | 1.00 | 0.239 | 0.65 | 5.38 |
| Age | 1.03 | 0.01 | 0.043 | 1.00 | 1.06 |
| Drug | 1.01 | 0.46 | 0.971 | 0.41 | 2.47 |
| Contrast medium | 1.43 | 0.97 | 0.601 | 0.37 | 5.47 |
| Vaccine | 1.76 | 1.47 | 0.495 | 0.34 | 9.09 |
| Food | 1.35 | 1.10 | 0.71 | 0.27 | 6.70 |
| Poison | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.044 | 0.04 | 0.96 |
| Object | 20.4 | 24.05 | 0.011 | 2.02 | 205.79 |
| Infarct | 1.83 | 0.88 | 0.211 | 0.70 | 4.74 |
| Death | 9.40 | 7.54 | 0.005 | 1.95 | 45.29 |
| Variable | Odds Ratio (OR) | Standard Error | p | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| Type I | |||||
| (Log likelihood: −93.80; pseudo R2: 0.13) | |||||
| Sex (male) | 0.33 | 0.12 | 0.005 | 0.15 | 0.71 |
| Age | 0.96 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.94 | 0.98 |
| Drug | 1.89 | 0.72 | 0.096 | 0.89 | 4.02 |
| Contrast medium | 0.73 | 0.50 | 0.656 | 0.19 | 2.82 |
| Food | 3.15 | 2.28 | 0.114 | 0.75 | 13.07 |
| Death | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.173 | 0.02 | 1.96 |
| Type II | |||||
| (Log likelihood: −73.84; pseudo R2: 0.19) | |||||
| Sex (male) | 5.97 | 3.26 | 0.001 | 2.04 | 17.41 |
| Age | 1.05 | 0.01 | 0.000 | 1.02 | 1.08 |
| Food | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 2.05 |
| Poison | 1.96 | 0.86 | 0.129 | 0.82 | 4.67 |
| Type III | |||||
| (Log likelihood: −52.87; pseudo R2: 0.19) | |||||
| Sex (male) | 2.57 | 1.62 | 0.132 | 0.75 | 8.85 |
| Age | 1.03 | 0.01 | 0.043 | 1.00 | 1.06 |
| Poison | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.066 | 0.05 | 1.10 |
| Object | 24.86 | 32.77 | 0.015 | 1.87 | 39.19 |
| Death | 6.91 | 6.96 | 0.055 | 0.95 | 49.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rochel-Perez, E.; Santaularia-Tomas, M.; Martin-Dorantes, M.; Villareal-Jimenez, E.; Olivera-Mar, A.; Sanchez-Felix, E.; Perez-Navarrete, A.; Millet-Herrera, J.L.; Huchim-Mendez, O.; Alejos-Briceño, R.; et al. Triggers, Types, and Treatments for Kounis Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15030059
Rochel-Perez E, Santaularia-Tomas M, Martin-Dorantes M, Villareal-Jimenez E, Olivera-Mar A, Sanchez-Felix E, Perez-Navarrete A, Millet-Herrera JL, Huchim-Mendez O, Alejos-Briceño R, et al. Triggers, Types, and Treatments for Kounis Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Clinics and Practice. 2025; 15(3):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15030059
Chicago/Turabian StyleRochel-Perez, Erick, Miguel Santaularia-Tomas, Mario Martin-Dorantes, Edgar Villareal-Jimenez, Amonario Olivera-Mar, Ely Sanchez-Felix, Adrian Perez-Navarrete, Jose Luis Millet-Herrera, Osvaldo Huchim-Mendez, Ricardo Alejos-Briceño, and et al. 2025. "Triggers, Types, and Treatments for Kounis Syndrome: A Systematic Review" Clinics and Practice 15, no. 3: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15030059
APA StyleRochel-Perez, E., Santaularia-Tomas, M., Martin-Dorantes, M., Villareal-Jimenez, E., Olivera-Mar, A., Sanchez-Felix, E., Perez-Navarrete, A., Millet-Herrera, J. L., Huchim-Mendez, O., Alejos-Briceño, R., & Mendez-Dominguez, N. (2025). Triggers, Types, and Treatments for Kounis Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Clinics and Practice, 15(3), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15030059







