Organochlorine Compounds in the Amur (Heilong) River Basin (2000–2020): A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Brief Characteristics of POPs
3. Sources of POPs in the Amur River Basin
4. OCP and PCB Concentrations in Components of Ecosystems of the Amur River Basin
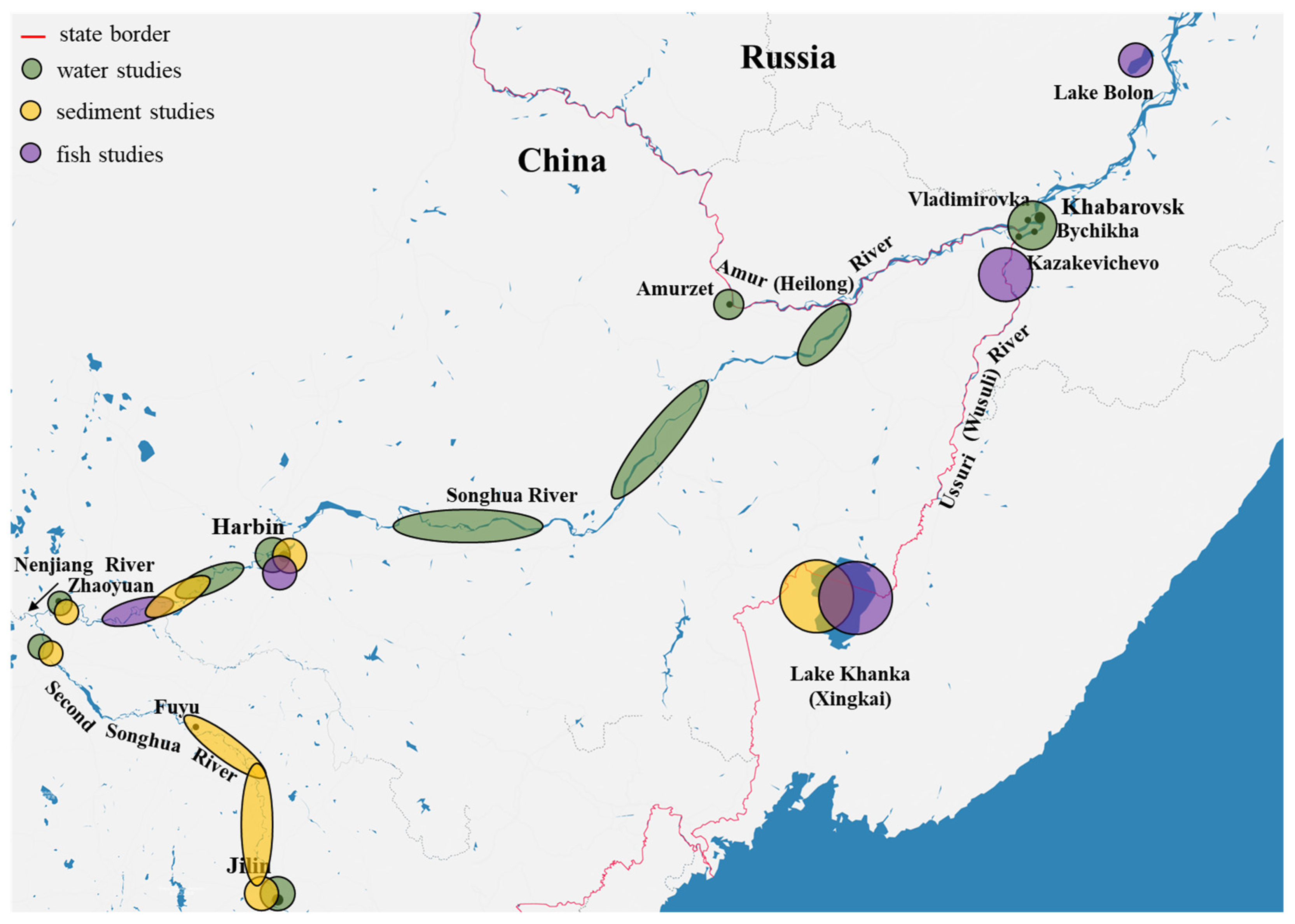
4.1. The Amur and the Ussuri
4.2. The Songhua
4.3. Lake Khanka/Xingkai
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borsch, S.V.; Simonov, Y.A.; Khristoforov, A.V.; Yumin, N.M. Short-Term Forecasting of Water Levels on the Amur River. Proc. Cent. Hydrometeorol. Res. Russ. Fed. 2015, 353, 26–45. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimchuk, M.M. (Ed.) Surface Water Quality in the Russian Federation: Yearbook 2021; Roshydromet: Rostov-on-Don, Russia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kryukov, V. Chapter 5. Possibility of Sustainable Development of the Basin of Amur River from Ecological Viewpoints. In Energy and Environment in Slavic Eurasia: Toward the Establishment of the Network of Environmental Studies in the Pan-Okhotsk Region; Slavic Research Center: Sapporo, Japan, 2008; pp. 127–156. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Berdnikov, N.V. Pollution of the Amur River in Connection with the Accident at a Chemical Plant in Jilin (China), November 13, 2005. Min. Informational Anal. Bull. Sci. Tech. J. 2007, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- WWF Pollution of the Songhua River Can Reach Amur. Available online: https://wwf.ru/en/resources/news/amur/zagryaznenie-na-sungari-mozhet-auknutsya-na-yuge-dalnego-vostoka-rossii/ (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- Grung, M.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Steen, A.O.; Huang, J.; Zhang, G.; Larssen, T. Pesticide Levels and Environmental Risk in Aquatic Environments in China—A Review. Environ. Int. 2015, 81, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ATSDR. Toxicological Profile for DDT, DDE, and DDD; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- ATSDR. Toxicological Profile for Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH); U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- ATSDR. Toxicological Profile for Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs); U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Ridding the World of POPs: A Guide to the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants; UNEP (United Nations Environmental Program): Switzerland, Geneva, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tsygankov, V.Y. Organochlorine Pesticides in Marine Ecosystems of the Far Eastern Seas of Russia (2000–2017). Water Res. 2019, 161, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockholm Convention. Available online: http://www.pops.int/ (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Ali, U.; Syed, J.H.; Malik, R.N.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Jones, K.C. Organochlorine Pesticides (OCPs) in South Asian Region: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovinsky, F.Y.; Voronova, L.D.; Afanasyev, M.I. Background Monitoring of Pollution of Terrestrial Ecosystems by Organochlorine Compounds; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Guéguen, F.; Stille, P.; Millet, M. Optimisation and Application of Accelerated Solvent Extraction and Flash Chromatography for Quantification of PCBs in Tree Barks and XAD-2 Passive Samplers Using GC–ECD with Dual Columns. Talanta 2013, 111, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vudamala, K.; Chakraborty, P.; Chatragadda, R.; Tiwari, A.K.; Qureshi, A. Distribution of Organochlorine Pesticides in Surface and Deep Waters of the Southern Indian Ocean and Coastal Antarctic Waters. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 321, 121206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, R.; Dong, C.; Qi, Z.; Liu, G.; Chen, Z.-F.; Cai, Z. GC-MS/MS Analysis for Source Identification of Emerging POPs in PM2.5. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 193, 110368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, W.; Kingston, H.M.; Dillard, A.; Macherone, A.; Stuff, J.; Pamuku, M. Quantification of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Human Whole Blood Samples Using Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction Coupled with GC/MS/MS and Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2020, 153, 104279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, K.; Debret, M.; Morin, C.; Cosme, J.; Portet-Koltalo, F. Direct Thermal Desorption-Gas Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry versus Microwave Assisted Extraction and GC-MS for the Simultaneous Analysis of Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs, PCBs) from Sediments. Talanta 2022, 250, 123735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macherone, A. Chapter 20—The Future of GC/Q-TOF in Environmental Analysis. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Advanced Techniques in Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS–MS and GC–TOF–MS) for Environmental, Chemistry; Ferrer, I., Thurman, E.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 61, pp. 471–490. [Google Scholar]
- Plaza-Bolaños, P.; Valera-Tarifa, N.M.; Frenich, A.G. Chapter 18—Current Applications of GC-(Q)TOF and GC–HRMS for the Determination of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Water and Sediments Samples. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Advanced Techniques in Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS–MS and GC–TOF–MS) for Environmental, Chemistry; Ferrer, I., Thurman, E.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 61, pp. 431–454. [Google Scholar]
- Saint-Hilaire, M.; Inthavong, C.; Bertin, T.; Lavison-Bompard, G.; Guérin, T.; Fournier, A.; Feidt, C.; Rychen, G.; Parinet, J. Development and Validation of an HPLC-MS/MS Method with QuEChERS Extraction Using Isotopic Dilution to Simultaneously Analyze Chlordecone and Chlordecol in Animal Livers. Food Chem. 2018, 252, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroudi, F.; Al-Alam, J.; Chimjarn, S.; Delhomme, O.; Fajloun, Z.; Millet, M. Conifers as Environmental Biomonitors: A Multi-Residue Method for the Concomitant Quantification of Pesticides, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Polychlorinated Biphenyls by LC-MS/MS and GC–MS/MS. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polder, A.; Savinova, T.N.; Tkachev, A.; Løken, K.B.; Odland, J.O.; Skaare, J.U. Levels and Patterns of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPS) in Selected Food Items from Northwest Russia (1998–2002) and Implications for Dietary Exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5352–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Zhu, T.; Yao, B.; Hu, J.; Hu, S. Contribution of Dicofol to the Current DDT Pollution in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4385–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, R. Silent Spring, 40th anniversary ed., 1st Mariner Books ed.; Houghton Mifflin: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-618-24906-0. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, D.; Tren, R.; Bate, R. Zambone Jennifer The Excelent Powder: DDT’s Political and Scientific History; Dog Ear Publishing: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwman, H.; Bornman, R.; va den Berg, H.; Kylin, H. 11 DDT: Fifty Years since Silent Spring. In Late Lessons from Early Warnings: Science, Precaution, Innovation; EEA Report; European Environmental Agency (EEA): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013; pp. 240–259. [Google Scholar]
- Vijgen, J.; Abhilash, P.C.; Li, Y.F.; Lal, R.; Forter, M.; Torres, J.; Singh, N.; Yunus, M.; Tian, C.; Schäffer, A.; et al. Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) as New Stockholm Convention POPs—A Global Perspective on the Management of Lindane and Its Waste Isomers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, K.L.; Ulrich, E.M.; Hites, R.A. Differential Toxicity and Environmental Fates of Hexachlorocyclohexane Isomers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2197–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadori, E. The Production and Use of HCH, HCH and Halogenated Pesticides—State of the Art for Risk Assessment and Technology Development. In Proceedings of the IWU—Tagungsberichte, Magdeburg, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.F.; Cai, D.J.; Shan, Z.J.; Zhu, Z.L. Gridded Usage Inventories of Technical Hexachlorocyclohexane and Lindane for China with 1/6° Latitude by 1/4° Longitude Resolution. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulkley, R.V.; Shannon, L.R.; Kellogg, R.L. Contamination of Channel Catfish with Dieldrin from Agricultural Runoff; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- ATSDR. Toxicological Profile for Aldrin/Dieldrin; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgenson, J.L. Aldrin and Dieldrin: A Review of Research on Their Production, Environmental Deposition and Fate, Bioaccumulation, Toxicology, and Epidemiology in the United States. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 113–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, F. Toxicology of Insecticides; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; ISBN 978-1-4612-9508-2. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Drinking Water Criteria Document for Endrin; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Endrin: Intent to Cancel Registrations and Denial of Applications for Registration of Pesticide Products Containing Endrin, and Statement of Reasons. Fed Regist 44:43632-43657; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- ATSDR. Toxicological Profile for Endrin; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kenaga, E.E. Predicted Bioconcentration Factors and Soil Sorption Coefficients of Pesticides and Other Chemicals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1980, 4, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, R.L.; Kapoor, I.P.; Lu, P.Y.; Schuth, C.K.; Sherman, P. Model Ecosystem Studies of the Environmental Fate of Six Organochlorine Pesticides. Environ. Health Perspect. 1973, 4, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, K.C.; Matsumura, F.; Boush, G.M. Metabolic Transformation of DDT, Dieldrin, Aldrin, and Endrin by Marine Microorganisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1972, 6, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkow, I.C.; Kallenborn, R. Sources and Transport of Persistent Pollutants to the Arctic. Toxicol. Lett. 2000, 112–113, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Aken, B.; Bhalla, R. 6.14—Microbial Degradation of Polychlorinated Biphenyls. In Comprehensive Biotechnology, 2nd ed.; Moo-Young, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, VT, USA, 2011; pp. 151–166. ISBN 978-0-08-088504-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kodavanti, P.R.S.; Loganathan, B.G. Chapter 25—Polychlorinated Biphenyls, Polybrominated Biphenyls, and Brominated Flame Retardants. In Biomarkers in Toxicology; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 433–450. ISBN 978-0-12-404630-6. [Google Scholar]
- Giesy, J.P.; Kannan, K. Dioxin-like and Non-Dioxin-like Toxic Effects of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs): Implications for Risk Assessment. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1998, 28, 511–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S. Bioindicators of POPs; KyotoUniversity Press and Trans Pacific Press: Kyoto, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Simonov, E.A.; Egidarev, E.G.; Menshikov, D.A.; Khalyapin, L.E.; Korolev, G.S. Comprehensive Environmental and Economic Assessment of the Development of Hydropower in the Amur River Basin; WWF Russia: Moscow, Russia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gotwanskiy, V.I. The Amur Basin: Mastering—to Save; Archipelago Fine Print: Khabarovsk, Russia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Amur Basin Water Agency. Information Bulletin on the Status of Surface Water Bodies, Water Management Systems, and Structures in the Area of Activity of the Amur Basin Water Agency for 2000; Amur Basin Water Agency: Khabarovsk, Russia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Naumov, Y.A. On the features of surface water pollution in the territory of the Russian Far East. Ecumene Reg. Stud. 2021, 3, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shesterkin, V.P. Khabarovsk Krai’s Transition to a Sustainable Development Model. In Proceedings of the Ecology; Environmental Management: Khabarovsk, Russia, 2000; pp. 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, P.; Xue, H.; Meng, D. Organic Pollutant Types and Concentration Changes of the Water from Songhua River, China, in 1975–2013. Water. Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryabkova, V.A.; Talovskaya, V.S.; Dobrych, V.A.; Filonov, V.A.; Ryabceva, E.G.; Radivoz, M.I.; Kovalsky, Y.G.; Brileva, I.N.; Trutenko, E.V.; Chepel, T.V. Medico-ecological evaluation of the impact to the biota caused by the pollution of the amur river and the health conditions of the population in the amur territory. Far East. Med. J. 2006, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Shesterkin, V.P.; Shesterkina, N.M. Hydro/Chemical Features of the Amur River Waters near Khabarovsk during a Very High Flood in 2020. Water Sect. Russ. Probl. Technol. Manag. 2022, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhulidov, A.V.; Headley, J.V.; Pavlov, D.F.; Robarts, R.D.; Korotova, L.G.; Vinnikov, Y.Y.; Zhulidova, O.V. Riverine Fluxes of the Persistent Organochlorine Pesticides Hexachlorcyclohexane and DDT in the Russian Federation. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-Y.; Jiang, A.-X.; Ren, N.-Q.; Jiang, G.-B.; Li, Y.-F. Gridded Inventories of Historical Usage for Selected Organochlorine Pesticides in Heilongjiang River Basin, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 18, 822–826. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.-R.; Pang, Y.-X.; Tang, X.-L.; Dong, H.-W.; Chen, B.-Q.; Sun, C.-H. Genotoxic Activity of Organic Contamination of the Songhua River in the North-Eastern Region of the People’s Republic of China. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2007, 634, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohe, T.; Watanabe, T.; Wakabayashi, K. Mutagens in Surface Waters: A Review. Mutat. Res. Mutat. Res. 2004, 567, 109–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonov, E.A. , Dahmer, T.D., Eds. Amur-Heilong River Basiin Reader; Simonov, E.A., Dahmer, T.D., Eds.; WWF, Ecosystems Ltd.: Hong Kong, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vaskovsky, M.T. Surface Water Resources of the USSR; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1972; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Shesterkin, V.P.; Krutikova, V.O. Salt Composition of the Waters of the Ussuri River. Reg. Issues 2018, 21, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Turbinskiy, V.V.; Khmelev, V.A. Carcinogenic and non-cancer health risk of the cross-border, interregional sources of drinking water supply. Sibbezopasnost Spassib. 2012, 123, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Minselkhoz Order of the Ministry of Agriculture of Russia “On Approval of Water Quality Standards for Water Bodies of Fishery Significance, Including Standards for Maximum Permissible Concentrations of Harmful Substances in the Waters of Water Bodies of Fishery Significance”. Available online: https://docs.cntd.ru/document/420389120?section=text (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Ivanova, E.G. Results of Joint Russian-Chinese Monitoring of the Amur and Ussuri Rivers in 2011. In Proceedings of the Materials of the VII International Scientific and Practical Conference, WWF, Moscow, Russia, 15 November 2012; pp. 132–133. [Google Scholar]
- Mishchenko, O.A.; Gladun, I.V.; Volosnikova, G.A. Monitoring of Pesticide Pollution of Surface Waters of the Amur River in the Area of the City of Khabarovsk. In Proceedings of the Materials of the XI Scientific-Practical Conference with International Participation; Pacific State University: Khabarovsk, Russia, 2022; Volume 11, pp. 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Lu, J.; Zhou, H.; Huang, S.; Wang, Z.; Spear, P.A. Occurrence and Distribution of Organochlorine Pesticides—Lindane, p,p’-DDT, and Heptachlor Epoxide—In Surface Water of China. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.; Ding, J.; Zhao, X.-S.; Li, Y.-F.; Liu, L.-Y.; Ma, W.-L.; Qi, H.; Shen, J.-M. Spatial and Seasonal Variation of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Songhua River, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2011, 33, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Sun, K.; Dong, S.; Wang, Y.M.; Wang, S.; Jia, L. Assessment of Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Water, Sediment, and Fish of the Songhua River, China. Environ. Forensics 2014, 15, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qu, B.; Liu, H.; Ding, J.; Ren, N. Analysis of Organochlorine Pesticides in Surface Water of the Songhua River Using Magnetoliposomes as Adsorbents Coupled with GC-MS/MS Detection. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qu, B.; Liu, H.; Ding, J.; Ren, N. Fast Determination of β-Endosulfan, α-Hexachlorocyclohexane and Pentachlorobenzene in the River Water from Northeast of China. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.N.; Holosha, O.A.; Glebova, E.V.; Kharenko, E.N.; Sopina, A.V. Development of technological standards for the production of food products from Amur sturgeon. Izv. TINRO 2001, 129, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Chukhlebova, L.M.; Kondratieva, L.M.; Rapoport, V.L.; Sirotskiy, S.E. Seasonal Change in Hygienic Indicators of Fish Quality in the Amur River. Hyg. Sanit. 2005, 2, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, S.; Ni, Y.; Chen, J. Bioaccumulation of Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls by Loaches Living in Rice Paddy Fields of Northeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyzova, A.V. Impact of Transboundary Pollution of the Amur River on Aquatic Biological Resources. Izv. TINRO 2007, 148, 262–274. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Meng, Q.; Wang, S.; Jiang, T.; Bai, L.; Yang, Y. Analysis and Evaluation of Pollutant Residues in Freshwater Fish at Jiamusi Section of Songhua River. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1732, 012092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyarova, M.D. Current Levels of Organochlorine Pesticides in Aquatic Organisms of Peter the Great Bay (Sea of Japan) and Lake Khanka. Ph.D. Thesis, Far Eastern Federal University, Vladivostok, Russia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Grankin, D.M. Cadastre of Specially Protected Natural Territories of the Khabarovsk Territory. Part 1: State Natural Reserves and Sanctuaries; DNIILH: Khabarovsk, Russia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lukyanova, O.N.; Tsygankov, V.Y.; Boyarova, M.D. Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in the Bering Flounder (Hippoglossoides Robustus) from the Sea of Okhotsk. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donets, M.M.; Tsygankov, V.Y.; Boyarova, M.D.; Gumovskiy, A.N.; Kulshova, V.I.; Elkhoury, J.A.; Gumovskaya, Y.P.; Lyakh, V.A.; Khristoforova, N.K. Flounders as Indicators of Environmental Contamination by Persistent Organic Pollutants and Health Risk. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 164, 111977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donets, M.M.; Tsygankov, V.Y.; Gumovskiy, A.N.; Gumovskaya, Y.P.; Boyarova, M.D.; Busarova, O.Y.; Litvinenko, A.V.; Khristoforova, N.K. Organochlorine Pesticides (OCPs) and Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in Pacific Salmon from the Kamchatka Peninsula and Sakhalin Island, Northwest Pacific. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donets, M.M.; Tsygankov, V.Y.; Gumovskiy, A.N.; Gumovskaya, Y.P.; Boyarova, M.D.; Kulshova, V.I.; Busarova, O.Y.; Litvinenko, A.V.; Khristoforova, N.K.; Lyakh, V.A. Fish as a Risk Source for Human Health: OCPs and PCBs in Pacific Salmon. Food Control 2022, 134, 108696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsygankov, V.Y.; Donets, M.M.; Gumovskiy, A.N.; Khristoforova, N.K. Temporal Trends of Persistent Organic Pollutants Biotransport by Pacific Salmon in the Northwest Pacific (2008–2018). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Fu, Q.; Li, Y.-F.; Li, W.; Li, T.; Wang, M.; Xing, Z.; Zhang, L. Levels, Congener Profile and Inventory of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Sediment from the Songhua River in the Vicinity of Cement Plant, China: A Case Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 15952–15962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wang, H.; Lin, C.; Quan, X.; Guo, W.; Yang, Z. Distribution of Persistent Organochlorine Residues in Sediments from the Songhuajiang River, Northeast China. Environ. Technol. 2008, 29, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L. The Research of PCBs and PAHs in Sediments of Songhua River. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, S.; Fu, Q.; Guo, L.; Li, Y.-F.; Li, T.; Ma, W.; Wang, M.; Li, W. Spatial–Temporal Variation, Possible Source and Ecological Risk of PCBs in Sediments from Songhua River, China: Effects of PCB Elimination Policy and Reverse Management Framework. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.-F.; Zhao, C.-D.; Liu, Y.-H.; Peng, M.; Li, K.; Yang, K.; Liu, F. Distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyl in sediments from Songhua River Basin. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2012, 33, 3434–3442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Huo, S.; Yu, Z.; Xi, B.; Yeager, K.M.; He, Z.; Ma, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, F. National Investigation of Semi-Volatile Organic Compounds (PAHs, OCPs, and PCBs) in Lake Sediments of China: Occurrence, Spatial Variation and Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.-J.; Maruya, K.A.; Snyder, S.A.; Zeng, E.Y. China’s Water Pollution by Persistent Organic Pollutants. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Tan, R.; Li, B.; Song, Y.; Zeng, P.; Li, Z. Overview of POPs and Heavy Metals in Liao River Basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 5007–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabodonirina, S.; Net, S.; Ouddane, B.; Merhaby, D.; Dumoulin, D.; Popescu, T.; Ravelonandro, P. Distribution of Persistent Organic Pollutants (PAHs, Me-PAHs, PCBs) in Dissolved, Particulate and Sedimentary Phases in Freshwater Systems. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Fu, Q.; Li, T.; Ma, W.; Liu, D.; Wang, M. Sediment-Water Exchange, Spatial Variations, and Ecological Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Songhua River, China. Water 2016, 8, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, C.H.; Lopes dos Santos, R.A.; Kim, A.W.; Moss-Hayes, V.; Fordyce, F.M.; Bearcock, J.M. Persistent Organic Pollutants (PAH, PCB, TPH) in Freshwater, Urban Tributary and Estuarine Surface Sediments of the River Clyde, Scotland, UK. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 2018, 108, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Fu, H.; Skøtt, K.; Yang, M. Modeling the Spill in the Songhua River after the Explosion in the Petrochemical Plant in Jilin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2008, 15, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsygankov, V.Y.; Boyarova, M.D.; Kiku, P.F.; Yarygina, M.V. Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) in Human Blood in the South of the Russian Far East. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14379–14382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsygankov, V.Y.; Khristoforova, N.K.; Lukyanova, O.N.; Boyarova, M.D.; Kiku, P.F.; Yarygina, M.V. Selected Organochlorines in Human Blood and Urine in the South of the Russian Far East. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iatrou, E.I.; Tsygankov, V.; Seryodkin, I.; Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Vakonaki, E.; Barbounis, E.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Chaika, V.V.; Sergievich, A.A.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; et al. Monitoring of Environmental Persistent Organic Pollutants in Hair Samples Collected from Wild Terrestrial Mammals of Primorsky Krai, Russia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 7640–7650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liagusha, M.S.; Cherniaev, A.P. Chapter 5. Current levels of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in the abiotic components of the Northwest Pacific ecosystems. In Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the Far Eastern Region: Seas, Organisms, Human: Monograph; Tsygankov, V.Y., Ed.; Publishing House of the Far Eastern Federal University: Vladivostok, Russia, 2020; pp. 101–127. ISBN 978-5-7444-4891-2. [Google Scholar]
- Egidarev, E.G.; Mishina, N.V.; Bazarov, K.Y. Current land use in the Khanka Lake basin. In Proceedings of the Collection of Scientific Articles; FSBIS PGI FEB RAS: Vladivostok, Russia, 2019; pp. 197–203. [Google Scholar]

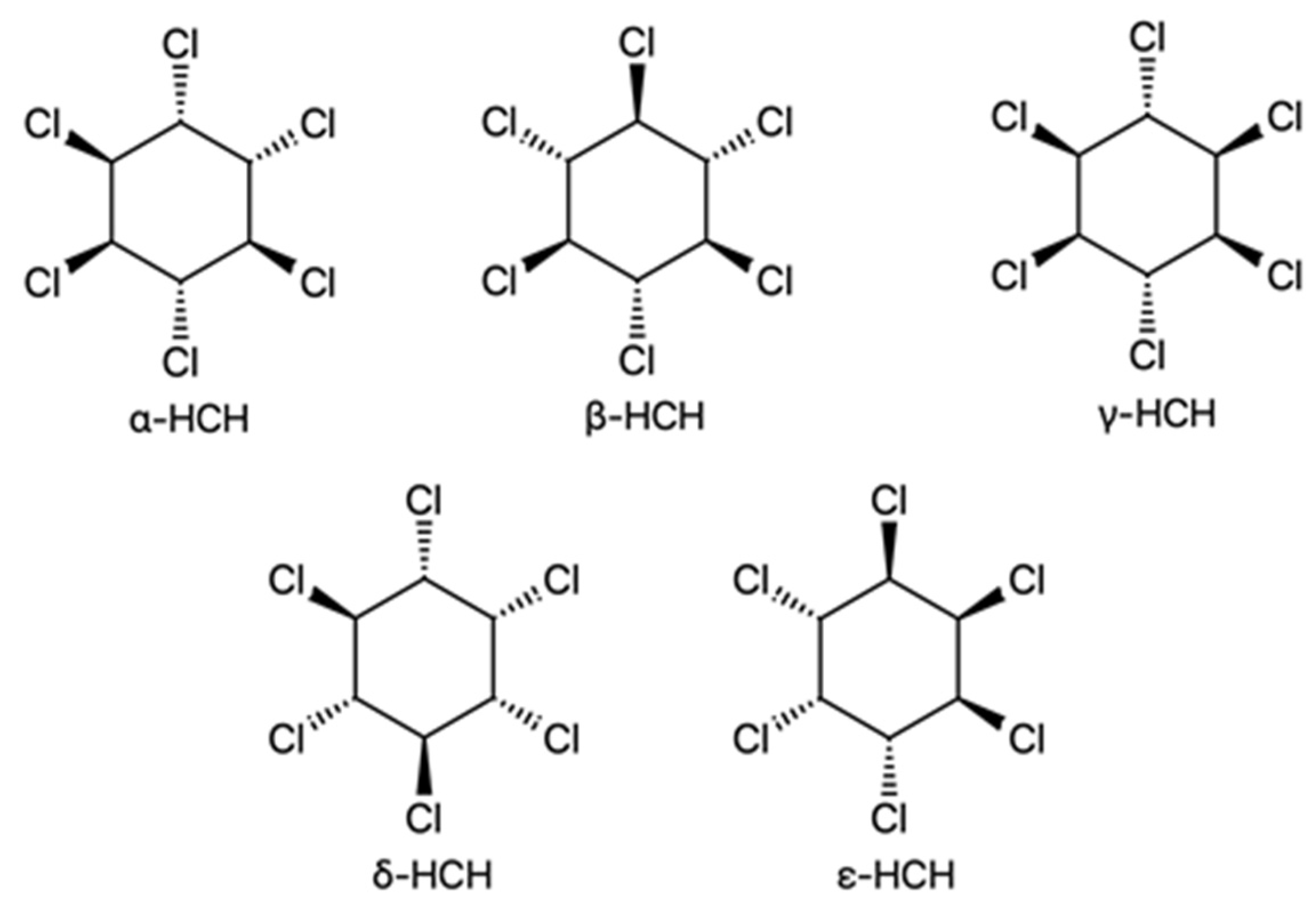
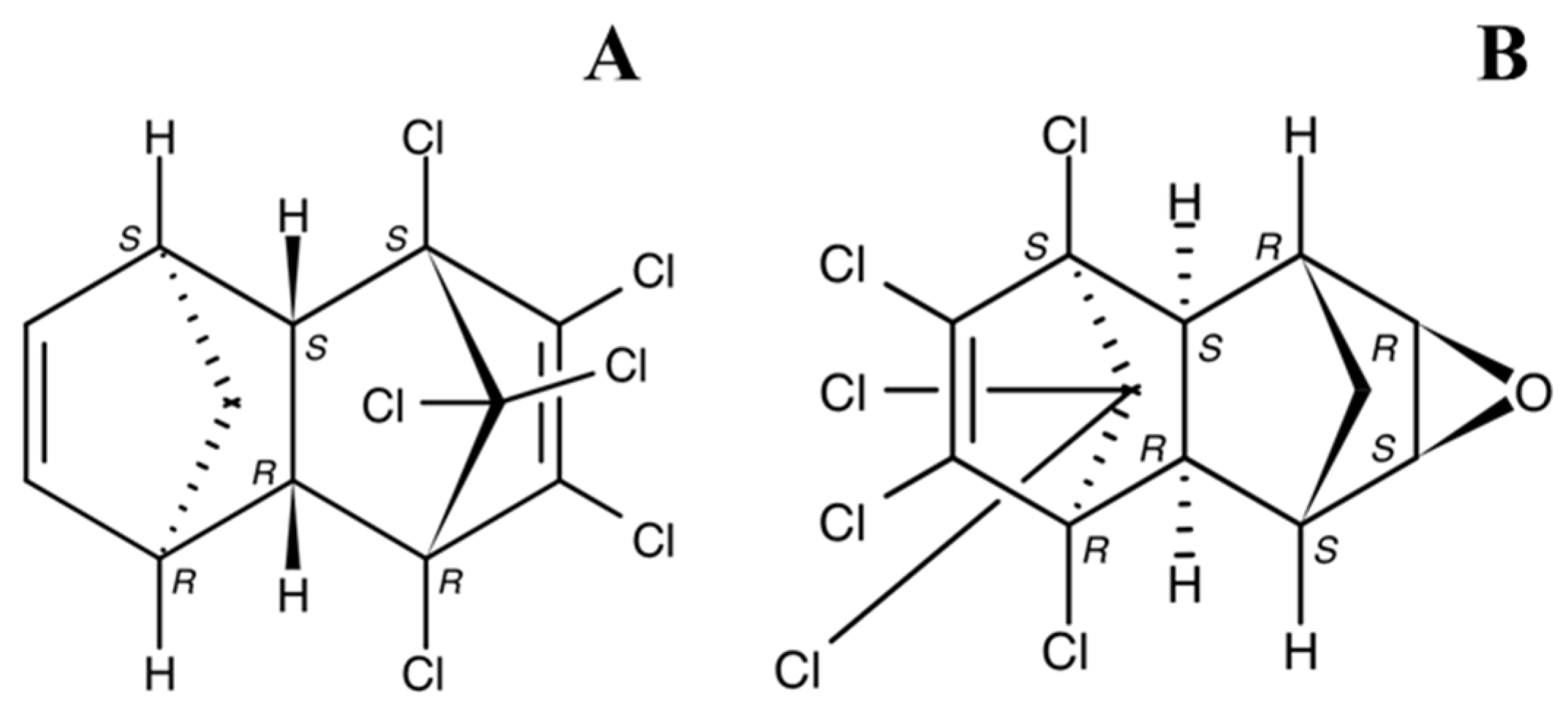
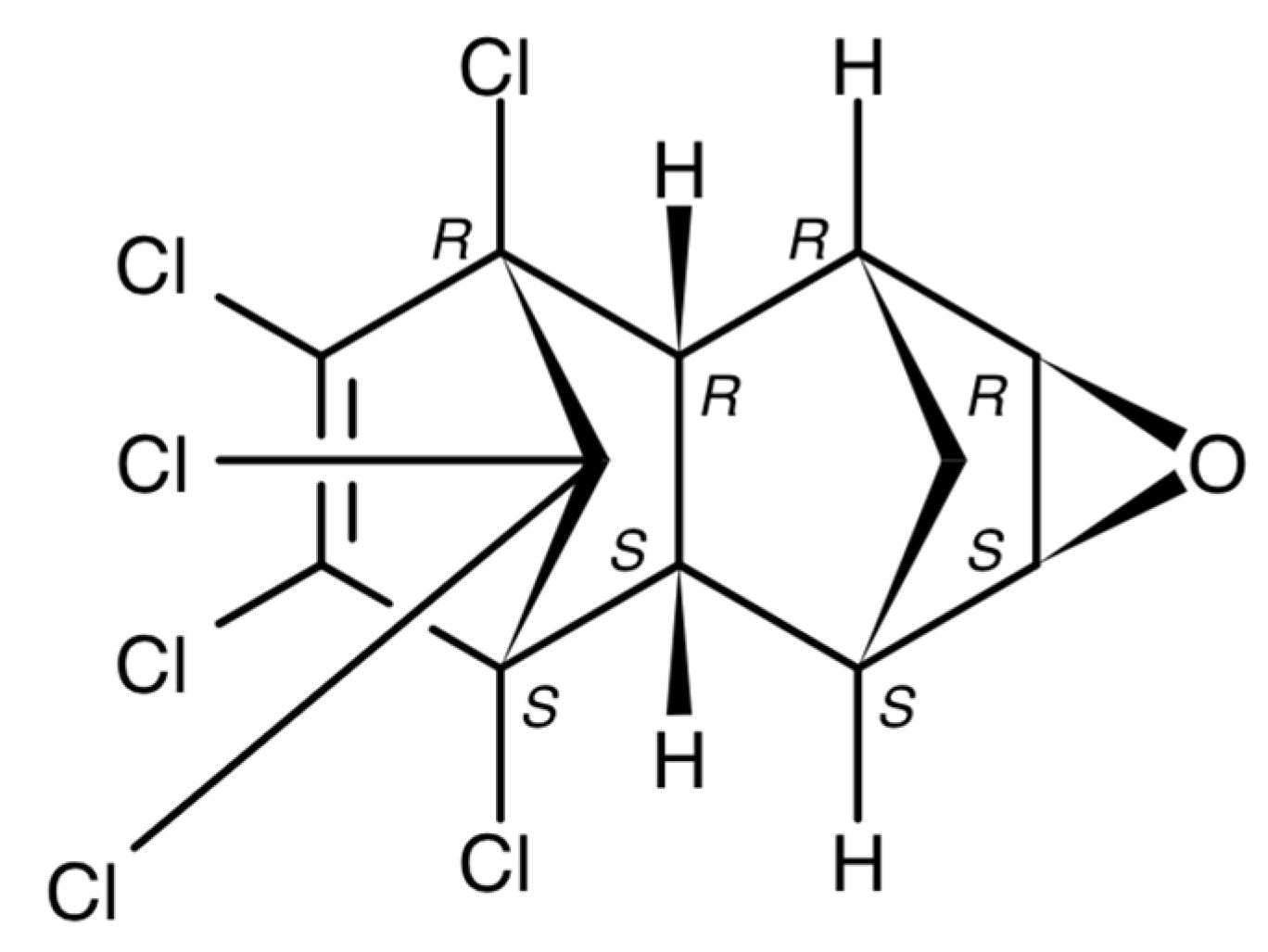
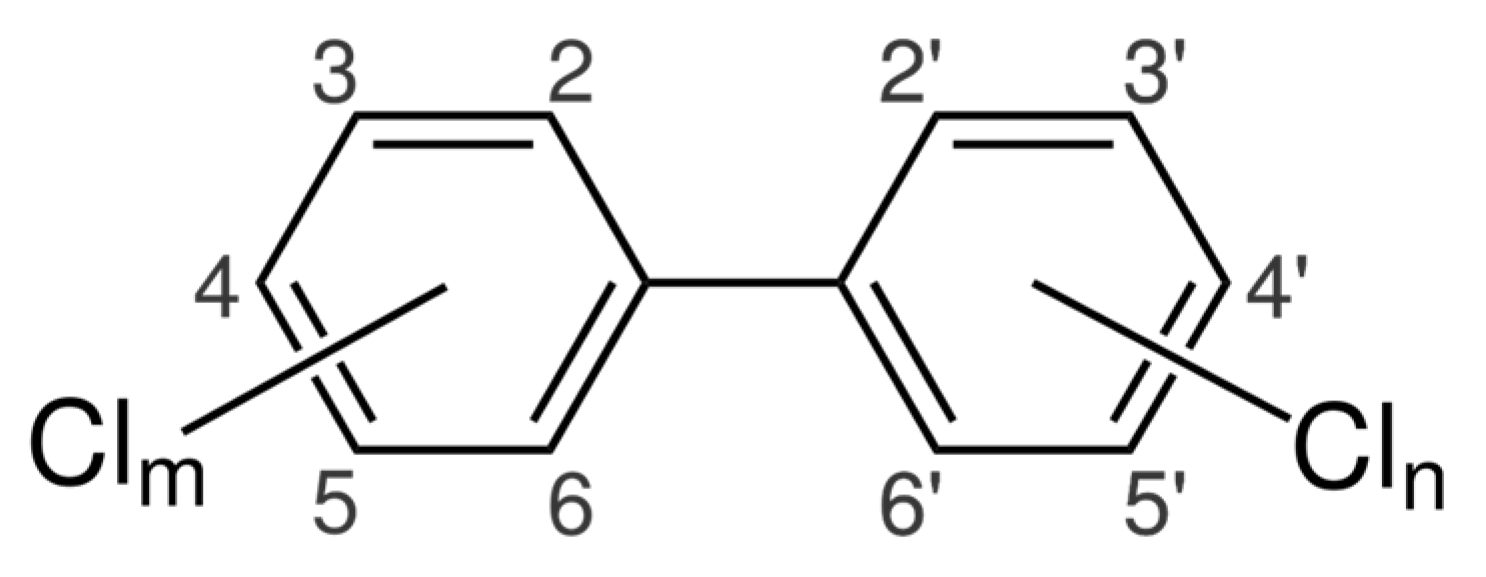
| River | Sampling Site | Year | Study Period | Concentration, ng/L | Method | Detection Limits | References | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΣDDT | ΣHCH | Aldrin | Dieldrin | Endrin | ΣPCB | |||||||
| Amur/Heilong River | Khabarovsk, Khabarovsk Krai | 2010 | Not specified | <10 1 | 2 2 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | NA 3 | NA | [63] |
| Amurzet village, Jewish Autonomous Oblast | 2011 | Not specified | – 4 | – | – | – | – | 63 5 | NA | NA | [65] | |
| Vladimirovka village, Khabarovsk Krai | 2019 | Summer | 20 | 13 | 40 | – | – | – | GC-ECD | NA | [66] | |
| Winter | 16 | 21 | <10 | – | – | – | ||||||
| 2020 | Summer | 777 | 161 | 82 | – | – | – | |||||
| Autumn | 279 | 24 | 28 | – | – | – | ||||||
| Winter | 73 | 18 | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| Ussuri/Wusuli River | Kazakevichevo village, Khabarovsk Krai | 2011 | Not specified | – | – | – | – | – | 90 5 | NA | NA | [65] |
| Bychikha village, Khabarovsk Krai | 2019 | Summer | 36 | 15 | 73 | – | – | – | GC-ECD | NA | [66] | |
| Winter | 23 | 48 | <10 | – | – | – | ||||||
| 2020 | Summer | 372 | 14 | 59 | – | – | – | |||||
| Autumn | 342 | 23 | 21 | – | – | – | ||||||
| Winter | 99 | 19 | <10 | – | – | – | ||||||
| Songhua River | Not specified | 2003–2004 | Not specified | <0.14 | 71 2 | – | – | – | – | GC-μECD | 0.11–0.17 ng/L | [67] |
| Mainstream of the Songhua River | 2007 | Spring | – | – | – | – | – | 10 | GC-MS | 0.003–0.032 ng/g | [68] | |
| Summer | – | – | – | – | – | 5.5 | ||||||
| 2008 | Winter | – | – | – | – | – | 4.4 | |||||
| Mainstream of the Songhua River (from the mouth of the Nenjiang River to Harbin) | 2012 | Summer | 32 | 28 | – | – | – | – | GC-ECD | NA | [69] | |
| Jilin, Harbin (not specified) | 2014–2015 | Rainy season (September, June, August) | <DL 6 | 2.2 2 | – | – | – | – | GC-MS/MS | 0.04–0.37 ng/L | [70] | |
| 2015–2016 | Dry season (March, October, April) | <DL 6 | 0.5 2 | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Harbin | 2015 | September–October | – | <DL 7 | – | – | – | – | GC-MS/MS | 0.1–0.15 ng/L | [71] | |
| Jilin | – | <DL 7 | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| River/Lake | Species | Organ | Year | Concentration, ng/g Wet Weight | Method | Detection Limits | References | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΣDDT | ΣHCH | Aldrin | Dieldrin | Endrin | ΣPCB | |||||||
| Amur/Heilong River | Sturgeon 1 | Not specified | 2000 | 20 | 10 | – 2 | – | – | – | NA 3 | NA | [72] |
| Redfin, catfish, barbel steed 4 | Muscle | 2002 | 0.062–0.075 5 | – | – | – | – | – | NA | NA | [73] | |
| Predatory carp, barbel steed | – | 0.023–0.025 5 | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| Ussuri/Wusuli River | Loach (Misgurnus mohoity) | Whole body | 2016 | 14.7 | 1.4 | 0.0002 | – | – | 0.44 | HRGC-HRMS | 0.000023–0.11223 ng/g dry weight (dw) | [74] |
| Lake Bolon 6 | Prussian carp (Carassius gibelio) | Muscle | 2006 | 0.0001 | – | – | – | – | – | NA | NA | [75] |
| Amur pike (Esox reichertii) | 0.0001 | – | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| Barbel steed (Hemibarbus labeo) | 0.0001 | – | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| Roach (Rutilus rutilus lacustris) | 0.0001 | – | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| Songhua River | Amur carp (Cyprinus rubrofuscus) | Muscle | 2012 | 3.3 7 | 2.7 | – | – | – | – | GC-ECD | NA | [69] |
| Loach (Misgurnus mohoity) | Whole body | 2016 | 4.2 | 1.5 | 0.0002 | – | – | 0.33 | HRGC-HRMS | 0.000023–0.11223 ng/g dw | [74] | |
| Large-scale (Paramisgurnus dabryanus) | 4.1 | 1.3 | 0.0002 | – | – | 0.29 | ||||||
| Amur carp (Cyprinus rubrofuscus) | Muscle | 2018 | 0.0001 | 0.11 | – | – | 0.079 | – | NA | NA | [76] | |
| 2019 | 0.06 | 0.10 | – | – | 0.034 | – | ||||||
| 2020 | 0.13 | 0.11 | – | – | 0.049 | – | ||||||
| Lake Khanka/Xingkai | Mussel (Cristaria herculea) | Soft tissues | 2004 | 27 | 13 | – | – | – | – | GC-ECD | NA | [77] |
| Yellohead catfish (Pseudobagrus fulvidraco) | Liver | 293 | 360 | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Predatory carp (Chanodichthys erythropterus) | Liver | 216 | 130 | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Amur pike (Esox reichertii) | Liver | 173 | 722 | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Spotted steed (Hemibarbus maculatus) | Liver | 99 | 32 | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Phytoplankton | – | 51 8 | 281 9 | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Zooplankton | 30 8 | 12 9 | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| River/Lake | Sampling Site | Year | Study Period | Concentration, ng/g Dry Weight | Method | Detection Limits | References | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΣDDT | ΣHCH | Aldrin | Dieldrin | Endrin | ΣPCB | |||||||
| Songhua River | Second Songhua River (Jilin) | 2005 | Summer | 2.1 | 6.2 | 0.26 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 7.5 | GC-ECD GC-MS | 0.01–0.8 ng/g | [85] |
| Not specified | – 1 | – | – | – | – | 3.2–85.9 2 | NA 3 | NA | [86,87] | |||
| Mainstream of the Songhua River (Harbin) | 2005 | Summer | 1.1 | 4.9 | 0.10 | 0.57 | 0.48 | 3.1 | GC-ECD GC-MS | 0.01–0.8 ng/g | [85] | |
| 2006 | Not specified | – | – | – | – | – | 0.40–16.70 2 | NA | NA | [86,87] | ||
| 2008 | Not specified | – | – | – | – | – | 1.7–6.3 2 | NA | NA | [87,88] | ||
| Mainstream of the Songhua River (from the mouth of the Nenjiang River to Harbin) | 2007 | Spring | – | – | – | – | – | 6.1 | GC-MS | 0.003–0.032 ng/g dw | [68] | |
| Summer | – | – | – | – | – | 5.03 | ||||||
| 2012 | Summer | 2.38 | 2.04 | – | – | – | – | GC-ECD | NA | [69] | ||
| Harbin | 2014 | Summer | – | – | – | – | – | 1.6 | GC-NICIMS | 0.003–0.032 ng/g dw | [84] | |
| Harbin | Summer | – | – | – | – | – | 2.3 | GC-NICIMS | 0.003–0.032 ng/g dw | [87] | ||
| Zhaoyuan | – | – | – | – | – | 3.4 | ||||||
| Fuyu | – | – | – | – | – | 12.4 | ||||||
| Jilin | – | – | – | – | – | 3.7 | ||||||
| Lake Khanka/Xingkai | Not specified | 2011–2013 | Not specified | 0.8 | <DL 4 | 0.3 4 | 0.18 | GC-MS triple quad | 0.003–0.041 ng/g C13 isotope standard used | [89] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Donets, M.M.; Tsygankov, V.Y. Organochlorine Compounds in the Amur (Heilong) River Basin (2000–2020): A Review. J. Xenobiot. 2023, 13, 439-462. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox13030028
Donets MM, Tsygankov VY. Organochlorine Compounds in the Amur (Heilong) River Basin (2000–2020): A Review. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2023; 13(3):439-462. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox13030028
Chicago/Turabian StyleDonets, Maksim M., and Vasiliy Yu. Tsygankov. 2023. "Organochlorine Compounds in the Amur (Heilong) River Basin (2000–2020): A Review" Journal of Xenobiotics 13, no. 3: 439-462. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox13030028
APA StyleDonets, M. M., & Tsygankov, V. Y. (2023). Organochlorine Compounds in the Amur (Heilong) River Basin (2000–2020): A Review. Journal of Xenobiotics, 13(3), 439-462. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox13030028







