Plasmatic Magnesium Deficiency in 101 Outpatients Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Baseline Characteristics
2.4. Plasmatic and Urinary Magnesium Levels Determination
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Ethics Statement
3. Results
3.1. Description of Participants with Plasmatic Magnesium Deficiency and Comparison of the Two Groups
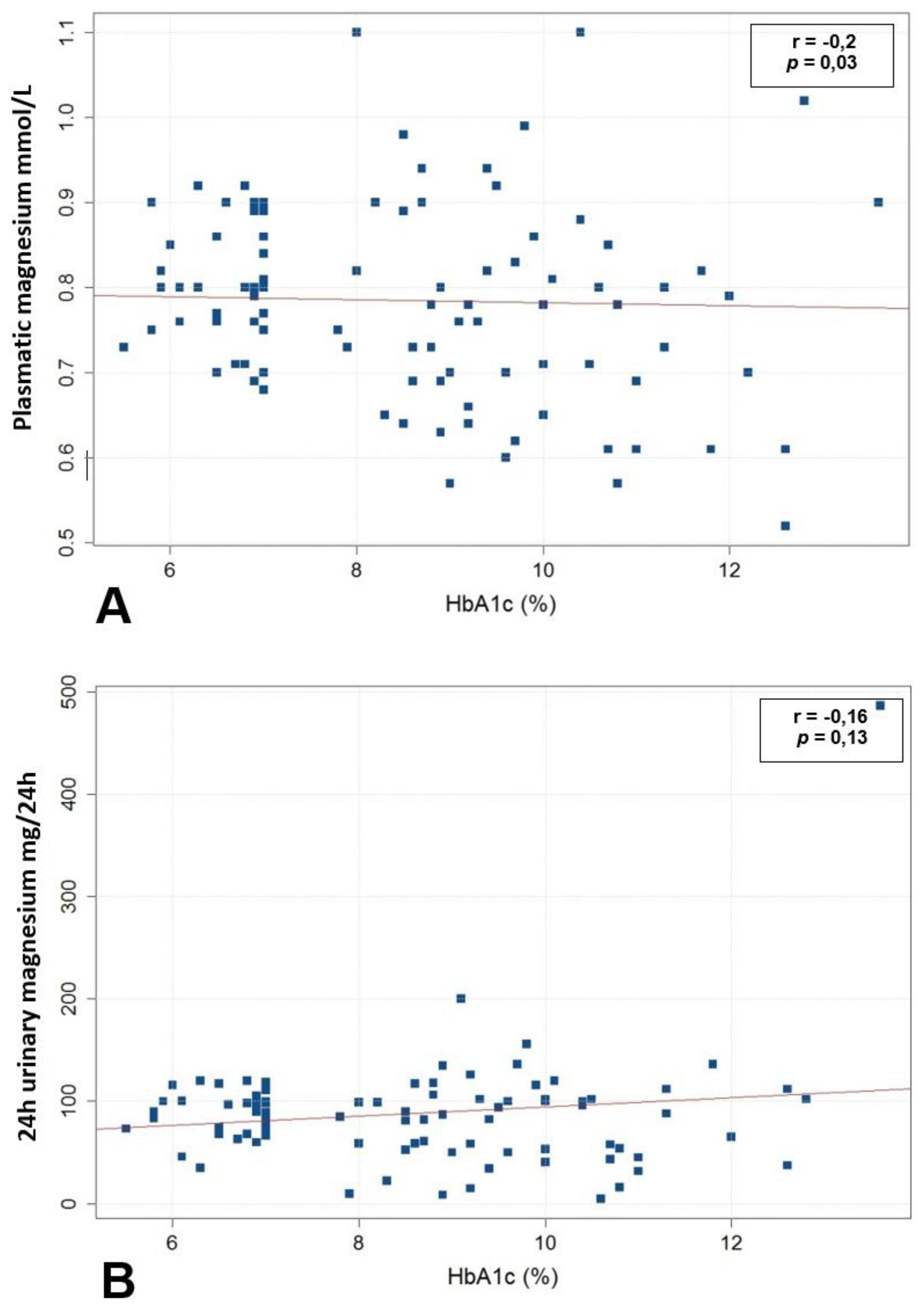
3.2. Association between Magnesium Status and Glycemic Control
3.3. Association between Magnesium Status and Long-Term Diabetes-Related Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saris, N.E.; Mervaala, E.; Karppanen, H.; Khawaja, J.A.; Lewenstam, A. Magnesium: An update on physiological, clinical and analytical aspects. Clin. Chim Acta 2000, 294, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, T. The biochemical function of Mg2+ in insulin secretion, insulin signal transduction and insulin resistance. Magn. Res. 2010, 23, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Office of Dietary Supplements—Magnesium. Available online: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-HealthProfessional/ (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- FoodData Central. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/ (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- Piuri, G.; Zocchi, M.; Della Porta, M.; Ficara, V.; Manoni, M.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Pinotti, L.; Maier, J.A.; Cazzola, R. Magnesium in Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Abou-Samra, A.B. Association of low serum magnesium with diabetes and hypertension: Findings from Qatar Biobank study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 158, 107903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, P.-C.T.; Pham, P.-M.T.; Pham, S.V.; Miller, J.M.; Pham, P.-T.T. Hypomagnesemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wälti, M.K.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Spinas, G.A.; Hurrell, R.F. Low plasma magnesium in type 2 diabetes. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2003, 133, 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.-Y.; Xun, P.; He, K.; Qin, L.-Q. Magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes: Meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, X.; Han, H.; Li, M.; Liang, C.; Fan, Z.; Aaseth, J.; He, J.; Montgomery, S.; Cao, Y. Dose-Response Relationship between Dietary Magnesium Intake and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Nutrients 2016, 8, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutia, H.; Lynrah, K.G. Association of Serum Magnesium Deficiency with Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Lab. Phys. 2015, 7, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ridaura, R.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Liu, S.; Stampfer, M.J.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B. Magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in men and women. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morais, J.B.S.; Severo, J.S.; de Alencar, G.R.R.; de Oliveira, A.R.S.; Cruz, K.J.C.; do Nascimento Marreiro, D.; de Carvalho, C.M.R.; Frota, K.D.M.G. Effect of magnesium supplementation on insulin resistance in humans: A systematic review. Nutrition 2017, 38, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciqual Table de Composition Nutritionnelle des Aliments. Available online: https://ciqual.anses.fr/ (accessed on 7 October 2021).
- Ramadass, S.; Basu, S.; Srinivasan, A.R. SERUM magnesium levels as an indicator of status of Diabetes Mellitus type 2. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2015, 9, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium and type 2 diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hruby, A.; McKeown, N.M.; Song, Y.; Djoussé, L. Dietary magnesium and genetic interactions in diabetes and related risk factors: A brief overview of current knowledge. Nutrients 2013, 5, 4990–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.L.; Yen, C.F.; Nadler, J.L. Insulin increases intracellular magnesium transport in human platelets. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 76, 549–553. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez, A.; Pulido, N.; Casla, A.; Casanova, B.; Arrieta, F.J.; Rovira, A. Impaired tyrosine-kinase activity of muscle insulin receptors from hypomagnesaemic rats. Diabetologia 1995, 38, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gommers, L.M.M.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M.; de Baaij, J.H.F. Hypomagnesemia in Type 2 Diabetes: A Vicious Circle? Diabetes 2016, 65, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolterman, O.G.; Gray, R.S.; Griffin, J.; Burstein, P.; Insel, J.; Scarlett, J.A.; Olefsky, J.M. Receptor and postreceptor defects contribute to the insulin resistance in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 68, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Rodríguez-Morán, M. Low serum magnesium levels and metabolic syndrome. Acta Diabetol. 2002, 39, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A.; Sarma, D.; Saikia, U.K. Hypomagnesemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, M.; Di Bella, G.; Brucato, V.; D’Angelo, D.; Damiani, P.; Monteverde, A.; Belvedere, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Serum ionized magnesium in diabetic older persons. Metabolism 2014, 63, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurstjens, S.; de Baaij, J.H.F.; Bouras, H.; Bindels, R.J.M.; Tack, C.J.J.; Hoenderop, J.G.J. Determinants of hypomagnesemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 176, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Odusan, O.O.; Familoni, O.B.; Odewabi, A.O.; Idowu, A.O.; Adekolade, A.S. Patterns and Correlates of Serum Magnesium Levels in Subsets of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in Nigeria. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 21, 439–442. [Google Scholar]
- Lotfi, Z.; Aboussaleh, Y.; Sbaibi, R.; Achouri, I.; Benguedour, R. Le surpoids, l’obésité et le contrôle glycémique chez les diabétiques du centre de référence provincial de diabète (CRD), Kénitra, Maroc. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2017, 27, 189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shahbah, D.; El Naga, A.A.; Hassan, T.; Zakaria, M.; Beshir, M.; Al Morshedy, S.; Abdalhady, M.; Kamel, E.; Rahman, D.A.; Kamel, L.; et al. Status of serum magnesium in Egyptian children with type 1 diabetes and its correlation to glycemic control and lipid profile. Medicine 2016, 95, e5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.A.; Kushi, L.H.; Jacobs, D.R.; Slavin, J.; Sellers, T.A.; Folsom, A.R. Carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and incident type 2 diabetes in older women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, P.C.T.; Pham, P.M.T.; Pham, P.A.T.; Pham, S.V.; Pham, H.V.; Miller, J.M.; Yanagawa, N.; Pham, P.T.T. Lower serum magnesium levels are associated with more rapid decline of renal function in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2. Clin. Nephrol. 2005, 63, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, J.P. Magnesium deficiency and diabetes mellitus. Magn. Trace Elem. 1992, 10, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, S.; Takemura, T.; Wada, M.; Akai, T.; Okuda, K. Magnesium levels of plasma, erythrocyte and urine in patients with diabetes mellitus. Horm. Metab. Res. 1982, 14, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, A.T.; Criqui, M.H.; Treat-Jacobson, D.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Creager, M.A.; Olin, J.W.; Krook, S.H.; Hunninghake, D.B.; Comerota, A.J.; Walsh, M.E.; et al. Peripheral arterial disease detection, awareness, and treatment in primary care. JAMA 2001, 286, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Peripheral arterial disease in people with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 3333–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marso, S.P.; Hiatt, W.R. Peripheral arterial disease in patients with diabetes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tin, A.; Grams, M.E.; Maruthur, N.M.; Astor, B.C.; Couper, D.; Mosley, T.H.; Selvin, E.; Coresh, J.; Kao, W.H.L. Results from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study suggest that low serum magnesium is associated with incident kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Dabla, S.; Agrawal, R.P.; Barjatya, H.; Kochar, D.K.; Kothari, R.P. Serum magnesium: An early predictor of course and complications of diabetes mellitus. J. Indian Med. Assoc. 2007, 105, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Laecke, S.; Van Biesen, W.; Vanholder, R. Hypomagnesaemia, the kidney and the vessels. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 4003–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cambray, S.; Ibarz, M.; Bermudez-Lopez, M.; Marti-Antonio, M.; Bozic, M.; Fernandez, E.; Valdivielso, J.M. Magnesium Levels Modify the Effect of Lipid Parameters on Carotid Intima Media Thickness. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Xun, P.; Tang, Q.; Cai, W.; He, K. Circulating magnesium levels and incidence of coronary heart diseases, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostov, K.; Halacheva, L. Role of Magnesium Deficiency in Promoting Atherosclerosis, Endothelial Dysfunction, and Arterial Stiffening as Risk Factors for Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Participants with Normal Magnesium Status (n = 88) (87.1%) | Participants with Plasmatic Magnesium Deficiency (n = 13) (12.9%) | n = 101 (%) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic and Baseline Characteristics | |||||
| Age, years (mean, SD, range) | 56.3 ± 8.2 (39–76) | 54.4 ± 5.8 (45–66) | 56 ± 7.9 (39–76) | 0.421 | |
| Sex (n, %) | Male | 36 (40.9) | 2 (15.4) | 38 (37.7) | 0.067 |
| Female | 52 (59.1) | 11 (84.6) | 63 (62.4) | 0.067 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) (mean, SD, range) Menopause (n, %) | 30 ± 4.6 (19.6–45.7) 36/52 (69.2) | 29 ± 2.9 (23.5–33.6) 9/11 (81.8) | 29.9 ± 4.5 (19.6–45.7) 45/63 (71.4) | 0.483 0.132 | |
| Diabetes duration, years (mean, SD, range) | 7.11 ± 5.6 (1–25) | 7.62 ± 3.9 (1–15) | 7.18 ± 5.4 (1–25) | 0.757 | |
| =<10 (n, %) | 72 (81.8) | 11 (84.6) | 83 (82.2) | 0.581 | |
| (11–20) (n, %) | 14 (15.9) | 2 (15.4) | 16 (15.8) | 0.662 | |
| >20 (n, %) | 2 (2.3) | 0 | 2 (2) | 0.758 | |
| Microvascular complications (n, %) | Diabetic retinopathy | 22 (26.8) | 5 (38.5) | 27 (26.7) | 0.289 |
| Diabetic neuropathy | 16 (21.6) | 5 (38.5) | 21 (20.8) | 0.129 | |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 12 (14.8) | 2 (15.4) | 14 (13.7) | 0.615 | |
| Macrovascular complications (n, %) | Coronary heart disease | 9 (10.2) | 1 (7.7) | 10 (9.9) | 0.636 |
| Cerebrovascular disease * | 6 (6.8) | 2 (15.4) | 8 (7.9) | 0.261 | |
| Peripheral artery disease | 0 (0) | 5 (38.5) | 5 (4.9) | <0.001 | |
| Plasmatic magnesium level (mmol/L)(mean, SD, range) 24 h urinary magnesium excretion (mg/24 h)(mean, SD, range) Magnesium intake ** (mg/24 h) (mean, SD, range) | 0.8 ± 0.1 (0.68–1.1) 93 ± 54.5 (4.8–486.2) 324.5 ± 111.8 (167–625) | 0.6 ± 0.3 (0.5–0.6) 56.4 ± 38 (8.6–136) 274.7 ± 105.8 (148–367) | 0.8 ± 0.1 (0.5–1.1) 87.8 ± 53.8 (4.8–486.2) 320.4 ± 111.2 (148–625) | <0.001 0.02 0.397 | |
| Fasting blood glucose (mmo/L) (mean, SD, range) | 9.8 ± 3.2 (4.3–19) | 11.2 ± 2.9 (6.4–15.4) | 10 ± 3.2 (4.3–19) | 0.145 | |
| HbA1c (%) (mean, SD, range) | 8.3 ± 1.9 (5.5–13.6) | 10 ± 1.3 (8.3–12.6) | 8.5 ± 1.9 (5.5–13.6) | 0.03 | |
| HbA1c > 7% | 47 (53.4) | 13 (100) | 60 (59.4) | 0.001 | |
| Clearance creatinine *** (>60 mmo/L) (mean, SD, range) | 99.8 ± 12.7 (61–140) | 101.2 ± 12 (70–121) | 99.9 ± 12.5 (61–140) | 0.698 | |
| Total cholesterol (normal range < 5.2 mmol/L (mean, SD, range) | 4.5 ± 0.9 (2.2–7) | 4.3 ± 0.8 (3.4–6.5) | 4.50 ± 0.9 (2.24–7.08) | 0.565 | |
| HDL-c (normal range > 1 mmol/L (M) and >1.3 mmol/L (F)) (mean, SD, range) | 1.1 ± 0.3 (0.5–1.8) | 1.2 ± 0.2 (1–1.6) | 1.16 ± 0.8 (0.51–1.80) | 0.325 | |
| LDL-c **** (normal range < 2.6 mmol/L) (mean, SD, range) | 1 ± 0.3 (0.3–2) | 0.9 ± 0.3 (0.5–1.6) | 1.02 ± 0.3 (0.35–2.03) | 0.242 | |
| Triglycerides (normal range < 1.7 mmol/L) (mean, SD, range) | 1.5 ± 0.8 (0.5–5.9) | 1.5 ± 0.7 (0.8–3.3) | 1.49 ± 0.8 (0.47–5.89) | 0.828 | |
| Diabetic Microvascular and Macrovascular Complications | Yes/No | Plasmatic Magnesium Level (mmol/L) (Mean, SD) | p-(Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microvascular complications | Diabetic retinopathy | Yes | 0.76 ± 0.12 | 0.3 |
| No | 0.78 ± 0.10 | |||
| Diabetic neuropathy | Yes | 0.73 ± 0.13 | 0.1 | |
| No | 0.78 ± 0.10 | |||
| Diabetic nephropathy | Yes | 0.71 ± 0.07 | 0.006 | |
| No | 0.79 ± 0.10 | |||
| Macrovascular complications | Coronary heart disease | Yes | 0.77 ± 0.10 | 0.63 |
| No | 0.79 ± 0.09 | |||
| Cerebrovascular disease | Yes | 0.74 ± 0.12 | 0.31 | |
| No | 0.78 ± 0.13 | |||
| Peripheral artery disease | Yes | 0.61 ± 0.08 | <0.001 | |
| No | 0.79 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zahra, H.; Berriche, O.; Mizouri, R.; Boukhayatia, F.; Khiari, M.; Gamoudi, A.; Lahmar, I.; Ben Amor, N.; Mahjoub, F.; Zayet, S.; et al. Plasmatic Magnesium Deficiency in 101 Outpatients Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, 791-800. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040095
Zahra H, Berriche O, Mizouri R, Boukhayatia F, Khiari M, Gamoudi A, Lahmar I, Ben Amor N, Mahjoub F, Zayet S, et al. Plasmatic Magnesium Deficiency in 101 Outpatients Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clinics and Practice. 2021; 11(4):791-800. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040095
Chicago/Turabian StyleZahra, Hajer, Olfa Berriche, Ramla Mizouri, Fatma Boukhayatia, Marwa Khiari, Amel Gamoudi, Ines Lahmar, Nadia Ben Amor, Faten Mahjoub, Souheil Zayet, and et al. 2021. "Plasmatic Magnesium Deficiency in 101 Outpatients Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Clinics and Practice 11, no. 4: 791-800. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040095
APA StyleZahra, H., Berriche, O., Mizouri, R., Boukhayatia, F., Khiari, M., Gamoudi, A., Lahmar, I., Ben Amor, N., Mahjoub, F., Zayet, S., & Jamoussi, H. (2021). Plasmatic Magnesium Deficiency in 101 Outpatients Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clinics and Practice, 11(4), 791-800. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040095






