Exposure and Health Risks Posed by Potentially Toxic Elements in Soils of Metal Fabrication Workshops in Mbarara City, Uganda
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
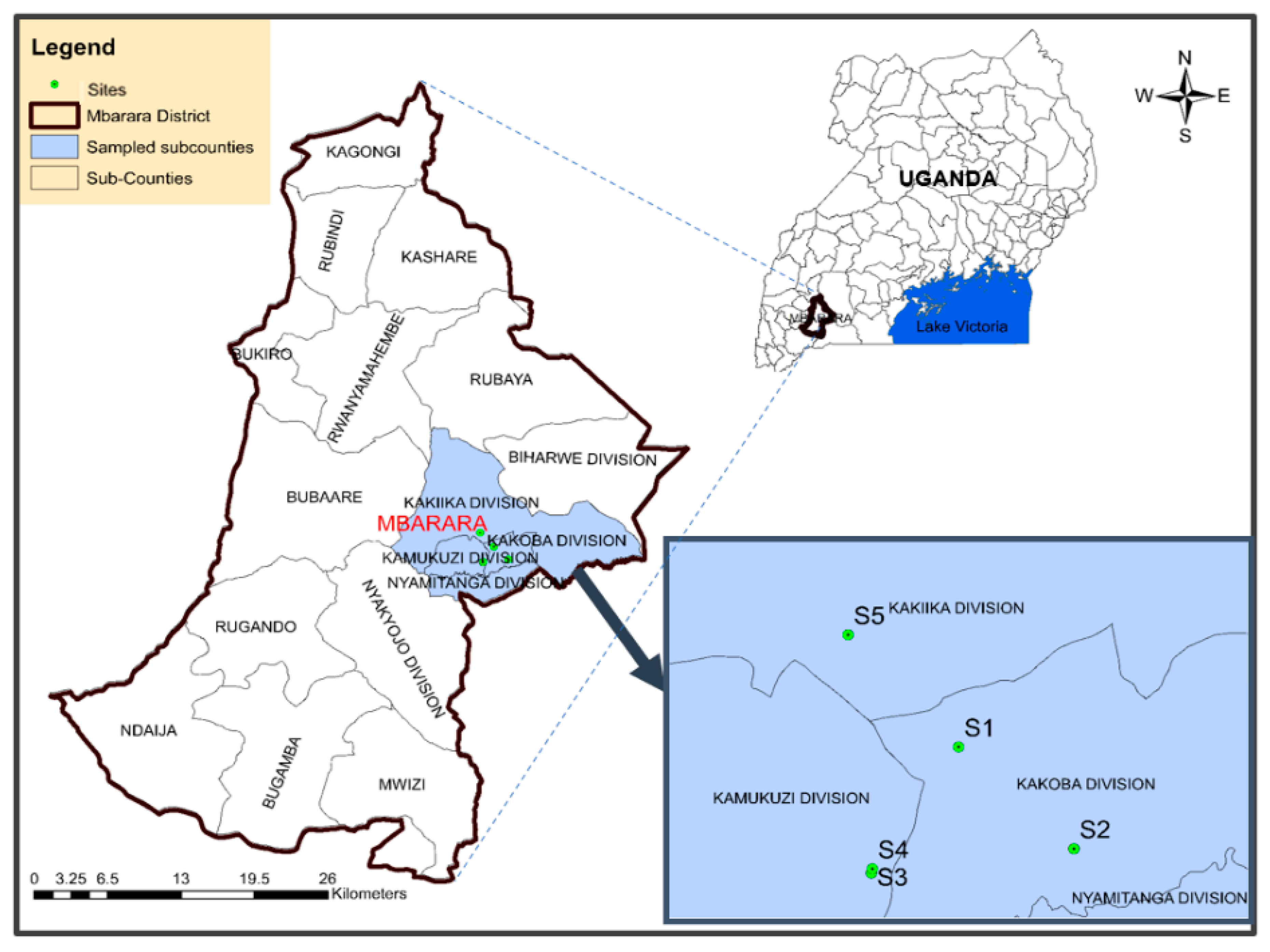
2.1. Study Area Description
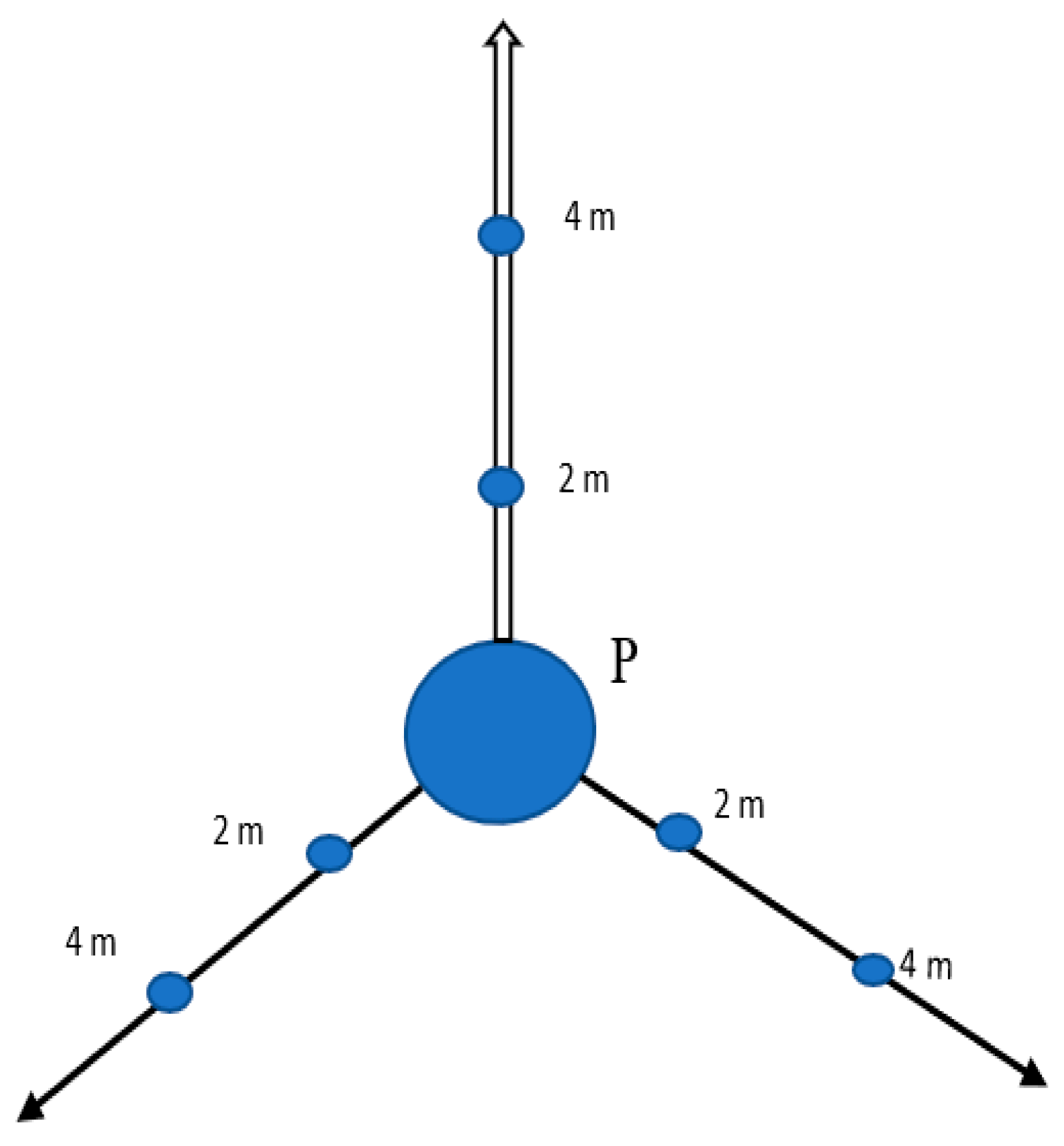
2.2. Sampling Procedure
2.3. Determination of PTEs Concentration
2.4. Human Exposure and Health Risk Assessment
2.4.1. Non-Carcinogenic Health Risk Assessment
2.4.2. Carcinogenic Health Risk Assessment
2.5. Assessment of Soil Pollution Levels
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
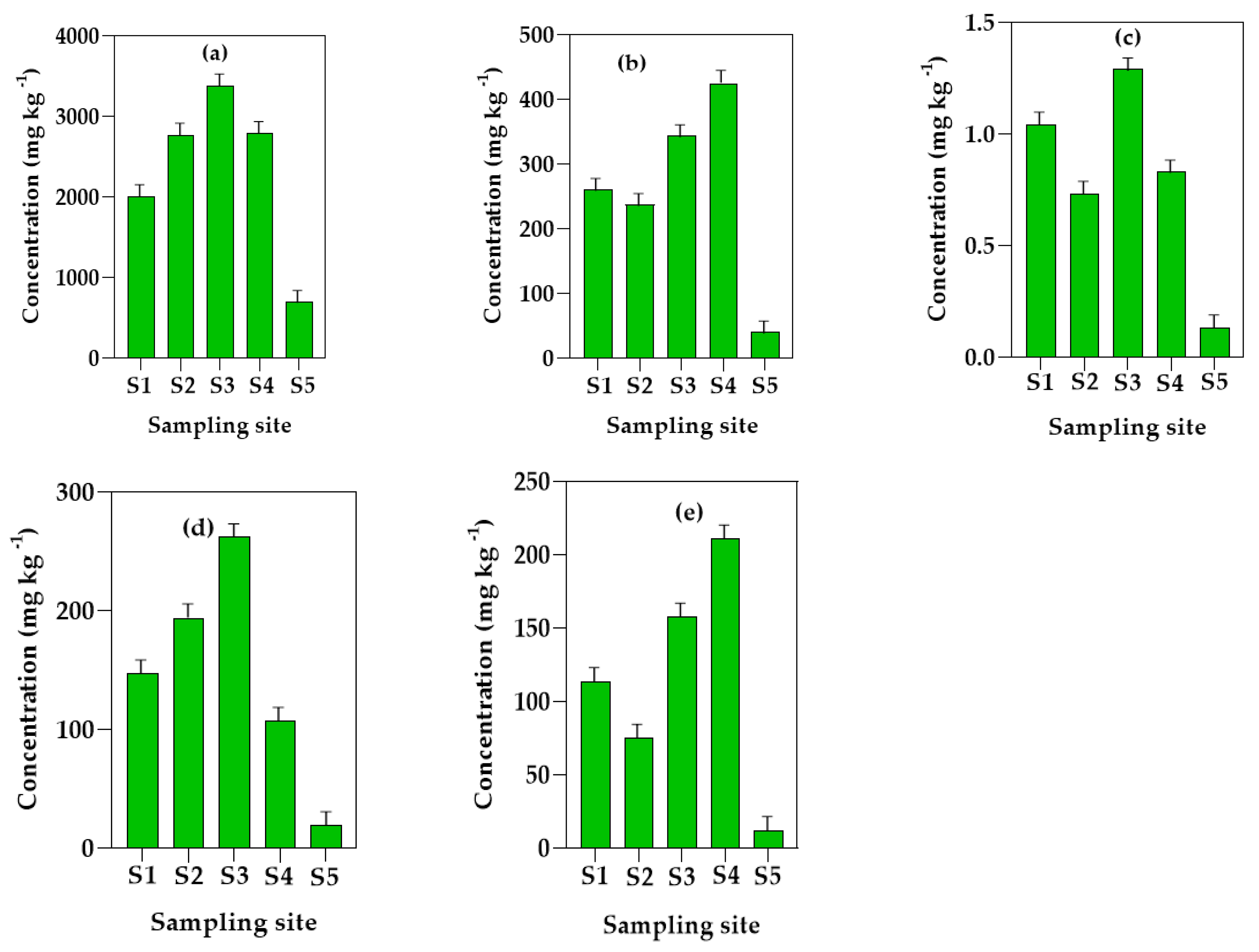
3.1. Concentration of the PTEs in the Soil Samples
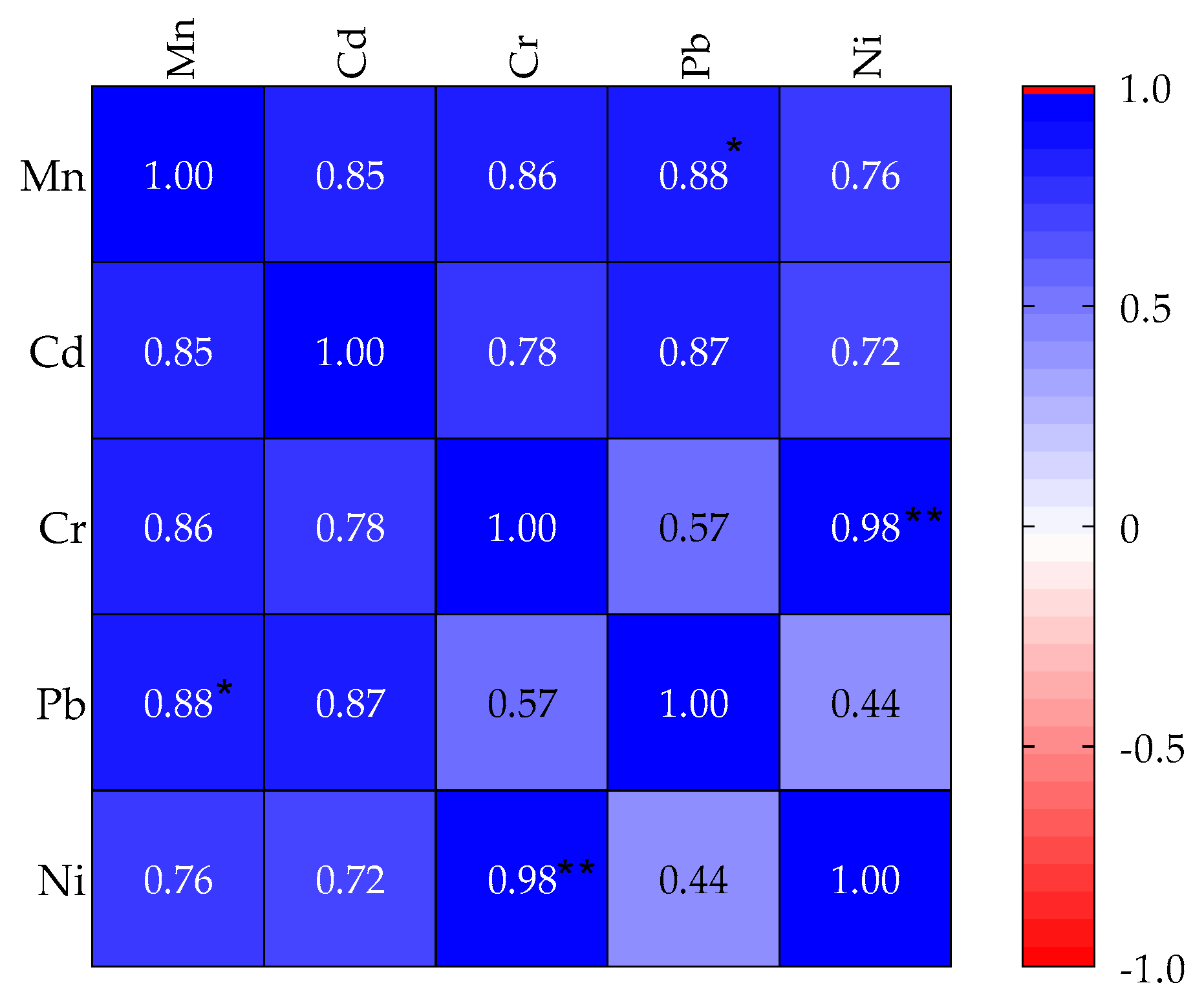
3.2. Inter-Elemental Correlation of the Concentration of the PTEs in the Soil Samples
3.3. Human Health Risk Assessment Indices
3.3.1. Non-Cancer Risk Results
3.3.2. Cancer Risk Estimations
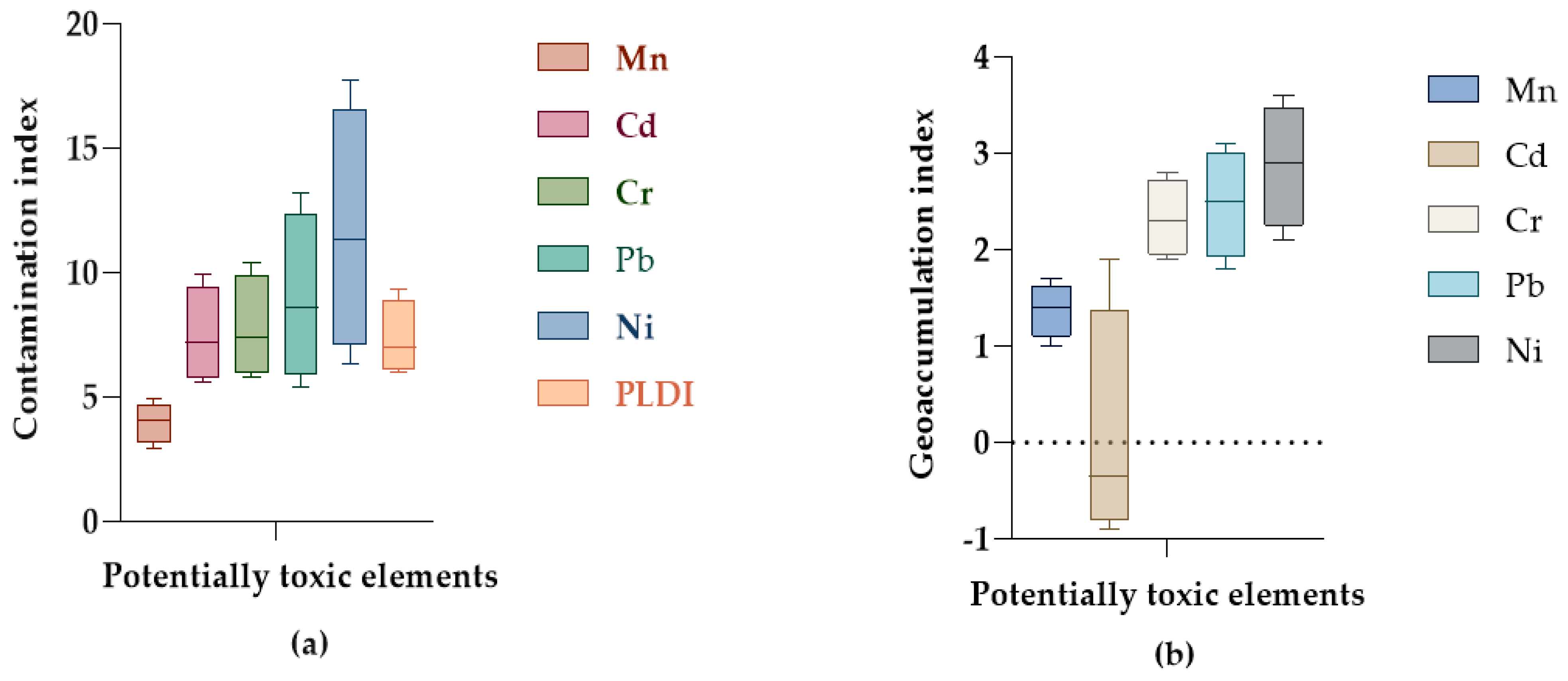
3.4. Pollution Level and Ecological Risk Assessment Indices
4. Discussion
4.1. Concentration and Inter-Elemental Corrlation of the PTEs in the Soil Samples
4.2. Human Health Risks Posed
4.3. Soil Pollution Levels and Ecological Risks Posed
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuddus, M.A.; Tynan, E.M. Urbanization: A problem for the rich and the poor? Public Health Rev. 2020, 41, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Clemente, R.; Strano, E.; Batty, M. Urbanization and economic complexity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, A. Addressing Challenges of Urbanization for Quality of Growth. In SDGs, Transformation, and Quality Growth; Sustainable Development Goals Series; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Radoine, H.; Bajja, S.; Chenal, J.; Ahmed, Z. Impact of urbanization and economic growth on environmental quality in western africa: Do manufacturing activities and renewable energy matter? Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Urban Development. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/urbandevelopment/overview#:~:text=Globally%2C%20over%2050%25%20of%20the,housing%20their%20expanding%20populations%20need (accessed on 19 November 2023).
- Balk, D.; Leyk, S.; Montgomery, M.R.; Engin, H. Global Harmonization of Urbanization Measures: Proceed with Care. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrigs, P. Africapolis: Understanding the dynamics of urbanization in Africa. Field Actions Sci. Rep. 2020, 22, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Mackay, H.; Tusabe, R.; Mugagga, F. Similar, yet different! Comparing Ugandan secondary cities’ food system and nutritional transformations to findings from African primary cities. Urban Transform. 2022, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Independent. Parliament Approves 15 New Cities for Uganda. Available online: https://www.independent.co.ug/parliament-approves-15-new-cities-for-uganda/ (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Angiro, C.; Abila, P.P.; Omara, T. Effects of industrial effluents on the quality of water in Namanve stream, Kampala Industrial and Business Park, Uganda. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalugyaa, A.; Kiguli, J.; Wafula, S.T.; Nuwematsiko, R.; Mugambe, R.K.; Oputan, P.; Tigaiza, A.; Isunju, J.B.; Ssekamatte, T. Knowledge, attitude and practices related to the use of personal protective equipment among welders in small-scale metal workshops in Nansana Municipality, Wakiso District, Uganda. Health Psychol. Behav. Med. 2022, 10, 731–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itiakorit, B.; Bayiga, E.; Osuret, J. Prevalence and determinants of occupational Injuries among welders in small scale metal workshops in Wakiso District, Uganda. East Afr. Health Res. J. 2021, 5, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yellow. Fabrication. Available online: https://www.yellow.ug/companies/fabrication (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Massa, R. Industrial Training Report at Afro Link Metal Works Uganda Limited; Unpublished Industirla Training Report; Busitema University, Busia, Uganda, 2021.
- AGRA-Sustainably Growing Africa’s Food Systems. Exploiting Local Fabrication Capacities to Enhance Post-Harvest. AGRA Impact Series. Available online: https://agra.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Impact-Series_REACTS-and-CARI_Mugenyera-Agro-Machinary-fabricator.pdf (accessed on 25 December 2023).
- Kirabira, J.B.; Semakula, A.N.; Makumbi, T. Estimating Energy Conservation Potential Of Local Metal Casting Units In Uganda Using Data Envelopment Analysis. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2015, 4, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Productivity SA. The South African Metal Fabrication Sector April 2021. Available online: https://productivitysa.co.za/downloads/ProductivitySA_Metal_Fabrication_Sector.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2023).
- Way, M.; Willingham, J.; Goodall, R. Brazing filler metals. Int. Mater. Rev. 2020, 65, 257–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Exp. Suppl. 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eid, R.; Arab, N.T.; Greenwood, M.T. Iron mediated toxicity and programmed cell death: A review and a re-examination of existing paradigms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 399–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Carocci, A.; Lauria, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Catalano, A. Nickel: Human Health and Environmental Toxicology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu, A.A.; Aderinola, O.J.; Kusemiju, V. An Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution by Various Allied Artisans in Automobile, Welding Workshop and Petrol Station in Lagos State, Nigeria. Sci. J. Environ. Eng. Res. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jimoh, A.; Agbaji, E.B.; Ajibola, V.O.; Funtua, M.A. Application of Pollution Load Indices, Enrichment Factors, Contamination Factor and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals Pollution of Soils of Welding Workshops at Old Panteka Market, Kaduna-Nigeria. Open J. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 4, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullahi, S.; Musa, M.S. Health Risk Assessment of Some Heavy Metals in Soil Samples Around Identified Metal Workshops. FUDMA J. Sci. 2023, 7, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, I.L.; Sani, A. Welding fumes composition and their effects on blood heavy metals in albino rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 1495–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.-Y.; Pan, C.-H.; Hsu, Y.-T.; Lai, C.-H. Effects of Heavy Metal Exposure on Shipyard Welders: A Cautionary Note for 8-Hydroxy-2-Deoxyguanosine. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. International Agency for Research on Cancer. Chromium, Nickel and Welding. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC: Lyon, France, 1990; Volume 49, pp. 1–648. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, E.M.S.; Schulte, P.A.; Straif, K.; Hopf, N.B.; Caldwell, J.C.; Carreon, T.; DeMarini, D.M.; Fowler, B.A.; Goldstein, B.D.; Hemminki, K.; et al. Research recommendations for selected IARC-classified agents. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, N.; Loomis, D.; Guyton, K.Z.; Grosse, Y.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Vilahur, N.; Muller, K.; Straif, K.; et al. Carcinogenicity of welding, molybdenum trioxide, and indium tin oxide. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 581–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, S.P.B.; Anguma, S.; Meng, Q. Spatio-Temporal Variation in the Concentration of Inhalable Particulate Matter (PM10) in Uganda. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbarara City Government. Mbarara City. Available online: https://mbararacity.go.ug/ (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- UN-Habitat. Mbarara Municipality Urban Profile. Available online: https://unhabitat.org/sites/default/files/download-manager-files/Mbarara%20Municipality%20Urban%20Profile%20%20Uganda.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- UBOS. Mbarara Population Statistics. Available online: https://www.citypopulation.de/en/uganda/cities/ (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Oladele, B.B.; Ugbede, F.O.; Arogunjo, A.M.; Ajayi, O.S.; Pereira, A. Gamma spectroscopy study of soil-plant transfer factor characteristics of 40K, 232Th and 226Ra in some crops cultivated in southwestern region of Nigeria. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajeh, E.A.; Modi, F.J.; Omoregi, I.P. Health risk estimations and geospatial mapping of trace metals in soil samples around automobile mechanic workshops in Benin City, Nigeria. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Recommended Use of BW3/4 as the Default Method in Derivation of the Oral Reference Dose. EPA/100/R11/001. Office of the Science Advisor. 2011. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/raf/publications/pdfs/recommended-use-of-bw34.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- US EPA. Risk-Based Concentration Table. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2010. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/reg3hwmd/risk/human/index.htm (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Ferreira-Baptista, L.; De Miguel, E. Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: A tropical urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4501–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, T.; Karungi, S.; Kalukusu, R.; Nakabuye, B.; Kagoya, S.; Musau, B. Mercuric pollution of surface water, superficial sediments, Nile tilapia (Oreochromis nilotica Linnaeus 1758 [Cichlidae]) and yams (Dioscorea alata) in auriferous areas of Namukombe stream, Syanyonja, Busia, Uganda. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opolot, M.; Omara, T.; Adaku, C.; Ntambi, E. Spatio-temporal Variations and Potential Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Water from River Manafwa, Uganda. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci 2024, 13, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Die Schwermetallbelastung der Sedimenten des Neckars und Seiner Nebenflüsse. Chemiker-Zeitung 1981, 6, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Kao, C.; Chen, C.; Dong, C. Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in the sediments of Kaohsiung harbor, Taiwan. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Feng, H.; Chang, J.; Qu, J.; Xie, H.; Yu, L. Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of Yangtze river intertidal zone: An assessment from different indexes. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Singh, G. Pollution evaluation, human health effect and tracing source of trace elements on road dust of Dhanbad, a highly polluted industrial coal belt of India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 2081–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denneman, C.A.J.; Robberse, J.G. Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment as a Base for Development of Soil Quality Criteria. In Contaminated Soil’90; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants; Kabata-Pendias, A., Pendias, H.K., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2011; Volume 548, p. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Han, X.; Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Luan, H. Distribution and health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soils around coal industrial areas: A global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 135292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taube, F. Manganese in Occupational Arc Welding Fumes—Aspects on Physiochemical Properties, with Focus on Solubility. Ann. Occupat. Hyg. 2013, 57, 6–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sriram, K.; Lin, G.X.; Jefferson, A.M.; Roberts, J.R.; Andrews, R.N.; Kashon, M.L.; Antonini, J.M. Manganese accumulation in nail clippings as a biomarker of welding fume exposure and neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Indust Health 2012, 2911, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrifar, Y.; Bahrami, M.; Sidabadi, E.; Pirami, H. The effects of occupational exposure to manganese fume on neurobehavioral and neurocognitive functions: An analytical cross-sectional study among welders. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heung, W.; Yun, M.-J.; Chang, D.P.Y.; Green, P.G.; Halm, C. Emissions of Chromium (VI) from Arc Welding. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2007, 57, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnu, B.R.; Sivapirakasam, S.P.; Satpathy, K.K.; Albert, S.K.; Chakraborty, G. Cr6+ reduction in welding fumes by nano composite coatings on stainless steel manual metal arc welding electrodes. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2018, 114, 334–346. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrifar, Y.; Zeverdegani, S.K.; Rismanchian, M. Chemical pollutants in the respiratory zone of welders: Determination of concentrations and hazard analysis. Work 2020, 67, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccelli, M.G.; Goldoni, M.; Poli, D.; Mozzoni, P.; Cavallo, D.; Corradi, M. Welding Fumes, a Risk Factor for Lung Diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, J. The Many Sides of Cadmium Plating. In Proceedings of the CORROSION 2003, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–20 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.-J.; Guo, J.-Y.; Zhang, G.-Y.; Kang, H.; Shi, X.-J.; Zhou, H.; Liang, Y.-F.; Shen, W.-T.; Lei, L.-J. Urinary cadmium and peripheral blood telomere length predict the risk of renal function impairment: A study of 547 community residents of Shanxi, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 71427–71438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Z. Cadmium-induced renal tubular dysfunction in a group of welders. Occupat. Med. 2011, 61, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, S.F.; Mehrifar, Y.; Ardalan, A. The Relationship between Exposure to Lead-Containing Welding Fumes and the Levels of Reproductive Hormones. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Exposure to Lead: A Major Public Health Concern, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240037656 (accessed on 6 September 2023).
- Saeed, S.; Hasan, S.; Kuldeep, K.; Choudhury, P. Lead Poisoning: A Persistent health Hazard-General and oral aspects. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2017, 10, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Lead in Drinking-Water: Health Risks, Monitoring and Corrective Actions. 2022. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1460455/retrieve (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Kim, H.C.; Jang, T.W.; Chae, H.J.; Choi, W.J.; Ha, M.N.; Ye, B.J.; Kim, B.G.; Jeon, M.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Hong, Y.S. Evaluation and management of lead exposure. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2015, 27, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Reddy, R.; Bagoji, I.; Das, S.; Bagali, S.; Mullur, L.; Khodnapur, J.; Biradar, M. Primary concept of nickel toxicity—An overview. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 30, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekeye, E.A.; Ojo, M.A.; Ajayi, O.O. Contributions of metal welding workshops to environmental pollution in Akure Metropolis, Ondo State, Nigeria. J. Environ. Issues Agric. Dev. Ctries 2011, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Baguma, G.; Musasizi, A.; Twinomuhwezi, H.; Gonzaga, A.; Nakiguli, C.K.; Onen, P.; Angiro, C.; Okwir, A.; Opio, B.; Otema, T.; et al. Heavy Metal Contamination of Sediments from an Exoreic African Great Lakes’ Shores (Port Bell, Lake Victoria), Uganda. Pollutants 2022, 2, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onen, P.; Akemkwene, R.; Nakiguli, C.K.; Nimusiima, D.; Ruma, D.H.; Khanakwa, A.V.; Angiro, C.; Bamanya, G.; Opio, B.; Gonzaga, A.; et al. Health Risks from Intake and Contact with Toxic Metal-Contaminated Water from Pager River, Uganda. J. Xenobiot. 2023, 13, 544–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimusiima, D.; Byamugisha, D.; Omara, T.; Ntambi, E. Physicochemical and Microbial Quality of Water from the Ugandan Stretch of the Kagera Transboundary River. Limnol. Rev. 2023, 23, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žibret, G.; Rokavec, D. Household dust and street sediment as an indicator of recent heavy metals in atmospheric emissions: A case study on a previously heavily contaminated area. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, W.; Bremmer, H.J.; van Engelen, J.G.M. Oral Exposure of Children to Chemicals via Hand-to-Mouth Contact. RIVM Report 320005004/2007. 2007. Available online: https://www.rivm.nl/bibliotheek/rapporten/320005004.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2023).
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol. Mar. Res. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Age Group | Sampling Site | Average Chronic Daily Intake (×10−6 mg kg−1 day−1) | Hazard Quotient | Hazard Index 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Cr | Cd | Pb | Ni | Mn | Cr | Cd | Pb | Ni | |||
| Children | S1 | 3531.7 | 9.3 | 303.7 | 247.9 | 95.7 | 0.076 | 0.093 | 0.304 | 0.071 | 0.0047 | 0.5487 |
| S2 | 25,724.2 | 13.3 | 333.1 | 188.7 | 144.7 | 0.559 | 0.133 | 0.333 | 0.054 | 0.0072 | 1.0862 | |
| S3 | 35,786.3 | 10.6 | 424.9 | 137.8 | 270.2 | 0.778 | 0.106 | 0.425 | 0.039 | 0.0135 | 1.3615 | |
| S4 | 43,178.1 | 16.5 | 543.3 | 335.0 | 201.3 | 0.939 | 0.165 | 0.543 | 0.096 | 0.0101 | 1.7531 | |
| S5 | 889.0 | 1.7 | 52.02 | 25.42 | 15.2 | 0.019 | 0.017 | 0.052 | 0.007 | 0.0008 | 0.0958 | |
| Adults | S1 | 4414.7 | 1.17 | 24.68 | 20.14 | 59.81 | 0.096 | 0.0012 | 0.0025 | 0.0058 | 0.0030 | 0.1085 |
| S2 | 3216.7 | 1.67 | 27.07 | 15.33 | 90.45 | 0.070 | 0.0017 | 0.0027 | 0.0044 | 0.0045 | 0.0833 | |
| S3 | 4472.3 | 1.33 | 44.14 | 11.20 | 168.90 | 0.097 | 0.0013 | 0.0044 | 0.0032 | 0.0084 | 0.1143 | |
| S4 | 5397.2 | 2.06 | 35.68 | 209.36 | 125.81 | 0.012 | 0.0021 | 0.0036 | 0.0060 | 0.0063 | 0.0300 | |
| S5 | 1111.2 | 0.21 | 4.23 | 15.89 | 9.52 | 0.0024 | 0.00021 | 0.0004 | 0.00045 | 0.00048 | 0.0039 | |
| Age Group | Sampling Site | Average Chronic Daily Intake (×10−15 mg kg−1 day−1) | Hazard Quotient (×10−10) | Hazard Index (×10−10) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Cr | Cd | Pb | Ni | Mn | Cr | Cd | Pb | Ni | |||
| Children | S1 | 2683.7 | 7.07 | 230.78 | 188.37 | 72.72 | 1876.70 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.36 | 0.13 | 1877.67 |
| S2 | 19,547.3 | 10.1 | 253.12 | 143.39 | 109.95 | 13,699.40 | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 13,700.50 | |
| S3 | 27,193.2 | 8.05 | 322.87 | 109.34 | 205.32 | 19,016.20 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.38 | 19,017.40 | |
| S4 | 32,810.1 | 12.54 | 412.84 | 254.56 | 152.96 | 22,944.13 | 0.44 | 0.41 | 0.48 | 0.28 | 22,945.70 | |
| S5 | 675.5 | 1.29 | 39.53 | 19.32 | 11.55 | 472.38 | 0.05 | 0.004 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 472.49 | |
| Adults | S1 | 3354.64 | 0.89 | 18.75 | 15.3 | 45.45 | 2345.90 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 2346.49 |
| S2 | 2444.3 | 1.27 | 20.57 | 11.65 | 68.73 | 1709.30 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 1709.89 | |
| S3 | 3398.4 | 1.01 | 33.54 | 8.51 | 128.34 | 2376.50 | 0.04 | 0.34 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 2377.28 | |
| S4 | 4101.22 | 1.57 | 27.11 | 15.91 | 95.6 | 2867.99 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.18 | 2868.79 | |
| S5 | 844.38 | 0.16 | 3.21 | 12.07 | 7.23 | 590.48 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.01 | 590.81 | |
| Age Group | Sampling Site | Average Chronic Daily Intake (×10−6 mg kg−1 day−1) | Hazard Quotient | Hazard Index | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Cr | Cd | Pb | Ni | Mn | Cr | Cd | Pb | Ni | |||
| Children | S1 | 98.89 | 0.026 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 0.27 | 0.0029 | 0.0043 | 0.00085 | 0.000019 | 0.000013 | 0.008082 |
| S2 | 72.06 | 0.037 | 0.93 | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.0016 | 0.0062 | 0.00093 | 0.000015 | 0.000020 | 0.008565 | |
| S3 | 100.20 | 0.029 | 1.52 | 0.38 | 0.76 | 0.0022 | 0.0048 | 0.00152 | 0.000011 | 0.000037 | 0.008568 | |
| S4 | 120.90 | 0.046 | 1.23 | 0.94 | 0.56 | 0.0026 | 0.0077 | 0.00123 | 0.000027 | 0.000027 | 0.011584 | |
| S5 | 24.89 | 0.005 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.0005 | 0.0008 | 0.00015 | 0.000002 | 0.000014 | 0.001466 | |
| Adults | S1 | 176.15 | 0.046 | 7.57 | 6.18 | 2.39 | 0.0038 | 0.0077 | 0.00757 | 0.00018 | 0.000116 | 0.019410 |
| S2 | 128.35 | 0.066 | 8.31 | 4.71 | 3.61 | 0.0028 | 0.0110 | 0.00831 | 0.00013 | 0.000175 | 0.022415 | |
| S3 | 178.48 | 0.052 | 13.55 | 3.44 | 6.74 | 0.0039 | 0.0087 | 0.01355 | 0.00010 | 0.000327 | 0.026493 | |
| S4 | 215.35 | 0.082 | 10.95 | 8.35 | 5.02 | 0.0047 | 0.0137 | 0.00110 | 0.00024 | 0.000243 | 0.019983 | |
| S5 | 44.34 | 0.008 | 1.29 | 0.63 | 0.38 | 0.0010 | 0.0013 | 0.00129 | 0.00002 | 0.000018 | 0.003628 | |
| Age Group | Sampling Site | Cancer Risk (×10−6) | Total Cancer Risk (×10−6) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Pb | Ni | |||
| Children | S1 | 152.2 | 2.1 | 80.4 | 234.7 |
| S2 | 166.9 | 1.6 | 121.5 | 290.0 | |
| S3 | 212.9 | 1.2 | 227.0 | 441.1 | |
| S4 | 272.2 | 2.8 | 169.1 | 444.1 | |
| S5 | 26.1 | 0.2 | 12.8 | 39.1 | |
| Adults | S1 | 12.4 | 0.17 | 50.2 | 62.77 |
| S2 | 13.6 | 0.13 | 76.0 | 89.73 | |
| S3 | 22.1 | 0.10 | 141.9 | 164.1 | |
| S4 | 17.9 | 1.78 | 105.7 | 125.38 | |
| S5 | 2.1 | 0.14 | 8.0 | 10.24 | |
| Sampling Site | PERI | Pollution Level | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Cd | Cr | Pb | Ni | |||
| S1 | 4.0 | 168.0 | 11.6 | 49.0 | 31.5 | 264.1 | Considerable |
| S2 | 2.9 | 240.0 | 12.8 | 37.0 | 47.5 | 340.2 | Considerable |
| S3 | 4.1 | 192.0 | 20.8 | 27.0 | 88.5 | 332.4 | Considerable |
| S4 | 4.9 | 297.0 | 16.8 | 15.5 | 66.0 | 400.2 | High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nuwamanya, E.; Byamugisha, D.; Nakiguli, C.K.; Angiro, C.; Khanakwa, A.V.; Omara, T.; Ocakacon, S.; Onen, P.; Omoding, D.; Opio, B.; et al. Exposure and Health Risks Posed by Potentially Toxic Elements in Soils of Metal Fabrication Workshops in Mbarara City, Uganda. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 176-192. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010011
Nuwamanya E, Byamugisha D, Nakiguli CK, Angiro C, Khanakwa AV, Omara T, Ocakacon S, Onen P, Omoding D, Opio B, et al. Exposure and Health Risks Posed by Potentially Toxic Elements in Soils of Metal Fabrication Workshops in Mbarara City, Uganda. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2024; 14(1):176-192. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleNuwamanya, Eunice, Denis Byamugisha, Caroline K. Nakiguli, Christopher Angiro, Alice V. Khanakwa, Timothy Omara, Simon Ocakacon, Patrick Onen, Daniel Omoding, Boniface Opio, and et al. 2024. "Exposure and Health Risks Posed by Potentially Toxic Elements in Soils of Metal Fabrication Workshops in Mbarara City, Uganda" Journal of Xenobiotics 14, no. 1: 176-192. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010011
APA StyleNuwamanya, E., Byamugisha, D., Nakiguli, C. K., Angiro, C., Khanakwa, A. V., Omara, T., Ocakacon, S., Onen, P., Omoding, D., Opio, B., Nimusiima, D., & Ntambi, E. (2024). Exposure and Health Risks Posed by Potentially Toxic Elements in Soils of Metal Fabrication Workshops in Mbarara City, Uganda. Journal of Xenobiotics, 14(1), 176-192. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox14010011










