Assessing the Role of Adalimumab in Treating Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Findings from a Retrospective Study at a Reference Center
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Clinical Characteristics
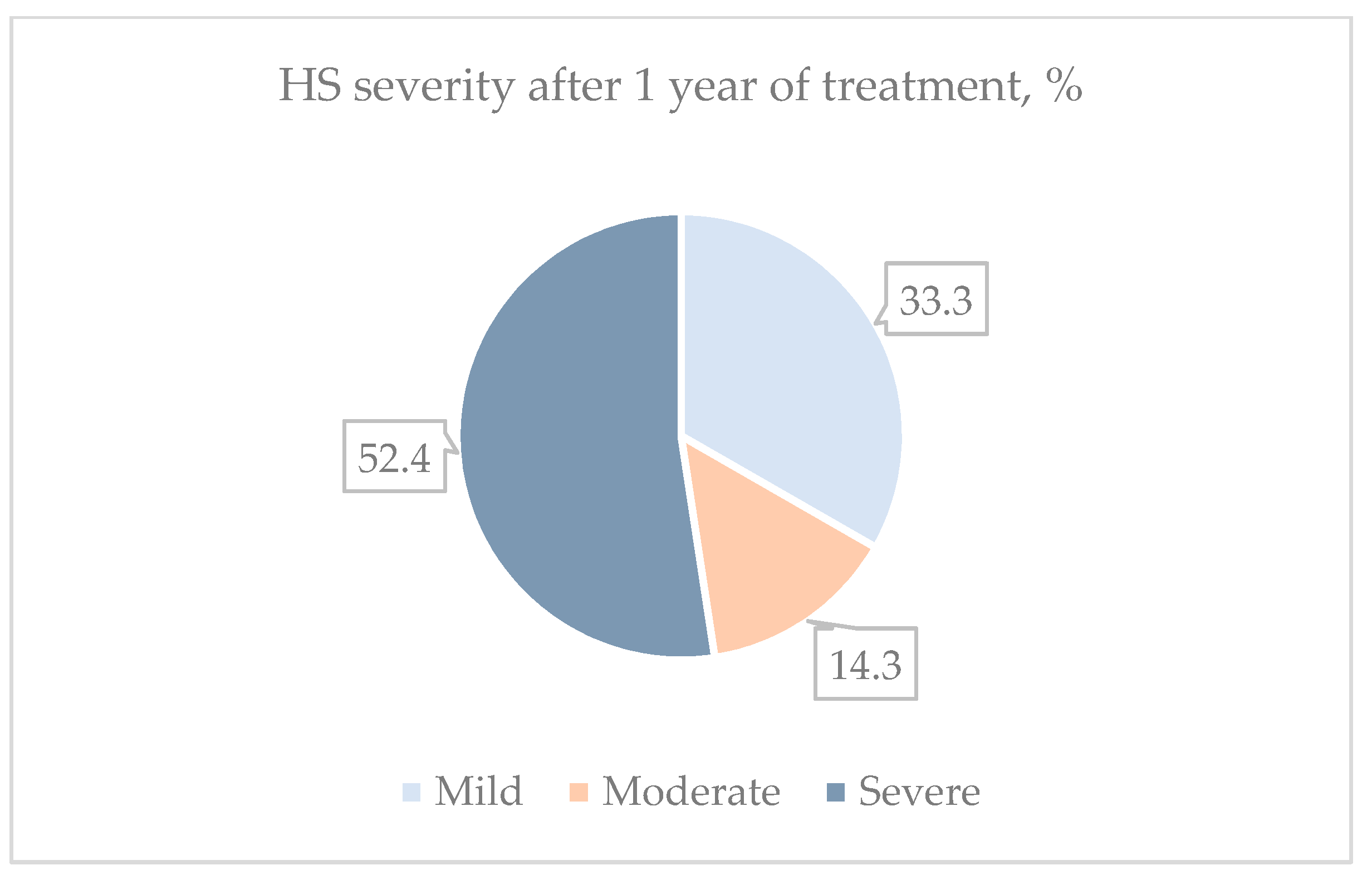
3.3. Adalimumab Effectiveness
3.4. Influence of BMI and Surgical Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alikhan, A.; Sayed, C.; Alavi, A.; Alhusayen, R.; Brassard, A.; Burkhart, C.; Crowell, K.; Eisen, D.B.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Hamzavi, I.; et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: A publication from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations: Part I: Diagnosis, evaluation, and the use of complementary and procedural management. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 81, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jfri, A.; Nassim, D.; O’Brien, E.; Gulliver, W.; Nikolakis, G.; Zouboulis, C.C. Prevalence of Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Systematic Review and Meta-regression Analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Damiani, G.; Orenstein, L.A.V.; Hamzavi, I.; Jemec, G.B. Hidradenitis suppurativa: An update on epidemiology, phenotypes, diagnosis, pathogenesis, comorbidities and quality of life. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, K.; Charlton, O.; Smith, S.D. Global prevalence of hidradenitis suppurativa and geographical variation—Systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed. Dermatol. 2020, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabat, R.; Jemec, G.B.E.; Matusiak, Ł.; Kimball, A.B.; Prens, E.; Wolk, K. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyed Jafari, S.M.; Hunger, R.E.; Schlapbach, C. Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Current Understanding of Pathogenic Mechanisms and Suggestion for Treatment Algorithm. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunte, D.; Boer, J.; Stratigos, A.; Szepietowski, J.; Hamzavi, I.; Kim, K.; Zarchi, K.; Antoniou, C.; Matusiak, L.; Lim, H.; et al. Diagnostic delay in hidradenitis suppurativa is a global problem. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 1546–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokolakis, G.; Wolk, K.; Schneider-Burrus, S.; Kalus, S.; Barbus, S.; Gomis-Kleindienst, S.; Sabat, R. Delayed Diagnosis of Hidradenitis Suppurativa and Its Effect on Patients and Healthcare System. Dermatology 2020, 236, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzano, A.V.; Genovese, G.; Casazza, G.; Moltrasio, C.; Dapavo, P.; Micali, G.; Sirna, R.; Gisondi, P.; Patrizi, A.; Dini, V.; et al. Evidence for a ‘window of opportunity’ in hidradenitis suppurativa treated with adalimumab: A retrospective, real-life multicentre cohort study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Straalen, K.R.; Schneider-Burrus, S.; Prens, E.P. Current and future treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, e178–e187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemec, G.B.E.; Wendelboe, P. Topical clindamycin versus systemic tetracycline in the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1998, 39, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gener, G.; Canoui-Poitrine, F.; Revuz, J.; Faye, O.; Poli, F.; Gabison, G.; Pouget, F.; Viallette, C.; Wolkenstein, P.; Bastuji-Garin, S. Combination therapy with clindamycin and rifampicin for hidradenitis suppurativa: A series of 116 consecutive patients. Dermatology 2009, 219, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettoli, V.; Zauli, S.; Borghi, A.; Toni, G.; Minghetti, S.; Ricci, M.; Virgili, A. Oral clindamycin and rifampicin in the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa-acne inversa: A prospective study on 23 patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouboulis, C.; Bechara, F.; Dickinson-Blok, J.; Gulliver, W.; Horváth, B.; Hughes, R.; Kimball, A.; Kirby, B.; Martorell, A.; Podda, M.; et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: A practical framework for treatment optimization–systematic review and recommendations from the HS ALLIANCE working group. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, A.B.; Okun, M.M.; Williams, D.A.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Papp, K.A.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Armstrong, A.W.; Kerdel, F.; Gold, M.H.; Forman, S.B.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Adalimumab for Hidradenitis Suppurativa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulliver, W.; Alavi, A.; Wiseman, M.C.; Gooderham, M.J.; Rao, J.; Alam, M.S.; Papp, K.A.; Desjardins, O.; Jean, C. Real-world effectiveness of adalimumab in patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa: The 1-year SOLACE study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettoli, V.; Manfredini, M.; Calamo, G.; Forconi, R.; Bencivelli, D.; Mantovani, L.; Pellacani, G.; Corazza, M. Long-term adalimumab treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: Results and practical insights from a real-life experience. Dermatol. Ther. 2018, 31, e12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martora, F.; Marasca, C.; Cacciapuoti, S.; Fariello, F.; Potestio, L.; Battista, T.; Scalvenzi, M.; Megna, M. Secukinumab in Hidradenitis Suppurativa Patients Who Failed Adalimumab: A 52-Week Real-Life Study. CCID 2024, 17, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, A.B.; E Jemec, G.B.; Alavi, A.; Reguiai, Z.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Bechara, F.G.; Paul, C.; Bourboulis, E.J.G.; Villani, A.P.; Schwinn, A.; et al. Secukinumab in moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa (SUNSHINE and SUNRISE): Week 16 and week 52 results of two identical, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase 3 trials. Lancet 2023, 401, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A.; Gonzalez, T.; Montgomery, M.O.; Cardenas, V.; Kerdel, F.A. Infliximab therapy for patients with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 62, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, T.; Lee, K.; Grogan, T.; De, D.R.; Shi, V.Y.; Hsiao, J.L. Infliximab in hidradenitis suppurativa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemec, G.B.E. Hidradenitis Suppurativa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N. Hidradenitis suppurativa: A treatment challenge. Am. Fam. Physician 2005, 72, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Jemec, G.; Okun, M.; Forman, S.; Gulliver, W.; Prens, E.; Mrowietz, U.; Armstrong, A.; Geng, Z.; Gu, Y.; Williams, D.; et al. Adalimumab medium-term dosing strategy in moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa: Integrated results from the phase III randomized placebo-controlled PIONEER trials. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Okun, M.M.; Prens, E.P.; Gniadecki, R.; Foley, P.A.; Lynde, C.; Weisman, J.; Gu, Y.; Williams, D.A.; Jemec, G.B. Long-term adalimumab efficacy in patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: 3-year results of a phase 3 open-label extension study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 60–69.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, A.; Jemec, G.; Yang, M.; Kageleiry, A.; Signorovitch, J.; Okun, M.; Gu, Y.; Wang, K.; Mulani, P.; Sundaram, M. Assessing the validity, responsiveness and meaningfulness of the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) as the clinical endpoint for hidradenitis suppurativa treatment. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N.; Hayama, K.; Takahashi, K.; Kurokawa, I.; Okazaki, M.; Kashiwagi, T.; Iwashita, E.; Terui, T. Real-world safety and effectiveness of adalimumab in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: 12-week interim analysis of post-marketing surveillance in Japan. J. Dermatol. 2022, 49, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetanova, A.; Marques, E.; Kojanova, M.; Arenberger, P.; Strosova, D.; Fialova, J.; Arenbergerova, M. Employing Adalimumab in Treatment of Moderate-to-Severe Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Real-Life Multicenter Data from the Czech Republic. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 2023, e3640285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Tzellos, T.; Kyrgidis, A.; Jemec, G.B.; Bechara, F.G.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Ingram, J.R.; Kanni, T.; Karagiannidis, I.; Martorell, A.; et al. Development and validation of the International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4), a novel dynamic scoring system to assess HS severity. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Giovanardi, G.; Garcovich, S.; Malvaso, D.; Caldarola, G.; Fossati, B.; Guerriero, C.; Simone, C.; Peris, K. Clinical and Ultrasonographic Profile of Adalimumab-treated Hidradenitis Suppurativa Patients: A Real-life Monocentric Experience. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, A.Y.; Khan, G.K. Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI)—A simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1994, 19, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, D.D.; McGrath, P.A.; Rafii, A.; Buckingham, B. The validation of visual analogue scales as ratio scale measures for chronic and experimental pain. Pain 1983, 17, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zee, H.H.; Laman, J.D.; Boer, J.; Prens, E.P. Hidradenitis suppurativa: Viewpoint on clinical phenotyping, pathogenesis and novel treatments. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Winter, K.; van der Zee, H.H.; Prens, E.P. Is mechanical stress an important pathogenic factor in hidradenitis suppurativa? Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzellos, T.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Gulliver, W.; Cohen, A.D.; Wolkenstein, P.; Jemec, G.B.E. Cardiovascular disease risk factors in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 1142–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.; Strunk, A.; Garg, A. Trends in body mass index before and after diagnosis of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 185, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosrati, A.; Torpey, M.E.; Shokrian, N.; Ch'En, P.Y.; Andriano, T.M.; Benesh, G.; Heibel, H.D.; Hosgood, H.D.; Campton, K.L.; Cohen, S.R. Adalimumab efficacy is inversely correlated with body mass index (BMI) in hidradenitis suppurativa. Int. J. Dermatol. 2023, 62, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, A.M.R.; Deckers, I.E.; Van Der Zee, H.H.; Boer, J.; Prens, E.P. Hidradenitis suppurativa: A retrospective study of 846 Dutch patients to identify factors associated with disease severity. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 71, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivanand, A.; Gulliver, W.P.; Josan, C.K.; Alhusayen, R.; Fleming, P.J. Weight Loss and Dietary Interventions for Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Systematic Review. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2020, 24, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromann, C.; Ibler, K.S.; Kristiansen, V.; Jemec, G.B.E. The Influence of Body Weight on the Prevalence and Severity of Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2014, 94, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, A. Hidradenitis suppurativa: Demystifying a chronic and debilitating disease. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFazio, M.V.; Economides, J.M.; King, K.S.; Han, K.D.; Shanmugam, V.K.M.; Attinger, C.E.; Evans, K.K. Outcomes After Combined Radical Resection and Targeted Biologic Therapy for the Management of Recalcitrant Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 77, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falola, R.A.; DeFazio, M.V.; Anghel, E.L.; Mitnick, C.D.B.; Attinger, C.E.; Evans, K.K. What Heals Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Surgery, Immunosuppression, or Both? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 138 (Suppl. 3), 219S–229S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, V.K.; Mulani, S.; McNish, S.; Harris, S.; Buescher, T.; Amdur, R. Longitudinal observational study of hidradenitis suppurativa: Impact of surgical intervention with adjunctive biologic therapy. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, P.; van Huijstee, J.C.; van der Zee, H.H.; van Doorn, M.B.A.; van Straalen, K.R.; Prens, E.P. Adalimumab in conjunction with surgery compared with adalimumab monotherapy for hidradenitis suppurativa: A Randomized Controlled Trial in a real-world setting. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023, 89, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Patients (n = 21) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Female, n, (%) | 8 (38.1%) |
| Male, n, (%) | 13 (61.9%) |
| Mean age, years, (±SD) | 42.9 (±14.1) |
| Mean BMI kg/m2 (±SD) | 30.33 (±7.13) |
| Normal (18.5–24.9), n, (%) | 5 (23.8%) |
| Overweight (25.0–29.9), n, (%) | 8 (38.1%) |
| Obese (≥30.0), n, (%) | 8 (38.1%) |
| Characteristic | Patients (n = 21) |
|---|---|
| Hurley stage, n, (%) | |
| II | 8 (38.1%) |
| III | 13 (61.9%) |
| Mean duration of HS, years, (±SD) | 15.48 (±12.83) |
| Prior systemic antibiotic use, n, (%) | 21 (100%) |
| Prior surgery for HS, n, (%) | 14 (66.7%) |
| Lesion counts | |
| Mean no. of inflammatory nodules (±SD) | 5.62 (±4.12) |
| Mean no. of abscesses (±SD) | 1.76 (±2.63) |
| Mean no. of fistulas (±SD) | 2.62 (±1.86) |
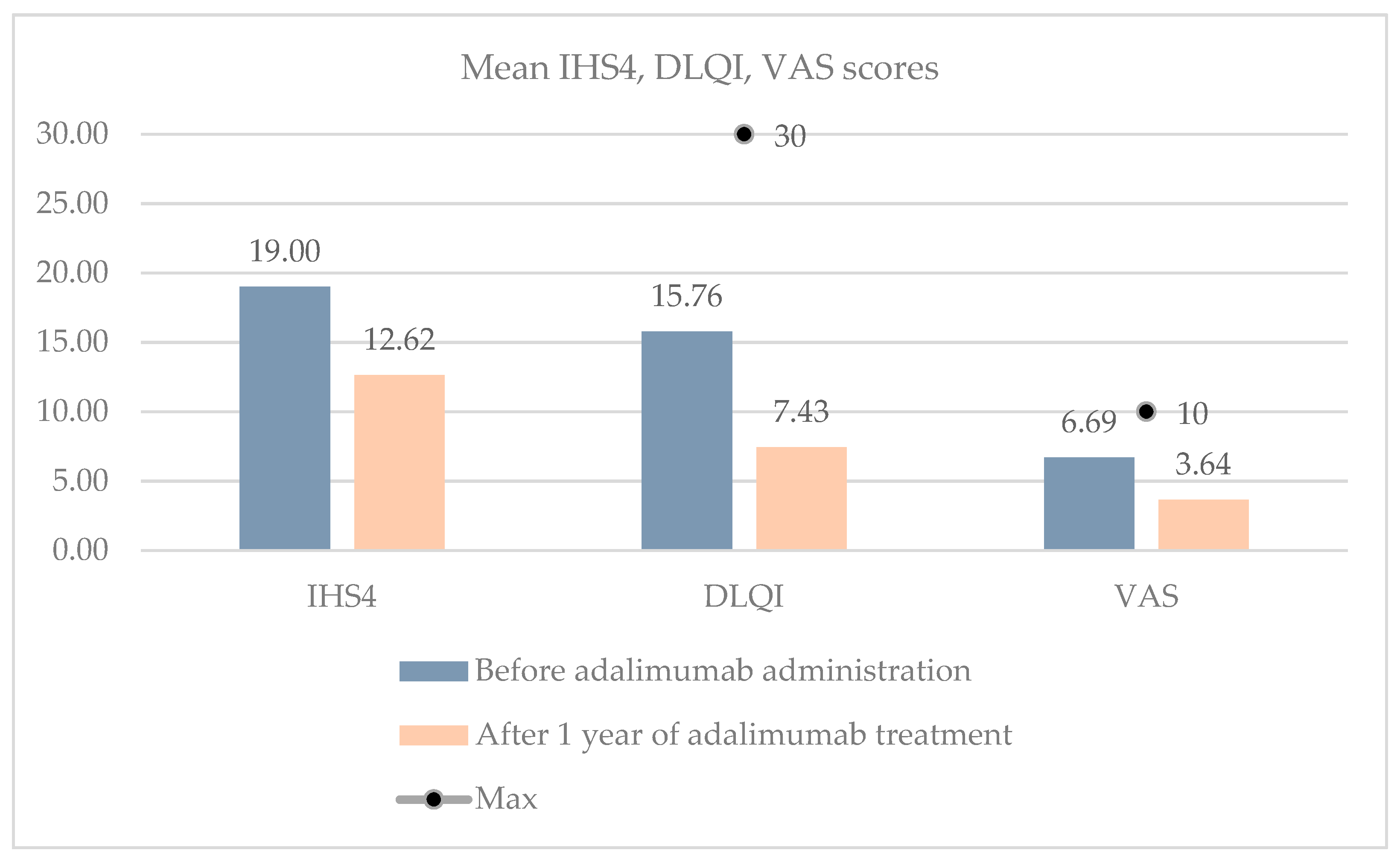
| Mean IHS4 score (±SD) | 19 (±10.78) |
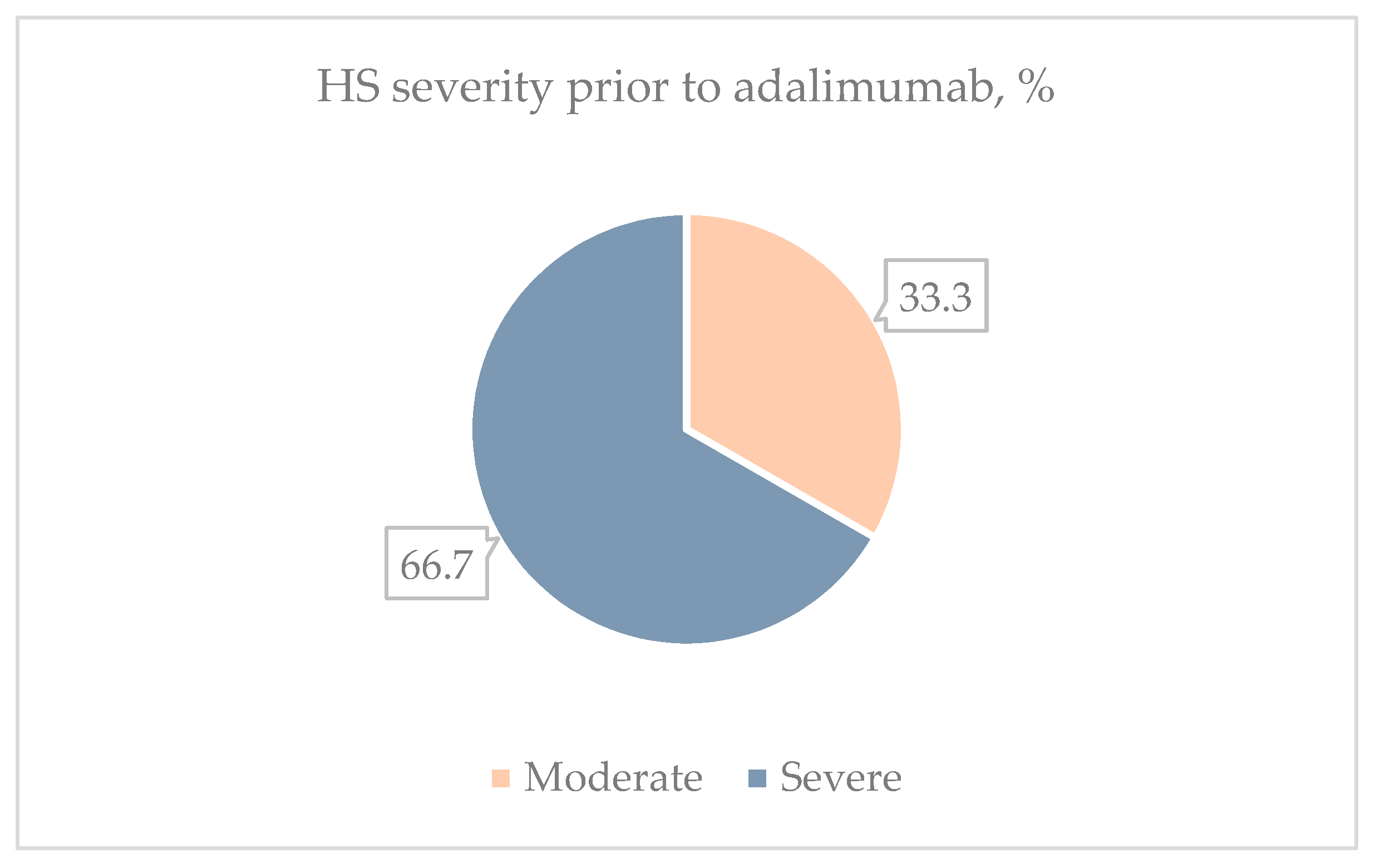
| Moderate (4–10), n, (%) | 7 (33.3%) |
| Severe (≥11), n, (%) | 14 (66.7%) |
| Mean DLQI score (±SD) | 15.76 (±7.73) |
| Mean VAS score (±SD) | 6.69 (±1.59) |
| Achieved HiSCR (n = 10) | Did Not Achieve HiSCR (n = 11) | Total (n = 21) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal BMI, Count (%) | 3 (60%) | 2 (40%) | 5 | 0.350 |
| Overweight, Count (%) | 5 (62.5%) | 3 (37.5%) | 8 | |
| Obese, Count (%) | 2 (25%) | 6 (75%) | 8 |
| Normal BMI | Overweight | Obese | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean IHS4 (±SD) | 20.4 (±13.01) | 19.75 (±13.18) | 17.38 (±7.52) | 0.928 |
| Mean DLQI (±SD) | 12.8 (±7.95) | 19.25 (±7.23) | 14.13 (±7.68) | 0.232 |
| Mean VAS (±SD) | 7.4 (±1.08) | 6.13 (±1.71) | 6.81 (±1.69) | 0.316 |
| Achieved HiSCR (n = 10) | Did Not Achieve HiSCR (n = 11) | Total (n = 21) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Had prior surgical treatment, count (%) | 6 (42.86%) | 8 (57.14%) | 14 | 0.659 |
| Did not have prior surgery, count (%) | 4 (57.14%) | 3 (42.86%) | 7 |
| Prior Surgery | No Prior Surgery | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean IHS4 (±SD) | 23.86 (±9.4) | 9.29 (±5.53) | 0.001 |
| Mean DLQI (±SD) | 15.5 (±8.92) | 16.29 (±5.12) | 0.585 |
| Mean VAS (±SD) | 6.46 (±1.82) | 7.14 (±0.9) | 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šakaitytė, A.; Česnavičiūtė, I.; Raudonis, T. Assessing the Role of Adalimumab in Treating Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Findings from a Retrospective Study at a Reference Center. Clin. Pract. 2024, 14, 1696-1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14050135
Šakaitytė A, Česnavičiūtė I, Raudonis T. Assessing the Role of Adalimumab in Treating Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Findings from a Retrospective Study at a Reference Center. Clinics and Practice. 2024; 14(5):1696-1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14050135
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠakaitytė, Austėja, Inga Česnavičiūtė, and Tadas Raudonis. 2024. "Assessing the Role of Adalimumab in Treating Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Findings from a Retrospective Study at a Reference Center" Clinics and Practice 14, no. 5: 1696-1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14050135
APA StyleŠakaitytė, A., Česnavičiūtė, I., & Raudonis, T. (2024). Assessing the Role of Adalimumab in Treating Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Findings from a Retrospective Study at a Reference Center. Clinics and Practice, 14(5), 1696-1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14050135






