Reduction of Azo Dyes by Flavin Reductase from Citrobacter freundii A1
Abstract
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Preparation of cell extracts, azoreductase and flavin reductase assays
Over expression and protein extraction
Reduction of azo dyes by Fre
Voltammetric analysis
Results
The azo reductase and flavin reductase activities of C. freundii A1 cell extracts
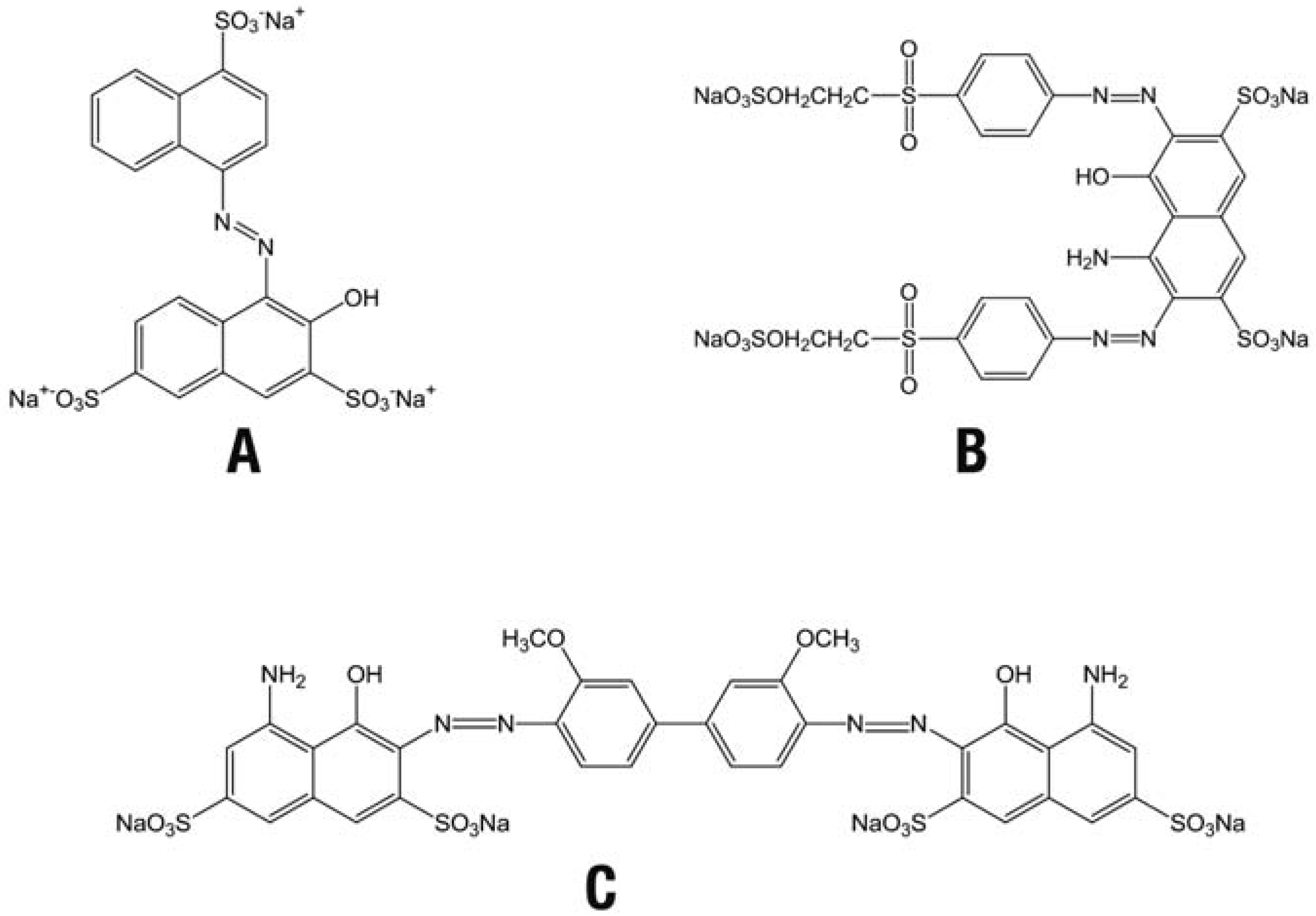
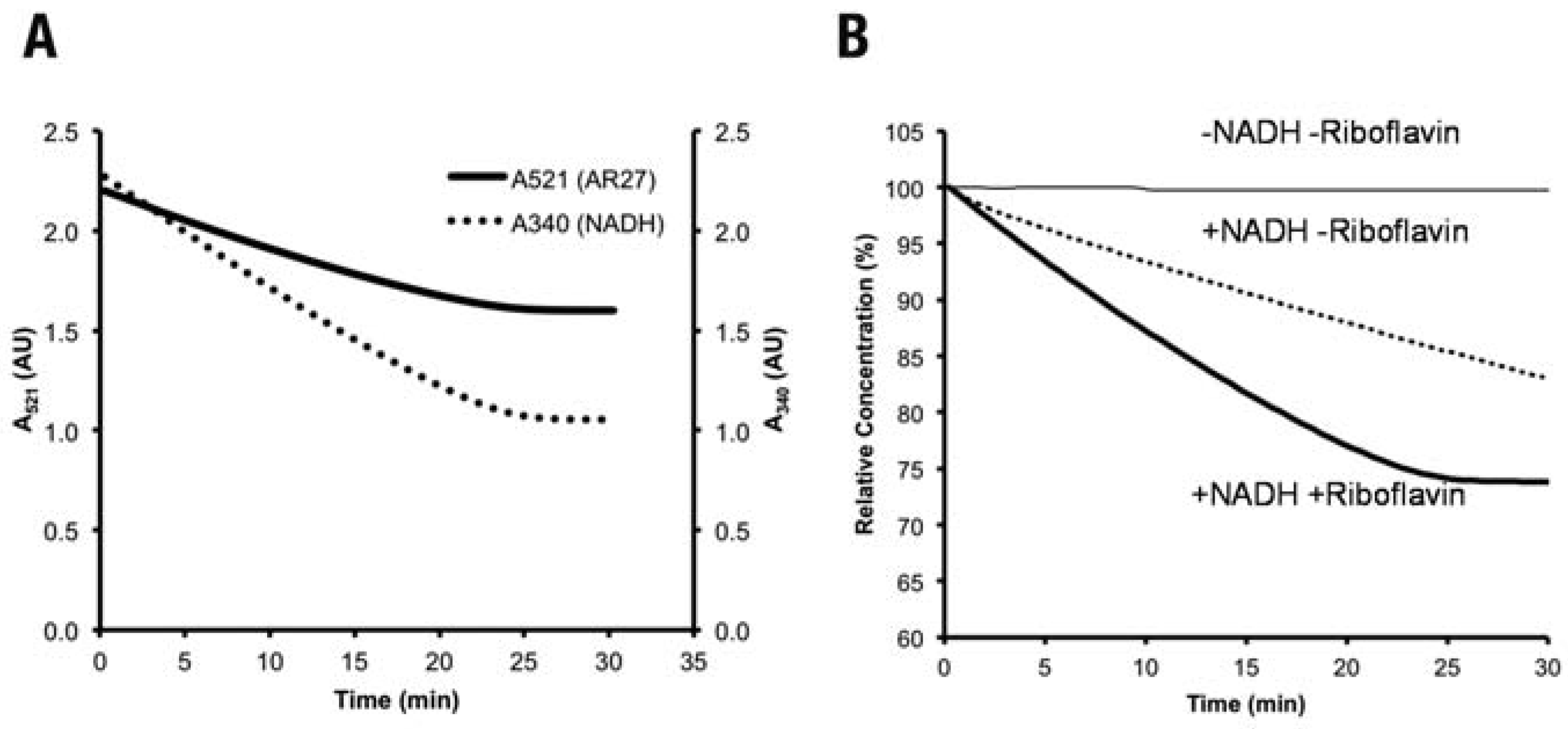
Reduction of azo dyes by the recombinant Fre
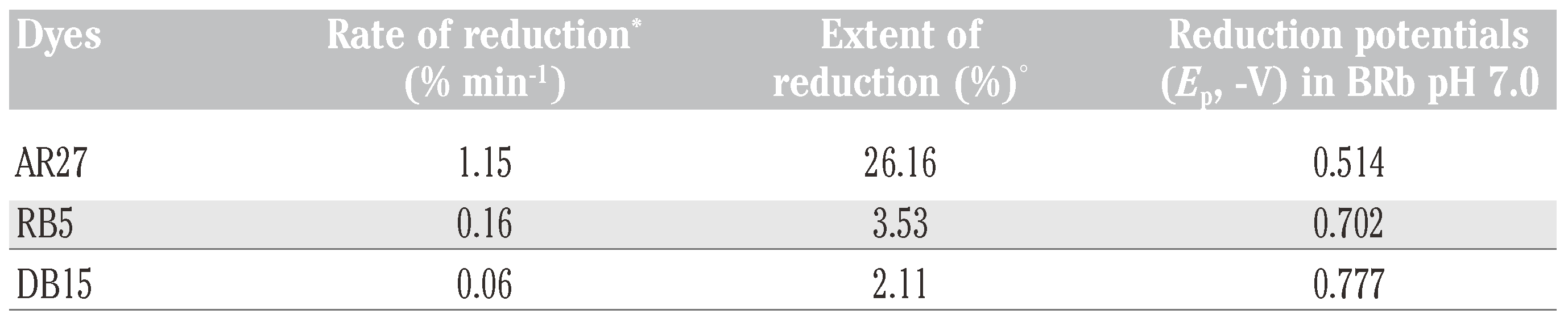
Voltammetric analysis of the azo dyes
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stolz, A. Basic and applied aspects in the microbial degradation of azo dyes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2001, 56, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedro Silva J, Sousa S, Rodrigues J; et al. Adsorption of Acid Orange 7 dye in aqueous solutions by spent brewery grains. Sep Purif Technol 2004, 40, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan-Alaton, I.; Ferry, J.L. Application of polyoxotungstates as environmental cata- lysts: Wet air oxidation of acid dye Orange II. Dyes Pigments 2002, 54, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chao, Y.; Yang, X.; Bao, H.; Qian, S. Biodecolorization of azo, anthraquinonic and triphenylmethane dyes by white-rot fungi and a laccase-secreting engineered strain. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 2004, 31, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinfling, A.; Ruiz-Dueñas, F.J.; Martínez, M.J.; Bergbauer, M.; Szewzyk, U.; Martínez, A.T. A study on reducing substrates of man- ganese-oxidizing peroxidases from Pleurotus eryngii and Bjerkandera adusta. FEBS Lett 1998, 428, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, M.; Sagami, I.; Daff, S.; Taiko Migita, C.; Shimizu, T. Azo reduction of methyl red by neuronal nitric oxide synthase: The impor- tant role of FMN in catalysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000, 275, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-S.; Chou, C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lin, P.-J.; Ho, J.-Y.; Lee Hu, T. Kinetic characteristics of bacteri- al azo-dye decolorization by Pseudomonas luteola. Water Res 2001, 35, 2841–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelman, M.; Ramaswamy, S.; Niviere, V.; Fontecave, M.; Eklund, H. Crystal structure of NAD(P)H:flavin oxidoreductase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 7040–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyrou, G.; Haggard-Ljungquist, E.; Krook, M.; Jornvall, H.; Nilsson, E.; Reichard, P. Characterization of the flavin reductase gene (fre) of Escherichia coli and construc- tion of a plasmid for overproduction of the enzyme. J. Bacteriol 1991, 173, 3673–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, R.; Rau, J.; Stolz, A. The function of cytoplasmic flavin reductases in the reduc- tion of azo dyes by bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 2000, 66, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Singh, P.; Iyengar, L. Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes. Int Biodeter Biodegr 2007, 59, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbanna, K.; Hassan, G.; Khider, M.; Mandour, R. Safe biodegradation of textile azo dyes by newly isolated lactic acid bacteria and detection of plasmids associated with degradation. J Bioremed Biodegr 2010, 1, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, A.; Arshad, M.; Crowley, D.E. Biodegradation potential of pure and mixed bacterial cultures for removal of 4- nitroaniline from textile dye wastewater. Water Res 2009, 43, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.F.; Rashid, N.A.A.; Chua, L.S.; Abllah, N.; Nasiri, R.; Ikubar, M.R.M. Communal microaerophilic-aerobic biodegradation of Amaranth by novel NAR-2 bacterial consor- tium. Bioresour Technol 2012, 105, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.F.; Rashid, N.A.A.; Yusoff, A.R.M.; Chua, L.S. Biosynthesis of autoinducer-2 as the possible mechanism to enhance decolouri- sation of azo dye by Citrobacter freundii A1. J Biol Sci 2012, 12, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chan, G.F.; Gan, H.M.; Rashid, N.A.A. Genome sequence of Citrobacter sp. strain A1, a dye-degrading bacterium. J Bacteriol 2012, 194, 5485–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, A.; Klein, J.; Kudlich, M.; Stolz, A.; Knackmuss, H.J.; Mattes, R. Reduction of azo dyes by redox mediators originating in the naphthalenesulfonic acid degradation pathway of Sphingomonas sp. strain BN6. Appl Environ Microbiol 1997, 63, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.F.; Rashid, N.A.A.; Yusoff, A.R.M. Expression, purification and characteriza- tion of flavin reductase from Citrobacter freundii A1. Ann Microbiol 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rouessac, F.; Rouessac, A. Chemical analy- sis: Modern instrumentation and tech- niques. John Wiley and Sons Ltd: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yusoff, A.R.H.M.; Fogg, A.G.; Ahmad, R. Cathodic stripping voltammetry of 2,3-dichloro- quinoxaline and 1,4-dichlorophthalazine reactive dyes and their hydrolysis prod- ucts: Reactive Red 41 and Reactive Red 96. Talanta 1998, 47, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaratini, C.C.I.; Fogg, A.G.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Assessment of the application of cathodic stripping voltammetry to the analysis of diazo reactive dyes and their hydrolysis products. Dyes Pigments 2001, 50, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florian, M.; Yamanaka, H.; Carneiro, P.A.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Determination of brilliant blue FCF in the presence and absence of erythrosine and quinoline yellow food colours by cathodic stripping voltammetry. Food Addit Contam 2002, 19, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, R.J.; Coulombe, R.A.; Sharma, R.P.; Grover, T.A.; Piette, L.H. Oxidation of NADH by vanadium compounds in the presence of thiols. Arch Biochem Biophys 1989, 271, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Wahab, M.F.; Abdul Rashid, N.A.; Yusoff, A.R.M. Degradation of Acid Red 27 by the recombinant flavin reductase. In: KUSTEM 5th Annual Seminar on Sustainability Science and Management, Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia, 2006.
- Field, J.A.; Brady, J. Riboflavin as a redox mediator accelerating the reduction of the azo dye mordant yellow 10 by anaerobic granular sludge. Water Sci Technol 2003, 48, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Huang, X.; Shen, H. Aromatic azo compounds as spectrophotometric kinetic assay substrate for HRP. Talanta 2001, 53, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, S.V.; Prasad, K.K.; Rao, N.C.; Sarma, P.N. Acid azo dye degradation by free and immobilized horseradish peroxidase (HRP) catalyzed process. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zee, F.P.; Bisschops, I.A.E.; Blanchard, V.G.; Bouwman, R.H.M.; Lettinga, G.; Field, J.A. The contribution of biotic and abiotic processes during azo dye reduction in anaerobic sludge. Water Res 2003, 37, 3098–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollinger, H. Color chemistry: Synthesis, properties and applications of organic dyes and pigments; VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH & VCH Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Santos de Paula, F.; Cioletti, A.G.; da Silva Filho, J.F.; Santana, A.E.G.; dos Santos, A.F.; et al. Electrochemical studies of biologically active arylazoxy compounds: The relation- ship between redox potentials and mollus- cicidal activities. J Electroanal Chem 2003, 544, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zille, A.; Ramalho, P.; Tzanov, T.; Millward, R.; Aires, V.; Cardoso, M.H.; et al. Predicting dye biodegradation from redox potentials. Biotechnol Prog 2004, 20, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, D.; Xiang, X.; Yu, H.; Tian, C.; et al. Correlation of anaerobic biodegradability and the electrochemical characteristic of azo dyes. Biodegradation 2006, 17, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2012 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdul-Wahab, M.F.; Chan, G.F.; Mohd Yusoff, A.R.; Abdul Rashid, N.A. Reduction of Azo Dyes by Flavin Reductase from Citrobacter freundii A1. J. Xenobiot. 2013, 3, e2. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2013.e2
Abdul-Wahab MF, Chan GF, Mohd Yusoff AR, Abdul Rashid NA. Reduction of Azo Dyes by Flavin Reductase from Citrobacter freundii A1. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2013; 3(1):e2. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2013.e2
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdul-Wahab, Mohd Firdaus, Giek Far Chan, Abdull Rahim Mohd Yusoff, and Noor Aini Abdul Rashid. 2013. "Reduction of Azo Dyes by Flavin Reductase from Citrobacter freundii A1" Journal of Xenobiotics 3, no. 1: e2. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2013.e2
APA StyleAbdul-Wahab, M. F., Chan, G. F., Mohd Yusoff, A. R., & Abdul Rashid, N. A. (2013). Reduction of Azo Dyes by Flavin Reductase from Citrobacter freundii A1. Journal of Xenobiotics, 3(1), e2. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2013.e2




