Optimizing Atrial Fibrillation Care: Comparative Assessment of Anticoagulant Therapies and Risk Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sagris, M.; Vardas, E.P.; Theofilis, P.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Oikonomou, E.; Tousoulis, D. Atrial fibrillation: Pathogenesis, predisposing factors, and Genetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lascalzo, J.; Fauci, A.S.; Kasper, D.L.; Longo, D.L.; Braunwald, E.; Hauser, S.L.; Jameson, J.L. (Eds.) Tachyarrhythmias. In Harrison’s Cardiovascular Medicine; McGraw-Hill Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Ramrakha, P.; Hill, J. (Eds.) Arrhythmias. In Oxford Handbook of Cardiology, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 504–507. [Google Scholar]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (eacts). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, B.P.; Zardkoohi, O. Tachyarrhythmias. In Manual of Cardiovascular Medicine.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 358–361. [Google Scholar]
- Katsanos, A.H.; Kamel, H.; Healey, J.S.; Hart, R.G. Stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2020, 142, 2371–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.W.; Barillari, G. Non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in cardiovascular disease management: Evidence and unanswered questions. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 39, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, D.; Rahman, F.; Schnabel, R.B.; Yin, X.; Benjamin, E.J.; Christophersen, I.E. Atrial fibrillation in women: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, presentation, and prognosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, L.; Norby, F.L.; Chen, L.Y.; O’Neal, W.T.; Lewis, T.T.; Loehr, L.R.; Soliman, E.Z.; Alonso, A. Lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation by race and socioeconomic status: ARIC Study (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities). Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2018, 11, e006350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabel, R.B.; Yin, X.; Gona, P.; Larson, M.G.; Beiser, A.S.; McManus, D.D.; Newton-Cheh, C.; Lubitz, S.A.; Magnani, J.W.; Ellinor, P.T.; et al. 50 year trends in atrial fibrillation prevalence, incidence, risk factors, and mortality in the Framingham Heart Study: A cohort study. Lancet 2015, 386, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolbrette, D.; Naccarelli, G.; Curtis, A.; Lehmann, M.; Kadish, A. Gender differences in arrhythmias. Clin. Cardiol. 2002, 25, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerman, S.; Wenger, N. Gender differences in atrial fibrillation: A review of Epidemiology, management, and outcomes. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 15, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staerk, L.; Sherer, J.A.; Ko, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Helm, R.H. Atrial fibrillation. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1501–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.J.; Deshmukh, A.; Pant, S.; Singh, V.; Patel, N.; Arora, S.; Shah, N.; Chothani, A.; Savani, G.T.; Mehta, K.; et al. Contemporary trends of hospitalization for atrial fibrillation in the United States, 2000 through 2010. Circulation 2014, 129, 2371–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyne, K.S.; Paramore, C.; Grandy, S.; Mercader, M.; Reynolds, M.; Zimetbaum, P. Assessing the direct costs of treating nonvalvular atrial fibrillation in the United States. Value Health 2006, 9, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, A.M.; Alonso, A.; Gersh, B.J.; Manemann, S.M.; Killian, J.M.; Weston, S.A.; Byrne, M.; Roger, V.L. Multimorbidity and the risk of hospitalization and death in atrial fibrillation: A population-based study. Am. Heart J. 2017, 185, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joglar, J.A.; Chung, M.K.; Armbruster, A.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Chyou, J.Y.; Cronin, E.M.; Deswal, A.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Gopinathannair, R.; et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/hrs guideline for the diagnosis and management of Atrial Fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2024, 149, e1–e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, T.; Joung, B.; Takahashi, Y.; Lim, T.W.; Choi, E.; Chan, Y.; Guo, Y.; Sriratanasathavorn, C.; Oh, S.; Okumura, K.; et al. 2021 focused update of the 2017 consensus guidelines of the Asia Pacific Heart rhythm society (APHRS) on stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. J. Arrhythmia 2021, 37, 1389–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.; Yang, P.-S.; Jang, E.; Yu, H.T.; Kim, T.-H.; Uhm, J.-S.; Kim, J.-Y.; Sung, J.-H.; Pak, H.-N.; Lee, M.-H.; et al. Improved population-based clinical outcomes of patients with atrial fibrillation by compliance with the simple ABC (atrial fibrillation better care) pathway for Integrated Care Management: A nationwide cohort study. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romiti, G.F.; Proietti, M.; Bonini, N.; Ding, W.Y.; Boriani, G.; Huisman, M.V.; Lip, G.Y.H. Adherence to the atrial fibrillation better care (ABC) pathway and the risk of major outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation: A post-hoc analysis from the prospective Gloria-AF Registry. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 55, 101757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.M.; Palazzolo, M.G.; Murphy, S.A.; Antman, E.M.; Braunwald, E.; Lanz, H.-J.; Lip, G.Y.; Giugliano, R.P.; Ruff, C.T. Evaluation of the atrial fibrillation better care pathway in the engage AF-TIMI 48 trial. EP Eur. 2022, 24, 1730–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, T.; Proietti, M.; Shantsila, A.; Romiti, G.F.; Teo, W.-S.; Park, H.-W.; Shimizu, W.; Tse, H.-F.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Chao, T.-F. Integrated care for atrial fibrillation using the ABC pathway in the prospective APHRS-AF Registry. JACC Asia 2023, 3, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Levy, D.; Vaziri, S.M.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Belanger, A.J.; Wolf, P.A. Independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation in a population-based cohort: The Framingham Heart Study. JAMA 1994, 271, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxley, R.R.; Lopez, F.L.; Folsom, A.R.; Agarwal, S.K.; Loehr, L.R.; Soliman, E.Z.; Maclehose, R.; Konety, S.; Alonso, A. Absolute and attributable risks of atrial fibrillation in relation to optimal and borderline risk factors: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Circulation 2011, 123, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.T.; Williamson, J.D.; Whelton, P.K.; Snyder, J.K.; Sink, K.M.; Rocco, M.V.; Reboussin, D.M.; Rahman, M.; Oparil, S.; Lewis, C.E.; et al. A randomized trial of intensive versus standard blood-pressure control. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2103–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokorney, S.D.; Piccini, J.P.; Stevens, S.R.; Patel, M.R.; Pieper, K.S.; Halperin, J.L.; Breithardt, G.; Singer, D.E.; Hankey, G.J.; Hacke, W.; et al. Cause of death and predictors of all-cause mortality in anticoagulated patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: Data from ROCKET AF. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.P.; Halvorsen, S.; Wojdyla, D.; Thomas, L.; Alexander, J.H.; Hylek, E.M.; Hanna, M.; Bahit, M.C.; Lopes, R.D.; De Caterina, R.; et al. Apixaban for Reduction in Sroke and Other Thromboembolic Events in Atrial Fibrillation Steering Committee and Investigators. Blood pressure control and risk of stroke or systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation: Results from the Apixaban for Reduction in Stroke and Other Thromboembolic Events in Atrial Fibrillation (ARISTOTLE) trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Heo, R.; Handschumacher, M.D.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.-S.; Kim, K.-R.; Shin, Y.; Park, H.-K.; Bischoff, J.; Aikawa, E.; et al. Mitral valve adaptation to isolated annular dilation. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoit, B.D. Atrial functional mitral regurgitation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 1482–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mountantonakis, S.E.; Grau-Sepulveda, M.V.; Bhatt, D.L.; Hernandez, A.F.; Peterson, E.D.; Fonarow, G.C. Presence of atrial fibrillation is independently associated with adverse outcomes in patients hospitalized with heart failure: An analysis of Get with The Guidelines–Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2012, 5, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksena, S.; Slee, A.; Waldo, A.L.; Freemantle, N.; Reynolds, M.; Rosenberg, Y.; Rathod, S.; Grant, S.; Thomas, E.; Wyse, D.G. Cardiovascular outcomes in the AFFIRM trial (Atrial Fibrillation Follow-Up Investigation of Rhythm Management): An assessment of individual antiarrhythmic drug therapies compared with rate control with propensity score-matched analyses. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 1975–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; Leip, E.P.; Wolf, P.A.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Murabito, J.M.; Kannel, W.B.; Benjamin, E.J. Temporal relations of atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure and their joint influence on mortality: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2003, 107, 2920–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, M.A.; Fudim, M.; DeVore, A.D.; Piccini, J.P. Heart failure and atrial fibrillation, like fire and fury. JACC Heart Fail. 2019, 7, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, E.L.; Sturgess, J.E.; O’Keefe, J.H.; Gupta, S.; Lavie, C.J. Prevention and treatment of atrial fibrillation via risk factor modification. Am. J. Cardiol. 2021, 160, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Bahnson, J.L.; Gaussoin, S.A.; Bertoni, A.G.; Johnson, K.C.; Lewis, C.E.; Vetter, M.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Jeffery, R.W.; Soliman, E.Z. Effect of an intensive lifestyle intervention on atrial fibrillation risk in individuals with type 2 diabetes: The look ahead randomized trial. Am. Heart J. 2015, 170, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alasady, M.; Abhayaratna, W.P.; Leong, D.P.; Lim, H.S.; Abed, H.S.; Brooks, A.G.; Mattchoss, S.; Roberts-Thomson, K.C.; Worthley, M.I.; Chew, D.P.; et al. Coronary artery disease affecting the atrial branches is an independent determinant of atrial fibrillation after myocardial infarction. Heart Rhythm. 2011, 8, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruddox, V.; Sandven, I.; Munkhaugen, J.; Skattebu, J.; Edvardsen, T.; Otterstad, J.E. Atrial fibrillation and the risk for myocardial infarction, all-cause mortality and heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2017, 24, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linz, D.; Dobrev, D. Outcome of atrial fibrillation ablation in pulmonary hypertension: Is pulmonary hypertension a modifiable risk factor? IJC Heart Vasc. 2019, 23, 100360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudis, C.A. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and atrial fibrillation: An unknown relationship. J. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.C.; Wallin, A.; Håkansson, N.; Stackelberg, O.; Bäck, M.; Wolk, A. Type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus and incidence of seven cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 262, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxley, R.R.; Filion, K.B.; Konety, S.; Alonso, A. Meta-analysis of cohort and case-control studies of type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 108, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Parise, H.; Levy, D.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Wolf, P.A.; Vasan, R.S.; Benjamin, E.J. Obesity and the risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation. JAMA 2004, 292, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertomeu-González, V.; Anguita, M.; Moreno-Arribas, J.; Cequier, Á.; Muñiz, J.; Castillo-Castillo, J.; Sanchis, J.; Roldán, I.; Marin, F.; Bertomeu-Martínez, V. Quality of anticoagulation with Vitamin K antagonists. Clin. Cardiol. 2015, 38, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P.A.; Abbott, R.D.; Kannel, W.B. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: The Framingham Study. Stroke 1991, 22, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.J.; Wolf, P.A.; Kelly-Hayes, M.; Beiser, A.S.; Kase, C.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; D’Agostino, R.B. Stroke severity in atrial fibrillation. Fram. Study. Stroke 1996, 27, 1760–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wańkowicz, P.; Nowacki, P.; Gołąb-Janowska, M. Atrial fibrillation risk factors in patients with ischemic stroke. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 17, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohla, M.; Weiss, T.W.; Pecen, L.; Patti, G.; Siller-Matula, J.M.; Schnabel, R.B.; Schilling, R.; Kotecha, D.; Lucerna, M.; Huber, K.; et al. Risk factors for thromboembolic and bleeding events in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation: The prospective, multicentre observational prevention of thromboembolic events—European registry in Atrial Fibrillation (prefer in AF). BMJ Open 2019, 9, e022478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.; Davis, S.; Kilpatrick, C.; Gerraty, R.; Campbell, D.; Greenberg, P. The morbidity related to atrial fibrillation at a Tertiary Centre in one year: 9.0% of all strokes are potentially preventable. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2002, 9, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, D.; Song, T.-J.; Kim, B.J.; Heo, S.H.; Jung, J.-M.; Oh, K.; Kim, C.K.; Yu, S.; Park, K.Y.; Kim, J.-M.; et al. Stroke-specific predictors of major bleeding in anticoagulated patients with stroke and atrial fibrillation: A nationwide Multicenter Registry-Based Study. J. Clin. Neurol. 2023, 19, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Cai, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W. Diagnostic accuracy of the has-bled bleeding score in VKA- or DOAC-treated patients with atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 757087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteve-Pastor, M.A.; García-Fernández, A.; Macías, M.; Sogorb, F.; Valdés, M.; Roldán, V.; Muñiz, J.; Badimon, L.; Roldán, I.; Bertomeu-Martínez, V.; et al. Is the orbit bleeding risk score superior to the has-bled score in anticoagulated atrial fibrillation patients? Circ. J. 2016, 80, 2102–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roldán, V.; Marín, F.; Fernández, H.; Manzano-Fernandez, S.; Gallego, P.; Valdés, M.; Vicente, V.; Lip, G.Y.H. Predictive value of the has-bled and atria bleeding scores for the risk of serious bleeding in a “real-world” population with atrial fibrillation receiving anticoagulant therapy. Chest 2013, 143, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, K.A.; Virdone, S.; Pieper, K.S.; Bassand, J.-P.; Camm, A.J.; Fitzmaurice, D.A.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Goto, S.; Haas, S.; Kayani, G.; et al. Garfield-AF risk score for mortality, stroke, and bleeding within 2 years in patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J.—Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes 2021, 8, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proietti, M.; Rivera-Caravaca, J.M.; Esteve-Pastor, M.A.; Romiti, G.F.; Marin, F.; Lip, G.Y. Predicting bleeding events in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation: A comparison between the has-bled and Garfield-AF Bleeding Scores. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, R.; Ruff, C.T.; Virdone, S.; Perreault, S.; Kakkar, A.K.; Palazzolo, M.G.; Dorais, M.; Kayani, G.; Singer, D.E.; Secemsky, E.; et al. Development and validation of the DOAC score: A novel bleeding risk prediction tool for patients with atrial fibrillation on direct-acting oral anticoagulants. Circulation 2023, 148, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, T.; Stewart, F.; Eisinga, A. NOACs versus warfarin for stroke prevention in patients with AF: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Open Heart 2016, 3, e000279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, R.D.; Alexander, J.H.; Al-Khatib, S.M.; Ansell, J.; Diaz, R.; Easton, J.D.; Gersh, B.J.; Granger, C.B.; Hanna, M.; Horowitz, J.; et al. Apixaban for reduction in stroke and other ThromboemboLic events in atrial fibrillation (ARISTOTLE) trial: Design and rationale. Am. Heart J. 2010, 159, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, S.; Wojdyla, D.M.; White, H.D.; Piccini, J.P.; Paolini, J.F.; Nessel, C.C.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Patel, M.R.; Becker, R.C.; Halperin, J.L.; et al. Predictors of major bleeding risk: Insights from the Rivaroxaban Once-daily Oral Direct Factor Xa Inhibition Compared with Vitamin K Antagonism of Stroke and Embolism Trial in Atrial Fibrillation (ROCKET AF). Circulation 2011, 124 (Suppl. S1), 340–347. [Google Scholar]
- Hori, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Tanahashi, N.; Momomura, S.I.; Uchiyama, S.; Goto, S.; Izumi, T.; Koretsune, Y.; Kajikawa, M.; Kato, M.; et al. Rivaroxaban vs. warfarin in Japanese patients with atrial fibrillation—The J-ROCKET AF study. Circ. J. 2012, 76, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikelboom, J.W.; Wallentin, L.; Connolly, S.J.; Ezekowitz, M.; Healey, J.S.; Oldgren, J.; Yang, S.; Alings, M.; Kaatz, S.; Hohnloser, S.H.; et al. Risk of bleeding with 2 doses of dabigatran compared with warfarin in older and younger patients with atrial fibrillation: An analysis of the randomized evaluation of long-term anticoagulant therapy (RE-LY) trial. Circulation 2011, 123, 2363–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Ruff, C.T.; Braunwald, E.; Murphy, S.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Halperin, J.L.; Waldo, A.L.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Jeffrey, D.P., III; Špinar, W.M.D.J.; et al. Edoxaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
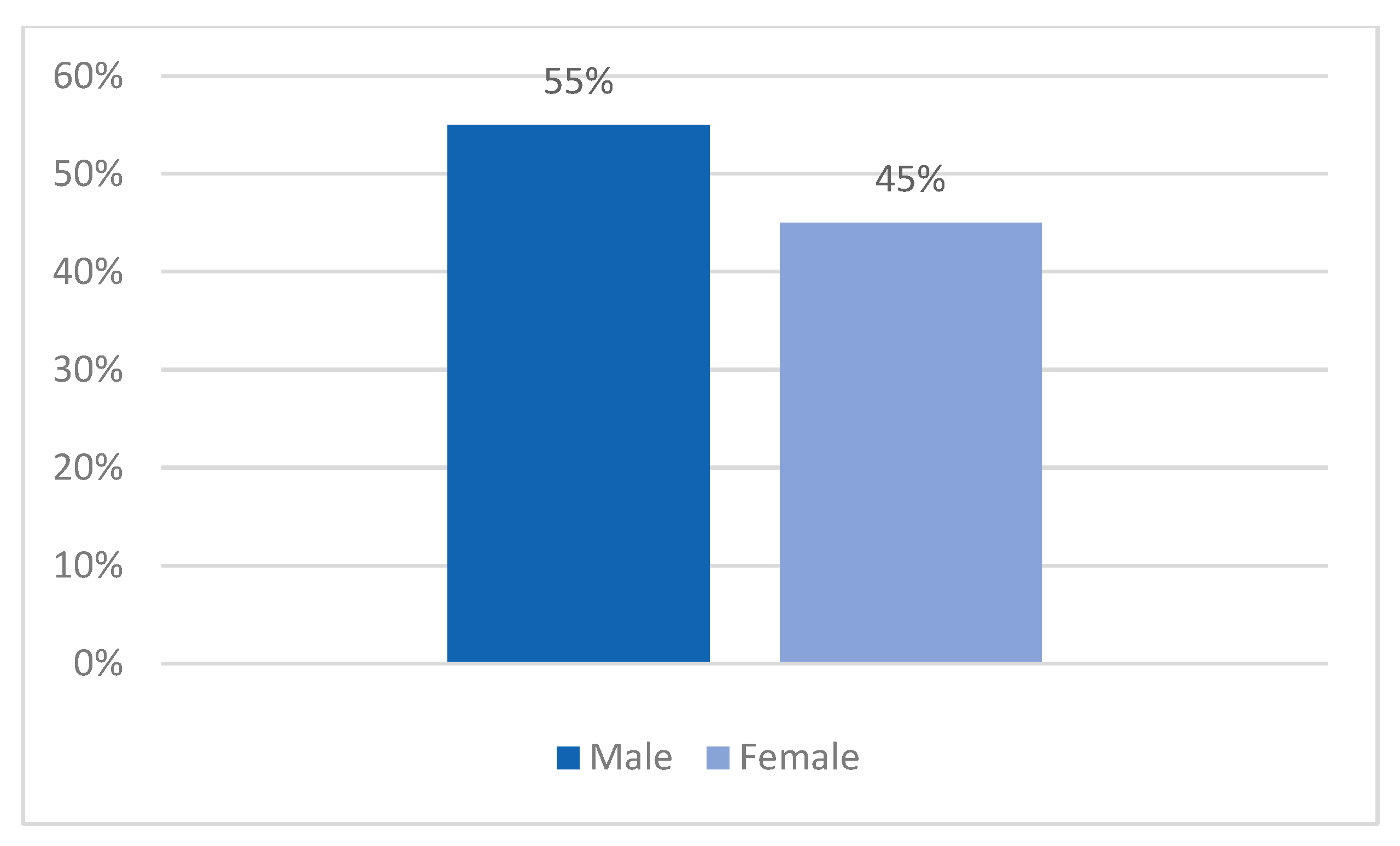





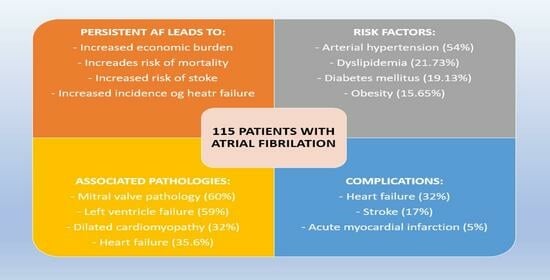
| Characteristics of the Patients at Baseline | |
|---|---|
| Characteristic | Total Sample (N = 345) |
| Sex distribution | |
| Male—no. (%) | 190 (55%) |
| Female—no. (%) | 155 (45%) |
| Age distribution | |
| 15–24 y.o.—no. (%) | 7 (2%) |
| 35–44 y.o.—no. (%) | 7 (2%) |
| 45–44 y.o.—no. (%) | 3 (1%) |
| 55–66 y.o.—no. (%) | 62 (18%) |
| 65–74 y.o.—no. (%) | 97 (33%) |
| >75 y.o.—no. (%) | 169 (49%) |
| Hospitalization days | |
| 3–5 days—no. (%) | 59 (17%) |
| 6–10 days—no. (%) | 241 (70%) |
| 11–15 days—no. (%) | 31 (9%) |
| >15 days—no. (%) | 14 (4%) |
| Complications | |
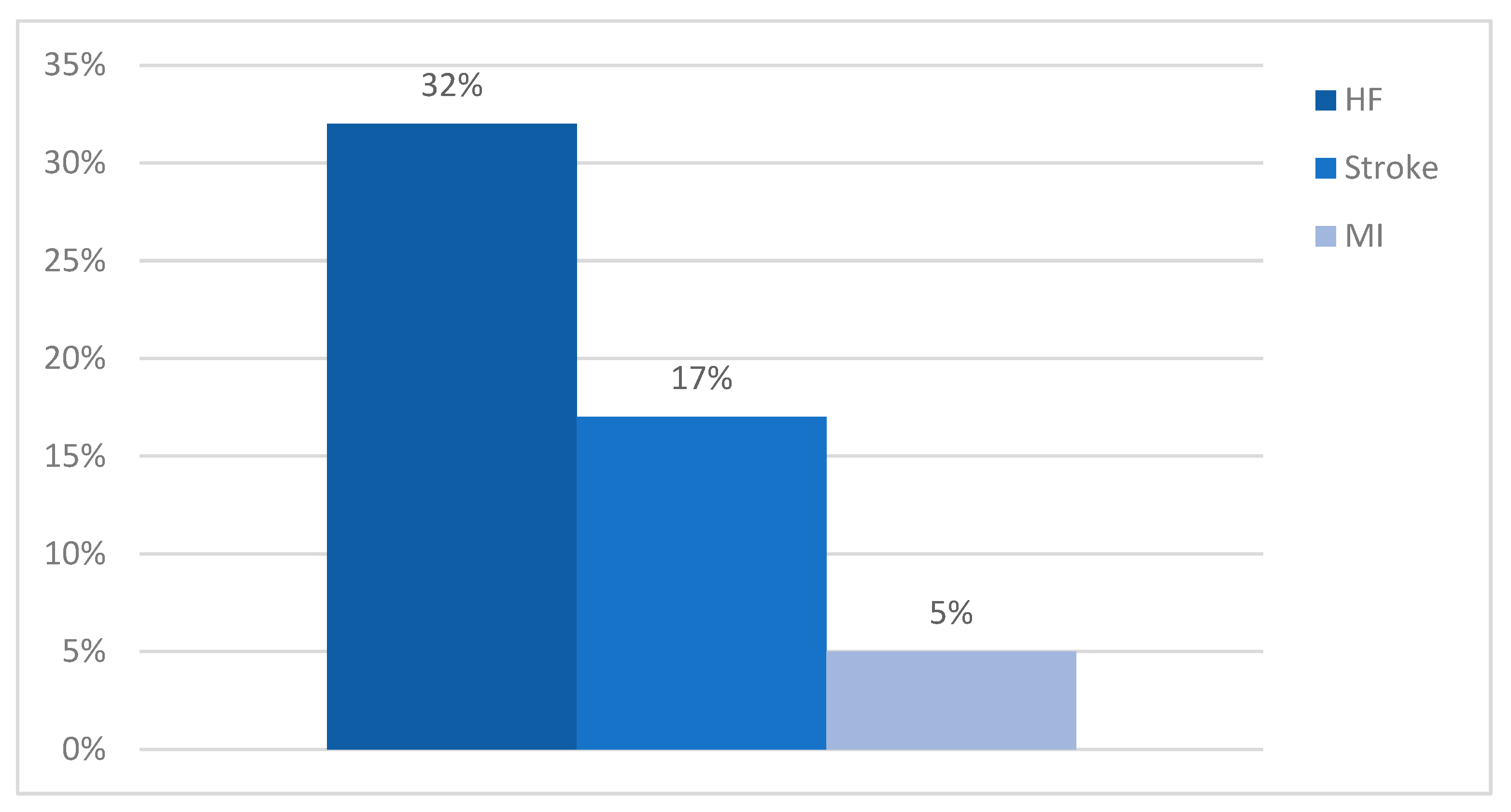
| HF—no. (%) | 110 (32%) |
| Stroke—no. (%) | 59 (17%) |
| MI—no. (%) | 17 (5%) |
| Risk factors/comorbidities | |
| HF—no. (%) | 123 (35.6%) |
| HBP—no. (%) | 186 (54%) |
| DM2—no. (%) | 66 (19.13%) |
| Obesity—no. (%) | 54 (15.65%) |
| LDL-c—no. (%) | 14 (4%) |
| HTG—no. (%) | 9 (2.6%) |
| TD—no. (%) | 9 (2.6%) |
| LVF—no. (%) | 204 (59%) |
| MR—no. (%) | 207 (60%) |
| TR—no. (%) | 90 (26%) |
| AR—no. (%) | 66 (19%) |
| MS—no. (%) | 21 (6%) |
| AS—no. (%) | 38 (11%) |
| DM—no. (%) | 110 (32%) |
| MI—no. (%) | 17 (5%) |
| AH and/or AR—no. (%) | 28 (8%) |
| HE—no. (%) | 34 (10%) |
| PH—no. (%) | 86 (25%) |
| COPD—no. (%) | 38 (11%) |
| Other—no. (%) | 21 (6%) |
| Labile INR—no. (%) | 104 (30%) |
| Anticoagulant therapy before admission | |
| NOACs—no. (%) | 252 (73%) |
| VKAs—no. (%) | 55 (16%) |
| VKAs + aspirin—no. (%) | 21 (6%) |
| Unspecified—no. (%) | 17 (5) |
| During hospitalization | |
| LMWH—no. (%) | 31 (9%) |
| LMWH + VKAs—no. (%) | 93 (27%) |
| LMVH + VKAs + aspirin—no. (%) | 21 (6%) |
| VKAs + aspirin—no. (%) | 21 (6%) |
| NOACs—no. (%) | 179 (52%) |
| After hospitalization | |
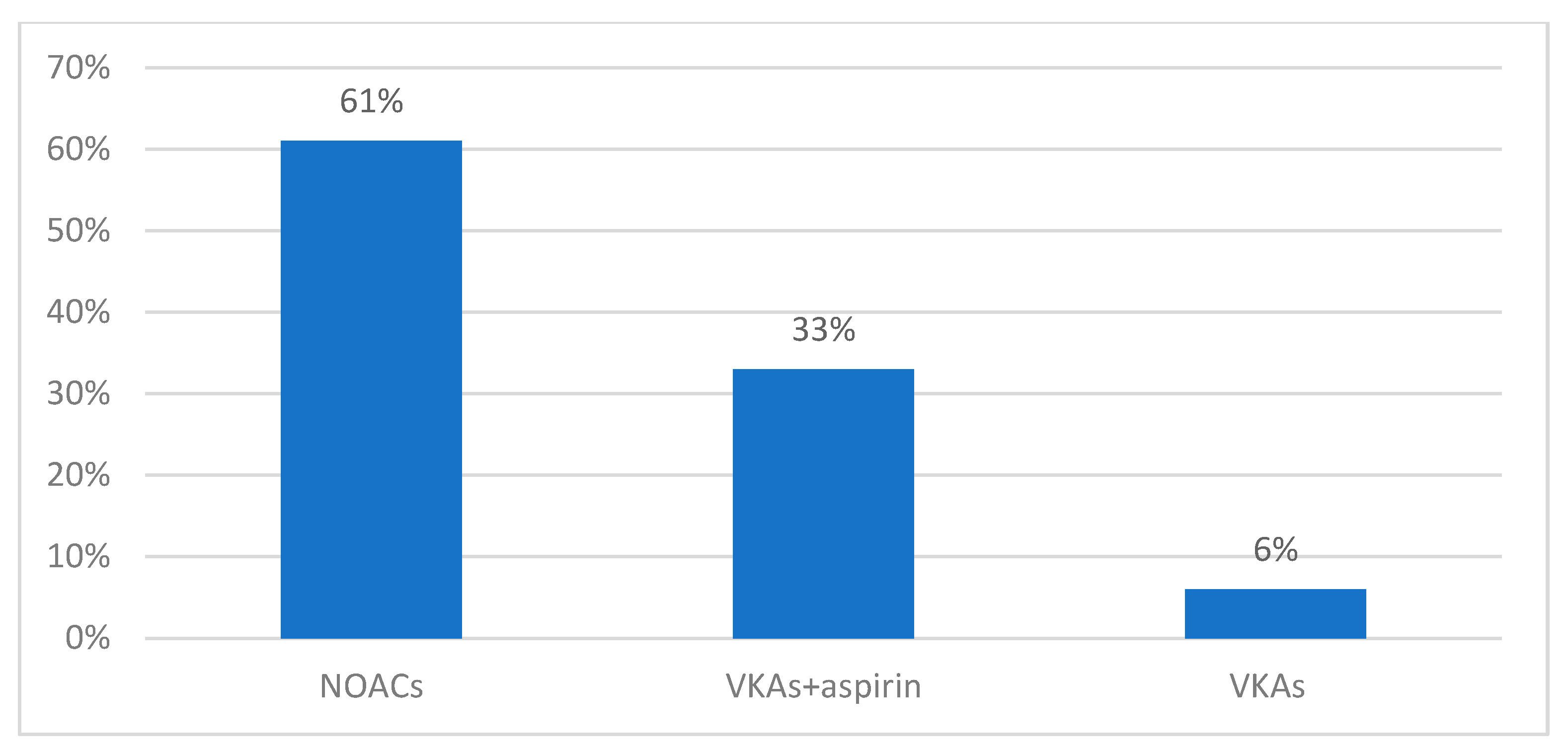
| NOACs—no. (%) | 210 (61%) |
| VKAs + aspirin—no. (%) | 114 (33%) |
| VKAs—no. (%) | 21 (6%) |
| Letter | Risk Factor | Score |
|---|---|---|
| C | Congestive heart failure/LV dysfunction | 1 |
| H | Hypertension | 1 |
| A2 | Age ≥ 75 | 2 |
| D | Diabetes mellitus | 1 |
| S2 | Stroke/TIA/thromboembolism | 2 |
| V | Vascular disease | 1 |
| A | Age 65–74 | 1 |
| S | Sex category (i.e., female sex) | 1 |
| Maximum score | 9 |
| Letter | Risk Factor | Score |
|---|---|---|
| H | Hypertension | 1 |
| A | Abnormal renal and liver function (1 point each) | 1 or 2 |
| S | Stroke | 1 |
| B | Bleeding | 1 |
| L | Labile INRs | 1 |
| E | Elderly (e.g., age > 65 years) | 1 |
| D | Drugs or alcohol (1 point each) | 1 or 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rus, M.; Ardelean, A.I.; Crisan, S.; Marian, P.; Pobirci, O.L.; Huplea, V.; Judea Pusta, C.; Osiceanu, G.A.; Stanis, C.E.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L. Optimizing Atrial Fibrillation Care: Comparative Assessment of Anticoagulant Therapies and Risk Factors. Clin. Pract. 2024, 14, 344-360. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14010027
Rus M, Ardelean AI, Crisan S, Marian P, Pobirci OL, Huplea V, Judea Pusta C, Osiceanu GA, Stanis CE, Andronie-Cioara FL. Optimizing Atrial Fibrillation Care: Comparative Assessment of Anticoagulant Therapies and Risk Factors. Clinics and Practice. 2024; 14(1):344-360. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleRus, Marius, Adriana Ioana Ardelean, Simina Crisan, Paula Marian, Oana Lilliana Pobirci, Veronica Huplea, Claudia Judea Pusta, Gheorghe Adrian Osiceanu, Claudia Elena Stanis, and Felicia Liana Andronie-Cioara. 2024. "Optimizing Atrial Fibrillation Care: Comparative Assessment of Anticoagulant Therapies and Risk Factors" Clinics and Practice 14, no. 1: 344-360. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14010027
APA StyleRus, M., Ardelean, A. I., Crisan, S., Marian, P., Pobirci, O. L., Huplea, V., Judea Pusta, C., Osiceanu, G. A., Stanis, C. E., & Andronie-Cioara, F. L. (2024). Optimizing Atrial Fibrillation Care: Comparative Assessment of Anticoagulant Therapies and Risk Factors. Clinics and Practice, 14(1), 344-360. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14010027