Abstract
Eosinophilic leukocytosis can be attributed to a number of clinical conditions such as parasitic infection, allergies, and neoplasms. Parasitic infection is the main cause of eosinophilia; however, a marked leukocytosis with hypereosinophilia secondary to Trichuris trichiura in adults has not been previously reported. We describe a case of a 39-year-old man who presented with fever and diarrhea. The investigation revealed a white blood cell (WBC) count of 20.69 × 109/L with an absolute eosinophil count of 12.44 × 109/L. Fecal microscopic examination demonstrated T. trichuria eggs. The WBC count returned to normal following treatment with albendazole. The literature pertaining to hematological findings associated with Trichuris trichiura is explored in this report. This case highlights that a significant elevation of leukocyte count with hypereosinophilia can be one of the manifestations of trichuriasis infection in adults. Empirical treatment with anti-helminthic agents may play a role in suspected cases to avoid severe complications, such as Trichuris dysentery syndrome.
1. Introduction
Eosinophilic leukocytosis can be caused by a variety of medical conditions, including allergies, infections, tumors, and immune diseases [1]. In countries with little exposure to parasites, allergies and reactions to medications are the main etiologies contributing to eosinophilia [2]. Eosinophilia can be one of the manifestations of the drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome, and the most common offending drugs are the antiepileptic agents, allopurinol, and antibiotics [3]. The DRESS syndrome should be suspected in a patient who receives new medication and develops cutaneous eruption, systemic symptoms (fever, lymphadenopathy), hematological abnormalities (eosinophilia, atypical lymphocytosis), as well as evidence of visceral organ involvements, such as abnormal liver and renal function tests [3].
In general, a parasitic infection is the main cause of eosinophilia, the most common being filariasis, followed by schistosomiasis, hookworm, Trichuris spp., and Strongyloides spp. [4,5]. Among the parasites, filariasis has a higher degree for causing eosinophilia [4,5]. Trichuris trichiura, commonly known as whipworm, rarely leads to hypereosinophilia (eosinophil count ≥ 1.5 × 109/L), especially among adults living in urban areas [6]. We present a case of a 39-year-old man with significant leukocytosis and hypereosinophilia from a Trichuris trichiura infection.
2. Case Presentation
A 39-year-old man was referred to our clinic with persistent leukocytosis. He complained of feeling feverish with myalgia for one month. He also had diarrhea, up to ten times per day, for five days prior to his presentation to the clinic. There was no abdominal pain or vomiting, and he was able to tolerate orally well. He did not have other constitutional symptoms, such as weight loss or night sweats. He did not have any rashes, cough, shortness of breath, or chest pain. All other systems review was unremarkable. There was no similar episode among other family members.
He worked as an operations manager in a factory and was primarily responsible for overseeing food preparation in the factory dining room. Thus, he was required to touch the raw materials, such as vegetables as part of the quality control measures. He lived in an urban residential area equipped with adequate sanitation and sewerage systems. There was no history of recent travel or recreational activities in the preceding six months. He was an active smoker of 24-pack-years. His past medical history was unremarkable. Specifically, he did not have any history of allergies or atopic medical conditions. He had not been on any medications for the past three months.
Physical examination did not show pallor, rashes, or finger clubbing. He was afebrile with temperature of 36 °C. His heart rate and blood pressure were all within the normal range. Abdominal examination was normal with no hepatosplenomegaly. He did not have any lymphadenopathy. His complete blood count (CBC) showed a white blood cell (WBC) count of 20.69 × 109/L with an absolute eosinophil count (AEC) of 12.44 × 109/L, hemoglobin of 17.1 g/dL, and platelet counts of 365 × 109/L. Hepatic and renal function tests were within the normal range. A peripheral blood film (PBF) showed leukocytosis and eosinophilia with no blast or immature granulocytes seen. There was also polycythemia, and the red bloods cells appeared normocytic and normochromic, with no nucleated red blood cells. The serum erythropoietin (EPO) level was normal (6.4 IU/L).
The fecal microscopic examination showed T. trichiura’s egg, characterized by a barrel-shaped, thick-shelled egg with a pair of polar “plugs” at each end (Figure 1). He was treated with albendazole 400 mg tablets twice a day for three days. The resolution of clinical symptoms and normalization of leukocyte counts following treatment supported the diagnosis of hypereosinophilia secondary to trichuriasis. Based on the findings of peripheral blood film (absence of immature granulocytes, no blast cells), normal platelet count, and normal serum EPO level, myeloproliferative neoplasms were unlikely [7]. The elevated hemoglobin was probably due to relative polycythemia (pseudopolycythemia), contributed by his smoking habit, thus an appropriate smoking cessation counselling was offered to the patient. The cytogenetic and molecular testing, such as identification of platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha gene (PDGFRA) and platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta gene (PDGFRB) rearrangements, was not carried out due to initial findings of T. trichiura’s egg in fecal microscopy and the normalization of eosinophil counts following treatment. His CBC results pre and post treatment with albendazole is shown in Table 1.
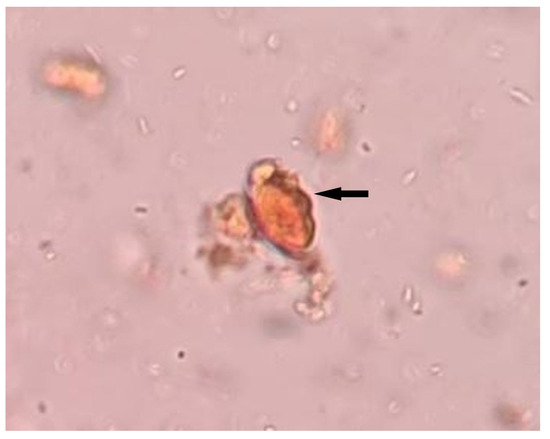
Figure 1.
Stool for ova and cyst shows presence of T. trichiura’s egg (black arrow).

Table 1.
Complete blood counts with differentials before and after treatment.
Other possible diagnosis such as DRESS colitis was highly unlikely as this patient had not been on any new medications which may trigger DRESS syndrome. Furthermore, apart from hypereosinophilia, he did not have any symptoms and signs suggesting this condition, such as rashes and enlarged lymph nodes. Other laboratory findings including liver and renal function tests were also normal.
3. Discussion
Eosinophilia refers to an elevation of absolute eosinophil counts of more than 0.5 × 109/L [8]. Continuing on this spectrum, hypereosinophilia (HE) is defined as a significant elevation of AEC of equal or more than 1.5 × 109/L [2,8]. HE can be subdivided into clonal (or primary), reactive (or secondary), familial, and idiopathic HE [2,8]. The primary form of HE is classified in the context of hematological malignancies [2]. Meanwhile, reactive HE is caused by underlying condition such as infections, allergies, drug reactions, autoimmune disorders, or solid tumors [2]. Idiopathic HE is concluded after the reactive and hematopoietic malignancies are excluded following thorough and comprehensive investigations [8]. If HE occurs in a familial cluster and after the primary or secondary cause has been ruled out, the term familial HE is used [2,8].
Reactive HE can be caused by various medical conditions such as infections, autoimmune diseases, malignancy, drug reactions, allergies, and hypersensitivity [8]. Drug-induced eosinophilia should be suspected among those with a history of recent drug use, although the reactions may be delayed for up to six weeks in some instances [8]. The DRESS syndrome is a more severe manifestation of adverse drug reaction, characterized by eosinophilia, extensive skin rashes, systemic symptoms, and multiple organ involvement [3]. This condition may potentially be life-threatening, and the symptoms are diverse, thus various diagnostic criteria have been proposed to support the diagnosis of DRESS, such as the RegiSCAR criteria [9]. While eosinophilia and diarrhea can be a first manifestation of the DRESS syndrome [10], we have excluded this etiology in our patient due to the lack of other visceral manifestation of DRESS syndrome. Furthermore, our patient did not fulfill the criteria for the diagnosis of this syndrome, which requires at least three of the following findings: (i) fever > 38 °C, (ii) lymphadenopathy at a minimum of two sites, (iii) evidence of involvement of at least one internal organ, and (iv) blood count abnormalities [9]. Other possible etiologies of reactive eosinophilia include solid tumors, such as renal cell carcinoma and breast cancer [8]; thus, a thorough clinical assessment, supported by appropriate investigations as indicated are essential, especially in the case of persistent eosinophilia.
Parasitic infections are the major cause of HE in tropical countries [2]. The most common parasitic infection causing eosinophilia is filariasis, followed by schistosomiasis and hookworm [4,5]. It was found that repetitive and prolong exposure to T-lymphocytes by parasites will lead to eosinophilic activation by the release of interleukin (IL) 3, 4, and 5, resulting in polyclonal eosinophils expansion [6]. Parasites tend to elicit marked eosinophilia during their migratory phase after their product comes into contact with immune cells [2,11]. Degranulation of granulated eosinophils within the tissue, releasing their performed mediators, will lead to tissue dysfunction and damage [2]. There is no reliable and precise level of eosinophilia that can trigger tissue or organ damage, but an arbitrary threshold of eosinophilia >1.5 × 109/L was classically considered as a risk [8]. Intestinal helminth infection is usually assumed as the main cause of eosinophilia among resource-poor populations [2]. A study done in a remote area in Brazil showed that eosinophilia occurred in half of the population and it was significantly associated with the presence of intestinal helminths [5]. Among immigrants from Africa, eosinophilia was frequently observed, with filariasis as the main etiology, followed by schistosomiasis and hookworm [4].
Trichuriasis infection begins with the ingestion of food or water contaminated with embryonated eggs of T. trichura [6,12]. The eggs hatch to form larva at the small intestine and then migrate to the cecum, where they mature into adult worms [6,12]. Female worm starts releasing eggs within the feces after a month of infection [6]. Infected individuals are commonly asymptomatic, but heavy colonic infection may cause Trichuris dysentery syndrome (TDS). TDS is mainly seen in children and characterized by mucoid diarrhea, rectal bleeding, rectal prolapse, iron deficiency anemia, and finger clubbing [6,13,14].
In Eastern Europe, Trichinella Spiralis is the most common parasites causing eosinophilia [15], while in Asia, T. trichiura is the main causative organism [6]. Asia contributes to 67% of global soil-transmitted helminths with the highest incidence in India (21%), followed by China (18%) [16]. Helminth infections are more common in the rural area compared to the urban, most possibly due to socioeconomic status, sanitary measures, and types of water supply [17]. The prevalence of trichuriasis is higher in school-age children living in tropical countries [14]. Compared to adults, T. trichura infection is more common in children due to the higher probability of exposure to contaminated soil when playing in the infected area [6]. In adults, infection or reinfection occurs mainly through the consumption of contaminated vegetables [6]. Recent studies have shown that mild to moderate trichuriasis in children can affect growth, physical health, and cognitive abilities [6,12,18].
A significant eosinophilia is not usually observed in trichuriasis, because this parasite usually remains in the colon and the mucosal inflammation is rare [12]. An earlier study among adults infected with intestinal helminths in a rural area in Brazil showed that the leukocyte counts ranged from 3.3 × 109/L to 16.1 × 109/L (median, 7.2 × 109/L) with the eosinophil counts between 0.04 and 1.46 × 109/L (median, 0.455 × 109/L) [5]. This study also concluded that while the probability of eosinophilia and HE increases with the number of parasite species present, the probability of leukocytosis did not [5].
While eosinophilia is commonly seen with trichuriasis infection [2,11], the literature pertaining to HE with marked leukocytosis secondary to this infection in adult remains scarce. Previous cases reported mild eosinophilia with normal leukocyte counts in adult with trichuriasis [19,20]. A case series from Korea reported that among four adult cases of trichuriasis, only one showed mild eosinophilia (AEC 0.48 × 109/L) with normal leukocyte counts [19]. Another case in Korea also reported normal leukocyte counts of 5.7 × 109/L without eosinophilia in a young adult with TDS [20]. Much higher leukocyte and eosinophil counts were previously reported in children infected by T. trichiura [21,22,23]. In one pediatric case of TDS in India, leukocytosis and HE were present, with leukocyte counts of 80 × 109/L and AEC of 40 × 109/L [23]. Another case study from Malaysia also reported that among four children diagnosed with TDS, only two had leukocytosis and HE, with the highest leukocyte counts of 34.94 × 109/L and the AEC of 22.78 × 109/ L [24].
In summary, a significant elevation of leukocyte count with hypereosinophilia can be one of the manifestations of trichuriasis infection in adults. Empirical treatment with anti-helminthic agents should be considered in suspected cases, especially in resource-poor populations where this infection is more prevalent.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.A. and N.B.; writing—original draft preparation, N.A.; writing—review and editing, N.A., N.B., F.R.M.R. and Z.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Riley, L.K.; Rupert, J. Evaluation of Patients with Leukocytosis. Am. Fam. Phys. 2015, 92, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar]
- van Balkum, M.; Kluin-Nelemans, H.; van Hellemond, J.; van Genderen, P.; Wismans, P. Hypereosinophilia: A diagnostic challenge. Neth J. Med. 2018, 76, 431–436. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.Y. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). In UpToDate; Corona, R., Ed.; UpToDate: Waltham, MA, USA, 2021; Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/drug-reaction-with-eosinophilia-and-systemic-symptoms(DRESS) (accessed on 12 October 2021).
- Pardo, J.; Carranza, C.; Muro, A.; Angel-Moreno, A.; Martín, A.-M.; Martín, T.; Hernández-Cabrera, M.; Pérez-Arellano, J.-L. Helminth-related eosinophilia in African immigrants, Gran Canaria. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heukelbach, J.; Poggensee, G.; Winter, B.; Wilcke, T.; Kerr-Pontes, L.; Feldmeier, H. Leukocytosis and blood eosinophilia in a polyparasitised population in north-eastern Brazil. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 100, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J. Helminth-Nematode: Trichuris trichiura. In Encyclopedia of Food Safety; Motarjemi, Y., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Teffari, A. Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of polycythemia vera. In UpToDate; Rosmarin, A.G., Ed.; UpToDate: Waltham, MA, USA, 2021; Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis-of-polycythemia-vera (accessed on 8 September 2021).
- Wang, S.A. The diagnostic work-up of hypereosinophilia. Pathobiology 2019, 86, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, S.; McLeod, M.; Torchia, D.; Romanelli, P. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2013, 6, 31. [Google Scholar]
- James, J.; Sammour, Y.M.; Virata, A.R.; Nordin, T.A.; Dumic, I. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome secondary to furosemide: Case report and review of literature. Am. J. Case Rep. 2018, 19, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roufosse, F.; Weller, P.F. Practical approach to the patient with hypereosinophilia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Else, K.J.; Keiser, J.; Holland, C.V.; Grencis, R.K.; Sattelle, D.B.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Bueno, L.L.; Asaolu, S.O.; Sowemimo, O.A.; Cooper, P.J. Whipworm and roundworm infections. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuroo, M.S.; Khuroo, M.S.; Khuroo, N.S. Trichuris dysentery syndrome: A common cause of chronic iron deficiency anemia in adults in an endemic area (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 71, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, L.S.; Holland, C.; Cooper, E. The public health importance of Trichuris trichiura. Parasitology 2000, 121, S73–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottstein, B.; Pozio, E.; Nockler, K. Epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and control of trichinellosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullan, R.L.; Brooker, S.J. The global limits and population at risk of soil-transmitted helminth infections in 2010. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattula, D.; Sarkar, R.; Ajjampur, S.S.R.; Minz, S.; Levecke, B.; Muliyil, J.; Kang, G. Prevalence & risk factors for soil transmitted helminth infection among school children in south India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2014, 139, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Parija, S.C.; Chidambaram, M.; Mandal, J. Epidemiology and clinical features of soil-transmitted helminths. Trop. Parasitol. 2017, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ok, K.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Song, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Ryu, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, J.S.; Whang, D.H.; Lee, H.K. Trichuris trichiura infection diagnosed by colonoscopy: Case reports and review of literature. Korean J. Parasitol. 2009, 47, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Seo, K.I. Trichuris trichiura Infection in North Korean Defector Resulted in Chronic Abdominal Pain and Growth Retardation. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 69, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachinmath, S.B.; Pratibha, S.; Dias, M.; Mallikarjun, P. Extensive persistent Trichuriasis: A case report. Int. J. Med. Public Health 2014, 4, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azira, N.M.; Zeehaida, M. Severe chronic iron deficiency anaemia secondary to Trichuris dysentery syndrome—A case report. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 29, 626–631. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Samanta, D.; Yadav, S. Trichuris dysentery syndrome with eosinophilic leukemoid reaction mimicking inflammatory bowel disease. J. Postgrad. Med. 2009, 55, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.; Zueter, A.; Zairi, N.Z. Trichuris dysentery syndrome: Do we learn enough from case studies? Trop. Biomed. 2015, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).