Nature of Chiral Drugs and Their Occurrence in Environment
Abstract
:Introduction
Global chiral drug market
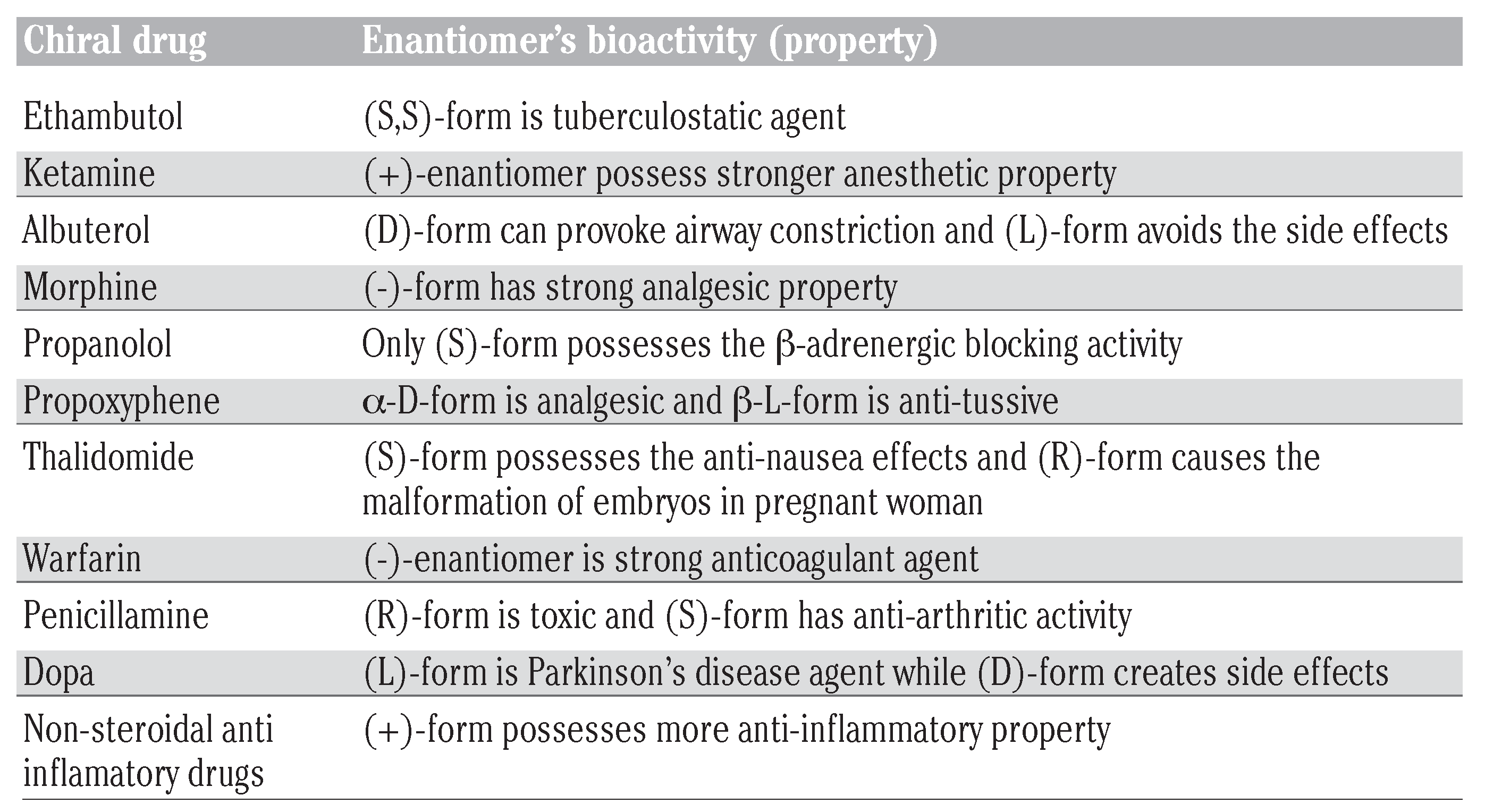
Important chiral drug enantiomers and their bioactivities
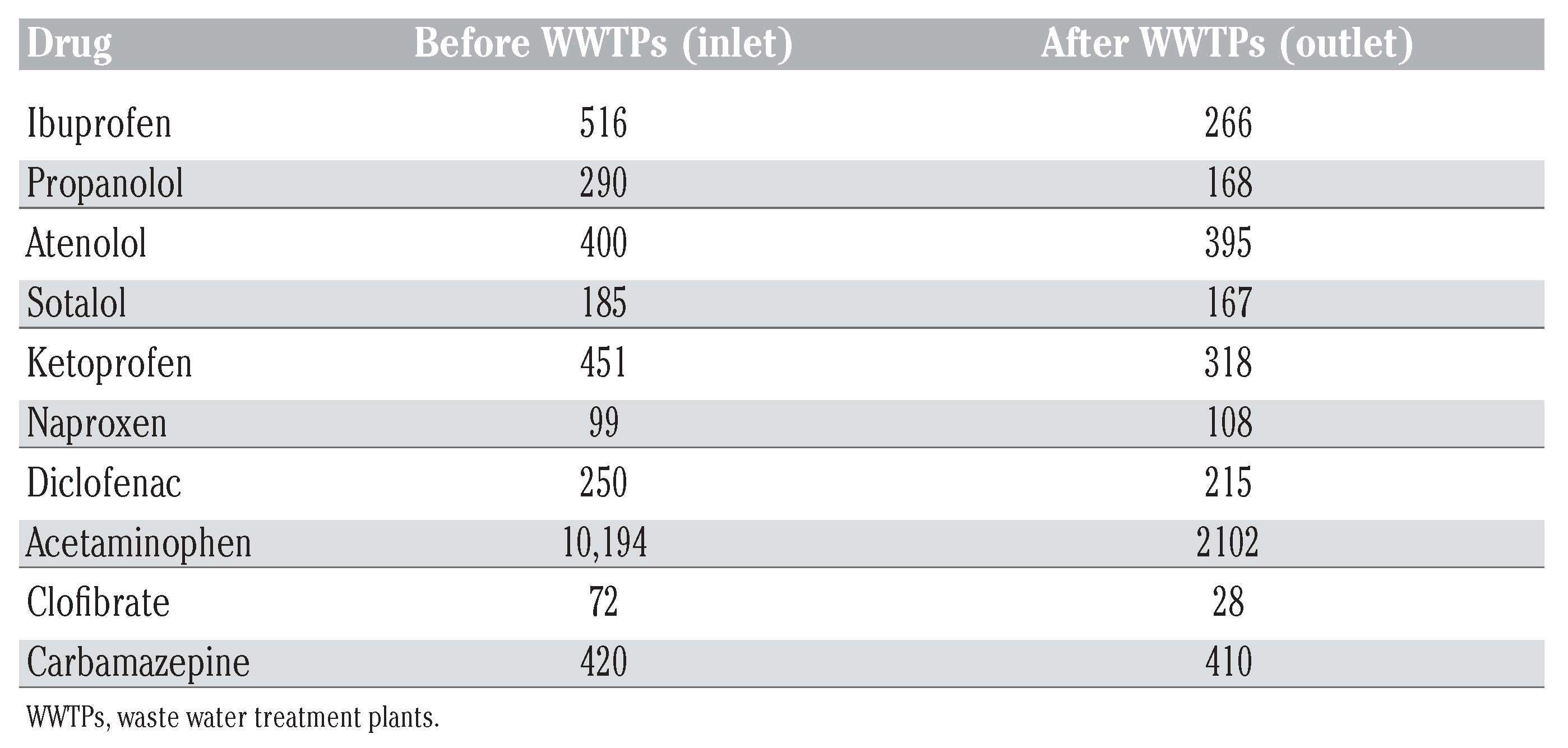
Chiral drugs in environment
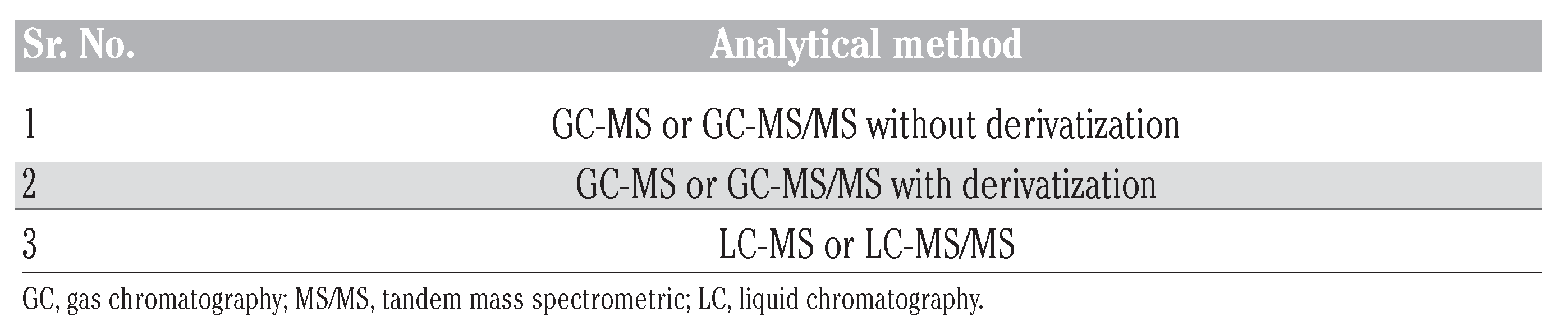
Chiral drug analysis
Futuristic aspects of chiral drugs
Conclusions
Research highlights
- -
- Nature and bioactivities of chiral drugs has been described along with global market and strategies.
- -
- Occurrence of chiral drugs in environmental matrices has been reviewed.
- -
- Analysis of chiral compounds in environmental samples has been described with their futuristic aspects.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drayer, D.E. The early history of stereochemistry. In Drug stereochemistry. Analytical methods and pharmacology, 2nd ed.; Wainer IW, Ed.; Marcel Dekker Publ.: New York, NY, 1993; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Gupta, V.K.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Chirality: a challenge to the environmental scientists. Curr Sci 2003, 84, 152–6. [Google Scholar]
- Novotony, M.; Soini, H.; Stefansson, M. Chiral separation through capillary electromigration methods. Anal Chem 1994, 66, 646A–55A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, T.J. Chiral media for capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem 1994, 66, 632A–40A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Gupta, V.K.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Singh, P.; Sharma, B. Role of racemization in optically active drugs development. Chirality 2007, 19, 453–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- [No authors listed]. FDA’s policy statement for the development of new stereoisomeric drugs. Chirality 1992, 4, 338–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Ali, I. Chiral separation by liquid chromatography and related technologies; Marcel Dekker Publ.: New York, NY, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sahajwalla, C. Regulatory considerations in drug development of stereoisomers. In Chirality in drug design and development; Reddy, I.K., Mehvar, R., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Publ.: New York, NY, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, G.T. Chiral switches. Lancet 2000, 355, 1085–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francotte, E.; Lindner, W. Chirality in drug research; Wiley VCH: Weinheim, 2006; Vol. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, M.; Lawrence, J.R.; Neu, T.R. Selective degradation of ibuprofen and clofibric acid in two model river biofilm systems. Water Res 2001, 35, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Singh, P.; Sharma, B. Chiral analyses of ibuprofen residues in water and sediment. Anal Lett 2009, 42, 1747–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku¨mmerer, K.; Al-Ahmadi, A.; Bertram, B.; Wiebler, M. Biodegradability of antineoplastic compounds in screening tests: Influence of glucosidation and of stereochemistry. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 767–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, H.R.; Poigner, T.; Muller, M.D. Occurrence and environmental behavior of chiral pharmaceutical drug ibuprofen in surface waters and in wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 1999, 33, 2529–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, W.M.; Trautwein, C.; Leder, C.; Kümmerer, K. Aquatic photochemistry, abiotic and aerobic biodegradability of thalidomide: identification of stable transformation products by LC-UV-MS(n). Sci Total Environ 2013, 463-464, 140–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Environment Protection Agency (EPA). Literature review of contaminants in livestock and poultry manure and implications for water quality. Office of Water (4304T); EPA 820-R-13-002; July 2013. Available online: http://water.epa.gov/scitech/cec/upload/Literature-Review-of-ContaminantsinLivestock-and-Poultry-Manure-and-Implications-for-Water-Quality.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2014).
- Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service/United States Department of Agriculture (APHIS/USDA). Highlights of health and management practices on breeder chicken farms in the United States, 2010. Info Sheet; November 2011. Available online: http://www.aphis.usda.gov/animal_health/nahms/poultry/downloads/poultry10/Poultry10_is_Breeder_highlights.pdf.
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Baker, D.R. Enantiomeric profiling of chiral drugs in wastewater and receiving waters. Environ Sci Technol 2012, 46, 1681–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carballa, M.; Omil, F.; Lema, J.M.; Llompart, M.; García-Jares, C.; Rodríguez, I.; et al. Behavior of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and hormones in a sewage treatment plant. Water Res 2004, 38, 2918–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling-Sørensen, B.; Nors Nielsen, S.; Lanzky, P.F.; Ingerslev, F.; Holten Lutzhoft, H.C.; Jorgensen, S.E. Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment-A review. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 357–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BCC Research. Global markets for chiral technology Focus on emerging markets. Report: BIO103A; April 2012. Available online: http://www.bccresearch.com/market-research/biotechnology/chiral-products-technology-global-markets-bio012f.html.
- McConalthy, J.; Owens, M.J. Sterochemistry in drug action. J Clin Psychiatr Primary Care Compan 2003, 5, 70–3. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.H.; AYH, Lu. Role of pharmacokinetics and metabolism in drug discovery and development. Pharmacol Rev 1997, 49, 40349. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Haynie, D.T. Chiral drug separation. In: Lee S, ed. Encyclopedia of chemical processing; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, 2006; Vol. 1, pp. 449–58. [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman, W.J.M.; Laane, W.P.J. Enantiomeric enrichment of chiral pesticides in the environment. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 2002, 173, 85–116. [Google Scholar]
- Fent, K.; Weston, A.A.; Caminada, D. Ecotoxicology of human pharmaceuticals. Aquatic Toxicol 2006, 76, 122–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, C.; Johansson, A.K.; Alvan, G.; Bergman, K.; Kuhler, T. Are pharmaceuticals potent environmental pollutants? Part I: Environmental risk assessments of selected active pharmaceutical ingredients. Sci Total Environ 2006, 364, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. The removal of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs during wastewater treatment and its impact on the quality of receiving waters. Water Res 2009, 43, 36380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Nuijs, L.N.; Pecceu, B.; Theunis, L.; Dubois, N.; Charlier, C.; Jorens, P.G.; et al. Erratum to “Cocaine and metabolites in waste and surface water across Belgium”. [Environmental Pollution 157(2009), 123–129], Environ Poll 2009, 157, 1968–69. [Google Scholar]
- Castiglioni, S.; Bagnati, R.; Calamari, D.; Fanelli, R.; Zuccato, E. A multiresidue analytical method using solid-phase extraction and high-pressure liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry to measure pharmaceuticals of different therapeutic classes in urban wastewaters. J Chromatogr A 2005, 1092, 206–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D.; Ternes, T.A. Water analysis: emerging contaminants and current issues. Anal Chem 2005, 77, 3807–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, H.; Thomsen, M. Comparative analysis of pharmaceuticals versus industrial chemicals acute aquatic toxicity classification according to the United Nations classification system for chemicals. Assessment of the (Q)SAR predictability of pharmaceuticals acute aquatic toxicity and their predominant acute toxic modeof-action. Toxicol Lett 2009, 187, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Jain, C.K. Groundwater contamination and health hazards by some of the most commonly used pesticides. Curr Sci 1998, 75, 1011. [Google Scholar]
- Kolpin, D.W.; Kalkhoff, S.J.; Goolsby, D.A.; Sneck-Fahrer, D.A.; Thurman, E.M. Occurrence of Selected Herbicides and Herbicide Degradation Products in Iowa's Ground Water. Ground Water 1997, 35, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutta, M.; Rybar, I.; Chalanyova, M. Liquid chromatographic method development for determination of fungicide epoxiconazole enantiomers by achiral and chiral column switching technique in water and soil. J Chromatogr A 2002, 959, 143–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.D.; Amato, S.; Falconer, R.L. Emission of chiral organochlorine pesticides from agricultural soils in the Cornbelt Region of the U.S. Environ Sci Technol 2001, 35, 459296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, W.; Bartha, R.; Stern, G.; Tomy, G. Enantioselective determination of two persistent chlorobornane congeners in sediment from a toxaphene-treated yukon lake. Environ Toxicol Chem 1999, 18, 277581. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.S.; Garrison, A.W.; Foreman, W.T. enantiomeric composition of chiral polychlorinated biphenyl atropisomers in aquatic bed sediment. Environ Sci Technol 2001, 35, 33–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylypiw, H.M.; Naughton, E.; Hankin, L. DDT persists in soil: uptake by squash plants. J Dairy Food Environ Sanit 1991, 11, 200–1. [Google Scholar]
- Mattina, M.J.I.M.; Iannucci-Berger, W.; Dykes, L. Chlordane uptake and its translocation in food crops. J Agric Food Chem 2000, 48, 1909–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando, M.D.; Mezcua, M.; Fernandez-Alba, A.R.; Barcelo, D. Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 2006, 69, 334–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lishman, L.; Smyth, S.A.; Sarafin, K.; Kleywegt, S.; Toito, J.; Peart, T. , et al. Occurrence and reductions of pharmaceuticals and personal care products and estrogens by municipal wastewater treatment plants in Ontario, Canada. Sci Total Environ 2006, 367, 544–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummerer, K. (Ed.) Pharmaceuticals in the environment, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, New-York, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gentili, A. Determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in environmental samples by chromatographic and electrophoretic techniques. Anal Bioanal Chem 2007, 387, 1185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miège, C.; Choubert, J.M.; Ribeiro, L.; Eusène, M.; Coquery, M. Fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in wastewater treatment plants Conception of a database and first results. Environ Pollut 2009, 157, 1721–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler, D.; Römbke, J.; Meller, M.; Ternes, T.A. Environmental fate of pharmaceuticals in water/sediment systems. Environ Sci Technol 2005, 39, 5209–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajeunesse, A.; Gagnon, C.; Sauvé, S. Determination of antidepressants and their N-desmethyl metabolites in raw sewage and wastewater using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 2008, 80, 5325–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberer, T. Occurrence, fate, and removal of pharmaceutical residues in the aquatic environment: a review of recent research data. Toxicol Lett 2002, 131, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, A.; Lofrano, G. Detection of transformation products of emerging contaminants (Chapter 2). In Green technologies for wastewater treatment Energy recovery and emerging compounds removal; Lofrano, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, 2012; pp. 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Pharmaceuticals in drinking water. Geneva: WHO; 2012. Available online: https://extranet.who.int/iris/restricted/bitstream/10665/44630/1/9789241502085_eng.pdf.
- Albero, B.; Pérez, R.A.; Sánchez-Brunete, C.; Tadeo, J.L. Occurrence and analysis of parabens in municipal sewage sludge from wastewater treatment plants in Madrid (Spain). J Hazard Mat 2012, 239-240, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatta, D.; Nikolaou, A.; Achilleos, A.; Meric, S. Analytical methods for tracing pharmaceutical residues in water and wastewater. Trends Anal Chem 2007, 26, 515–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, S.L.; Sudhir, P.; Wong, C.S. Stereoisomer analysis of wastewaterderived β-blockers, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and salbutamol by highperformance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 2007, 1170, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matamoros, V.; Hijosa, M.; Bayona, J.M. Assessment of the pharmaceutical active compounds removal in wastewater treatment systems at enantiomeric level. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 200–05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhnerfuss, H.; Shah, M.R. Enantioselective chromatography a powerful tool for the discrimination of biotic and abiotic transformation processes of chiral environmental pollutants. J Chromatogr A 2009, 1216, 481–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolai, L.N.; McClure, E.L.; MacLeod, S.L.; Wong, C.S. Stereoisomer quantification of the -blocker drugs atenolol, metoprolol, and propranolol in wastewaters by chiral high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 2006, 1131, 103–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fono, L.J.; Sedlak, D.L. Use of the chiral pharmaceutical propranolol to identify sewage discharges into surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 2005, 39, 9244–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stan, H.J.; Linkerhägner, M. Identifizierung von 2-(4-Chlorphenoxy)-2-methylpropionsäure im Grundwasser mittels KapillarGaschromatographie mit Atomemissionsdetektion und Massenspe-ktrometrie [Identification of 2-(4chlorophenoxy)-2-methyl-propionic acid in ground water using capillary-gas chromatography with atomic emission detection and mass spectrometry]. Vom Wasser 1992, 79, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ternes, T.A.; Hirsch, R. occurrence and behavior of x-ray contrast media in sewage facilities and the aquatic environment. Environm Sci Technol 2000, 34, 2741–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A. Occurrence of drugs in German sewage treatment plants and rivers. Water Res 1998, 32, 3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hühnerfuss, H.; Selke, S.; Kallenborn, R.; Kuhlmann, J.; Weigel, S. Enzymatic transformation of chiral pharmaceuticals in the environment as revealed by enantioselective chromatography. Organohalogen Compounds 2006, 68, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Gagnon, C.; Lajeunesse, A. Low removal of acidic and hydrophilic pharmaceutical products by various types of municipal wastewater treatment plants. J Xenobiot 2012, 2, 13–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, M.; Hernando, M.D.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Liquid chromatography– tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of pharmaceutical residues in environmental samples: a review. J Chromatogr A 2005, 1067, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Gupta, V.K. Nano chromatography and capillary electrophoresis: pharmaceutical and environmental analyses. Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Albero, B.; Sánchez-Brunete, C.; Miguel, E.; Pérez, R.A.; Tadeo, J.L. Analysis of naturaloccurring and synthetic sexual hormones in sludge-amended soils by matrix solidphase dispersion and isotope dilution gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 2013, 1283, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Meric, S.; Nikolaou, A. Pharmaceutical residues in environmental waters and wastewater: current state of knowledge and future research. Anal Bioanal Chem 2011, 399, 251–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, B.; Montgomery-Brown, J.; Naumann, A.; Reinhard, M. Occurrence and fate of pharmaceuticals and alkyl phenol ethoxylate metabolites in an effluent-dominated river and wetland. Environ Toxicol Chem 2004, 23, 2074–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, Z.; Schmutzer, G.; Tusa, F.; Calin, R.; Alder, A.C. An overview of pharmaceuticals and personal care products contamination along the River Somes watershed, Romania. J Environ Monit 2007, 9, 986–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier, C.; Singer, H.P.; Oellers, S.; Müller, S.R. Occurrence and fate of carbamazepine, clofibric acid, diclofenac, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, and naproxen in surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 2003, 37, 1061–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauxe-Wuersch, A.; De Alencastro, L.F.; Grandjean, D.; Tarradellas, J. Occurrence of several acidic drugs in sewage treatment plants in Switzerland and risk assessment. Water Res 2005, 39, 1761–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler, D.; Ternes, T.A. Determination of acidic pharmaceuticals, antibiotics, and ivermection in river sediment using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 2003, 1021, 133–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrouzo, M.; Reverte, S.; Borrull, F.; Pocurull, E.; Marce, R.M. Pharmaceutical determination in surface and waste waters using high-performance liquid chromatography (electrospray) mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 2007, 30, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorita, S.; Barri, T.; Mathiasson, L. A novel hollow-fibre microporous membrane liquid–liquid extraction for determination of free 4-isobutylacetophenone concentration at ultra trace level in environmental aqueous samples. J Chromatogr A 2007, 1157, 30–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basheer, C.; Chong, H.G.; Hii, T.M.; Lee, H.K. Application of porous membrane-protected micro-solid-phase extraction combined with HPLC for the analysis of acidic drugs in waste water. Anal Chem 2007, 79, 684550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebot, C.; Gibb, S.W.; Boyd, K.G. Quantification of human pharmaceuticals in water samples by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 2007, 598, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bound, J.P.; Voulvoulis, N. Predicted and measured concentrations for selected pharmaceuticals in UK rivers: Implications for risk assessment. Water Res 2006, 40, 2885–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Peldszus, S.; Huck, P.M. Optimizing gas chromatographic mass spectrometric analysis of selected pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting substances in water using factorial experimental design. J Chromatogr A 2007, 1148, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, M.; Lawrence, J.R.; Neu, T.R. Selective degradation of ibuprofen and clofibric acid in two model river biofilm systems. Water Res 2001, 35, 3197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Darisaw, S.; Ehie, O.; Wang, G. Simutaneous quantification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and pharmaceuiticals and personal care products (PPCBs) in Mississippi River water, in New Orleans, Louisiana, USA. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1057–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Wainer, I.W. The impact of stereochemistry on drugs development and use. Wiley: New York, NY, 1997; Vol. 142. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Gaitonde, V.D.; Singh, P.; Rawat, M.S.M.; Sharma, B. Chiral separations of imidazole antifungal drugs on AmyCoat RP column in HPLC. Chromatographia 2009, 70, 223–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Tyagi, S.; Singh, R.; Singh, P. Monitoring of organochlorine pesticides in fresh water samples by gas chromatography and bioremediation approaches. Natl Acad Sci Lett 2012, 35, 401–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, D.; Henderson, D.J. Chirality: a blueprint for the future. Br J Anesth 2002, 88, 563–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© Copyright B. Sharma, 2014 Licensee PAGEPress, Italy. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 3.0 License (CC BYNC 3.0).
Share and Cite
Sharma, B. Nature of Chiral Drugs and Their Occurrence in Environment. J. Xenobiot. 2014, 4, 2272. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2014.2272
Sharma B. Nature of Chiral Drugs and Their Occurrence in Environment. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2014; 4(1):2272. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2014.2272
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Bhavtosh. 2014. "Nature of Chiral Drugs and Their Occurrence in Environment" Journal of Xenobiotics 4, no. 1: 2272. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2014.2272
APA StyleSharma, B. (2014). Nature of Chiral Drugs and Their Occurrence in Environment. Journal of Xenobiotics, 4(1), 2272. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2014.2272




