Granulomatous Mastitis Due to Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Dilemma
Abstract
1. Introduction
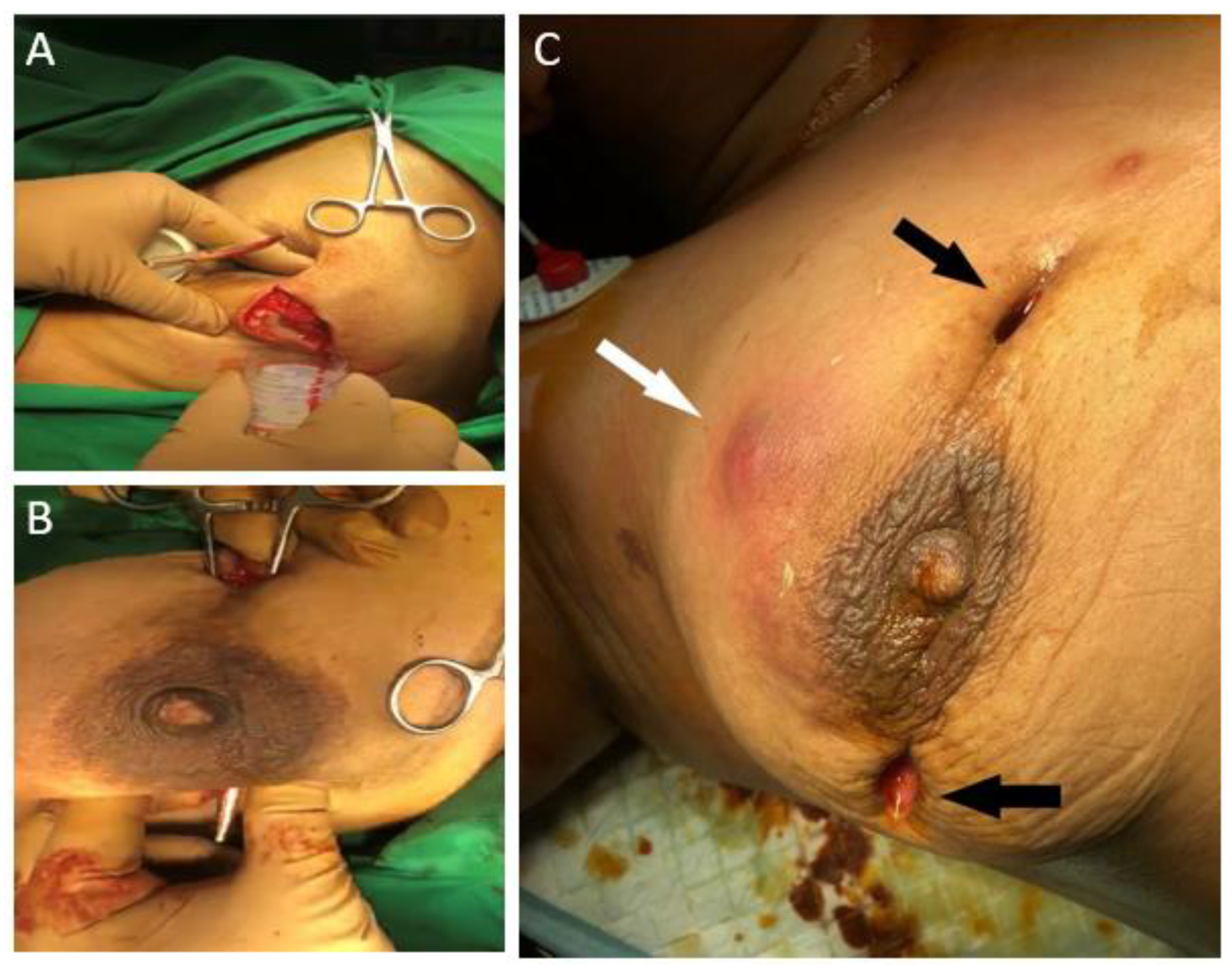
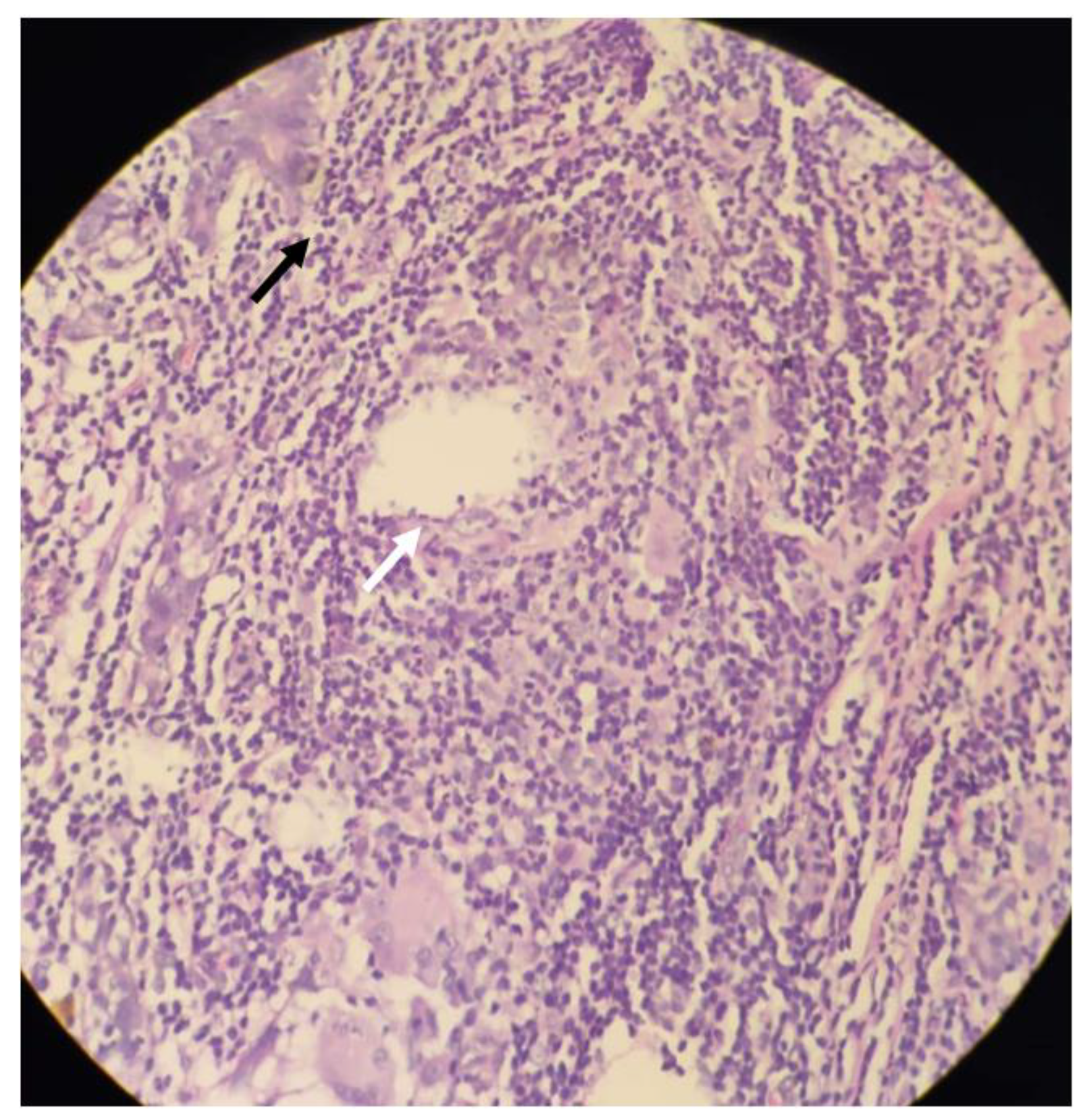
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kessler, E.; Wolloch, Y. Granulomatous mastitis: A lesion clinically simulating carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1972, 58, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfrum, A.; Kümmel, S.; Theuerkauf, I.; Pelz, E.; Reinisch, M. Granulomatous Mastitis: A Therapeutic and Diagnostic Challenge. BRC 2018, 13, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.M.; Turashvili, G. Cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis: An update. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 73, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trupiano, J.K.; Sebek, B.A.; Goldfarb, J.; Levy, L.R.; Hall, G.S.; Procop, G.W. Mastitis Due to Mycobacterium abscessus after Body Piercing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fox, L.P.; Geyer, A.S.; Husain, S.; Della-Latta, P.; Grossman, M.E. Mycobacterium abscessus cellulitis and multifocal abscesses of the breasts in a transsexual from illicit intramammary injections of silicone. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 50, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, E.M.; Ellsworth, W.; Yuksel, E.; Allen, S. Mycobacterium abscessus infection after breast augmentation: A case of contaminated implants? J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2009, 62, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.L.; Palmer, S.M. Mycobacterium abscessus chest wall and pulmonary infection in a cystic fibrosis lung transplant recipient. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2006, 25, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasticci, M.B.; Lapalorcia, L.M.; Antonini, G.; Mencacci, A.; Mazzolla, R.; Baldelli, F. Community-acquired mastitis due to Mycobacterium abscessus: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2009, 3, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackowe, D.J.; Murariu, D.; Parsa, N.N.; Parsa, F.D. Chronic fistulas after breast augmentation secondary to Mycobacterium abscessus. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 38–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasar, K.K.; Pehlivanoglu, F.; Sengoz, G.; Cabioglu, N. Successfully treated Mycobacterium abscessus mastitis: A rare cause of breast masses. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 29, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urgancı, A.U.; Yorulmaz, İ.; Karaca, B.Y. Granulomatous mastitis due to mycobacterium abcessus. J. Breast Health 2011, 7, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg, E.; Cheretakis, A.; Modarressi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Pittet-Cuénod, B. Multisite Infection with Mycobacterium abscessus after Replacement of Breast Implants and Gluteal Lipofilling. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2015, 2015, 361340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baroudi, R.; Flaugher, M.; Hemadeh, O. An Unusual Infection of Breast Tissue. Fed. Pract. 2016, 33, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wankhade, A.B.; Ghadage, D.; Bhore, A.V. Breast abscess due to Mycobacterium abscessus: A rare case. Ann. Trop. Med. Public Health 2017, 10, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Li, Q.W.; Zhou, L.; Guan, R.F.; Zhou, X.M.; Wu, J.H.; Rao, N.Y.; Zhu, S. Granulomatous Lobular Mastitis Associated with Mycobacterium abscessus in South China: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, E.; Holst-Albrechtsen, S.; Christensen, K.Ø.; Birk-Sørensen, L.; Juel, J. [Mycobacterium abscessus infection after cosmetic breast surgery in India]. Ugeskr Laeger 2018, 180, V09170655. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramachandra, S.; Al Kindi, M.; Al Amri, F.S.S. Granulomatous Mastitis—A Rare Presentation of Atypical Mycobacterial Infection. J. Pathol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 2, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, A.; Vohra, L.M. Mycobacterium Abscessus: A Rare Cause of Peri-Ductal Mastitis in Endemic Regions. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2020, 30, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.B.; Paviour, S.D.; Musaad, S.; Jones, W.O.; Holland, D.J. A clinicopathological review of 34 cases of inflammatory breast disease showing an association between corynebacteria infection and granulomatous mastitis. Pathology 2003, 35, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naik, M.A.; Korlimarla, A.; Shetty, S.T.; Fernandes, A.M.; Pai, S.A. Cystic Neutrophilic Granulomatous Mastitis: A Clinicopathological Study With 16s rRNA Sequencing for the Detection of Corynebacteria in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 28, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case Report | Age | Predisposition | Presentation | Histopathology | Treatment | Antimicrobial | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trupiano JK (2001) [4] | 17 | Nipple piercing | Breast Mass | Granulomatous inflammation with AFB | Surgical Resection | Antimicrobials not received | No recurrence |
| Fox LP (2004) [5] | 29 | Breast Augmentation Surgery | Abscess | Histiocytic and giant cell reaction, granulation, AFB | Surgical Drainage | Clarithromycin x 24 weeks, Cefoxitin x3 weeks | No recurrence |
| Feldman EM (2007) [6] | 48 | Breast Augmentation Surgery | Sinus | not performed | Surgical Drainage | Clarithromycin x 24 weeks | No recurrence |
| Taylor JL (2006) [7] | 21 | Breast Augmentation Surgery with Cystic Fibrosis on Prednisone, Azathioprine, Tacrolimus | Sinus | Not reported | Surgical Drainage | Clarithromycin, Levaquin x44 weeks | Clinical deterioration & death |
| Pasticci (2009) [8] | 54 | Autoimmune Haemolytic Anaemia on prednisone | Abscess | Chronic inflammatory reaction with giant cells with AFB | Surgical Drainage | Clarithromycin x10 weeks, Amikacin | Recurrence |
| Jackowe DJ (2010) [9] | 44 | Breast Augmentation Surgery | Sinus | Not performed | Surgical Drainage | Not reported | No recurrence |
| Yasar et al. (2011) [10] | 38 | None | Breast Mass with sinus | Not performed | Aspiration | Clarithromycin x 16 weeks, Linezolid 8 weeks | No recurrence |
| Urganci AU (2011) [11] | 27 | None | Breast Mass | Granulomatous mastitis with AFB | Surgical Drainage | Clarithromycin x6 weeks | No recurrence |
| Ruegg (2015) [12] | 39 | Breast Augmentation Surgery | Abscess | Not performed | Surgical Drainage | Clarithromycin x20 weeks, Tigecycline, Linezolid, Amikacin | No recurrence |
| Baroudi el at. (2016) [13] | 50 | Crohn’s disease, off treatment | Abscess | Micro abscesses with mastitis | Antimicrobials | Clarithromycin x 12 weeks | No recurrence |
| Wankhade AB (2017) [14] | 30 | None | Breast Mass | Chronic Granulomatous mastitis | Surgical resection | Rifampin, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide, Ethambutol, Clarithromycin, duration unknown | no follow up |
| Wang YS (2017) [15] | 29 | None | Abscess | CNGM | Surgical Drainage | Rifampin, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide | No recurrence |
| Jensen et al. (2018) [16] | 36 | Breast Augmentation Surgery | Sinus | Not performed | Antimicrobials | Cefalexin x 8 weeks | Recurrence |
| Ramchandra S (2019) [17] | 33 | None | Breast Mass | CNGM | Antimicrobials | Clarithromycin, duration unknown | no follow up |
| Shaikh A (2020) [18] | 32 | None | Breast Mass | Mixed inflammatory infiltrate with granulomatous reaction with fat necrosis | Surgical resection | Clarithromycin x4 weeks, Amikacin 4 weeks | no follow up |
| Present Case | 34 | None | Abscess | CNGM | Surgical Drainage | Clarithromycin, Amikacin x 8 weeks | No recurrence |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, O.A.; Bakhshi, G.D.; Nadkarni, A.R.; Rangwala, Z.S. Granulomatous Mastitis Due to Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Dilemma. Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, 228-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11020034
Patel OA, Bakhshi GD, Nadkarni AR, Rangwala ZS. Granulomatous Mastitis Due to Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Dilemma. Clinics and Practice. 2021; 11(2):228-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11020034
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Owais Ahmed, Girish D. Bakhshi, Amogh R. Nadkarni, and Zarin S. Rangwala. 2021. "Granulomatous Mastitis Due to Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Dilemma" Clinics and Practice 11, no. 2: 228-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11020034
APA StylePatel, O. A., Bakhshi, G. D., Nadkarni, A. R., & Rangwala, Z. S. (2021). Granulomatous Mastitis Due to Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Dilemma. Clinics and Practice, 11(2), 228-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11020034







