Ameliorative Effect of Gallic Acid on Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rat
Abstract
:Introduction
Materials and Methods
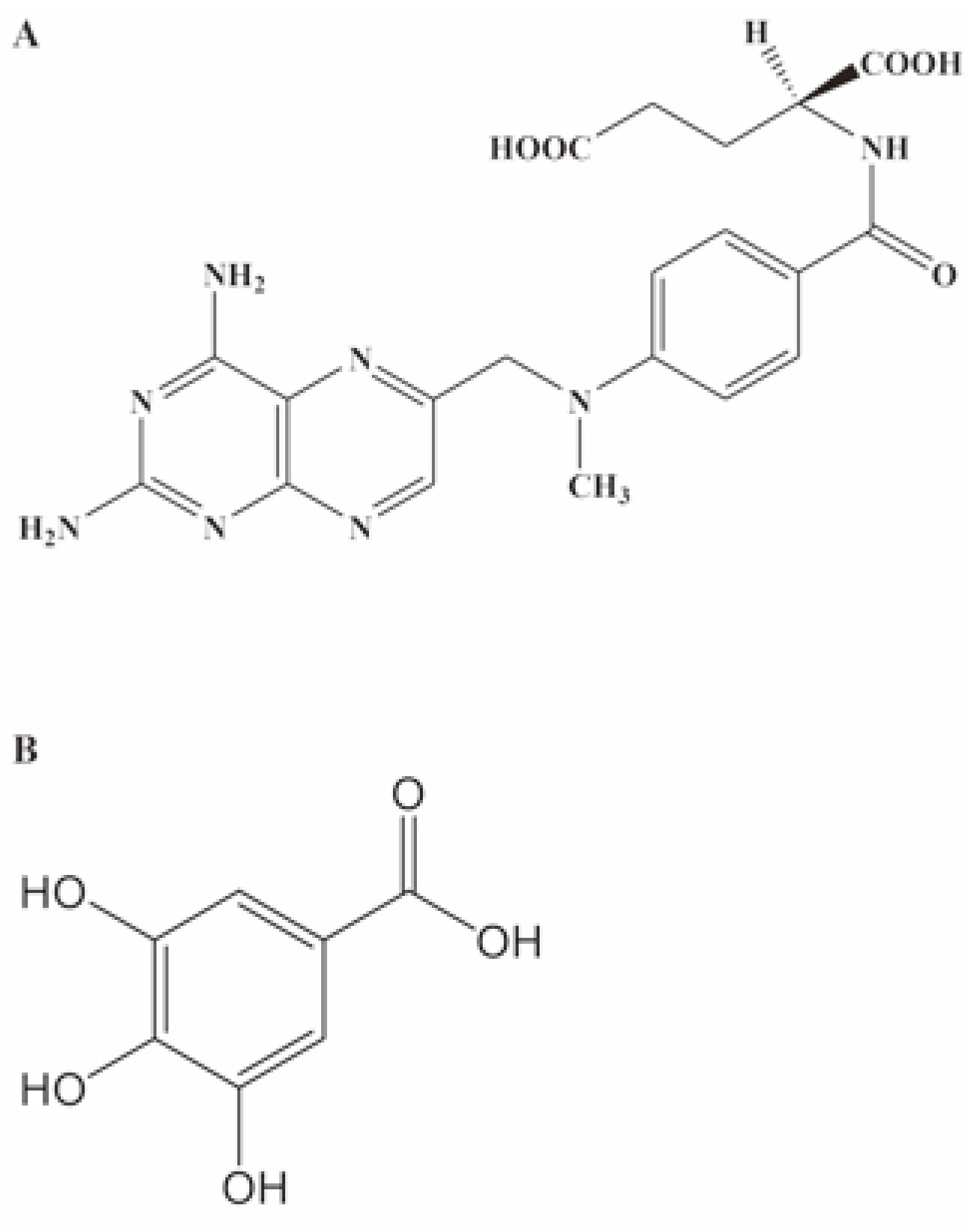
Drug, chemicals and reagents
Animals
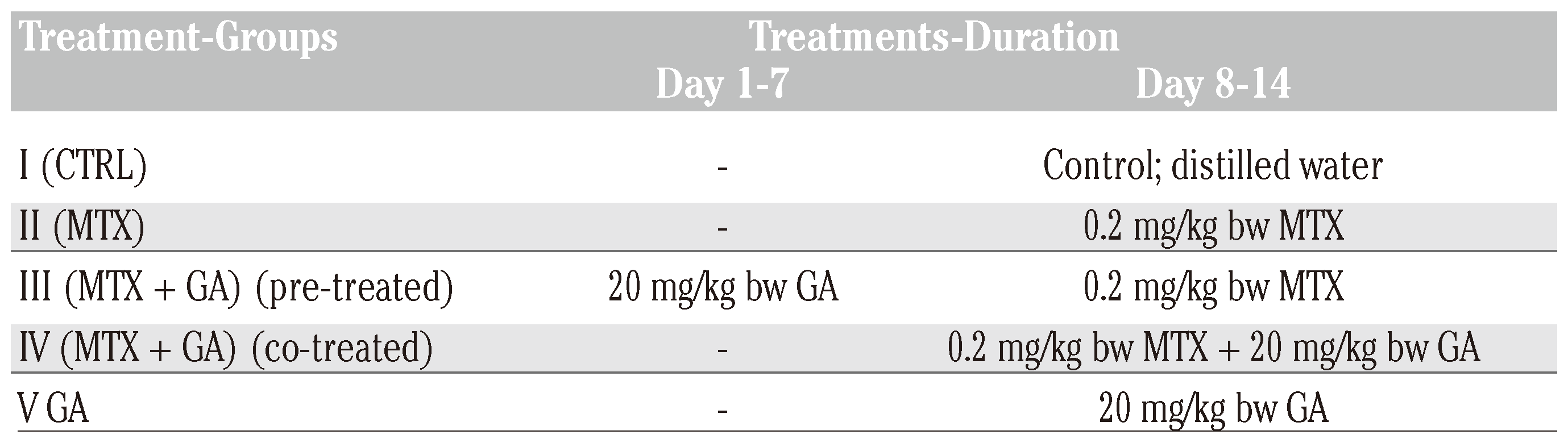
Experimental design
Plasma and tissue preparation
Biochemical analysis
Total protein
Biomarkers of renal function
Biomarkers of hepatic function
Biomarkers of oxidative stress
Statistical analysis
Results
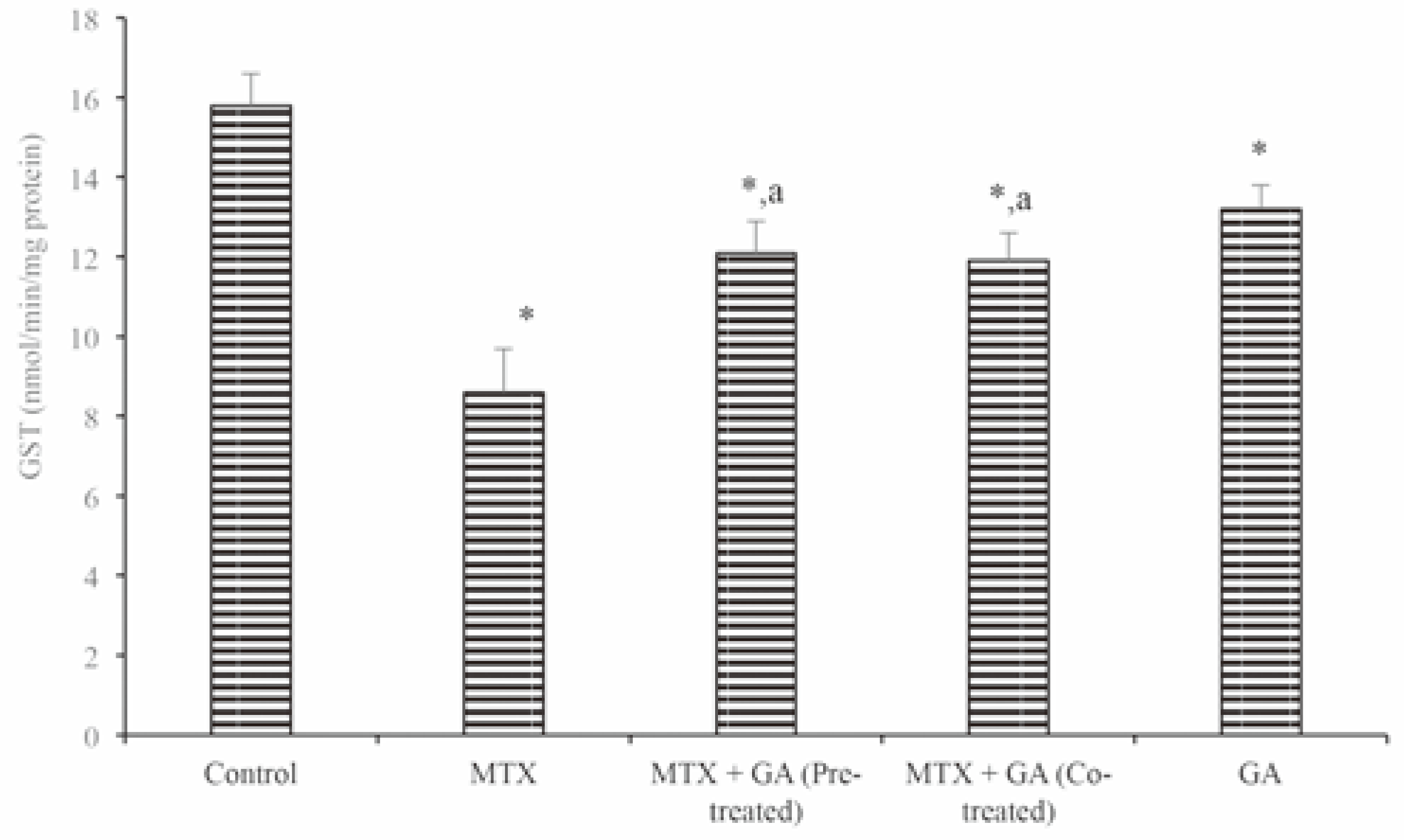
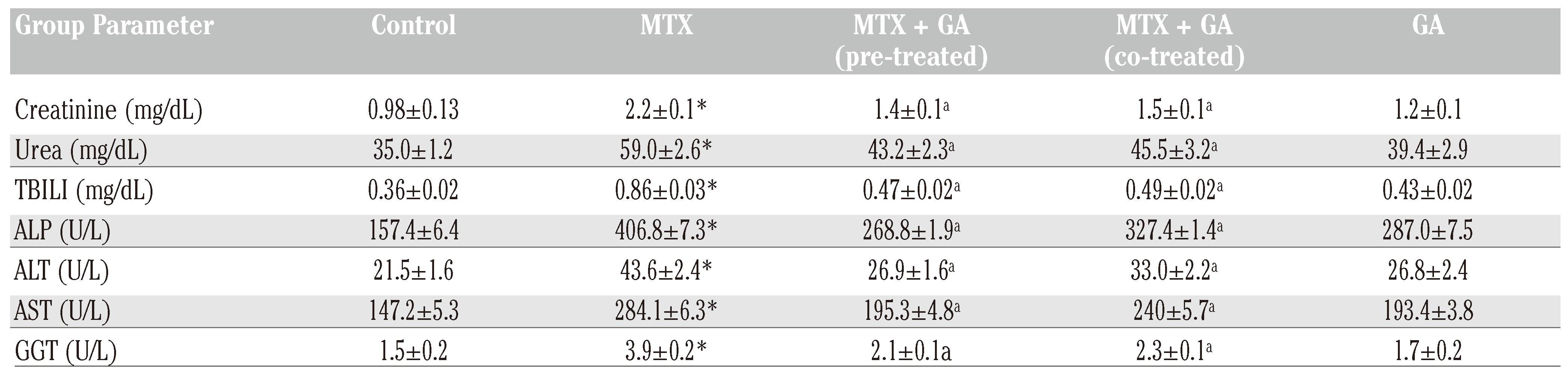
Protective effects of gallic acid on MTX-induced changes in markers of hepatic and renal toxicity
Discussion and Conclusions
Research highlights
- -
- Chemotherapy-associated oxidative stress is a relevant side effect of most anticancer agents.
- -
- Methotrexate (MTX) acts as an antimetabo- lite as its anticancer mechanism.
- -
- Gallic acid is a plant derived antioxidant.
- -
- Hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress was observed following exposure to methotrexate.
- -
- Administration of gallic acid as a pre-treat- ment or co-administered with MTX amelio- rated MTX induced toxicity in rats.
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sirotnak, F.M.; Donsbach, R.C. The intracellu- lar concentration dependence of antifolate inhibition of DNA synthesis in L1210 leukemia cells. Cancer Res 1974, 34, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonadonna, G.; Brusamolino, E.; Valagussa, P.; Rossi, A.; Brugnatelli, L.; Brambilla, C.; et al. Combination chemotherapy as an adju- vant treatment in operable breast cancer. N Engl J Med 1976, 294, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.C.; Woollard, K.J.; Griffiths, H.R. The anti-infammatory actions of methotrexate are critically dependent upon the produc- tion of reactive oxygen species. Br J Pharmacol 2003, 138, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galivan, J.; Nimec, Z.; Balinska, M. Regulation of methotrexate polyglutamate accumulation in vitro: effects of cellular folate content. Biochem Pharmacol 1983, 32, 3344–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, S. Imparment of methotrexate (MTX)-polyglutamate formation of MTX- resistant K562 cell lines. Jpn J Cancer Res 1988, 79, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conklin, K.A. Chemotherapy-associated oxidative stress: impact on chemothera- peutic effectiveness. Integr Cancer Ther 2004, 3, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Hsu, P.C.; Hung, Y.C.; Liao, Y.F.; Liu, C.C.; Hour, C.T.; et al. Ornithine decarboxy- lase prevents methotrexate-induced apop- tosis by reducing intracellular reactive oxygen species production. Apoptosis 2005, 10, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, A.; Kaynar, L.; Kocyigit, I.; Hacioglu, S.K.; Saraymen, R.; Ozturk, A.; Sari, I.; et al. Role of grape seed extract on methotrexate induced oxidative stress in rat liver. Am J Chin Med 2008, 36, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saigal, S.; Singh, R.K.; Poddar, B. Acute methotrexate toxicity presenting as multi- organ failure and acute pneumonitis: a rare case report. Indian J Crit Care Med 2012, 16, 225–227. [Google Scholar]
- Yea, Z.; Zhanga, J.; Townsendb, D.M.; Tew, K.D. Oxidative stress, redox regulation and dis- eases of cellular differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015, 1850, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, L.F. Theoretical elucida- tion on structure-antioxidant activity rela- tionships for indolinonic hydroxylamines. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2002, 12, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L. Naturally occurring food tox- icants: phenolic substances of plant origin common in foods. Adv Food Res 1981, 27, 149–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahed, A.; Bouhlel, I.; Skandrani, I.; Valenti, K.; Kadri, M.; Guiraud, P.; et al. Study of antimutagenic and antioxidant activi- ties of gallic acid and 1,2,3,4,6-pentagal- loylglucose from Pistacia lentiscus. Confirmation by microarray expression profiling. Chem Biol Interact 2007, 165, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olayinka, E.T.; Ore, A.; Ola, O.S.; Adeyemo, O.A. Ameliorative effect of gallic acid on cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative injury and hepatic dysfunction in rats. Med Sci 2015, 3, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council. Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals, 8th ed.; National Research; The National Academies Press;: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Punithavathi, V.R.; Prince, P.S.; Kumar, R.; Selvakumari, J. Antihyperglycaemic, antilipid peroxidative and antioxidant effects of gallic acid on streptozotocin induced diabetic Wistar rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2011, 650, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornall, A.C.; Bardwawill, C.J.; David, M.M. Determination of serum protein by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem 1949, 177, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, E.R. Oxidative hemolysis, or what made the red cell break? N Engl J Med 1972, 286, 156–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietz, N.W. Clinical guide to laboratory tests, 3rd ed.; W.B. Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tietz, N.W.; Pruden, E.L.; Siggaard-Andersen, O. Liver function. In Tietz textbook of clinical chem- istry; Burtis, A.C., Ashwood, E.R., Eds.; WB Saunders: London, UK, 1994; pp. 1354–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Reltman, S.; Frankel, S.A. Colorimetric method for the determination of serum ALT and AST. Am J Clin Pathol 1957, 28, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szasz, G. A kinetic photometric method for serum γ-glutamyl transpeptidase. Clin Chem 1969, 15, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jollow, D.J.; Mitchell, J.R.; Zampaghone, N.; Gillete, J.R. Bromobenzene induced liver necrosis, protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology 1974, 11, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagota, S.K.; Dani, H.M. A new colorimetric technique for the estimation of vitamin C using Folin phenol reagent. Anal Biochem 1982, 127, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habig, W.A.; Pabst, M.J.; Jacoby, W.B. Glutathione transferases. The first enzy- matic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, H.P.; Fridovich, I. The role of superox- ide anion in the autoxidation of epineph- rine and a simple assay for superoxide dis- mutase. J Biol Chem 1972, 247, 3170–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, A.K. Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal Biochem 1972, 47, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, R.; Kale, R.K. Effect of calmodulin antagonist on radiation induced lipid per- oxidation in microsomes. Int J Radiat Biol 1990, 58, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousson, E.; Zaki, Z.T.; Abu-Shaeir, W.A.; Hassan, H. Methotrexate-induced hepatic and renal toxicity: role of L-carnitine in treatment. Biomed Biotechnol 2014, 2, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Johovic, N.; Cevik, H.; Sehirli, O.A.; Yegen, B.Ç.; Şener, G. Melatonin prevents methotrexate induced hepatorenal oxidative injury in rats. J Pineal Res 2003, 34, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressier, B.; Lebegue, S.; Brunet, C.; Luyckx, M.; Dine, T.; Cazin, M.; et al. Pro-oxidant properties of methotrexate: evaluation and prevention by an anti-oxidant drug. Pharmazie 1994, 49, 679–681. [Google Scholar]
- Priscilla, D.H.; Prince, P.S. Cardioprotective effect of gallic acid on cardiac troponin-T, cardiac marker enzymes, lipid peroxida- tion products and antioxidants in experi- mentally induced myocardial infarction in Wistar rats. Chem Biol Interact 2009, 179, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Velmurugan, B.; Rajamanickam, S.; Agarwal, R.; Agarwal, C. Gallic acid, an active constituent of grape seed extract, exhibits anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic and anti- tumorigenic effects against prostate carci- noma xenograft growth in nude mice. Pharm Res 2009, 26, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.K.; Sabina, E.P.; Ramya, S.R.; Preety, P.; Patel, S.; Mandal, N.; et al. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of gallic acid in paracetamol-induced liver damage in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol 2010, 62, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, G.S.; Wakasi, M.E.; Egoro, E. Creatinine and urea levels as critical markers in end-stage renal failure. Res Rev J Med Health Sci 2014, 3, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Uz, E.; Oktem, F.; Yilmaz, H.R.; Uzar, E.; Ozgüner, F. The activities of purine catabolizing enzymes and the level of nitric oxide in rat kidneys subjected to methotrexate: protec- tive effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester. Mol Cell Biochem 2005, 277, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardi, N.; Parlakpinar, H.; Cetin, A.; Erdogan, A.; Ozturk, C. Protective effect of β-carotene on methotrexate-induced oxidative liver damage. Toxicol Pathol 2010, 38, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boone, L.; Meyer, D.; Cusick, P.; Ennulat, D.; Bolliger, A.P.; Everds, N.; et al. Selection and interpretation of clinical pathology indica- tors of hepatic injury in preclinical stud- ies. Vet Clin Pathol 2005, 34, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaiah, S.K. A toxicologist guide to the diagnostic interpretation of hepatic bio- chemical parameters. Food Chem Toxicol 2007, 45, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasagayam, T.P.A.; Tilak, J.C.; Boloor, K.K.; Sane, K.S.; Ghaskadbi, S.S.; Lele, R.D. Free rad- icals and antioxidants in human health: current status and future prospects. JAPI 2004, 52, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kojo, S. Vitamin C: basic metabolism and its function as an index of oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem 2004, 11, 1041–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, R.; Zhang, J.; Johansson, K. Microsomal glutathione transferase: Mechanism and functional roles. Drug Metab Rev 2011, 43, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, R.H.; Barakat, H. The protective effect of gallic acid and caffeine against CCl4-induced oxidative hepatotoxicity and mitochondrial DNA depletion in male albi- no rats. Egypt J Biochem Mol Biol 2010, 28, 543–562. [Google Scholar]
- Masella, R.; di Benedetto, R.; Var, R.; Filesi, C.; Giovannini, C. Novel mechanisms of natu- ral antioxidant compounds in biological systems: involvement of glutathione and glutathionerelated enzymes. J Nutr Biochem 2005, 16, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© Copyright E.T. Olayinka et al., 2016 Licensee PAGEPress, Italy. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 License (CC BY-NC 4.0).
Share and Cite
Olayinka, E.; Ore, A.; Adeyemo, O.; Ola, O. Ameliorative Effect of Gallic Acid on Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rat. J. Xenobiot. 2016, 6, 6092. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2016.6092
Olayinka E, Ore A, Adeyemo O, Ola O. Ameliorative Effect of Gallic Acid on Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rat. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2016; 6(1):6092. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2016.6092
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlayinka, Ebenezer, Ayokanmi Ore, Oluwatobi Adeyemo, and Olaniyi Ola. 2016. "Ameliorative Effect of Gallic Acid on Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rat" Journal of Xenobiotics 6, no. 1: 6092. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2016.6092
APA StyleOlayinka, E., Ore, A., Adeyemo, O., & Ola, O. (2016). Ameliorative Effect of Gallic Acid on Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rat. Journal of Xenobiotics, 6(1), 6092. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2016.6092





