Distribution of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and Hexachlorocyclohexane in Urban Soils and Risk Assessment
Abstract
:Introduction
Material and Methods
Study area and sampling
Chemicals and solvents
Sample extraction
Chromatographic column cleanup
Instrumental analysis
Analytical quality control
Assessment of human health risk
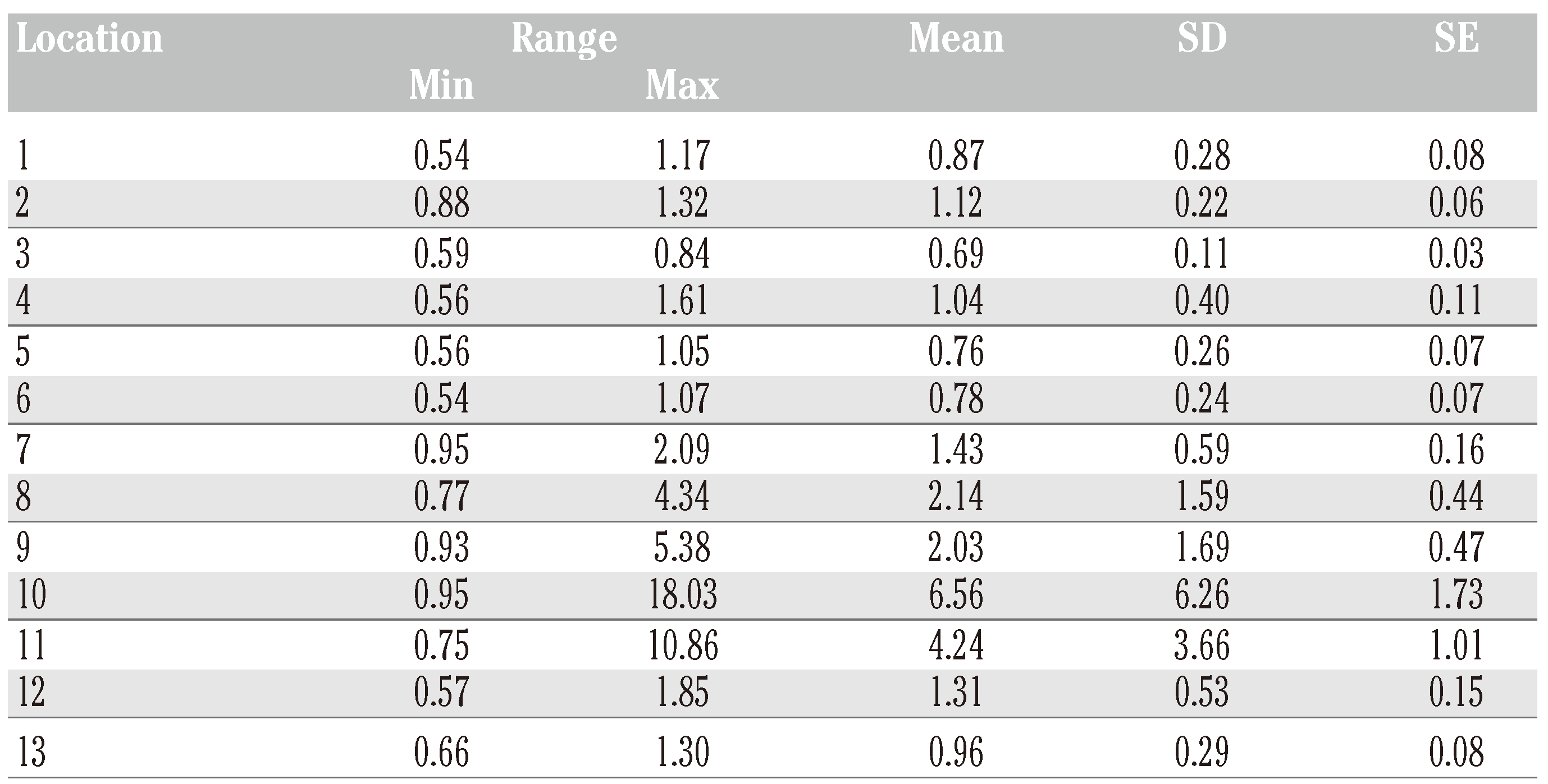
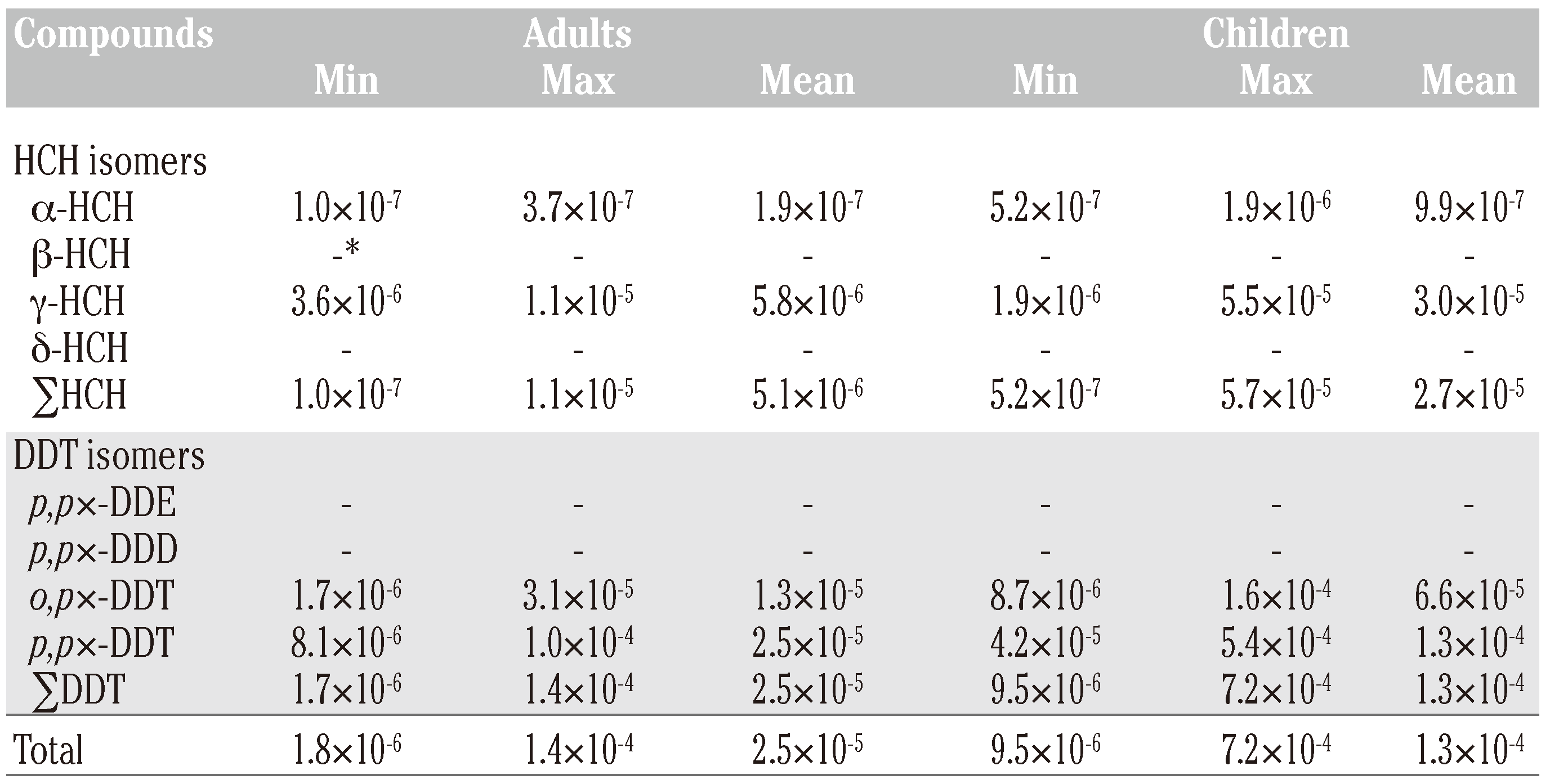
Results
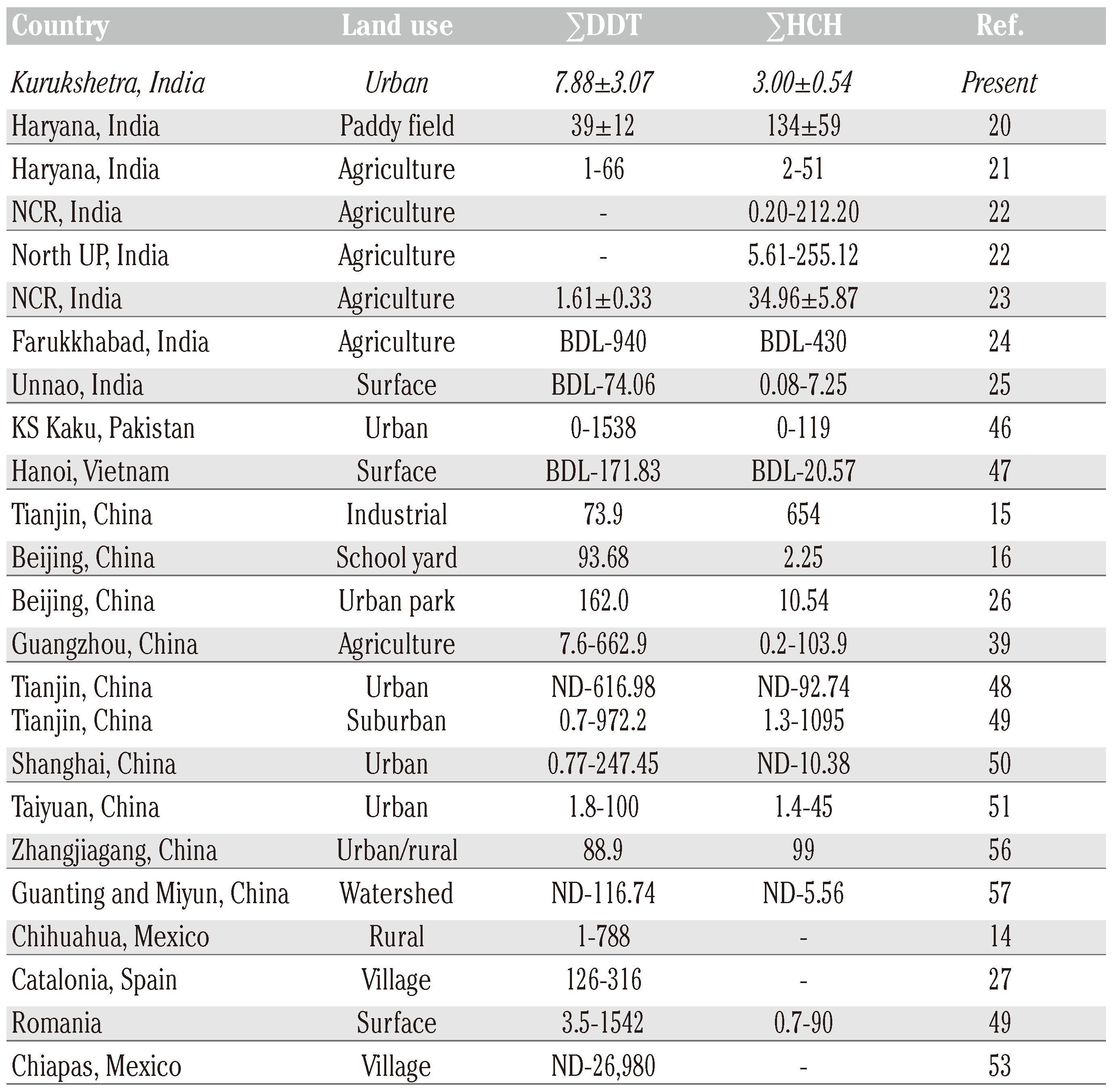
Discussion
Possible source identification of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethanes and hexachlorocyclohexanes
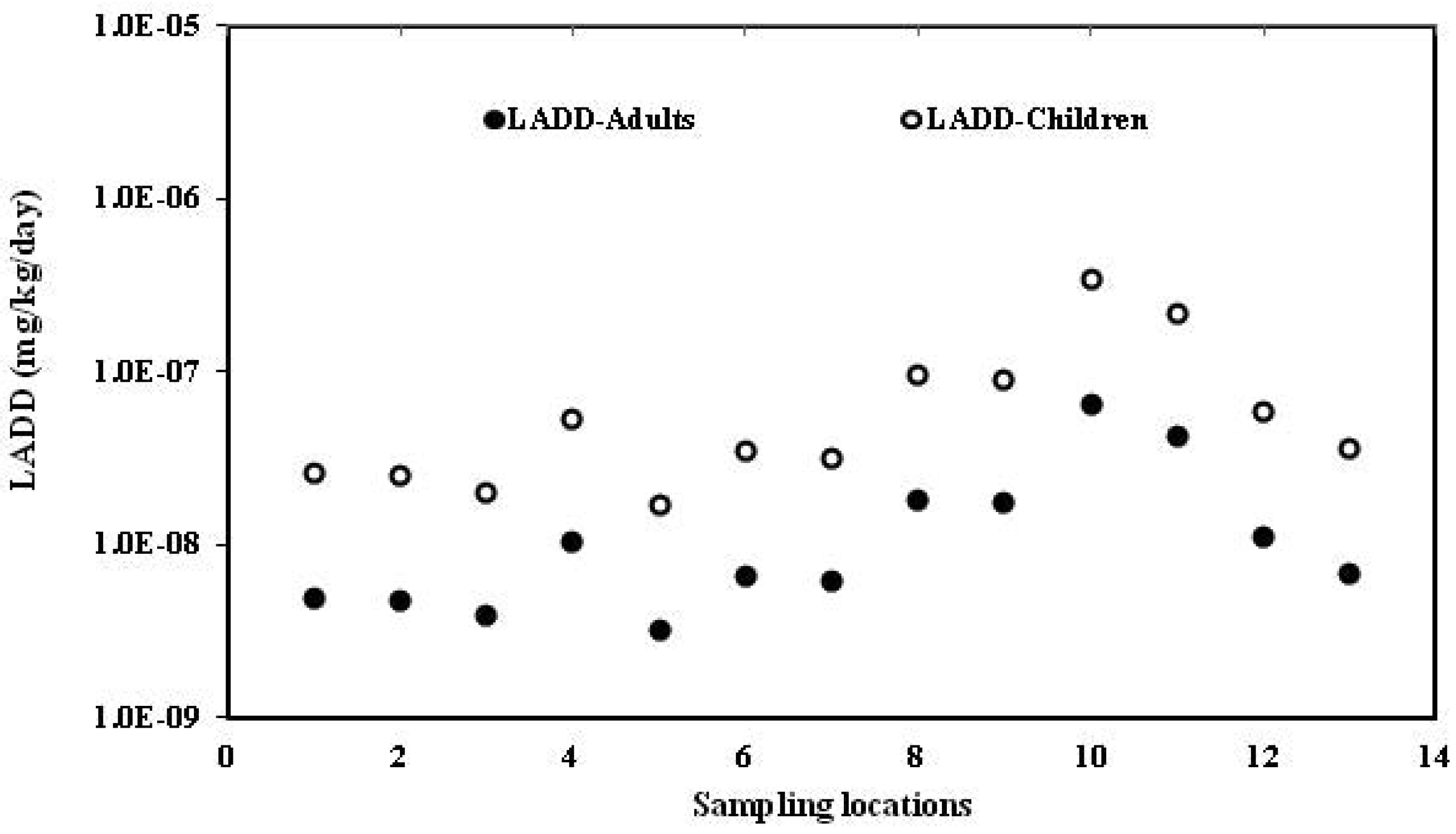
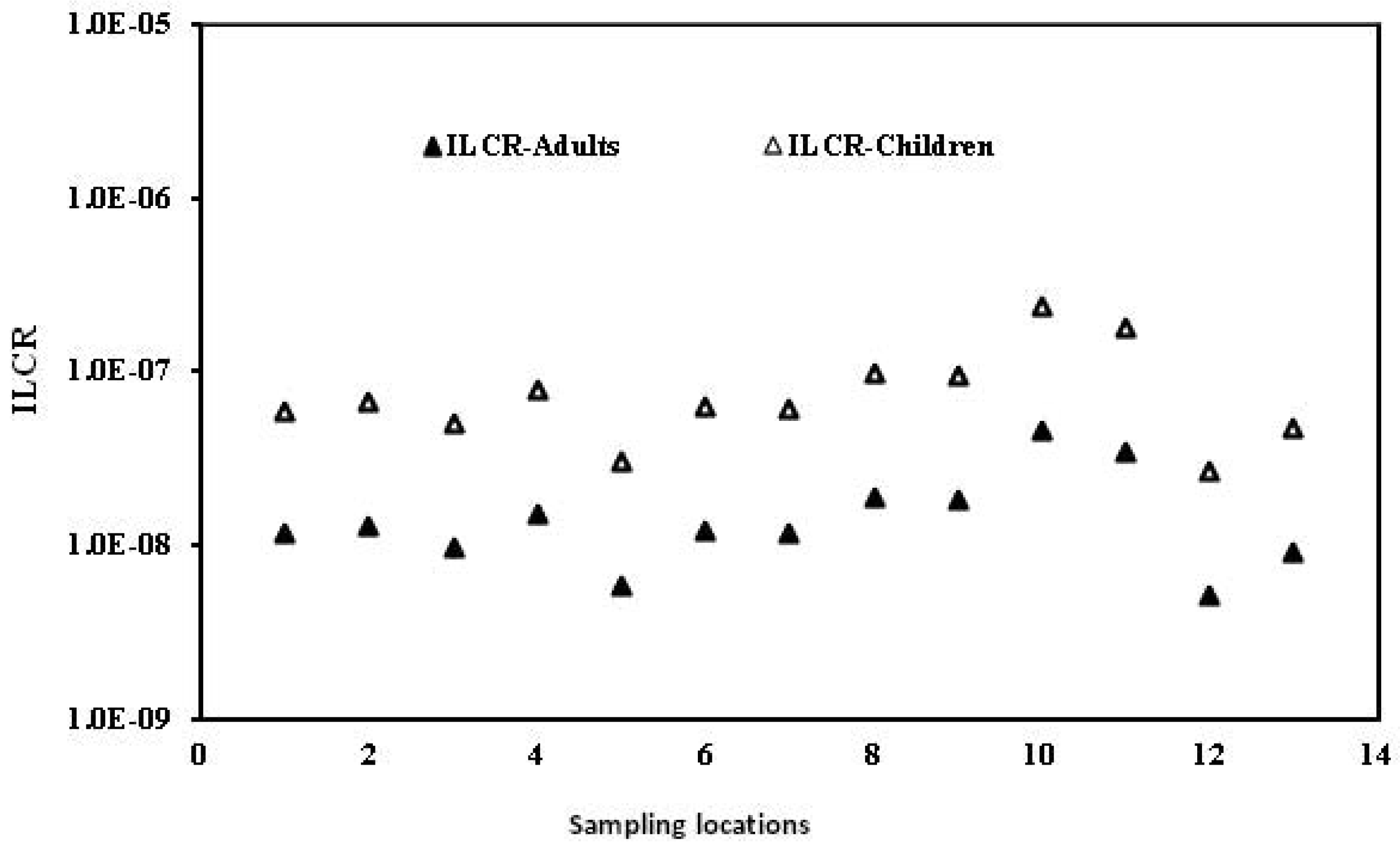
Human health risk assessment of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethanes and hexachlorocyclohexanes
Ecological risk assessment of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethanes and hexachlorocyclohexanes
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wania, F.; Mackay, D. Tracking of distribu- tion of persistent organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme). Report of the Conference of the Parties of the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants on the work of its fourth meeting UNEP/ POPS/COP4/38. Available online: http://chm.pops.int/Convention/ConferenceoftheParties(COP)/Meetings/COP4/COP4Documents/tabid/531/ctl/Download/mid/1874/Default.aspx?id=401 (accessed on 8 May 2009).
- Iwata, H.; Tanabe, S.; Sakai, N.; Nishimura, A.; Tatsukawa, R. Geographical distributions of persistent organochlorines in air, water and sediments from Asia and Oceania and their implications for global redistribution from lower latitudes. Environ. Poll. 1994, 85, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shahawi, M.S.; Hamza, A.; Bashammakh, A.S.; Al-Saggaf, W.T. An overview on the accu- mulation, distribution, transformations, toxicity and analytical methods for the monitoring of persistent organic pollu- tants. Talanta 2010, 80, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances Disease Registry). Toxicological profile for, D.D.T.; DDE; DDD; US Public Health Service: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- ATSDR Toxicological profile for hexa- chlorocyclohexanes. US Department of Health & Human. Services Public. Health Service Agency for Toxic. Substances and Disease Registry; 2005. Available online: http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp43.
- Ejaz S, Akram W, Lim CW, Lee JJ, Hussain Endocrine disrupting pesticides: A lead-ing cause of cancer among rural people in Pakistan. Exper Oncol. 2004, 26, 98–105.
- Nakata H, Kawazoe M, Arizono K, Abe S, Kitano T, Shimada H, et al. Orga-nochlo- rine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyl residues in foodstuffs and human tissues from China: status of con- tamination, historical trend, and human dietary exposure. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 43, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferencz, L.; Balog, A. A pesticide survey in soil, water and foodstuffs from central Romania. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2010, 5, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Bidleman, T.F.; Leone, A.D.; Wong, F.; Van, V.L.; Szeto, S.; Ripley, B.D. Emission of legacy chlorinated pesticides from agricultural and orchard soils in British Columbia, Canada. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (NRC). Pesticides in the diets of infants and chil- dren; National Academic Science Research Council: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Morra, P.; Bagli, S.; Spadoni, G. The analysis of human health risk with a detailed pro- cedure operating in a GIS environment. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damalas, C.A.; Eleftherohorinos, I.G. Pesticide exposure, safety issues and risk assessment indicators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2011, 8, 1402–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dıaz-Barriga, M.F.; Trejo-Acevedo, A.; Betanzos, A.F.; Espinosa-Reyes, G.; Alegrıa- Torres, J.A.; Perez Maldonado, I.N. Assessment of DDT and DDE levels in soil, dust, and blood samples from Chihuahua, Mexico. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 62, 351–358. [Google Scholar]
- Li J, Lu YL, Shi YJ, Wang TY, Wang GA, Luo W, et al. Environmental pollution by per- sistent toxic substances and health risk in an industrial area of China. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Qin, X.; Xu, X. Residues of organochlorine pesticides in surface soils from college school yards in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, M. Human exposures from dioxin in soil - a meeting report. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1991, 32, 205–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, P.W. Soils: their implications to human health. Sci. Total Environment 2002, 291, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Qi, S.; Li, X.; Peng, X. Concentrations, enantiomeric composi- tions, and sources of HCH, DDT and chlor- dane in soils from the Pearl River Delta, South China. Sci. Total Environment 2006, 372, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari B, Singh R, Madan VK, Kumar R, Kathpal TS. DDT and HCH compounds in soils, ponds, and drinking water of Haryana, India. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1996, 57, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, B.; Madan, V.K.; Kathpal, T.S. Status of insecticide contamination of soil and water in Haryana, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Om Prakash, Suar M, Raina V, Dogra C, Pal R, Rup Lal. Residues of Hexachlorocyclo- hexane isomers in soil and water samples from Delhi and adjoining areas. Curr. Sci. 2004, 87, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar B, Kumar S, Gaur R, Goel G, Mishra M, Singh SK, et al. Persistent organochlo- rine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in intensive agricultural soils from North India. Soil. Water Res. 2011, 6, 190–197. [Google Scholar]
- Agnihotri, N.R.; Kulshrestha, G.; Gajbhiye, V.T.; Mohapatra, S.R.; Singh, S.B. Organochlorine insecticide residues in agricultural soils of the Indo-Gangetic plain. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1996, 40, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Sinha, S. Persistent organochlorine pesticide residues in soil and surface water of northern Indo- Gangetic alluvial plains. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 125, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li XH, Wang W, Wang J, Cao XL, Wang XF, Liu JC, et al. Contamination of soils with organochlorine pesticides in urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferre-Huguet N, Bosch C, Lourencetti C, Nadal M, Schuhmacher M, Grimalt JO, et al. Human health risk assessment of envi- ronmental exposure to organochlorine compounds in the Catalan stretch of the Ebro River, Spain. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiros-Alcala L, Bradman A, Nishioka M, E-Harnly M, Hubbard A, E-McKone T, et al. Pesticides in house dust from urban and farmworker households in California: an observational measurement study. Environ. Health 2011, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Method 3545: SW-846; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dionex. Application Note 352; Dionex: Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Risk assessment guid- ance for superfund. Human health evalua- tion manual (Part A). EPA 540-1-89- 002; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Available online: http://www.epa.gov/ reg3hwmd/risk/human (accessed on 20 September 2012).
- Qui, X.H.; ZhuT; LiJ; Pan, H. S.; Li, Q.L.; Miao, G.F.; et al. Organochlorine pesticides in air around the Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Willett, L.; Ulrich, E.M.; Hites, H.A. Differential toxicity and environmental fates of Hexachlorocyclohexane isomers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2197–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.; Vallero, D.A.; Lewis, R.G. Factors influencing the distributionof lindane and other hexachlorocyclohexanes in the envi- ronment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 4373–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benezet, H.J.; Matsumura, F. Isomerization of (gamma)-BHC to (alpha)-BHC in the environment. Nature 1973, 243, 480–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaiyandi, M.; Shah, S. Evidence of photoi- somerization of hexachlorocyclohexanei- somers in the ecosphere. J. Environ. Sci. Health 1980, A19, 887–910. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Mu, D. Levels, seasonal varia- tions and sources of OCPs in ambient air of Guangzhou, China. Atm. Environ. 2008, 42, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Jia, J.; Wang, X. Occurrence and ordi- nation of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane- and hexachlorocyclohexane in agricultural soils fromGuangzhou, China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 54, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, T.M.; Beretta, M.; Costa, M.C. Ratio of DDT/DDE in the all Saints Bay, Brazil, and its use in environmental management. Chemosphere 1999, 38, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, W.; Cliath, M.M. Volatility of DDT and related compounds. J Agric Food Chem 1972, 20, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). DDT and its derivatives-environmental aspects, 1989. Environ Health Criteria 83. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1989.
- Atlas, E.; Giam, C.S. Ambient concentration and precipitation scavenging of atmos- pheric organic pollutants. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 1988, 38, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aislabie, J.M.; Richards, N.K.; Boul, H.L. Microbial degradation of DDT and its residues-a review. New Zeal J. Agric. Res. 1997, 40, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talekar, N.S.; Sun, L.T.; Lee, E.M.; Chen, J.S. Persistence of some insecticides in sub- tropical soils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1977, 25, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, J.H.; Malik, R.N. Occurrence and source identification of organochlorine pesticides in the surrounding surface soils of the Ittehad Chemical Industries Kalashah Kaku Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toan, V.D.; Thao, V.D.; Walder, J.; Schmutz, H.R.; Ha, C.T. Contamination by selected organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in sur- face soils in Hanoi, Vietnam. Bull. Environ. Conta Toxicol. 2007, 78, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv J, Shi R, Cai Y, Liu Y, Wang Z, Feng J, et al. Assessment of 20 organochlorine pesti- cides (OCPs) pollution in suburban soil in Tianjin, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.Y.; Mo, C.H.; Wu, Q.T.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Zeng, Q.Y. The status of soil contamination by semivolatile organic chemicals (SVOCs) in China: a review. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 389, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang YF, Wang XT, Jia Y, Wang F, Wu MH, Sheng GY, et al. Occurrence, distribution and possible sources of organochlorine pesticides in agricultural soil of Shanghai, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Cheng, H.X.; Liu, Y.H.; Xu, X.B. Levels and distribution of organochlorine pesticides in various media in a mega-city, China. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Huang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, W.; Gu, Z. Organochlorine pesticides in soils from a typical alluvial plain of the Yangtze River delta region, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 87, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebeca, I.M.; Diaz-Barriga, F.; Batres- Esquivel, L.E.; Perez-Maldonado, I.N. Assessment of the levels of DDT and its metabolites in soil and dust samples from Chiapas, Mexico. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 86, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME). A protocol for the derivation of environmental and human health soil quality guidelines; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME). Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME). Canadian soil qual- ity guidelines for the protection of envi- ronmental and human health: Summary tables Updated September, 2007. In Canadian environmental quality guide- lines; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Winnipeg, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Buckman, MF. NOAA screening quick refer- ence tables (SQuiRTs), HAZMAT REPORT 99-1 (updated Feb 2004), Seattle Washington Coastal Protection and Restoration Division, National Oceano- graphy and Atmospheric Administration; 1999. p 12.
- Hu W, Lu Y, Wang G, Wang T, Luo W, Shi Y, et al. Organochlorine pesticides in soils around watersheds of Beijing reservoirs: A case study in Guanting and Miyunreservoirs. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 82, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2012 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, B.; Mishra, M.; Verma, V.K.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, C.S. Distribution of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and Hexachlorocyclohexane in Urban Soils and Risk Assessment. J. Xenobiot. 2013, 3, e1. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2013.e1
Kumar B, Mishra M, Verma VK, Kumar S, Sharma CS. Distribution of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and Hexachlorocyclohexane in Urban Soils and Risk Assessment. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2013; 3(1):e1. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2013.e1
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Bhupander, Meenu Mishra, Virendra Kumar Verma, Sanjay Kumar, and Chandra Shekhar Sharma. 2013. "Distribution of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and Hexachlorocyclohexane in Urban Soils and Risk Assessment" Journal of Xenobiotics 3, no. 1: e1. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2013.e1
APA StyleKumar, B., Mishra, M., Verma, V. K., Kumar, S., & Sharma, C. S. (2013). Distribution of Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and Hexachlorocyclohexane in Urban Soils and Risk Assessment. Journal of Xenobiotics, 3(1), e1. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2013.e1




