Introduction
Anthropogenic pressures lead to profound deleterious effects on coastal aquatic ecosys- tems. Many chemicals released in the environment generate toxicity in aquatic organisms. In response to these environmental disturbances, there is a growing concern about the consequences of environmental contaminants on the immune system of aquatic species [1,2]. Various environmental surveys have been set up to monitor these changes. They allow medium and long-term monitoring of coastal ecosystems exposed to chemical contamination through the study of selected sentinel species. As sessile filter-feeder, bivalve mollusks are directly exposed to environmental contaminants. They bioaccumulate most environmental pollutants, including heavy metals [3,4,5].Therefore, they reflect the surrounding contamination by integrating the environmental exposure. Immune defense in bivalves is coordinated primarily by circulating hemocytes. Those multifunctional cells are able to recognize foreign particles and respond through phagocytic ingestion [6]. In mussels, hemocytes circulating in the hemolymph rep- resent the main component of their immune system [7,8]. Hence, the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis, is considered as interesting sentinel specie in immunotoxicological studies.
The use of hemocytes and the monitoring of their phagocytic activity may represent an ideal biological endpoint [9]. The present study aims to validate the use of phagocytic responses in Mytilus edulis as biomarker of heavy metals contamination. The purpose of this present study is to establish dose–response curves of viability and phagocytic activity on marine bivalve Mytilus edulis exposed to various heavy metals [cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), silver (Ag)].
Materials and Methods
Animals
Mytilus edulis were collected in the Baie de Plaisance from Îles de la Madeleine (47°29’N, 61°87’W). They are located in the center of Gulf of St Lawrence, a place exempt from industrial activities. Upon arrival to the laboratory, all bivalves were transferred and maintained in aquaria filled with salted artificial marine water (15°C, salinity 31-1 psu) and fed ad libitum.
Hemolymph collection and viability of cells
Hemolymph was collected individually from the posterior adductor muscle using a 3 mL syringe with a 23G gauge needle. Immediately after the hemolymph collection, hemocytes viability was evaluated by flow cytometry using the Guava PCA flow cytometer (Guava Technologies, Hayward, CA, USA) and the Viacount kit (Guava technologies) according to the supplier’s instructions. Briefly, an aliquot of 50 μL of hemolymph was mixed with 200 μL of Viacount and at least 1000 events were recorded. Only individuals whose cell via- bility was higher than 75% were kept.
Heavy metals and exposure proto- col
Heavy metals used in this study were reagent grade: cadmium chloride (CdCl2), lead chloride (PbCl2), mercuric chloride (HgCl2) and silver nitrate (AgNO3) (Sigma, ON, Canada). The concentrations tested were the same for all four metals, ranging from 10–3 to 10–9 mol. Working solutions of each metal were then prepared by serial dilutions in distilled water.
Phagocytosis and cell viability
For each metal, dose-response curves were performed on nine different mussels. Phagocytosis was assessed by determining the ingestion of latex fluorescent beads by flow cytometry according to Brousseau et al. [10] Briefly, 500 μL of hemolymph containing 100,000 cells were mixed with 25 μL of each metal working solution and exposed during 3 h at 15°C under constant agitation. After the incubation, latex fluorescent beads (Yellow- green Fluoresbrite, Polysciences®) were added to each tube at a ratio of 100:1 beads/cell and suspensions were re-incubated for another 18 hours. At the end of the expo- sure period, the cells were layered over a 3% bovine serum albumin gradient in RPMI-1640 medium containing 31 g.l–1 of marine salt and centrifuged at 138 x g for 8 min at 4°C to remove free beads. The cell pellets were then re-suspended in 0.5 mL of 0.5% formaldehyde and 0.2% sodium azide in 31 g.l–1 salt water. The number of engulfed beads was deter- mined using a FACSCalibur (Becton–Dickinson, CA, USA) flow cytometer. Fluorescence emission was read in FL1 (λ=530 nm), with at least 10,000 events in the region of interest.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean standard devia- tion. The results were tested for homogeneity using an analysis of variance (ANOVA). Significant differences between treatments and control were determined using the SigmaStat™ Software version 3.5. (Jandel, Scientific Software, San Rafael, CA, USA). Then, we used the Holm-Sidak method to per- form multiple comparisons versus control group to identify significant differences (P<0.05).
Results
Effects of heavy metals on cell viability
Regarding hemocyte viability, as illustrated in Figure 1, silver nitrate appeared to be more cytotoxic than mercury for this population of cells. We noticed a significant decrease in via- bility at 10–5 M for Ag (Figure 1D) and Hg (Figure 1C). Cadmium (Figure 1A) and lead (Figure 1B) showed similar results on cell viability with a significant decrease at 10–3 M.
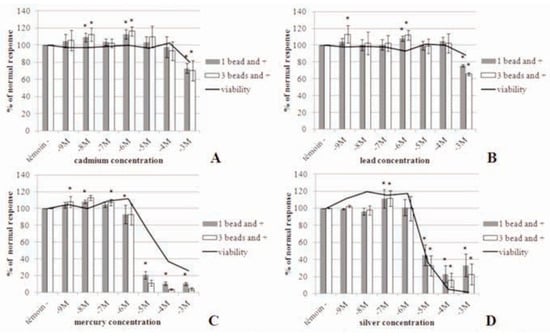
Figure 1.
Phagocytosis and viability of hemocytes from Mytilus edulis exposed at different concentrations ranging from 10–9 M to 10–3 M. Gross values of phagocytosis’s control for 1 bead and more: A) Cd 48.3%; B) Pb 44.0%; C) Hg 41.7%; D) Ag 44.7% *P≤0.05.
Effects of heavy metals on phago- cytosis
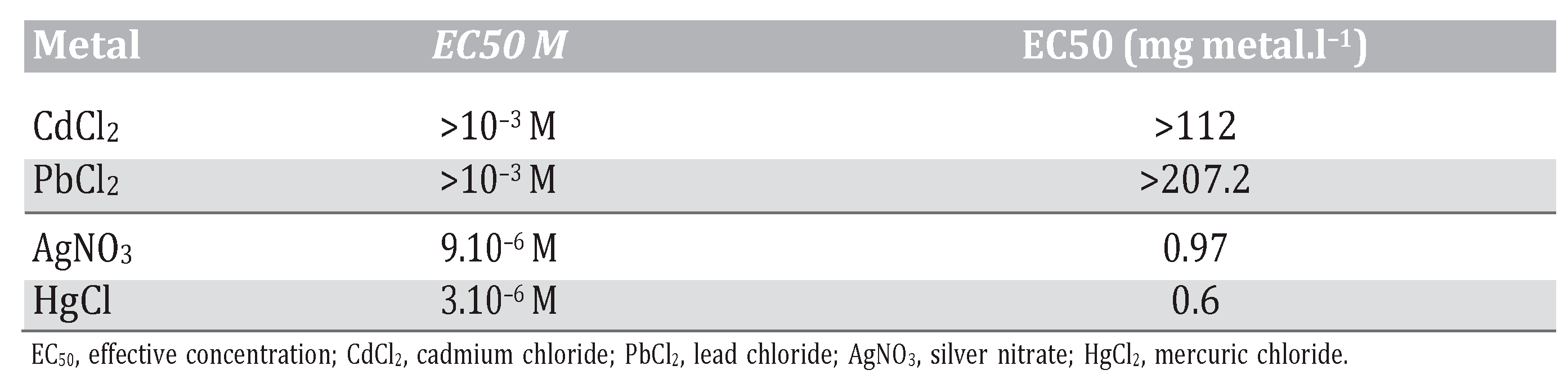
In vitro analysis of metal toxicity on hemo- cytes ranked the metals as follows: mercury > silver > lead > cadmium. These heavy metals also lead to a significant increase in the immune response at low concentrations. These concentrations tested are much higher than those found in the ocean. Silver induced a significant decrease of phagocytosis at con- centrations ranging from 10–5 M to 10–3 M (Figure 1D). Dissolved Ag concentrations in seawater ranging from 1-20.10–12 M (0.1-2.0 ng.L–1) in pristine offshore waters up to 300.10–12 M (30 ng.L–1) in estuaries close to point source discharges [11]. A significant increase of phagocytosis at 10–7 M is noticed. The IC50 value obtained (calculated with a linear regression) for the hemocytes exposed to silver nitrate is 9.10–6 M (Table 1). Mercury induced a significant decrease of phagocytosis at concentrations ranging from 10–6 M to 10–3 M (Figure 1C). We can also notice a significant increase of phagocytosis at concentrations ranging from 10–9 M to 10–7 M. The IC50 value calculated for the hemocytes exposed to mer- cury chloride is 3.10–6 M (Table 1). Total Hg concentrations are low and range from 0.2 to 4.10–12 M (40 to 802 pg.L–1), with the higher concentrations found near the coast likely due to riverine inputs [12]. Cadmium and lead induced a significant decrease of phagocytosis at 10–3 M (Figure 1A and B). For both metals the IC50 values calculated are greater than 10–3 M (Table 1). CdCl2 and PbCl2 compounds sig- nificantly increased the immune response at low concentrations ranging from 10–9 M to 10–6 M. In seawater, dissolved lead is between 7,2 and 72.10–11 M (15-150 ng.L–1) in the North Atlantic and total dissolved Cd exists at low concentrations usually less than 1.8.10–6 M (0.2 mg.L–1) [13].

Table 1.
Nominal metal concentrations inducing 50% inhibition of phagocytosis relative to controls.
Discussion
Environmental concentrations do not induce short-term responses, so we tested higher concentrations ranges. These concentrations tested are found in oceans for cadmium, while silver, lead and mercury are present in lesser amounts. Hemocyte cells of Mytilus edulis showed a classical pattern of the in vitro toxicity of heavy metals. At low concentrations, there is a lack of cell cytotoxicity and stimulation of the phagocytosis then followed with normal phagocytosis. At moderate concentrations, phagocytosis is dramatically reduced which is accompanied by low changes in cell viability. At high concentrations, cytotoxicity is relatively high, accompanied by a drastic inhibition of the phagocytosis. Similar results sup- port the observation that exposure to low levels may stimulate phagocytic activity whereas increasing concentrations induce suppression [9,14]. The average sensitivity for phagocytosis can be ranked in decreasing order of toxicity: HgCl2, AgNO3, and CdCl2. The impact of lead on phagocytosis was never analysed in the blue mussel and was ranked between Hg and Cd. In Mya arenaria, it was suggested by others [9] that hemocyte mortality only partially explained the decrease of the phagocytic index. Similarly, for the blue mussel, cytotoxicity is not the sole mechanism for phagocytosis inhibition. For example, cells incubated with HgCl2 at 10–5 M show an almost normal level of viability (80% of control), while phago- cytosis is strongly inhibited with only 20% of the control value. The phagocytosis dose–response curves for AgNO3, HgCl2 suggest that the toxicity tends to be threshold rather than linear. For example, AgNO3 concentrations lower than 10–6 M, HgCl2 lower than 10–7 M had no apparent negative effect on phagocytosis. Yet, next higher dose shows inhibition levels sometimes exceeding 60%. Compared to lethal or acute bioassays, the measurement of phagocytosis by flow cytometry in bivalves represents a sensitive endpoint to study the adverse effects of heavy metals at sublethal concentrations [15]. However, exposure was done under acute and short-term conditions which differ from environmental expo- sures i.e., under chronic and low concentrations.
References
- Fisher, W.S.; Oliver, L.M.; Walker, W.W.; Manning, C.S.; Lytle, T.F. Decreased resist- ance of eastern oysters (Crassostrea vir- ginica) to a protozoan pathogen (Perki- nsus marinus) after sublethal exposure to tributyltin oxide. Mar Environ Res 1999, 47, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, M.; Cyr, D.; Blakley, B.; Boermans, H.; Brousseau, P. Phagocytosis as a biomarker of immunotoxicity in wildlife species exposed to environmental xenobiotics. Am Zool 2000, 40, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zatta, P.; Gobbo, S.; Rocco, P.; Perazzolo, M.; Favarato, M. Evaluation of heavy metal pol- lution in the Venetian lagoon by using Mytilus galloprovincialis as biological indi- cator. Science of the Total Environ 1992, 119, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, D.J.H. The chemistries and envi ronmental fates of trace metals and organochlorines in aquatic ecosystems. Mar Pollut Bull 1995, 31, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, A.J.; Davis, J.A.; Hardin, D.D.; Gold, J.; Bell, D.; Crick, J.R.; et al. Long-term bioaccumulation monitoring with transplanted bivalves in the San Francisco Estuary. Mar Pollut Bull 1999, 38, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipe, R.K.; Coles, J.A. Environmental contam- inants influencing immunefunction in marine bivalve molluscs. Fish Shellfish Immunol 1995, 5, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.C. Biochemical and ultrastructural evidence for the double role of phagocytosis in mollusks: defense and nutrition. Comparat Pathobiol 1977, 3, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Adema, C.M.; Van der Knapp, W.P.W.; Sminia, T. Molluscan hemocyte-mediated cytotoxicity: the role of reactive oxygen intermediates. Rev Aquat Sci 1991, 4, 201–223. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, M.; Pellerin, J.; Lebeuf, M.; Brousseau, P.; Morin, Y.; Cyr, D. Effects of exposure of Mya arenaria and Mactromeris polynyma to contaminated marine sediments on phagocytic activity of hemocytes. Aquat Toxicol 2002, 59, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brousseau, P.; Payette, Y.; Tryphonas, H.; Blakley, B.; Boernaus, H.; Flipo, D.; et al. Manual of immunological methods; CRS Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, J.R.; Benoit, G.; Bowles, K.C.; DiToro, D.M.; Herrin, R.T.; Luther, G.W.I.I.I.; et al. Environmental chemistry of silver. In Silver in the environment: transport, fate, and effects; Andren, A.W., Bober, T.W., Eds.; Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC): Pensacola, FL, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, R.P.; Gill, G.A. Mercury in the marine environment. In Mercury Sources, measurements, cycles and effects. Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course Series, Vol. 34; Mineralogical Association of Canada: Halifax, 2005; pp. 179–216. [Google Scholar]
- Pan J, Plant JA, Voulvoulis N, Oates CJ, Ihlenfeld C. Cadmium levels in Europe: implications for human health. Environ Geochem Health 2010, 32, 1–12.
- Brousseau P, Pellerin J, Morin Y, Cyr D, Blakley B, Boermans H, et al. Flow cytome- try as a tool to monitor the disturbance of phagocytosis in the clam Mya arenaria hemocytes following in vitro exposure to heavy metals. Toxicology 2000, 142, 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Sauvé S, Brousseau P, Pellerin J, Morin Y, Senécal L, Goudreau P, et al. Phagocytic activity of marine and freshwater bivalves: In vitro exposure of hemocytes to metals (Ag, Cd, Hg and Zn). Aquat Toxicol 2002, 58, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© Copyright P. Rault et al., 2013 Licensee PAGEPress, Italy. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 3.0 License (CC BYNC 3.0). (CC BY-NC 3.0).