Incubation Time Influences Organic Anion Transporter 1 Kinetics and Renal Clearance Predictions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Transport Experiments
2.4. PBPK-MechKiM Model Development for PAH
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
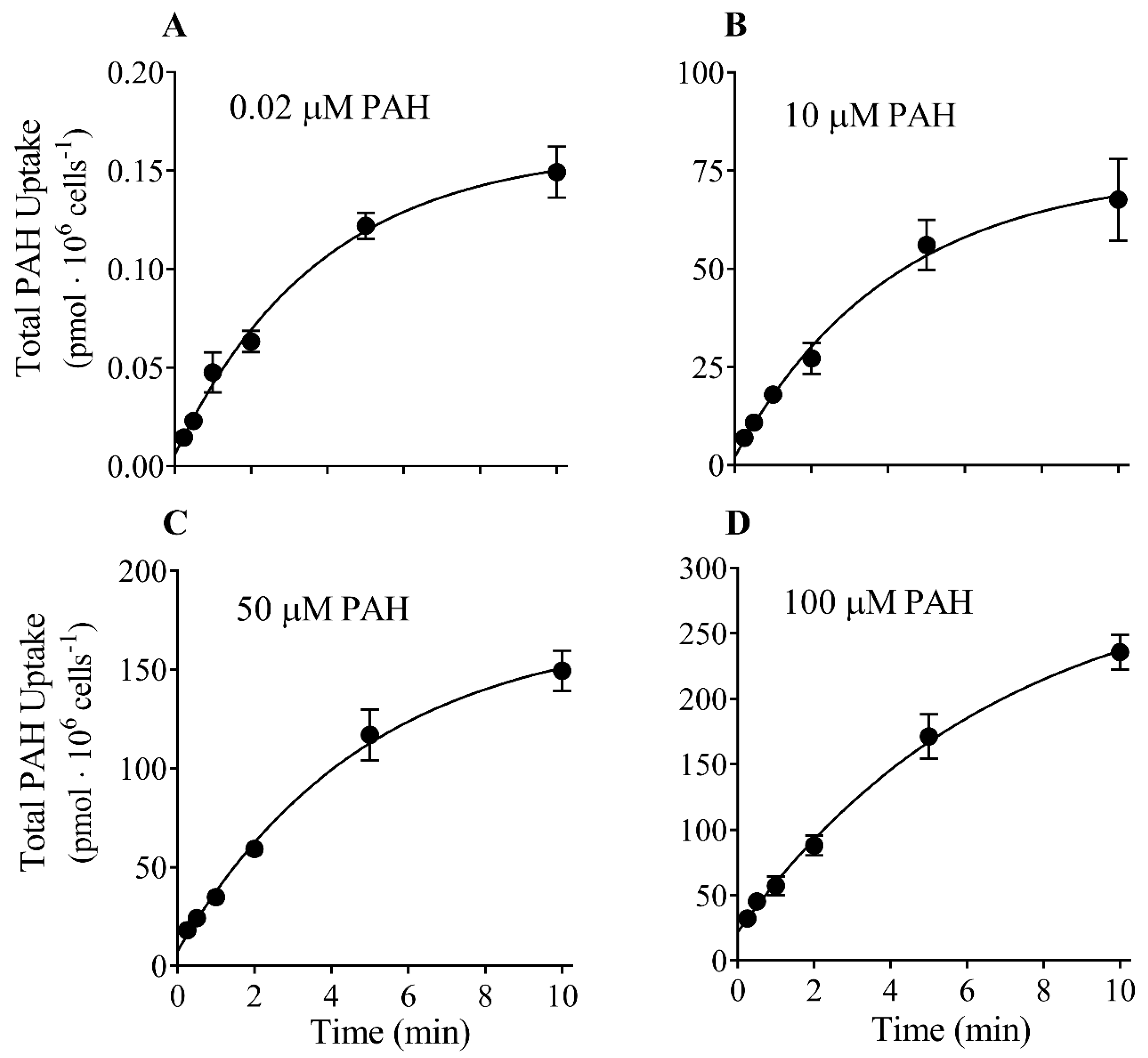
3.1. Time Course of PAH Uptake into CHO-OAT1 Cells
3.2. Effect of Time on Transport Kinetics
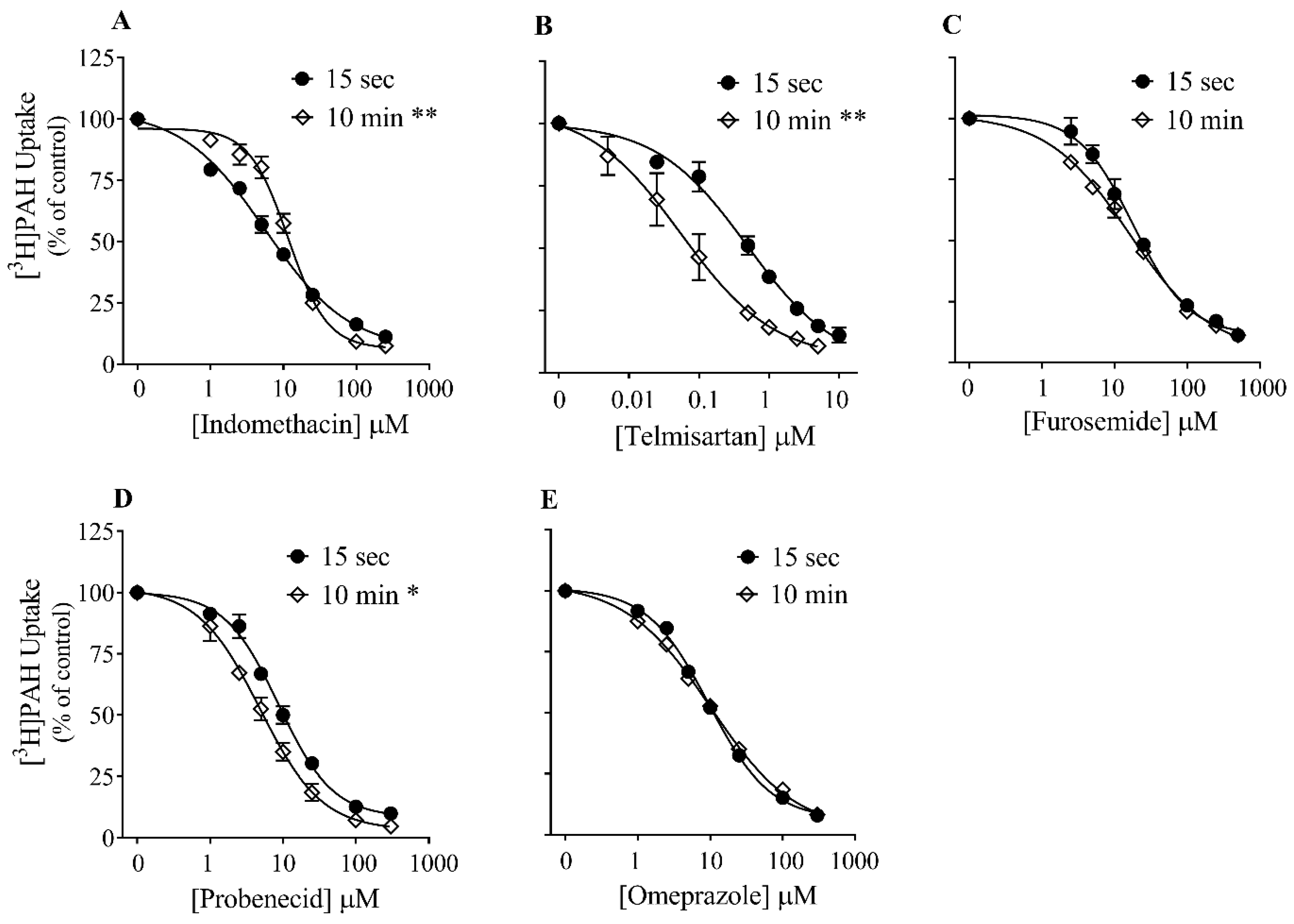
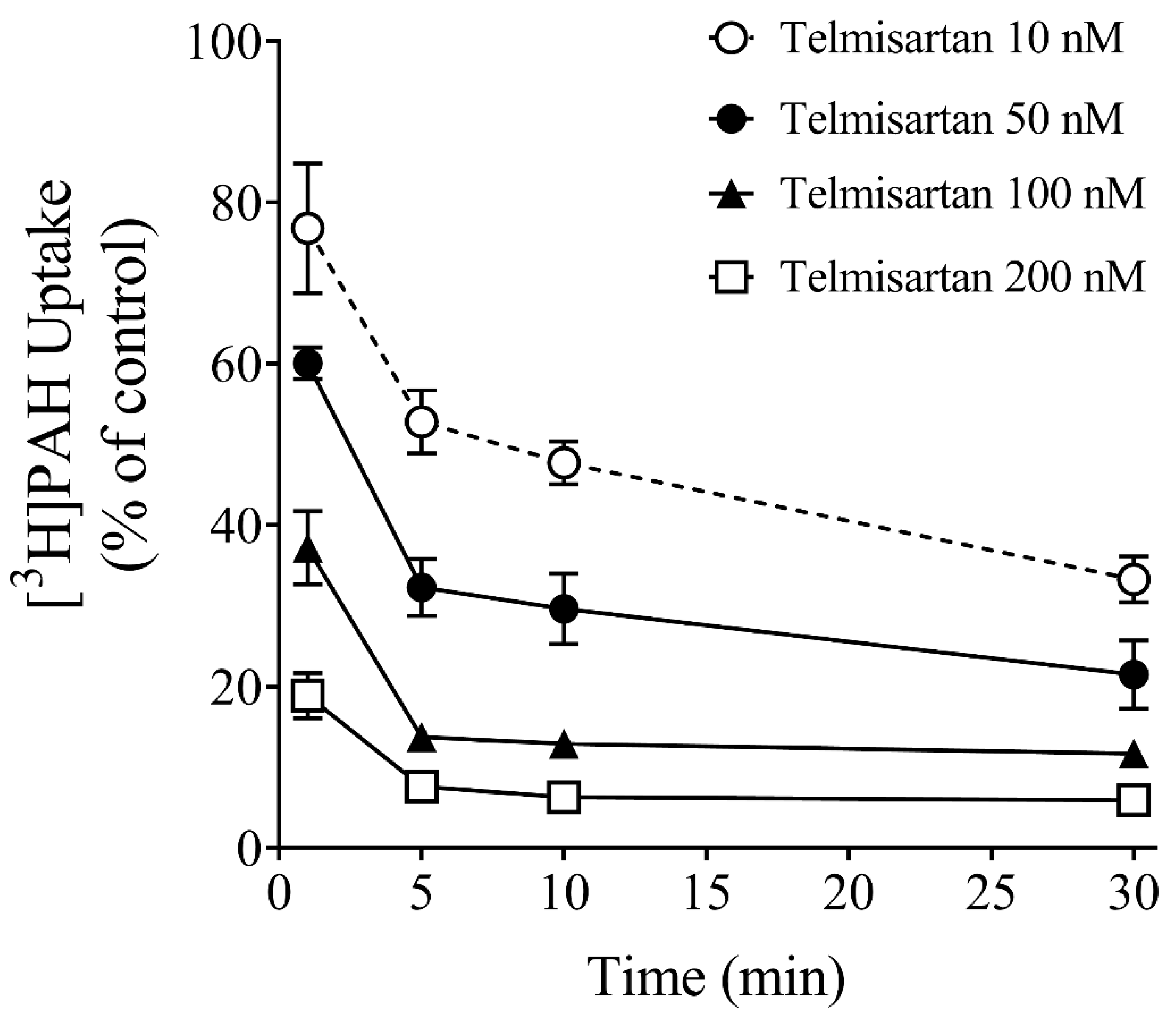
3.3. Effect of Time on Inhibition Potency
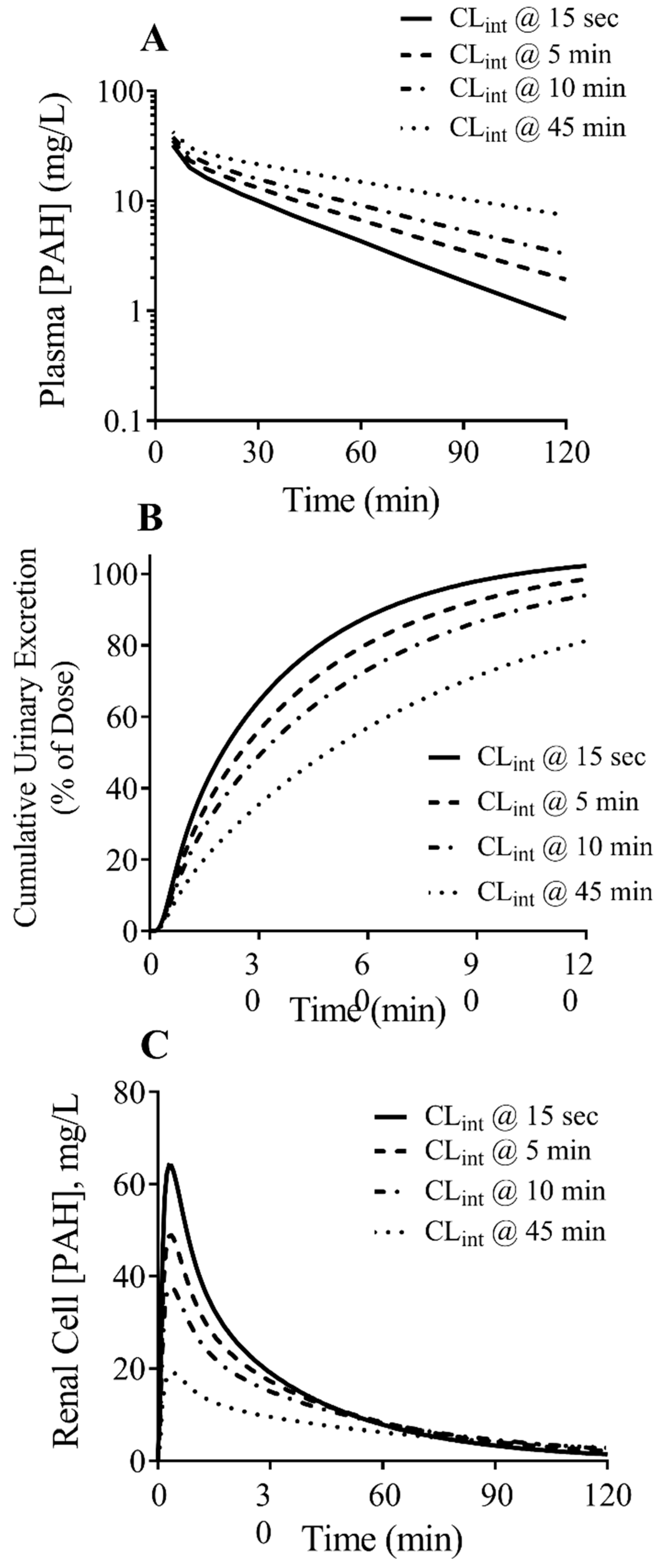
3.4. PBPK Model Predictions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pelis, R.M.; Wright, S.H. Renal transport of organic anions and cations. Compr. Physiol. 2011, 1, 1795–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrissey, K.M.; Stocker, S.L.; Wittwer, M.B.; Xu, L.; Giacomini, K.M. Renal transporters in drug development. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 503–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, B.; You, D.; Joy, M.S.; Aleksunes, L.M. Xenobiotic transporters and kidney injury. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 116, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on the Investigation of Drug Interactions; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- United States Food and Drug Administration. In Vitro Drug Interaction Studies—Cytochrome P450 Enzyme- and Transporter-Mediated Drug Interactions Guidance for Industry; United States Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Sweet, D.H. Renal organic anion transporters (SLC22 family): Expression, regulation, roles in toxicity, and impact on injury and disease. AAPS J. 2013, 15, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.; Shi, B.; Zeng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, B.; Ouyang, B.; Cai, Z.; Liu, M. Drug transporters in the kidney: Perspectives on species differences, disease status, and molecular docking. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 746208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, K.L.R.; Keppler, D.; Hoffmaster, K.A.; Bow, D.A.J.; Cheng, Y.; Lai, Y.; Palm, J.E.; Stieger, B.; Evers, R. In vitro methods to support transporter evaluation in drug discovery and development. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 94, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, K.M.; Huang, S.M.; Tweedie, D.J.; Benet, L.Z.; Brouwer, K.L.R.; Chu, X.; Dahlin, A.; Evers, R.; Fischer, V. Membrane transporters in drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamek-Gliszczynski, M.J.; Lee, C.A.; Poirier, A.; Bentz, J.; Chu, X.; Ellens, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Jamei, M.; Kalvass, J.C.; Nagar, S.; et al. ITC recommendations for transporter kinetic parameter estimation and translational modeling of transport-mediated PK and DDIs in humans. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 94, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingraham, L.; Li, M.; Renfro, J.L.; Parker, S.; Vapurcuyan, A.; Hanna, I.; Pelis, R.M. A plasma concentration of α-ketoglutarate influences the kinetic interaction of ligands with organic anion transporter 1. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 86, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata-Dulas, C.A.; Awni, W.M.; Matzke, G.R.; Halstenson, C.E.; Guay, D.R. Evaluation of two intravenous single-bolus methods for measuring effective renal plasma flow. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1994, 23, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, L.F.; Freestone, S.; McAuslane, J.A. The concentration-dependent disposition of intravenous p-aminohippurate in subjects with normal and impaired renal function. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1993, 35, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meisel, A.D.; Diamond, H.S. Inhibition of probenecid uricosuria by pyrazinamide and para-aminohippurate. Am. J. Physiol. 1977, 232, F222–F226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhoff, S.G.L.; Burt, H.; Jamei, M.; Li, L.; Tucker, G.T.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. Accounting for transporters in renal clearance: Towards a mechanistic kidney model (MechKiM). In Transporters in Drug Development; Sugiyama, Y., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 155–177. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, W.D. Transport and Diffusion Across Cell Membranes; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chu, X.; Parrott, N.J.; Brouwer, K.L.; Hsu, V.; Nagar, S.; Matsson, P.; Sharma, P.; Snoeys, J.; Sugiyama, Y.; et al. Advancing predictions of tissue and intracellular drug concentrations using in vitro, imaging and physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling approaches. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 104, 865–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.; Chen, Y.; Gibson, C.; Heimbach, T.; Parrott, N.; Peters, S.; Snoeys, J.; Upreti, V.; Zheng, M.; Hall, S. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling in drug discovery and development: A pharmaceutical industry perspective. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 97, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Hsu, V.; Grimstein, M.; Zhang, L.; Arya, V.; Sinha, V.; Grillo, J.A.; Zhao, P. The application of physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling to predict the role of drug transporters: Scientific and regulatory perspectives. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 56 (Suppl. S7), S122–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotcher, D.; Jones, C.; Posada, M.; Galetin, A.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. Key to opening kidney for in vitro-in vivo extrapolation entrance in health and disease: Part II: Mechanistic models and in vitro-in vivo extrapolation. AAPS J. 2016, 18, 1082–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, A.G.; Gao, T.; Khan, U.; Berrigan, L.; Li, M.; Ingraham, L.; Pelis, R.M. Organic anion transporter 1 is inhibited by multiple mechanisms and shows a transport mode independent of exchange. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundsen, R.; Christensen, H.; Zabihyan, B.; Åsberg, A. Cyclosporine A, but not tacrolimus, shows relevant inhibition of organic anion-transporting protein 1B1-mediated transport of atorvastatin. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, M.; Cartwright, C.M.; Hobbs, M.J.; Kenworthy, K.E.; Rowland, M.; Houston, J.B.; Galetin, A. Cyclosporine inhibition of hepatic and intestinal CYP3A4, uptake and efflux transporters: Application of PBPK modeling in the assessment of drug-drug interaction potential. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 761–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallinas, G. Understanding transporter specificity and the discrete appearance of channel-like gating domains in transporters. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaler, G.; Truong, D.; Khandelwal, A.; Nagle, M.; Eraly, S.A.; Swaan, P.; Nigam, S.K. Structural variation governs substrate specificity for organic anion transporter (OAT) homologs. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23841–23853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajapati, R.; Sangamwar, A.T. Translocation mechanism of P-glycoprotein and conformational changes occurring at drug-binding site: Insights from multi-targeted molecular dynamics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 2882–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonge, P.J. Drug–target kinetics in drug discovery. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, H.W.; Finkelstein, N.; Aliminosa, L.; Crawford, B.; Graber, M. The renal clearances of substituted hippuric acid derivatives and other aromatic acids in dog and man 1. J. Clin. Investig. 1945, 24, 388–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, T.; Rowland, M. Mechanistic approaches to volume of distribution predictions: Understanding the processes. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 918–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, T.; Frye, R.; Fraley, D.S.; Matzke, G.R. Characterization of tubular functional capacity in humans using para-aminohippurate and famotidine. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, H.; Kusuhara, H.; Chida, M.; Fuse, E.; Sugiyama, Y. Is the monkey an appropriate animal model to examine drug-drug interactions involving renal clearance? Effect of probenecid on the renal elimination of H2 receptor antagonists. Experiment 2005, 316, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, P.H.; van Aubel, R.A.A.A.; Wouterse, A.C.; Heuvel, J.J.V.D.; Russel, F.G. Contribution of multidrug resistance protein 2 (MRP2/ABCC2) to the renal excretion of p-aminohippurate (PAH) and identification of mrp4 (ABCC4) as a novel pah transporter. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2828–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathialagan, S.; Piotrowski, M.A.; Tess, D.A.; Feng, B.; Litchfield, J.; Varma, M.V. Quantitative prediction of human renal clearance and drug-drug interactions of organic anion transporter substrates using in vitro transport data: A relative activity factor approach. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2017, 45, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatsudthipong, V.; Dantzler, W.H. PAH-alpha-KG countertransport stimulates PAH uptake and net secretion in isolated snake renal tubules. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 261 Pt 2, F858–F867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatsudthipong, V.; Dantzler, W.H. PAH/alpha-KG countertransport stimulates PAH uptake and net secretion in isolated rabbit renal tubules. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 263 Pt 2, F384–F391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Maeda, K.; Kondo, T.; Nakayama, H.; Horita, S.; Kusuhara, H.; Sugiyama, Y. Prediction of the hepatic and renal clearance of transporter substrates in rats using in vitro uptake experiments. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buaben, A.O.; Pelis, R.M. Incubation Time Influences Organic Anion Transporter 1 Kinetics and Renal Clearance Predictions. J. Xenobiot. 2023, 13, 205-217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox13020016
Buaben AO, Pelis RM. Incubation Time Influences Organic Anion Transporter 1 Kinetics and Renal Clearance Predictions. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2023; 13(2):205-217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox13020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuaben, Aaron O., and Ryan M. Pelis. 2023. "Incubation Time Influences Organic Anion Transporter 1 Kinetics and Renal Clearance Predictions" Journal of Xenobiotics 13, no. 2: 205-217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox13020016
APA StyleBuaben, A. O., & Pelis, R. M. (2023). Incubation Time Influences Organic Anion Transporter 1 Kinetics and Renal Clearance Predictions. Journal of Xenobiotics, 13(2), 205-217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox13020016




