Abstract
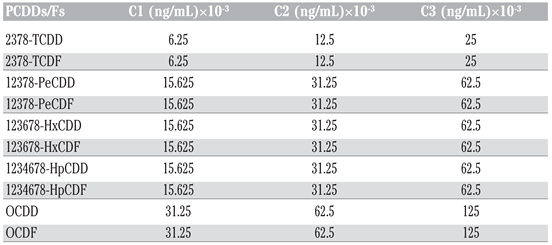
In this study, we assessed in vitro the effects of PCDD/Fs on the NK-like cell activity in Eisenia andrei earthworms using flow cytometry for analysis. NK-like coelomocytes isolated from E. andrei and used as effectors were exposed to various concentrations of PCDDs/Fs mixture, C1 (6.25 × 10−3 ng 2378-TCDD/mL), C2 (12.5 × 10−3 ng 2378-TCDD/mL) and C3 (25 × 10−3 ng 2378-TCDD/mL), before adding them to human tumoral cells (K562) used as targets. We evaluated the percentage of targets lysed by Nk-like cells. The results showed a significant stimulation of the NK-like activity at C3 when PCDD/Fs were not removed from effectors before contact with targets, while no effects were noted when the effectors were washed (PCDD/Fs removed) or fixed. Assessment of the viability of the targets (K562), exposed alone and separately from effectors, to the three concentrations of PCDD/Fs, C1, C2 and C3, showed that all these concentrations were cytotoxic for K562. Results suggest that PCDD/Fs concentrations tested in this assay may be considered too low to induce suppressive effects on the immune function such as the NK-like activity in E. andrei earthworms.
Introduction
Earthworms play an important role in soil formation processes and in maintaining soil structure and fertility. They are interesting soil bio-indicators due to their ability to ingest organic and inorganic particles. [1] Currently, Eisenia andrei is recommended in standardized acute toxicity protocols [2] because of their sensitivity and ability to concentrate some insecticides, [3,4] heavy metals [5,6,7] and persistent organic pollutants (POPs) [8] in their body tissue. Moreover, this species was used to evaluate the sub-lethal effects of several xenobiotics. [9] In addition, numerous studies of the action of chemicals on a variety of acute toxic endpoints and subchronic-chronic processes, have demonstrated that a spectrum of chemicals alter the immune system of earthworms. [10,11,12,13,14] Thus, the immune system’s potential was defined as a target organ system for use in assessing the toxicity of exposure to xenobiotics. [15] Because the immune responses are important host defense mechanisms, their modulation may result in an increased incidence of infections that could influence the survival of individuals and their populations. [15] Subcellular, cellular and organismal immunological indicators were previously used as assessment tools. Recently, there has been specific interest in effector molecules in antimicrobial and cytotoxic responses. Published data demonstrated cellular cytotoxic effects of coelomocytes in xenogeneic and allo-geneic culture of earthworm coelomocytes, as well as coelomocyte cytotoxicity against mammalian tumor cell lines. [16,17] Cell-mediated cytotoxicity studies also demonstrated that some persistent organic pollutants, such as PCBs [18] and PAHs, [19] exerted immunosuppressive effects on NK-like effector cells.
To date, there are few reports in literature describing the immunotoxicity of PCDDs/Fs in earthworms or in other invertebrate model; studies have only been carried out on mammalian models. [20] It is well recognized that PCDDs and PCDFs enter the environment as by-products of combustion processes, and represent the most toxic anthropogenic chemicals in the environment associated to their stability, lipophilicity, bioaccumulation and high persistence. In addition, numerous studies have reported that prolonged exposure to TCDD presents adverse health effects, including immunotoxicity, neurotoxicity, hepatotoxicity and carcinogenesis. [21,22,23,24,25] Moreover, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) evaluated TCDD as a Group 1 carcinogen, i.e. a human carcinogen. [26,27,28] Environmental exposure concentrations of 1 ng 2378-TCDD/g soil were considered a level of concern for causing cancer. [29] Thus, the presence of these toxic contaminants in soils may have direct harmful effects to the earth’s ecosystem.
The objective of our study was to investigate, in vitro, the effects of a mixture of PCDDs/Fs on the NK-like cell activity of E. andrei earthworm coelomocytes to lyse human tumor cells (K562), using flow cytometry for analysis.
Materials and Methods
Reagents
The mixture of PCDDs/Fs in nonane solution was obtained from Wellington laboratories (Ontario, Canada) and stored at 1°C. Dimethyl sulfoxide 99.5% (DMSO) was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (USA). RPMI 1640, containing 25 mM HEPES buffer, L-glutamine and sodium bicarbonate, was supplemented with 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin. K562 (Sigma Aldrich) was cultured in this complete RPMI. The 3, 3’-dioctadecyloxacarbocyanine (DiO) was dissolved in DMSO to yield 3 mM. A stock solution of propidium iodide (PI) of 1 mg/mL in water was prepared. Purified water was obtained from a Milli-Q water purification system.
Earthworms
The E. andrei earthworms were initially purchased from the Carolina Biological Supply (Burlington, NC, USA) and were used to establish the laboratory culture. Prior to the experiment, the animals were maintained in earthworm bedding (Magic Products, Amherst Junction, WI, USA) at 20±1°C, 70-80% (w/w) moisture, a 16:8 h light:dark cycle, and fed once a week with cereal (Magic Worm Food, Magic Products).
Cell extrusion
Before the experiments, the earthworms were placed for 24 h on moist Whatman filter paper in Petri dishes [30] to extract ingested soil prior to cell extrusion. Six purged earthworms were used to measure the NK-like cell activity, and the assay was carried out in duplicate. A single worm was inserted into a 15 mL tube containing 3 mL of Lumbricus balanced salt solution (LBSS) composed of 1.5 mM NaCl, 4.8 mM KCL, 1.1 mM MgSO4.7H2O, 0.4 mM KH2PO4, 0.3 mM Na2PO4.7H2O, 3.8 mM CaCl2, and 4.3 mM NaHCO3. [12,31,32] Coelomocytes were extracted using an electrical extrusion method which consists of submitting the liquid medium to a 6 V current (lantern battery) for 20-30 s using aluminium wires. [13] The worm was then removed from the tube and the solution was gently shaken.
Cell yield and initial cell viability were determined by diluting 50 μL of cell suspension with 50 µL of 0.4% trypan blue (Sigma Chemical Co. St. Louis, MO, USA). This mixture was placed into an improved Neubauer hemacytometer and examined under the microscope (Table 1). [12,13]

Table 1.
Mean values of worm weights, cell yield and cell viability.
Preparation of effector cells
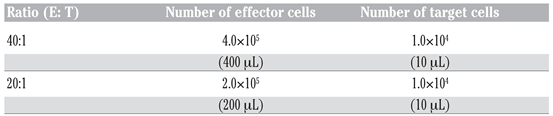
Effector cells were prepared according to Brousseau et al. [32] The coelomocyte concentration was adjusted in supplemented RPMI at 1×106 cells/mL and the dilutions were prepared according to the respective effector:target (E: T) ratios needed (Table 2).

Table 2.
Effector and target cell ratios.
Preparation of target cells
The target cells were prepared according to Brousseau et al. [32] Briefly, after 2-3 days culture, the concentration and viability of the K562, at exponential phase, were determined. The viability measured was greater than 95% (the condition in which the test could continue). The cells (1×107) were then centrifuged at 300×g for 10 min at room temperature to pellet. The supernatant and loosened pellets were gently discarded using a Pasteur pipette. Aliquots of 10 μL of 3 mM DiO were placed into polystyrene tubes. Then 1 mL of the K562 cells was added forcefully to disperse the dye (DiO). The tubes were incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 20 min, then washed twice with RPMI and the cells were resuspended in RPMI at a concentration of 1×106 cells/mL.
Exposure protocol
To establish the in vitro dose-response curves, three series of glass tubes containing the effector cell suspension (each ratio separately) were exposed to three different dilutions of a PCDDs/Fs mixture, C1, C2 and C3 (Table 3), respectively. These dilutions were made in DMSO (final concentration 0.004% per tube). Therefore, a set of tubes containing coelomocytes with DMSO (vehicle) was added as control. Negative controls receiving no PCDD/Fs were included along the test with controls, which received DMSO (without PCDD/Fs) to evaluate any effect due to the solvent (vehicle). Effector cells were exposed for 3 h to PCDDs/Fs and then the target cells were added to measure the NK-like cell activity. Effectors and targets were incubated together in the dark for another 3 h at ratios of 40:1 and 20:1 (Table 2). After 3 h of incubation, 15 μL of PI (1 mg/mL) was added to each tube followed by a centrifugation at 1000×g for 30 s to pellet the cells. The tubes were then incubated in the dark for 1 h before flow cytometric analysis. To identify and understand the effects of the contaminated cell washing before contact with target cells, we carried out two experiments. In the first test, the contaminated effector cells were not washed (PCDD/Fs were not removed) and were put directly in contact with K562. The second test consisted of washing the effector cells twice with RPMI before contact with K562. Also, another test was added to understand whether chemical particles not eliminated by cells and present in cell suspension can exert effects on K562. So, effector cells were fixed with a fixation solution composed of 37% formaldehyde and sodium azide, before being added to K562. In parallel with these tests, the effects of PCDD/Fs mixtures on the viability of the target cells (K562) were studied separately.

Table 3.
Final concentrations of PCDD/Fs in tubes before incubation for 3 h.
Evaluation of NK-like activity
In order to evaluate the effects of PCDD/Fs on NK-like cell activity, flow cytometry was used to determine lysis of human erythroleukemic tumor cell line (K562). This method uses two fluorescent dyes to discriminate between effectors and target cells, and between live and dead target cells. DIO, green fluorescent dye, was used to label the membranes of K562, while PI (red fluorescent dye) was added during the assay when K562 membranes were disrupted by effectors. Data were acquired using a FACScalibur (Becton Dickinson, San José, USA) flow cytometer, and analyzed by the CellQuest Pro software (Becton Dickinson) to determine target cell death. A minimum of 5000 events was acquired for each sample. [32] Results were expressed as percentage of target cell (K562) lysis.
Statistical analysis
Data were expressed as arithmetic means±standard deviations. Statistical significances of differences among treatments were determined by ANOVA one-way followed by Tukey HSD post hoc test for specific comparison of means (P<0.05), significantly different from the vehicle control: *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001. Statistica software, Version 6.0 (StatSoft, Tulsa, OK, USA) was used.
Results
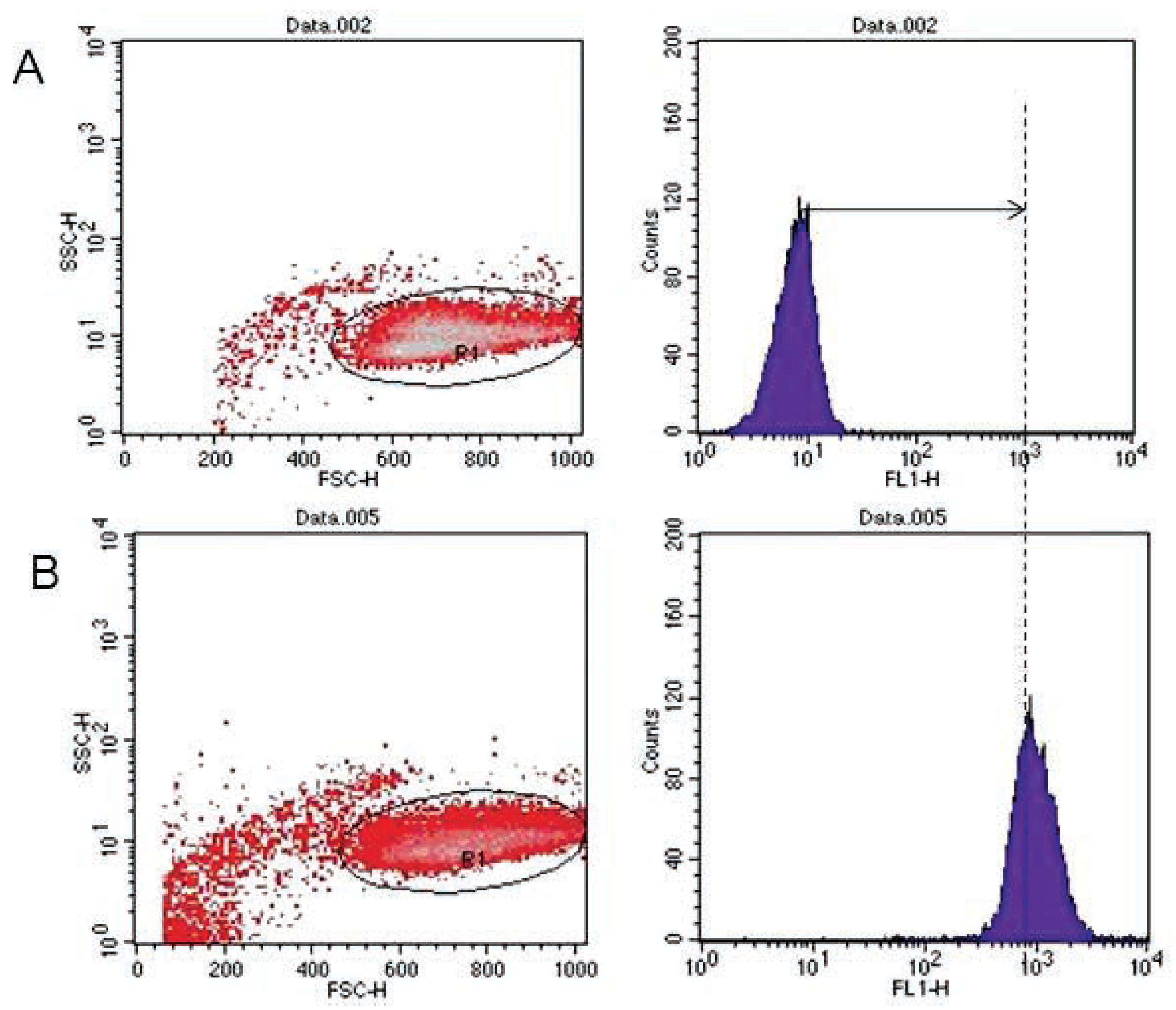
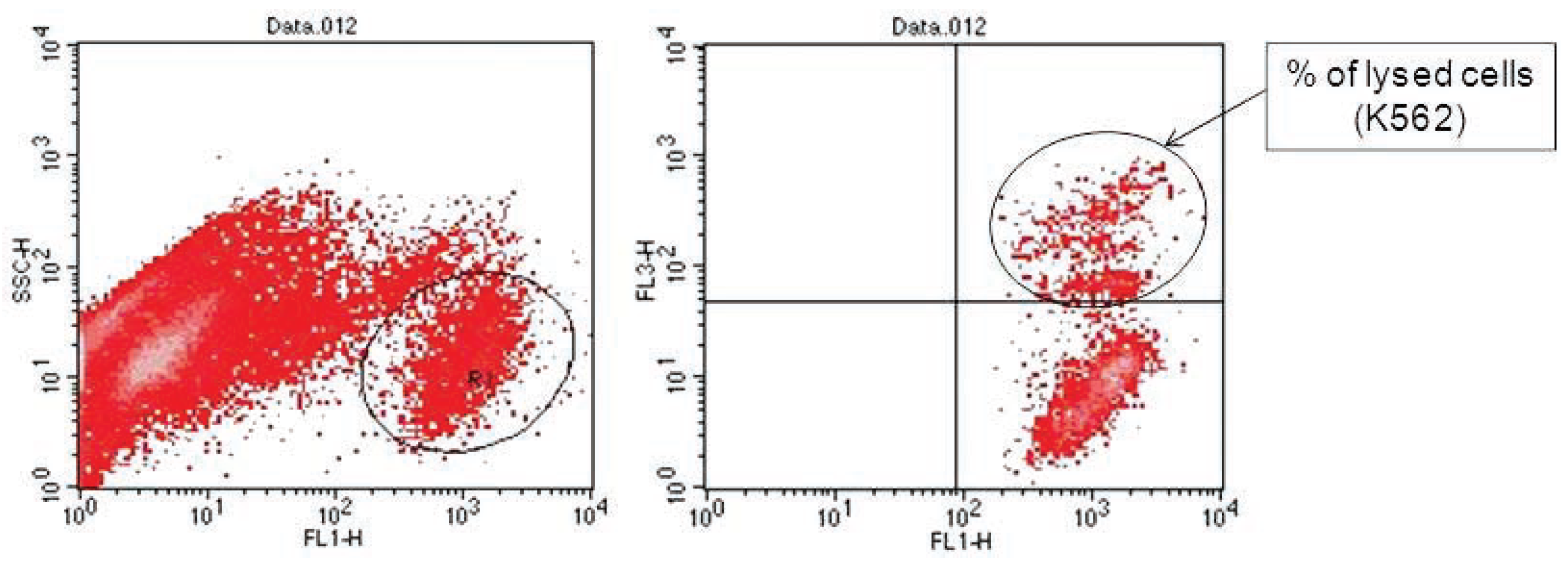
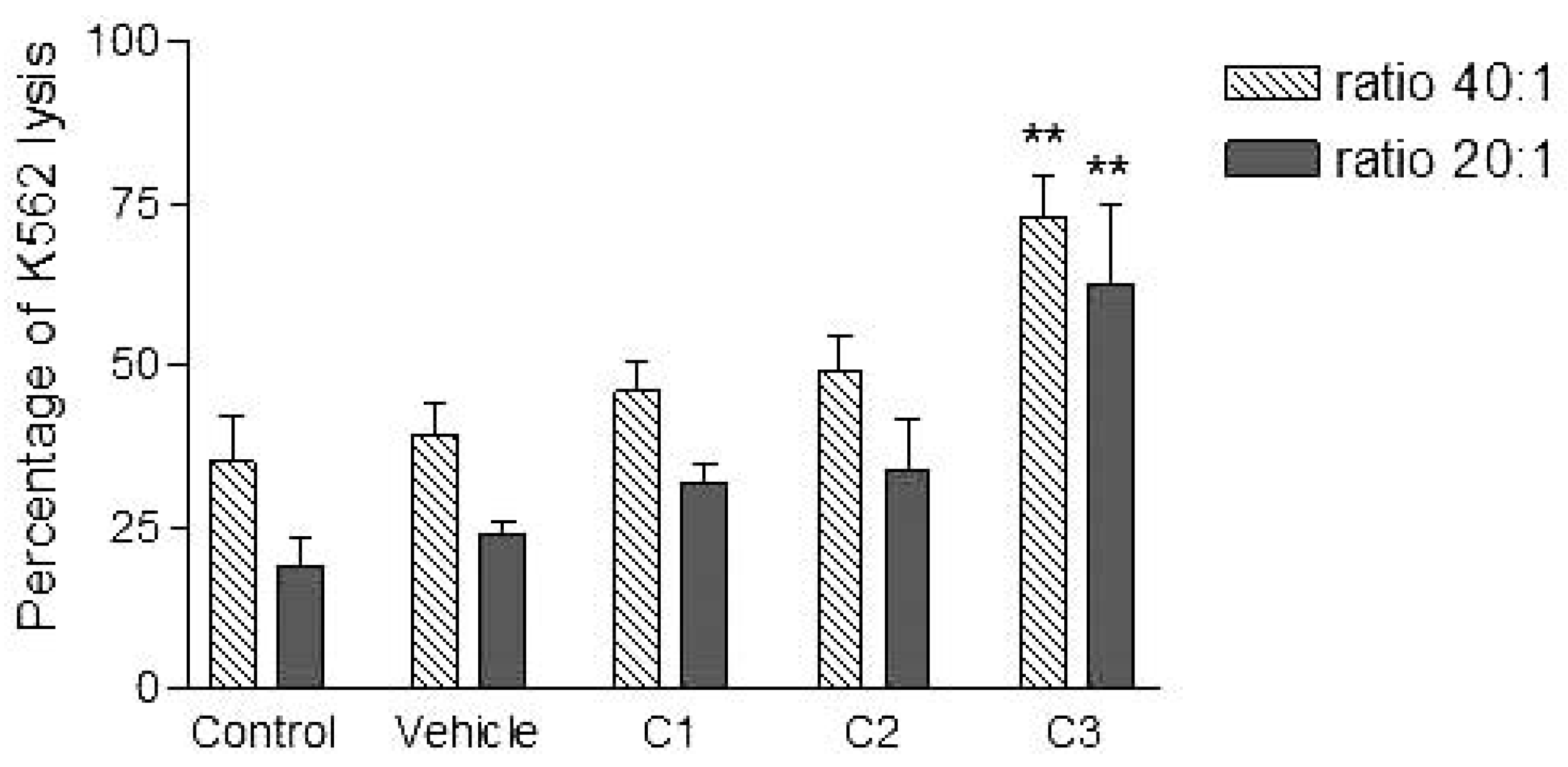
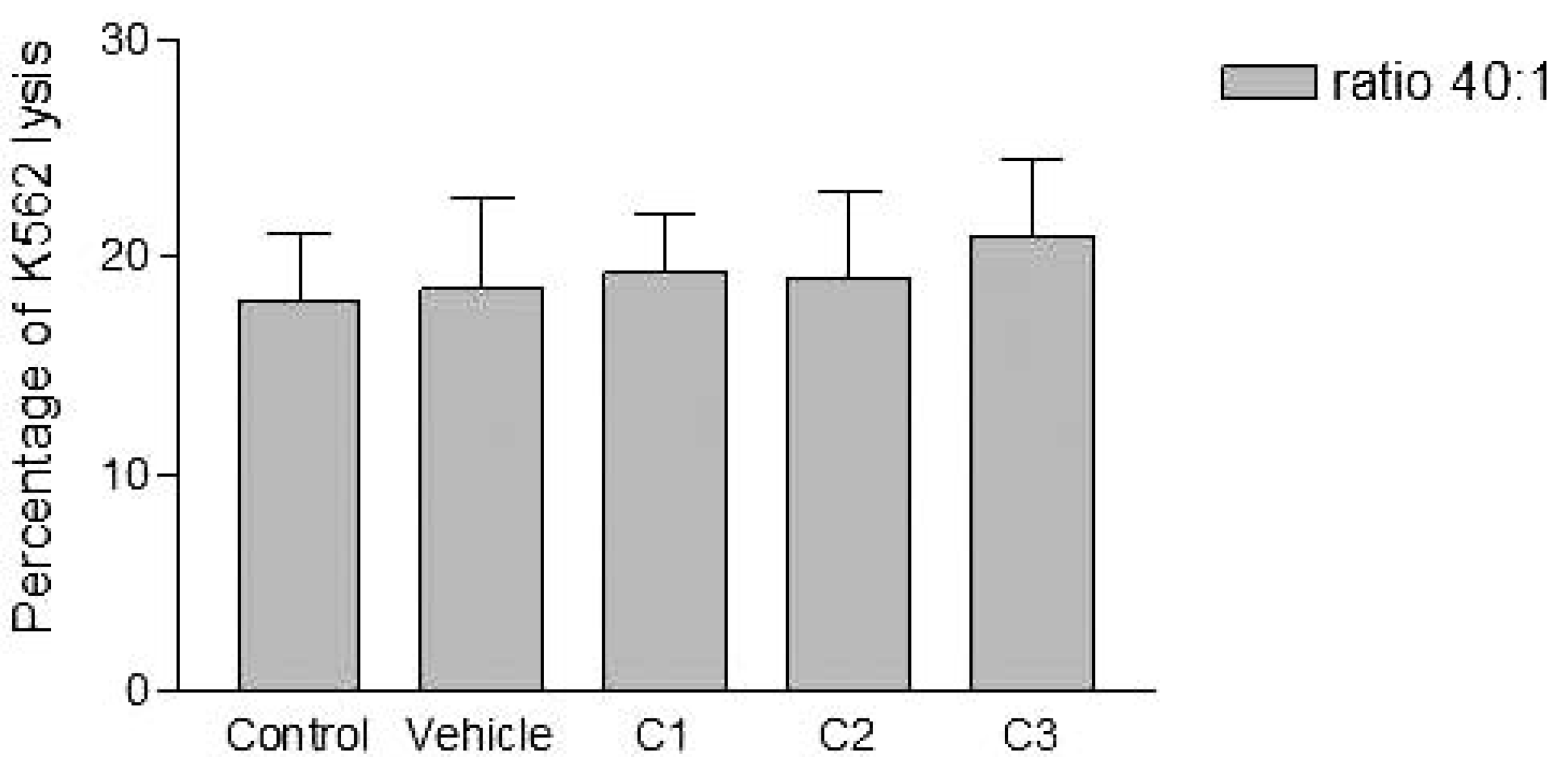
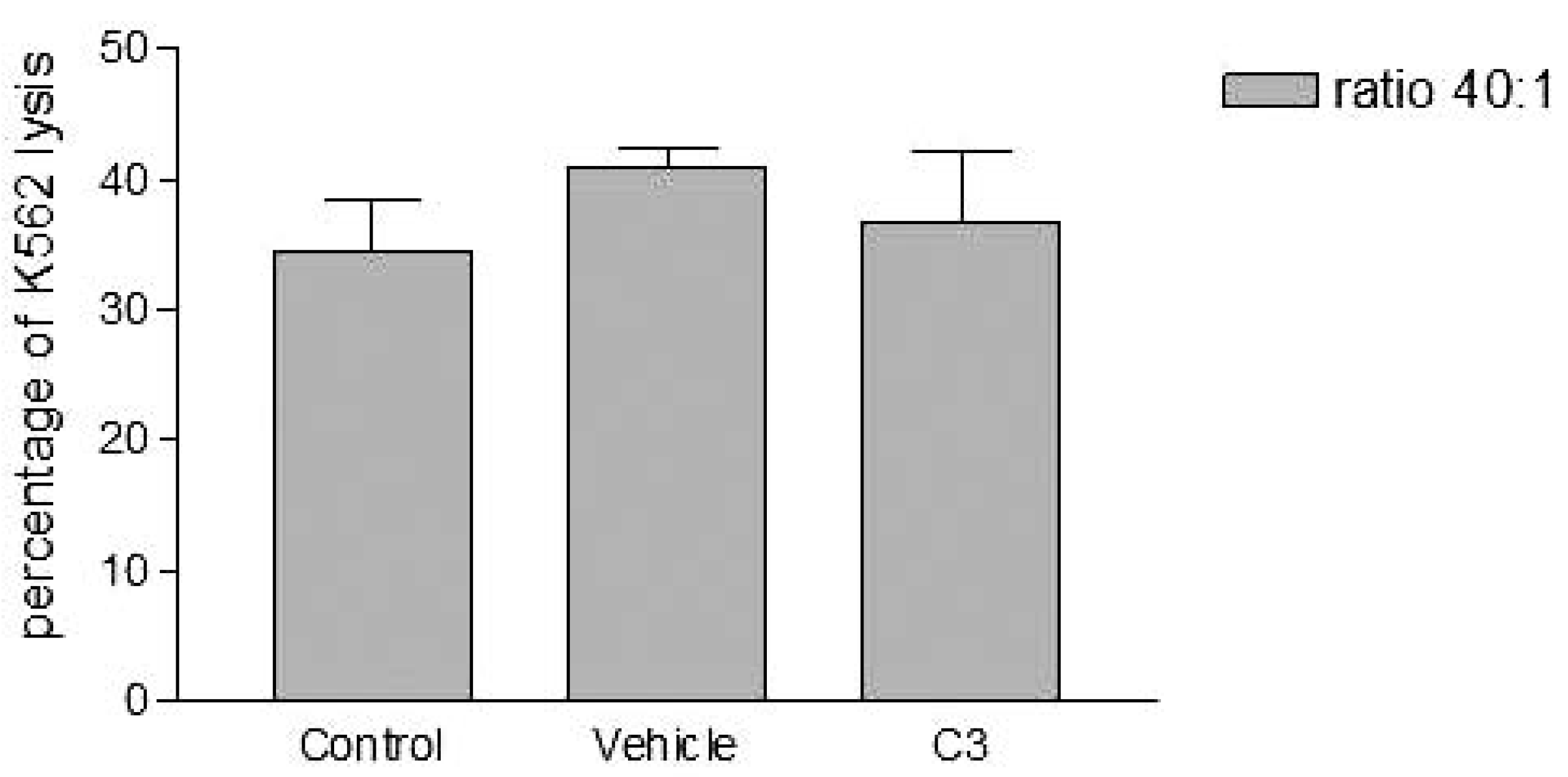
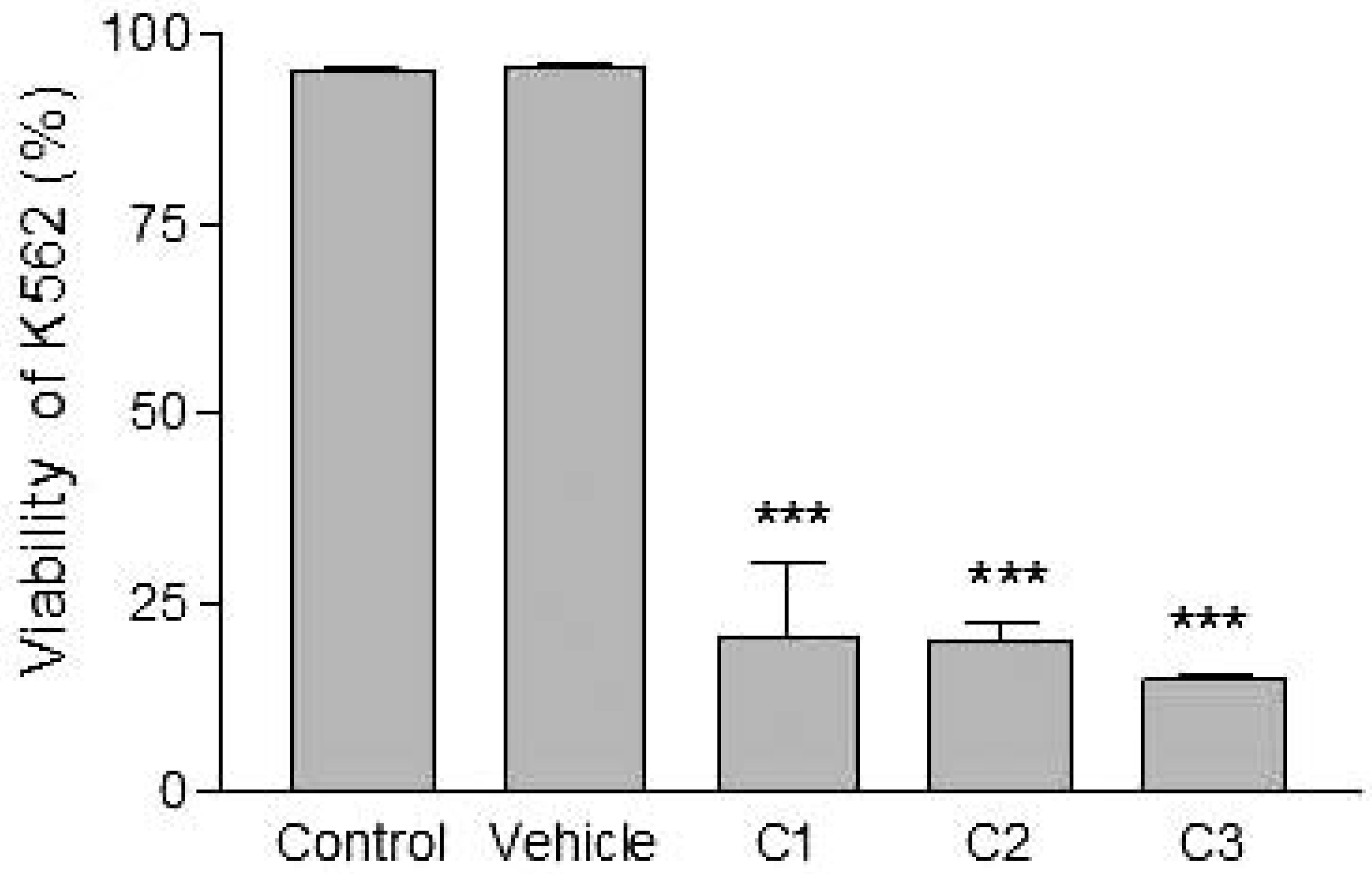
Analyses of target cells are shown in Figure 1. In a Forward versus Side scatter dot plot, a gate (R1) was drawn around the target cells. A single parameter FL-1 histogram (gated on R1) was created. Figure 1A shows the negative control (the cells before labeling to DiO) (left peak), while Figure 1B represented DiO-labeled targets (right peak). After incubation of effector-DiO-labeled targets-PI, analysis of target cells was made using FL-1 (DiO) versus FL-3 (PI) dot plots gated on R1 (Figure 2). The right panel in Figure 2 represents DiO-labeled targets after exposure to contaminated effectors with PCDD/Fs. The upper right quadrant indicates that the targets were double positive, which means that targets were lysed. The lower right quadrant indicates DiO+ representing intact target cells. Results from the first assay (PCDD/Fs not removed from effector cells before contact with targets) are shown in Figure 3. The profiles of NK-like cell function were similar between the 40:1 and 20:1 ratios. The results showed a significant increase (P<0.01) in the percentage of K562 lysis in coelomocytes exposed to the higher PCDD/Fs concentrations C3 (containing 25×10-3 ng 2378-TCDD/ mL). In the second assay, performed with washed effector cells, only the 40:1 ratio was considered. No significant differences were observed at any of the PCDD/Fs mixture concentrations (Figure 4). In the third assay, where the effectors contaminated with PCDD/Fs were fixed before being put in contact with targets, the higher concentration C3 was tested (Figure 5). No significant difference was observed at C3 compared to controls. Parallel to these tests, the direct effects of the same concentrations of PCDD/Fs mixture (C1, C2 and C3) were tested on the target cells (K562) alone (1×106 cell/mL). The results shown in Figure 6 showed a significant decrease in the K562 viability at all concentrations, C1, C2 and C3, compared to controls (P<0.001).
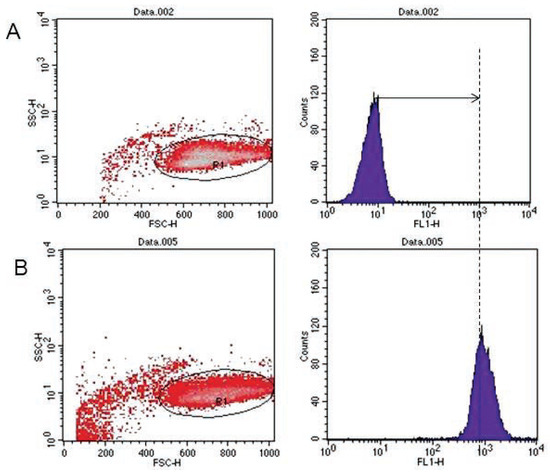
Figure 1.
Flow cytometric analysis of DiO-labeled target cells. (A) Negative control (left peak). (B) DiO positive events identified (right peak).
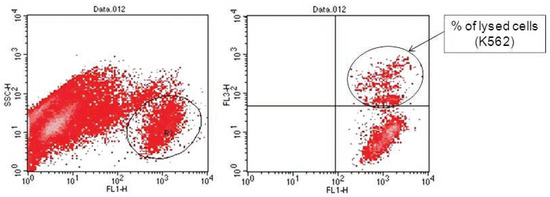
Figure 2.
Flow cytometric analysis of target cells using FL-1 versus FL-3 dot plots gated on R1. The right panel showed the DiO-labeled targets after exposure to effectors. The upper right quadrant represents double positive events (targets). The lower right quadrant represents DiO-positive events (intact targets).
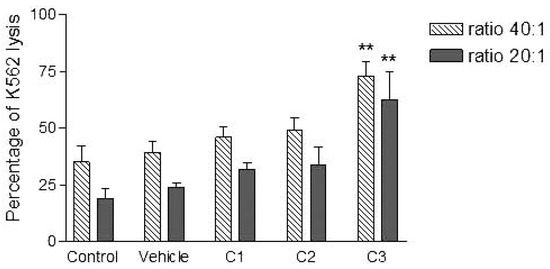
Figure 3.
Effects of various concentrations of PCDD/Fs mixture on the E. andrei NK-like cell activity to lyse the human tumor cells (K562). The effectors were not washed to remove PCDD/Fs before contact with K562. Asterisks represent significant difference compared with vehicle controls (*P<0.05, **P<0.01).
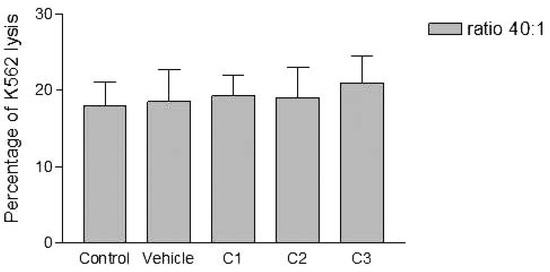
Figure 4.
Effects of various concentrations of PCDD/Fs mixture on the E. andrei NK-like cell activity to lyse the human tumor cells (K562). The effectors were washed of the PCDD/Fs before contact with K562.
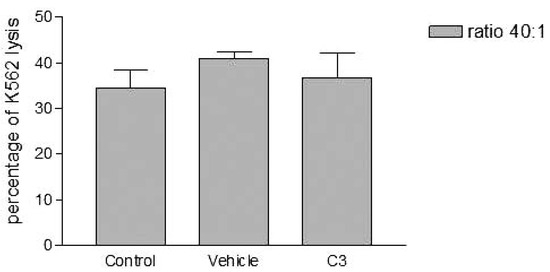
Figure 5.
Effects of the higher concentration of PCDD/Fs mixture (C3) on the E. andrei NK-like cell activity to lyse the human tumor cells (K562). The effectors were fixed before contact with K562.
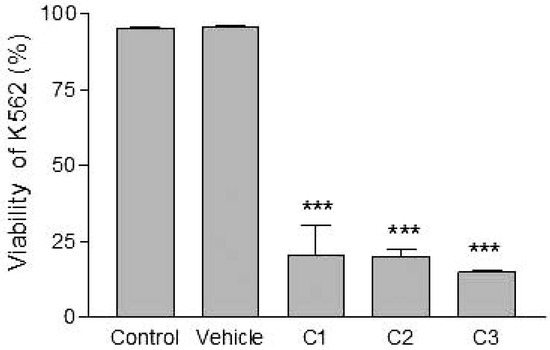
Figure 6.
Effects of various concentrations of PCDD/Fs mixture on the human tumor cells (K562) after 3 h of in vitro exposure. Asterisks represent significant difference compared with vehicle controls (*** P<0.001).
Discussion
In the present work, the flow cytometry was used to study the cell-mediated cytotoxicity of earthworm NK-like cells isolated from the coelomic cavity of E. andrei and exposed in vitro to various concentrations of PCDDs/Fs mixture. The target cells used were human tumor cells (K562).
Without washing the contaminated effector cells (coelomocytes), the in vitro PCDDs/Fs exposure significantly stimulated NK-like cell activity at C3 (25x10-3 ng 2378-TCDD/mL) compared to controls, while no effect was shown at C1 and C2 (Figure 3). Generally, the enhancement of the NK cell activity was seen for low concentrations.33 Comparable results have been reported with a mammalian laboratory model exposed to an endocrine disruptor and persistent contaminant, tributyltin chloride (TBTCl). This in vivo study observed enhancing effects of TBTCl on NK cell activity only in the low dose group (0.025 mg/kg/day) in old female rats. [33] Thus, the results concluded that the increase in NK cell activity was non-linear dose-response. The PCDD/Fs-associated immunostimulation observed in our study at concentrations of C3 was considered to be an immunotoxicological effect, since it may result in the loss of regulation within the immune system and can lead to adverse outcomes including autoimmune disease, anergy, and cancer. [34,35] In the second assay, it was noted that washing contaminated effectors before adding to DiO-labeled K562 targets did not have any effect and no statistically significant differences were observed between groups (Figure 4). Similar results were obtained for the third assay where the contaminated effectors were fixed (no active). So, the cell fixation did not present any effect on the percentage of K562 lysis (Figure 5). This cell fixation assay was conducted to verify if the PCDD/Fs were rejected by cells when fixed and could kill the targets. As shown in Figure 6, the PCDD/Fs alone were cytotoxic for K562 at the various concentrations used. In fact, significant inhibition was observed for all concentrations compared to controls.
To our knowledge, this is the first study of the immunotoxicological effects of a mixture of dioxins and furans on NK-like cell activity in earthworms. Therefore, the absence of data means we cannot compare our results. However, some studies on persistent organic pollutants (POPs) have been carried out. It was demonstrated that PCBs [18] and PAHs [19] exerted immunosuppressive effects on NK-like effector cells. It is important to note here that Patel et al. [19] have tested washed and non-washed effectors before adding DiO-labeled targets and they have demonstrated that in these two cases, exposure to the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon DMBA resulted in statistically significant immunosuppression of NK-like cell activity in earthworms. As far as mammalian laboratory models are concerned, different results were shown for dioxins depending on doses, species, and sex. For example, in mice, Wang et al. [36] have demonstrated that acute 30 μg TCDD/kg-treatment of female mice suppressed the NK cell activity. While, Funseth and Ilbäck [37] have shown that TCDD induces an increased activity of NK cells of male A/J mice after a loading dose of 5 μg TCDD/kg body weight, followed by 3 weekly maintenance doses of 1.42 μg TCDD/kg b.w. In humans, it has not yet been clarified whether dioxins have any effect on the NK cell activity. Some studies have compared the quantitative levels of immune components such as NK cells (CD16+, CD56+) in breast-fed and bottle-fed infants whose mothers were exposed to PCDDs/Fs and PCBs. It was shown that the content of dioxins in breast milk was not enough to induce any change in theses-examined immunological parameters during the first year of life. [38,39]
In conclusion, in our in vitro study, it would appear that the PCDDs/Fs presented enhancing effects on NK-like cell activity at the dose of 25×10-3 ng 2378-TCDD/mL in E. andrei earthworms. This effect may be explained as a compensatory activation of the body’s defences brought about by disturbances in the function of other arms of the immune system. [37]
Acknowledgments
this work was conducted in the environmental immunotoxicology laboratory at Institut Armand Frappier (IAF-INRS). Financial support has been provided by the Canada Research Chair in Environmental Immunotoxicology (Dr. Michel Fournier). The authors are thankful to Marlene Fortier and also appreciate her excellent technical assistance. We wish to thank Dr Pierre Yves Robidoux (CNRC-IRB) for donating the earthworms.
References
- Edwards, C.A. The importance of earthworms as key representatives of the soil fauna. In Earthworm ecology, 2nd ed.; Edwards, C.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 2004; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Guideline for the testing of chemicals. Earthworm reproduction Test (Eiseniafetida/andrei) Draft Document. OECD, January 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, E.L.; Roch, P. Earthworm immunity: a model of immune competence: The 7th international symposium on earthworm ecology Cardiff, Wales, 2002. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 676–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakra Reddy, N.; Venkateswara Rao, J. Biological response of earthworm, Eisenia foetida (Savigny) to an organophosphorous pesticide, profenofos. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2008, 71, 574–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homa, J.; Olchawa, E.; Stürzenbaum, S.R.; et al. Early-phase immunodetection of metal-lothionein and heat shock proteins in extruded earthworm coelomocytes after dermal exposure to metal ions. Environ Pollut 2005, 135, 275–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asensio, V.; Kille, P.; Morgan, A.J.; et al. Metallothionein expression and Neutral Red uptake as biomarkers of metal exposure and effect in Eisenia fetida and Lumbricus terrestris exposed to Cd. Eur J Soil Biol 2007, 43, S233–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.T.; Kim, K.W. Arsenic accumulation and toxicity in the earthworm Eisenia feti-da affected by chloride and phosphate. Environ Toxicol Chem 2008, 27, 2488–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, F.; Covaci, A.; D’Haven, H.; et al. Accumulation of background levels of persistent organochlorine and organobromine pollutants through the soil-earthworm-hedgehog food chain. Environ Int 2010, 36, 721–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, A.J.; Reinecke, S.A. Earthworms as test organisms in ecotoxicological assessment of toxicant impacts on ecosystems. Earthworm ecology, 2nd ed. Edwards, C.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 2004; 299–320. [Google Scholar]
- Ville, P.; Roch, P.; Cooper, E.L.; et al. PCBs increase molecular-related activities (lysozyme, antibacterial, hemolysis, proteases) but inhibit macrophage-related functions (phagocytosis, wound healing) in earthworms. J Invertebr Pathol 1995, 65, 217–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, M.; Cyr, D.; Blakley, B.; et al. Phagocytosis as a biomarker of immunotoxicity in wildlife species exposed to environmental xenobiotics. Am Zool 2000, 40, 412–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvé, S.; Hendawi, M.; Brousseau, P.; Fournier, M. Phagocytic response of terrestrial and aquatic invertebrates following in vitro exposure to trace elements. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2002, 52, 21–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massicotte, R.; Robidoux, P.Y.; Sauvé, S.; et al. Immune response of earthworms (Lumbricus terrestris, Eisenia andrei and Aporrectodea tuberculata) following in situ soil exposure to atmospheric deposition from a cement factory. J Environ Monit 2003, 5, 774–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvé, S.; Fournier, M. Age-specific immunocompetence of the earthworm Eisenia andrei: Exposure to methylmercury chloride. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2005, 60, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goven, A.J.; Fitzpatrick, L.C.; Venables, B.J. Chemical toxicity and host defense in earthworms. An invertebrate model. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1994, 712, 280–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, E.L.; Cossarizza, A.; Suzuki, M.M.; et al. Autogeneic but Not Allogeneic Earthworm Effector Coelomocytes Kill the Mammalian Tumor Cell Target K562. Cell Immunol 1995, 166, 113–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.M.; Cooper, E.L. Killing of intrafamilial leukocytes by earthworm effector cells. Immunol Lett 1995, 44, 45–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.M.; Cooper, E.L.; Eyambe, G.S.; et al. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) depress allogeneic natural cytotoxicity by earthworm coelomocytes. Environ Toxicol Chem 1995, 14, 1697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Francis, J.; Cooper, E.L.; Fuller-Espie, S.L. Development of a flow cytometric, non-radioactive cytotoxicity assay in Eisenia fetida: An in vitro system designed to analyze immunosuppression of natural killer-like coelomocytes in response to 7, 12 dimethylbenz [a]anthracene (DMBA). Eur J Soil Biol 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, K.; Suzuki, T.; Murai, H.; et al. Comparison of immunotoxicity among tetrachloro-, pentachloro-, tetrabromo- and pentabro- mo-dibenzo-p-dioxins in mice. Toxicology 2009, 256, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaluusua, S.; Calderara, P.; Gerthoux, P.M.; et al. Developmental dental aberrations after the dioxin accident in Seveso. Environ Health Perspect 2004, 112, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccarelli, A.; Pfeiffer, R.; Consonni, D.; et al. Handling of dioxin measurement data in the presence of non-detectable values: Overview of available methods and their application in the Seveso chloracne study. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskenazi, B.; Warner, M.; Marks, A.R.; et al. Serum dioxin concentrations and age at menopause. Environ Health Perspect 2005, 113, 858–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyde, M.E.; Cambre, T.; Lebetkin, M.; et al. Promotion of altered hepatic foci by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and 17B-estradiol in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol Sci 2002, 68, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lin, P.H.; Lin, C.H.; Huang, C.C.; et al. 2, 3, 7, 8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) induces oxidative stress, DNA strand breaks, and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activation in human breast carcinoma cell lines. Toxicol Lett 2007, 172, 146–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Polychlorinated dibenzo-para-dioxine and polychlorinated dibenzo-furans; WHO, Ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- ATSDR. Toxicological profile for chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins; Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service: USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- ATSDR. Dioxins. Division of Toxicology and Environmental Medicine (DTEM): USA, March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, H.; DeRosa, C.; Holler, J. Public health assessment for dioxins exposure from soil. Chemosphere 1995, 31, 2437–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furst, A.; Nguyen, Q. Cadmium-induced metallothionein in earthworms (Lumbricus terrestris). Biol Trace Elem Res 1989, 21, 81–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brousseau, P.; Fugère, N.; Bernier, J.; et al. Evaluation of earthworm exposure to contaminated soil by cytometric assay of coelomocytes phagocytosis in Lumbricus terrestris (Oligochaeta). Soil Biol Biochem 1997, 29, 681–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brousseau, P.; Payette, Y.; Tryphonas, H. (Eds.) Manual of immunological methods, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Tryphonas, H.; Cooke, G.; Caldwell, D.; et al. Oral (gavage), in utero and post-natal exposure of Sprague-Dawley rats to low doses of tributyltin chloride: Part II: Effects on the immune system. Food Chem Toxicol 2004, 42, 227–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descotes, J.; Choquet-Kastylevsky, G.; Van Ganse, E.; Vial, T. Responses of the immune system to injury. Toxicol Pathol 2000, 28, 479–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frouin, H.; Lebeuf, M.; Saint-Louis, R.; et al. Toxic effects of tributyltin and its metabolites on harbour seal (Phoca vitulina) immune cells in vitro. Aquat Toxicol 2008, 90, 243–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Zhou, X.Q.; Xu, J.P.; et al. The effects of vitamin e on NK cell activity and lymphocyte proliferation in treated mice by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 2009, 31, 432–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funseth, E.; Ilbäck, N.-G. Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on blood and spleen natural killer (NK) cell activity in the mouse. Toxicol Lett 1992, 60, 247–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, H.; Matsui, E.; Shinoda, S.; et al. Effects of dioxins on the quantitative levels of immune components in infants. Toxicol Indus Health 2006, 22, 131–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisglas-Kuperus, N.; Sas, T.C.J.; Koopman-Esseboom, C.; et al. Immunologic effects of background prenatal and postnatal exposure to dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls in Dutch infants. Pediatr Res 1995, 38, 404–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© Copyright C. Lorin-Nebel et al., 2012. Licensee PAGEPress, Italy. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 3.0 License (CC BY-NC 4.0).