Review of Pediatric Tuberculosis in the Aftermath of COVID-19
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathogenesis of Childhood TB
3. Immunology of Active TB Infection
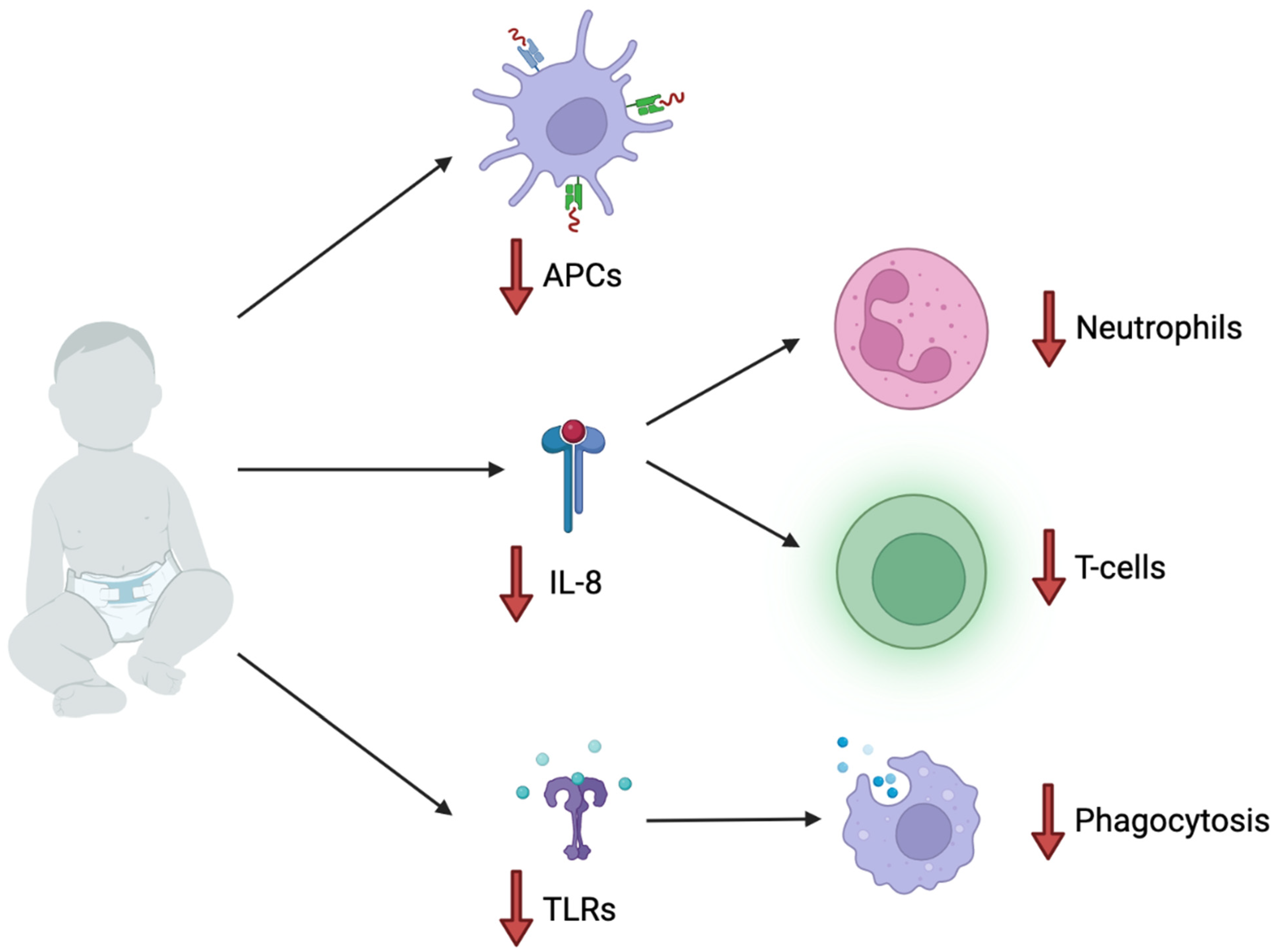
4. Pediatric Immunology and Increased Susceptibility
5. SARS-CoV-2 Co-Infection in Children
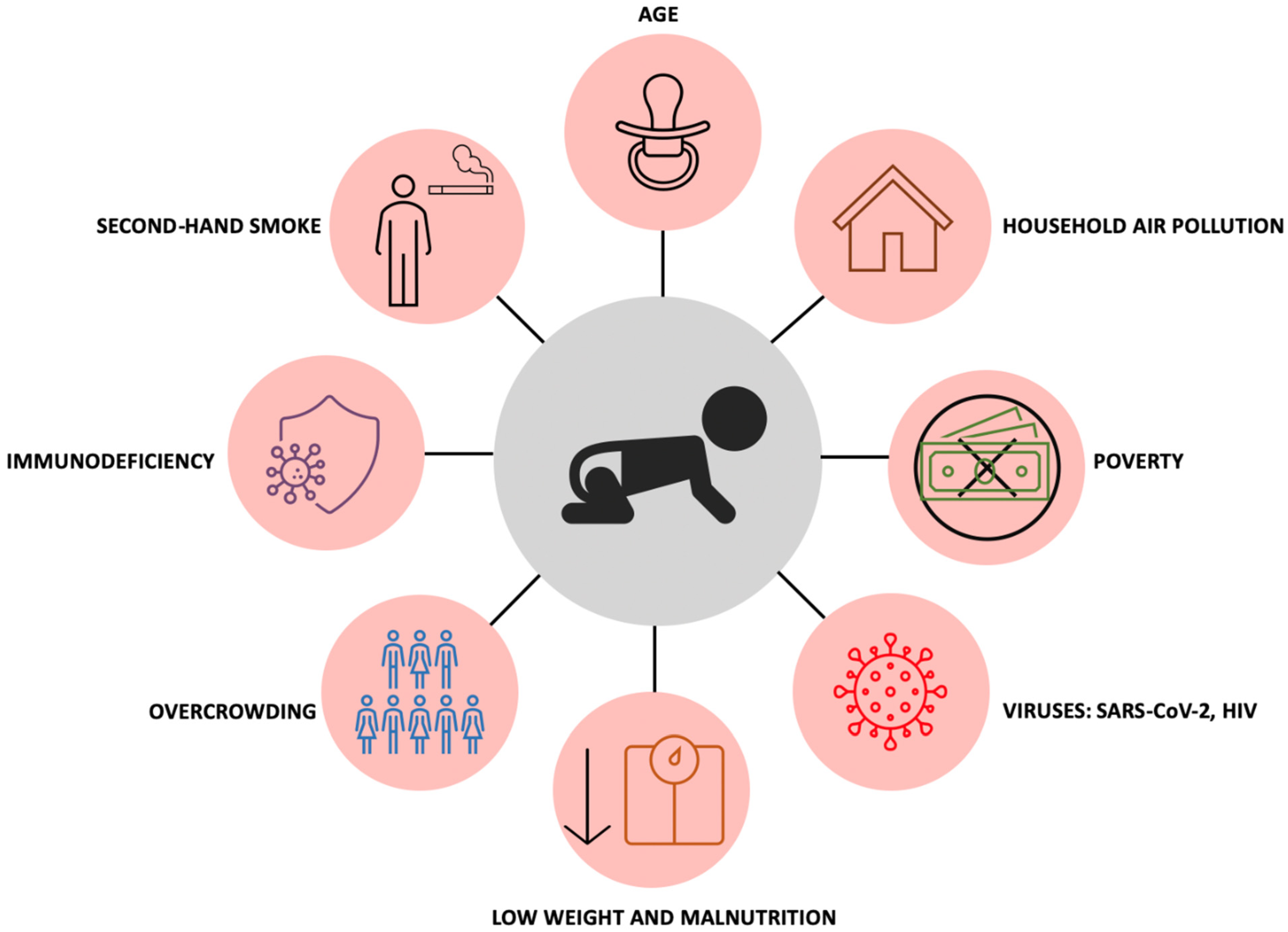
6. Childhood Tuberculosis: Risk Factors
7. Current Screening and Diagnosis Guidelines
8. Impact of COVID-19 on Pediatric Tuberculosis Cases
9. A Prevention Mechanism: BCG Vaccine
10. Prophylactic Treatment
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- John, C.A. Realizing the World Health Organization’s End TB Strategy (2016–2035): How Can Social Approaches to Tuberculosis Elimination Contribute to Progress in Asia and the Pacific? Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, M.; Kasaeva, T.; Swaminathan, S. COVID-19’s Devastating Effect on Tuberculosis Care—A Path to Recovery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1490–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Johnson, H.L.; Cousens, S.; Perin, J.; Scott, S.; Lawn, J.E.; Rudan, I.; Campbell, H.; Cibulskis, R.; Li, M.; et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality: An updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet 2012, 379, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, P.J.; Yuen, C.M.; Sismanidis, C.; Seddon, J.A.; Jenkins, H.E. The global burden of tuberculosis mortality in children: A mathematical modelling study. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e898–e906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Aznar, M.L.; Espinosa-Pereiro, J.; Saborit, N.; Jové, N.; Martinez, F.S.; Pérez-Recio, S.; Vitoria, A.; Sanjoaquin, I.; Gallardo, E.; Llenas-García, J.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on tuberculosis management in Spain. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 108, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, H.J.; Winston, C.A.; Holtz, T.H.; Cain, K.P.; Mac Kenzie, W.R. Epidemiology of tuberculosis among US- and foreign-born children and adolescents in the United States, 1994–2007. Am. J. Public Health 2010, 100, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Reported Tuberculosis in the US 2020; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, L.; Lo, N.C.; Cords, O.; Hill, P.C.; Khan, P.; Hatherill, M.; Mandalakas, A.; Kay, A.; Croda, J.; Horsburgh, C.R.; et al. Paediatric tuberculosis transmission outside the household: Challenging historical paradigms to inform future public health strategies. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.; Cords, O.; Horsburgh, C.R.; Andrews, J.R.; Acuna-Villaorduna, C.; Ahuja, S.D.; Altet, N.; Augusto, O.; Baliashvili, D.; Basu, S.; et al. The risk of tuberculosis in children after close exposure: A systematic review and individual-participant meta-analysis. Lancet 2020, 395, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.T.; Starke, J.R. Clinical manifestations of tuberculosis in children. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2007, 8, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eamranond, P.; Jaramillo, E. Tuberculosis in children: Reassessing the need for improved diagnosis in global control strategies. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2001, 5, 594–603. [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan, S.; Rekha, B. Pediatric Tuberculosis: Global Overview and Challenges. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50 (Suppl. S3), S184–S194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marais, B.J.; Gie, R.P.; Schaaf, H.S.; Beyers, N.; Donald, P.R.; Starke, J.R. Childhood pulmonary tuberculosis: Old wisdom and new challenges. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 1078–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, B.J.; Pai, M. Recent advances in the diagnosis of childhood tuberculosis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2007, 92, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdusalomova, M.; Denisiuk, O.; Davtyan, H.; Gadoev, J.; Abdusamatova, B.; Parpieva, N.; Sodikov, A. Adverse Drug Reactions among Children with Tuberculosis in Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 2019. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkereuwem, E.; Kampmann, B.; Togun, T. The need to prioritise childhood tuberculosis case detection. Lancet 2021, 397, 1248–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Roadmap towards Ending TB in Children and Adolescents; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, T.A. Tuberculosis in Children. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 64, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennelly, K.P.; Martyny, J.W.; Fulton, K.E.; Orme, I.M.; Cave, D.M.; Heifets, L.B. Cough-generated aerosols of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A new method to study infectiousness. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 169, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.B.; Whittaker, E.; A Seddon, J.; Kampmann, B. Tuberculosis susceptibility and protection in children. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, e96–e108. [Google Scholar]
- Marais, B.J.; Gie, R.P.; Schaaf, H.S.; Hesseling, A.C.; Obihara, C.C.; Nelson, L.J.; A Enarson, D.; Donald, P.R.; Beyers, N. The clinical epidemiology of childhood pulmonary tuberculosis: A critical review of literature from the pre-chemotherapy era. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2004, 8, 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Driessche, K.V.; Persson, A.; Marais, B.J.; Fink, P.J.; Urdahl, K.B. Immune vulnerability of infants to tuberculosis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 781320. [Google Scholar]
- Winston, C.A.; Menzies, H.J. Pediatric and adolescent tuberculosis in the United States, 2008–2010. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e1425–e1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, G.S.; Starke, J.R. Tuberculosis in Infants and Children. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, 541–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Velez, C.M.; Marais, B.J. Tuberculosis in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roya-Pabon, C.L.; Perez-Velez, C.M. Tuberculosis exposure, infection and disease in children: A systematic diagnostic approach. Pneumonia 2016, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulenga, H.; Tameris, M.D.; Luabeya, A.K.K.; Geldenhuys, H.; Scriba, T.; Hussey, G.D.; Mahomed, H.; Landry, B.S.; Hanekom, W.A.; McShane, H.; et al. The Role of Clinical Symptoms in the Diagnosis of Intrathoracic Tuberculosis in Young Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anane, T.; Grangaud, J.P. Diagnosis of tuberculosis in children. Child. Trop. 1992, 196–197, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wallgren, A. The time-table of tuberculosis. Tubercle 1948, 29, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.D. The natural history of tuberculosis in children. A study of child contacts in the Brompton Hospital Child Contact Clinic from 1930 to 1952. Tubercle 1961, 42, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Marais, B.J.; Gie, R.P.; Schaaf, H.S.; Starke, J.R.; Hesseling, A.C.; Donald, P.R.; Beyers, N. A proposed radiological classification of childhood intra-thoracic tuberculosis. Pediatr. Radiol. 2004, 34, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, P.R.; Schaaf, H.S.; Schoeman, J.F. Tuberculous meningitis and miliary tuberculosis: The Rich focus revisited. J. Infect. 2005, 50, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse van Rensburg, P.; Andronikou, S.; van Toorn, R.; Pienaar, M. Magnetic resonance imaging of miliary tuberculosis of the central nervous system in children with tuberculous meningitis. Pediatr. Radiol. 2008, 38, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, S.S.; Khan, F.A.; Milstein, M.B.; Tolman, A.W.; Benedetti, A.; Starke, J.R.; Becerra, M.C. Treatment outcomes of childhood tuberculous meningitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, N.D.; Caws, M.; Truc, T.T.; Duong, T.N.; Dung, N.H.; Ha, D.T.M.; Thwaites, G.E.; Heemskerk, D.; Tarning, J.; Merson, L.; et al. Clinical presentations, diagnosis, mortality and prognostic markers of tuberculous meningitis in Vietnamese children: A prospective descriptive study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, G.E.; Chan, E.D. Tuberculous meningitis: Diagnosis and treatment overview. Tuberc. Res. Treat. 2011, 2011, 798764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daffé, M.; Etienne, G. The capsule of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its implications for pathogenicity. Tuber. Lung Dis. 1999, 79, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, I. Mycobacteriumtuberculosis pathogenesis and molecular determinants of virulence. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 463–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, J.K.; Rengarajan, J. Immunology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infections. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambier, C.J.; Falkow, S.; Ramakrishnan, L. Host evasion and exploitation schemes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell 2014, 159, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanabalan, R.D.; Lee, L.J.; Lee, T.Y.; Chong, P.P.; Hassan, L.; Ismail, R.; Chin, V.K. Human tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex: A review on genetic diversity, pathogenesis and omics approaches in host biomarkers discovery. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 246, 126674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena, A.M.; Fortune, S.M.; Flynn, J.L. Heterogeneity in tuberculosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.L.; Flynn, J.L. Understanding latent tuberculosis: A moving target. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, I.; Goletti, D.; Manga, S.; Silva, D.; Manissero, D.; Migliori, G.B. Managing latent tuberculosis infection and tuberculosis in children. Pulmonology 2018, 24, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Garra, A.; Redford, P.S.; McNab, F.W.; Bloom, C.I.; Wilkinson, R.J.; Berry, M.P. The immune response in tuberculosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 475–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, N.K.; Karakousis, P.C. Latent tuberculosis infection: Myths, models, and molecular mechanisms. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 343–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankley, L.; Thomas, S.; Olive, A.J. Fighting Persistence: How Chronic Infections with Mycobacterium tuberculosis Evade T Cell-Mediated Clearance and New Strategies To Defeat Them. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00916-19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Chen, R.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Shen, M.; Lin, X. Multifunctional T cell response in active pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 107898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.; Chen, Y.; Ji, Q.; Zhu, G.; De Silva, A.D.; Vilchèze, C.; Weisbrod, T.; Li, W.; Xu, J.; Larsen, M.; et al. Targeting Mycobacterium tuberculosis Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha-Downregulating Genes for the Development of Antituberculous Vaccines. mBio 2016, 7, e01023-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Mazhar, H.; Saleha, S.; Tipu, H.N.; Muhammad, N.; Abbas, M.N. Interferon-Gamma Improves Macrophages Function against M. tuberculosis in Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Patients. Chemother. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 7295390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasenosky, L.D.; Scriba, T.J.; Hanekom, W.A.; Goldfeld, A.E. T cells and adaptive immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in humans. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 264, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-J.; Barreira-Silva, P.; Boyce, S.; Powers, J.; Cavallo, K.; Behar, S.M. CD4 T cell help prevents CD8 T cell exhaustion and promotes control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, L.; Rojas, M.; Franken, K.L.M.C.; Ottenhoff, T.H.M.; Barrera, L.F. Multifunctional T Cell Response to DosR and Rpf Antigens Is Associated with Protection in Long-Term Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Infected Individuals in Colombia. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016, 23, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vooren, J.P.; Schepers, K. Screening for tuberculosis. Rev. Med. Brux. 2013, 34, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Surve, S.; Bhor, V.; Naukariya, K.; Begum, S.; Munne, K.; Tipre, P.; Sutar, N.; Jaiswal, A.; Bhonde, G.; Chauhan, S.; et al. Discordance between TST and QFT-TBGold Plus for Latent Tuberculosis Screening among Under-Five Children: An Interim Analysis. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2021, 67, fmab103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford-Led Study Shows Kids Exposed to TB at Higher risk of Disease than Thought. Available online: https://med.stanford.edu/news/all-news/2020/03/stanford-led-study-shows-high-tb-risk-in-kids-exposed-to-disease.html#:~:text=In%20the%20study%2C%201%2C299%20children,during%20the%20follow%2Dup%20period (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Snow, K.J.; Cruz, A.T.; Seddon, J.A.; Ferrand, R.A.; Chiang, S.S.; Hughes, J.A.; Kampmann, B.; Graham, S.M.; Dodd, P.J.; Houben, R.M.; et al. Adolescent tuberculosis. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.; Pedersen, K.K.; Rosenfeldt, V.; Johansen, I.S. Challenges in diagnosing tuberculosis in children. Dan. Med. J. 2012, 59, A4463. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghi, K.; Berger, A.; Langgartner, M.; Prusa, A.R.; Hayde, M.; Herkner, K.; Pollak, A.; Spittler, A.; Forster-Waldl, E. Immaturity of infection control in preterm and term newborns is associated with impaired toll-like receptor signaling. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 195, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreto-Binaghi, L.E.; Juárez, E.; Guzmán-Beltrán, S.; Herrera, M.T.; Torres, M.; Alejandre, A.; Martínez-Orozco, J.A.; Becerril-Vargas, E.; Gonzalez, Y. Immunological Evaluation for Personalized Interventions in Children with Tuberculosis: Should It Be Routinely Performed? J. Immunol Res. 2020, 2020, 8235149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, E.W.; Dooley, K.E. Preclinical tools for the evaluation of tuberculosis treatment regimens for children. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2018, 22, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadolini, M.; Codecasa, L.; García-García, J.-M.; Blanc, F.-X.; Borisov, S.; Alffenaar, J.-W.; Andréjak, C.; Bachez, P.; Bart, P.-A.; Belilovski, E.; et al. Active tuberculosis, sequelae and COVID-19 co-infection: First cohort of 49 cases. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2001398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanza, C.; Romenskaya, T.; Manetti, A.C.; Franceschi, F.; La Russa, R.; Bertozzi, G.; Maiese, A.; Savioli, G.; Volonnino, G.; Longhitano, Y. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: Immunopathogenesis and Therapy. Medicina 2022, 58, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, A.B.; Jewell, B.L.; Sherrard-Smith, E.; Vesga, J.F.; Watson, O.J.; Whittaker, C.; Hamlet, A.; Smith, J.A.; Winskill, P.; Verity, R.; et al. Potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria in low-income and middle-income countries: A modelling study. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e1132–e1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapela, K.; Ochieng’ Olwal, C.; Quaye, O. Parallels in the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 and M. tuberculosis: A synergistic or antagonistic alliance? Future Microbiol. 2020, 15, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etna, M.P.; Giacomini, E.; Severa, M.; Coccia, E.M. Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in tuberculosis: A two-edged sword in TB pathogenesis. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Meng, M.; Kumar, R.; Wu, Y.; Huang, J.; Deng, Y.; Weng, Z.; Yang, L. Lymphopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ding, J.; Huang, Q.; Tang, Y.Q.; Wang, Q.; Miao, H. Lymphopenia predicts disease severity of COVID-19: A descriptive and predictive study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorlag, S.; Arts, R.; van Crevel, R.; Netea, M. Non-specific effects of BCG vaccine on viral infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, L.A.J.; Netea, M.G. BCG-induced trained immunity: Can it offer protection against COVID-19? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustman, D.L.; Lee, A.; Hostetter, E.R.; Aristarkhova, A.; Ng, N.C.; Shpilsky, G.F.; Tran, L.; Wolfe, G.; Takahashi, H.; Dias, H.F.; et al. Multiple BCG vaccinations for the prevention of COVID-19 and other infectious diseases in type 1 diabetes. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 15, 100728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.B.; Saxena, R.; Pallavi, P.; Jain, R.; Mishra, D.; Jhamb, U. Effect of Concomitant Tuberculosis Infection on COVID-19 Disease in Children: A Matched, Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2022, 68, fmac056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Addressing Poverty in TB Control Options for National TB Control Programmes; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Marais, B.J.; Gie, R.P.; Schaaf, H.S.; Hesseling, A.C.; Obihara, C.C.; Starke, J.J.; Enarson, D.A.; Donald, P.R.; Beyers, N. The natural history of childhood intra-thoracic tuberculosis: A critical review of literature from the pre-chemotherapy era [State of the Art]. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2004, 8, 392–402. [Google Scholar]
- Oztürk, A.B.; Kiliçaslan, Z.; Işsever, H. Effect of smoking and indoor air pollution on the risk of tuberculosis: Smoking, indoor air pollution and tuberculosis. Tuberk. Toraks 2014, 62, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nakaoka, H.; Lawson, L.; Squire, S.B.; Coulter, B.; Ravn, P.; Brock, I.; Hart, C.A.; Cuevas, L.E. Risk for tuberculosis among children. Emerg. Infect. Dis 2006, 12, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, R.; Racow, K.; Bekker, L.G.; Morrow, C.; Middelkoop, K.; Mark, D.; Lawn, S.D. Indoor Social Networks in a South African Township: Potential Contribution of Location to Tuberculosis Transmission. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.K.; Islam, M.N.; Ferdous, J.; Alam, M.M. An Overview on Epidemiology of Tuberculosis. Mymensingh Med. J. 2019, 28, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boccia, D.; Hargreaves, J.; De Stavola, B.L.; Fielding, K.; Schaap, A.; Godfrey-Faussett, P.; Ayles, H. The Association between Household Socioeconomic Position and Prevalent Tuberculosis in Zambia: A Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lule, S.A.; Mawa, A.P.; Nkurunungi, G.; Nampijja, M.; Kizito, D.; Akello, F.; Muhangi, L.; Elliott, A.M.; Webb, E.L. Factors associated with tuberculosis infection, and with anti-mycobacterial immune responses, among five year olds BCG-immunised at birth in Entebbe, Uganda. Vaccine 2015, 33, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjellstrom, T.; Mercado, S.; Barten, F.; Ompad, D. Our Cities, Our Health, Our Future: Acting on Social Determinants for Health Equity in Urban Settings: Report to the WHO Commission on Social Determinants of Health from the Knowledge Network on Urban Settings; WHO Kobe Centre: Kobe, Japan, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jafta, N.; Jeena, P.M.; Barregard, L.; Naidoo, R.N. Childhood tuberculosis and exposure to indoor air pollution: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2015, 19, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetifa, I.M.O.; Kendall, L.; Donkor, S.; Lugos, M.D.; Hammond, A.S.; Owiafe, P.K.; Ota, M.O.; Brookes, R.H.; Hill, P.C. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection in Close Childhood Contacts of Adults with Pulmonary Tuberculosis is Increased by Secondhand Exposure to Tobacco. Am. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolappan, C.; Subramani, R. Association between biomass fuel and pulmonary tuberculosis: A nested case–control study. Thorax 2009, 64, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Deng, J.; Su, C.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Abuaku, B.K.; Hu, S.; Tan, H.; Wen, S.W. Impact of passive smoking, cooking with solid fuel exposure, and MBL/MASP-2 gene polymorphism upon susceptibility to tuberculosis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellez-Navarrete, N.A.; Ramon-Luing, L.A.; Muñoz-Torrico, M.; Osuna-Padilla, I.A.; Chavez-Galan, L. Malnutrition and tuberculosis: The gap between basic research and clinical trials. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2021, 15, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnroth, K.; Williams, B.; Cegielski, P.; Dye, C. A consistent log-linear relationship between tuberculosis incidence and body mass index. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 39, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Nutritional Care and Support for Patients with Tuberculosis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Osório, D.-V.; Munyangaju, I.; Muhiwa, A.; Nacarapa, E.; Nhangave, A.-V.; Ramos, J.-M. Lipoarabinomannan Antigen Assay (TB-LAM) for Diagnosing Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Children with Severe Acute Malnutrition in Mozambique. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2020, 67, fmaa072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisson-Dupuis, S.; Bustamante, J.; El-Baghdadi, J.; Camcioglu, Y.; Parvaneh, N.; El Azbaoui, S.; Agader, A.; Hassani, A.; El Hafidi, N.; Mrani, N.A.; et al. Inherited and acquired immunodeficiencies underlying tuberculosis in childhood. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 264, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesseling, A.C.; Cotton, M.F.; Jennings, T.; Whitelaw, A.; Johnson, L.F.; Eley, B.; Roux, P.; Godfrey-Faussett, P.; Schaaf, H.S. High Incidence of Tuberculosis among HIV-Infected Infants: Evidence from a South African Population-Based Study Highlights the Need for Improved Tuberculosis Control Strategies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selwyn, P.A.; Sckell, B.M.; Alcabes, P.; Friedland, G.H.; Klein, R.S.; Schoenbaum, E.E. High risk of active tuberculosis in HIV-infected drug users with cutaneous anergy. JAMA 1992, 268, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenberg, P.; Glynn, J.R.; Fielding, K.; Murray, J.; Godfrey-Faussett, P.; Shearer, S. How soon after infection with HIV does the risk of tuberculosis start to increase? A retrospective cohort study in South African gold miners. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelar, A.; Gatell, J.M.; Verdejo, J.; Podzamczer, D.; Lozano, L.; Aznar, E.; Miró, J.M.; Mallolas, J.; Zamora, L.; González, J.; et al. A prospective study of the risk of tuberculosis among HIV-infected patients. AIDS 1993, 7, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelar, A.; Gatell, J.M.; Verdejo, J.; Podzamczer, D.; Lozano, L.; Aznar, E.; Miró, J.M.; Mallolas, J.; Zamora, L.; González, J.; et al. Indoor air pollution from secondhand tobacco smoke, solid fuels, and kerosene in homes with active tuberculosis disease in South Africa. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 591. [Google Scholar]
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Routine Vaccinations: Reflections during World Immunization Week. 2020. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/eap/stories/impact-covid-19-routine-vaccinations (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Life-Saving Vaccinations Must Not ‘Fall Victim’ to COVID-19 Pandemic. Available online: https://news.un.org/en/story/2020/03/1060402 (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Alene, K.A.; Wangdi, K.; Clements, A.C.A. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tuberculosis Control: An Overview. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilloni, L.; Fu, H.; Vesga, J.F.; Dowdy, D.; Pretorius, C.; Ahmedov, S.; Nair, S.A.; Mosneaga, A.; Masini, E.; Sahu, S.; et al. The potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the tuberculosis epidemic a modelling analysis. eClinicalMedicine 2020, 28, 100603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reznik, M.; Ozuah, P.O. Tuberculin skin testing in children. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolt, D.; Starke, J.R. Tuberculosis Infection in Children and Adolescents: Testing and Treatment. Pediatrics 2021, 148, e2021054663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Universal TB Testing of School-Aged Children Not Required. Available online: http://publichealth.lacounty.gov/tb/docs/2012.3%20-%20March.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Pediatric Tuberculosis Risk Assessment. Available online: https://doh.wa.gov/sites/default/files/legacy/Documents/Pubs//343-145-PediatricTBRiskAssessment.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Imsanguan, W.; Bupachat, S.; Wanchaithanawong, V.; Luangjina, S.; Thawtheong, S.; Nedsuwan, S.; Pungrassami, P.; Mahasirimongkol, S.; Wiriyaprasobchok, A.; Kaewmamuang, K.; et al. Contact tracing for tuberculosis, Thailand. Bull. World Health Organ. 2020, 98, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togun, T.; Kampmann, B.; Stoker, N.G.; Lipman, M. Anticipating the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on TB patients and TB control programmes. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2020, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, A.K.; Aggarwal, D. The (in)significance of TB and COVID-19 co-infection. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2002105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effect of COVID-19 on Tuberculosis in the U.S. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2022/s0324-tuberculosis-covid-19.html#:~:text=In%20the%20United%20States%2C%20reported,preliminary%20CDC%20data%20published%20today (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Think. Test. Treat TB. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/thinktesttreattb/ (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Golandaj, J.A. Pediatric TB detection in the era of COVID-19. Indian J. Tuberc. 2022, 69, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuberculosis Preventive Therapy for Children and Adolescents: An Emergency Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Available online: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanchi/article/PIIS2352-4642(21)00003-1/fulltext (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Fatima, S.; Kumari, A.; Das, G.; Dwivedi, V.P. Tuberculosis vaccine: A journey from BCG to present. Life Sci. 2020, 252, 117594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangtani, P.; Abubakar, I.; Ariti, C.; Beynon, R.; Pimpin, L.; Fine, P.E.M.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Smith, P.G.; Lipman, M.; Whiting, P.F.; et al. Protection by BCG vaccine against tuberculosis: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. BCG vaccine: WHO position paper, February 2018—Recommendations. Vaccine 2018, 36, 3408–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thysen, S.M.; Benn, C.S.; Gomes, V.F.; Rudolf, F.; Wejse, C.; Roth, A.; Kallestrup, P.; Aaby, P.; Fisker, A. Neonatal BCG vaccination and child survival in TB-exposed and TB-unexposed children: A prospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trunz, B.B.; Fine, P.E.M.; Dye, C. Effect of BCG vaccination on childhood tuberculous meningitis and miliary tuberculosis worldwide: A meta-analysis and assessment of cost-effectiveness. Lancet 2006, 367, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, A.; Goetghebuer, T.; Ota, M.O.; Wolfe, I.; Ceesay, S.J.; De Groote, D.; Corrah, T.; Bennett, S.; Wheeler, J.; Huygen, K.; et al. Newborns Develop a Th1-Type Immune Response to Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Vaccination. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 2249–2255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ota, M.O.; Vekemans, J.; Schlegel-Haueter, S.E.; Fielding, K.; Sanneh, M.; Kidd, M.; Newport, M.J.; Aaby, P.; Whittle, H.; Lambert, P.H.; et al. Influence of Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guérin on Antibody and Cytokine Responses to Human Neonatal Vaccination. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekemans, J.; Amedei, A.; Ota, M.O.; D’Elios, M.M.; Goetghebuer, T.; Ismaili, J.; Newport, M.J.; Del Prete, G.; Goldman, M.; McAdam, K.P.; et al. Neonatal bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccination induces adult-like IFN-γ production by CD4+ T lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 1531–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.P.; Scriba, T.; Joseph, S.; Harbacheuski, R.; Murray, R.A.; Gelderbloem, S.J.; Hawkridge, A.; Hussey, G.D.; Maecker, H.; Kaplan, G.; et al. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Vaccination of Human Newborns Induces T Cells with Complex Cytokine and Phenotypic Profiles. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 3569–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.P.; Chung, C.K.C.K.; Choice, T.; Hughes, E.J.; Jacobs, G.; van Rensburg, E.J.; Khomba, G.; de Kock, M.; Lerumo, L.; Makhethe, L.; et al. Longitudinal Changes in CD4+ T-Cell Memory Responses Induced by BCG Vaccination of Newborns. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P. A Perspective on the Success and Failure of BCG. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 778028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis: Tuberculosis Preventive Treatment: Module 1: Prevention [Internet]; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Villarino, M.E.; Scott, N.A.; Weis, S.E.; Weiner, M.; Conde, M.B.; Jones, B.; Nachman, S.; Oliveira, R.; Moro, R.N.; Shang, N.; et al. Treatment for Preventing Tuberculosis in Children and Adolescents: A Randomized Clinical Trial of a 3-Month, 12-Dose Regimen of a Combination of Rifapentine and Isoniazid. JAMA Pediatrics 2015, 169, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, L.; Sari, A.H.; Mane, S.; Scardigli, A.; Brigden, G.; Rouzier, V.; Becerra, M.C.; Hesseling, A.C.; Amanullah, F. Pediatric Tuberculosis Research and Development: Progress, Priorities and Funding Opportunities. Pathogens 2022, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.T.; Starke, J.R. Safety and Adherence for 12 Weekly Doses of Isoniazid and Rifapentine for Pediatric Tuberculosis Infection. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, A.T.; Starke, J.R. Safety and completion of a 4-month course of rifampicin for latent tuberculous infection in children. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2014, 18, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryckman, T.; Robsky, K.; Cilloni, L.; Zawedde-Muyanja, S.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Kendall, E.A.; Shrestha, S.; Turyahabwe, S.; Katamba, A.; Dowdy, D.W. Ending tuberculosis in a post-COVID-19 world: A person-centred, equity-oriented approach. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rangchaikul, P.; Ahn, P.; Nguyen, M.; Zhong, V.; Venketaraman, V. Review of Pediatric Tuberculosis in the Aftermath of COVID-19. Clin. Pract. 2022, 12, 738-754. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12050077
Rangchaikul P, Ahn P, Nguyen M, Zhong V, Venketaraman V. Review of Pediatric Tuberculosis in the Aftermath of COVID-19. Clinics and Practice. 2022; 12(5):738-754. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12050077
Chicago/Turabian StyleRangchaikul, Patrida, Phillip Ahn, Michelle Nguyen, Vivian Zhong, and Vishwanath Venketaraman. 2022. "Review of Pediatric Tuberculosis in the Aftermath of COVID-19" Clinics and Practice 12, no. 5: 738-754. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12050077
APA StyleRangchaikul, P., Ahn, P., Nguyen, M., Zhong, V., & Venketaraman, V. (2022). Review of Pediatric Tuberculosis in the Aftermath of COVID-19. Clinics and Practice, 12(5), 738-754. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12050077






