Hard and Soft Tissue Facial Landmarks for Mandibular Angle Reduction: A Clinical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Selection
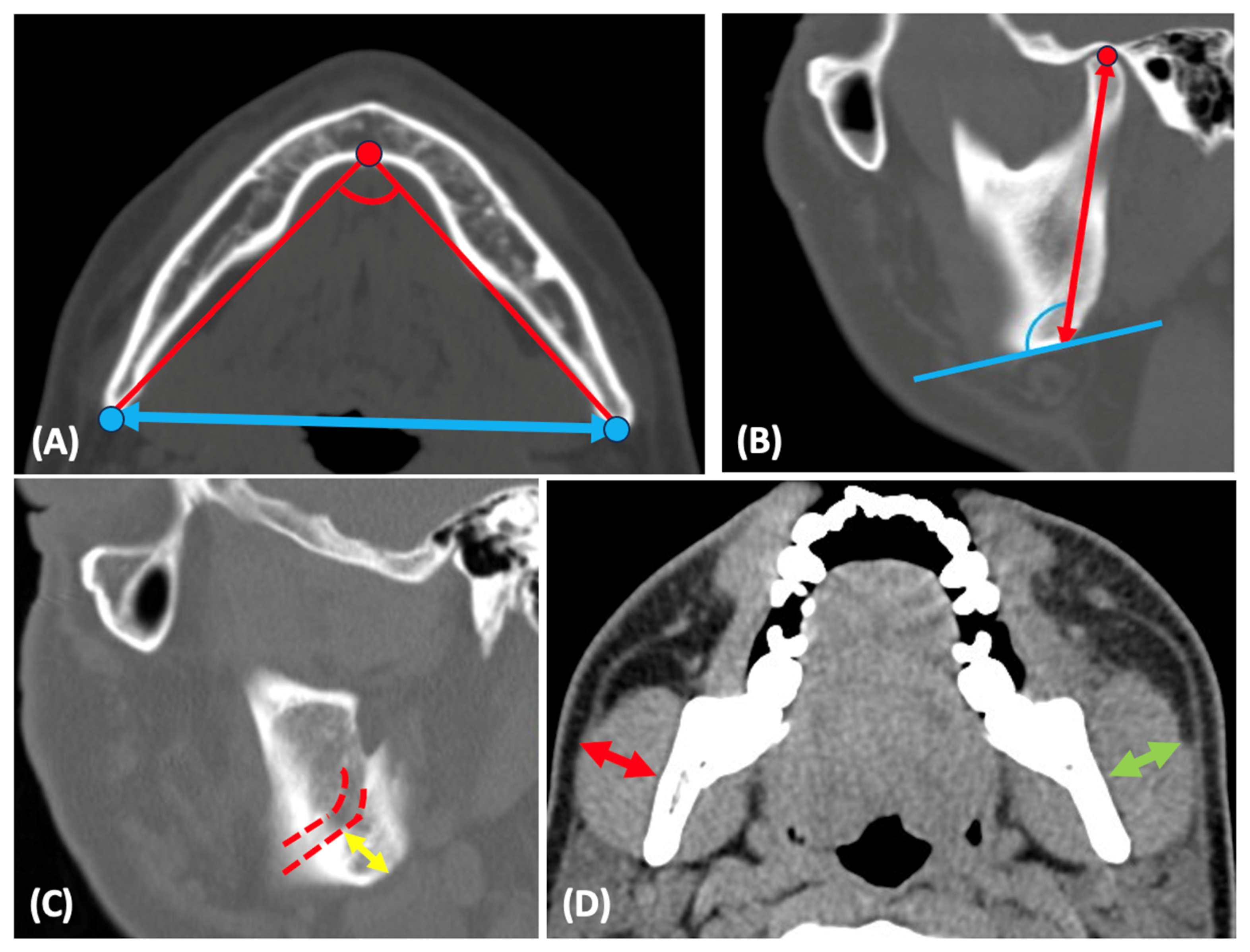
2.2. Anatomic Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Demographics
3.2. Correlations between Patients’ Anthropometric Measures and Mandibular Hard and Soft Tissue Characteristics
3.3. Comparison of Clinical Parameters between Both Sexes and Sides
3.4. Correlations between Hard and Soft Tissue Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cole, J.B.; Manyama, M.; Larson, J.R.; Liberton, D.K.; Ferrara, T.M.; Riccardi, S.L.; Li, M.; Mio, W.; Klein, O.D.; Santorico, S.A.; et al. Human facial shape and size heritability and genetic correlations. Genetics 2017, 205, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, N.; Kothari, R.; Shah, N.; Sandhu, S.; Tripathy, D.M.; Galadari, H.; Gold, M.H.; Goldman, M.P.; Kassir, M.; Schepler, H.; et al. Efficacy of botulinum toxin in masseter muscle hypertrophy for lower face contouring. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hsu, Y.; Khadka, A.; Hu, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D. Surgical designs and techniques for mandibular contouring based on categorisation of square face with low gonial angle in orientals. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2012, 65, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Rehman, S.; Rizwan, S.; Shah Faisal, S.; Sheeraz Hussain, S. Association of gonial angle on panoramic radiograph with the facial divergence on lateral cephalogram. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2020, 30, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windhager, S.; Schaefer, K.; Fink, B. Geometric morphometrics of male facial shape in relation to physical strength and perceived attractiveness, dominance, and masculinity. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2011, 23, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.Y.; Chou, C.Y.; Liang, Y.M.; Chang, K.W.; Wu, C.H. A digital photograph study evaluating facial taperness and square face perception of Taiwanese females. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2021, 84, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.D.; Kwon, T.G. Zygoma and mandibular angle reduction: Contouring surgery to correct the square face in Asians. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 35, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhu, S.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Luo, E. The effect of different reduction mandibuloplasty types on lower face width and morphology. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2008, 32, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, L.; Chen, Y.R. The Asian face lift. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2009, 23, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, J. Reducing prominent mandibular angle osteotomy complications: 10-year retrospective review. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2018, 81, S5–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, E.S.; Seo, Y.S.; Kang, D.H.; Koo, S.H.; Park, S.H. Analysis of incidences and types of complications in mandibular angle ostectomy in Koreans. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2006, 57, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Chung, J.H.; Park, R.H.; Park, J.B. The use of botulinum toxin type A in aesthetic mandibular contouring. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 115, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Park, R.H.; Park, J.B. Botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of hypertrophy of the masseter muscle. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 125, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreishchev, A.R.; Nicot, R.; Ferri, J. Mandibular angle resection and masticatory muscle hypertrophy—A technical note and morphological optimization. Rev. Stomatol. Chir. Maxillofac. Chir. Orale 2014, 115, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, C.H. Correlation between mandibular morphology and masticatory muscle thickness in normal occlusion and mandibular prognathism. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 46, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersberger-Zurfluh, M.A.; Motro, M.; Kantarci, A.; Will, L.A.; Eliades, T.; Papageorgiou, S.N. Genetic and environmental impact on mandibular growth in mono- and dizygotic twins during adolescence: A retrospective cohort study. Int. Orthod. 2024, 22, 100842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.S.; Lima, E.M. Mandibular growth during adolescence. Angle Orthod. 2006, 76, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Arora, A.; Valiathan, A. Age changes of jaws and soft tissue profile. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 301501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sairam, V.; Geethamalika, M.V.; Kumar, P.B.; Naresh, G.; Raju, G.P. Determination of sexual dimorphism in humans by measurements of mandible on digital panoramic radiograph. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2016, 7, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayemi, A.B. Assessment and determination of human mandibular and dental arch profiles in subjects with lower third molar impaction in Port Harcourt, Nigeria. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 1, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrazabal-Moron, C.; Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A. Gonial angle growth patterns according to age and gender. Ann. Anat. 2018, 215, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulut, O.; Freudenstein, N.; Hekimoglu, B.; Gurcan, S. Dilemma of gonial angle in sex determination: Sexually dimorphic or not? Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2019, 40, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquerelle, M.; Bookstein, F.L.; Braga, J.; Halazonetis, D.J.; Weber, G.W.; Mitteroecker, P. Sexual dimorphism of the human mandible and its association with dental development. Am. J. Phys. Anthr. 2011, 145, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Gómez, J.J.; Pérez Castrillón, J.L.; de Luis Román, D.A. Impact of obesity on bone metabolism. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, L.A.; Miller, S.F.; Caplin, J.; Galang-Boquiren, M.T.; Alrayyes, S.; Nicholas, C.L. Childhood obesity may accelerate timing of human facial growth. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 121, 104964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satiroğlu, F.; Arun, T.; Işik, F. Comparative data on facial morphology and muscle thickness using ultrasonography. Eur. J. Orthod. 2005, 27, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzi, V.; Colangelo, G.; Scotti, L. Correlation between facial height and body height during the prepubertal period. Dent. Cadmos 1983, 51, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Pelin, C.; Zağyapan, R.; Yazici, C.; Kürkçüoğlu, A. Body height estimation from head and face dimensions: A different method. J. Forensic Sci. 2010, 55, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.N.; Moyer, B.A.; DuBois, L.M. Skeletal maturation and craniofacial growth. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1990, 98, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Beek, M.C.; Hoeksma, J.B.; Prahl-Andersen, B. Vertical facial growth and statural growth in girls: A longitudinal comparison. Eur. J. Orthod. 1996, 18, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliaridis, S.; Georgiakaki, I.; Katsaros, C. Masseter muscle thickness and maxillary dental arch width. Eur. J. Orthod. 2003, 25, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tircoveluri, S.; Singh, J.R.; Rayapudi, N.; Karra, A.; Begum, M.; Challa, P. Correlation of masseter muscle thickness and intermolar width—An ultrasonography study. J. Int. Oral Health 2013, 5, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kubota, M.; Nakano, H.; Sanjo, I.; Satoh, K.; Sanjo, T.; Kamegai, T.; Ishikawa, F. Maxillofacial morphology and masseter muscle thickness in adults. Eur. J. Orthod. 1998, 20, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonemitsu, I.; Muramoto, T.; Soma, K. The influence of masseter activity on rat mandibular growth. Arch. Oral Biol. 2007, 52, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hsu, Y.; Hu, J.; Khadka, A.; Chen, T.; Li, J. Comprehensive consideration and design for treatment of square face. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 71, 1761.e1–1761.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Male | 50 (50%) |
| Female | 50 (50%) |
| Median age (years) | 32.05 (9.16) |
| Median height (cm) | 167.6 (8.73) |
| Median weight (kg) | 65.82 (16.1) |
| Median BMI (kg/m2) | 23.215 (4.62) |
| Parameters | Height | Weight | BMI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mandibular width | <0.00001 | 0.0004 | 0.06 |
| Mandibular divergence | 0.11 | 0.43 | 0.14 |
| Ramus height | <0.00001 | <0.00001 | 0.15 |
| Gonial angle | 0.55 | 0.97 | 0.64 |
| Masseter thickness | 0.00004 | <0.00001 | 0.00005 |
| Angle to IAN | 0.0006 | 0.09 | 0.79 |
| Parameters | Sex | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | p-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right ramus height (mm) | Male | 66.55 (4.61) | 66.48 (4.28) | 0.88 | <0.00001 |
| Left ramus height (mm) | 66.4 (4.56) | ||||
| Right ramus height (mm) | Female | 59.7 (4.36) | 59.35 (4.05) | 0.42 | |
| Left ramus height (mm) | 59 (4.33) | ||||
| Right gonial angle (°) | Male | 118.06 (7.54) | 117.6 (7.02) | 0.54 | 0.5 |
| Left gonial angle (°) | 117.14 (7.27) | ||||
| Right gonial angle (°) | Female | 119.61 (6.92) | 118.52 (6.66) | 0.12 | |
| Left gonial angle (°) | 117.43 (7.08) | ||||
| Right masseter thickness (mm) | Male | 15.23 (2.36) | 15.46 (2.35) | 0.35 | <0.00001 |
| Left masseter thickness (mm) | 15.7 (2.61) | ||||
| Right masseter thickness (mm) | Female | 12.67 (2.43) | 12.67 (2.23) | 0.99 | |
| Left masseter thickness (mm) | 12.68 (2.27) | ||||
| Right angle to IAN (mm) | Male | 18.51 (3.26) | 18.35 (3.19) | 0.62 | 0.00008 |
| Left angle to IAN (mm) | 18.18 (3.44) | ||||
| Right angle to IAN (mm) | Female | 16.07 (2.14) | 16.14 (2.05) | 0.74 | |
| Left angle to IAN (mm) | 16.21 (2.2) | ||||
| Mandibular width (mm) | Male | 102.47 (6.47) | <0.00001 | ||
| Female | 96.25 (5.93) | ||||
| Mandibular divergence (°) | Male | 72.34 (5.82) | 0.041 | ||
| Female | 74.69 (5.57) | ||||
| Parameters | Mandibular Width | Mandibular Divergence | Ramus Height | Gonial Angle | Masseter Thickness | Angle to IAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mandibular width | - | <0.00001 | <0.00001 | 0.57 | 0.00004 | 0.1 |
| Mandibular divergence | <0.00001 | - | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.16 | 0.00001 |
| Ramus height | <0.00001 | 0.003 | - | 0.043 | <0.00001 | <0.00001 |
| Gonial angle | 0.57 | 0.001 | 0.043 | - | 0.042 | <0.00001 |
| Masseter thickness | 0.00004 | 0.16 | <0.00001 | 0.042 | - | 0.005 |
| Angle to IAN | 0.1 | 0.00001 | <0.00001 | <0.00001 | 0.005 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tseng, F.-F.; Li, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-W. Hard and Soft Tissue Facial Landmarks for Mandibular Angle Reduction: A Clinical Study. Clin. Pract. 2024, 14, 1707-1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14050136
Tseng F-F, Li Y-H, Chen Y-W. Hard and Soft Tissue Facial Landmarks for Mandibular Angle Reduction: A Clinical Study. Clinics and Practice. 2024; 14(5):1707-1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14050136
Chicago/Turabian StyleTseng, Fei-Fan, Yu-Hsuan Li, and Yuan-Wu Chen. 2024. "Hard and Soft Tissue Facial Landmarks for Mandibular Angle Reduction: A Clinical Study" Clinics and Practice 14, no. 5: 1707-1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14050136
APA StyleTseng, F.-F., Li, Y.-H., & Chen, Y.-W. (2024). Hard and Soft Tissue Facial Landmarks for Mandibular Angle Reduction: A Clinical Study. Clinics and Practice, 14(5), 1707-1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14050136





