Abstract
The plastic manufacturing industry has a crucial role in the global economy with a significant impact in a wide range of fields. The chemical risk to which workers are potentially exposed is difficult to characterize and strictly related to both the products and processes adopted. Among the chemicals used, we can cite styrene, phenol, butadiene and phthalates, but nano- and microplastic particles can also be released in the work environment. In this pilot study, we present for the first time an NMR-based metabolomic approach for assessing urinary profiles of workers employed in a plastic manufacturing company. Urine samples from twelve workers and thirteen healthy volunteers were collected and analyzed by NMR spectroscopy. Forty-six urinary metabolites belonging to different chemical classes were univocally identified and quantified. The dataset so obtained was then subjected to multivariate statistical analysis to characterize each profile and highlight any differences. An alteration in some metabolites involved in several pathways, such as amino acid metabolism and NAD metabolism, was found, and a strong impact on gut microflora was also speculated. Ultimately, our work has the objective of adding a tile to the knowledge of biological effects possibly related to occupational exposure even if it is below the threshold limit values.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, the Chemical Abstracts Service has univocally identified and cataloged approximately 219 million chemical substances (data updated to April 2024). In accordance with the European Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006, for the registration, evaluation and authorization of chemicals, aimed to ensure a higher level of protection of human health, while not penalizing the European chemical industry; among all those cataloged, 26,865 different substances are in possession of marketing authorization. It is interesting to underline that the number of substances for which a professional exposure limit is foreseen, according to national legislation, is approximately 170, despite the more than 25 thousand present on the market as previously mentioned. These data suggest a condition of underestimation of occupational diseases caused by chemical agents, even in the case of full compliance with the current legislation. Metabolomics allows for early evaluation of occupational exposures, and it could be a useful tool that focuses attention on aspects that remain unclear today, such as the long-term effects at concentrations of toxics below the threshold limit values, or the evaluation of exposure to mixtures of substances or again exposures to both physical and chemical agents. The scope is to promote targeted risk assessments and develop personalized protective measures for the health of specific individuals or vulnerable groups, improving safety standards and potentially lowering occupational healthcare costs by focusing on prevention rather than treatment.
Plastic manufacturing represents one of the largest industrial sectors all over the world, with a critical role in the global economy and a significant impact in a wide range of applications such as packaging, construction, automotive and transportation, aerospace, electronics and even healthcare. According to a study by Grand View Research, the global plastic manufacturing industry was valued at over USD 700 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow in the next years. This market has surely experienced exponential growth over the past few decades [1], thanks to the increasing demand for plastic products, advancements in technology and low production costs. The entire production chain, from manufacturing and production to research and development, employs millions of people worldwide, and the Asia-Pacific region dominates the global market. Despite this, the industry is also facing important challenges, mainly related to the high environmental impact of plastic materials [2]. At the same time, from the point of view of occupational hygiene, the chemical risk correlated to this compartment is complex to characterize based on the wide range of products, subproducts and processes adopted. A detailed report published by the International Labour Organization [3] in 2023 indicates the potential risks to which workers employed in plastic manufacturing are exposed. Among this had to be included exposure to many chemicals such as hydrogen chloride, styrene, phenol, butadiene, formaldehyde, phthalates, lead, polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and perfluorinated substances (PFASs), used as additives or produced as by-products. These substances guarantee the desired modulation of material properties, and they are released mainly during the heating of raw materials for creating plastic products, in the form of fumes [4,5,6]. Moreover, a recent significant concern, not only from the occupational health point of view, is represented by microplastics. Microplastics (MPs) are defined as plastic particles with dimensions smaller than 5 mm [7] manufactured with the purpose of being added to other products (i.e., cosmetics, fertilizer, detergents) or accidentally created by the fragmentation and degradation of plastics. MPs exist in many different forms, including spheres, fibers or pellets, being present nowadays in all environmental matrices as ubiquitous pollutants [8]. These particles can also act as carriers for dangerous microorganisms or hazards present in the atmosphere [9,10]. More and more studies have shown potential risks for health related to MP exposure in terms of effects on the cardiovascular system, inflammatory lesions, metabolic disturbances, oxidative stress and even neurotoxicity [11,12,13]. Workers employed in the plastic manufacturing industry may be exposed to microplastic dusts, considering that exposure in workplaces can occur mainly through inhalation and ingestion. Nano- and microplastic particles (NMPs) can be generated during several activities related to the production of polymer beads or powder, or from processes such as extrusion, chopping, injection molding, 3D printing, utensil coating, laser cutting, high-speed drilling and treatment of polymer composites. Emission rates of NMPs would depend on the type of polymer and process employed [14,15].
In view of the above, the scenario appears very intricate, and consequently, the observable effects on the organism should be interpreted as a complex response to the global exposure conditions. In this regard, metabolomics, defined as “the quantitative measurement of the dynamic multiparametric metabolic response of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli or genetic modification” [16], has proven to be up to the task. The chosen analytical platform is the NMR spectroscopy because, as just demonstrated [17,18,19], it allows not only the simultaneous qualitative and quantitative analysis of hundreds of endogenous compounds in complex matrices but also a structural characterization and dosage of potentially unknown xenobiotic metabolites. It is important to note that to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study with the aim of investigating the urinary metabolic profile of workers employed in plastic manufacturing compartments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
For this study, twelve workers employed in a plastic molding company and thirteen healthy volunteers as control group were enrolled. The characteristics of the subjects are reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the investigated subjects.
All samples were collected at the beginning of the working shift, after an overnight fasting, and in the middle of the working week. The control group consists of subjects enrolled on a voluntary basis, age- and sex-matched to the exposed subjects, whose occupation was known in order to verify the absence of occupational exposure to chemical agents of the same or different types compared to those examined. Each subject included in this study agreed to provide information on health status and main lifestyle habits. The absence of metabolic diseases, liver disease, diabetes, neoplastic pathologies, kidney disease or other pathologies that could seriously affect metabolism was checked. The absence of an impact of mean age differences between groups in relation to the main effect of exposure was also assessed (further details in Supplementary Figure S2).
All experiments were conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki and followed the International Code of Ethics for Occupational Health Professionals, published by the International Committee of Occupational Health (ICOH). The information gathered was used as aggregate data referring to the whole group of workers, with no risk of individual identification. This study was approved by the Ethical Committee “Lazio 2”, study number: 31.23, protocol ID: 0041631 (no-profit study), 2 March 2023. Written informed consent was obtained from all the involved subjects.
2.2. Sample Preparation
All samples were prepared following a previously described protocol for biofluid metabolomics analysis [20] with some modifications. Briefly, an aliquot of 1200 µL of each sample was first added with 12 µL of NaN3 in order to obtain a bacteriostatic effect. Then, each sample was centrifuged at 4 °C for 15 min at 11,000 rpm to remove any cellular debris. Finally, 400 µL of the supernatant was added with 200 µL of buffer solution (PBS 200 mM, pH = 7) and with 60 µL of a solution of the internal standard 3-(trimethylsilyl) propionic-2,2,3,3-d4 acid sodium salt (TSP) in D2O for a final concentration of TSP in urine of 1.82 mM. All samples were stored at −80 °C until the NMR analysis.
2.3. 1H-NMR Spectroscopy for Urinary Metabolomics
NMR spectra were recorded according to [21]. In greater detail, all spectra were acquired with a JEOL JNM-ECZR spectrometer (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), equipped with a magnet operating at 14.09 T and 600.17 MHz for the 1H frequency. For the acquisitions, the following setting parameters were employed: temperature of 298 K, 64 K points and 64 scans, spectral width at 9.03 kHz (15 ppm), presaturation pulse length of 2.00 s, relaxation delay of 5.72 s. All spectra were processed using ACD Labs software v.12.0 (Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc., 8 King Street East, Toronto, ON, Canada). After the multiplication for an exponential window function (LB = 0.3 Hz) and the application of Fourier Transform, spectra were manually phased and baseline corrected by applying the baseline correction FID reconstruction (BCFR) procedure. To allow compound identification, bidimensional experiments were also carried out on selected samples. Total Correlation Spectroscopy (TOCSY) 1H-1H experiments and Heteronuclear Single Quantum Coherence (HSQC) 1H-13C experiments were performed according to [22]. The assignment of the resonances (reported in Supplementary Table S1) was performed by the analysis of cross-correlated signals in 2D spectra and by comparison with the literature and open access databases [23,24]. For quantitative analysis, only signals free from overlapping have been chosen, manually integrated and normalized for the number of protons generating the signal. These values were then compared with the normalized integral of TSP (internal concentration standard), and the obtained concentrations were further normalized for creatinine concentration, referring to the singlet signal at 4.05 ppm. Quantities were finally expressed as μmol/mmol of creatinine (Supplementary Table S2).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Firstly, Principal Component Analysis was applied to the dataset after autoscaling. Subsequently, with the aim of identifying variables significant for discriminating between two groups of healthy volunteers (CTRL) and exposed workers (Exposed), a Partial Least Square discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) model was built, choosing repeated double cross-validation (DCV) as the validation procedure as reported in other studies [25]. Model performance was evaluated by the following figures of merit: sensitivity, specificity, accuracy and percentage of correct classification. Finally, we considered only those variables whose sign along the first canonical variate (CV1) remained consistent during the cross-validation steps as significant [26].
From the univariate point of view, after evaluating the normality and homoscedasticity of the distribution for each variable, the Wilcoxon rank sum test or Student’s t-test was applied. Statistics were carried out employing MATLAB ver. R2023a equipped with the Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox (Natick, MA, USA: The MathWorks Inc.) and in-house-written functions.
3. Results
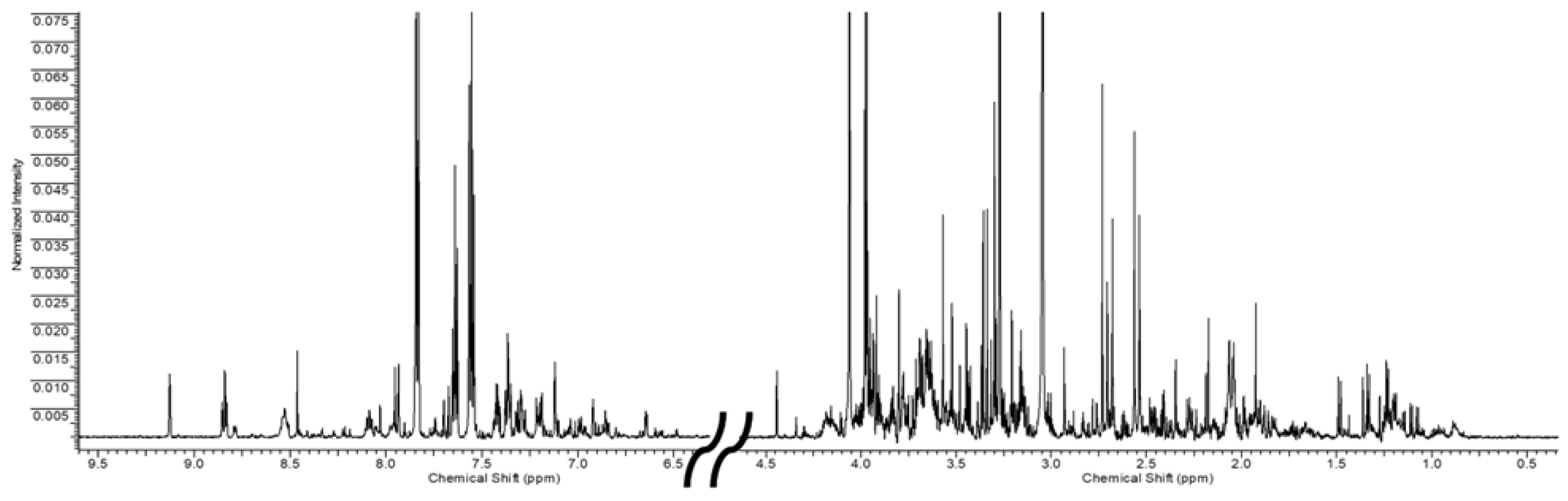
Since no qualitative differences were found in urinary samples between the worker and healthy volunteer groups, a representative 1H-NMR spectrum is reported in Figure 1. Forty-six urinary metabolites, belonging to different chemical classes, were identified and quantified. In addition, four unknown compounds were also observed and quantified. The list of all quantified metabolites with the relative resonance chemical shifts is reported in Supplementary Table S1.
Figure 1.
Representative 1H-NMR spectrum of human urine of both aromatic and aliphatic regiorns (to allow for better visualization, the portion of the spectrum containing the water and urea signals was removed).
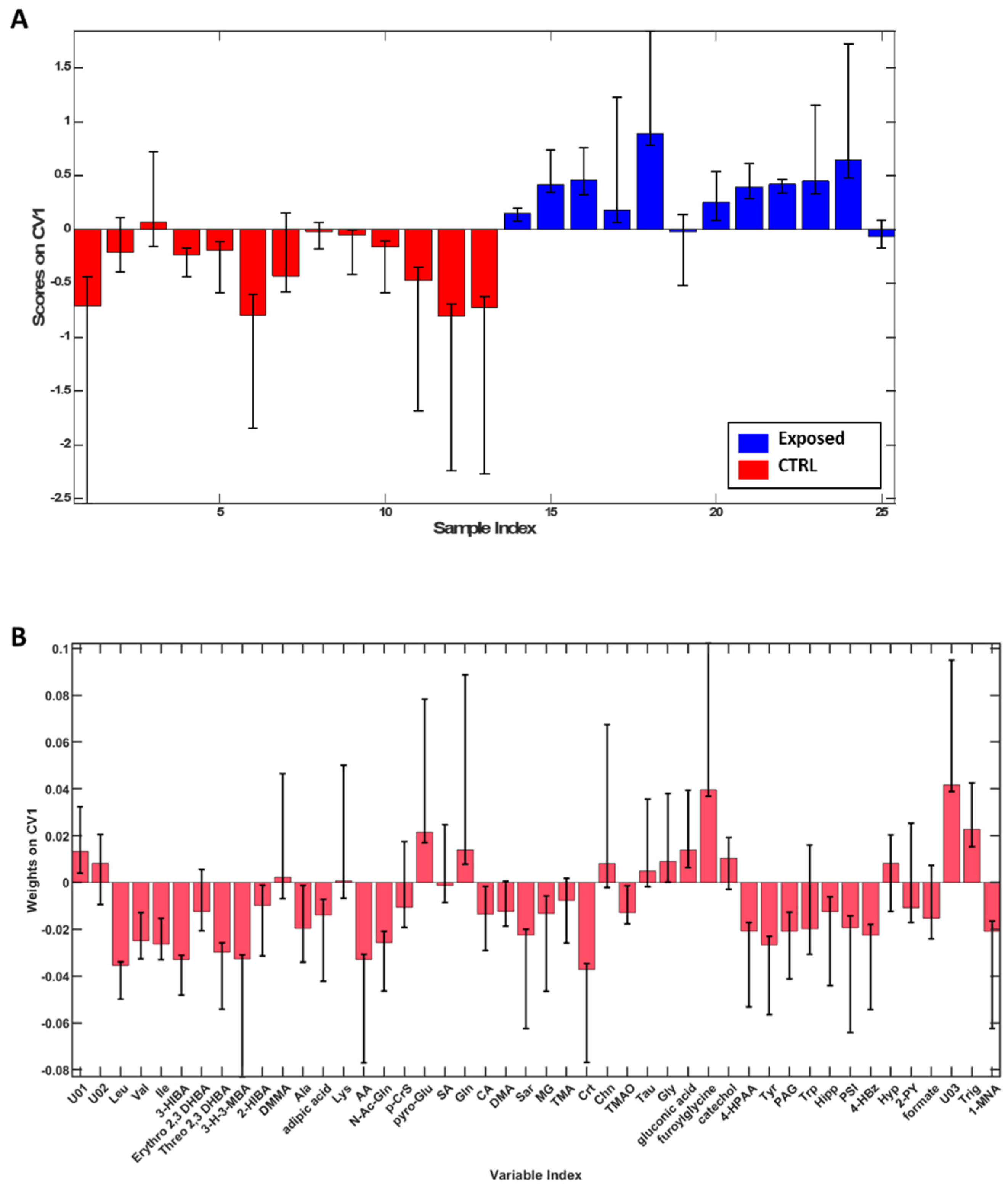
To highlight spontaneous grouping or the presence of any outliers, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was initially applied to the dataset, and it was possible to observe a tendency towards clustering based on exposure as shown in Supplementary Figure S1. Therefore, to better define the differences between groups, a supervised analysis, PLS-DA, was employed. The model built proved to be robust with an overall accuracy of 87.8 ± 4.1% and sensitivity and specificity of 85.5 ± 4.1% and 89.8 ± 6.1%, respectively, in distinguishing Exposed from CTRL. Then, with the aim to evaluate the contribution of each metabolite in discriminating two groups, variable weights along the first canonical variate were evaluated (Figure 2). According to the described method, leucine (Leu), valine (Val), isoleucine (Ile), 3-hydroxyisobutyrate (3-HIBA), threo 2,3 dihydroxybutyrate (Threo 2,3 DHBA), 3-hydroxy-3-methylbutyrate (3-H-3MBA), alanine (Ala), acetate (AA), N-acetylglutamine (N-AcGln), citrate (CA), sarcosine (Sar), methyl-guanidine (MG), creatine (Crt), trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), 4-hydroxyphenylacetate (4-HPAA), tyrosine (Tyr), phenylacetylglycine (PAG), hippurate (Hipp), pseudouridine (PSI), 4-hydroxybenzoate (4-HbzA), formate (FA) and 1-methylnicotinate (1-MNA) were found significant for CTRL, while pyro-Glutamate (pyro-Glu), glutamine (Gln), glycine (Gly), furoylglycine, trigonelline (Trig) and the unknown compound 3 (U03) were significant for the Exposed group.
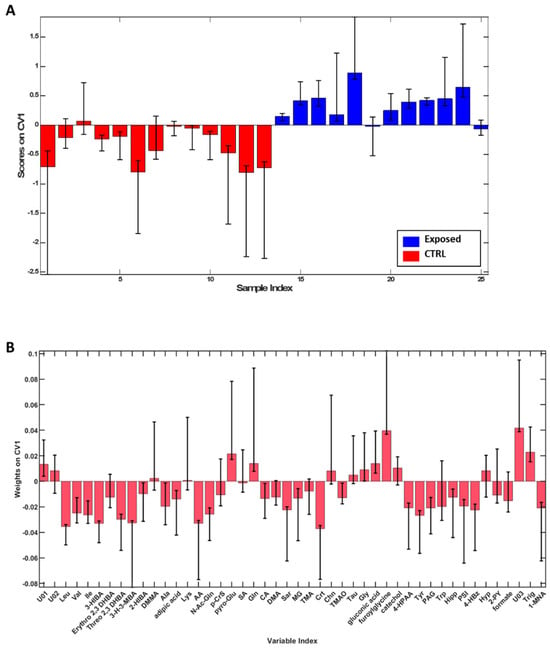
Figure 2.
PLS-DA scores (A), weights on CV1 (B) plots for the comparison between the CTRL (red) and workers (blue). Only variables whose confidence interval bounds do not cross the threshold of 0 are considered significant. According to the described method, leucine (Leu), valine (Val), isoleucine (Ile), 3-hydroxyisobutyrate (3-HIBA), threo 2,3 dihydroxybutyrate (Threo 2,3 DHBA), 3-hydroxy-3-methylbutyrate (3-H-3MBA), alanine (Ala), acetate (AA), N-acetylglutamine (N-AcGln), citrate (CA), sarcosine (Sar), methyl-guanidine (MG), creatine (Crt), trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), 4-hydroxyphenylacetate (4-HPAA), tyrosine (Tyr), phenylacetylglycine (PAG), hippurate (Hipp), pseudouridine (PSI), 4-hydroxybenzoate (4-HbzA), formate (FA) and 1-methylnicotinate (1-MNA) were found significant for CTRL, while pyro-Glutamate (pyro-Glu), glutamine (Gln), glycine (Gly), furoylglycine, trigonelline (Trig) and the unknown compound 3 (U03) were significant for the Exposed group.
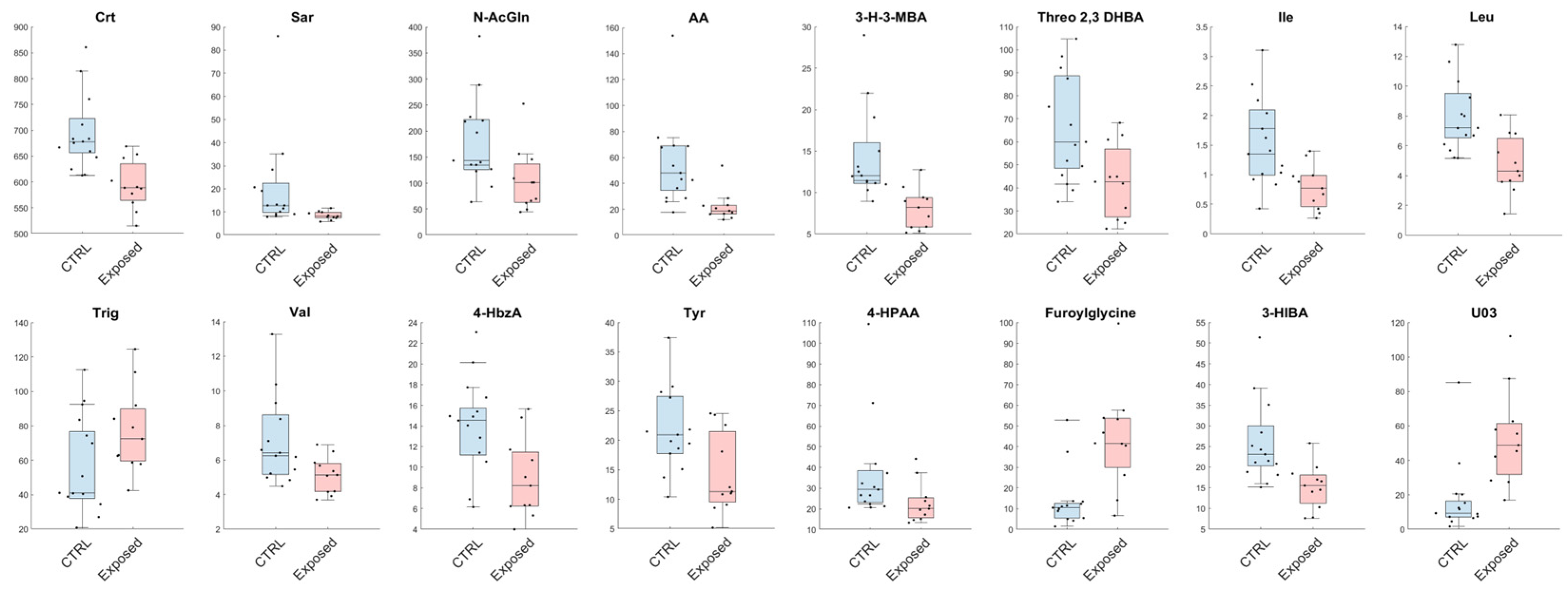
Analogously, from the univariate analysis, we have observed a reduction in urinary levels of Leu, Ile, Threo 2,3 DHB, 3-H-3-MBA, AA, N-AcGln, Sar, Crt, Val, 3-HIBA, 4-HPAA, Tyr and 4-HbzA in the Exposed group, with a contextual increase in concentration of furoylglycine and U03 in comparison to CTRL (Figure 3).
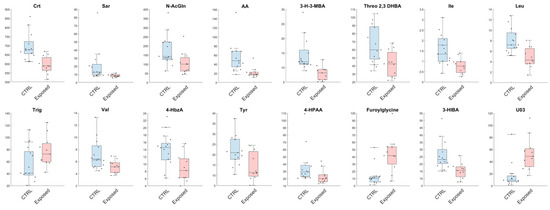
Figure 3.
Metabolites found significant between healthy volunteers (CTRL) and exposed workers (Exposed) with a confidence level of 95% in the univariate statistical analysis. Details are reported in the Statistical Analysis section. The black dots represent the actual distribution of data for each variable. All data are expressed as µmol/mmol of urinary creatinine.
4. Discussion
As mentioned before, the complexity of exposure makes it impossible to untangle single effects related to specific xenobiotics; therefore, in our opinion, it is more correct to talk about a multiparametric response of an organism generated from adaptation to exposure. In this context, the first observation that stands out from the results shown in this work is a general decrease in the urinary concentration of branched-chain amino acids (Ile, Leu and Val) as well as of their principal catabolites 3-HIBA and 3-H-3MBA [27]. Beyond that, a similar trend was also observed in Ala and Tyr levels. Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) are essential amino acids whose catabolism, conversely to most others, does not take place in the liver due to low hepatic activity of branched-chain-amino-acid aminotransferase (BCAT), the first enzyme involved in their catabolic pathway, but in skeletal muscle [28]. BCAAs are principally involved in protein synthesis as well as energy production in addition to performing several important metabolic and signaling functions. Alanine is a non-essential amino acid derived from the reductive amination of pyruvate operated from the enzyme alanine transaminase. This molecule has a crucial role in energy metabolism and helps to maintain blood glucose levels during exercise or fasting but is also involved in ensuring an organism’s proper immune function and protein biosynthesis [29]. Tyrosine represents another example of a non-essential aromatic amino acid obtained starting from phenylalanine by the phenylalanine 4-hydroxylase complex [30,31]. Tyr is the precursor for catecholamine biosynthesis as well as for a few thyroid hormones and neurotransmitters. The ability to synthesize this compound was found to be depleted in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) [32,33]. Based on what has been stated, such a generalized response including a decrease in both essential and non-essential amino acids leads to different possible hypotheses regarding the causes of that variation. The first one considers this phenomenon as related to the influence of xenobiotics on renal amino acid transport systems. Effects of this kind of various substances were described before in the literature [34]. An alternative explanation could be related to an imbalance in nitrogen homeostasis. It is known for example that BCAAs are linked, via a series of transamination reactions, to the maintenance of nitrogen levels in the organism [35]. At the same time, a depletion of such metabolites at the peripheral level was found to reflect a deeper imbalance in nitrogen homeostasis in patients affected by chronic fatigue syndrome. On the other hand, is also possible to speculate about the involvement of gut microbiota. The host–microbiome relationship and its alteration following exposure to chemicals is a topic widely investigated [36,37,38,39]. It was shown, for instance, how halogenated compounds possess a negative impact on the gut microbiota, changing the Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio to a dysbiotic one, or how polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are capable of decreasing the gut richness, increasing pathogenic bacteria abundance and modulating bacterial metabolism in different animal models [39]. Last but not least, several examples were reported where MPs are considered as potential triggers of intestinal inflammation status and dysbiosis, resulting in a notable decrease in gut diversity in humans as well as in other species [40,41]. Regarding the results shown in this study, it was just demonstrated that the microbiota may modulate host amino acid availability through several mechanisms, including affecting intestinal protein digestion enzymes or modifying intestinal permeability [42,43,44], highlighting that changes in microbiome composition or metabolism could influence the host systemic amino acid pool [45,46,47]. To strengthen this last hypothesis presented, it should be noted that among the urinary metabolites considered significant in the discrimination between exposed and healthy volunteers, many were directly related to the intestinal microflora. In particular, we observed a generalized decrease in 2-HIB, acetate, PAG, hippurate, formate, 4-HPAA, 4-HBz, TMA and TMAO, all molecules included in bacterial pathways such as phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolism (PAG, AA and 4-HPAA), catabolism of dietary phenols (hippurate) and quaternary amines (TMA/TMAO) or anaerobic fermentation (formate) [48,49,50] and so all potentially influenced by the composition and activity of microbiota.
A completely opposite trend was observed for the amino acids glycine and glutamine, whose levels were found to be increased in workers. Glycine is the smallest proteinogenic amino acid, and although it can be endogenously produced, it was considered a conditionally essential amino acid [51] based on its crucial role in several biological functions and on the impact of its deficiency on health status in the long term. It was also suggested that glycine concentration represents the rate-limiting step in glutathione (GSH) synthesis [52]. Glutathione is a tripeptide involved in cellular defense mechanisms from oxidatively generated damage and in xenobiotic metabolism. Conjugation with GSH belongs to the phase II metabolic reactions operated by the CYP-450 complex through the GSH S-transferase enzyme [53]. Thus, high glycine levels could represent a biological strategy to maintain an adequate synthesis rate of glutathione employed for xenobiotic elimination.
Glutamine, an amino acid generated by glutamine synthetase (GS) through the condensation of glutamate and ammonia, is principally involved in urea synthesis, nitrogen clearance and gluconeogenesis [33]. Higher concentrations of this compound were also found in cases of occupational exposure to styrene vapors [54] and welding fumes [21], both related to the hyperactivity of the GS enzyme following potentially hepatotoxic xenobiotic exposure.
N1-methylnicotinamide (1-MNA) together with N1-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide (2-Py) and N1-methyl-4-pyridone-3-carboxamide (4-Py) are the major metabolites of NAD, and their urinary outputs are employed to investigate NAD turnover [55]. In this study, we did not measure concentrations of 2-Py and 4-Py because they were below the NMR limit of quantification; however, it could be interesting to highlight that we observed a similar trend in 1-MNA levels to that occurring in other occupational exposures [54]. In that case, an explanation was provided in terms of metabolic response for restoring the NAD+/NADH ratio as an effect of oxidative state imbalance in exposed workers, and the hypothesis was supported by a contextual change in oxidative stress biomarkers in urine. For this reason, we can speculate about a similar response to that just observed even if a deeper understanding of that mechanism through the analysis of such biomarkers could surely represent a valid perspective for future studies.
The last aspect we want to focus on is the significant increase (about 4 times), in the workers group, in the metabolite 2-furoylglycine. 2-Furoylglycine is a carboxamide obtained from the condensation reaction between the amino group of the amino acid glycine and 2-furoic acid that happens in the liver [56]. The role of this metabolite in urine is poorly investigated in the literature. Some studies associated 2-furoylglycine with changes in the gut microbiome or altered mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation [57], but it also was proposed as a putative biomarker of coffee consumption [58]. However, in our opinion, the high level of this compound found in urine could be correlated with occupational exposure to 2-furoic acid. It is known that 2-furoic acid is largely used as a plasticizer, beyond being the main component in the production of furan resins to be used as casts in plastic molding plants [59]. Furfuryl alcohol, a wetting agent, a solvent for dyes and a corrosion inhibitor for fiber-reinforced plastics, and furfural, a rubber additive, are two further compounds widely used in plastic manufacturing and structurally related to 2-furoic acid, which could be rapidly converted in the liver [60]. The inhalation exposure to vapors of these compounds can happen during the thermal processing of plastic products, and it was demonstrated in the past how they were expelled predominantly as their glycine conjugate metabolites [61,62]. Regarding this last observation, we consider it could be interesting information obtained from our results, but surely, the purpose of 2-furoylglycine as a candidate new biomarker of exposure needs further studies with a greater sample size, which can also control sources of uncertainty about the nature of this metabolite such as diet or coffee consumption.
5. Conclusions
In this pilot study, for the first time, the urinary metabolic profiles of workers employed in plastic manufacturing were evaluated. The results found an altered amino acid metabolism after exposure, and a strong gut microbiota involvement was also hypothesized. An increment in urinary levels of Gln and Gly was found in common with other kinds of exposure suggesting active hepatic metabolism potentially related to xenobiotic elimination. The high concentration of 1-MNA was explained in terms of an imbalance in the NAD+/NADH ratio according to the literature data. Therefore, a novel potential role of 2-furoylglycine in correlation with 2-furoic acid exposure was also presented.
A limitation of this study is surely represented by the small number of subjects for each group, but this is strictly related to the principle of voluntary participation which requires individuals to consent to take part in the research, as well as to the specific characteristics of the Italian production structure, predominantly composed of small- and medium-sized enterprises. In addition to this, it is certainly worth underlining that it is impossible to completely eliminate the possible impact of confounding factors that could affect the metabolomic analysis, including both genetics and environmental elements such as lifestyle, diet or drugs. Despite this constraint, in our opinion, the present work contributes to addressing a significant gap in the existing literature on this topic. Our findings underscore the utility and applicability of the presented innovative approach by demonstrating the potential of the metabolomic platform in exploring unique and specific exposure scenarios. Future research endeavors could focus on expanding the sample size to improve the statistical power and robustness of the results. Additionally, subsequent studies may aim to integrate metabolomic data with findings obtained through other advanced analytical platforms, such as metagenomics, which could provide the information needed to validate the hypothesis of the real involvement of the intestinal microbiota in the metabolic variations observed following exposure. This would enable a more comprehensive and multidimensional understanding of urinary metabolic profiles, providing deeper insights into the complex interplay between exposure scenarios and their biological effects.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jox15020039/s1: Figure S1: PCA analysis between CTRL and Worker groups; Figure S2: PCA analysis performed for age factor; Table S1: 1H-NMR resonance assignment; Table S2: Table of metabolite concentrations; Workplace Description. Reference [63] is cited in the supplementary materials
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S., G.T., A.R.F. and M.S.; subject enrollment and sampling, A.P. (Agostino Paolino), L.I., A.P. (Antonio Pietroiusti), A.M. and R.S.; methodology, M.D.R., F.S. and O.G., software, F.M. and M.D.R.; validation, F.M., M.D.R. and A.P. (Adriano Patriarca); formal analysis, M.D.R., O.G. and A.P. (Adriano Patriarca); investigation, M.D.R., O.G., A.P. (Adriano Patriarca) and F.M.; resources, A.P. (Agostino Paolino), R.S., A.P. (Antonio Pietroiusti) and L.I.; data curation, F.M. and M.D.R.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D.R., O.G. and F.S.; writing—review and editing, M.S., F.S., O.G., A.P. (Adriano Patriarca) and M.D.R.; supervision, M.S., F.S., G.T. and R.S.; funding acquisition, A.R.F. and R.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare financial support was received for the research, authorship and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Grant BRIC ID09 PAR 2019–2021 from INAIL Research.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All experiments were conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki and following the International Code of Ethics for Occupational Health Professionals, published by the International Committee of Occupational Health (ICOH). The information gathered was used as aggregate data referring to the whole group of workers, with no risk of individual identification. This study was approved by the Ethical Committee “Lazio 2”, study number: 31.23, protocol ID: 0041631 (no-profit study), 2 March 2023. Written informed consent was obtained from all the involved subjects.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to warmly thank all the workers who consented to participate in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Oktavilia, S.; Hapsari, M.; Firmansyah; Setyadharma, A.; Wahyuningsum, I.F.S. Plastic Industry and World Environmental Problems. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 202, 05020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD Global Plastics Outlook: Policy Scenarios to 2060; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, France, 2022.
- Hazardous Exposures to Plastics in the World of Work: Research Report—International Labour Organization. Available online: https://researchrepository.ilo.org/esploro/outputs/report/Hazardous-exposures-to-plastics-in-the/995331818702676 (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- UN Environment. Chemicals in Plastics—A Technical Report|UNEP—UN Environment Programme. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/report/chemicals-plastics-technical-report (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Teuten, E.L.; Saquing, J.M.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Barlaz, M.A.; Jonsson, S.; Björn, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S.; Yamashita, R.; et al. Transport and Release of Chemicals from Plastics to the Environment and to Wildlife. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groh, K.J.; Backhaus, T.; Carney-Almroth, B.; Geueke, B.; Inostroza, P.A.; Lennquist, A.; Leslie, H.A.; Maffini, M.; Slunge, D.; Trasande, L.; et al. Overview of Known Plastic Packaging-Associated Chemicals and Their Hazards. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3253–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.G.L.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a Consensus on the Definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.; Hollman, P.C.H.; Mendoza-Hill, J. Microplastics in Fisheries and Aquaculture: Status of Knowledge on Their Occurrence and Implications for Aquatic Organisms and Food Safety; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2017; ISBN 978-92-5-109882-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kirstein, I.V.; Kirmizi, S.; Wichels, A.; Garin-Fernandez, A.; Erler, R.; Löder, M.; Gerdts, G. Dangerous Hitchhikers? Evidence for Potentially Pathogenic Vibrio Spp. on Microplastic Particles. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 120, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Sonne, C.; Brown, R.J.C.; Younis, S.A.; Kim, K.-H. Adsorption of Environmental Contaminants on Micro- and Nano-Scale Plastic Polymers and the Influence of Weathering Processes on Their Adsorptive Attributes. J. Hazard Mater. 2022, 427, 127903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Feng, Q.; Wang, J. Mini-Review of Microplastics in the Atmosphere and Their Risks to Humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Environmental Exposure to Microplastics: An Overview on Possible Human Health Effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tao, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Song, M. Potential Health Impact of Microplastics: A Review of Environmental Distribution, Human Exposure, and Toxic Effects. Environ. Health 2023, 1, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashov, V.; Geraci, C.L.; Schulte, P.A.; Howard, J. Nano- and Microplastics in the Workplace. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2021, 18, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poikkimäki, M.; Koljonen, V.; Leskinen, N.; Närhi, M.; Kangasniemi, O.; Kausiala, O.; Dal Maso, M. Nanocluster Aerosol Emissions of a 3D Printer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13618–13628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. “Metabonomics”: Understanding the Metabolic Responses of Living Systems to Pathophysiological Stimuli via Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Biological NMR Spectroscopic Data. Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NMR-Based Metabolomics for Biomarker Discovery. Available online: http://ouci.dntb.gov.ua/en/works/4kjbwB67/ (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Gowda, G.A.N.; Raftery, D. (Eds.) NMR-Based Metabolomics: Methods and Protocols; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2037, ISBN 978-1-4939-9689-6. [Google Scholar]
- Dehghani, F.; Yousefinejad, S.; Walker, D.I.; Omidi, F. Metabolomics for Exposure Assessment and Toxicity Effects of Occupational Pollutants: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Metabolomics 2022, 18, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckonert, O.; Keun, H.C.; Ebbels, T.M.; Bundy, J.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic Profiling, Metabolomic and Metabonomic Procedures for NMR Spectroscopy of Urine, Plasma, Serum and Tissue Extracts. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, M.; Giampaoli, O.; Sciubba, F.; Marini, F.; Tranfo, G.; Sisto, R.; Miccheli, A.; Tricarico, L.; Fetoni, A.R.; Spagnoli, M. NMR-Based Metabolomics for Investigating Urinary Profiles of Metal Carpentry Workers Exposed to Welding Fumes and Volatile Organic Compounds. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1386441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassini, A.; Sciubba, F.; Di Cocco, M.E.; Capuani, G.; Delfini, M.; Aureli, W.; Miccheli, A. 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics Reveals a Pedoclimatic Metabolic Imprinting in Ready-to-Drink Carrot Juices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5284–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BMRB—Biological Magnetic Resonance Bank. Available online: https://bmrb.io/ (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Szymańska, E.; Saccenti, E.; Smilde, A.K.; Westerhuis, J.A. Double-Check: Validation of Diagnostic Statistics for PLS-DA Models in Metabolomics Studies. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, I.-G.; Jun, C.-H. Performance of Some Variable Selection Methods When Multicollinearity Is Present. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2005, 78, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Honda, A.; Ikegami, T.; Iwamoto, J.; Monma, T.; Hirayama, T.; Saito, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Matsuzaki, Y. Simultaneous Quantification of Salivary 3-Hydroxybutyrate, 3-Hydroxyisobutyrate, 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylbutyrate, and 2-Hydroxybutyrate as Possible Markers of Amino Acid and Fatty Acid Catabolic Pathways by LC–ESI–MS/MS. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holeček, M. Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Health and Disease: Metabolism, Alterations in Blood Plasma, and as Supplements. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem Alanine Metabolism. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pathway/PathBank:SMP0000055 (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Matthews, D.E. An Overview of Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Kinetics in Humans123. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1549S–1555S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, A.R.; Schoenheimer, R. The conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine in normal rats. J. Biol. Chem. 1940, 135, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizianello, A.; De Ferrari, G.; Garibotto, G.; Gurreri, G.; Robaudo, C. Renal Metabolism of Amino Acids and Ammonia in Subjects with Normal Renal Function and in Patients with Chronic Renal Insufficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 65, 1162–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knol, M.G.E.; Wulfmeyer, V.C.; Müller, R.-U.; Rinschen, M.M. Amino Acid Metabolism in Kidney Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024, 20, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleck, C.; Schwertfeger, M.; Taylor, P.M. Regulation of Renal Amino Acid (AA) Transport by Hormones, Drugs and Xenobiotics—A Review. Amino Acids 2003, 24, 347–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niblett, S.H.; King, K.E.; Dunstan, R.H.; Clifton-Bligh, P.; Hoskin, L.A.; Roberts, T.K.; Fulcher, G.R.; McGregor, N.R.; Dunsmore, J.C.; Butt, H.L.; et al. Hematologic and Urinary Excretion Anomalies in Patients with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 232, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.S.; Christiani, D.C. Impact of Occupational Exposure on Human Microbiota. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Division on Earth and Life Studies; Board on Life Sciences; Board on Environmental Studies and Toxicology; Committee on Advancing Understanding of the Implications of Environmental-Chemical Interactions with the Human Microbiome. Environmental Chemicals, the Human Microbiome, and Health Risk: A Research Strategy; The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-309-46869-5. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.; Fan, Y.; Schlezinger, J.J.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Webster, T.F.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Pedersen, O.; Orešič, M. Exposure to Environmental Toxicants Is Associated with Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis, Insulin Resistance and Obesity. Environ. Int. 2024, 186, 108569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teffera, M.; Veith, A.C.; Ronnekleiv-Kelly, S.; Bradfield, C.A.; Nikodemova, M.; Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Malecki, K. Diverse Mechanisms by Which Chemical Pollutant Exposure Alters Gut Microbiota Metabolism and Inflammation. Environ. Int. 2024, 190, 108805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza-Silva, T.G.; Oliveira, I.A.; da Silva, G.G.; Giusti, F.C.V.; Novaes, R.D.; de Almeida Paula, H.A. Impact of Microplastics on the Intestinal Microbiota: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Evidence. Life Sci. 2022, 294, 120366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demarquoy, J. Microplastics and Microbiota: Unraveling the Hidden Environmental Challenge. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Watanabe, E.; Kawashima, Y.; Plichta, D.R.; Wang, Z.; Ujike, M.; Ang, Q.Y.; Wu, R.; Furuichi, M.; Takeshita, K.; et al. Identification of Trypsin-Degrading Commensals in the Large Intestine. Nature 2022, 609, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crommen, S.; Simon, M.-C. Microbial Regulation of Glucose Metabolism and Insulin Resistance. Genes 2018, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakaroun, R.M.; Massier, L.; Kovacs, P. Gut Microbiome, Intestinal Permeability, and Tissue Bacteria in Metabolic Disease: Perpetrators or Bystanders? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojda, J.; Cahova, M. Gut Microbiota as the Link between Elevated BCAA Serum Levels and Insulin Resistance. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardinoglu, A.; Shoaie, S.; Bergentall, M.; Ghaffari, P.; Zhang, C.; Larsson, E.; Bäckhed, F.; Nielsen, J. The Gut Microbiota Modulates Host Amino Acid and Glutathione Metabolism in Mice. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2015, 11, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-T.; Chen, X.; Huo, D.; Arifuzzaman, M.; Qiao, S.; Jin, W.-B.; Shi, H.; Li, X.V.; Iliev, I.D.; Artis, D.; et al. Microbiota Metabolism of Intestinal Amino Acids Impacts Host Nutrient Homeostasis and Physiology. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 661–675.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, I.K.S.; Brown, I.J.; Chan, Q.; Wijeyesekera, A.; Garcia-Perez, I.; Bictash, M.; Loo, R.L.; Chadeau-Hyam, M.; Ebbels, T.; Iorio, M.D.; et al. Metabolome-Wide Association Study Identifies Multiple Biomarkers That Discriminate North and South Chinese Populations at Differing Risks of Cardiovascular Disease: INTERMAP Study. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 6647–6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kałużna-Czaplińska, J.; Gątarek, P. Trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) in Human Health. EXCLI J. 2021, 20, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietzke, M.; Meiser, J.; Vazquez, A. Formate Metabolism in Health and Disease. Mol. Metab. 2020, 33, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.A.; Badaloo, A.V.; Forrester, T.; Hibbert, J.M.; Persaud, C. Urinary Excretion of 5-Oxoproline (Pyroglutamic Aciduria) as an Index of Glycine Insufficiency in Normal Man. Br. J. Nutr. 1987, 58, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, M.F.; O’Keefe, J.H.; DiNicolantonio, J.J. Dietary Glycine Is Rate-Limiting for Glutathione Synthesis and May Have Broad Potential for Health Protection. Ochsner J. 2018, 18, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Sipes, I.G.; Wiersma, D.A.; Armstrong, D.J. The Role of Glutathione in the Toxicity of Xenobiotic Compounds: Metabolic Activation of 1,2-Dibromoethane by Glutathione. In Biological Reactive Intermediates III: Mechanisms of Action in Animal Models and Human Disease; Kocsis, J.J., Jollow, D.J., Witmer, C.M., Nelson, J.O., Snyder, R., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 457–467. ISBN 978-1-4684-5134-4. [Google Scholar]
- Giampaoli, O.; Sciubba, F.; Tranfo, G.; Sisto, R.; Pigini, D.; De Rosa, M.; Patriarca, A.; Miccheli, A.; Fetoni, A.R.; Tricarico, L.; et al. NMR Untargeted and HPLC-MS/MS Targeted Metabolomic Approaches for Evaluating Styrene Exposure in the Urine of Shipyard Workers. Toxics 2024, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Ishikawa, A.; Yoshitake, Y.; Kodama, N.; Nishimuta, M.; Fukuwatari, T.; Shibata, K. Diurnal Variations in Human Urinary Excretion of Nicotinamide Catabolites: Effects of Stress on the Metabolism of Nicotinamide. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, J.E.; Jellum, E. The Identification and Metabolic Origin of 2-Furoylglycine and 2,5-Furandicarboxylic Acid in Human Urine. Clin. Chim. Acta 1972, 41, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugwitz, L.; Zizmare, L.; Santhanakumaran, V.; Cannet, C.; Böhringer, J.; Okun, J.G.; Spraul, M.; Krägeloh-Mann, I.; Groeschel, S.; Trautwein, C. Identification of Neurodegeneration Indicators and Disease Progression in Metachromatic Leukodystrophy Using Quantitative NMR-based Urinary Metabolomics Laugwitz. JIMD Rep. 2022, 63, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzmann, S.S.; Holmes, E.; Kochhar, S.; Nicholson, J.K.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. 2-Furoylglycine as a Candidate Biomarker of Coffee Consumption. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8615–8621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydson, J.A. Plastics Materials; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1999; ISBN 978-0-7506-4132-6. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, Y.; Hori, H.; Higashi, T.; Nagatomo, H.; Hino, Y.; Ohsato, A.; Uchino, B. Biological Marker of Furfural, Chemicals without Administrative Control Level. J. UOEH 2007, 29, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Flek, J.; Sedivěc, V. The Absorption, Metabolism and Excretion of Furfural in Man. Int. Arch. Occup. Env. Heath 1978, 41, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfäffli, P.; Tossavainen, A.; Savolainen, H. Comparison of Inhaled Furfuryl Alcohol Vapour with Urinary Furoic Acid Excretion in Exposed Foundry Workers by Chromatographic Techniques. Analyst 1985, 110, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccuni, F.; Ferrante, R.; Tombolini, F.; Iavicoli, S.; Pelliccioni, A. Measurement of airborne ultrafine particles in work and life environments: study design and preliminary trends in an Italian university site. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).