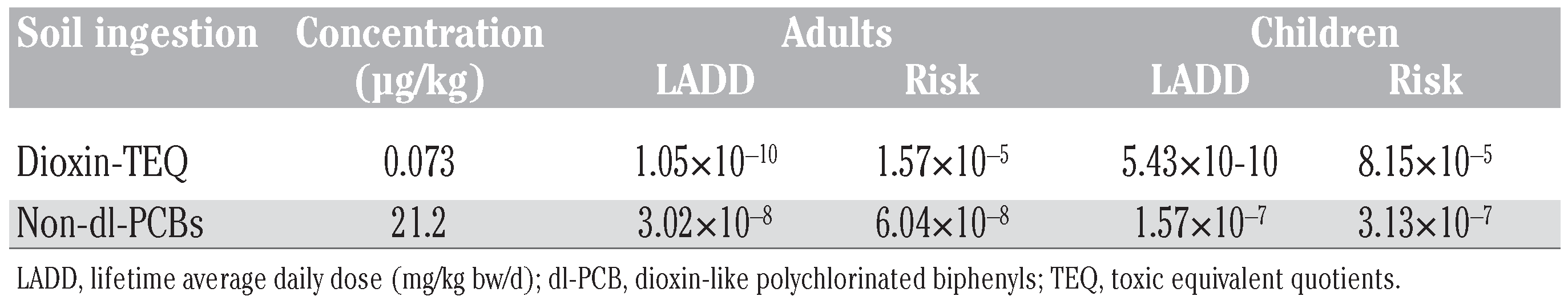Abstract
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) were primarily used in transformers and capacitors, lubricants, flame retardants, plasticizers, paint, carbonless papers, etc. These are capable of long-range atmospheric transport and have been designated as persistent organic pollutants by the Stockholm Convention. Due to their characteristic properties, PCBs are found worldwide in all environmental matrices (including human) and biota. Soils are usually considered to be the source as well as sink for environmental pollutants, with cumulative effects of long-range atmospheric transport and local sources. Around the world, comparatively higher concentrations of PCBs have been reported in urban soils than suburban or rural soils. Higher amount of PCBs in urban soils may cause toxicological health risks to urban residents through ingestion, inhalation and skin contact. This paper presents the PCB distribution in soils from Delhi, India, and exposure risk estimates for human health through soil ingestion. The concentration of ΣPCBs ranged between 1.08–100.67 ng g−1 (mean 21.16 ng g−1 ± 5.24 ng g−1), which was much lower than the Canadian soil quality guideline value of 1.3 mg/kg or 1300 ng g−1. Human health risk estimates through the soil ingestion pathway were made in terms of lifetime average daily dose (LADD), incremental lifetime cancer risks and non-carcinogenic hazard quotient (HQ). The LADD for Delhi adults and children was 3.02 × 10−8 mg kg−1 d−1 and 1.57 × 10−7 mg kg−1 d−1, respectively, which corresponds to toxic equivalent quotients (TEQ) intake of 0.105 pg TEQ kg−1 d−1 (0.735 pg TEQ kg−1 week−1) and 0.543 pg TEQ kg−1 d−1 (3.801 pg TEQ kg−1 week−1), respectively. The estimated LADD for Delhi residents was lower than the acceptable intake values recommended by the World Health Organization (1 pg TEQ kg−1 d−1), the European Commission (14 pg TEQ kg−1 week−1) and by the Japanese government (4 pg TEQ kg−1 d−1). The probability of cancer risk ranges from 6.04 × 10−8 (ΣPCBs) to 1.57 × 10−5 (ΣTEQ) and 3.13 × 10−7 (ΣPCBs) to 8.15 × 10−5 (ΣTEQ) for adults and children, respectively, and was within acceptable ranges of 10−6 to 10−4. The non-carcinogenic risk in terms of health HQ was 0.105 and 0.330 for adults and children, respectively, which was lower than the acceptable limit of 1. The study found lower concentrations of PCBs than guideline values and low health risk estimates through the soil ingestion pathway within acceptable levels, indicating a minimum risk for Delhi residents.
Introduction
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are a group of 209 congeners and have been desig- nated as persistent organic pollutants by the Stockholm Convention. PCBs were primarily used in transformers and capacitors as dielec- tric and coolant fluids and in lubricants, flame retardants, plasticizers, paint, etc.[1] Even though the production has been banned since the 1970s and usage of these contaminants are restricted in many countries, PCBs continue to be detected in environmental samples from around the world.[2]
PCBs are toxic, bioaccumulative, and can undergo long-range atmospheric transport world-wide to regions such as the Arctic, Antarctic and high altitude regions of Mount Everest.[3,4,5] PCBs are characterized by high thermal and chemical stabilities, low vapor pressures, high dielectric constants, hydropho- bicity, high lipophilicity, and extreme resistant to degradation. Because of these characteris- tics, PCBs accumulate in soil, sediments and biota.[6]
Soils of urban areas are usually known as the source as well as sink for environmental pollutants, where cumulative effects of long- range atmospheric transport and local sources are the important factors.[7,8] As a result, com- paratively higher concentrations of PCBs have been reported in urban soils than suburban or rural soils.[9,10] Humans are exposed to PCBs mainly through the consumption of contami- nated food, and occupational exposure to PCBs occurs mainly via the inhalation and dermal routes. Higher amount of PCBs in soils, espe- cially dioxin-like PCBs (dl-PCBs), may cause toxicological health risks to urban residents through ingestion, inhalation and skin con- tact.[11] In earlier studies, the potential risk to human health from PCBs in urban soils has been reported.[12,13] Therefore, more attention should be given to the status of PCBs in urban soils and the possible risk to human and envi- ronmental health.
In earlier investigations, occurrence of PCBs had been reported in environmental and biological samples from India.[14,15,16,17,18,19,20] In this study we quantified the levels of PCBs and their risk estimates in urban soils from the Delhi metro-politan area. This is probably the first study to present the 28 PCB-congener levels, including dioxin-like PCBs, in soils from Delhi, and may provide the base-line statistical data needed for health effect assessments. For this pur- pose, PCBs were extracted from soils using accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) and quantified.
Materials and Methods
Study area and sampling
The sampling area was the national capital territory (NCT), Delhi, which is the capital of India with a population of 1.67 million. The total area of NCT, Delhi, is approximately 1483 km2 and is located in northern India between 28°24’17”N to 28°53’00”N and between 76°50’24”E to 77°20’37”E. Average annual rainfall is 714 mm. The climate in Delhi is hot and humid. During summer, temperatures rise up to 40-45°C and in winters temperatures fall to 4-5°C.[21]
The soil samples were collected during June 2011 from 14 urban locations on streets and roads near residential areas in Delhi. Approximately 1/2 kg of soil sample was collect-ed from each sampling location, and after removing pebbles, sticks and leaves the sample was mixed thoroughly until homogenized. One part was then transferred to clean, wide- mouthed amber glass containers that were then labeled. After collection, samples were transported to the laboratory and kept at 4°C until analysis.
Chemicals and solvents
Chemicals (sodium sulfate, potassium hydroxide and sulfuric acid) and solvents (high performance liquid chromatography grade acetone, hexane and dichloromethane) were purchased from Merck India. Pre-cleaned silica gel 60 (0.063-0.100 mm) was obtained from Supelco (Sigma-Aldrich Corp., St. Louis, MO, USA) and used as adsorbent in column chromatography. Prior to use, anhydrous sodi- um sulfate was cleaned separately with methanol, dichloromethane and acetone in Soxhlet extractor for 8 h each, and stored in air-tight conditions at 130°C. Reference stan- dard solutions of PCBs were purchased from Dr. Ehrenstorfer (Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH, Augsburg, Germany) and used for the instru- ment calibration and quantification.
Sample extraction, clean up and analysis
Sample extraction and clean up was carried out according to validated methods.[22] Briefly, a homogenized 20 g sample was dried by mixing with diatomaceous earth (ASE prep DE, Dionex Corp., Sunnyvale, CA, USA) until a free-flowing powder was obtained. The extrac- tion was carried out with accelerated solvent extractor (ASE-350, Dionex Corp.) using ace- tone/hexane (v/v, 1:1) solvent mixture in two cycles with 5 min static time. The ASE was operated at 1500 psi and the oven temperature was maintained at 100°C. The extracts were concentrated to 2.0 mL using a rotatory vacu- um evaporator (Eyela, Tokyo, Japan). Multilayered silica gel column chromatography on a tri-functional column with neutral, basic and acidic silica was performed to remove interfering organic and polar compounds. Details of methodology for clean up and instru- mental analysis are reported elsewhere.[20]
Quality control analysis
Appropriate quality assurance quality con- trol analysis was performed, including analysis of procedural blanks (analyzed concentra- tions<method detection limit, MDL), random duplicate samples (standard deviation, SD<5%), calibration standard verification (SD<15%) and matrix spike recovery (100±20%).[20] PCB congeners were identified in the sample extract by comparing the accu- rate retention time from the standard mixture and quantified using the response factors from multi-level calibration curves of the standards (r2 value 0.999).
A signal to noise ratio of 3:1 was used to cal- culate instrument detection limits by using a valid quantifiable peak. Each sample was ana- lyzed in duplicate and the average was used in calculations. Method detection limits were established by processing 8 aliquots of a sam- ple spiked with a quantity sufficient to produce a detectable response (s/n>3) and multiplying the standard deviation by the tstudents value (3.0 for 8 replicates). For statistical calculations the non-detect values of PCB congeners have been reported as <0.01 ng g−1 (MDL of all 28 individ- ual congeners being less than 0.01ng g−1). Furthermore, it may be noted that our labora- tory is ISO 17025 accredited and had been par- ticipating in proficiency testing exercises con- ducted by international agencies, including the Centre d’expertise en analyse environ- nementale du Québec, and performance scores were satisfactory for PCBs.
Toxic equivalent quotients (TEQ) of each congener were calculated by multiplying the concentration of individual dl-PCB congener with the toxic equivalent factors (TEFs)[11] with reference to 2,3,7,8-tetrachloro dibenzo-p- dioxin (TCDD) and reported as pg WHO2005- TEQ g−1 dry-weight (dw).
Health risk assessment for poly- chlorinated biphenyls exposure
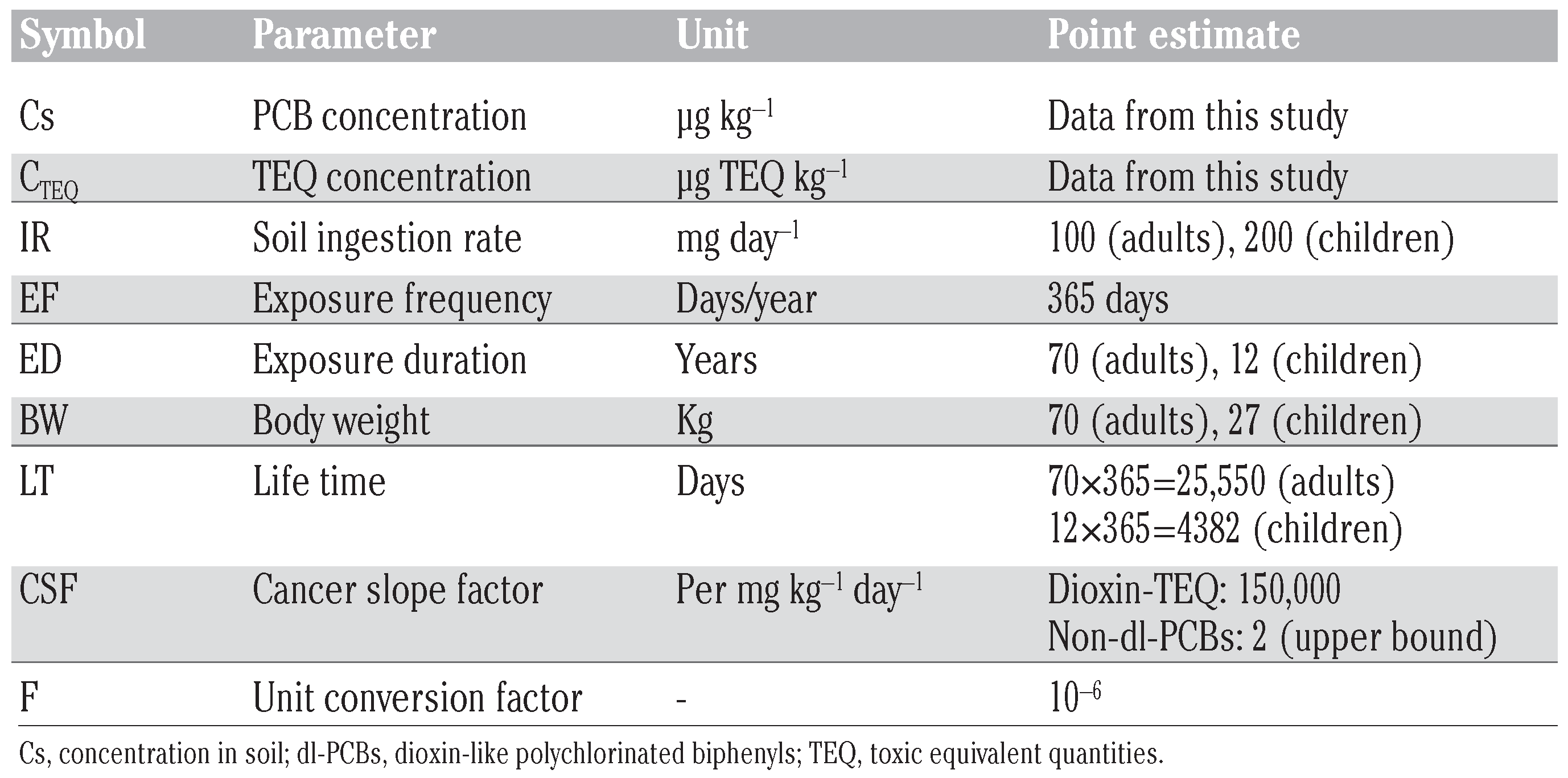
In this study, assessment of human health risk is discussed as the calculated estimates of the upper-bound excess probabilistic lifetime cancer risk and non-carcinogenic hazards. Hazard is the exact measure of the magnitude of exposure potential or a quantifiable poten- tial for developing non-carcinogenic health effects after averaged exposure period. Risk is the probability of cancer development in a life- time after a uniform exposure.[23] We estimated the human exposure to PCBs through soil ingestion and the consequent health risk by using equations presented by United States Environmental Protection Agency.[24,25,26] For this purpose, the LADD (lifetime average daily dose), non-cancer risk HQ (hazard quotient) and probabilistic incremental lifetime cancer risks (ILCR) were calculated. LADD is an amount a person takes in as a result of expo- sure to a chemical in contaminated air, water, soil or food. The input parameters used in the health risk estimation for PCBs are given in Table 1. The equations used for estimating LADD, HQ (non-cancer risk) and probable can- cer risk were as follows:
where:
LADD (mg kg−1 day−1)=(Cs x IR x F x EF x ED)/(BW x LT)
HQ=LADD/RfD
ILCR=LADD x cancer slope factor oral

Table 1.
Summary of input parameters used in calculations for health risk assessment.
- Cs is the total PCBs concentration in soil (µg kg−1);
- IR is the soil ingestion rate (mg day−1);
- is the unit conversion factor (10−9);
- EF is exposure frequency (days/year);
- ED is the exposure duration (year);
- BW is the body weight (kg);
- LT is the lifetime which is equal to exposure duration x 365 days (days);
- RfD is the reference dose for individual dl-PCB congener (mg kg−1 day−1).
An RfD is a daily intake rate that is estimat- ed to cause no adverse health effects over a specific exposure duration. Non-carcinogenic risks (HQ) were assessed by comparing expo- sure with RfD of each dl-PCB and the total was reported for each sampling location. Cancer risk for dioxin-TEQ was calculated for each of the 12 dl-PCB congeners from LADD by multi- plying slope factor for dioxin (150,000/mg kg−1 day−1) and the total was reported. Cancer risk for non-dl-PCBs was calculated from LADD of 28 PCBs by multiplying the upper bound can- cer slope factor (2/mg kg−1 d−1). The upper bound slope factor is used for those exposure pathways for which environmental processes are likely to increase health risk, such as expo- sure from consumption of foods, sediment or soil ingestion, and dust or aerosol inhalation.
Results
Polychlorinated biphenyls concen- trations in soil
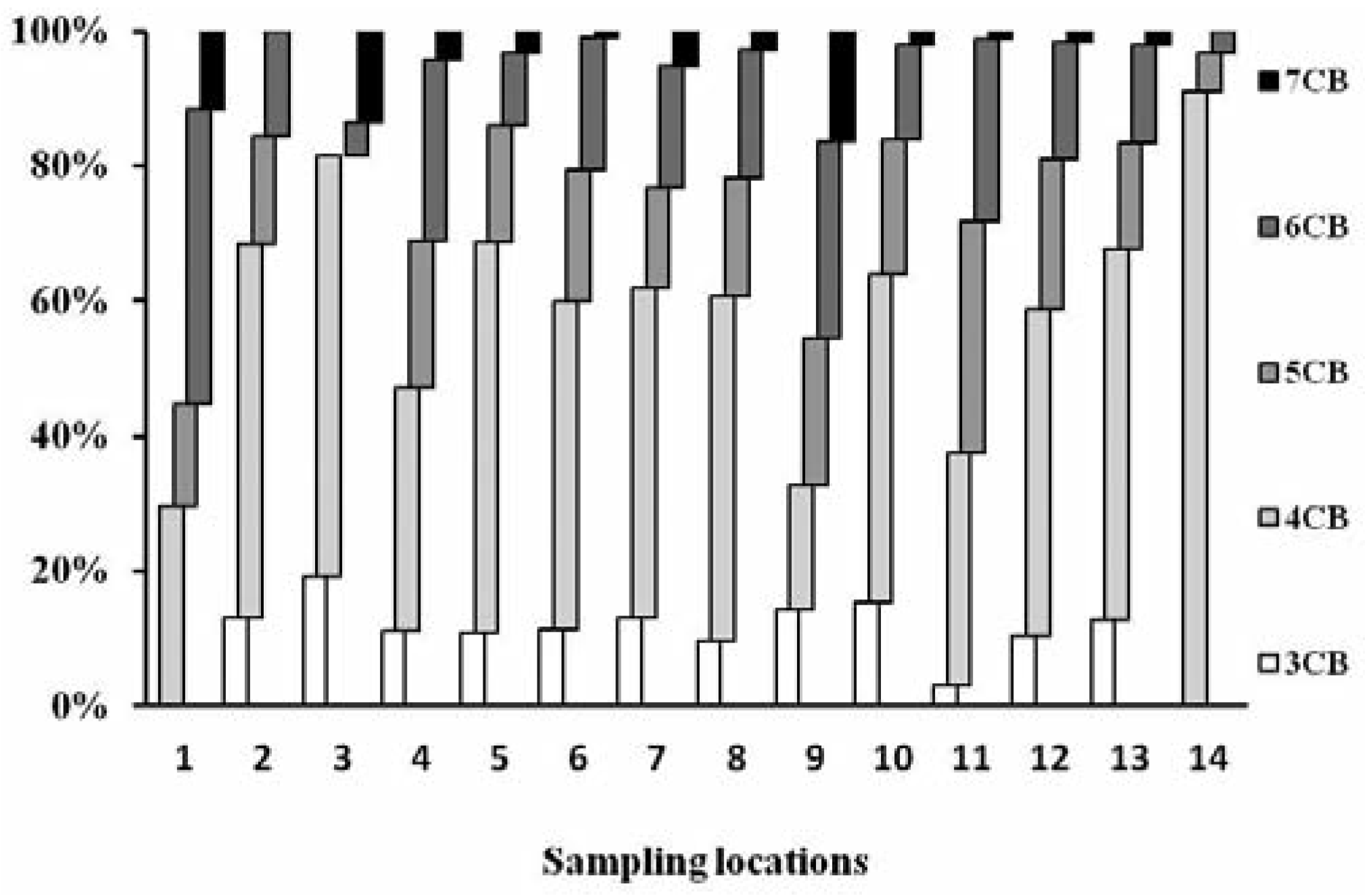
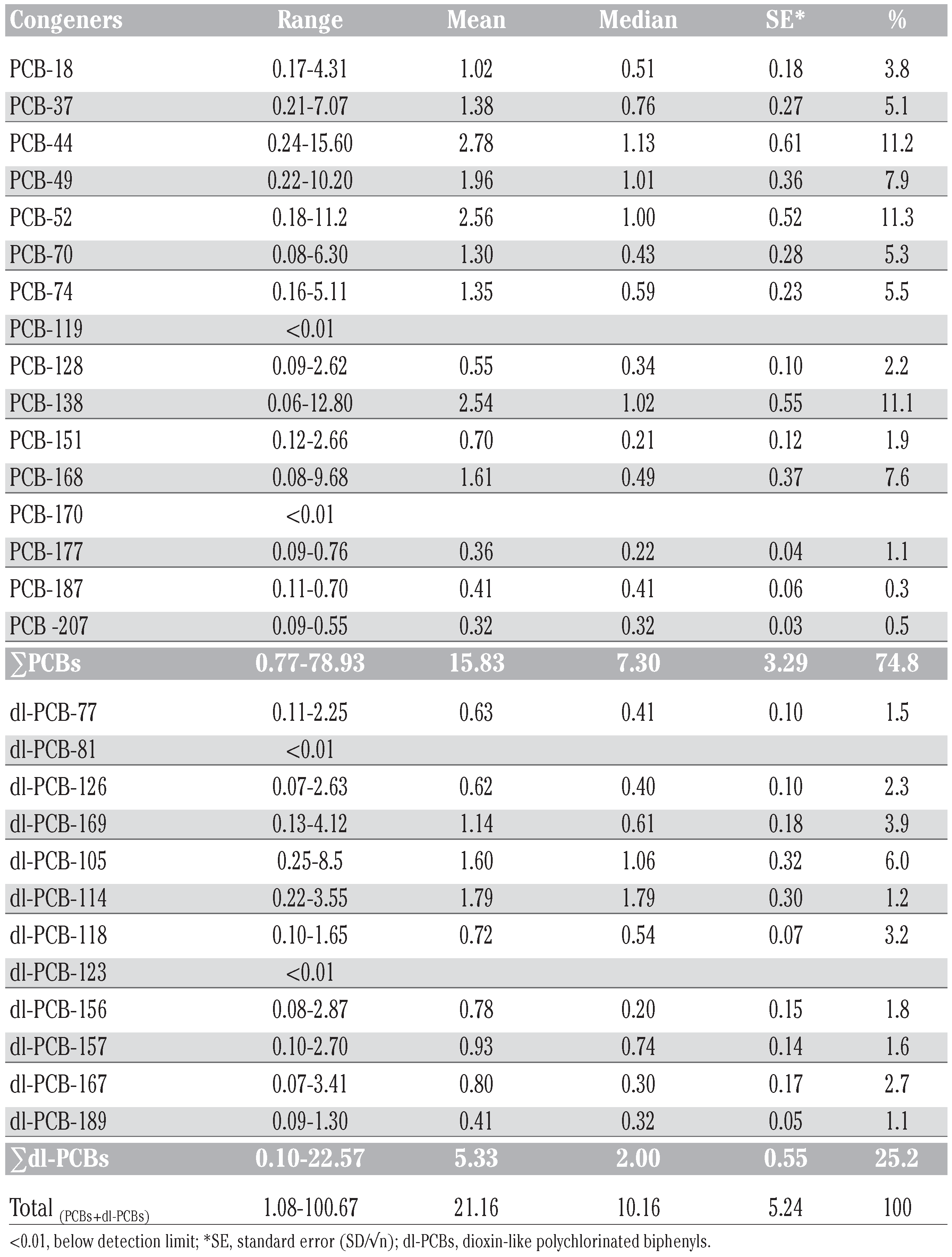
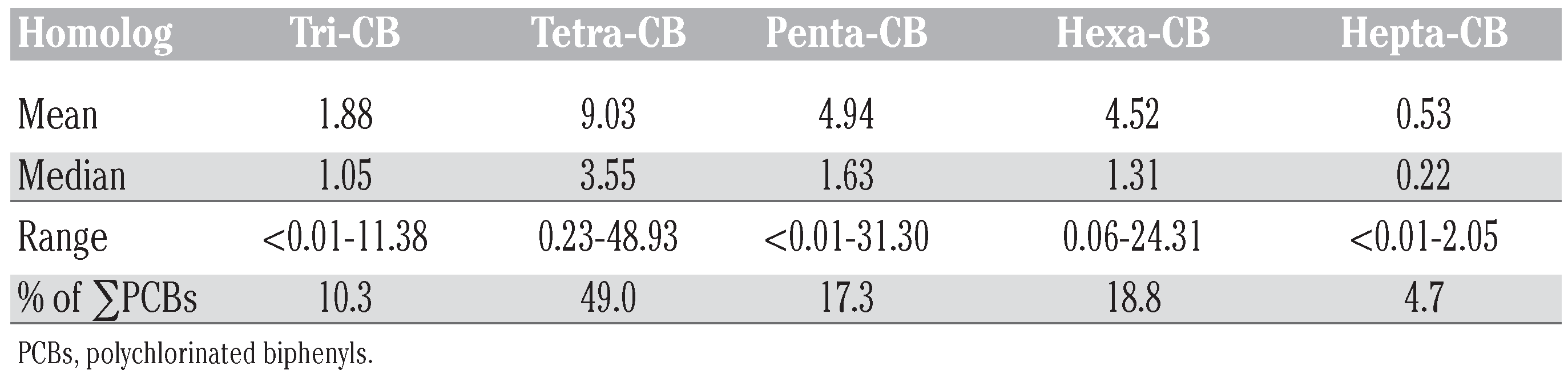
The concentrations of ΣPCBs and individual 28 congeners in urban soils from Delhi, India, are presented in Table 2. The observed levels of total PCBs ranged between 1.08- 100.67 ng g−1 (dw) with the mean and median of 21.16 ng g−1 and 10.16 ng g−1 (±5.24 ng g−1), respectively, which is at par with those of other cities around the world. The most common congener num- bers among studied PCBs were CB-44, CB-52 and CB-138. The concentration range of 12 dl- PCBs was 0.10-22.57 ng g−1 (mean 5.33 ng g−1±0.55 ng g−1, median 2.00 ng g−1±0.55 ng g−1) and accounted for approximately 25% of total PCBs. TEQ of 12 dl-PCBs, calculated using WHO 2005-TEFs, ranged from less than 1 to 387 pg-TEQ g−1 (mean 73±28 pg-TEQ g−1). Non-ortho-PCBs (CB-77, CB-81, CB-126 and CB-169) were the sole contributors and accounted for over 99% of total TEQ (Table 3). Tetrachorinated, pentachlo- rinated and hexachlorinated biphenyls were the dominant homologues groups of PCBs (Table 4, Figure 1).

Table 2.
Polychlorinated biphenyl congener concentrations (ng/g dw) in urban soils from Delhi, India.

Table 3.
Toxic equivalent quotients of dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in urban soils from Delhi, India.

Table 4.
Polychlorinated biphenyl homologues (3-7 CB) in urban soils from Delhi, India (ng/g dw).
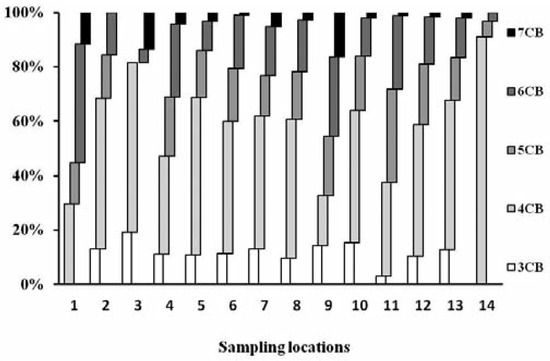
Figure 1.
Polychlorinated biphenyl homologs in soil at different locations in Delhi, India.
Health risk assessment
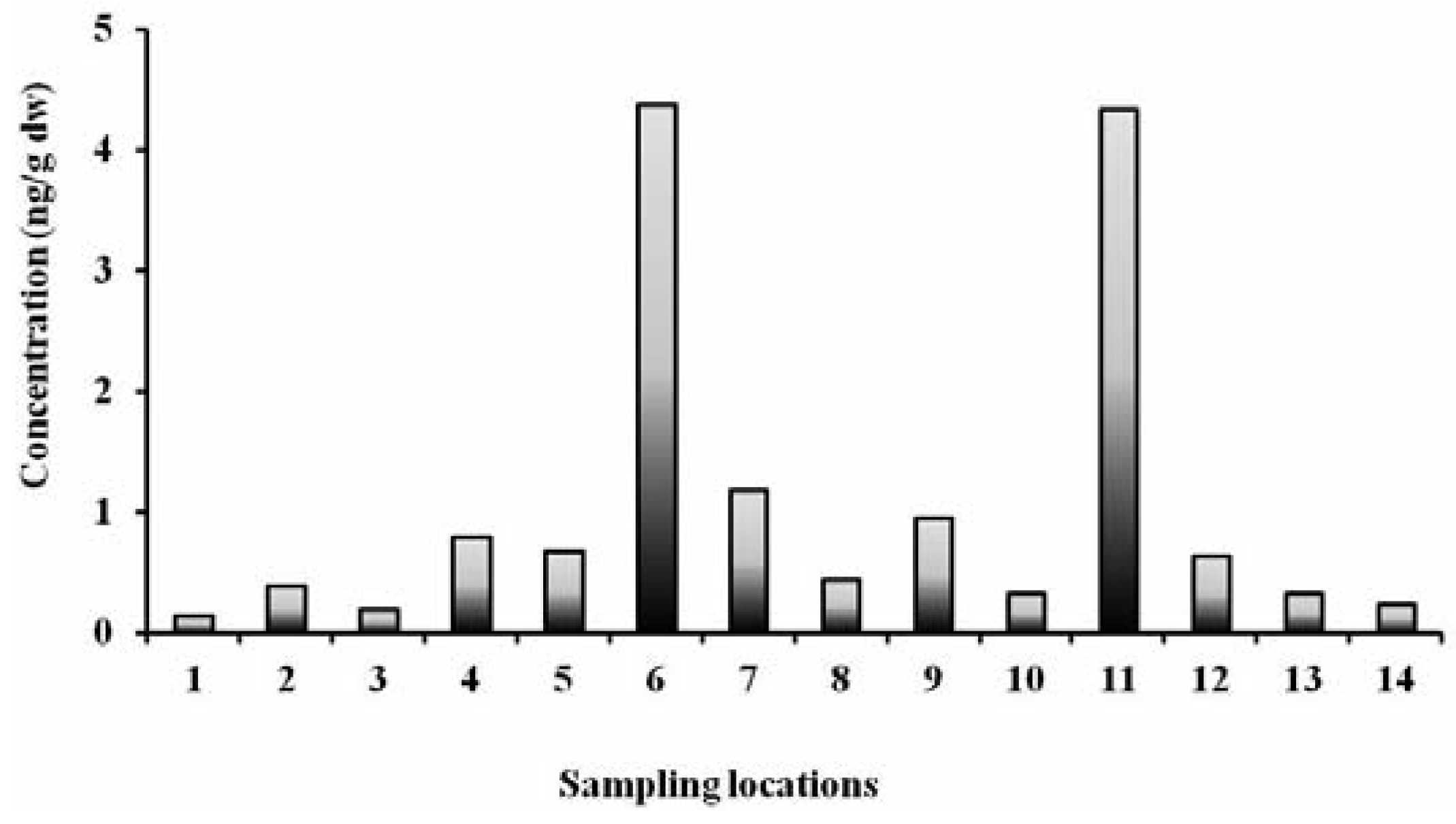
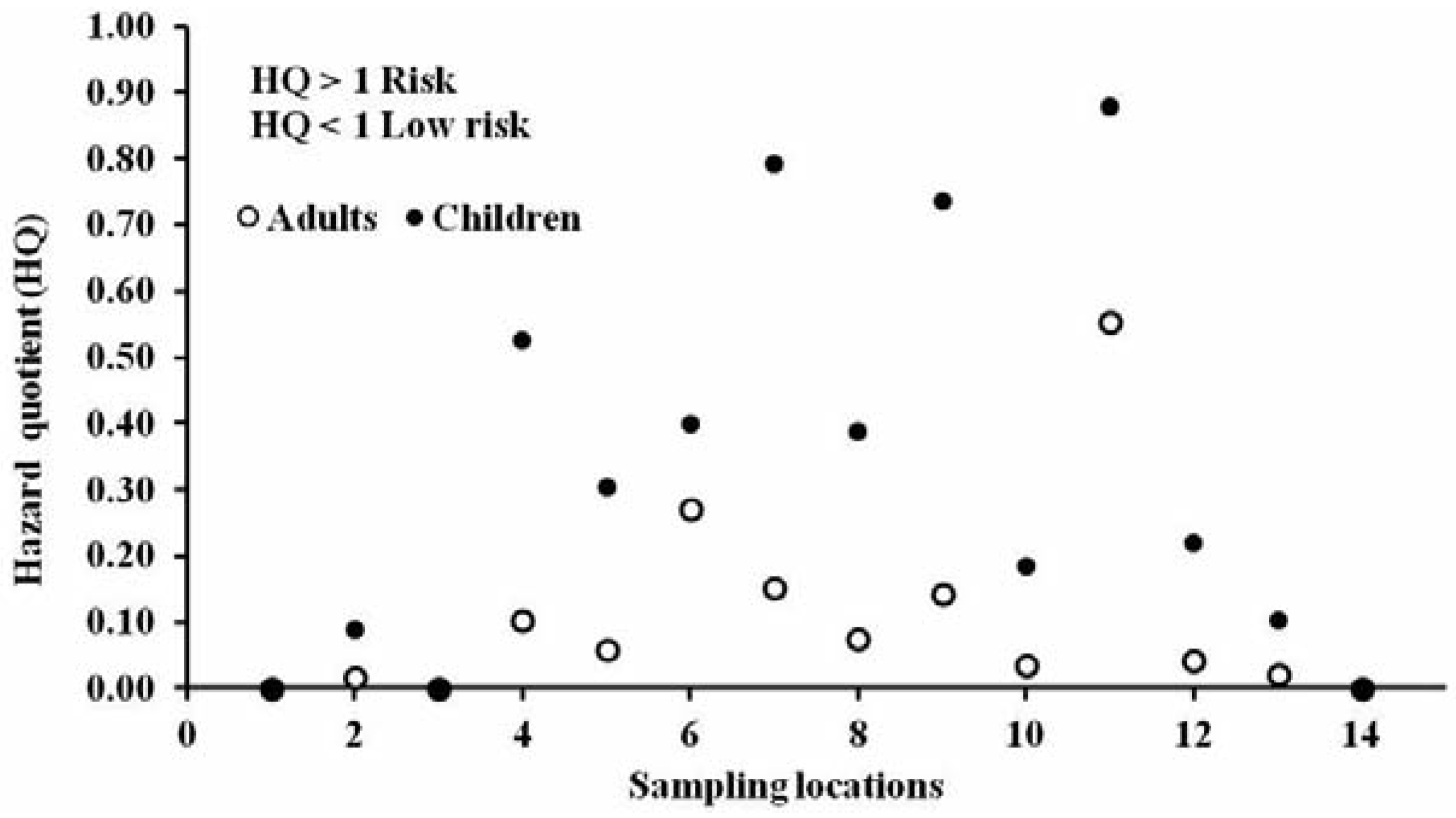
Adults and children may be exposed to con- taminants in soil and may also take chemicals from soil through different intake pathways, such as ingestion, inhalation and dermal con- tact. Figure 2 shows average of ΣPCBs in urban soil at different locations in Delhi, India. The calculated average daily intake of PCBs through soil ingestion by adults and children in Delhi was 3.02×10−8 mg kg−1 d−1 and 1.57x10−7 mg kg−1 d−1, respectively (Table 5), for a soil PCB concentration of 21.2 µg kg−1. With respect to RfD, the average LADD for adults and children was less than 1% and less than 5%, respectively, of the RfD. The calculated value of TCDD substituted WHO-TEQ daily intake for adults and children was 1.05x10−10 mg TEQ kg−1 d−1 and 5.43×10−10 mg TEQ kg−1 d−1, respectively, when soil TEQ was 0.073 µg kg−1 (Table 5). The calculated probability cancer risk estimate for PCB exposure from ingestion of soil was 6.04x10−8 (ΣPCBs) to 1.57×10−5 (ΣTEQ) and 3.13x10−7 (ΣPCBs) to 8.15×10−5 (ΣTEQ) for Delhi adults and children, respec-tively (Table 5). The quantified non-carcino- genic HQ for soil ingestion pathway of PCBs was 0.105 and 0.330 for Delhi adults and chil- dren, respectively (Figure 3).
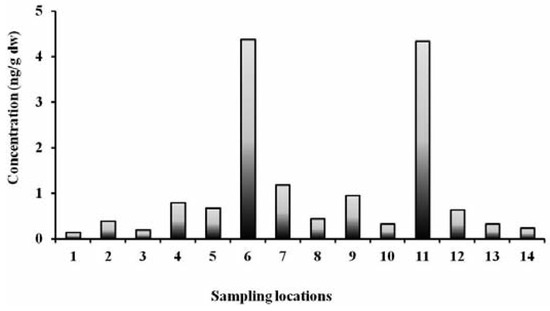
Figure 2.
Average of ∑polychlorinated biphenyls in urban soil at different locations in Delhi, India.

Table 5.
Calculated polychlorinated biphenyl exposure from urban soil and risk for adults and children.
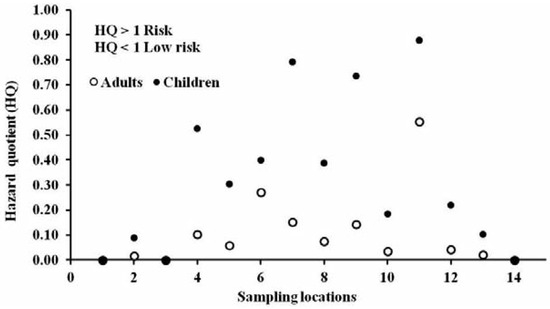
Figure 3.
Health risk hazards of polychlorinated biphenyls for adults and children through soil ingestion.
Discussion
Concentrations and possible sources
The PCBs contamination levels in soils from Delhi were much lower than soil quality guide- lines (1.3 mg/kg or 1300 ng g−1).[27] The results of this study were similar to observations reported for urban soils from Kathmandu,[7] urban soils of Beijing[28] and from Tibet.[29] However, the concentrations of PCBs in Delhi soils were lower than those of Vietnam,[30] Switzerland,[31] Romania,[32] China,[33] San Felipe, Nuevo Mercurio, Zacatecas, Mexico,[34] Moscow[35] and Guangdong Province, South China,[36] but higher than PCBs reported in soils from Turkey.[37]
The PCB patterns show that the low molecu- lar weighted PCBs were major contributors (60%) compared to high molecular weight PCBs (with 40%). Low molecular weight PCBs were primarily used in electrical equipments while high molecular weight PCBs were main- ly used as additives in various applications.[38] PCBs had never been produced in India, but are used in industrial applications.[39] Possible sources of PCBs releases in the study area may be from electronic and electrical waste recy- cling and industrial emission depositions. During the burning of different mixtures of waste content, garden waste, paper, plastics, PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and painted wood may produce relatively large amounts of dioxin like- PCBs.[40,41,42]
Risk estimates
To ensure public health safety, a tolerable daily intake (TDI) has been set by internation- al agencies. The TDI is the amount of intake per kg of body weight per day of a chemical substance suspected of having adverse health effects when absorbed into the body over a long period of time. The joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives[43] recommended a TDI of 1.0 pg TEQ kg−1d−1 for acute, sub- chronic and chronic exposures to dioxins. The European Commission[44] established an accept- able weekly intake of 14 pg WHO-TEQ/kg body weight for dioxins and 12 pg dioxin-like PCBs. The Japanese government[45] established the TDI of dioxins at 4 pg-TEQ kg−1d−1.
The observed LADD of TEQ intake for adults (1.05×10−10 mg TEQ kg−1 d−1) and children (5.43×10−10 mg TEQ kg−1 d−1) are much lower than recommended acceptable daily intake. The acceptable risk distribution is equal or lower than 10−6 for carcinogens and may be up to 10−4. The observed ILCR (10−8-10−5) and HQ values less than the acceptable risk level (HQ=1) (Figure 3) suggests minimum risk to the adults and children due to exposure to PCBs through urban soils in Delhi.
Conclusions
Low concentrations of PCBs in Delhi soils, and subsequently their intake values, were lower than those established in international guidelines. Therefore, estimates of cancer and non-carcinogenic risk through soil ingestion were low, indicating no harmful effects on the population of Delhi. In future, it may be useful to conduct more intensive assessments for persistent organic pollutants, in response to human health and environmental concerns.
Author Contributions
the authors contributed equally.
Acknowledgments
the authors express their sincere gratitude to the Chairman and Member Secretary of the Central Pollution Control Board for encouragement to conduct the study on POPs. Authors also thank Mr. SK Singh and Ms. Richa Gaur for their help during sample processing and analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
the authors declare no potential conflict of interests
References
- ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry). Toxicological profile for polychlorinated biphenyls (update); US Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Harrad, S.J.; Sewart, A.P.; Al cock, R.; Boumphrey, R.; Burnett, V.; Duarte-Davidson, R.; et al. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in the British environment: sinks sources and temporal trends. Environ Pollut 1994, 85, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harner, T.; Kylin, H.; Bidleman, T.F.; Halshall, C.; Strachan, W.M.J.; Barrie, L.A.; et al. Polychlorinated naphthalene and coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls in arctic air. Environ Sci Technol 1998, 32, 3257–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewen, M.D.; Sharma, S.; Tomy, G.; Wang, F.; Bullock, P.; Wania, F. Persistent organic pol- lutants and mercury in the Himalaya. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manage 2005, 8, 223–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, H.S. Polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in soils and lichens from King George Island South Shetland Islands Antarctica. Antarct Sci 2010, 22, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanathan, G.; Isobe, T.; Subramanian, A.; Asante, K.A.; Natarajan, S.; Palaniappan, P.; et al. Contamination status of polychlorinat- ed biphenyls and brominated flame retar- dants in environmental and biota samples from India. In Interdisciplinary studies on environmental chemistry-environmental pollution and ecotoxicology; Kawaguchi, M., Misaki, K., Sato, H., Yokokawa, T., Itai, T., Nguyen, M.T., et al., Eds.; TER- RAPUB: Tokyo, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Aichner, B.; Glaser, B.; Zech, W. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinat- ed biphenyls in urban soils from Kathmandu, Nepal. Organic Geochem 2007, 38, 700–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachada, A.; Lopes, L.V.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Biasioli, M.; Grcman, H.; Otabbong, E.; et al. The variability of polychlorinated biphenyls levels in urban soils from five European cities. Environ Pollut 2009, 157, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcke, W.; Krauss, M.; Safronov, G.; Fokin, A.D.; Kaupenjohann, M. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in soils of the Moscow region: concentrations and small-scale distribution along an urban-rural transect. Environ Pollut 2006, 141, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.B.; Luo, Y.M.; Wong, M.H.; Zhao, Q.G.; Zhang, G.L. Concentrations and possible sources of polychlorinated biphenyls in the soils of Hong Kong. Geoderma 2007, 138, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, M.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Michael, D.; Mike, D.; William, V.; Mark, F.; et al. The 2005 World Health Organization re-evaluation of human and mammalian toxic equiva- lency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol Sci 2006, 93, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.G.; Yang, M.; Jia, H.L.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.F. Levels distributions and profiles of poly- chlorinated biphenyls in surface soils of Dalian, China. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.L.; Li, Y.F.; Sun, D.Z.; Qi, H. Polycyclic Aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinat- ed biphenyls in topsoils of Harbin, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 2009, 57, 670–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, K.; Ramu, K.; Kajiwara, N.; Sinha, R.K.; Tanabe, S. Organochlorine pesticides poly- chlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in Irrawaddy dolphins from India. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 2005, 49, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Chakraborty, P.; Li, J.; Sampathkumar, P.; Balasubramanian, T.; Kathiresan, K.; et al. Passive atmospheric sampling of organochlorine pesticides polychlorinated biphenyls and polybromi- nated diphenyl ethers in urban rural and wetland sites along the coastal length on India. Environ Sci Technol 2008, 42, 8218–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanathan, G.; Subramanian, A.; Someya, M.; Sundaryanto, A.; Isobe, T.; Takahashi, S.; et al. Persistent organochlorines in human breast milk from major metropolitan cities in India. Environ. Pollution 2008, 157, 148–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Kumar, S.; Gaur, R.; Goel, G.; Mishra, M.; Singh, S.K.; et al. Persistent organochlo- rine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in intensive agricultural soils from North India. Soil Water Res 2011, 6, 190–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Mishra, M.; Goel, G.; Gaur, R.; Singh, S.K.; Prakash, D.; et al. Distribution and eco- toxicological risk assessment of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in river sedi- ments from Delhi, India. Adv Life Sci Technol 2011, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, B.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, C.S. Distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls in surface waters of various sources from National Capital Region Delhi, India. J Natural Sci Res 2012, 2, 26–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, B.; Singh, S.K.; Mishra, M.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, C.S. Assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in water samples from Yamuna River. J Xenobiotics 2012, 2, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DoEF (Department of Environment and Forest). State of environment report for Delhi 2010. New Delhi: Department of Environment and Forest - Secretariat; 2010. Available online: http://www.delhi. gov.in/wps/wcm/connect/9e24b08042c3760 2aaafaa6c8168d2a2/SoE+Delhi+2010.pdf? MOD=AJPERES&CACHEID=9e24b08042c 37602aaafaa6c8168d2a2.
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Method 3545, Pressurized fluid extraction EPA SW-846; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Morra, P.; Bagli, S.; Spadoni, G. The analysis of human health risk with a detailed pro- cedure operating in a GIS environment. Environ Int 2006, 32, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Risk assessment guid- ance for superfund human health evalua- tion manual (Part A). EPA 540-1-89-002; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). PCBs: cancer dose–response assessment and applica- tion to environmental mixtures. EPA 600- P-96-001F; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Regional screening level (RSL): Summary Table: updated 2011. Available online: http://www.epa. gov/region9/superfund/prg/index.html.
- CCME (Canadian Council of Ministers for the Environment). Canadian soil quality guidelines for the protection of environ- mental and human health, polychlorinated biphenyls (total); Canadian Council of Ministers for the Environment: Winnipeg, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, W.; Xia, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H. Distribution source and risk assessment of polychlori- nated biphenyls (PCBs) in urban soils of Beijing, China. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 732–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Altitude dependence of polychlori- nated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominat- ed diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in surface soil from Tibetan Plateau, China. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 1498–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishida, M.; Imamura, K.; Maeda, Y.; Lan, T.T.N.; Thao, N.T.P.; Viet, P.H. Distribution of persist- ent organic pollutants and polycyclic aro-matic hydrocarbons in sediment samples from Vietnam. J Health Sci 2007, 53, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Erika, G.; Markus, Z.; Thomas, D.B.; Andre, D. Correlation of PCDD/F and PCB concentrations in soil samples from the Swiss soil monitoring network (NABO) to specific parameters of the observation sites. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, D.; Simona, C.; Dirtu, A.; Mocanu, R.; Vaeck van, L.; Covaci, A. Occurrence of organochlorine pesticides and polychlori- nated biphenyls in soils and sediments from Eastern Romania. Int J Environ Anal Chem 2006, 86, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Z.J.; Cui, H.; Xu, Y.; Tan, F.X. Dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls contamination and distribution in soils from the Modern Yellow River Delta, China. Soil Sediment Contam 2009, 18, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costilla-Salazar, R.; Trejo-Acevedo, A.; Rocha-Amador, D.; Gaspar-Ramirez, O.; Diaz- Barriga, F.; Perez-Maldonado, I.N. Asses- sment of polychlorinated biphenyls and mercury levels in soil and biological sam- ples from San Felipe, Nuevo Mercurio Zacatecas, Mexico. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 2011, 86, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelepchikov, A.A.; Brodskii, E.S.; Feshin, D.B.; ZhilNikov, V.G.; Mir-Kadyrova, E.; Ya Balashova, S.P. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins dibenzofurans and biphenyls in soils of Moscow. Eurasian Soil Sci 2011, 44, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, C.L; Li, J.; Yin, H.; Li, X.D.; Zhang, G. Characterization and risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls in soils and vegetations near an electronic waste recy- cling site South China. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salihoglu, G.; Salihoglu, N.K.; Aksoy, E.; Tasdemir, Y. Spatial and temporal distribu- tion of polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) concentrations in soils of an industrialized city in Turkey. J Environ Manage 2011, 92, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Ding, J.; Zhao, X.S.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, L.Y.; Ma, W.L.; et al. Spatial and seasonal variation of polychlorinated biphenyls in Songhua River, China. Environ Geochem Health 2011, 33, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockholm Convention. National imple- mentation plans guidance on persistent organic pollutants (POPs), 2012. Châtelaine, Switzerland: Secretariat of the Stockholm Convention; 2012. Available online: http://chm.pops.int/.
- Wevers, M.; De Fre, R.; Desmedt, M. Effect of backyard burning on dioxin deposition and air concentrations. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Ottesen, R.T. Levels of diox-ins and furans in urban surface soil in Trondheim, Norway. Environ Pollut 2008, 152, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.U; Kim, J.G; Masunaga, S.; Kim, K.S. Source identification and concentration distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls in environmental media around industrial complexes. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 2009, 83, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JECFA (Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives). Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants (57th report), 2001. Report Series 909; World Health Organization: Geneva, 2001; pp. 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Amending regula- tion (EC) No. 466/2001, Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in food- stuffs as regards dioxins and dioxin-like PCBs, EC No. 199/2006 of 3 February 2006. Official Journal L 32/34, 4/2/2006. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/ LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2006:032:0034:00 38:EN:PDF.
- Government of Japan. Dioxin. Tokyo: Office of Dioxins Control, Environmental Management Bureau, Ministry of the Environment, Government of Japan; 2009. Available online: http://www.env.go.jp/en/ chemi/dioxins/brochure2009.pdf.
© Copyright B. Kumar et al., 2012. Licensee PAGEPress, Italy. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 3.0 License (CC BY-NC 3.0).