Introduction
Circumpolar studies have provided strong evidence of the vulnerability of marine ecosystems in response to anthropogenic activities. Such ecological disturbances are particularly impactful on biodiversity, which helps protect ecosystems from extreme conditions. It is thus imperative to develop biomarkers for long term monitoring of changes in marine biodiversity and to better assess comparative responses of different species. Because of their wide geographic distribution and their seeding and filter-feeding nature, mussels, such as Mytilus edulis and its closely related species, have been commonly used as sentinel species in ecotoxicological monitoring programs around the globe [1,2,3]. Extensive research has been performed on their physiology and their genetic content in order to develop sensitive and specific biomarkers. This is especially true for M. edulis, which has been extensively characterized at the cellular and molecular levels, not only because of their ecological importance, but also because of their economical impact [4,5,6]. However, because of their distinctive anatomy and physiology, it is logical to believe that other mussel species will respond differently to climate change and exposure to pollutants [7]. Our recent comparative study between Mytilus desolationis (M. desolationis) and Aulacomya ater (A. ater) supports this hypothesis [8]. A better knowledge of A. ater could thus provide a new and complementary tool for monitoring global climate changes in marine ecosystems, most notably in the Southern hemisphere, which is particularly sensitive to climate change.
Because of its strategically geographical position, the Kerguelen archipelago is considered an important site to investigate the effects of global change on marine ecosystems [9]. Although M. desolationis is normally the dominant species in most mussel beds in the Kerguelen archipelago, we found that some mussel beds, such as one found at tide depth at Port-aux-Français, is largely dominated by A. ater [8]. Whether such diversity is permanently maintained or will change following environmental parturbation will depend on the ability of mussel species to respond to environmental stress. Because heat shock proteins (Hsps) play an important role of protection and maintenance of many vital cellular functions in response to thermal and toxic stress, they are commonly used as stress biomarkers [10,11]. Their structural features are highly conserved among eukaryotes and prokaryotes, especially in the case of hsp70, a widely used biomarker to monitor the impact of environmental factors on various animal species, including mussels [12,13,14,15,16]. Unfortunately, while a considerable amount of data exists on blue mussel stress response genes, our knowledge on A. ater remains fragmentary. In the present work, we report a detailed comparative analysis of hsp70 stress response gene from Mytilus desolationis (M. desolationis) and Aulacomya ater (A. ater).
Materials and Methods
Collection of specimens
Adult specimens (55–70 mm length) of blue mussels, M. edulis desolationis, and ribbed mussels, A. ater were collected on the intertidal rocky shore of Port-aux-Français (Kerguelen Islands, France). Mussels were immediately transferred to the marine laboratory of Port-aux-Français and placed in a temperature-controlled (12°C) aerated aquarium containing filtered recirculating seawater maintained on a 12 h:12 h light/dark cycle. Mussels were dissected, tissues frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at –80°C until further analysis.
RT-PCR and sequencing
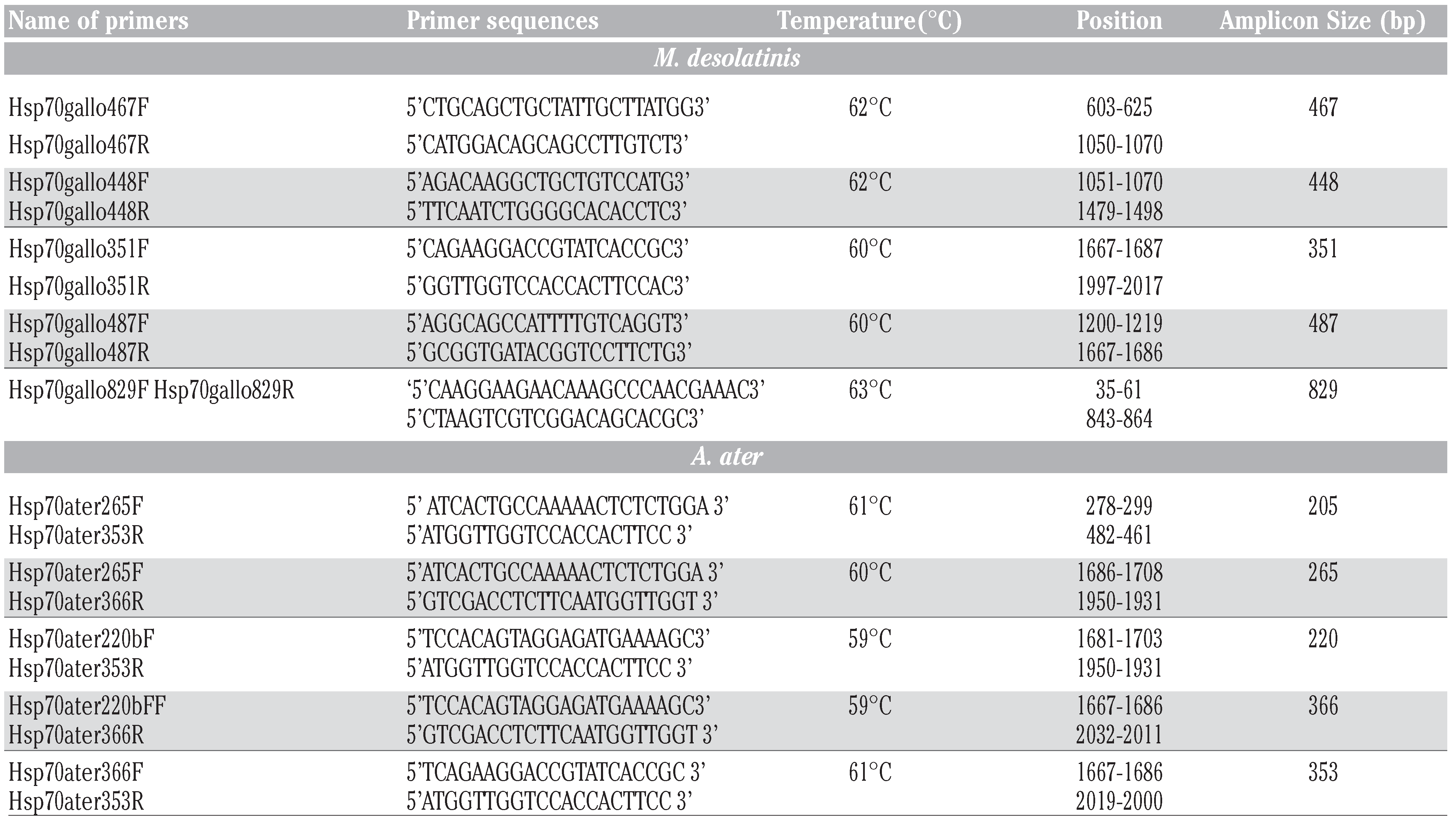
Tissues (gills) were homogenized by sonication and total cellular RNA was isolated using the TRIzol reagent (Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ultraviolet (UV) absorbance was used to assess the quality and the concentrations of RNA. First-strand cDNA was prepared from cellular RNA using the reverse transcriptase Omniscript (QIAGEN, Mississauga, ON, Canada). cDNAs were amplified using specific primers (Table 1) with the following conditions: 94ºC for 3 min, followed by 30 to 35 cycles of the following: 94°C for 40 sec, 60°C for 40 sec (unless otherwise indicated), and 72°C for 40 sec, followed by a final extension step at 72°C for 10 min. PCR was performed in a thermal cycler (MJ Research, Watertown, MA). The amplified products were analyzed by electrophoresis using 1.5% [w/v] agarose gels, SYBR Safe (Life Technologies) DNA gel staining and UV illumination. Sequencing of the amplicons was performed by the Genome Quebec sequencing platform. Structure figures were prepared in PyMOL (The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System).

Table 1.
List of oligoprimers used for amplification of hsp70 of A. ater and M. desolationis.
Results
Stress-induced ATP-bound hsp70 binds to newly synthesize unfolded or partially folded proteins via interaction with hydrophobic peptide segments and prevents their aggregation into nonfunctional structure. Once the entire protein is synthesized, it binds to nucleotide exchange factors (NEFs), such as BAG, thereby inducing the release of ADP and binding of fresh ATP, opening the binding pocket (reviewed in [17]). Hsp70 binds ATP via its N-terminal ATPase domain (NBD), which consists of two lobes with a deep cleft between them, at the bottom of which nucleotide (ATP and ADP) binds. The substrate binding domain (SBD) of hsp70 is responsible for binding to neutral, hydrophobic amino acid residues in a groove made of subdomains containing sheets and helical segments in a manner that is reminiscent of the MHC peptide binding groove [18]. This groove is closed by an alpha helical-rich C-terminal «lid» that opens and closes to allow for substrate binding and release.
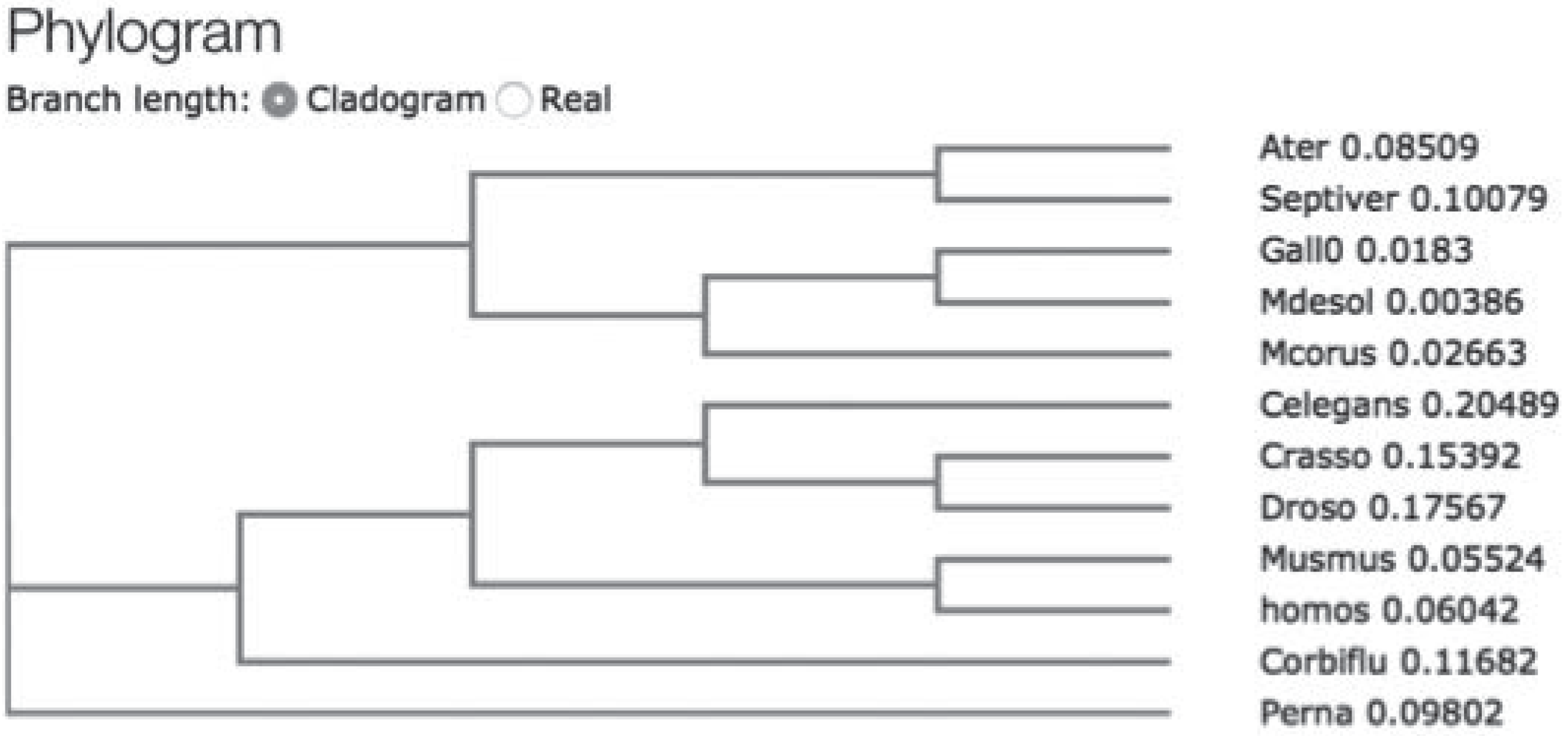
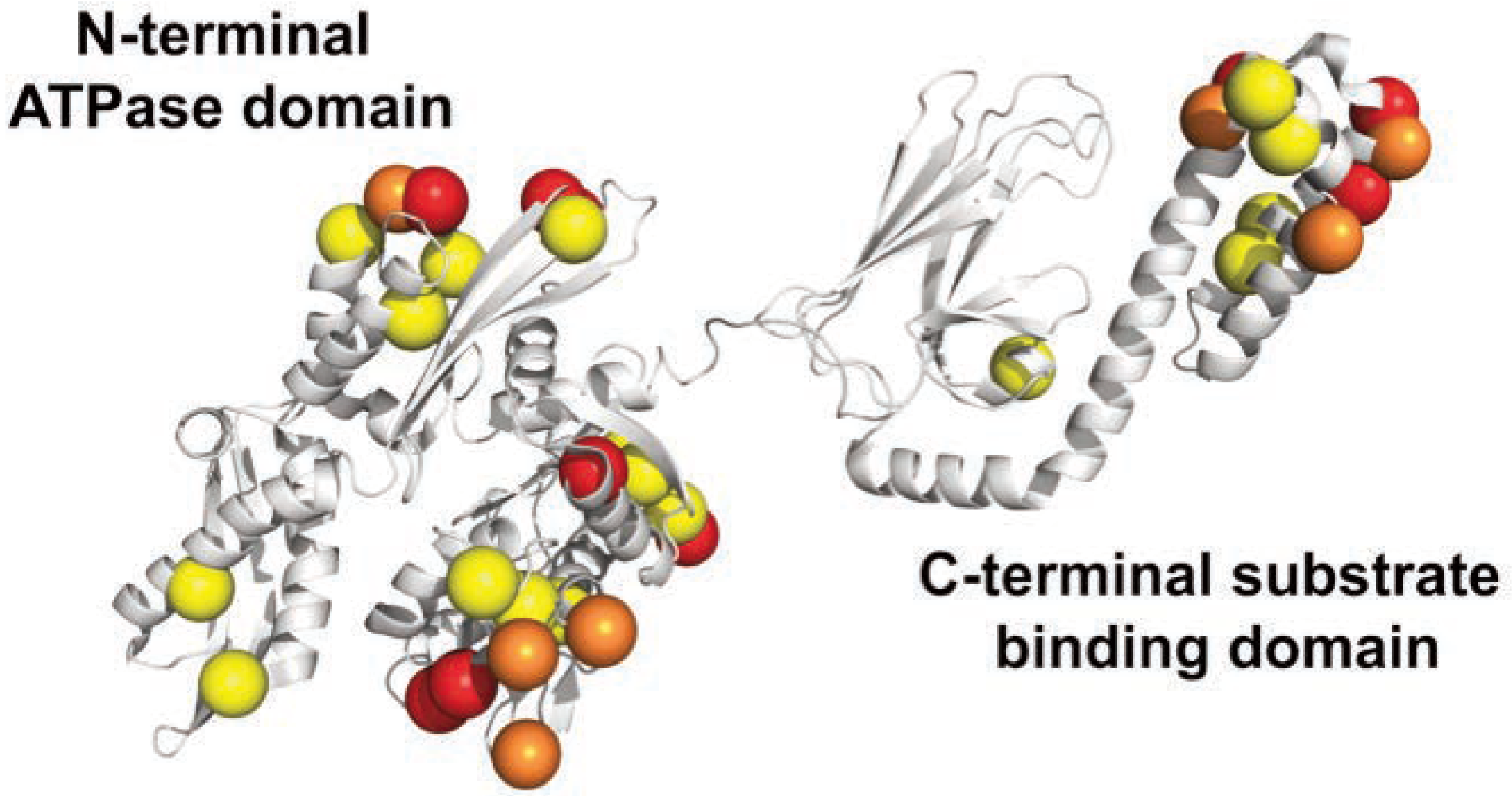
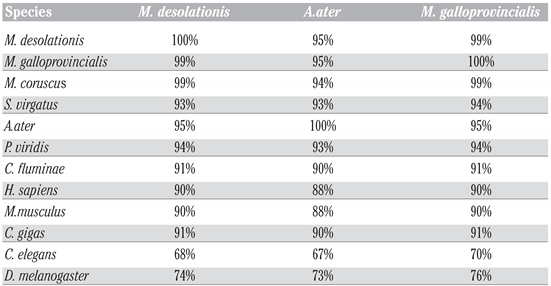
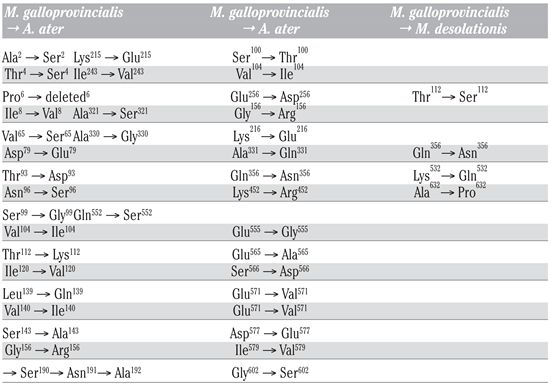
To study hsp70 in A. ater, we performed PCR amplification of hsp70 gene fragments using specific primers designed following analysis of multiple sequence hsp70 coding sequence alignment with the purpose of PCR amplifying the coding region of hsp70. Following PCR, amplicons were directly sequenced and analyzed using BLASTn and BLASTp hosted by Web servers of the National Center of Biotechnology Information (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast). At the DNA level, we found that the sequence of hsp70 of M. desolationis was 98% homologous to that of M. gallopro incialis, a well-characterized cosmopolitan Mediterranean mussels species. By comparison, the percent homology of hsp70 sequence from A. ater was 81% with M. gallopro incialis. The sequence of hsp70 of A. ater was closer to that of Septifer irgatus, the black mussel, than that of the blue mussel (Figure 1). At the amino acid level, Hsp70 from M. desolationis was very close (99% identity) to that of its closely related species, M. gallopro incialis and M. coruscus (Table 2). By comparison, the percent of identity between hsp70 from M. desolationis and hsp70 from A. ater and Septifer irgatus was 95% and 94% respectively. The major differences at the amino acid level between hsp70 of A. ater and hsp70 of the blue mussels were located in the N-terminal NBD domain (Figure 2). Most of these differences involved conservative of semi-conservative substitutions, although a number non-conservative substitutions were found, most notably on the external surface of the SBD, suggesting that hsp70 from the ribbed mussel A. ater differs from the blue mussel in its functional activity (Table 3).
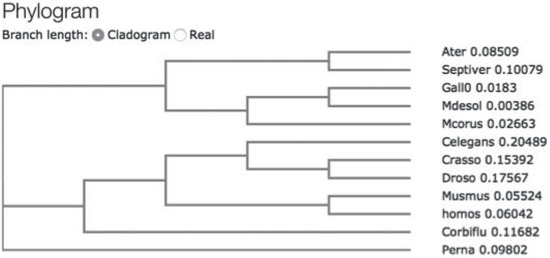
Figure 1.
Simplified cladogram showing relationships between mussel species based upon Hsp70 sequence. The cladogram was constructed using the CLUSTAL W (1.83) multiple sequence T-coffe alignment software (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/tcoffee/).

Table 2.
Percentages of identity of hsp70 at the amino acid level between species.
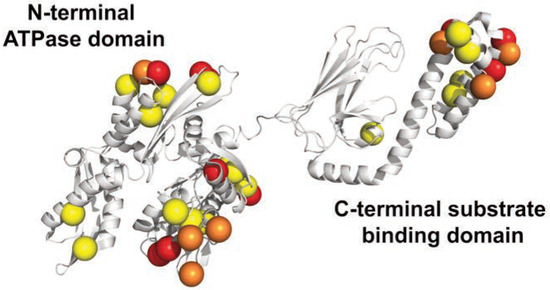
Figure 2.
3D structure of hsp70 from M. galloprovincialis. The location of mutated residues from A. ater are shown. Yellow and orange spheres represent conservative and semi-conservative substitutions. In red, non-conservative substitutions.

Table 3.
Amino acid substitutions in hsp70 of M. desolationis and A. ater as compared to hsp70 of M. galloprovincialis.
Because of cellular abundance and high degree of conservation, hsp70 is perhaps the best-studied stress biomarker in all taxonomic groups. In the present work, we provide the first molecular characterization of hsp70 in A. ater. In contrast to other mussel species, such as M. edulis and M. gallopro incialis, which
have been studied in details for many years, molecular characterization of A. ater genes remains anecdotic at best. Our results showed that hsp70 from A. ater is significantly different from that of M. desolationis. Such difference can be exploited as a tool to discriminate between M. desolationis and A. ater samples at the molecular level. The technique is simple to perform and can be implemented in all settings where PCR is available. The molecular characterization of hsp70 in both species thus provides a new tool to better assess in the future the ability of both species to environmental stress. Our recent study did indeed show that both species respond differently two cadmium-induced apoptosis [8]. Although hsp70 is among the most highly conserved gene during evolution, at the protein level, our results also showed that hsp70 of A. ater harbors more than 30 amino acid substitutions when compared to hsp70 of blue mussels. Because the substrate specificity of chaperones like hsp70 is dictated by minor changes in the primary amino acid sequence [19], these changes may indicate fundamental differences between hsp70 activity in M. desolationis and A. ater. Whether such differences may alter their ability to respond to environmental stress is an interesting possibility given the progressive disappearance of A. ater from many marine habitats [7]. The development of novel molecular stress biomarkers of A. ater could provide a new and complementary tool for monitoring global climate changes in marine ecosystems in the Southern hemispheres, which is particularly sensitive to climate change.
In conclusion, we report the molecular characterization of hsp70 in A. ater and highlight major differences at the nucleic acid and protein levels with M. desolationis. This information will be useful for the development of new molecular tools to monitor the effect of environmental stress on both mussel populations, which are well known for their ability to co-exist in the same marine habitat. This information will also be useful for learning the phylogenetic relationships between both mussel species and with other A. ater populations present in various marine ecosystems in the Southern hemisphere.
Discussion
Because of cellular abundance and high degree of conservation, hsp70 is perhaps the best-studied stress biomarker. In the present work, we provide the first molecular characterization of hsp70 in A. ater. In contrast to other mussel species, such as M. edulis and M. gallopro incialis, which have been studied in details for many years, molecular characterization of A. ater genes remains anecdotic at best. Our results showed that hsp70 from A. ater is significantly different from that of M. desolationis. Such difference can be exploited as a tool to discriminate between M. desolationis and A. ater samples at the molecular level. The technique is simple to perform and can be implemented in all settings where PCR is available. Most importantly, the molecular characterization of hsp70 in both species provide a new tool to better assess the ability of both species to environmental stress. Our recent study did indeed show that both species respond differently two cadmium-induced apoptosis [8]. Although hsp70 is among the most highly conserved gene during evolution, at the protein level, our results also showed that hsp70 of A. ater harbors more than 30 amino acid substitutions when compared to hsp70 of blue mussels. Because the substrate specificity of chaperones like hsp70 is dictated by minor changes in the primary amino acid sequence [19], these changes may indicate fundamental differences between hsp70 activity in M. desolationis and A. ater. Whether such differences may alter their ability to respond to environmental stress is an interesting possibility given the progressive disappearance of A. ater from many marine habitats [7]. The development of novel molecular stress biomarkers of A. ater could provide a new and complementary tool for monitoring global climate changes in marine ecosystems in the Southern hemispheres, which is particularly sensitive to climate change.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we report the molecular characterization of hsp70 in A. ater and highlight major differences at the nucleic acid and protein levels with M. desolationis. This information will be useful for the development of new molecular tools to monitor the effect of environmental stress on both mussel populations, which are well known for their ability to co-exist in the same marine habitat. This information will also be useful for learning the phylogenetic relationships between both mussel species and with other A. ater populations present in various marine ecosystems in the Southern hemisphere.
Funding
Supported by the National Science and Engineering Council of Canada (NSERC), the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR), the French Polar Institute Paul Émile Victor (IPEV, Project N°409 IMMUNOTOXKER), and the Terres Australes et Antarctiques Françaises (TAAF).
Acknowledgments
the authors would like to thank Ms. Marlène Fortier and M. Philippe Egesborg for their technical help, all the personnel from the French Polar Institute Paul Emile Victor (IPEV) for their logistic support, and Vincent Terol, Jean-François Laclavetine and Didier Boutenet for their kind help and hospitality during our stay in the Kerguelen archipelago.
References
- Goldberg, E.D. The mussel watch - a first step in global marine monitoring. Mar. Poll. Bull. 1975, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.D.; Webster, L.; Martínez-Gómez, C.; Burgeot, T.; Gubbins, M.J.; Thain, J.E.; et al. Assessment of contaminant concentrations in sediments, fish and mussels sampled from the North Atlantic and European regional seas within the ICON project. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 124, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, A.L.; Ovaert, J.; Arias, A.H.; Souissi, S.; Marcovecchio, J.E. Mussels as bioindicators of PAHs pollution within Argentinean Coastal Environments, South America. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Philipp, E.E.; Kraemer, L.; Melzner, F.; Poustka, A.J.; Thieme, S.; Findeisen, U.; et al. Massively parallel RNA sequencing identifies a complex immune gene repertoire in the lophotrochozoan Mytilus edulis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poynton, H.C.; Robinson, W.E.; Blalock, B.J.; Hannigan, R.E. Correlation of transcriptomic responses and metal bioaccumulation in Mytilus edulis L. reveals early indicators of stress. Aqua Toxicol. 2014, 155, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.; Apraiz, I.; da Fonseca, R.R.; Cristobal, S. Shotgun analysis of the marine mussel Mytilus edulis hemolymph proteome and mapping the innate immunity elements. Proteomics 2015, 15, 4021–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caza, F.; Cledon, M.; St-Pierre, Y. Biomonitoring climate change and pollution in marine ecosystems: A review on Aulacomya ater. J. Mar. Biol. 2016, e2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caza, F.; Betoulle, S.; Auffret, M.; Brousseau, P.; Fournier, M.; St-Pierre, Y. Comparative analysis of hemocyte properties from Mytilus edulis desolationis and Aulacomya ater in the Kerguelen Islands. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 110, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebouvier, M.; Laparie, M.; Hulle, M.; Marais, A.; Cozic, Y.; Lalouette, L.; et al. The significance of the sub-Antarctic Kerguelen Islands for the assessment of the vulnerability of native communities to climate change, alien insect invasions and plant viruses. Biol. Invasions 2011, 13, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, M.E.; Hofmann, G.E. Heat shock proteins, molecular chaperones and their stress response: Evolutionary and ecological physiology. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1999, 61, 243–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, M. Emergency services: A bird’s eye perspective on the many different functions of stress proteins. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2004, 5, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, M.J.; Girvetz, E.; Mulder, E.P. Induction of marine mollusc stress proteins by chemical or physical stress. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bodin, N.; Burgeot, T.; Stanisiere, J.Y.; Bocquené, G.; Menard, D.; Minier, C.; et al. Seasonal variations of a battery of biomarkers and physiological indices for the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis transplanted into the northwest Mediterranean Sea. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C: Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2004, 138, 411–427. [Google Scholar]
- Hamer, B.; Hamer, D.P.; Müller, W.E.; Batel, R. Stress-70 proteins in marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis as biomarkers of environmental pollution: A field study. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.S.; Peck, L.S. HSP70 heat shock proteins and environmental stress in Antarctic marine organisms: A minireview. Mar. Genomics 2009, 2, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miovi, V.; Bulog, A.; Kui, N.; Jakovac, H.; Radoševi-Staši, B. Metallothioneins and heat shock proteins 70 in marine mussels as sensors of environmental pollution in Northern Adriatic Sea. Env. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 28, 439–447. [Google Scholar]
- Clerico, E.M.; Tilitsky, J.M.; Meng, W.; Gierasch, L.M. How hsp70 molecular machines interact with their substrates to mediate diverse physiological functions. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippmann, F.; Taylor, W.R.; Rothbard, J.B.; Green, N.M. A hypothetical model for the peptide binding domain of hsp70 based on the peptide binding domain of HLA. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, K.L.; Shorter, J. Engineering and evolution of molecular chaperones and protein disaggregases with enhanced activity. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2016, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
©Copyright F. Caza et al., 2016 Licensee PAGEPress, Italy. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 License (CC BYNC 4.0).