Comparison between Conventional and Simple Measuring Methods of Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance in Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
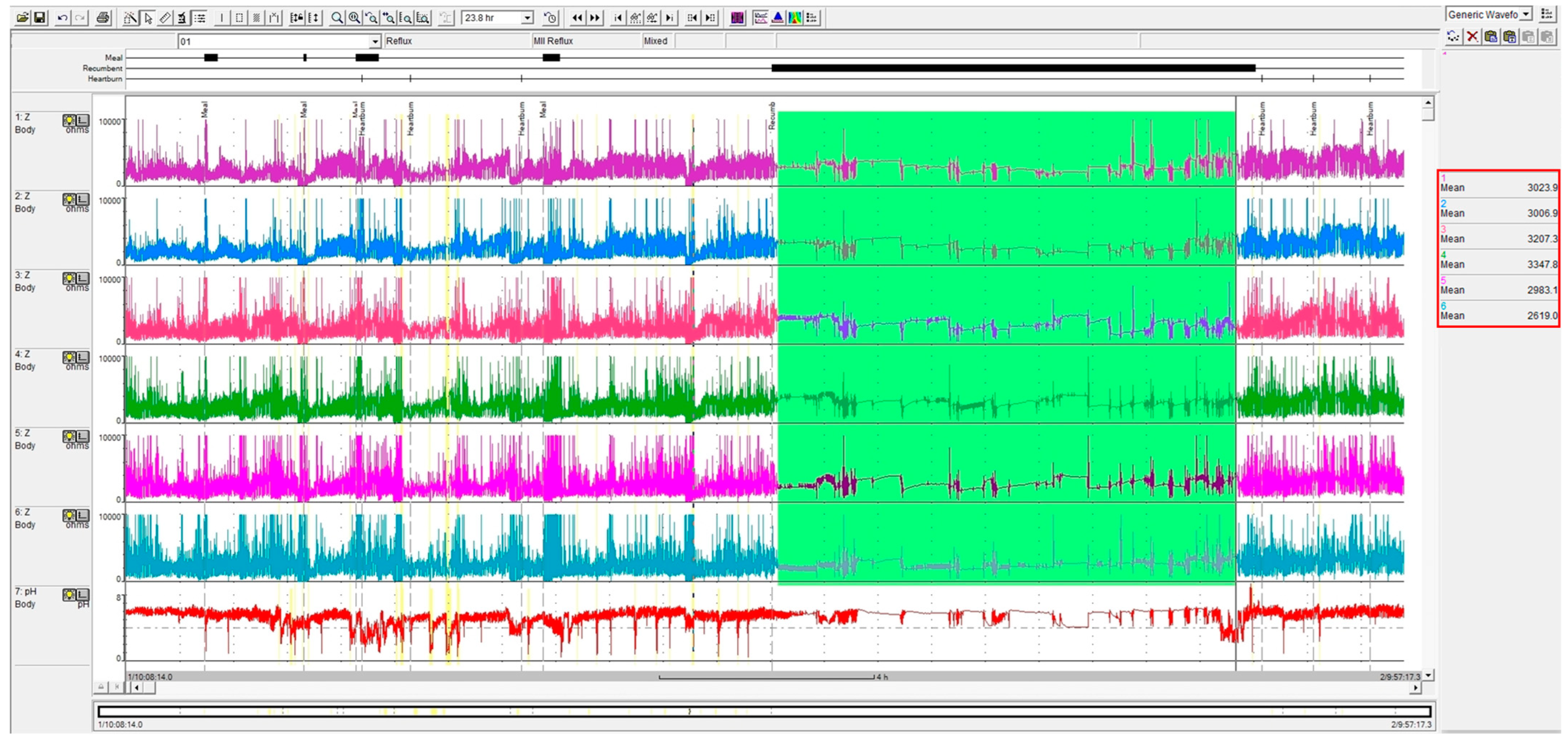
2.2. Twenty-Four-Hour Impedance–pH Monitoring
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics and pH–Impedance Measurements
3.2. Conventional MNBI Measurement
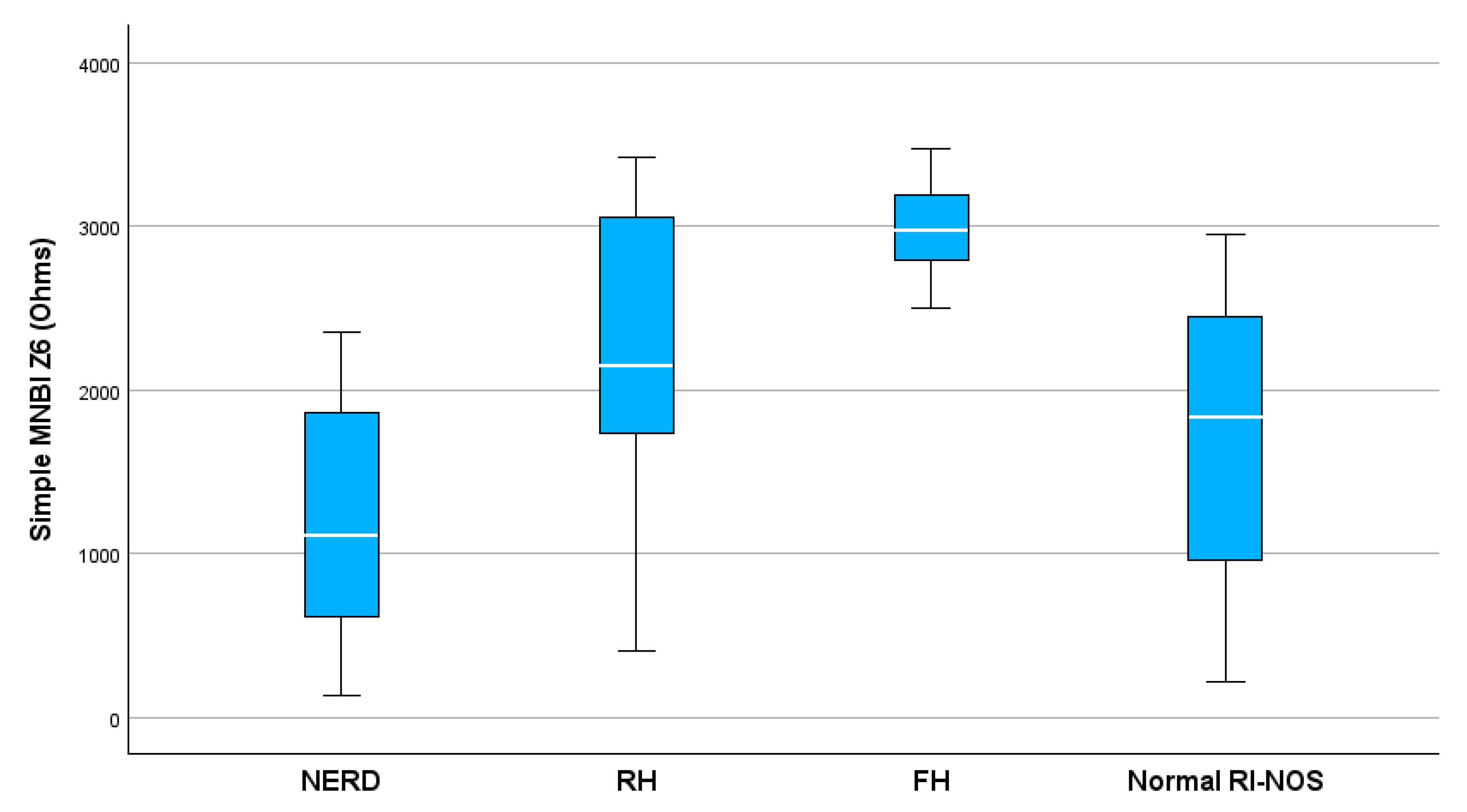
3.3. Simple MNBI Measurement
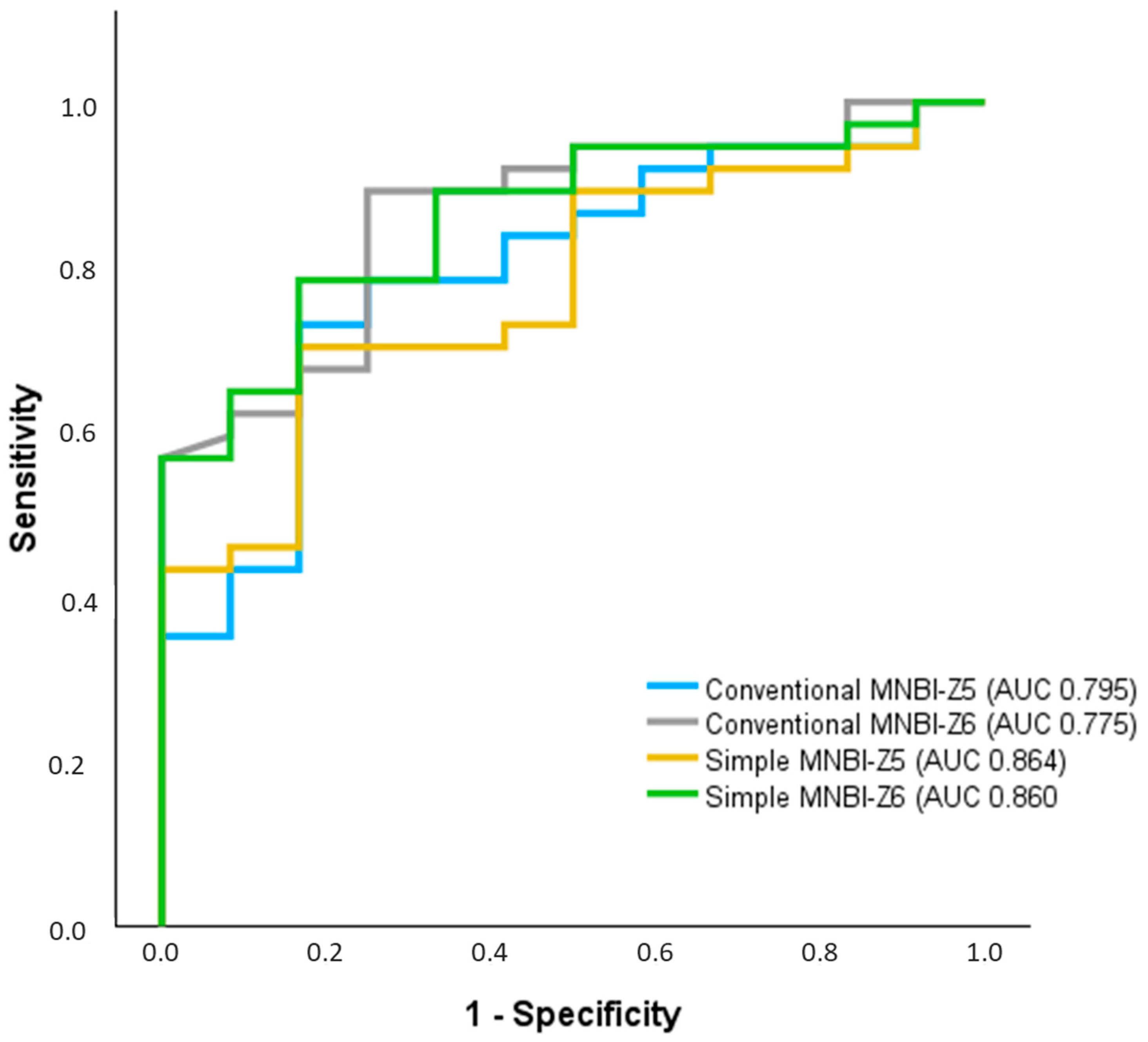
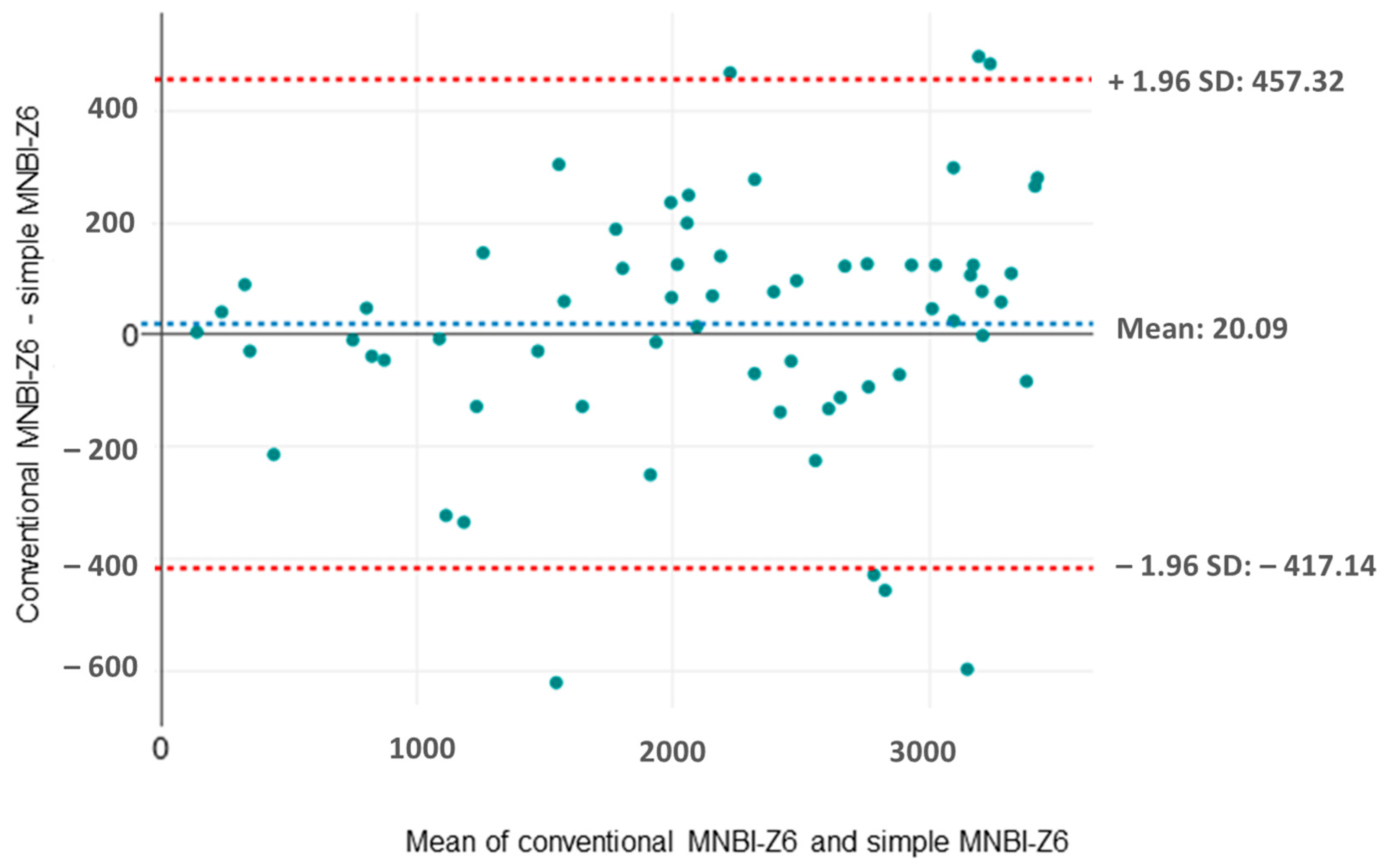
3.4. Comparison between Conventional and Simple MNBI Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vandenplas, Y.; Rudolph, C.D.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Hassall, E.; Liptak, G.; Mazur, L.; Sondheimer, J.; Staiano, A.; Thomson, M.; Veereman-Wauters, G.; et al. Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Clinical Practice Guidelines: Joint Recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN). J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 498–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, R.; Vandenplas, Y.; Singendonk, M.; Cabana, M.; DiLorenzo, C.; Gottrand, F.; Gupta, S.; Langendam, M.; Staiano, A.; Thapar, N.; et al. Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Clinical Practice Guidelines: Joint Recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutritio. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 516–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özen, M.A.; Uzuner, S.; Gökçe, S.; Tekin, M.; Eroğlu, E.; Gündoğdu, G. Nissen Fundoplikasyon Sonrası Nüks Oluşum Mekanizmalarının Yeniden Değerlendirilmesi. Turk. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2019, 33, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tural, D.A.; Büyükşahin, H.N.; Yalçın, E.G.; Soyer, T.; Ozsezen, B.; Guzelkas, İ.; Sunman, B.; Emiralioğlu, N.; Dogru, D.; Özçelik, U.; et al. Opere Özofagus Atrezisi ve Trakeoözofagial Fistülü Olan Çocukların Solunum Sistemi Problemleri. Turk. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2022, 36, 006–010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Orsi, M.; Benninga, M.; Gatcheco, F.; Rosen, R.; Thomson, M. Infant Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Management Consensus. Acta Paediatr. Int. J. Paediatr. 2024, 113, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singendonk, M.; Goudswaard, E.; Langendam, M.; Van Wijk, M.; Van Etten-Jamaludin, F.; Benninga, M.; Tabbers, M. Prevalence of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Symptoms in Infants and Children: A Systematic Review. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Pérez, J.C.; Abdo-Francis, J.M. Fenotipos de La Enfermedad Por Reflujo Gastroesofágico: Una Visión Basada En Su Fisiopatología. Cirugía Cir. 2023, 91, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junko, F.; Moore, D.; Omari, T.; Seiboth, G.; Abu-Assi, R.; Hammond, P.; Couper, R. Multichannel Impedance Monitoring for Distinguishing Nonerosive Reflux Esophagitis with Minor Changes on Endoscopy in Children. Ther. Adv. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 14, 26317745211030464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, S.; Rosen, R. The Real Relevance of Nonacid Reflux in Pediatric Patients. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 57, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, L.B.; Nurko, S.; Rosen, R. The Prevalence of Rome IV Nonerosive Esophageal Phenotypes in Children. J. Pediatr. 2017, 189, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash Gyawali, C.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Savarino, E.; Zerbib, F.; Mion, F.; Smout, A.J.P.M.; Vaezi, M.; Sifrim, D.; Fox, M.R.; Vela, M.F.; et al. Modern Diagnosis of GERD: The Lyon Consensus. Gut 2018, 67, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Alonso, M.; Moya, M.J.; Cabo, J.A.; Ribas, J.; del Carmen Macías, M.; Silny, J.; Sifrim, D. Twenty-Four-Hour Esophageal Impedance-PH Monitoring in Healthy Preterm Neonates: Rate and Characteristics of Acid, Weakly Acidic, and Weakly Alkaline Gastroesophageal Reflux. Pediatrics 2006, 118, e299–e308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quitadamo, P.; Tambucci, R.; Mancini, V.; Cristofori, F.; Baldassarre, M.; Pensabene, L.; Francavilla, R.; Di Nardo, G.; Caldaro, T.; Rossi, P.; et al. Esophageal PH-Impedance Monitoring in Children: Position Paper on Indications, Methodology and Interpretation by the SIGENP Working Group. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1522–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilic, D.; Fröhlich, T.; Nöh, F.; Pappas, A.; Schmidt-Choudhury, A.; Köhler, H.; Skopnik, H.; Wenzl, T.G. Detection of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children Using Combined Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance and PH Measurement: Data from the German Pediatric Impedance Group. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 650–654.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, H.; Machado, R.; Orsi, M.; Chao, C.S.; Alhajj, T.; Alhajj, M.; Port, C.; Skaggs, B.; Woodley, F.W. Combined Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance-PH (MII-PH): Multicenter Report of Normal Values from 117 Children. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2014, 16, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, S.; Salvatoni, A.; Van Steen, K.; Ummarino, D.; Hauser, B.; Vandenplas, Y. Behind the (Impedance) Baseline in Children. Dis. Esophagus 2014, 27, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatore, S.; Salvatoni, A.; Van Berkel, M.; Van Steen, K.; Unmarino, D.; Ghanma, A.; Hauser, B.; Vandenplas, Y. Esophageal Impedance Baseline Is Age Dependent. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilic, D.; Hankel, S.; Koerner-Rettberg, C.; Hamelmann, E.; Schmidt-Choudhury, A. The Role of Baseline Impedance as a Marker of Mucosal Integrity in Children with Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, O.; Salvatore, S.; Mancini, V.; Ribolsi, M.; Gentile, M.; Bizzarri, B.; Cicala, M.; Lindley, K.J.; de’Angelis, G.L. Relationship between Baseline Impedance Levels and Esophageal Mucosal Integrity in Children with Erosive and Non-Erosive Reflux Disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 828-e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazzoni, M.; de Bortoli, N.; Frazzoni, L.; Tolone, S.; Savarino, V.; Savarino, E. Impedance-PH Monitoring for Diagnosis of Reflux Disease: New Perspectives. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzoni, M.; de Bortoli, N.; Frazzoni, L.; Furnari, M.; Martinucci, I.; Tolone, S.; Farioli, A.; Marchi, S.; Fuccio, L.; Savarino, V.; et al. Impairment of Chemical Clearance and Mucosal Integrity Distinguishes Hypersensitive Esophagus from Functional Heartburn. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Wang, D.; Sainani, N.; Sayuk, G.S.; Gyawali, C.P. Distal Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance on PH-Impedance Monitoring Predicts Reflux Burden and Symptomatic Outcome in Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 44, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzoni, M.; Savarino, E.; de Bortoli, N.; Martinucci, I.; Furnari, M.; Frazzoni, L.; Mirante, V.G.; Bertani, H.; Marchi, S.; Conigliaro, R.; et al. Analyses of the Post-Reflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index and Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Parameters Increase the Diagnostic Yield of Impedance-PH Monitoring of Patients with Reflux Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Guo, Z.H.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhang, C. Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance: Influencing Factors and Diagnostic Value in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Technol. Health Care 2023, 31, 1875–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, B.D.; Rengarajan, A.; Ribolsi, M.; Ghisa, M.; Quader, F.; Penagini, R.; de Bortoli, N.; Mauro, A.; Cicala, M.; Savarino, E.; et al. Postreflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index from PH-Impedance Monitoring Associates with Esophageal Body Motility and Esophageal Acid Burden. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e13973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sararu, E.R.; Peagu, R.; Fierbinteanu-Braticevici, C. Association between Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance (MNBI) and Post-Reflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index (PSPW) in GERD Patients. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengarajan, A.; Savarino, E.; Della Coletta, M.; Ghisa, M.; Patel, A.; Gyawali, C.P. Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Correlates with Symptom Outcome When Acid Exposure Time Is Inconclusive on Esophageal Reflux Monitoring. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribolsi, M.; De Bortoli, N.; Frazzoni, M.; Marchetti, L.; Savarino, E.; Cicala, M. Proximal Esophageal Impedance Baseline Increases the Yield of Impedance-PH and Is Associated with Response to PPIs in Chronic Cough Patients. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2024, 36, e14775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzoni, L.; Frazzoni, M.; de Bortoli, N.; Tolone, S.; Furnari, M.; Martinucci, I.; Bertani, H.; Marchi, S.; Conigliaro, R.; Fuccio, L.; et al. Postreflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index and Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Can Link PPI-Responsive Heartburn to Reflux Better than Acid Exposure Time. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e13116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, B.; Wang, M.; Lin, L.; Jiang, L. Esophageal Nocturnal Baseline Impedance and Post-Reflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index in Identifying Proton Pump Inhibitor-Refractory Non-Erosive Reflux Disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 27, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, C.P.; Yadlapati, R.; Fass, R.; Katzka, D.; Pandolfino, J.; Savarino, E.; Sifrim, D.; Spechler, S.; Zerbib, F.; Fox, M.R.; et al. Updates to the Modern Diagnosis of GERD: Lyon Consensus 2.0. Gut 2023, 73, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.N.; Wang, C.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Chuang, C.Y.; Tsou, Y.A.; Fu, J.C.; Yang, S.S.; Chang, C.S.; Lien, H.C. Distal Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Predicts Pathological Reflux of Isolated Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Symptoms. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 29, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshikawa, Y.; Sawada, A.; Sonmez, S.; Nikaki, K.; Woodland, P.; Yazaki, E.; Sifrim, D. Measurement of Esophageal Nocturnal Baseline Impedance: A Simplified Method. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 26, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Van der Wall, H.; Falk, G.L. Conventional and Simple Methods of Measuring Esophageal Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Show Excellent Agreement. J. Dig. Dis. 2021, 22, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutalib, M.; Sintusek, P.; Punpanich, D.; Thapar, N.; Lindley, K. A New Method to Estimate Catheter Length for Esophageal Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance Monitoring in Children. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutalib, M.; Rawat, D.; Lindley, K.; Borrelli, O.; Perring, S.; Auth, M.K.H.; Thapar, N. BSPGHAN Motility Working Group Position Statement: Paediatric Multichannel Intraluminal PH Impedance Monitoring-Indications, Methods and Interpretation. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2017, 8, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, E.; Stefanelli, E.; Tambucci, R.; Salvatore, S.; De Angelis, P.; Quitadamo, P.; Pacchiarotti, C.; Di Nardo, G.; Crocco, F.; Felici, E.; et al. Prevalence of Non-Erosive Esophageal Phenotypes in Children: A European Multicenter Study. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 29, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinucci, I.; De Bortoli, N.; Savarino, E.; Piaggi, P.; Bellini, M.; Antonelli, A.; Savarino, V.; Frazzoni, M.; Marchi, S. Esophageal Baseline Impedance Levels in Patients with Pathophysiological Characteristics of Functional Heartburn. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, R.S.; Pop, D.; Chiperi, L.E.; Nechita, V.-I.; Man, S.C.; Dumitrașcu, D.L. Utility of the Post-Reflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index and Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance for the Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Phenotypes in Children. Children 2024, 11, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobey, N.A.; Carson, J.L.; Alkiek, R.A.; Orlando, R.C. Dilated Intercellular Spaces: A Morphological Feature of Acid Reflux- Damaged Human Esophageal Epithelium. Gastroenterology 1996, 111, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobey, N.A.; Hosseini, S.S.; Argote, C.M.; Dobrucali, A.M.; Awayda, M.S.; Orlando, R.C. Dilated Intercellular Spaces and Shunt Permeability in Nonerosive Acid-Damaged Esophageal Epithelium. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustaoglu, A.; Nguyen, A.; Spechler, S.; Sifrim, D.; Souza, R.; Woodland, P. Mucosal Pathogenesis in Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e14022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Lee, J.W.; Liu, T.T.; Yi, C.H.; Chen, C.L. Relevance of Ultrastructural Alterations of Intercellular Junction Morphology in Inflamed Human Esophagus. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 19, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosado-Arias, Y.M.R.; Monjaraz, E.M.T.; Mayans, J.A.R.; Mondragón, F.E.Z.; Arellano, K.R.I.; Barrios, E.M.; León, J.F.C.; Mayer, A.L.; Bustamante, R.C. Baseline Impedance and Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Values in Children with Erosive Oesophagitis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 72, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiamkulbutr, S.; Dumrisilp, T.; Sanpavat, A.; Sintusek, P. Prevalence of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children with Extraesophageal Manifestations Using Combined-Video, Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance-PH Study. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2023, 12, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosado-Arias, Y.; Toro-Monjaraz, E.M.; Cervantes-Bustamante, R.; Zarate-Mondragon, F.; Cadena-Leon, J.; Ignorosa-Arellano, K.; Loredo-Mayer, A.; Ramírez-Mayans, J. Low Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance Is Associated with a Pathological Acid Exposure Time in Children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2022, 74, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribolsi, M.; Gyawali, C.P.; Savarino, E.; Rogers, B.; Rengarajan, A.; Della Coletta, M.; Ghisa, M.; Cicala, M. Correlation between Reflux Burden, Peristaltic Function, and Mucosal Integrity in GERD Patients. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visaggi, P.; Mariani, L.; Svizzero, F.B.; Tarducci, L.; Sostilio, A.; Frazzoni, M.; Tolone, S.; Penagini, R.; Frazzoni, L.; Ceccarelli, L.; et al. Clinical Use of Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance and Post-Reflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index for the Diagnosis of Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease. Esophagus 2022, 19, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condino, A.A.; Sondheimer, J.; Pan, Z.; Gralla, J.; Perry, D.; O’Connor, J.A. Evaluation of Infantile Acid and Nonacid Gastroesophageal Reflux Using Combined PH Monitoring and Impedance Measurement. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 42, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodley, F.W.; Fernandez, S.; Mousa, H. Diurnal Variation in the Chemical Clearance of Acid Gastroesophageal Reflux in Infants. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, S.; Pagliarin, F.; Huysentruyt, K.; Bosco, A.; Fumagalli, L.; Van De Maele, K.; Agosti, M.; Vandenplas, Y. Distress in Infants and Young Children: Don’t Blame Acid Reflux. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 71, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijk, M.P.; Benninga, M.A.; Omari, T.I. Role of the Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance Technique in Infants and Children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 48, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loots, C.M.; Wijnakker, R.; van Wijk, M.P.; Davidson, G.; Benninga, M.A.; Omari, T.I. Esophageal Impedance Baselines in Infants before and after Placebo and Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 758–762, e351-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.W.; Rogers, B.D.; Liu, M.X.; Lei, W.Y.; Liu, T.T.; Yi, C.H.; Hung, J.S.; Liang, S.W.; Tseng, C.W.; Wang, J.H.; et al. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Measuring Novel PH-Impedance Metrics for Optimal Diagnosis of GERD. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, B.; Samanta, S.; Ghobadi, K.; Patel, A.; Savarino, E.; Roman, S.; Sifrim, D.; Gyawali, C.P. Artificial Intelligence Automates and Augments Baseline Impedance Measurements from PH-Impedance Studies in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.W.; Liu, M.X.; Lei, W.Y.; Liu, T.T.; Yi, C.H.; Hung, J.S.; Liang, S.W.; Lin, L.; Tseng, C.W.; Wang, J.H.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Facilitates Measuring Reflux Episodes and Postreflux Swallow-Induced Peristaltic Wave Index from Impedance-PH Studies in Patients with Reflux Disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 35, e14506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group 1 (n = 15) | Group 2 (n = 49) * | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GERD (n = 10) | Normal (n = 5) | p-Value | NERD (n = 12) | RH (n = 20) | FH (n = 13) | Normal RI-NOS (n = 4) | p-Value | |
| Age (months/years) (mean ± SD) | 6 ± 3.27 | 8 ± 3.67 | 0.302 | 13.42 ± 2.27 | 13.4 ± 3.6 | 14.46 ± 2.07 | 12.75 ± 4.72 | 0.69 |
| Sex (male, %) | 40 | 40 | NS | 75 | 40 | 23.08 | 75 | 0.03 |
| Weight-for-length/BMI-for-age percentile (%) | 34 ± 31.9 | 33 ± 30.4 | NS | 49.9 ± 28.3 | 47.4 ± 30.7 | 51.4 ± 38.4 | 63.5 ± 40.84 | 0.85 |
| Acid exposure time (%, median, IQR) | 1.8 (1.2–2.5) | 0.4 (0.3–0.6) | 0.04 | 5.9 (5.28–7.18) | 1.35 (0.5–2.5) | 0.4 (0.3–1.9) | 0.95 (0.7–1.15) | <0.001 |
| Total reflux episodes number (mean ± SD) | 69.5 ± 26.7 | 51.8 ± 19.6 | 0.21 | 94.7 ± 44.3 | 66.3 ± 45.4 | 32.8 ± 15 | 36 ± 29.5 | 0.003 |
| Acid reflux episode number | 33.2 ± 23.3 | 17.2 ± 15.1 | 0.14 | 76.3 ± 37.8 | 31.6 ± 22.2 | 18.9 ± 11.8 | 20.8 ± 11.4 | <0.001 |
| Proximal reflux episodes | 42.9 ± 22.3 | 31 ± 14.4 | 0.3 | 53.4 ± 24 | 34 ± 27.1 | 15.8 ± 6.7 | 17.3 ± 15.02 | 0.001 |
| Mean acid clearance time (s) (median, IQR) | 76.5 (61.5–126.75) | 32.0 (32.0–51.0) | 0.07 | 120.6 ± 79.8 | 62.7 ± 46.7 | 53.8 ± 51.8 | 44.5 ± 30.3 | 0.015 |
| Bolus clearance time (s) (mean ± SD) | 15.5 ± 4.6 | 13.6 ± 2.3 | 0.4 | 12.3 ± 3.55 | 15.4 ± 5.9 | 12.5 ± 3.18 | 16.5 ± 6.76 | 0.16 |
| PSPW index (%) | 36.4 ± 12.9 | 52.9 ± 12.6 | 0.03 | 36.1 ± 13.9 | 47.6 ± 14.8 | 69.9 ± 14.4 | 65.4 ± 11.3 | <0.001 |
| Conventional MNBI-Z1 | 1559 ± 775 | 1411 ± 650 | 0.72 | 2327 ± 1057 | 2724 ± 959 | 2453 ± 585 | 1725 ± 1233 | 0.23 |
| Conventional MNBI-Z2 | 1674 ± 661 | 1795 ± 506 | 0.72 | 2536 ± 1066 | 2492 ± 721 | 2497 ± 537 | 1748 ± 1182 | 0.37 |
| Conventional MNBI-Z3 | 1892 ± 560 | 2209 ± 351 | 0.27 | 2796 ± 1152 | 2895 ± 1013 | 2912 ± 594 | 2180 ± 1313 | 0.59 |
| Conventional MNBI-Z4 | 2170 ± 528 | 2197 ± 418 | 0.92 | 2388 ± 1038 | 2887 ± 995 | 2811 ± 623 | 2127 ± 1298 | 0.108 |
| Conventional MNBI-Z5 | 2334 ± 752 | 2155 ± 576 | 0.65 | 1812 ± 875 | 2645 ± 984 | 3256 ± 613 | 1941 ± 1146 | 0.001 |
| Conventional MNBI-Z6 | 2342 ± 911 | 2357 ± 426 | 0.97 | 1121 ± 773 | 2281 ± 890 | 2882 ± 526 | 1652 ± 1225 | <0.001 |
| Group 1 | Group 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GERD (n = 10) | Normal (n = 5) | p-Value | NERD (n = 12) | RH (n = 20) | FH (n = 13) | Normal RI-NOS (n = 4) | p-Value | |
| Simple MNBI-Z1 | 1731 ± 804 | 1526 ± 715 | 0.63 | 2300 ± 900 | 2697 ± 803 | 2469 ± 563 | 1803 ± 1244 | 0.203 |
| Simple MNBI-Z2 | 1758 ± 578 | 1851 ± 335 | 0.74 | 2398 ± 946 | 2472 ± 634 | 2482 ± 605 | 1791 ± 1199 | 0.751 |
| Simple MNBI-Z3 | 1883 ± 532 | 2180 ± 224 | 0.25 | 2641 ± 1089 | 2887 ± 995 | 2811 ± 623 | 2127 ± 1298 | 0.520 |
| Simple MNBI-Z4 | 2177 ± 565 | 2062 ± 232 | 0.68 | 2257 ± 1044 | 2868 ± 1045 | 3136 ± 756 | 2084 ± 1276 | 0.088 |
| Simple MNBI-Z5 | 2318 ± 760 | 2156 ± 538 | 0.6 | 1872 ± 853 | 2609 ± 976 | 3172 ± 600 | 2101 ± 1263 | 0.005 |
| Simple MNBI-Z6 | 2259 ± 871 | 2342 ± 500 | 0.84 | 1194 ± 735 | 2233 ± 820 | 2868 ± 517 | 1708 ± 1128 | <0.001 |
| Absolute Values (Means) | Correlation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional MNBI | Simple MNBI | p-Value | r-Value | p-Value | |
| MNBI-Z1 | 1510 | 1663 | 0.873 | 0.95 | <0.001 |
| MNBI-Z2 | 1714 | 1789 | 0.320 | 0.88 | <0.001 |
| MNBI-Z3 | 1998 | 1982 | 0.143 | 0.93 | <0.001 |
| MNBI-Z4 | 2179 | 2138 | <0.001 | 0.88 | <0.001 |
| MNBI-Z5 | 2274 | 2264 | 0.806 | 0.98 | <0.001 |
| MNBI-Z6 | 2347 | 2287 | 0.972 | 0.96 | <0.001 |
| Absolute Values (Means) | Correlation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional MNBI | Simple MNBI | p-Value | r-Value | p-Value | |
| MNBI-Z1 | 2473 | 2466 | 0.873 | 0.95 | <0.001 |
| MNBI-Z2 | 2444 | 2401 | 0.320 | 0.93 | <0.001 |
| MNBI-Z3 | 2817 | 2744 | 0.143 | 0.94 | <0.001 |
| MNBI-Z4 | 2840 | 2725 | <0.001 | 0.98 | <0.001 |
| MNBI-Z5 | 2545 | 2536 | 0.806 | 0.97 | <0.001 |
| MNBI-Z6 | 2105 | 2104 | 0.972 | 0.97 | <0.001 |
| MNBI Impedance Channel | GERD Phenotype | Correlation Coefficient (r-Value) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| MNBI-Z5 | NERD | 0.952 | <0.001 |
| RH | 0.980 | <0.001 | |
| FH | 0.897 | <0.001 | |
| Normal RI-NOS | 0.4 | 0.6 | |
| MNBI-Z6 | NERD | 0.953 | <0.001 |
| RH | 0.973 | <0.001 | |
| FH | 0.816 | <0.001 | |
| Normal RI-NOS | 0.969 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pop, R.S.; Chiperi, L.E.; Nechita, V.-I.; Man, S.C.; Dumitrașcu, D.L. Comparison between Conventional and Simple Measuring Methods of Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance in Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Clin. Pract. 2024, 14, 1682-1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14050134
Pop RS, Chiperi LE, Nechita V-I, Man SC, Dumitrașcu DL. Comparison between Conventional and Simple Measuring Methods of Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance in Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Clinics and Practice. 2024; 14(5):1682-1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14050134
Chicago/Turabian StylePop, Radu Samuel, Lăcrămioara Eliza Chiperi, Vlad-Ionuț Nechita, Sorin Claudiu Man, and Dan Lucian Dumitrașcu. 2024. "Comparison between Conventional and Simple Measuring Methods of Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance in Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease" Clinics and Practice 14, no. 5: 1682-1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14050134
APA StylePop, R. S., Chiperi, L. E., Nechita, V.-I., Man, S. C., & Dumitrașcu, D. L. (2024). Comparison between Conventional and Simple Measuring Methods of Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance in Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Clinics and Practice, 14(5), 1682-1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14050134








