Impact of Legacy Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) on GABA Receptor-Mediated Currents in Neuron-Like Neuroblastoma Cells: Insights into Neurotoxic Mechanisms and Health Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.3. Electrophysiological Recordings
3. Results
3.1. Acute Toxicity of PFAS in S1 Cells
3.2. Electrophysiological Characterization of S1 Neuron-Like Neuroblastoma Cells
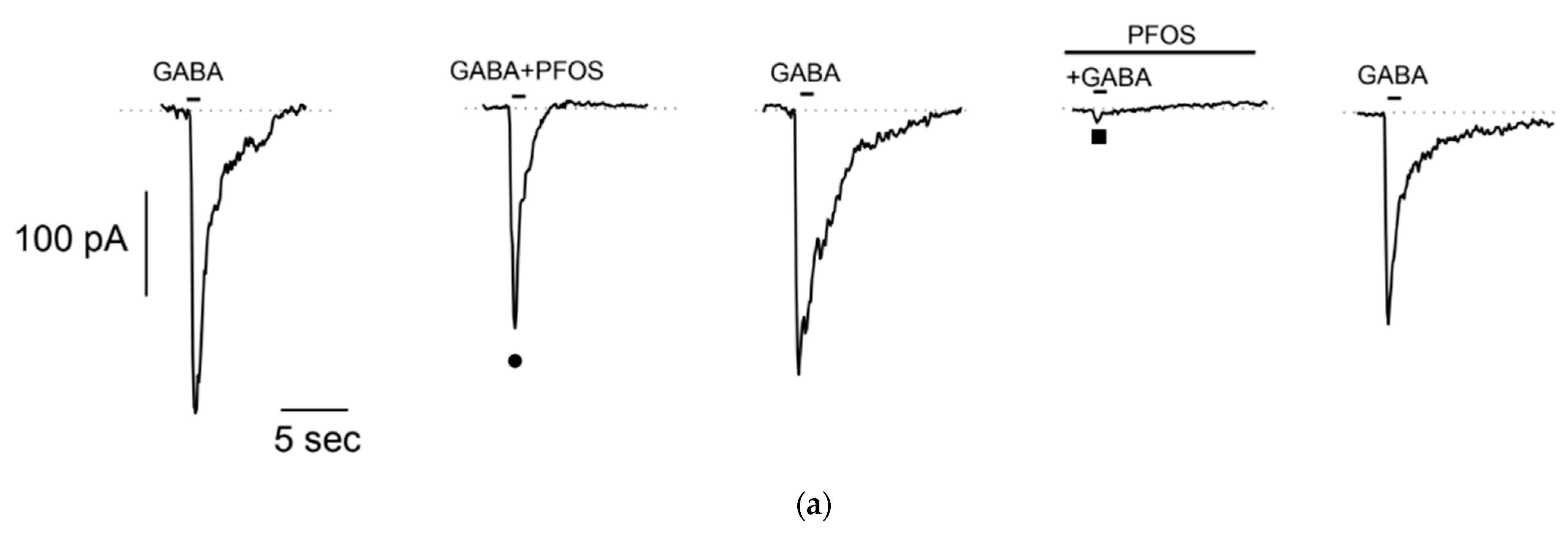
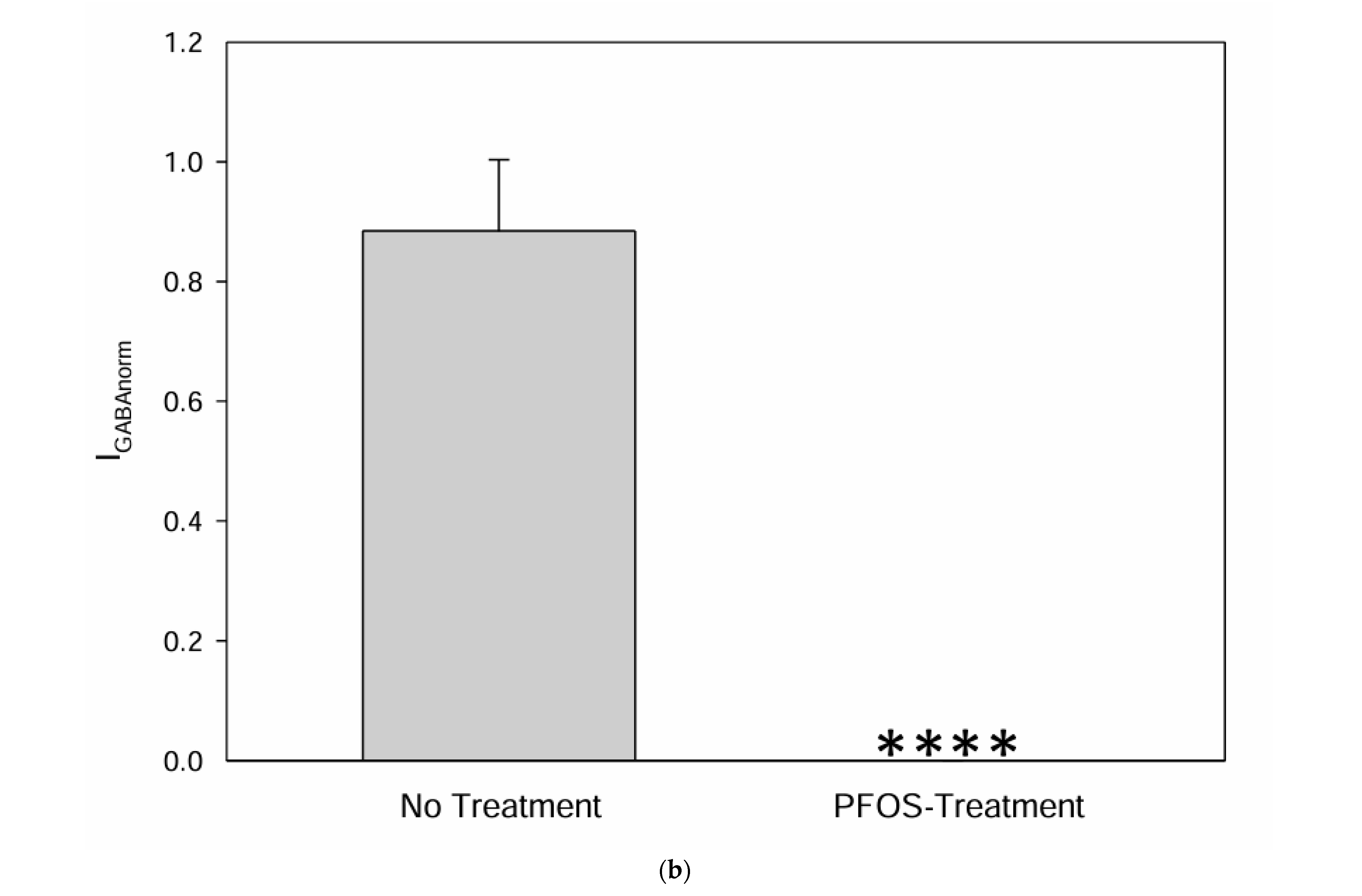
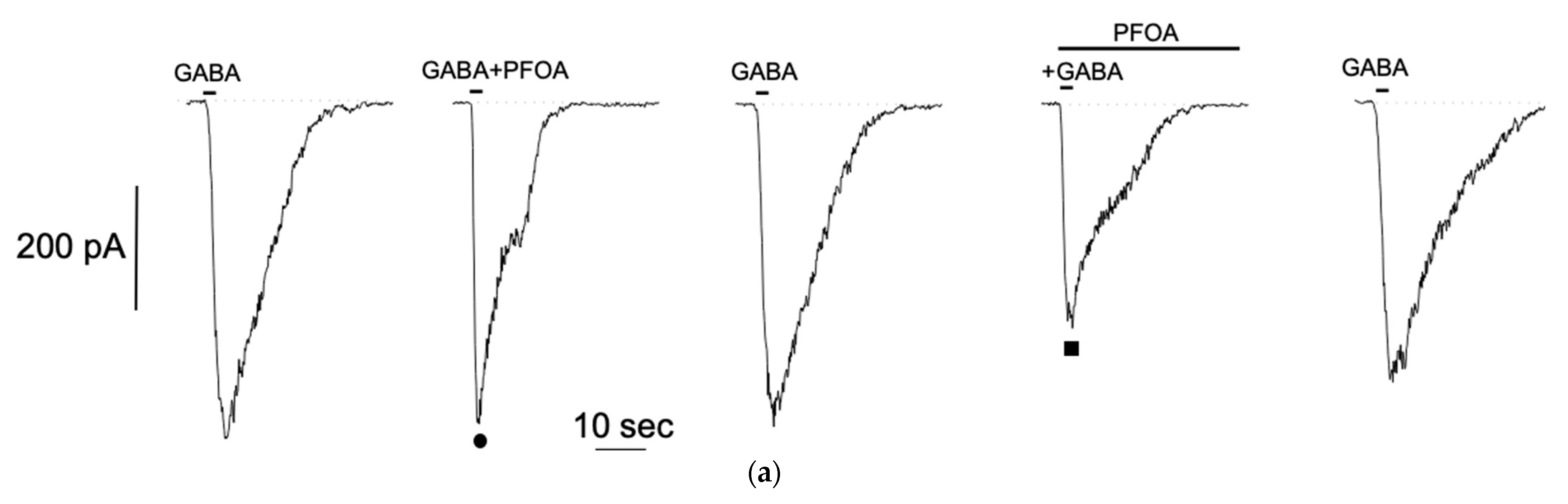
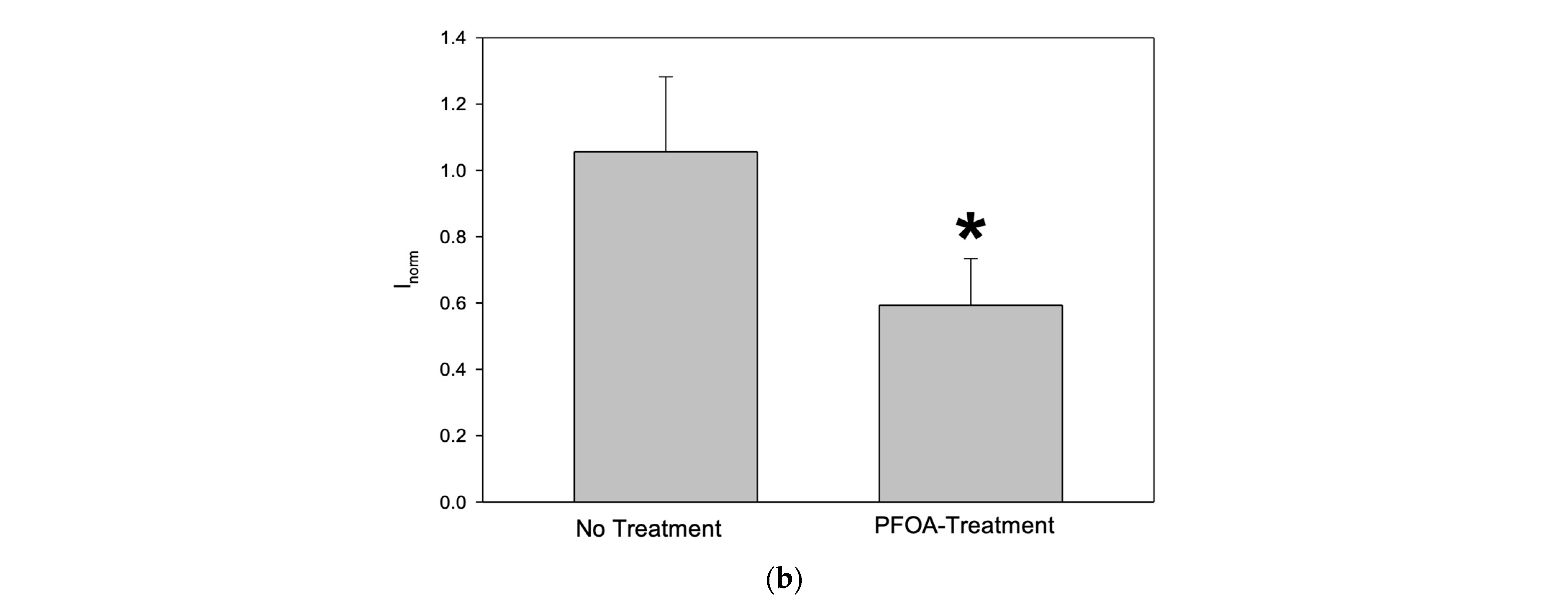
3.3. Effect of PFOS and PFOA on GABA-Evoked Currents in Neuron-Like S1 Neuroblastoma Cells
4. Discussion
5. Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zahm, S.; Bonde, J.P.; Chiu, W.A.; Hoppin, J.; Kanno, J.; Abdallah, M.; Blystone, C.R.; Calkins, M.M.; Dong, G.H.; Dorman, D.C.; et al. Carcinogenicity of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, L.; Ji, M.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, X.M.; Wang, S.L. Perfluorooctane sulfonate disrupts the blood brain barrier through the crosstalk between endothelial cells and astrocytes in mice. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown-Leung, J.M.; Cannon, J.R. Neurotransmission Targets of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Neurotoxicity: Mechanisms and Potential Implications for Adverse Neurological Outcomes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 35, 1312–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starnes, H.M.; Rock, K.D.; Jackson, T.W.; Belcher, S.M. A critical review and meta-analysis of impacts of per-and polyfluorinated substances on the brain and behavior. Front. Toxicol. 2022, 4, 881584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nisio, A.; De Toni, L.; Sabovic, I.; Guidolin, D.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Sfriso, M.M.; Rocca, M.S.; De Filippis, V.; Foresta, C.; Garolla, A. Impairment of human dopaminergic neurons at different developmental stages by perfluoro-octanoic acid (PFOA) and differential human brain areas accumulation of perfluoroalkyl chemicals. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieghart, W.; Fuchs, K.; Tretter, V.; Ebert, V.; Jechlinger, M.; Hoger, H.; Adamiker, D. Structure and subunit composition of GABA(A) receptors. Neurochem. Int. 1999, 34, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, J.L.; Russek, S.J. GABAA receptors: Building the bridge between subunit mRNAs, their promoters, and cognate transcription factors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 101, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghit, A.; Assal, D.; Al-Shami, A.S.; Hussein, D.E.E. GABA(A) receptors: Structure, function, pharmacology, and related disorders. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, U.; Knoflach, F. Beyond classical benzodiazepines: Novel therapeutic potential of GABAA receptor subtypes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigel, E.; Baur, R.; Trube, G.; Mohler, H.; Malherbe, P. The effect of subunit composition of rat brain GABAA receptors on channel function. Neuron 1990, 5, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallard, E.; Letourneur, D.; Legendre, P. Electrophysiology of ionotropic GABA receptors. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 5341–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.W.; Olsen, R.W. GABAA receptor associated proteins: A key factor regulating GABAA receptor function. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, T.C.; Moss, S.J.; Jurd, R. GABA(A) receptor trafficking and its role in the dynamic modulation of neuronal inhibition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigel, E.; Luscher, B.P. A closer look at the high affinity benzodiazepine binding site on GABAA receptors. Curr. Top Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Neurosteroids and GABA-A Receptor Function. Front. Endocrinol. 2011, 2, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Durkin, K.A.; Casida, J.E. Structural model for γ-aminobutyric acid receptor noncompetitive antagonist binding: Widely diverse structures fit the same site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5185–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonorov, I.M.; Blanck, T.J.; Recio-Pinto, E. G-protein Activation Decreases Isoflurane Inhibition of N-type Ba2+ Currents. Anesthesiology 2003, 99, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavazzo, P.; Vella, S.; Marchetti, C.; Nizzari, M.; Cancedda, R.; Pagano, A. Acquisition of neuron-like electrophysiological properties in neuroblastoma cells by controlled expression of NDM29 ncRNA. J. Neurochem. 2011, 119, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampersad, S.N. Multiple applications of Alamar Blue as an indicator of metabolic function and cellular health in cell viability bioassays. Sensors 2012, 12, 12347–12360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukker, A.M.; Bouwman LM, S.; van Kleef, R.; Hendriks, H.S.; Legler, J.; Westerink, R.H.S. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) acutely affect human alpha(1)beta(2)gamma(2L) GABA(A) receptor and spontaneous neuronal network function in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giudice, G.; Migliaccio, G.; D’Alessandro, N.; Saarimäki, L.A.; Torres Maia, M.; Annala, M.E.; Leppänen, J.; Möbus, L.; Pavel, A.; Vaani, M.; et al. Advancing chemical safety assessment through an omics-based characterization of the test system-chemical interaction. Front. Toxicol. 2023, 5, 1294780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmett, E.A.; Shofer, F.S.; Zhang, H.; Freeman, D.; Desai, C.; Shaw, L.M. Community exposure to perfluorooctanoate: Relationships between serum concentrations and exposure sources. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2006, 48, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woskie, S.R.; Gore, R.; Steenland, K. Retrospective exposure assessment of perfluorooctanoic acid serum concentrations at a fluoropolymer manufacturing plant. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2012, 56, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, G.W.; Burris, J.M.; Ehresman, D.J.; Froehlich, J.W.; Seacat, A.M.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Zobel, L.R. Half-life of serum elimination of perfluorooctanesulfonate, perfluorohexanesulfonate, and perfluorooctanoate in retired fluorochemical production workers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Teng, M.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhao, W.; Ruan, Y.; Leung KM, Y.; Wu, F. Insight into the binding model of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances to proteins and membranes. Environ. Int. 2023, 175, 107951. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Ng, C. Absorption, distribution, and toxicity of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the brain: A review. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.H.; Ishii, T.M.; Takatsuka, K.; Koizumi, A.; Ohmori, H. Effects of perfluorooctane sulfonate on action potentials and currents in cultured rat cerebellar Purkinje cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, A.; Alesio, J.; Poonia, M.; Bothun, G.D. PFAS fluidize synthetic and bacterial lipid monolayers based on hydrophobicity and lipid charge. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleszczynski, K.; Skladanowski, A.C. Mechanism of cytotoxic action of perfluorinated acids. I. alteration in plasma membrane potential and intracellular pH level. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 234, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, M.E.; Kasturi, B.S.; Barber, M.; Kannan, K.; MohanKumar, P.S.; MohanKumar, S.M. Neuroendocrine effects of perfluorooctane sulfonate in rats. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Wu, B.; Duan, S.M.; Jiang, G.B. Acute enhancement of synaptic transmission and chronic inhibition of synaptogenesis induced by perfluorooctane sulfonate through mediation of voltage-dependent calcium channel. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5335–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panieri, E.; Baralic, K.; Djukic-Cosic, D.; Buha Djordjevic, A.; Saso, L. PFAS Molecules: A Major Concern for the Human Health and the Environment. Toxics 2022, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reardon, A.J.F.; Hajihosseini, M.; Dinu, I.; Field, C.J.; Kinniburgh, D.W.; MacDonald, A.M.; Dewey, D.; England-Mason, G.; Martin, J.W.; APrON Study. Maternal co-exposure to mercury and perfluoroalkyl acid isomers and their associations with child neurodevelopment in a Canadian birth cohort. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lagostena, L.; Rotondo, D.; Gualandris, D.; Calisi, A.; Lorusso, C.; Magnelli, V.; Dondero, F. Impact of Legacy Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) on GABA Receptor-Mediated Currents in Neuron-Like Neuroblastoma Cells: Insights into Neurotoxic Mechanisms and Health Implications. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 1771-1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14040094
Lagostena L, Rotondo D, Gualandris D, Calisi A, Lorusso C, Magnelli V, Dondero F. Impact of Legacy Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) on GABA Receptor-Mediated Currents in Neuron-Like Neuroblastoma Cells: Insights into Neurotoxic Mechanisms and Health Implications. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2024; 14(4):1771-1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14040094
Chicago/Turabian StyleLagostena, Laura, Davide Rotondo, Davide Gualandris, Antonio Calisi, Candida Lorusso, Valeria Magnelli, and Francesco Dondero. 2024. "Impact of Legacy Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) on GABA Receptor-Mediated Currents in Neuron-Like Neuroblastoma Cells: Insights into Neurotoxic Mechanisms and Health Implications" Journal of Xenobiotics 14, no. 4: 1771-1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14040094
APA StyleLagostena, L., Rotondo, D., Gualandris, D., Calisi, A., Lorusso, C., Magnelli, V., & Dondero, F. (2024). Impact of Legacy Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) on GABA Receptor-Mediated Currents in Neuron-Like Neuroblastoma Cells: Insights into Neurotoxic Mechanisms and Health Implications. Journal of Xenobiotics, 14(4), 1771-1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14040094










