Carcinogenic Risk from Lead and Cadmium Contaminating Cow Milk and Soya Beverage Brands Available in the Portuguese Market
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Treatment
2.2. Carcinogenic Risk Assessments
2.2.1. Excess Lifetime Carcinogenic Risk
2.2.2. Metal Levels in Cow Milk and Soya Beverages
2.3. Carcinogenic Risk Assessment per Brand of Cow Milk or Soya Beverage
Relative Contribution of Pb and Cd to Carcinogenic Risk
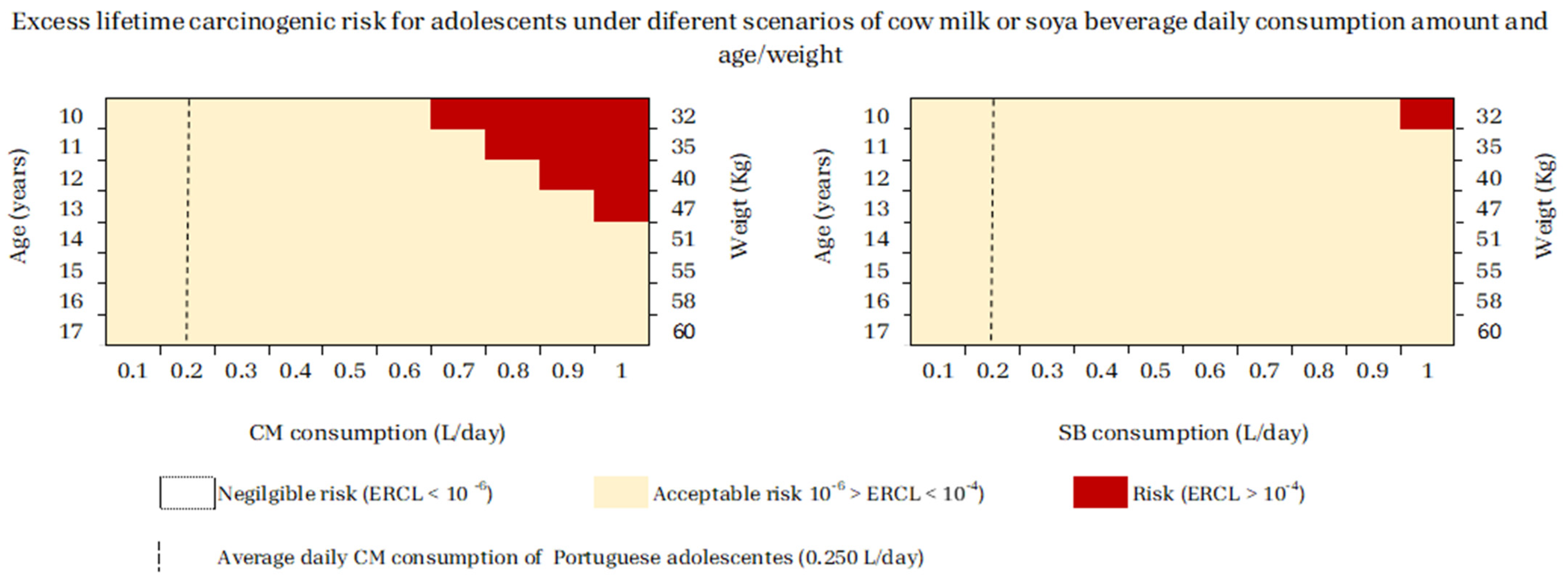
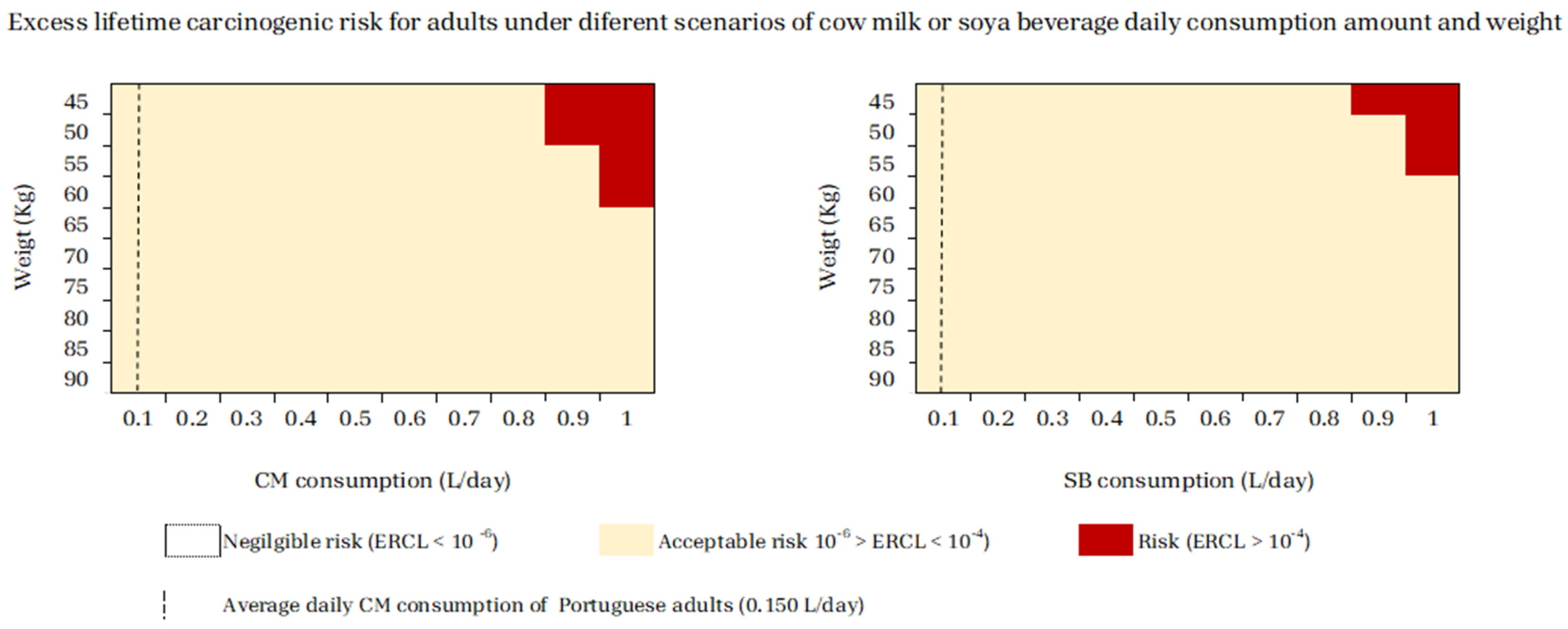
2.4. Carcinogenic Risk Assessments in Several Scenarios of Daily Consumption of Cow Milk or Soya Beverage per Age/Weight
3. Results
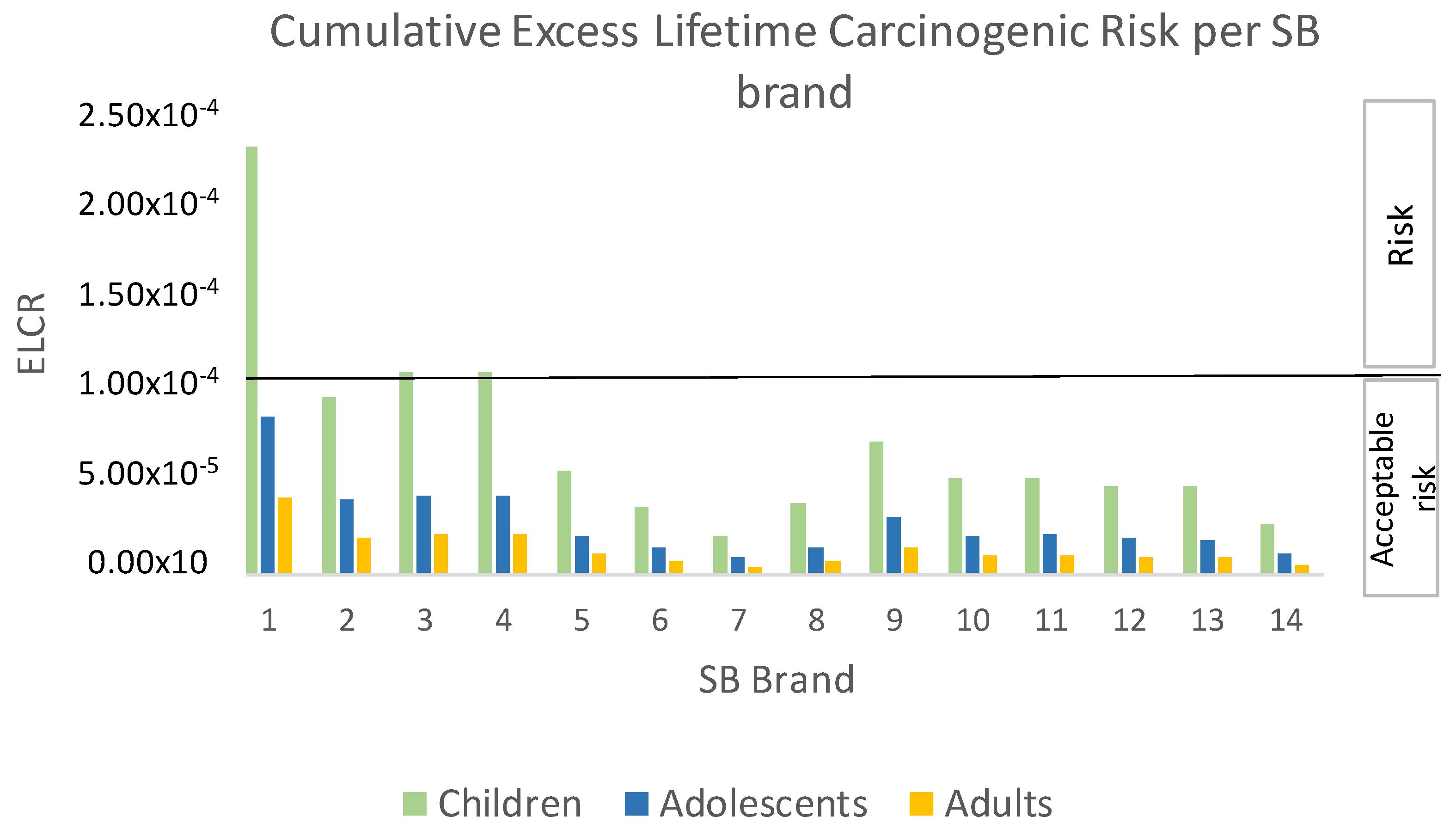
Carcinogenic Risk Assessments per Brand of Cow Milk or Soya Beverage
4. Discussion
4.1. Children
4.2. Adolescents and Adults
4.3. Environmental Issues
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sugrue, I.; Tobin, C.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Hill, C. Foodborne Pathogens and Zoonotic Diseases in Raw Milk Balance between Hazards and Benefits; Nero, L.A., De Carvalho, A.F., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Vanga, S.K.; Raghavan, V. How well do plant-based alternatives fare nutritionally compared to cow’s milk? J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalupa-Krebzdak, S.; Long, C.J.; Bohrer, B.M. Nutrient density and nutritional value of milk and plant-based milk alternatives. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 87, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, B.C.; John, S.M.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Cordain, L.; Leitzmann, C.; Weiskirchen, R.; Schmitz, G. The Role of Cow’s Milk Consumption in Breast Cancer Initiation and Progression. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2023, 12, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, A.S. Cow’s Milk Consumption and Child Growth. In Dairy in Human Health and Disease Across the Lifespan; Watson, R.R., Collier, R.J., Preedy, V.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, S.; Singh, A.K. Human health risk assessment due to metals in cow’s milk from Singhbhum copper and iron mining areas, India. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudebbouz, A.; Boudalia, S.; Bousbia, A.; Habila, S.; Boussadia, M.I.; Gueroui, Y. Heavy metals levels in raw cow milk and health risk assessment across the globe: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojinova, P.; Georgiev, B.; Krasteva, V.; Chuldjian, H.; Stanislavova, L. Investigation about the heavy metal pollution in soils and agricultural crops in the region of nonferrous metal works ‘D. Blagoev’. Soil Sci. Agrochem. Ecol. 1994, 4, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Candeias, C.; Ferreira da Silva, E.; Salgueiro, A.R.; Pereira, H.G.; Reis, A.P.; Patinha, C.; Matos, J.X.; Ávila, P.H. Assessment of soil contamination by potentially toxic elements in the aljustrel mining area in order to implement soil reclamation strategies. Land Degrad. Dev. 2011, 22, 565–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, C.J.; Seixas, F.; Gonzalo-Orden, J.M.; Patinha, C.; Pato, P.; Ferreira da Silva, E.; Casero, M.; Brazio, E.; Brandão, R.; Costa, D.; et al. The first full study of heavy metal(loid)s in western-European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) from Portugal. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 11983–11994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, C.; Gutiérrez, Á.J.; Hardisson, A.; Martín, V.; Revert, C.; Pestana Fernandes, P.J.; Horta Lopes, D.J.; Paz-Montelongo, S. Dietary Exposure to Toxic Metals (Cd, Pb and Hg) from Cereals Marketed in Madeira and the Azores. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 5861–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, C.; Slencu, B.G.; Cuciureanu, R. Estimation of dietary intake of cadmium and lead through food consumption. Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat. Iasi. 2012, 116, 617–623. [Google Scholar]
- Nag, R.; Cummins, E. Human health risk assessment of lead (Pb) through the environmental-food pathway. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 151168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes de Andrade, V.; Ribeiro, I.; Marreilha dos Santos, A.P.; Aschner, M.; Mateus, M.L. Metals in Cow Milk and Soy Beverages: Is There a Concern? Toxics 2023, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida, L.; Patel, T.N. Systemic impact of heavy metals and their role in cancer development: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- [CDC] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Lead Toxicity. What Are Possible Health Effects from Lead Exposure? 2023. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/csem/leadtoxicity/physiological_effects.html (accessed on 4 February 2024).
- Wani, A.L.; Ara, A.; Usmani, J.A. Lead toxicity: A review. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2015, 8, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- [ATSDR] Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Lead Tox Facts. 2020. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/ToxFAQs/ToxFAQsDetails.aspx?faqid=93&toxid=22 (accessed on 23 March 2024).
- Charkiewicz, A.E.; Backstrand, J.R. Lead Toxicity and Pollution in Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadmium and Cadmium Compounds (Group 1). International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)—Summaries & Evaluations. 1997. Available online: https://www.inchem.org/documents/iarc/vol58/mono58-2.html (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Rahimzadeh, R.M.; Rafati Rahimzadeh, M.; Kazemi, S.; Moghadamnia, A.A. Cadmium toxicity and treatment: An update. Caspian J. Intern. Med. 2017, 8, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satarug, S.; Gobe, G.C.; Vesey, D.A.; Phelps, K.R. Cadmium and Lead Exposure, Nephrotoxicity, and Mortality. Toxics 2020, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirovic, A.; Soisungwan, S. Toxicity Tolerance in the Carcinogenesis of Environmental Cadmium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimta, A.A.; Schitcu, V.; Gurzau, E.; Stavaru, C.; Manda, G.; Szedlacsek, S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Biological and molecular modifications induced by cadmium and arsenic during breast and prostate cancer development. Environ. Res. 2019, 178, 108700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbergeld, E.K.; Waalkes, M.; Rice, J.M. Lead as a carcinogen: Experimental evidence and mechanisms of action. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2000, 38, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; DesMarais, T.; Costa, M. Metals and Mechanisms of Carcinogenesis. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 59, 537–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branca, J.J.V.; Fiorillo, C.; Carrino, D.; Paternostro, F.; Taddei, N.; Gulisano, M.; Pacini, A.; Becatti, M. Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress: Focus on the Central Nervous System. Antioxidants 2020, 5, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.C.B.A.; Peixe, T.S.; Mesas, A.E.; Paoliello, M.M.B. Lead Exposure and Oxidative Stress: A Systematic Review. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; de Voogt, P., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 236, pp. 193–238. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.R.D.; Dotson, G.S.; Maier, A. Cumulative Risk Assessment (CRA): Transforming the Way We Assess Health Risks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10868–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.; Campbell, C.; Naidenko, O.V. Cumulative risk analysis of carcinogenic contaminants in United States drinking water. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badeenezhad, A.; Soleimani, H.; Shahsavani, S.; Parseh, I.; Mohammadpour, A.; Azadbakht, O.; Javanmardi, P.; Faraji, H.; Nalosi, K.B. Comprehensive health risk analysis of heavy metal pollution using water quality indices and Monte Carlo simulation in R software. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radfard, M.; Hashemi, H.; Baghapour, M.A.; Samaei, M.R.; Yunesian, M.; Soleimani, H.; Azhdarpoor, A. Prediction of human health risk and disability-adjusted life years induced by heavy metals exposure through drinking water in Fars Province, Iran. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, Y.; Zheng, J.; Tang, T.; Li, S.; Cao, S.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; He, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Risk assessment of combined exposure to lead, cadmium, and total mercury among the elderly in Shanghai, China. Ecotoxicol. Environm. Saf. 2023, 256, 114874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, A.S.; Nasseri, E.; Esfarjani, F.; Mohammadi-Nasrabadi, F.; Moosavi, M.H.; Hoseini, H. A systematic review and meta-analysis of lead and cadmium concentrations in cow milk in Iran and human health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10147–10159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- (NYHD) New York Health Department. Hopewell Precision Area Contamination. Appendix C—NYS DOH Procedure for Evaluating Potential Health Risks for Contaminants of Concern. 2007. Available online: https://www.health.ny.gov/environmental/investigations/hopewell/appendc.htm (accessed on 6 April 2024).
- Lopes, C.; Torres, D.; Oliveira, A.; Severo, M.; Alarcão, V.; Guiomar, S.; Mota, J.; Teixeira, P.; Rodrigues, S.; Lobato, L.; et al. National Food, Nutrition, and Physical Activity Survey of the Portuguese General Population, IAN-AF 2015-2016: Summary of Results; 2018; Edition: University of Porto, Portugal. ISBN 978-989-746-202-3. Available online: www.ian-af.up.pt (accessed on 24 February 2024).
- Estimativa Provisória da Esperança de Vida Aos 65 Anos Para 2021–2023. 29 November 2023 (INE) Instituto Nacional de Estatística. 2023. Available online: https://www.ine.pt/xportal/xmain?xpid=INE&xpgid=ine_destaques&DESTAQUESdest_boui=594932669&DESTAQUESmodo=2 (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- (WHO) World Health Organization. WHO Weight for Age Charts. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/child-growth-standards/standards/weight-for-age (accessed on 26 March 2024).
- Average Height and Weight by Country. Worlddata. 2023. Available online: https://www.worlddata.info/average-bodyheight.php (accessed on 23 March 2024).
- Singh, J.A.; Siddiqi, M.; Parameshwar, P.; Chandra-Mouli, V. World Health Organization Guidance on Ethical Considerations in Planning and Reviewing Research Studies on Sexual and Reproductive Health in Adolescents. J. Adolesc. Health 2019, 64, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- (CDC) Centre for Disease Control and Prevention. Cow’s Milk and Milk Alternatives. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nutrition/infantandtoddlernutrition/foods-and-drinks/cows-milk-and-milk-alternatives.html (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- Visioli, F.; Strata, A. Milk, dairy products, and their functional effects in humans: A narrative review of recent evidence. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingone, F.; Bucci, C.; Iovino, P.; Ciacci, C. Consumption of milk and dairy products: Facts and figures. Nutrition 2017, 33, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olías, R.; Delgado-Andrade, C.; Padial, M.; Marín-Manzano, M.C.; Clemente, A. An Updated Review of Soy-Derived Beverages: Nutrition, Processing, and Bioactivity. Foods 2023, 12, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziarati, P.; Shirkhan, F.; Mostafidi, M.; Zahedi, M.T. An Overview of the Heavy Metal Contamination in Milk and Dairy Products. Acta Sci. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- (ATSDR) Agency for Toxic Substance and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for Lead-Update; U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, Public Health Service: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2007.
- Sujka, M.; Pankiewicz, U.; Kowalski, R.; Mazurek, A.; Ślepecka, K.; Góral, M. Determination of the content of Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn in dairy products from various regions of Poland. Open Chem. 2019, 17, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, P.; Lopez-Villalobos, N.; Tobin, J.T.; Murphy, E.; McDonagh, A.; Crowley, S.V.; Kelly, A.L.; Shalloo, L. The Effect of Compositional Changes Due to Seasonal Variation on Milk Density and the Determination of Season-Based Density Conversion Factors for Use in the Dairy Industry. Foods 2020, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- (DGS) Portuguese Directorate-General for Health. Alimentação Saudável dos 0 aos 6 anos. 2019. Available online: https://alimentacaosaudavel.dgs.pt/alimentacao-saudavel-dos-0-aos-6-anos (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- Au, W.W. Susceptibility of children to environmental toxic substances. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2002, 205, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroquino, M.J.; Posada, M.; Landrigan, P.J. Environmental Toxicology: Children at Risk. In Environmental Toxicology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 239–291. [Google Scholar]
- Sly, P.D.; Flack, F. Susceptibility of Children to Environmental Pollutants. Environ. Chall. Pac. Basin 2008, 1140, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- (APN) Portuguese Association of Nutricionists. Conhecer o Leite 2016. E-book. 2016. Available online: https://www.apn.org.pt/documentos/ebooks/Ebook_Conhecer_o_Leite.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Fabbiano, S.; Bellafante, E.; Ramu, S.; Emambokus, N. Planetary health is human health. Med 2021, 2, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, D.H.; Karlsson, J.O.; Baker, P.; McCoy, D. Examining the Environmental Impacts of the Dairy and Baby Food Industries: Are First-Food Systems a Crucial Missing Part of the Healthy and Sustainable Food Systems Agenda Now Underway? Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, H. Dairy vs. Plant-Based Milk: What Are the Environmental Impacts? Published online at OurWorldInData.org. 2022. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/environmental-impact-milks (accessed on 3 January 2024).


| Parameter | Unit | Children | Adolescents | Adults | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (C) | mg/L | - | - | - | [14] |
| Ingestion rate (IR) | L/day | 0.267 | 0.25 | 0.15 | [37] |
| Exposure frequency (EF) | days/year | 365 (1) | 365 (1) | 365 (1) | |
| Age (2) | years | 6 | 14 | 85 | [38] |
| Exposure duration (ED) (2) | years | 5 | 13 | 84 | [16] |
| Body weight (BW) (2) | Kg | 21 | 49 | 65 | [39,40] |
| Average time (AT) | days | ED × 365 | ED × 365 | ED × 365 | [32] |
| Cancer slope factor (CSF) | mg/kg/day | Pb: 0.28; Cd: 0.38 | [34] | ||
| CM Brand | ELCR | Relative Contribution (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Cd | Pb Cd Aditivity | Pb | Cd | |
| 1 | 1.08 × 10−4 | 2.03 × 10−5 | 1.28 × 10−4 | 84.2 | 15.8 |
| 2 | 1.42 × 10−4 | 3.29 × 10−5 | 1.75 × 10−4 | 81.2 | 18.8 |
| 3 | 1.42 × 10−4 | 2.08 × 10−5 | 1.63 × 10−4 | 87.2 | 12.8 |
| 7 | 8.94 × 10−5 | 1.11 × 10−5 | 1.00 × 10−4 | 88.9 | 11.1 |
| 12 | 1.06 × 10−4 | 2.90 × 10−6 | 1.09 × 10−4 | 97.3 | 2.7 |
| mean | 87.8 | 12.2 | |||
| sd | 3.4 | ||||
| SB Brand | ELCR | Relative Contribution (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Cd | Pb Cd Aditivity | Pb | Cd | |
| 1 | 1.48 × 10−4 | 7.23 × 10−5 | 2.21 × 10−4 | 67.2 | 32.8 |
| 3 | 5.13 × 10−5 | 5.31 × 10−5 | 1.04 × 10−4 | 49.2 | 50.8 |
| 4 | 5.07 × 10−5 | 5.40 × 10−5 | 1.05 × 10−4 | 48.4 | 51.6 |
| mean | 54.9 | 45.1 | |||
| sd | 12.8 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Andrade, V.L.; Ribeiro, I.; dos Santos, A.P.M.; Aschner, M.; Mateus, M.L. Carcinogenic Risk from Lead and Cadmium Contaminating Cow Milk and Soya Beverage Brands Available in the Portuguese Market. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 798-811. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14020045
de Andrade VL, Ribeiro I, dos Santos APM, Aschner M, Mateus ML. Carcinogenic Risk from Lead and Cadmium Contaminating Cow Milk and Soya Beverage Brands Available in the Portuguese Market. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2024; 14(2):798-811. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14020045
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Andrade, Vanda Lopes, Iolanda Ribeiro, Ana Paula Marreilha dos Santos, Michael Aschner, and Maria Luisa Mateus. 2024. "Carcinogenic Risk from Lead and Cadmium Contaminating Cow Milk and Soya Beverage Brands Available in the Portuguese Market" Journal of Xenobiotics 14, no. 2: 798-811. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14020045
APA Stylede Andrade, V. L., Ribeiro, I., dos Santos, A. P. M., Aschner, M., & Mateus, M. L. (2024). Carcinogenic Risk from Lead and Cadmium Contaminating Cow Milk and Soya Beverage Brands Available in the Portuguese Market. Journal of Xenobiotics, 14(2), 798-811. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14020045







