A Systematic Review of Estrogens as Emerging Contaminants in Water: A Global Overview Study from the One Health Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Screening
2.3. Data Extraction
3. Results
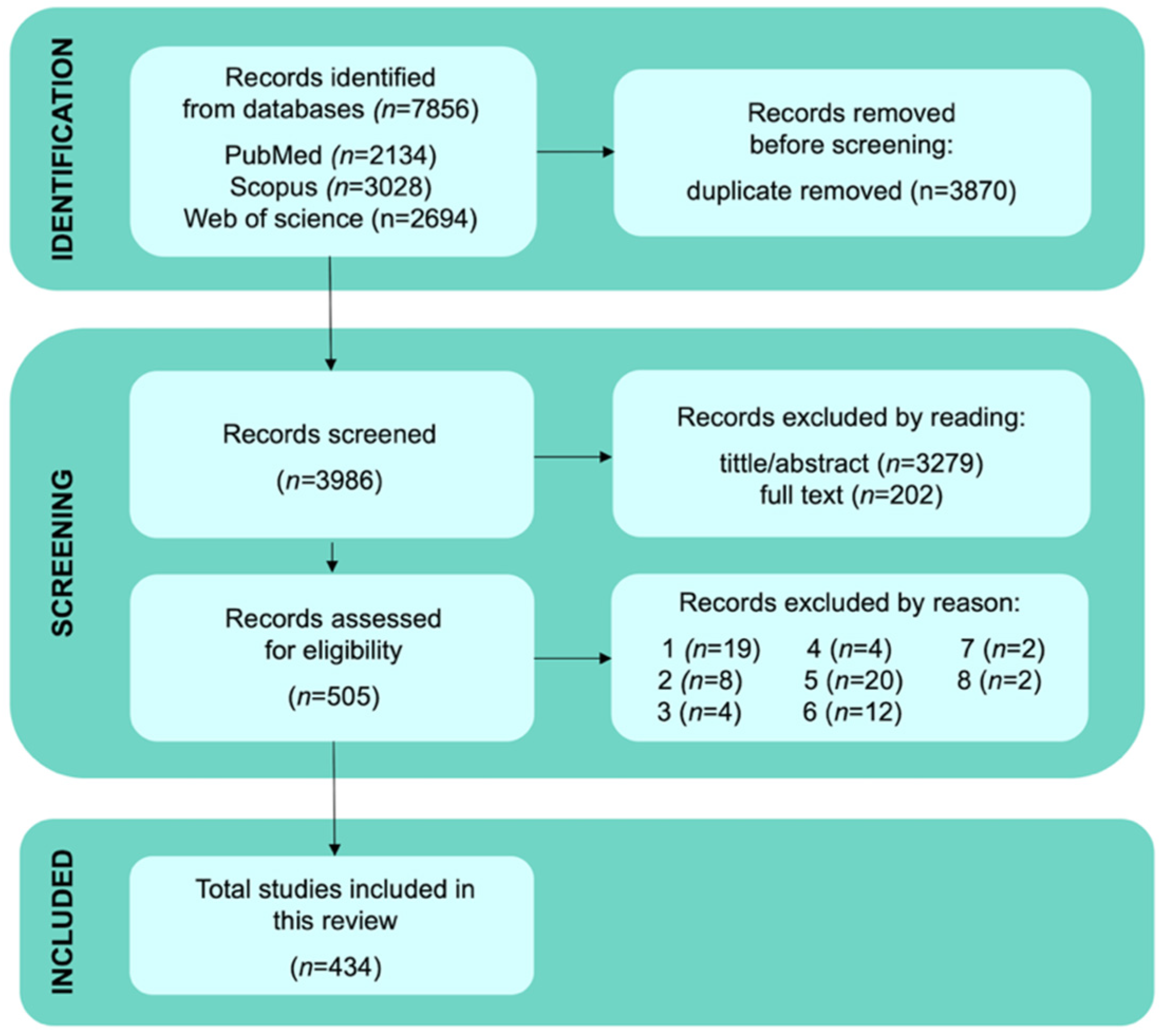
3.1. Studies Selected
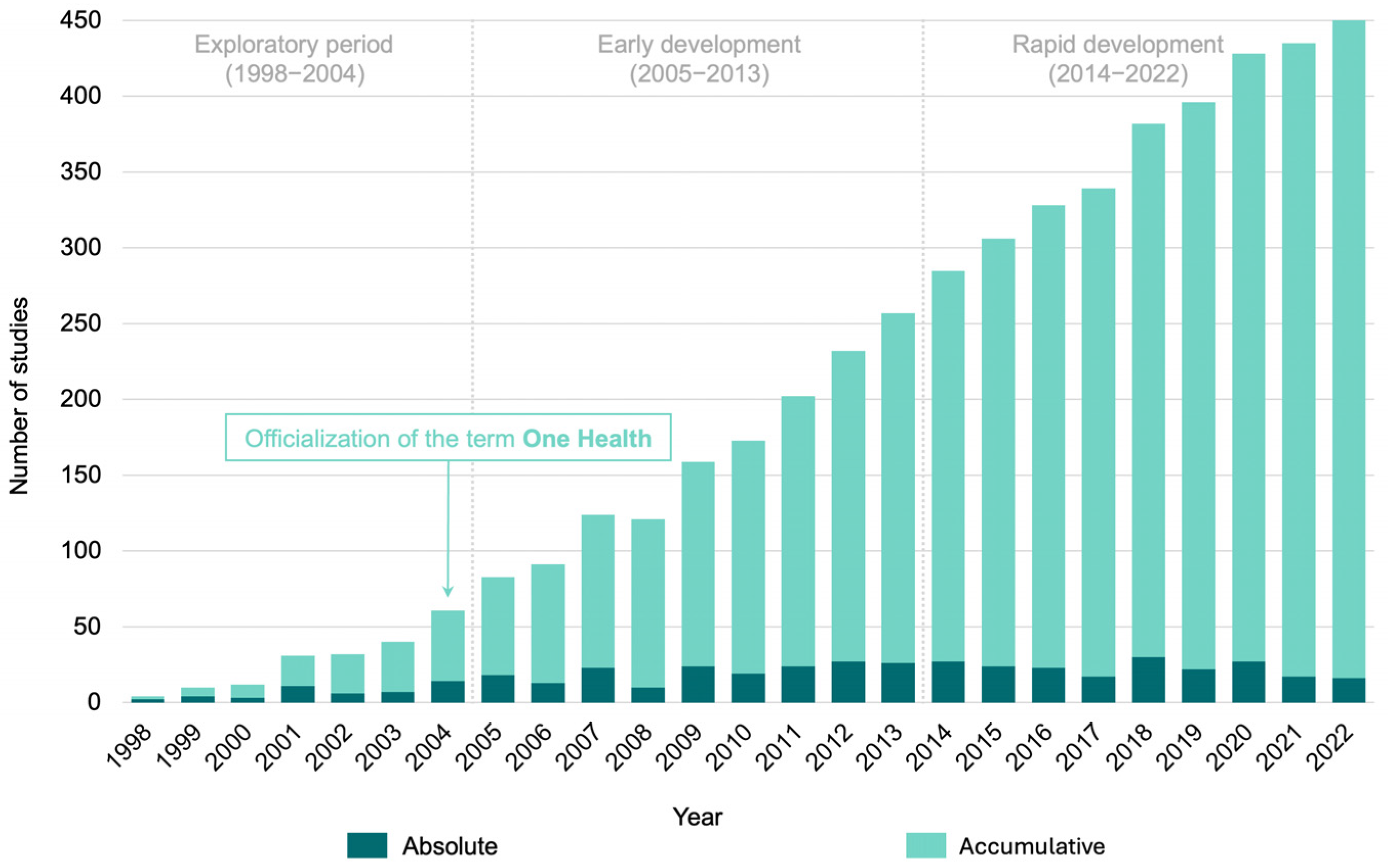
3.2. Historical Overview
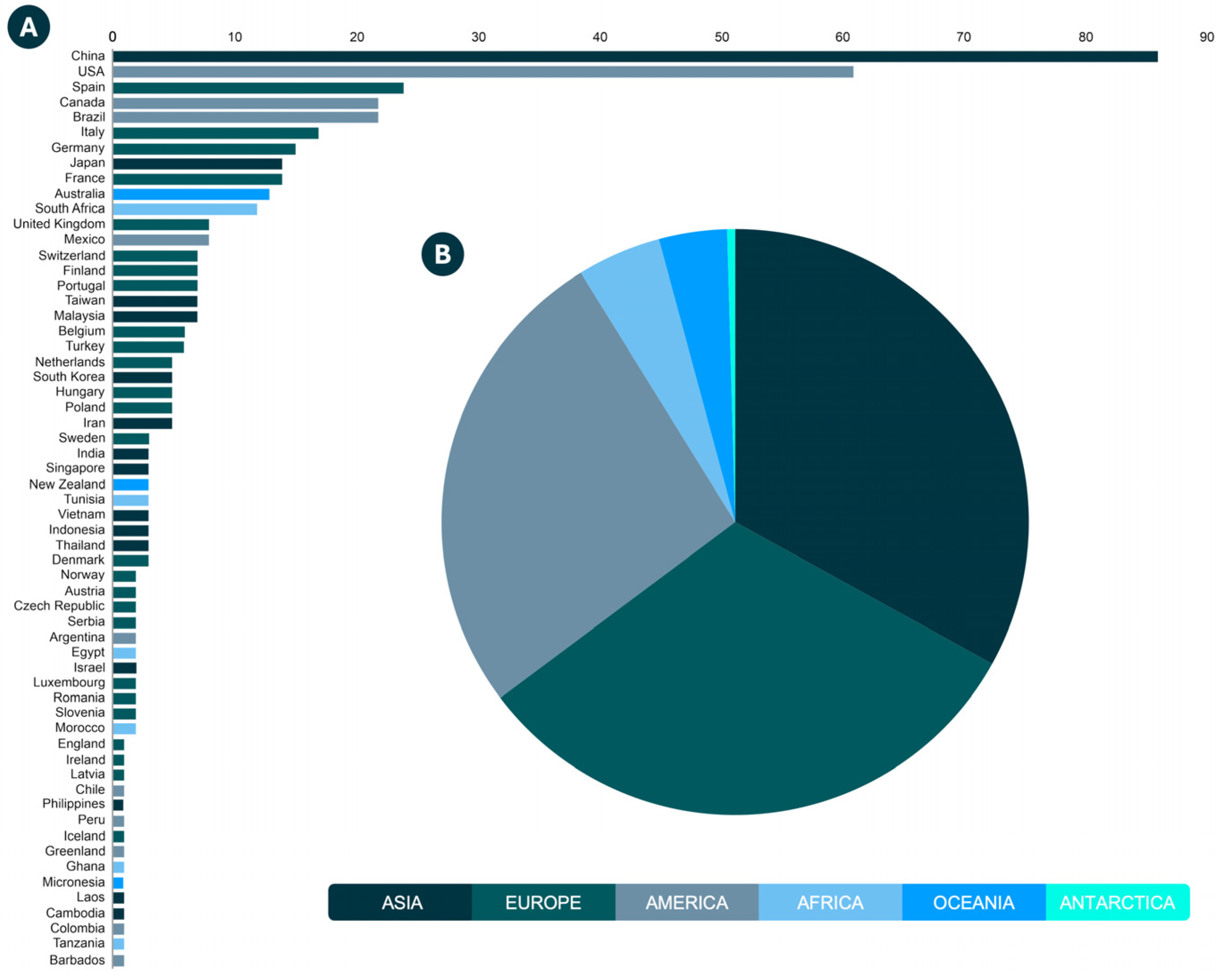
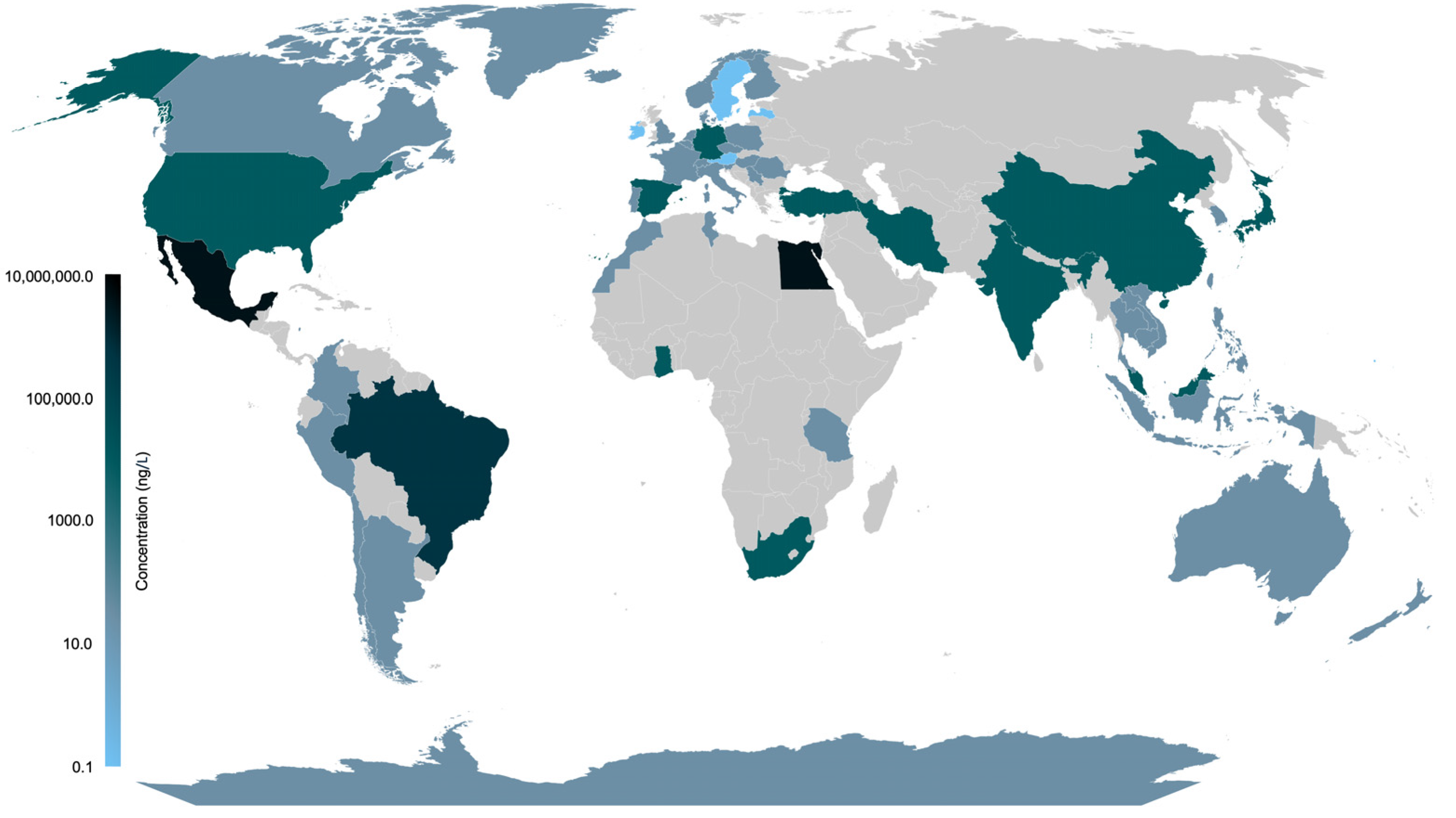
3.3. Geographical Distribution of Estrogen in Water Resources
3.4. Estrogens Detected in Water Resources
4. Discussion
4.1. General
4.2. Water Quality Current Regulatory Frameworks
4.3. Current Environmental Monitoring Challenges of Estrogens
- Lack of standardized methods for the detection and quantification of estrogens in water resources.
- Several estrogens are present at trace levels (ng/L to µg/L) in water resources, requiring highly sensitive and selective analytical instruments.
- Complex environmental matrices can interfere with detection, requiring extensive sample preparation.
- Matrix effects and instrument limitations can lead to errors (false positives/negatives) in the detection and quantification of estrogens in different water resources.
- Lack of data on the interactions of estrogens with traditional and emerging contaminants and their effects on human, animal, and environmental health.
5. A One Health Approach
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mackenzie, J.S.; Jeggo, M. The One Health Approach-Why Is It So Important? Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- One Health High-Level Expert Panel (OHHLEP); Adisasmito, W.B.; Almuhairi, S.; Behravesh, C.B.; Bilivogui, P.; Bukachi, S.A.; Casas, N.; Becerra, N.C.; Charron, D.F.; Chaudhary, A.; et al. One Health: A new definition for a sustainable and healthy future. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiang, L.; Sze-Yin Leung, K.; Elsner, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pan, B.; Sun, H.; An, T.; Ying, G.; et al. Emerging contaminants: A One Health perspective. Innovation 2024, 5, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norrman, K.-E. World Population Growth: A Once and Future Global Concern. World 2023, 4, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Tapia, I.; Salazar-Martínez, T.; Acosta-Castro, M.; Meléndez-Castolo, K.A.; Mahlknecht, J.; Cervantes-Avilés, P.; Capparelli, M.V.; Mora, A. Occurrence of emerging organic contaminants and endocrine disruptors in different water compartments in Mexico—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaseer, S.S.; Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Xu, X.; Abdulrahman, S.A.M.; Ezzati, P.; Habibzadeh, S.; Hollert, H.; Rabiee, N.; Lima, E.C.; et al. Microplastics in water resources: Global pollution circle, possible technological solutions, legislations, and future horizon. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 173963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhandu, Z.; Mashifana, T. Active pharmaceutical contaminants in drinking water: Myth or fact? Daru 2024, 32, 925–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, P.; Saravanan, V.; Rajeshkannan, R.; Arnica, G.; Rajasimman, M.; Baskar, G.; Pugazhendhi, A. Comprehensive review on toxic heavy metals in the aquatic system: Sources, identification, treatment strategies, and health risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2024, 258, 119440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Rawat, M.; Malyan, S.K.; Singh, R.; Tyagi, V.K.; Singh, K.; Kashyap, S.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, M.; Panday, B.K.; et al. Global distribution of pesticides in freshwater resources and their remediation approaches. Environ. Res. 2023, 225, 115605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, V.; Mittal, A.; Das, D.K.; Sethi, S.; Yadav, S.; Vallamkonda, B.; Vashistha, V.K. Radioactive elements in wastewater and potable water: Sources, effects, and methods of analysis and removal. Water Environ. Res. 2024, 96, e11106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, S.; Shah, S.T.A.; Mamoulakis, C.; Docea, A.O.; Kalantzi, O.-I.; Zachariou, A.; Calina, D.; Carvalho, F.; Sofikitis, N.; Makrigiannakis, A.; et al. Endocrine Disruptors Acting on Estrogen and Androgen Pathways Cause Reproductive Disorders through Multiple Mechanisms: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Kishor, K.; Mlsna, T.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Pharmaceuticals of Emerging Concern in Aquatic Systems: Chemistry, Occurrence, Effects, and Removal Methods. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3510–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werkneh, A.A.; Gebru, S.B.; Redae, G.H.; Tsige, A.G. Removal of endocrine disrupters from the contaminated environment: Public health concerns, treatment strategies and future perspectives—A review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Du, B.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, C.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, M. Occurrence, sorption, and transformation of free and conjugated natural steroid estrogens in the environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 9443–9468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, S.Y.; Aris, A.Z. Endocrine disrupting compounds in drinking water supply system and human health risk implication. Environ. Int. 2017, 106, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sheng, C.; Nnanna, G.A. Detection of Selected Pharmaceutical Contaminants and Removal Efficiency of Emerging Contaminants by Application of Membrane Filtration Technology; ASME: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bilal, M.; Rizwan, K.; Adeel, M.; Barceló, D.; Awad, Y.A.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Robust strategies to eliminate endocrine disruptive estrogens in water resources. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aris, A.Z.; Shamsuddin, A.S.; Praveena, S.M. Occurrence of 17α-ethynylestradiol (EE2) in the environment and effect on exposed biota: A review. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; He, X.; Lin, H.; Lin, X.; Mo, J.; Chen, C.; Dai, X.; Liao, D.; Gao, C.; Li, Y. Occurrence and distribution of natural and synthetic progestins, androgens, and estrogens in soils from agricultural production areas in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehalt Macedo, H.; Lehner, B.; Nicell, J.; Grill, G.; Li, J.; Limtong, A.; Shakya, R. Distribution and characteristics of wastewater treatment plants within the global river network. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odehnalová, K.; Přibilová, P.; Maršálková, E.; Zezulka, Š.; Pochylý, F.; Rudolf, P.; Maršálek, B. Hydrodynamic cavitation-enhanced activation of sodium percarbonate for estrogen removal. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 2905–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.G.R.; Costa, E.P.; Starling, M.C.V.M.; Dos Santos Azevedo, T.; Bottrel, S.E.C.; Pereira, R.O.; Sanson, A.L.; Afonso, R.J.C.F.; Amorim, C.C. LED irradiated photo-Fenton for the removal of estrogenic activity and endocrine disruptors from wastewater treatment plant effluent. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 24067–24078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdarta, J.; Nguyen, L.N.; Jankowska, K.; Jesionowski, T.; Nghiem, L.D. A contemporary review of enzymatic applications in the remediation of emerging estrogenic compounds. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 2661–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.L. Removal of estrone and 17beta-estradiol from water by adsorption. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3991–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniero, M.G.; Bila, D.M.; Dezotti, M. Degradation and estrogenic activity removal of 17beta-estradiol and 17alpha-ethinylestradiol by ozonation and O3/H2O2. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 407, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.H.; Reinhard, M.; Gin, K.Y.-H. Occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater treatment plants from different geographical regions-a review. Water Res. 2018, 133, 182–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreiros, L.; Queiroz, J.F.; Magalhães, L.M.; Silva, A.M.T.; Segundo, M.A. Analysis of 17-β-estradiol and 17-α-ethinylestradiol in biological and environmental matrices—A review. Microchem. J. 2016, 126, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabet, V.; Miège, C.; Bados, P.; Coquery, M. Analysis of estrogens in environmental matrices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 1113–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, S.M.; Hedman, C.J.; Hemming, J.D.C.; Mieritz, M.G.; Shafer, M.M.; Schauer, J.J. Stability, preservation, and quantification of hormones and estrogenic and androgenic activities in surface water runoff. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 2481–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, N.H.; Santos, G.d.O.S.; Romanholo Ferreira, L.F.; Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P.; Eguiluz, K.I.B.; Salazar-Banda, G.R. Environmental aspects of hormones estriol, 17β-estradiol and 17α-ethinylestradiol: Electrochemical processes as next-generation technologies for their removal in water matrices. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, C.S.; Mesquita, D.P.; Amaral, A.L.; Amaral, A.M.; Ferreira, E.C. Environmental impact and biological removal processes of pharmaceutically active compounds: The particular case of sulfonamides, anticonvulsants and steroid estrogens. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 698–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, C.L.S.; Bassin, J.P.; Peixoto, R.S. Water contamination by endocrine disruptors: Impacts, microbiological aspects and trends for environmental protection. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhat, G.N.; Cummings, S.R.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Parimi, N.; Cauley, J.A.; Rohan, T.E.; Huang, A.J.; Vitolins, M.; Hubbell, F.A.; Manson, J.E.; et al. Sex hormone levels and risks of estrogen receptor-negative and estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missmer, S.A.; Eliassen, A.H.; Barbieri, R.L.; Hankinson, S.E. Endogenous estrogen, androgen, and progesterone concentrations and breast cancer risk among postmenopausal women. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 1856–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolfo, A.; Nuzzo, A.M.; De Amicis, R.; Moretti, L.; Bertoli, S.; Leone, A. Fetal–Maternal Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors: Correlation with Diet Intake and Pregnancy Outcomes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.F.; Hasan, N.; Soto, A.M.; Sonnenschein, C. Environmental Endocrine Disruptors: Effects on the human male reproductive system. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2015, 16, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, A.A.; Wheeler, H.B.; Blumberg, B. Obesity and endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Endocr. Connect. 2021, 10, R87–R105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, M.; Micu, R.; Neamtiu, I. Female Infertility and “Emerging” Organic Pollutants of Concern. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2016, 3, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannarella, R.; Gül, M.; Rambhatla, A.; Agarwal, A. Temporal decline of sperm concentration: Role of endocrine disruptors. Endocrine 2023, 79, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishan, A.; Khalid, N.K.; Rayaroth, M.P.; Thomas, S.; Nazim, A.; Aravindakumar, C.T.; Aravind, U.K. Occurrence and distribution of steroid hormones (estrogen) and other contaminants of emerging concern in a south indian water body. Chemosphere 2024, 351, 141124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciślak, M.; Kruszelnicka, I.; Zembrzuska, J.; Ginter-Kramarczyk, D. Estrogen pollution of the European aquatic environment: A critical review. Water Res. 2023, 229, 119413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, G.; Guo, Q.; Yan, C. Estrogenic compounds and estrogenicity in surface water, sediments, and organisms from Yundang Lagoon in Xiamen, China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 61, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami Matin, B.; Shakiba, E.; Moradi, M.; Zereshki, E.; Karami, A.; Vasseghian, Y.; Dragoi, E.-N.; Khaneghah, A.M. The concentration of estrogen in water resources: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 101, 2937–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, D.N.; Mounteer, A.H.; Arcanjo, G.S. Estrogenic compounds in drinking water: A systematic review and risk analysis. Chemosphere 2024, 360, 142463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerdsuwanrut, N.; Zamani, R.; Akrami, M. Environmental and Human Health Risks of Estrogenic Compounds: A Critical Review of Sustainable Management Practices. Sustainability 2025, 17, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbrow, C.; Routledge, E.J.; Brighty, G.C.; Sumpter, J.P.; Waldock, M. Identification of Estrogenic Chemicals in STW Effluent. 1. Chemical Fractionation and in Vitro Biological Screening. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1549–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.B.; Peart, T.E. Determination of 17 beta-estradiol and its metabolites in sewage effluent by solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. AOAC Int. 1998, 81, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, E.P.J. The evolution of One Health: A decade of progress and challenges for the future. Vet. Rec. 2014, 174, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildlife Conservation Society. One World, One Health: Building Interdisciplinary Bridges to Health in a Globalized World; One World, One Health: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pamplona-Silva, M.; Mazzeo, D.; Bianchi, J.; Marin-Morales, M. Estrogenic Compounds: Chemical Characteristics, Detection Methods, Biological and Environmental Effects. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokai-Tatrai, K.; Prokai, L. The impact of 17β-estradiol on the estrogen-deficient female brain: From mechanisms to therapy with hot flushes as target symptoms. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1310432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christin-Maitre, S. History of oral contraceptive drugs and their use worldwide. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 27, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kangasniemi, M.H.; Arffman, R.K.; Joenväärä, S.; Haverinen, A.; Luiro, K.; Tohmola, T.; Renkonen, R.; Heikinheimo, O.; Tapanainen, J.S.; Piltonen, T.T. Ethinylestradiol in combined hormonal contraceptive has a broader effect on serum proteome compared with estradiol valerate: A randomized controlled trial. Hum. Reprod. 2023, 38, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-López, F.R.; Phillips, N.; Vieira-Baptista, P.; Cohen-Sacher, B.; Fialho, S.C.A.V.; Stockdale, C.K. Management of postmenopausal vulvovaginal atrophy: Recommendations of the International Society for the Study of Vulvovaginal Disease. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2021, 37, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swart, J.C.; Pool, E.J. Estrogenic Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals. In Encyclopedia of Aquatic Ecotoxicology; Férard, J.-F., Blaise, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeel, M.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Francis, D.; Yang, Y. Environmental impact of estrogens on human, animal and plant life: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojnarowski, K.; Podobiński, P.; Cholewińska, P.; Smoliński, J.; Dorobisz, K. Impact of Estrogens Present in Environment on Health and Welfare of Animals. Animals 2021, 11, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.; Klerks, P. Effects of the synthetic estrogen 17α-ethinylestradiol on Heterandria formosa populations: Does matrotrophy circumvent population collapse? Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 229, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, N.P.; Colombo, R.E.; Gaines, K.F.; Maia, A. Exposure to 17β estradiol causes erosion of sexual dimorphism in Bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 6450–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filby, A.L.; Shears, J.A.; Drage, B.E.; Churchley, J.H.; Tyler, C.R. Effects of advanced treatments of wastewater effluents on estrogenic and reproductive health impacts in fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4348–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, K.L.; Maack, G.; Benstead, R.; Tyler, C.R. Estrogenic wastewater treatment works effluents reduce egg production in fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2976–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Hernández, L.; Gutiérrez-Gómez, A.A.; SanJuan-Reyes, N.; Islas-Flores, H.; García-Medina, S.; Galar-Martínez, M.; Dublán-García, O.; Natividad, R.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M. 17β-Estradiol induces cyto-genotoxicity on blood cells of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Chemosphere 2018, 191, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.-P.; Li, B.-B.; Wei, F.-L.; Yu, M.; Zhan, W.; Liu, F.; Lou, B. Growth and gonadal development retardations after long-term exposure to estradiol in little yellow croaker, Larimichthys polyactis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturantabut, S.; Shwartz, A.; Evason, K.J.; Cox, A.G.; Labella, K.; Schepers, A.G.; Yang, S.; Acuña, M.; Houvras, Y.; Mancio-Silva, L.; et al. Estrogen Activation of G-Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor 1 Regulates Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase and mTOR Signaling to Promote Liver Growth in Zebrafish and Proliferation of Human Hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1788–1804.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, G.W.; Legro, R.S. Longterm management of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 373, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macer, M.L.; Taylor, H.S. Endometriosis and infertility: A review of the pathogenesis and treatment of endometriosis-associated infertility. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 39, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocciadiferro, L.; Miceli, V.; Granata, O.M.; Carruba, G. Merlin, the product of NF2 gene, is associated with aromatase expression and estrogen formation in human liver tissues and liver cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 172, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, P.H.; Mezzomo, L.C.; Ferreira, N.P.; Roehe, A.V.; Kohek, M.B.F.; Oliveira, M.d.C. Aromatase P450 expression in human pituitary adenomas. Neuropathology 2015, 35, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izawa, M.; Inoue, M.; Osaki, M.; Ito, H.; Harada, T.; Terakawa, N.; Ikeguchi, M. Cytochrome P450 aromatase gene (CYP19) expression in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2008, 11, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari, R.; Zhang, L.; Kebebew, E. Thyroid cancer gender disparity. Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.K.; Miki, Y.; Abe, K.; Nagasaki, S.; Niikawa, H.; Suzuki, S.; Kondo, T.; Sasano, H. Co-expression of estrogen receptor beta and aromatase in Japanese lung cancer patients: Gender-dependent clinical outcome. Life Sci. 2012, 91, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.-J.; William, J.; Bulun, S. Endometriosis and ovarian cancer: A review of clinical, pathologic, and molecular aspects. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2011, 30, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosnoe-Shipley, L.E.; Elkelany, O.O.; Rahnema, C.D.; Kim, E.D. Treatment of hypogonadotropic male hypogonadism: Case-based scenarios. World J. Nephrol. 2015, 4, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuhaci, N.; Polat, S.B.; Evranos, B.; Ersoy, R.; Cakir, B. Gynecomastia: Clinical evaluation and management. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 18, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togola, A.; Budzinski, H. Multi-residue analysis of pharmaceutical compounds in aqueous samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1177, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, E.O.; Foureaux, A.F.S.; Rodrigues, J.S.; Moreira, V.R.; Lebron, Y.A.R.; Santos, L.V.S.; Amaral, M.C.S.; Lange, L.C. Occurrence, removal and seasonal variation of pharmaceuticals in Brasilian drinking water treatment plants. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibola, A.S.; Amoniyan, O.A.; Ekoja, F.O.; Ajibola, F.O. QuEChERS Approach for the Analysis of Three Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics in Wastewater: Concentration Profiles and Ecological Risk in Two Nigerian Hospital Wastewater Treatment Plants. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero-Coy, A.M.; Martínez-Pachón, D.; Boix, C.; Rincón, R.J.; Castillo, N.; Arias-Marín, L.P.; Manrique-Losada, L.; Torres-Palma, R.; Moncayo-Lasso, A.; Hernández, F. An investigation into the occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals in Colombian wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Le, N.; Hoang, A.Q.; Hoang, T.T.H.; Nguyen, T.A.H.; Duong, T.T.; Pham, T.M.H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Hoang, V.C.; Phung, T.X.B.; Le, H.T.; et al. Antibiotic and antiparasitic residues in surface water of urban rivers in the Red River Delta (Hanoi, Vietnam): Concentrations, profiles, source estimation, and risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 10622–10632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotola, E.O.; Olatunji, O.S. Quantification of selected pharmaceutical compounds in water using liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS). Heliyon 2020, 6, e05787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S.M.; Brigham, M.E.; Lee, K.E.; Banda, J.A.; Choy, S.J.; Gefell, D.J.; Minarik, T.A.; Moore, J.N.; Jorgenson, Z.G. Contaminants of emerging concern in tributaries to the Laurentian Great Lakes: I. Patterns of occurrence. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafuri, Y.; Yunesian, M.; Nabizadeh, R.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Dehghani, M.H.; Alimohammadi, M. Platinum cytotoxic drugs in the municipal wastewater and drinking water, a validation method and health risk assessment. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 24, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husk, B.; Sanchez, J.S.; Leduc, R.; Takser, L.; Savary, O.; Cabana, H. Pharmaceuticals and pesticides in rural community drinking waters of Quebec, Canada—A regional study on the susceptibility to source contamination. Water Qual. Res. J. 2019, 54, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassour, C.; Nabhani-Gebara, S.; Barton, S.J.; Barker, J. Determination of Anticancer Drugs in the Aquatic Environment by SPE–LC–MS/MS—A Lebanese Case Study. Water 2023, 15, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento, R.F.; de Carvalho Filho, J.A.A.; Napoleão, D.C.; Ribeiro, B.G.; da Silva Pereira Cabral, J.J.; de Paiva, A.L.R. Presence Of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatories In Brazilian Semiarid Waters. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibuye, F.A.; Gall, H.E.; Elkin, K.R.; Ayers, B.; Veith, T.L.; Miller, M.; Jacob, S.; Hayden, K.R.; Watson, J.E.; Elliott, H.A. Fate of pharmaceuticals in a spray-irrigation system: From wastewater to groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Ye, B.; Han, J.; Jin, N. Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in raw, finished, and drinking water from seven large river basins in China. J. Water Health 2019, 17, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benotti, M.J.; Trenholm, R.A.; Vanderford, B.J.; Holady, J.C.; Stanford, B.D.; Snyder, S.A. Pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in U.S. drinking water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brieudes, V.; Lardy-Fontan, S.; Vaslin-Reimann, S.; Budzinski, H.; Lalere, B. Development of a multi-residue method for scrutinizing psychotropic compounds in natural waters. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1047, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassmeyer, S.T.; Furlong, E.T.; Kolpin, D.W.; Batt, A.L.; Benson, R.; Boone, J.S.; Conerly, O.; Donohue, M.J.; King, D.N.; Kostich, M.S.; et al. Nationwide reconnaissance of contaminants of emerging concern in source and treated drinking waters of the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Gautam, L.; Hall, S.W. The detection of drugs of abuse and pharmaceuticals in drinking water using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2019, 223, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Tröger, R.; Ahrens, L.; Wiberg, K.; Yin, D. Screening of organic micropollutants in raw and drinking water in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottoni, P.; Caroli, S.; Caracciolo, A.B. Pharmaceuticals as priority water contaminants. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2010, 92, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, O.A.; Lester, J.N.; Voulvoulis, N. Pharmaceuticals: A threat to drinking water? Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovac, T. Pharmaceuticals in the Water: The Need for Environmental Bioethics. J. Med. Humanit. 2023, 44, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren-Vega, W.M.; Campos-Rodríguez, A.; Zárate-Guzmán, A.I.; Romero-Cano, L.A. A Current Review of Water Pollutants in American Continent: Trends and Perspectives in Detection, Health Risks, and Treatment Technologies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, J.L.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Kolpin, D.W.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Lai, R.W.S.; Galbán-Malagón, C.; Adell, A.D.; Mondon, J.; Metian, M.; Marchant, R.A.; et al. Pharmaceutical pollution of the world’s rivers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113947119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, A.; Meric, S.; Fatta, D. Occurrence patterns of pharmaceuticals in water and wastewater environments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Pharmaceuticals in Drinking-Water; WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. Pharmaceutical Residues in Freshwater: Hazards and Policy Responses, OECD Studies on Water; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.O.; Moreira, N.F.F.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M.T. Occurrence and removal of organic micropollutants: An overview of the watch list of EU Decision 2015/495. Water Res. 2016, 94, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Neves-Silva, P.; Heller, L. The human right to water and sanitation: A new perspective for public policies. Ciênc. Saúde Coletiva 2016, 21, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Water Framework Directive. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/water/water-framework-directive_en (accessed on 11 September 2024).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sdwa (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Simon, E.; Duffek, A.; Stahl, C.; Frey, M.; Scheurer, M.; Tuerk, J.; Gehrmann, L.; Könemann, S.; Swart, K.; Behnisch, P.; et al. Biological effect and chemical monitoring of Watch List substances in European surface waters: Steroidal estrogens and diclofenac—Effect-based methods for monitoring frameworks. Environ. Int. 2022, 159, 107033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Basic Information on the CCL and Regulatory Determination. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ccl/basic-information-ccl-and-regulatory-determination (accessed on 11 September 2024).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Contaminant Candidate List 5—CCL 5. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ccl/contaminant-candidate-list-5-ccl-5 (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Hecker, M.; Hollert, H. Endocrine disruptor screening: Regulatory perspectives and needs. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2011, 23, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedeken, E.J.; Tahar, A.; McHugh, B.; Rowan, N.J. Monitoring, sources, receptors, and control measures for three European Union watch list substances of emerging concern in receiving waters—A 20 year systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1140–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S. The sustainable development goals of the United Nations: A comparative midterm research review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 453, 142272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. A Health Perspective on the Role of the Environment in One Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, S.; Sengupta, P.; Bagchi, S.; Chhikara, B.S.; Pavlík, A.; Sláma, P.; Roychoudhury, S. Reproductive toxicity of combined effects of endocrine disruptors on human reproduction. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1162015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takesono, A.; Kudoh, T.; Tyler, C.R. Application of Transgenic Zebrafish Models for Studying the Effects of Estrogenic Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals on Embryonic Brain Development. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 718072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojnarowski, K.; Cholewińska, P.; Palić, D.; Bednarska, M.; Jarosz, M.; Wiśniewska, I. Estrogen Receptors Mediated Negative Effects of Estrogens and Xenoestrogens in Teleost Fishes-Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asare, E.A. Status of pharmaceuticals in the Korle Lagoon and their toxicity to non-target organisms. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Abdollahi, M. Environmental Distribution of Personal Care Products and Their Effects on Human Health. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2021, 20, 216–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.P.; Silva-Pavez, E.; Carrillo-Beltrán, D.; Calaf, G.M. Occurrence and exposure assessment of glyphosate in the environment and its impact on human beings. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tao, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Song, M. Potential Health Impact of Microplastics: A Review of Environmental Distribution, Human Exposure, and Toxic Effects. Environ. Health 2023, 1, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataba, A.; Botha, T.L.; Nakayama, S.M.M.; Yohannes, Y.B.; Ikenaka, Y.; Wepener, V.; Ishizuka, M. Environmentally relevant lead (Pb) water concentration induce toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 252, 109215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Guo, Y.; Jin, L.; Liang, X.; Chen, G.; Sun, W.; Xiao, L.; Qian, G.; Ge, C. ESR1 mediates estrogen-induced feminization of genetic male Chinese soft-shelled turtle. Biol. Reprod. 2022, 107, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.B.P.; Carreiró, F.; Ramos, F.; Sanches-Silva, A. The role of endocrine disruptors in female infertility. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 7069–7088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Lv, Y.; Meng, X.; Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; Kou, G.; Yang, X.; Luo, J. The potential toxic effects of estrogen exposure on neural and vascular development in zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 283, 116862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagno, W.A.; de Oliveira Sofiatti, J.R.; Alves, C.; Sutorillo, N.T.; Vanin, A.P.; Bilibio, D.; Pompermaier, A.; Barcellos, L.J.G. Synthetic estrogen bioaccumulates and changes the behavior and biochemical biomarkers in adult zebrafish. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 92, 103857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamagno, W.A.; Alves, C.; Vanin, A.P.; Bilibio, D.; Varela, A.C.C.; Mozzato, M.T.; Barcellos, L.J.G. A transferência dietética de 17α-etinilestradiol altera os biomarcadores bioquímicos e comportamentais em peixes-zebra adultos (Danio rerio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 262, 109472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Liang, M.; Chen, R.; Hong, X.; Zha, J. Reproductive toxicity and estrogen activity in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations of octocrylene. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Matos, M.; Coimbra, A.M. Developmental toxicity of endocrine disruptors in early life stages of zebrafish, a genetic and embryogenesis study. Neurotoxicology Teratol. 2014, 46, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Mavingui, P.; Boetsch, G.; Boissier, J.; Darriet, F.; Duboz, P.; Fritsch, C.; Giraudoux, P.; Le Roux, F.; Morand, S.; et al. The One Health Concept: 10 Years Old and a Long Road Ahead. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumford, E.L.; Martinez, D.J.; Tyance-Hassell, K.; Cook, A.; Hansen, G.R.; Labonté, R.; Mazet, J.A.K.; Mumford, E.C.; Rizzo, D.M.; Togami, E.; et al. Evolution and expansion of the One Health approach to promote sustainable and resilient health and well-being: A call to action. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1056459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulio, V.; van Bavel, B.; Brorström-Lundén, E.; Harmsen, J.; Hollender, J.; Schlabach, M.; Slobodnik, J.; Thomas, K.; Koschorreck, J. Emerging pollutants in the EU: 10 years of NORMAN in support of environmental policies and regulations. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanganyado, E. Chapter 19—Policies and regulations for the emerging pollutants in freshwater ecosystems: Challenges and opportunities. In Emerging Freshwater Pollutants; Dalu, T., Tavengwa, N.T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Estrogenic Compound | Min. | Max. |
|---|---|---|
| alfatradiol (17α-estradiol) | 0.026 | 1250.0 |
| diClE2 | 0.041 | 17.0 |
| estradiol | 0.002 | 7,988,120.0 |
| estradiol-glucoside | 105.5 | 105.5 |
| estradiol-3-glucuronide | 47.0 | 210.0 |
| estradiol-3-sulfate | 0.041 | 141.0 |
| estradiol-3-β-D-glucuronide | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| estradiol-17-acetate | 1.1 | 176.0 |
| estradiol-17-glucuronide | 1.1 | 7.34 |
| estradiol-17-sulfate | 79.8 | 79.8 |
| estradiol-17-valerate | 2.3 | 8.47 |
| estradiol-17-β-D-glucuronide | 0.4 | 1.8 |
| estriol | 0.003 | 83,430.0 |
| estriol-3-glucuronide | 37.0 | 150.0 |
| estriol-3-sulfate | 0.100 | 160.0 |
| estriol-3-β-D-glucuronide | 2.7 | 2.7 |
| estriol-16-glucuronide | 0.34 | 2.67 |
| estrone | 0.03 | 10,380,000.0 |
| estrone-3-glucuronide | 3.0 | 40.0 |
| estrone-3-sulfate | 0.041 | 255.0 |
| estrone-3-β-D-glucuronide | 0.2 | 17.0 |
| ethinylestradiol | 0.002 | 624,300.0 |
| ethinylestradiol-3-glucuronide | 0.23 | 5.85 |
| ethinylestradiol-3-sulfate | 0.080 | 178.0 |
| E2-diS | 160.0 | 1500.0 |
| E2-monoS | 3.3 | 6.6 |
| E2-S&G | 3.7 | 17.0 |
| mestranol | 1.94 | 110.0 |
| monoBrEE2 | 0.041 | 0.041 |
| 2-bromo-17β-estradiol | 21.0 | 36.0 |
| 2-hydroxyestrone | 3.9 | 6.6 |
| 4-hydroxyestrone | 6.3 | 10.3 |
| 2,4-dibromo-17β-estradiol | 7.6 | 7.6 |
| 2,4-dichloro-17β-estradiol | 15.0 | 18.0 |
| 4-chloro-estriol | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| 4-chloro-17α-ethynylestradiol | 4.2 | 4.2 |
| 16α-hydroxyestrone | 2.4 | 51.7 |
| 16-ketoestradio | 5.1 | 16.6 |
| 17α-estradiol-3-sulfate | 170.0 | 170.0 |
| Water Body | Min. | Max. |
|---|---|---|
| Bay water | 1.62 | 20.9 |
| Canal | 0.018 | 10,380,000.0 |
| Creek | 0.125 | 4240.0 |
| Coastal water | 0.10 | 278.4 |
| Dam water | 0.004 | 7.0 |
| Drainage extension | 284,220.0 | 1,065,000.0 |
| Drinking water | 0.002 | 1,878,140.0 |
| Effluent of domestic wastewater treatment plants | 2.1 | 47.0 |
| Effluent of fish farm | 2.25 | 3.6 |
| Effluent of livestock wastewater treatment plants | 1.5 | 10,000.0 |
| Embayment | 1.58 | 1.87 |
| Effluent of industrial wastewater treatment plants | 1.8 | 120.0 |
| Effluent of sewage treatment plants | 0.04 | 102,500.0 |
| Estuarine | 0.04 | 176.0 |
| Effluent of wastewater treatment plants | 0.02 | 83,430.0 |
| Groundwater | 0.11 | 1745.0 |
| Lake | 0.03 | 925,240.0 |
| Lagoon | 0.58 | 5,142,900.0 |
| Ocean | 0.16 | 0.5 |
| Pond | 1.2 | 25.0 |
| Reclaimed water | 1.1 | 18.1 |
| Reservoir | 0.01 | 15.0 |
| Residual water | 270.0 | 400.0 |
| River | 0.002 | 7,988,120.0 |
| Sea canal | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Seawater | 0.041 | 9.2 |
| Spring water | 0.01 | 0.17 |
| Storm water runoff | 2.3 | 240.0 |
| Surface water | 0.01 | 624,300.0 |
| Tap water | 0.1 | 9570.0 |
| Tributary | 0.5 | 12.0 |
| Treated water | 1.0 | 1.5 |
| Unidentified water | 0.75 | 1.68 |
| Untreated wastewater discharged into surface waters | 5.9 | 640.0 |
| Waterway | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| Well water | 0.1 | 47,310.0 |
| Wetland water | 0.3 | 103.0 |
| Stream | 0.04 | 556,340.0 |
| Swimming pool water | 4.0 | 43.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Silva, R.L.; Lima e Silva, M.A.; Teixeira, T.P.; Farnesi de Assunção, T.S.; Teixeira, P.P.; Tamagno, W.A.; Rocha, T.L.; Gonçalves, J.C.d.S.I.; Marcon, M. A Systematic Review of Estrogens as Emerging Contaminants in Water: A Global Overview Study from the One Health Perspective. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15050148
da Silva RL, Lima e Silva MA, Teixeira TP, Farnesi de Assunção TS, Teixeira PP, Tamagno WA, Rocha TL, Gonçalves JCdSI, Marcon M. A Systematic Review of Estrogens as Emerging Contaminants in Water: A Global Overview Study from the One Health Perspective. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2025; 15(5):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15050148
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Silva, Rhitor Lorca, Marco Antonio Lima e Silva, Tiago Porfírio Teixeira, Thaís Soares Farnesi de Assunção, Paula Pinheiro Teixeira, Wagner Antonio Tamagno, Thiago Lopes Rocha, Julio Cesar de Souza Inácio Gonçalves, and Matheus Marcon. 2025. "A Systematic Review of Estrogens as Emerging Contaminants in Water: A Global Overview Study from the One Health Perspective" Journal of Xenobiotics 15, no. 5: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15050148
APA Styleda Silva, R. L., Lima e Silva, M. A., Teixeira, T. P., Farnesi de Assunção, T. S., Teixeira, P. P., Tamagno, W. A., Rocha, T. L., Gonçalves, J. C. d. S. I., & Marcon, M. (2025). A Systematic Review of Estrogens as Emerging Contaminants in Water: A Global Overview Study from the One Health Perspective. Journal of Xenobiotics, 15(5), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15050148









