Corticosteroid Use and Recurrence Risk Factors in Granulomatous Mastitis: A 17-Year Saudi Arabian Cohort Study—Steroids in Granulomatous Mastitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Patient Selection and Data Collection
2.3. Study Variables and Definitions
2.4. Treatment Protocol
2.5. Ethical Considerations
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Data
3.2. Presentation and Management
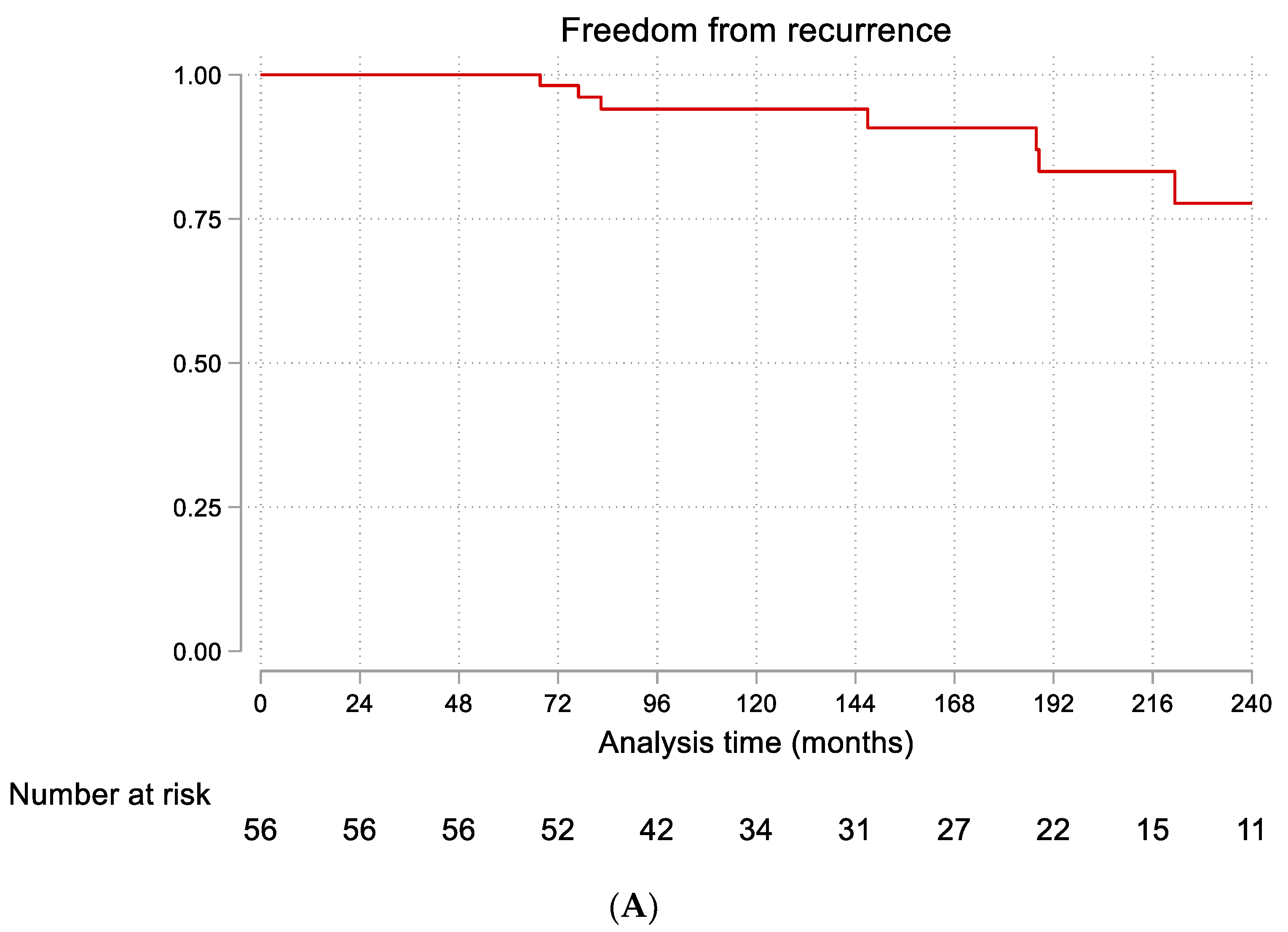
3.3. Follow-Up and Recurrence
3.4. Risk Factors for Recurrence
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Characteristics and Presentation
4.2. Diagnostic Approach
4.3. Treatment Efficacy and Recurrence
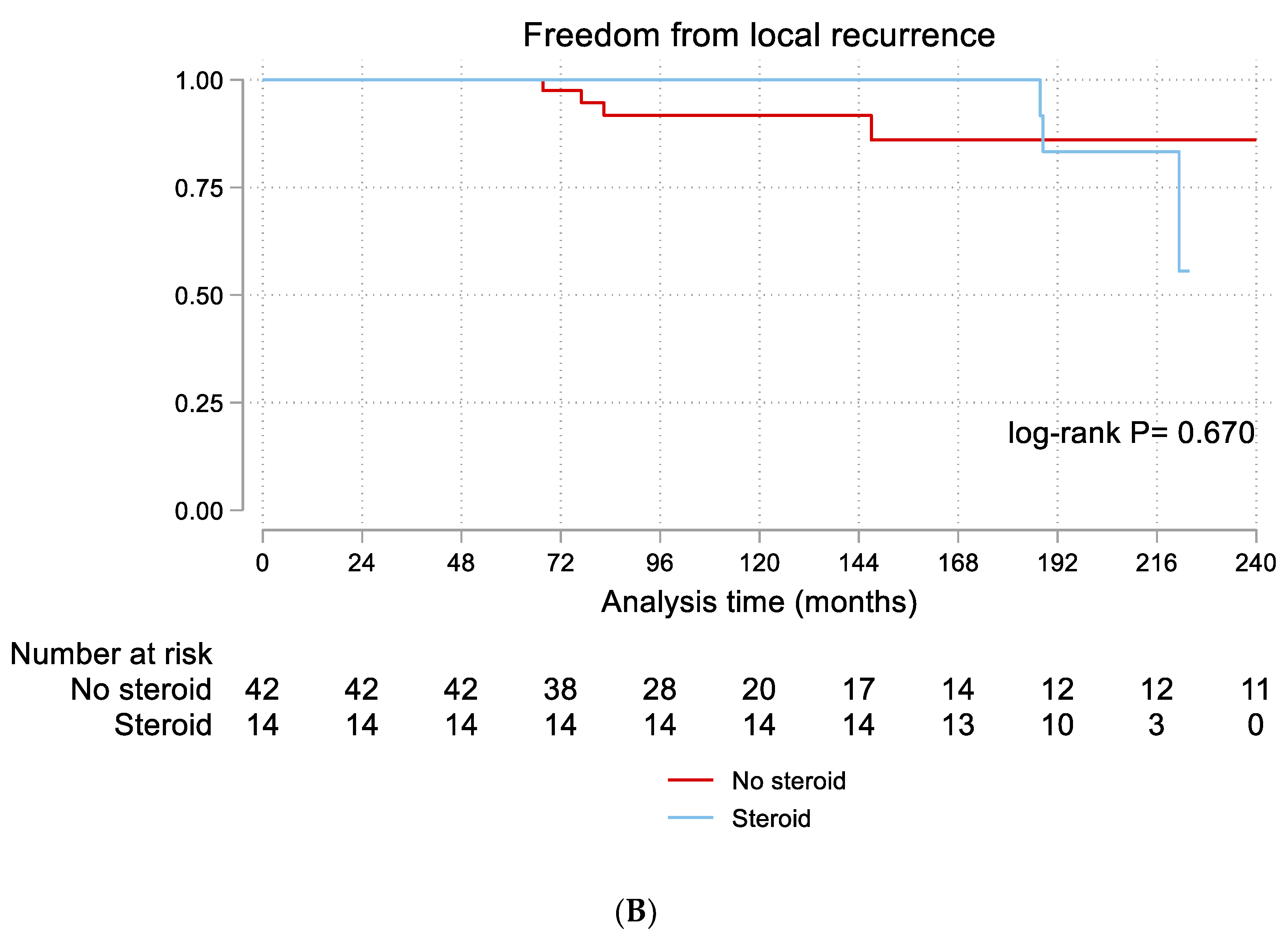
4.4. Risk Factors for Recurrence
4.5. Potential Mechanisms Underlying Recurrence Risk Factors
4.6. International Context and Regional Differences in GM
4.7. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kessler, E.; Wolloch, Y. Granulomatous Mastitis: A Lesion Clinically Simulating Carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1972, 58, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Going, J.J.; Anderson, T.J.; Wilkinson, S.; Chetty, U. Granulomatous lobular mastitis. J. Clin. Pathol. 1987, 40, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbulut, S.; Yilmaz, D.; Bakir, S. Methotrexate in the Management of Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis: Review of 108 Published Cases and Report of Four Cases. Breast J. 2011, 17, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintoprak, F.; Kıvılcım, T.; Ozkan, O.V. Aetiology of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. World J. Clin. Cases 2014, 2, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baslaim, M.M.; Khayat, H.A.; Al-Amoudi, S.A. Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis: A Heterogeneous Disease with Variable Clinical Presentation. World J. Surg. 2007, 31, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheybani, F.; Sarvghad, M.; Naderi, H.; Gharib, M. Treatment for and Clinical Characteristics of Granulomatous Mastitis. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 125, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyak, G.; Dumlu, E.G.; Kilinc, I.; Tokaç, M.; Akbaba, S.; Gurer, A.; Ozkardes, A.B.; Kilic, M. Management of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: Dilemmas in diagnosis and treatment. BMC Surg. 2014, 14, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacambra, M.; Thai, T.A.; Lam, C.C.F.; Yu, A.M.C.; Pham, H.T.; Tran, P.V.T.; Law, B.K.B.; Van Nguyen, T.; Pham, D.X.; Tse, G.M. Granulomatous mastitis: The histological differentials. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 64, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oran, E.Ş.; Gürdal, S.Ö.; Yankol, Y.; Öznur, M.; Calay, Z.; Tunacı, M.; Soybir, G.R. Management of Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis Diagnosed by Core Biopsy: A Retrospective Multicenter Study. Breast J. 2013, 19, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHertogh, D.A.; Rossof, A.H.; Harris, A.A.; Economou, S.G. Prednisone Management of Granulomatous Mastitis. New Engl. J. Med. 1980, 303, 799–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, E.C.H.; Chan, W.C.; Ma, T.K.F.; Tang, A.P.Y.; Poon, C.S.P.; Leong, H.T. The role of conservative treatment in idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Breast J. 2005, 11, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukawa, M.; Watatani, M.; Isono, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tsujie, M.; Kitani, K.; Hara, J.; Kato, H.; Takeyama, H.; Kanaizumi, H.; et al. Management of Granulomatous Mastitis: A Series of 13 Patients Who Were Evaluated for Treatment Without Corticosteroids. Int. Surg. 2015, 100, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.T.; Tay, S.P.; Gudi, M.A.; Nadkarni, N.V.; Lim, S.H.; Chuwa, E.W.L. Granulomatous Mastitis and Factors Associated with Recurrence: An 11-Year Single-Centre Study of 113 Patients in Singapore. World J. Surg. 2019, 43, 1737–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akahane, K.; Tsunoda, N.; Kato, M.; Noda, S.; Shimoyama, Y.; Ishigakis, S.; Satake, H.; Nakamura, S.; Nagino, M. Therapeutic strategy for granulomatous lobular mastitis: A clinicopathological study of 12 patients. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Khaffaf, B.; Knox, F.; Bundred, N.J. Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis: A 25-Year Experience. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2008, 206, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuschieri, S. The STROBE guidelines. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2019, 13 (Suppl. 1), 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bani-Hani, K.E.; Yaghan, R.J.; Matalka, I.I.; Shatnawi, N.J. Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis: Time to Avoid Unnecessary Mastectomies. Breast J. 2004, 10, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, L.J.H.; Peyvandi, B.; Klipfel, N.; Grant, E.; Iyengar, G. Granulomatous Lobular Mastitis: Imaging, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 193, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, N.; Lalonde, L.; Tran-Thanh, D.; El Khoury, M.; David, J.; Labelle, M.; Patocskai, E.; Trop, I. Chronic granulomatous mastitis: Imaging, pathology and management. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, e165–e175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, D.S.; Sedgwick, E.L.; Nagi, C.S.; Benveniste, A.P. Granulomatous mastitis: Etiology, imaging, pathology, treatment, and clinical findings. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 171, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluguez-Turull, C.W.; Nanyes, J.E.; Quintero, C.J.; Alizai, H.; Mais, D.D.; Kist, K.A.; Dornbluth, N.C. Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis: Manifestations at Multimodality Imaging and Pitfalls. RadioGraphics 2018, 38, 330–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, T.S.; Mackinnon, J.C.; Bressler, L.; Millar, A.; Marcus, E.E.; Ganschow, P.S. Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis—A Prospective Study of 49 Women and Treatment Outcomes with Steroid Therapy. Breast J. 2014, 20, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaviani, A.; Vasigh, M.; Omranipour, R.; Mahmoudzadeh, H.; Elahi, A.; Farivar, L.; Zand, S. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: Looking for the most effective therapy with the least side effects according to the severity of the disease in 374 patients in Iran. Breast J. 2019, 25, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.B.; Paviour, S.D.; Musaad, S.; Jones, W.O.; Holland, D.J. A clinicopathological review of 34 cases of inflammatory breast disease showing an association between corynebacteria infection and granulomatous mastitis. Pathology 2003, 35, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-W.; Tsao, T.-Y.; Chou, J. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis associated with risperidone-induced hyperprolactinemia. Diagn. Pathol. 2012, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanzadeh, M.; Hassanzadeh, R.; Sefat, S.A.; Alavi, A.; Hemmati, H.; Delshad, M.S.E.; Alavi, C.E.; Rimaz, S.; Geranmayeh, S.; Ashtiani, M.N.; et al. Granulomatous mastitis: Presentations, diagnosis, treatment and outcome in 206 patients from the north of Iran. Breast 2015, 24, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, E.; Soran, A.; Sezgin, E.; Granulomatous Mastitis Study Group. Factors related to recurrence of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: What do we learn from a multicentre study? ANZ J. Surg. 2017, 88, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaee, L.; Rahmani, N.; Moradi, S.; Motamedi, A.; Godazandeh, G. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: Challenges of treatment in iranian women. BMC Surg. 2021, 21, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Total (n = 56) | No Steroid (n = 42) | Steroid (n = 14) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 46.3 ± 13.2 | 46.3 ± 13.9 | 48.1 ± 11 | 0.648 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 28 (26–30) | 29 (27–31) | 27 (26–28) | 0.061 |
| Smokers | 1 (1.79%) | 1 (2.38%) | 0 | >0.99 |
| Married | 53 (94.64%) | 39 (91.86%) | 14 (100%) | 0.565 |
| Age of menarche (n = 52) (years) | 12.7 ± 1.7 | 12.9 ± 1.6 | 12.3 ± 1.6 | 0.349 |
| Menopause | 26 (46.43%) | 20 (47.62%) | 6 (42.86%) | 0.757 |
| History of oral contraceptive pills | 28 (50%) | 18 (42.86%) | 10 (71.43%) | 0.064 |
| Number of pregnancies | 5 (3–7) | 5 (3–8) | 5 (3–6) | 0.972 |
| History of breast feeding | 46 (82.14%) | 36 (85.71%) | 10 (71.43%) | 0.247 |
| Family history of breast cancer | 11 (19.64%) | 7 (16.67%) | 4 (28.57%) | 0.332 |
| History of infections | 7 (12.50%) | 4 (9.52%) | 3 (21.43%) | 0.350 |
| Autoimmune disease | 13 (23.21%) | 9 (21,43%) | 4 (28.57%) | 0.584 |
| Antidepressant | 3 (5.36%) | 2 (4.76%) | 1 (7.14%) | >0.99 |
| Hormonal disorders (Hyperprolactinemia) | 1 (1.79%) | 1 (2.38%) | 0 | >0.99 |
| Extrinsic trauma | 4 (7.14%) | 4 (9.52%) | 0 | 0.562 |
| Variables | Total (n = 56) | No Steroid (n = 42) | Steroid (n = 14) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Presentation (n = 52) | 0.295 | |||
| Mass | 17 (32.69%) | 14 (36.84%) | 3 (21.43%) | |
| Mass + abscess | 13 (25%) | 8 (21.05%) | 5 (35.71%) | |
| Mass + abscess + pain + nipple changes | 1 (1.92%) | 0 | 1 (7.14%) | |
| Mass + abscess + ulcer | 1 (1.92%) | 1 (2.63%) | 0 | |
| Mass + pain | 4 (7.69%) | 4 (10.53%) | 0 | |
| Mass + pain + fistula | 4 (7.69%) | 2 (5.26%) | 2 (14.29%) | |
| Mass + nipple discharge or change | 1 (1.92%) | 1 (2.63%) | 0 | |
| Mass + fistula | 1 (1.92%) | 0 | 1 (7.14%) | |
| Abscess | 2 (3.85%) | 2 (5.26%) | 0 | |
| Pain | 8 (15.38%) | 6 (15.79%) | 2 (14.29%) | |
| Location | 0.18 | |||
| Not documented | 13 (23.21%) | 12 (28.57%) | 1 (7.14%) | |
| UOQ | 15 (26.79%) | 11 (26.83%) | 4 (28.57%) | |
| LOQ | 6 (10.71%) | 3 (7.32%) | 3 (21.43%) | |
| LOQ + LIQ | 1 (1.79%) | 1 (2.44%) | 0 | |
| UIQ | 9 (16.07%) | 7 (17.07%) | 2 (14.29%) | |
| UIQ + LIQ | 1 (1.79%) | 1 (2.44%) | 0 | |
| LIQ | 7 (12.50%) | 3 (7.32%) | 4 (28.57%) | |
| Retroareolar | 4 (7.14%) | 4 (9.76%) | 0 | |
| Side | 0.162 | |||
| Right | 25 (44.64%) | 21 (50%) | 4 (28.57%) | |
| Left | 31 (55.36%) | 21 (50%) | 10 (71.43%) | |
| Biopsy type | 0.441 | |||
| FNA | 12 (21.43%) | 10 (23.81%) | 2 (14.29%) | |
| FNA + core biopsy | 4 (7.14%) | 4 (9.52%) | 0 | |
| FNA + tissue biopsy | 2 (3.57%) | 2 (4.76%) | 0 | |
| FNA + core + tissue biopsy | 1 (1.79%) | 1 (2.38%) | 0 | |
| Core biopsy | 29 (51.79%) | 18 (42.86%) | 11 (78.57%) | |
| Tissue biopsy | 8 (14.29%) | 7 (16.67% | 1 (7.14%) | |
| Imaging findings | 0.483 | |||
| Asymmetry | 4 (7.41%) | 4 (10%) | 0 | |
| Asymmetry + mass | 1 (1.85%) | 0 | 1 (7.14%) | |
| Mass | 19 (35.19%) | 14 (35%) | 5 (35.71%) | |
| Mass + collections/abscess | 1 (1.85% | 1 (2.5%) | 0 | |
| Collections/abscess | 4 (7.41%) | 4 (10%) | 0 | |
| Others | 11 (20.37%) | 7 (17.5%) | 4 (28.57%) | |
| No images | 14 (25.93%) | 10 (25%) | 4 (28.57%) | |
| Incision and drainage | 35 (63.64%) | 26 (63.41%) | 9 (64.29%) | 0.839 |
| Antibiotic use | 55 (98.21%) | 41 (9762%) | 14 (100%) | >0.99 |
| Variables | HR (95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||
| Age | 0.98 (0.92–1.04) | 0.577 |
| Body mass index | 1.17 (0.98–1.27) | 0.091 |
| Married | 0.59 (0.07–4.85) | 0.622 |
| Age of menarche | 0.65 (0.39–1.05) | 0.078 |
| Menopause | 0.28 (0.06–1.29) | 0.103 |
| Clinical factors | ||
| History of oral contraceptive pills | 1.13 (0.32–4.06) | 0.849 |
| Number of pregnancies | 0.95 (0.76–1.21) | 0.709 |
| History of breast feeding | 0.33 (0.08–1.23) | 0.098 |
| Family history of breast cancer | 2.77 (0.34–22.26) | 0.338 |
| History of infections | 5.85 (1.60–21.44) | 0.008 |
| Autoimmune disease | 2.99 (0.80–11.22) | 0.104 |
| Hormonal disorders (Hyperprolactinemia) | 13.90 (1.43–135.52) | 0.024 |
| Anatomical factors | ||
| Location | 1.44 (0.88–2.34) | 0.139 |
| Side | 1.27 (0.36–4.53) | 0.710 |
| Imaging findings | 1.29 (0.84–1.98) | 0.243 |
| Treatment | ||
| Incision and drainage | 0.16 (0.02–1.27) | 0.084 |
| Steroid | 1.40 (0.30–6.52) | 0.671 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albugami, S.J.; AlRasheed, R.F.; Alharbi, H.A.; Alobaid, S.S.; Alqahtani, H.S.; Alharbi, M.N.; AlKharashi, E.; Alhajri, K. Corticosteroid Use and Recurrence Risk Factors in Granulomatous Mastitis: A 17-Year Saudi Arabian Cohort Study—Steroids in Granulomatous Mastitis. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15100185
Albugami SJ, AlRasheed RF, Alharbi HA, Alobaid SS, Alqahtani HS, Alharbi MN, AlKharashi E, Alhajri K. Corticosteroid Use and Recurrence Risk Factors in Granulomatous Mastitis: A 17-Year Saudi Arabian Cohort Study—Steroids in Granulomatous Mastitis. Clinics and Practice. 2025; 15(10):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15100185
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbugami, Shoag J., Rema F. AlRasheed, Hussam A. Alharbi, Sarah S. Alobaid, Hawazin S. Alqahtani, Mays N. Alharbi, Eyad AlKharashi, and Khalid Alhajri. 2025. "Corticosteroid Use and Recurrence Risk Factors in Granulomatous Mastitis: A 17-Year Saudi Arabian Cohort Study—Steroids in Granulomatous Mastitis" Clinics and Practice 15, no. 10: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15100185
APA StyleAlbugami, S. J., AlRasheed, R. F., Alharbi, H. A., Alobaid, S. S., Alqahtani, H. S., Alharbi, M. N., AlKharashi, E., & Alhajri, K. (2025). Corticosteroid Use and Recurrence Risk Factors in Granulomatous Mastitis: A 17-Year Saudi Arabian Cohort Study—Steroids in Granulomatous Mastitis. Clinics and Practice, 15(10), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract15100185





