Metabolic Costs of Emerging Contaminants: Cellular Energy Allocation in Zebrafish Embryos
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Test Solutions
2.2. Danio rerio Embryos
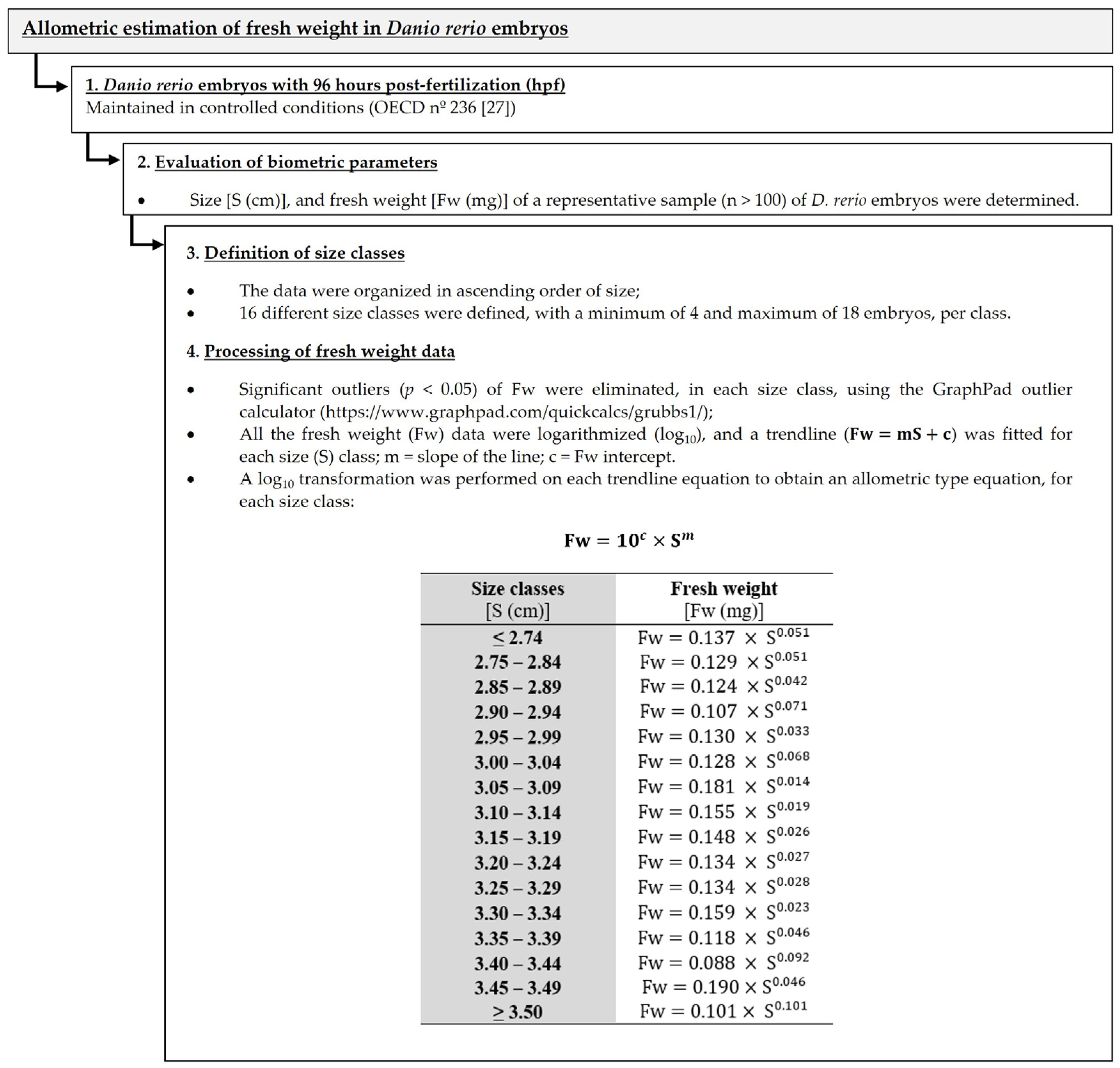
2.3. Allometric Estimation of Fresh Weight in Danio rerio Embryos
2.4. Bioassay Conditions
2.5. Cellular Energy Allocation (CEA)
2.5.1. Available Energy Reserves (Ea)
2.5.2. Energy Consumed (Ec)
2.5.3. Cellular Energy Allocation (CEA) Calculation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
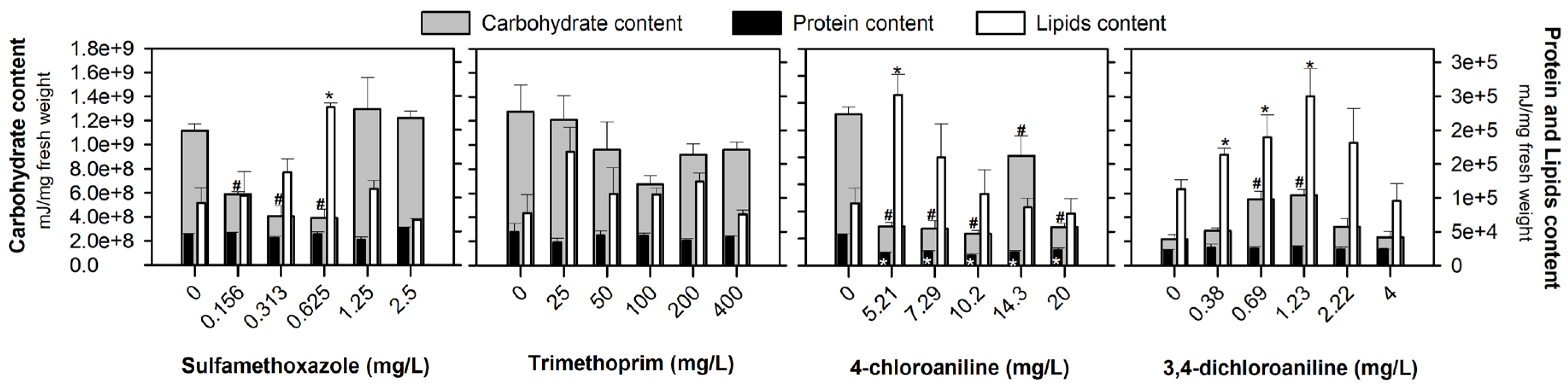
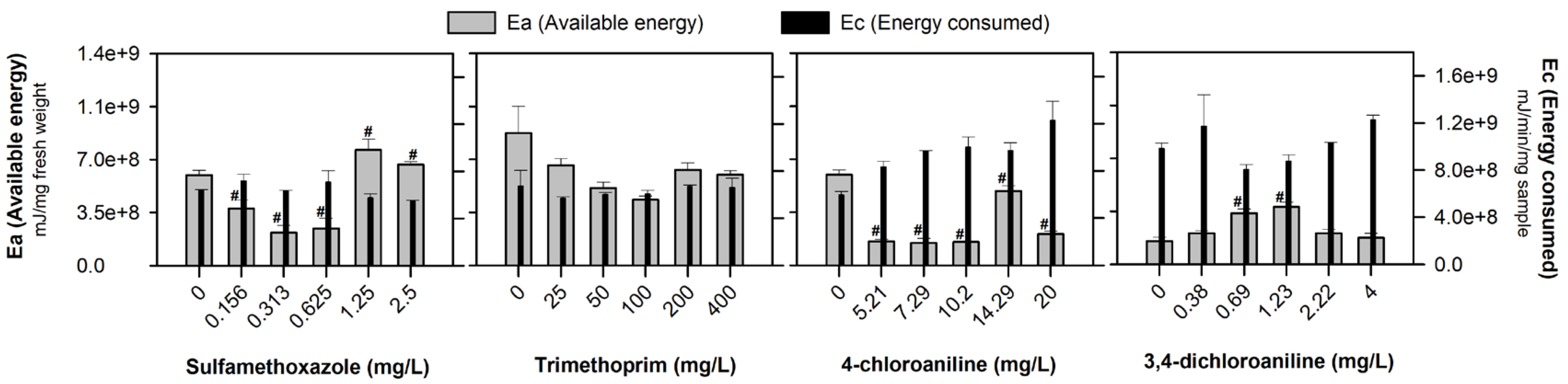
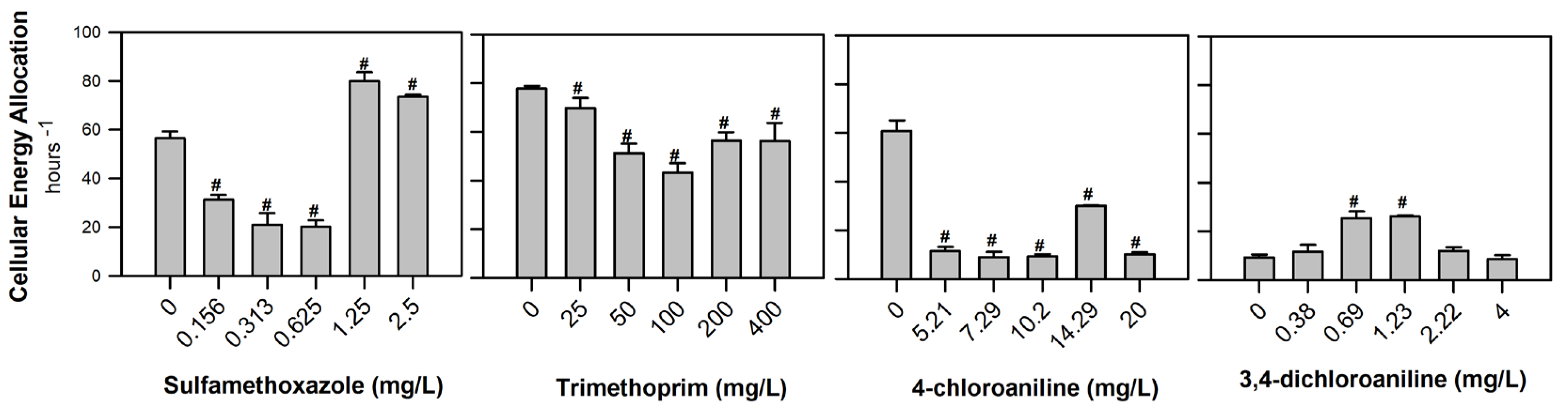
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morin-Crini, N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Liu, G.; Balaram, V.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Lu, Z.; Stock, F.; Carmona, E.; Teixeira, M.R.; Picos-Corrales, L.A.; et al. Emerging Contaminants: Analysis, Aquatic Compartments and Water Pollution. In Emerging Contaminants Vol. 1: Occurrence and Impact; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–111. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Xiang, L.; Sze-Yin Leung, K.; Elsner, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pan, B.; Sun, H.; An, T.; Ying, G.; et al. Emerging Contaminants: A One Health Perspective. Innovation 2024, 5, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebelo, D.; Antunes, S.C.; Rodrigues, S. The Silent Threat: Exploring the Ecological and Ecotoxicological Impacts of Chlorinated Aniline Derivatives and the Metabolites on the Aquatic Ecosystem. J. Xenobiotics 2023, 13, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diogo, B.S.; Rodrigues, S.; Antunes, S.C. Antibióticos. Do Passado Ao Presente, Passando Pelo Ambiente. Rev. Ciência Elem. 2023, 11, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coen, W.M.; Janssen, C.R. The Missing Biomarker Link: Relationships between Effects on the Cellular Energy Allocation Biomarker of Toxicant-Stressed Daphnia magna and Corresponding Population Characteristics. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, L.; Marinov, D.; Sanseverino, I.; Cuenca, A.; Niegowska, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Lettieri, T. Selection of Substances for the 3rd Watch List under the Water Framework Directive; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, L.G.; Marinov, D.; Sanseverino, I.; Cuenca, A.N.; Niegowska, M.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Lettieri, T. Selection of Substances for the 4th Watch List Under the Water Framework Directive; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Diogo, B.S.; Rodrigues, S.; Golovko, O.; Antunes, S.C. From Bacteria to Fish: Ecotoxicological Insights into Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Cui, H.; Jia, X.; Huang, X. Occurrence and Ecotoxicity of Sulfonamides in the Aquatic Environment: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.; Santos, L. Antibiotics in the Aquatic Environments: A Review of the European Scenario. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 736–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanpradit, P.; Byeon, E.; Lee, J.-S.; Jeong, H.; Kim, H.S.; Peerakietkhajorn, S.; Lee, J.-S. Combined Effects of Nanoplastics and Elevated Temperature in the Freshwater Water Flea Daphnia magna. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.; Teixeira, M.I.; Diogo, B.S.; Antunes, S.C. Assessment of the Ecotoxicological Effects of Deltamethrin to Daphnia magna: Linking Sub-Individual and Supra-Individual Parameters. Watershed Ecol. Environ. 2023, 5, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coen, W.M.; Janseen, C.R. The Use of Biomarkers in Daphnia magna Toxicity Testing. IV. Cellular Energy Allocation: A New Methodology to Assess the Energy Budget of Toxicant-Stressed Daphnia Populations. J. Aquat. Ecossystem Stress Recovery 1997, 6, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, R.; Bervoets, L.; De Coen, W.; Blust, R. Cellular Energy Allocation in Zebra Mussels Exposed along a Pollution Gradient: Linking Cellular Effects to Higher Levels of Biological Organization. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 129, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, P.K.S. Use of Biomarkers in Environmental Monitoring. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2009, 52, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, F.R.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Oliveira, D.P.d.; Gravato, C. Toxicity of Dyes to Zebrafish at the Biochemical Level: Cellular Energy Allocation and Neurotoxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coen, W.M.; Wim, M.; Janssen, C.; Persoone, G. Biochemical Assessment of Cellular Energy Allocation in Daphnia magna Exposed to Toxic Stress as an Alternative to the Conventional ‘Scope for Growth’ Methodology. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Biological Markers of Pollution; Association Nationale de Protection des Plantes: Chinon, France, 1995; pp. 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Gravato, C.; Almeida, J.R.; Silva, C.; Oliveira, C.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Using a Multibiomarker Approach and Behavioural Responses to Assess the Effects of Anthracene in Palaemon serratus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 149, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.C.M.; Gravato, C.; Quintaneiro, C.; Golovko, O.; Žlábek, V.; Barata, C.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Pestana, J.L.T. Life History and Biochemical Effects of Chlorantraniliprole on Chironomus riparius. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, I.M.; Frederich, M.; Bagwe, R.; Lannig, G.; Sukhotin, A.A. Energy Homeostasis as an Integrative Tool for Assessing Limits of Environmental Stress Tolerance in Aquatic Invertebrates. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 79, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderemi, A.O.; Novais, S.C.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Alves, L.M.; Hunter, C.; Pahl, O. Oxidative Stress Responses and Cellular Energy Allocation Changes in Microalgae Following Exposure to Widely Used Human Antibiotics. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 203, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, R.; Ceriani, L.; Ippolito, A.; Lettieri, T. Development of the First Watch List under the Environmental Quality Standards Directive; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxemburg, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tourinho, P.S.; Silva, A.R.R.; Santos, C.S.A.; Prodana, M.; Ferreira, V.; Habibullah, G.; Kočí, V.; van Gestel, C.A.M.; Loureiro, S. Microplastic Fibers Increase Sublethal Effects of AgNP and AgNO in Daphnia magna by Changing Cellular Energy Allocation. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, A.S.; Sarmento, R.A.; Gravato, C.; Rodrigues, A.C.M.; Campos, D.; Simão, F.C.P.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Strategies of Cellular Energy Allocation to Cope with Paraquat-Induced Oxidative Stress: Chironomids vs Planarians and the Importance of Using Different Species. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heugens, E.H.W.; Verbruggen, E.M.J. Environmental Risk Limits for Monochloroanilines; National Institute for Public Health and the Environment: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, G.; Patring, J.; Kreuger, J.; Norrgren, L.; Oskarsson, A. Toxicity of 15 Veterinary Pharmaceuticals in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD Test, No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2013; ISBN 9789264203709.
- Iftikhar, N.; Konig, I.; English, C.; Ivantsova, E.; Souders, C.L.; Hashmi, I.; Martyniuk, C.J. Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) Alters Immune and Apoptotic Endpoints in Developing Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxics 2023, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebelo, D.; Correia, A.T.; Nunes, B. Acute and Chronic Effects of Environmental Realistic Concentrations of Simvastatin in Danio rerio: Evidences of Oxidative Alterations and Endocrine Disruptive Activity. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 81, 103522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirth, C.K.; Anthony Frankino, W.; Shingleton, A.W. Allometry and Size Control: What Can Studies of Body Size Regulation Teach Us about the Evolution of Morphological Scaling Relationships? Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2016, 13, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, J.; Schouman, A.; Lyphout, L.; Cousin, X.; Lefrancois, C. Allometric Relationship between Body Mass and Aerobic Metabolism in Zebrafish Danio rerio. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 84, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.L.; Marques, C.R.; Gonçalves, F. Allometric Relations for Ceriodaphnia spp. and Daphnia spp. Ann. Limnol.—Int. J. Limnol. 2004, 40, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogo, B.S.; Antunes, S.C.; Pinto, I.; Amorim, J.; Teixeira, C.; Teles, L.O.; Golovko, O.; Žlábek, V.; Carvalho, A.P.; Rodrigues, S. Insights into Environmental Caffeine Contamination in Ecotoxicological Biomarkers and Potential Health Effects of Danio rerio. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A New and Rapid Colorimetric Determination of Acetylcholinesterase Activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, S.C.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; De Coen, W.; Amorim, M.J.B. Exposure of Enchytraeus albidus to Cd and Zn—Changes in Cellular Energy Allocation (CEA) and Linkage to Transcriptional, Enzymatic and Reproductive Effects. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeonyejiaku, C.D.; Ifedigbo, I.I.; Okoye, C.O.; Ezenwelu, C.O. Cellular Energy Budget in Tropical Freshwater Fish Following Exposure to Sublethal Concentrations of Cadmium. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2019, 11, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, R.; De Boeck, G.; Blust, R. Changes in Cellular Energy Budget as a Measure of Whole Effluent Toxicity in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbrouck, T.; Soetaert, A.; van der Ven, K.; Blust, R.; De Coen, W. Nickel and Binary Metal Mixture Responses in Daphnia magna: Molecular Fingerprints and (Sub)Organismal Effects. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 92, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanungo, S.; Wells, K.; Tribett, T.; El-Gharbawy, A. Glycogen Metabolism and Glycogen Storage Disorders. Ann Transl Med 2018, 6, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherkas, A.; Holota, S.; Mdzinarashvili, T.; Gabbianelli, R.; Zarkovic, N. Glucose as a Major Antioxidant: When, What for and Why It Fails? Antioxidants 2020, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J. Liver Physiology: Metabolism and Detoxification. In Pathobiology of Human Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1770–1782. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Legradi, J.; Leonards, P. Using Comprehensive Lipid Profiling to Study Effects of PFHxS during Different Stages of Early Zebrafish Development. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 151739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Li, F.; Mortimer, M.; Li, Z.; Peng, B.-X.; Li, M.; Guo, L.-H.; Zhuang, G. Antibiotics Disrupt Lipid Metabolism in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Larvae and 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Song, J.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, W.-K.; Yoon, S.; Chun, H.-S. 3,4-Dichloroaniline Promotes Fatty Liver in Zebrafish Larvae. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Oulmi, Y.; Schroeder, A.; Storch, V.; Braunbeck, T. Toxicity of 4-Chloroaniline in Early Life Stages of Zebrafish (Danio rerio): II. Cytopathology and Regeneration of Liver and Gills after Prolonged Exposure to Waterborne 4-Chloroaniline. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulmi, Y.; Braunbeck, T. Toxicity of 4-Chloroaniline in Early Life-Stages of Zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio): I. Cytopathology of Liver and Kidney after Microinjection. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1996, 30, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Oost, R.; Beyer, J.; Vermeulen, N.P. Fish Bioaccumulation and Biomarkers in Environmental Risk Assessment: A Review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 13, 57–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chang, X.; Sokolova, I.M.; Wei, S.; Liu, W.; Fang, J.K.H.; Hu, M.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y. The Effect of Microplastics on the Bioenergetics of the Mussel Mytilus coruscus Assessed by Cellular Energy Allocation Approach. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 754789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenton, D.; Smirnova, J.B.; Selley, J.N.; Carroll, K.; Hubbard, S.J.; Pavitt, G.D.; Ashe, M.P.; Grant, C.M. Global Translational Responses to Oxidative Stress Impact upon Multiple Levels of Protein Synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 29011–29021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasuri, K.; Zhang, L.; Keller, J.N. Oxidative Stress, Neurodegeneration, and the Balance of Protein Degradation and Protein Synthesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, L.; Dansen, T.B. Cross-Talk between Redox Signalling and Protein Aggregation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Kesharwani, R.K.; Keservani, R.K. Protein, Carbohydrates, and Fats: Energy Metabolism. In Sustained Energy for Enhanced Human Functions and Activity; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moolman, L.; Van Vuren, J.H.J.; Wepener, V. Comparative Studies on the Uptake and Effects of Cadmium and Zinc on the Cellular Energy Allocation of Two Freshwater Gastropods. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2007, 68, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.; Antunes, S.C.; Correia, A.T.; Nunes, B. Toxicity of Erythromycin to Oncorhynchus mykiss at Different Biochemical Levels: Detoxification Metabolism, Energetic Balance, and Neurological Impairment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovačević, M.; Stjepanović, N.; Hackenberger, D.K.; Lončarić, Ž.; Hackenberger, B.K. Comprehensive Study of the Effects of Strobilurin-Based Fungicide Formulations on Enchytraeus albidus. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 1554–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.I.L.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Amorim, M.J.B. Changes in Cellular Energy Allocation in Enchytraeus crypticus Exposed to Copper and Silver—Linkage to Effects at Higher Level (Reproduction). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14241–14247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simcic, T.; Lukancic, S.; Brancelj, A. Comparative Study of Electron Transport System Activity and Oxygen Consumption of Amphipods from Caves and Surface Habitats. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Båmstedt, U. ETS Activity as an Estimator of Respiratory Rate of Zooplankton Populations. The Significance of Variations in Environmental Factors. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1980, 42, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erk, M.; Ivanković, D.; Strižak, Ž. Cellular Energy Allocation in Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) from the Stratified Estuary as a Physiological Biomarker. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, H. Assessing the Sub-Lethal Effects of Copper, Cadmium, Pentachlorophenol and 3,4-Dichloroaniline on Freshwater Rotifers Brachionus calyciflorus Using the Energy Budget Biomarkers. Ph.D. Thesis, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rebelo, D.; Antunes, S.C.; Rodrigues, S. Hidden Dangers: Aromatic Amines and Their Impact on Freshwater Species. Chem. Ecol. 2025, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compounds Name | Properties | Literature Data (mg/L) | Stock Solutions and Treatments (mg/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS nº | Classification Group | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Purity (%) | |||
| Sulfamethoxazole | 723-46-6 | Antibiotic | C10H11N3O3S | 253.28 | ≥98.0 | 0.013 to 5.00 a | Stock solution: 2.50 0.156 to 2.50 (Dilution factor 2×) |
| Trimethoprim | 738-70-5 | Antibiotic | C14H18N4O3 | 290.30 | ≥98.5 | 10.0 b | Stock solution: 400 25.0 to 400 (Dilution factor 2×) |
| 4-chloroaniline | 106-47-8 | Aromatic amine | C6H6ClN | 127.57 | 98.0 | 41.2 c | Stock solution: 20.0 5.21 to 20.0 (Dilution factor 1.4×) |
| 3,4-dichloroaniline | 95-76-1 | Aromatic amine | C6H5Cl2N | 162.02 | 98.0 | 4.00 d | Stock solution: 4.00 0.38 to 4.00 (Dilution factor 1.8×) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diogo, B.S.; Rebelo, D.; Antunes, S.C.; Rodrigues, S. Metabolic Costs of Emerging Contaminants: Cellular Energy Allocation in Zebrafish Embryos. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040099
Diogo BS, Rebelo D, Antunes SC, Rodrigues S. Metabolic Costs of Emerging Contaminants: Cellular Energy Allocation in Zebrafish Embryos. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2025; 15(4):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040099
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiogo, Bárbara S., Daniela Rebelo, Sara C. Antunes, and Sara Rodrigues. 2025. "Metabolic Costs of Emerging Contaminants: Cellular Energy Allocation in Zebrafish Embryos" Journal of Xenobiotics 15, no. 4: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040099
APA StyleDiogo, B. S., Rebelo, D., Antunes, S. C., & Rodrigues, S. (2025). Metabolic Costs of Emerging Contaminants: Cellular Energy Allocation in Zebrafish Embryos. Journal of Xenobiotics, 15(4), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15040099









