Effect of Phenolic Compounds and Osmotic Stress on the Expression of Penicillin Biosynthetic Genes from Penicillium chrysogenum var. halophenolicum Strain
Abstract
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Strains
Chemicals
Culture conditions
Quantification of gene expression by qPCR
Antibiotic production
Phenol and phenolic compound concentrations
Results
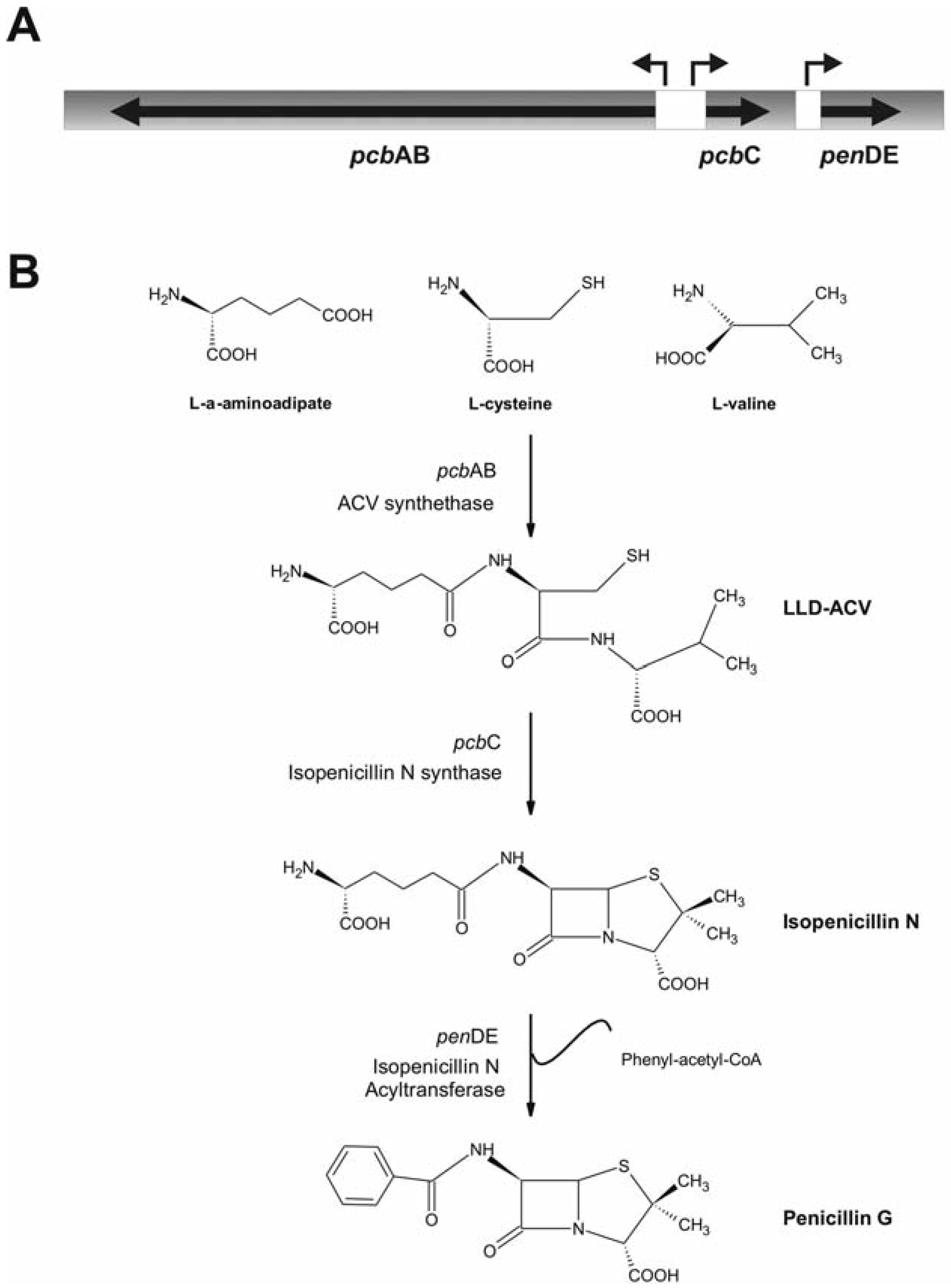
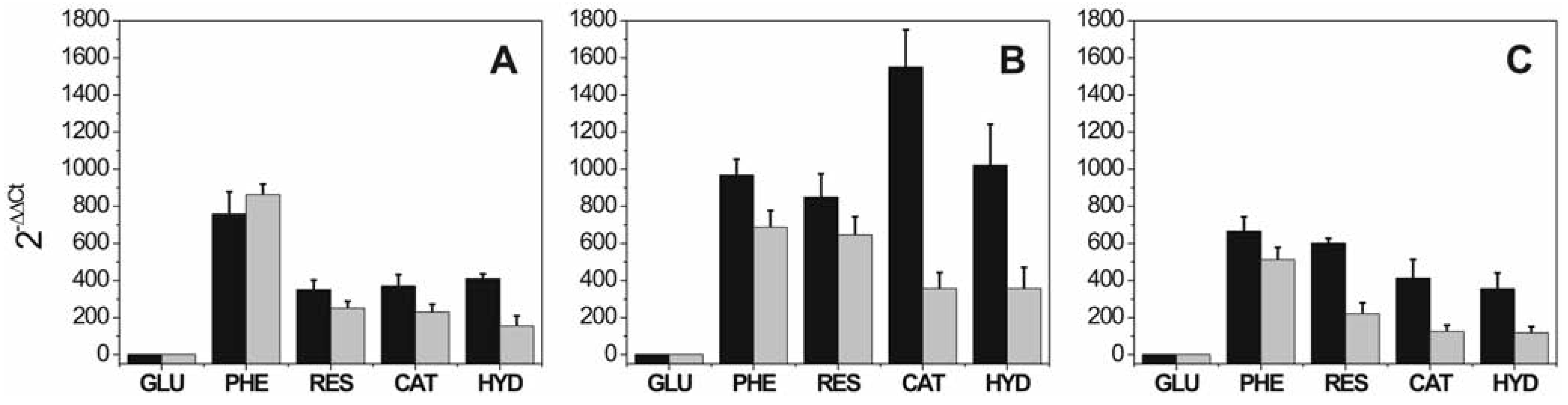
Effect of phenol and phenolic compounds in the expression level of penicillin biosynthetic cluster
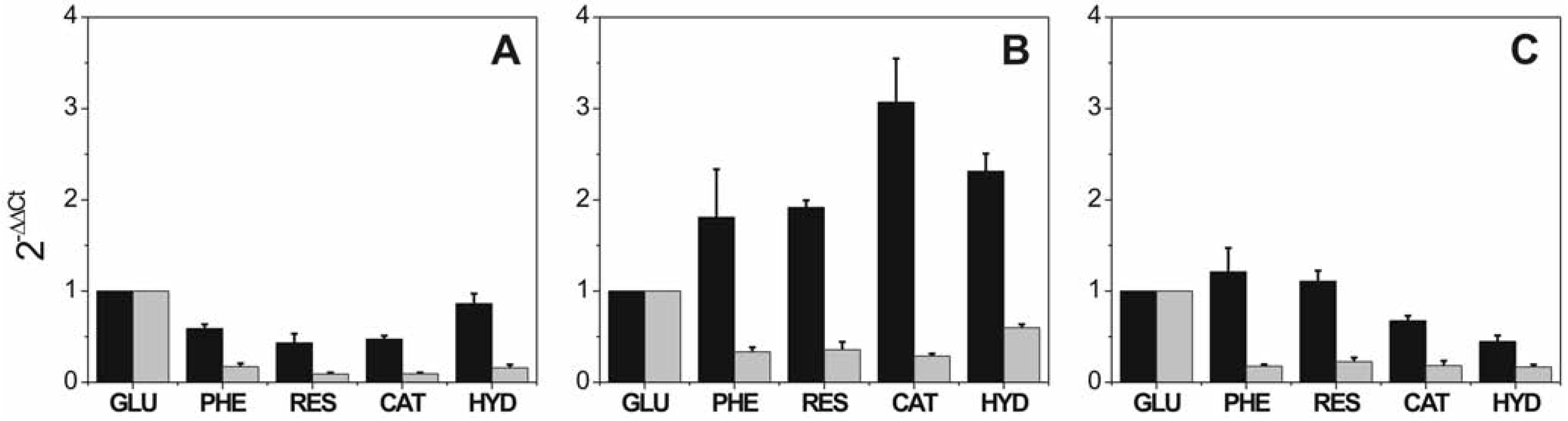
Effect of salt, phenol and phenolic compounds on the expression level of penicillin biosynthetic cluster
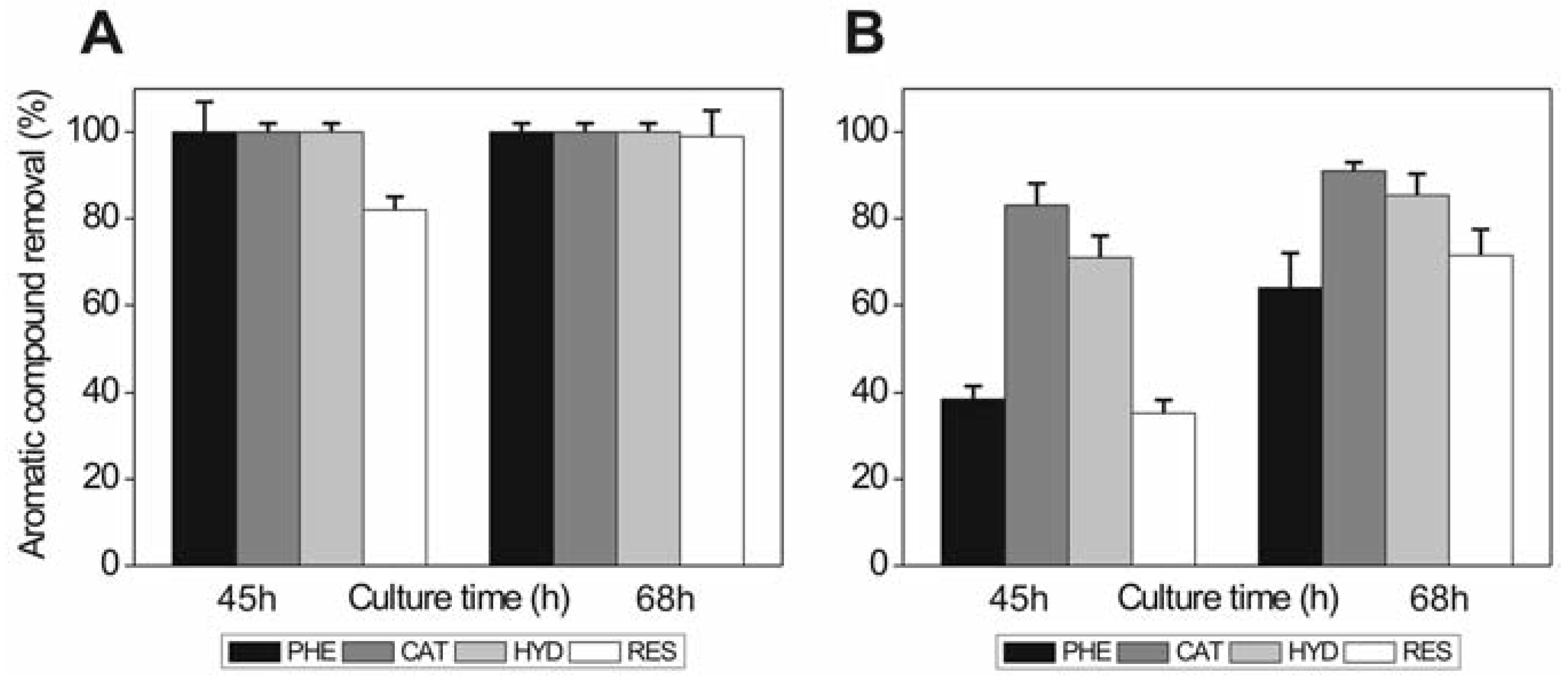
Phenol and phenolic compounds are used with different efficiency by the P. chrysogenum var. halophenolicum strain
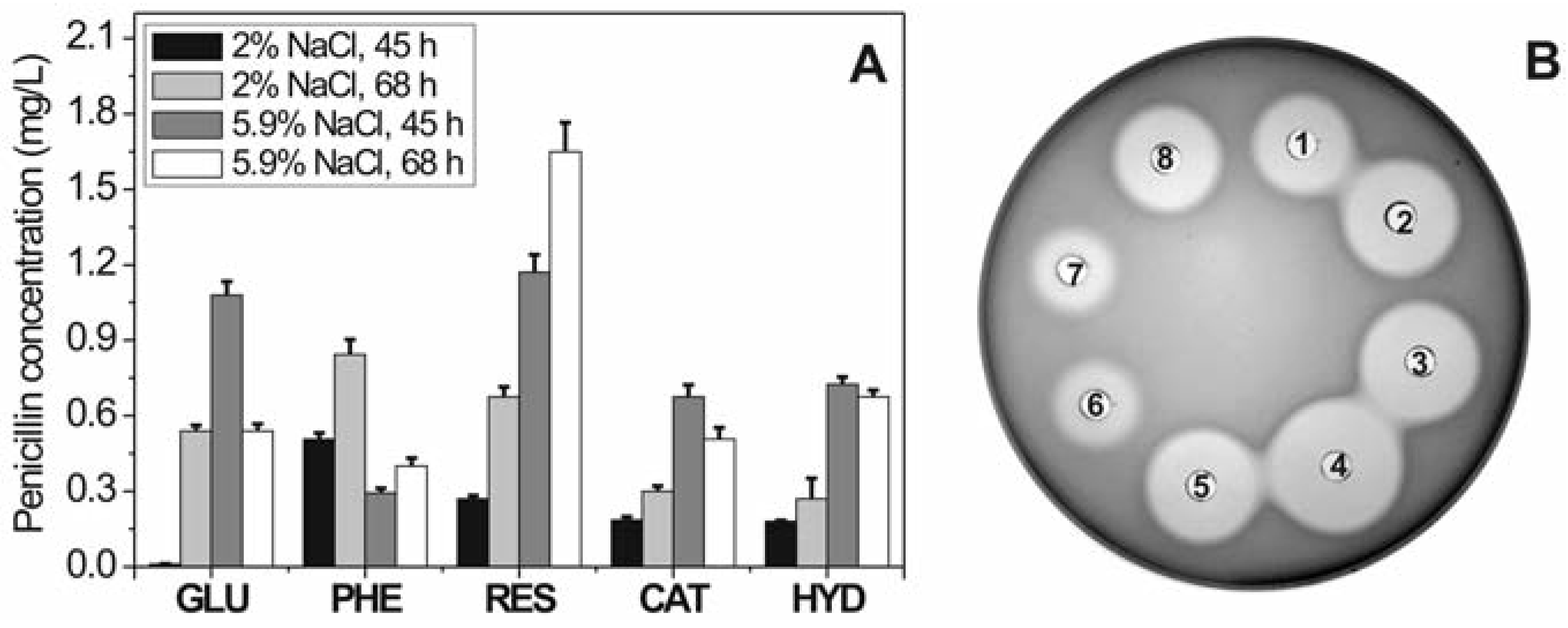
Effect of phenol and phenolic compounds on penicillin biosynthesis
Discussion
Author Contributions
References
- Elander, R.P. Industrial production of beta- lactam antibiotics. Appl Microbiol Biote- chnol 2003, 61, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Estrada, C.; Vaca, I.; Lamas-Maceiras, M.; Martin, J.F. In vivo transport of the inter- mediates of the penicillin biosynthetic pathway in tailored strains of Penicillium chrysogenum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2007, 76, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.F.; Liras, P. Organization and expression of genes involved in the biosynthesis of antibiotics and other sec- ondary metabolites. Annu Rev Microbiol 1989, 43, 173–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbert, R.W.; Barton, B.; Greaves, P.; Harper, J.; Turner, G. Analysis of a commercially improved Penicillium chrysogenum strain series: involvement of recombinogenic regions in amplification and deletion of the penicillin biosynthesis gene cluster. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 1997, 19, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.F. Molecular control of expression of penicillin biosynthesis genes in fungi: regulatory proteins interact with a bidirec- tional promoter region. J Bacteriol 2000, 182, 2355–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, B.; Gutierrez, S.; Barredo, J.L.; van Solingen, P.; van der Voort, L.H.; Martin, J.F. The cluster of penicillin biosynthetic genes. Identification and characterization of the pcbAB gene encoding the alpha- aminoadipyl-cysteinyl-valine synthetase and linkage to the pcbC and penDE genes. J Biol Chem 1990, 265, 16358–16365. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, F.R.; Lopez-Nieto, M.J.; Martin, J.F. Isopenicillin N synthetase of Penicillium chrysogenum, an enzyme that converts delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl- D-valine to isopenicillin N. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1985, 27, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, W.H.; van der Krift, T.P.; Krouwer, A.J.; Wosten, H.A.; van der Vort, L.H.; Smaal, E.B.; et al. Localization of the pathway of the peni- cillin biosynthesis in Penicillium chryso- genum. EMBO J 1991, 10, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla, G.; Lopez-Nieto, M.J.; Luengo, J.M.; Martin, J.F. Carbon catabolite repression of penicillin biosynthesis by Penicillium chrysogenum. J Antibiot 1984, 37, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, N.I.; Fierro, F.; Gutierrez, S.; Martin, J.F. Genome-wide analysis of differentially expressed genes from Penicillium chryso- genum grown with a repressing or a non- repressing carbon source. Curr Genet 2006, 49, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alva, V.A.; Peyton, B.M. Phenol and catechol biodegradation by the haloalkaliphile Halomonas campisalis: influence of pH and salinity. Environ Sci Technol 2003, 37, 4397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, A.E.; Moon, D.H.; Rossi, A.; Trevors, J.T.; Tsai, S.M. Salt-tolerant phenol-degrading microorganisms isolated from Amazonian soil samples. Arch Microbiol 2000, 174, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinteregger, C.; Streichsbier, F. Halomonas sp. , a moderately halophilic strain, for biotreatment of saline phenolic waste- water. Biotechnol Lett 1997, 19, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Peyton, B.M.; Wilson, T.; Yonge, D.R. Kinetics of phenol biodegradation in high salt solu- tions. Water Res 2002, 36, 4811–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, A.L.; Garcia-Estrada, C.; Ullan, R.V.; Guedes, S.F.; Martin-Jimenez, Mendes B.; et al. Penicillium chrysogenum var. halophe- nolicum, a new halotolerant strain with potential in the remediation of aromatic compounds in high salt environments. Microbiol Res 2012, 167, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, S.F.; Mendes, B.; Leitao, A.L. Resorcinol degradation by a Penicillium chrysogenum strain under osmotic stress: mono and binary substrate matrices with phenol. Biodegradation 2011, 22, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, A.L.; Duarte, M.P.; Oliveira, J.S. Degradation of phenol by a halotolerant strain Penicillium chrysogenum. Int Biodeter Biodeg 2007, 59, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Nijveen, H.; Rao, X.; Bisseling, T.; Geurts, R.; Leunissen, J.A. Primer3Plus, an enhanced web interface to Primer3. Nucleic Acids Res 2007, 35, W71–W74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Estrada, C.; Vaca, I.; Fierro, F.; Sjollema, K.; Veenhuis, M.; Martin, J.F. The unpro- cessed preprotein form IATC103S of the isopenicillin N acyltransferase is trans- ported inside peroxisomes and regulates its self-processing. Fungal Genet Biol 2008, 45, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aharonowitz, Y.; Cohen, G.; Martin, J.F. Penicillin and cephalosporin biosynthetic genes: structure, organization, regulation, and evolution. Annu Rev Microbiol 1992, 46, 461–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.F.; Gutierrez, S. Genes for beta-lac- tam antibiotic biosynthesis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1995, 67, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thykaer, J.; Nielsen, J. Metabolic engineer- ing of beta-lactam production. Metab Eng 2003, 5, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakhage, A.A.; Browne, P.; Turner, G. Regulation of Aspergillus nidulans peni- cillin biosynthesis and penicillin biosyn- thesis genes acvA and ipnA by glucose. J Bacteriol 1992, 174, 3789–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douma, R.D.; Verheijen, P.J.; de Laat, W.T.; Heijnen, J.J.; van Gulik, W.M. Dynamic gene expression regulation model for growth and penicillin production in Penicillium chrysogenum. Biotechnol Bioeng 2010, 106, 608–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, S.; Marcos, A.T.; Casqueiro, J.; Kosalkova, K.; Fernandez, F.J.; Velasco, J.; et al. Transcription of the pcbAB, pcbC and penDE genes of Penicillium chrysogenum AS-P-78 is repressed by glucose and the repression is not reversed by alkaline pHs. Microbiology 1999, 145, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.; Jorgensen, H.S. Metabolic control analysis of the penicillin biosynthetic pathway in a high-yielding strain of Penicillium chrysogenum. Biotechnol Prog 1995, 11, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla, G.; Ramos, F.R.; Lopez-Nieto, M.J.; Alvarez, E.; Martin, J.F. Glucose represses for- mation of delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L- cysteinyl-D-valine and isopenicillin N syn- thase but not penicillin acyltransferase in Penicillium chrysogenum. J Bacteriol 1986, 168, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chary, V.K.; de la Fuente, J.L.; Leitão, A.L.; Liras, P.; Martin, J.F. Overexpression of the lat gene in Nocardia lactamdurans from strong heterologous promoters results in very high levels of lysine-6-aminotrans- ferase and up to two-fold increase in cephamycin C production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2000, 53, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasution, U.; van Gulik, W.M.; Ras, C.; Proell, A.; Heijnen, J.J. A metabolome study of the steady-state relation between central metabolism, amino acid biosynthesis and penicillin production in Penicillium chrysogenum. Metab Eng 2008, 10, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gulik, W.M.; Antoniewicz, M.R.; deLaat, W.T.; Vinke, J.L.; Heijnen, J.J. Energetics of growth and penicillin production in a high- producing strain of Penicillium chryso- genum. Biotechnol Bioeng 2001, 72, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikkema, J.; de Bont, J.A.; Poolman, B. Mechanisms of membrane toxicity of hydrocarbons. Microbiol Rev 1995, 59, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gulik, W.M.; de Laat, W.T.; Vinke, J.L.; Heijnen, J.J. Application of metabolic flux analysis for the identification of metabolic bottlenecks in the biosynthesis of peni- cillin-G. Biotechnol Bioeng 2000, 68, 602–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.F.; Casqueiro, J.; Liras, P. Secretion systems for secondary metabolites: how producer cells send out messages of inter- cellular communication. Curr Opin Micro- biol 2005, 8, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© Copyright S. Ferreira Guedes and A.L. Leitão, 2012. Licensee PAGEPress srl, Italy. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 3.0 License (CC BY-NC 3.0).
Share and Cite
Ferreira Guedes, S.; Leitão, A.L. Effect of Phenolic Compounds and Osmotic Stress on the Expression of Penicillin Biosynthetic Genes from Penicillium chrysogenum var. halophenolicum Strain. J. Xenobiot. 2012, 2, e2. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2012.e2
Ferreira Guedes S, Leitão AL. Effect of Phenolic Compounds and Osmotic Stress on the Expression of Penicillin Biosynthetic Genes from Penicillium chrysogenum var. halophenolicum Strain. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2012; 2(1):e2. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2012.e2
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira Guedes, Sumaya, and Ana Lúcia Leitão. 2012. "Effect of Phenolic Compounds and Osmotic Stress on the Expression of Penicillin Biosynthetic Genes from Penicillium chrysogenum var. halophenolicum Strain" Journal of Xenobiotics 2, no. 1: e2. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2012.e2
APA StyleFerreira Guedes, S., & Leitão, A. L. (2012). Effect of Phenolic Compounds and Osmotic Stress on the Expression of Penicillin Biosynthetic Genes from Penicillium chrysogenum var. halophenolicum Strain. Journal of Xenobiotics, 2(1), e2. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2012.e2




