Adalimumab-Induced Rhupus Syndrome in a Female Patient Affected with Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody (ACPA)-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): A Case Report and Review of Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schur, P. Systemic lupus erythematosus. In Cecil-Loeb Textbook of Medicine; Beeson, P.B., Mc Dermott, W., Eds.; WB Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1971; p. 821. [Google Scholar]
- Tani, C.; D’Aniello, A.; Sedie, D.; Carli, L.; Cagnoni, M.; Possemato, N.; Carbone, M.; Della Rossa, A.; Riente, L.; Baldini, C.; et al. Rhupus syndrome: Assessment of its prevalence and its clinical and instrumental characteristics in a prospective cohort of 103 SLE patients. Autoimm. Rev. 2013, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wu, H.; Huang, X.; Xu, D.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, W.; Zeng, X. Clinical analysis of 56 patients with rhupus syndrome. Medicine 2014, 93, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, L.; Le Mauff, B.; Marcelli, C.; Aouba, A.; de Boysson, H. Rhupus: A systematic literature review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 102612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, L.M.; Keating, G.M. Adalimumab: A review of its use in rheumatoid arthritis. Biodrugs 2004, 18, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizinga, T.W.J.; Torii, Y.; Muniz, R. Adalimumab biosimilars in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review of the evidence for biosimilarity. Rheumatol. Ther. 2021, 8, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, J.M.; Ricart, J.M.; Alcácer, J.; Rausell, N.; Arana, G. Adalimumab-induced lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2008, 17, 676–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, F.C.; Edworthy, S.M.; Bloch, D.A.; McShane, D.J.; Fries, J.F.; Cooper, N.S.; Healey, L.A.; Kaplan, S.R.; Liang, M.H.; Luthra, H.S.; et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 31, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransen, J.; van Riel, P.L. The Disease Activity Score and the EULAR response criteria. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2005, 23 (Suppl. 39), S93–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DAS Score NL. Disease Activity Score in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Available online: https://www.das-score.nl/nl-nl/ (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- Dahlström, Ö.; Sjöwall, C. The diagnostic accuracies of the 2012 SLICC criteria and the proposed EULAR/ACR criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus classification are comparable. Lupus 2019, 28, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sawalha, A.H. Drug-induced lupus erythematosus: An update on drugs and mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2018, 30, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchers, A.T.; Keen, C.L.; Gershwin, M.E. Drug-induced lupus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1108, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, L.; Mertz, P.; Gavand, P.-E.; Martin, T.; Chasset, F.; Tebacher-Alt, M.; Lambert, A.; Muller, C.; Sibilia, J.; Lebrun-Vignes, B.; et al. Drug-induced systemic lupus: Revisiting the ever-changing spectrum of the disease using the WHO pharmacovigilance database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 99, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, M.H.; Burmester, G.R.; Kent, J.D.; Pangan, A.L.; Kupper, H.; Fitzpatrick, S.B.; Donovan, C. Safety analyses of adalimumab (HUMIRA) in global clinical trials and US postmarketing surveillance of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burmester, G.R.; Mease, P.; Dijkmans, B.A.C.; Gordon, K.; Lovell, D.; Panaccione, R.; Perez, J.; Pangan, A.L. Adalimumab safety and mortality rates from global clinical trials of six immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amezcua-Guerra, L.M.; Springall, R.; Marquez-Velasco, R.; Gomez-Garsía, L.; Vargas, A.; Bojalil, R. Presence of antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptides in patients with ‘rhupus’: A cross-sectional study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orozco, G.; Eyre, S.; Hinks, A.; Bowes, J.; Morgan, A.; Wilson, A.G.; Wordsworth, P.; Steer, S.; Hocking, L.J.; Thomson, W.; et al. Study of the common genetic background for rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buosi, A.L.; Natour, J.; Machado, F.S.; Takahashi, R.D.; Nely, R.; Furtado, V. Hand ultrasound: Comparative study between “no Rhupus” lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2014, 24, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, J.F.; Hanaoka, B.; Szyper-Kravitz, M.; Shoenfeld, Y. C-Reactive protein and its implications in systemic lupus erythematosus. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2007, 32, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- AlFadhli, S.; Nizam, R. Rhupus: A crosswalk between lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. OA Arthritis 2014, 2, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Devrimsel, G.; Beyazal, M.S. Three Case Reports of Rhupus Syndrome: An Overlap Syndrome of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2018, 21, 6194738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa-Orantes, A.; Hernandez-Vera, M.A.; Juarez-Villa, J.D.; Guadalupe, G.-E.A.; Flore, G. Rheumatoid Arthritis and Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia as First Manifestation of Rhupus. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2020, 9, 8870643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, C.A.; Lyons, S.; Stamps, B.K. Autoimmune haemolysis: An 18-year study of 865 cases referred to a regional transfusional centre. Br. Med. J. 1981, 282, 2023–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brand, C.A.; Rowley, M.J.; Tail, B.D.; Muirden, K.D.; Whittingham, S.F. Coexistent rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus: Clinical, serological and phenotypic feature. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1992, 51, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frade-Sosa, B.; Narvaez, J.; Salman-Monte, T.C.; Castellanos-Moreira, R.; Ortiz-Santamaria, V.; Torrente-Segarra, V.; Castellvi, I.; Magallares, B.; Reina, D.; Minguez, S.; et al. A comparative study on clinical and serological characteristics between patients with rhupus and those with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Lupus 2020, 29, 1216–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danion, F.; Sparsa, L.; Arnaud, L.; Alsaleh, G.; Lefebvre, F.; Gies, V.; Martin, T.; Lukas, C.; Durckel, J.; Ardizzone, M.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of antitumour necrosis factor alpha treatment in rhupus: An open-label study of 15 patients. RMD Open 2017, 3, e000555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanau, R.M.; Neuman, M.G. Safety of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapies in arthritis patients. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 17, 324–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewè, R.B.M.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Burmester, G.R.; Dougados, M.; Kerschbaumer, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Sepriano, A.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; de Wit, M.; et al. EULAR reccomendations for the management of rheumatoid arthirtis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 79, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.T.; Lee, J.U.; Son, J.Y.; Shin, W.; Heo, Y.-S. Structural biology of the TNFa antagonists used in the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plant, D.; Wilson, A.G.; Barton, A. Genetic and epigenetic predictors of responsiveness to treatment in RA. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bek, S.; Bojesen, A.B.; Nielsen, J.V.; Sode, J.; Bank, S.; Vogel, U.; Andersen, V. Systematic review and meta-analysis: Pharmacogenetics of anti-TNF treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm. J. 2017, 17, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
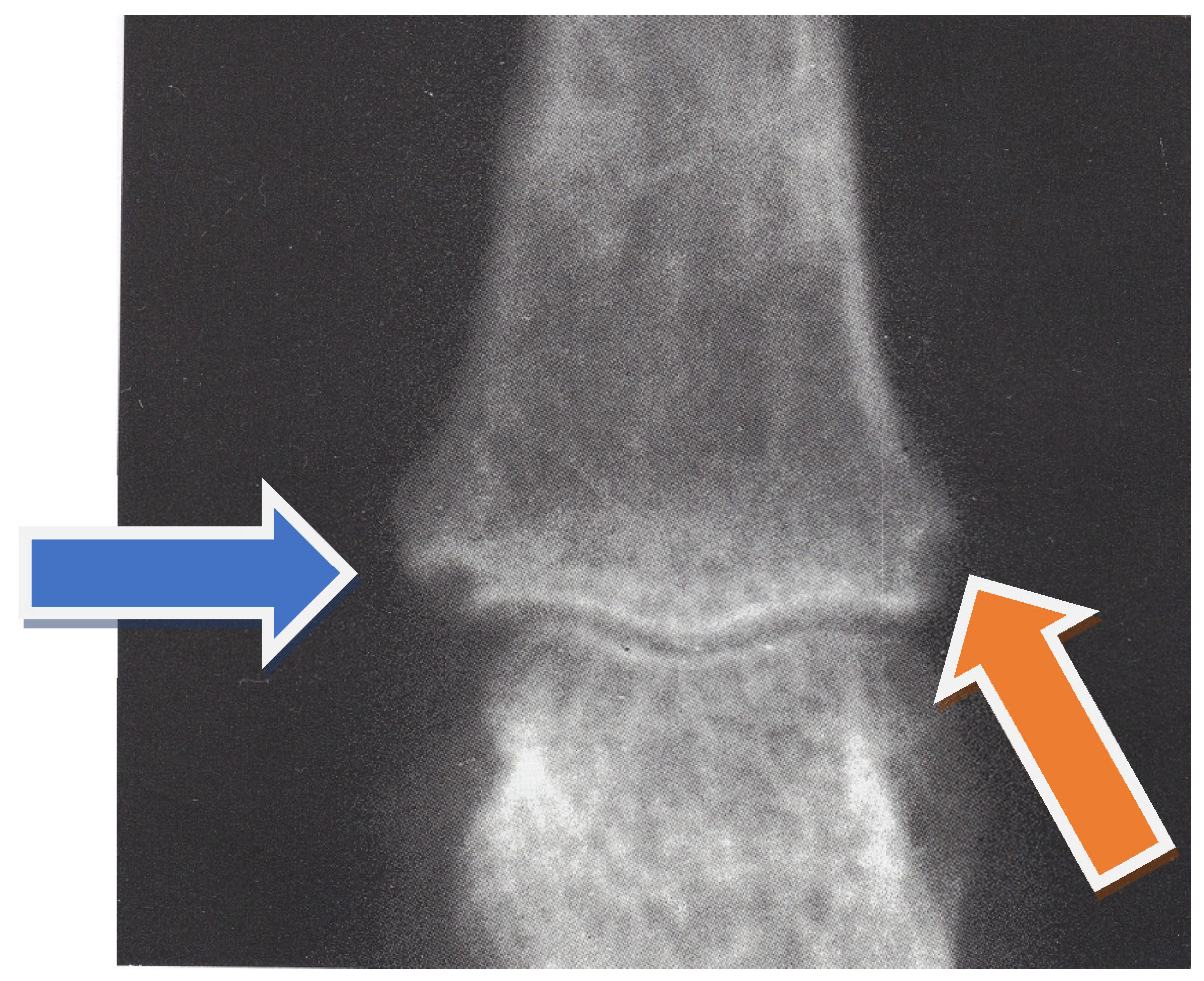

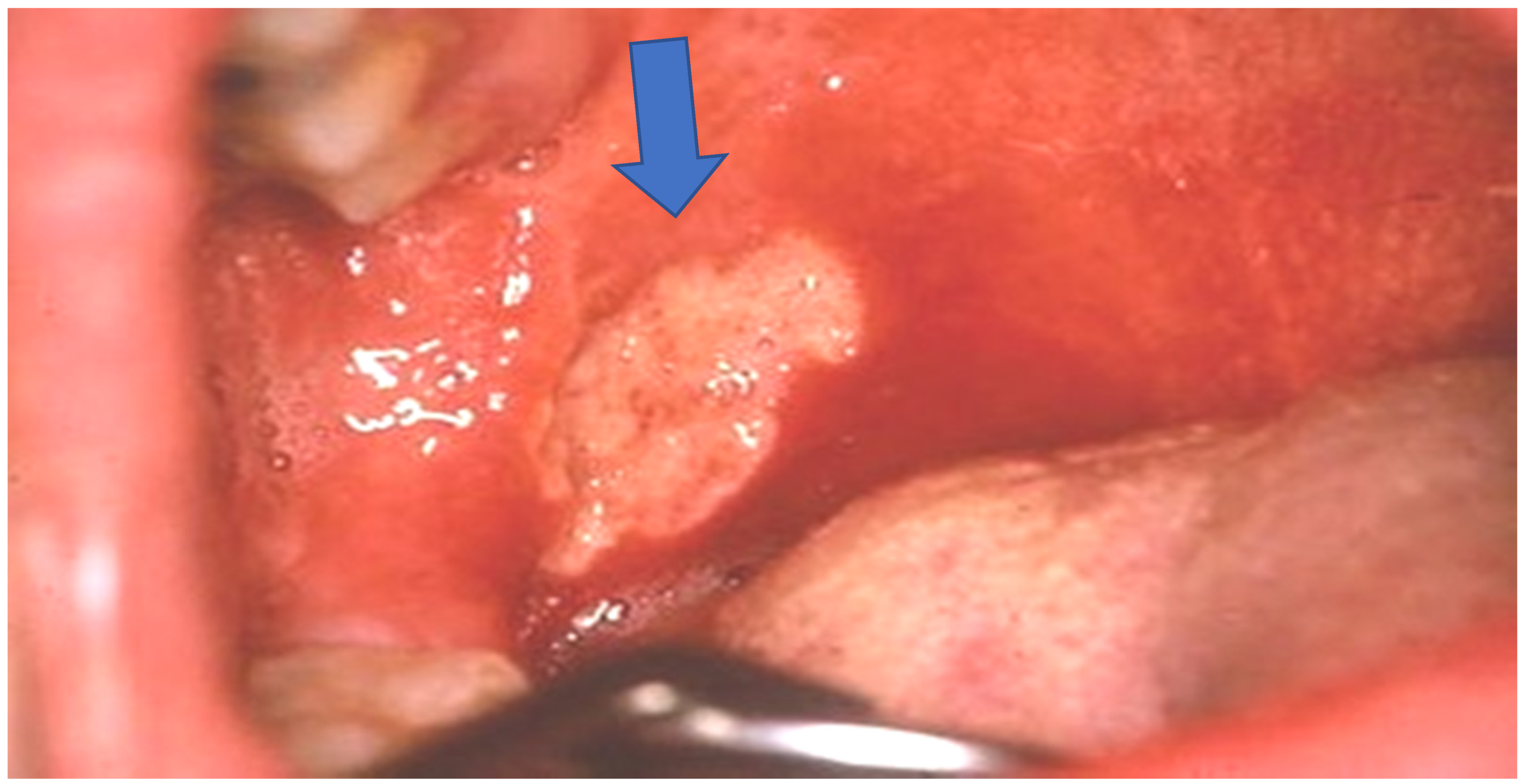
| ESR = 55 mm/h (n.v. < 15) |
| CRP concentrations = 15 mg/dL (n.v. < 0.3) |
| Hemoglobin = 12.2 gr/dL (n.v. > 12) |
| RF = 80 IU/mL (n.v. < 20) |
| ACPA = 200 IU/mL (n.v. < 18) |
| ANA < 1.40 |
| LAC, p-ANCA, c-ANCA: normal ranges |
| Renal and hepatic function tests: within their normal ranges |
| Occult blood testing in the stool: negative |
| Faecal calprotectin dosage: within normal range. |
| Hepatitis A, B and C serology: negative |
| ESR = 38 mm/h (n.v. < 15) |
| CRP concentration = 1 mg/dL (n.v. < 0.3) |
| Hemoglobin = 10.5 gr/dL (n.v. > 12) |
| Reticulocyte count = 6.2 % (n.v. < 2.3%) |
| Total bilirubin = 1.8 mg/dL (n.v. < 1.0) |
| Indirect bilirubin = 1.2 mg/dL (n.v. < 0.6) |
| Iron = 193 mcg/dL (n.v. < 140) |
| Ferritin = 450 ng/mL (n.v. < 120)Haptoglobin = 300 mg/dL (n.v. < 150) |
| Direct Coombs test = positive |
| ACPA = 256.6 IU/mL (n.v. < 18) |
| ANA = 1:1280, homogeneous pattern (n.v. < 1:80) |
| Anti-dsDNA antibodies = 400 IU/mL (n.v. < 200) |
| Anti-phospholipid antibodies = negative |
| LAC = negative |
| Anti- beta2 glycoprotein 1 = negative |
| p-ANCA = negativec-ANCA =negative |
| Renal and hepatic function tests: within their normal ranges |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manzo, C.; Castagna, A. Adalimumab-Induced Rhupus Syndrome in a Female Patient Affected with Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody (ACPA)-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): A Case Report and Review of Literature. Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, 404-409. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11030055
Manzo C, Castagna A. Adalimumab-Induced Rhupus Syndrome in a Female Patient Affected with Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody (ACPA)-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): A Case Report and Review of Literature. Clinics and Practice. 2021; 11(3):404-409. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11030055
Chicago/Turabian StyleManzo, Ciro, and Alberto Castagna. 2021. "Adalimumab-Induced Rhupus Syndrome in a Female Patient Affected with Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody (ACPA)-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): A Case Report and Review of Literature" Clinics and Practice 11, no. 3: 404-409. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11030055
APA StyleManzo, C., & Castagna, A. (2021). Adalimumab-Induced Rhupus Syndrome in a Female Patient Affected with Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody (ACPA)-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): A Case Report and Review of Literature. Clinics and Practice, 11(3), 404-409. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11030055






