Abstract
Since 1974, more than 800 disinfection byproducts (DBPs) have been identified from disinfected drinking water, swimming pool water, wastewaters, etc. Some DBPs are recognized as contaminants of high environmental concern because they may induce many detrimental health (e.g., cancer, cytotoxicity, and genotoxicity) and/or ecological (e.g., acute toxicity and development toxicity on alga, crustacean, and fish) effects. However, the information on whether DBPs may elicit potential endocrine-disrupting effects in human and wildlife is scarce. It is the major objective of this paper to summarize the reported potential endocrine-disrupting effects of the identified DBPs in the view of adverse outcome pathways (AOPs). In this regard, we introduce the potential molecular initiating events (MIEs), key events (KEs), and adverse outcomes (AOs) associated with exposure to specific DBPs. The present evidence indicates that the endocrine system of organism can be perturbed by certain DBPs through some MIEs, including hormone receptor-mediated mechanisms and non-receptor-mediated mechanisms (e.g., hormone transport protein). Lastly, the gaps in our knowledge of the endocrine-disrupting effects of DBPs are highlighted, and critical directions for future studies are proposed.
1. Introduction
Disinfection processes, used for the public water system and aimed at inactivating viable pathogenic microorganisms and protecting against the occurrence of water-borne diseases, were considered as a significant public health triumph in the beginning of the 20th century [1,2,3]. However, it has been well demonstrated that several disinfection byproducts (DBPs) are unavoidably formed from the reaction between disinfectants and naturally organic matter, organic contaminants, or halides during water purification treatment [4,5]. Since the first group of DBPs, i.e., trihalomethanes (THMs), was found in 1974 [6], more than 800 DBPs belonging to various classes have been gradually determined both in real disinfection plants and in controlled laboratory tests [7,8]. With the development of analytical methods, it is conceivable that more DBPs will be continuously identified [9,10,11,12]. For example, Zhang, et al. [13] recently analyzed the DBPs in ozonated wastewater, and they identified eight new Br-DBPs, including 2-bromostyrene, 2-bromo-benzaldehyde, and 2-bromophenylacetonitrile. What are the potential harmful effects of the exposure of DBPs on human and wildlife?
It was reported that DBPs could enter organisms through a variety of exposure routes [10,14]. Individuals could intake DBPs not only through drinking water, but also via skin penetration and inhalation pathways when showering or swimming. DBPs have been detected in human biological matrices such as blood, urine, and alveolar air samples [15,16,17]. DBP exposure might adversely lead to health risks, including neurotoxicity, mutagenicity, teratogenicity, genotoxicity, developmental and reproductive issues, cytotoxicity, and carcinogenesis [4,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. For instance, there is convincing evidence that exposure to THMs and haloacetic acids (HAAs) is associated with a high risk of bladder and colorectal cancer [4,27,28]. Recently, the results from epidemiological studies also implied that nitrogenous byproducts (haloamides, amines, halonitriles, and nitrosamines) may trigger bladder cancer [29]. To circumvent this health problem, the concentrations of a small fraction of DBPs, mainly THMs and HAAs in drinking water, are regulated by World Health Organization (WHO), United States Environmental Protection Agency, European Union, etc. [30,31,32]. However, recent studies revealed that commonly regulated DBPs cannot be the major contributor to the adverse health effects induced by consuming chlorinated drinking water [33,34]. Compared with regulated DBPs, some emerging DBPs, such as halobenzoquinones, iodinated DBPs, nitrogenous DBPs, and aromatic DBPs, are more worthy of attention [35,36].
Recently, concern has grown regarding the potential acute toxicity of certain wastewater-derived DBPs toward aquatic organisms. This concern is based upon the belief that the aquatic organisms may be exposed to increasing types of wastewater-derived DBPs because those compounds may enter the aquatic environment with the discharge of disinfected wastewater. To date, the potential acute toxicity of certain DBPs on typical aquatic organisms, such as alga, crustacean, and fish, has been reported [8,14,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47]. For instance, we investigated the acute toxicity of seven wastewater-derived phenolic DBPs that belong to the typical five groups of phenolic DBPs (i.e., 2,4,6-trihalo-phenols, 3,5-dihalo-4-hydroxybenzaldehydes, 2,6-dihalo-4-nitrophenols, halo-salicylic acids, and 3,5-dihalo-4-hydroxybenzoic acids) toward Gobiocypris rarus and found that the half lethal concentration (LC50) values of 2,4,6-trihalo-phenols and 2,6-dihalo-4-nitrophenols was in the 1–10 mg/L range, indicating that their acute toxicity should not be neglected [48]. In addition to the aforementioned health and ecological effects, can DBPs elicit other potential adverse effects, such as endocrine-disrupting effects?
The endocrine hormones of organisms such as thyroid hormones (THs), estrogen, and androgen regulate many critical physiological processes, e.g., growth and metamorphosis [49,50,51]. However, it is well known that a number of anthropogenic substances named endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) can elicit potential endocrine-disrupting effects on human and wildlife [52,53,54]. In this regard, EDCs are recognized as a serious threat to human health and the environment. In order to minimize the adverse health and environment impacts of EDCs, it is urgent to identify and screen potential EDCs from artificial chemical substances and unintentional production chemicals (e.g., DBPs) [55]. Actually, despite more than 800 individual DBPs having been identified in previous studies, only a few have been assessed for their potential endocrine-disrupting potency. Recently, Gonsioroski et al. reviewed the adverse reproductive effects in nonhuman animals and humans for some groups of EDCs in water such as DBPs, fluorinated compounds, bisphenol A, phthalates, pesticides, and estrogens [26]. However, it deserves mention that no comprehensive information related to the potential endocrine-disrupting effects of DBPs in the view of adverse outcome pathways (AOPs) is available up to now. Thus, it is significant to clarify which types of DBPs can exhibit endocrine-related detrimental effects, and which endocrine-related targets can be disturbed by DBPs.
Here, we attempted to present a significant overview of the potential endocrine-disrupting effects of DBPs in the view of AOPs on the basis of data derived from the published literature. The aim of this work was to (1) provide an updated, systematic and comprehensive review on the aspects of molecular initiating events (MIEs) disturbed by DBPs, (2) review the underlying toxicological key events (KEs) of DBPs, and (3) present adverse outcomes (AOs) of DBPs in mammals and aquatic vertebrates.
2. Performance of Publications
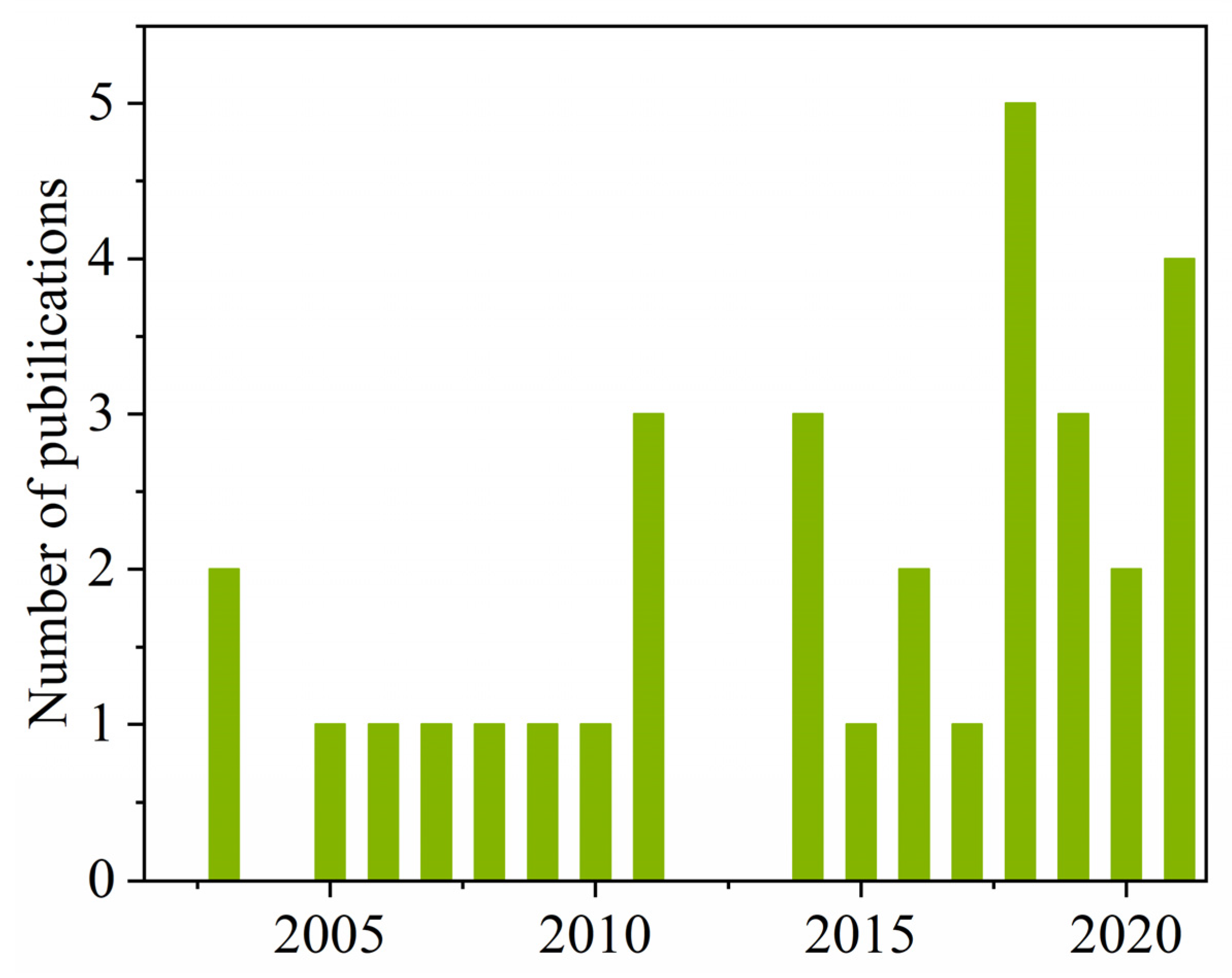
The endocrine-disrupting data of disinfection byproducts referred to in this study were obtained from published papers identified in the database of Web of Science (www.isiwebofknowledge.com, accessed on 7 January 2022) within the years 2000 to 2022. The search terms were “disinfection byproducts” and “endocrine”. The available literature was further refined by considering whether MIEs were defined or not. Finally, 32 studies related to the endocrine system-disrupting effects of DBPs were selected in the present investigation [28,49,50,51,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83]. As expected, most of the research on the endocrine-related detrimental effects of various DBPs were published in the last ten years even though the first publication dated back to 2003 (only seven publications from 2000 to 2009 and 25 from 2010 until now) (Figure 1). This means that the endocrine-perturbing effects of DBPs have gradually attracted people’s attention. In total, 131 DBPs and 14 endocrine-related targets were summarized from these studies. Detailed information of the studies, DBPs, and endocrine-related targets is listed in Supplementary Table S1.
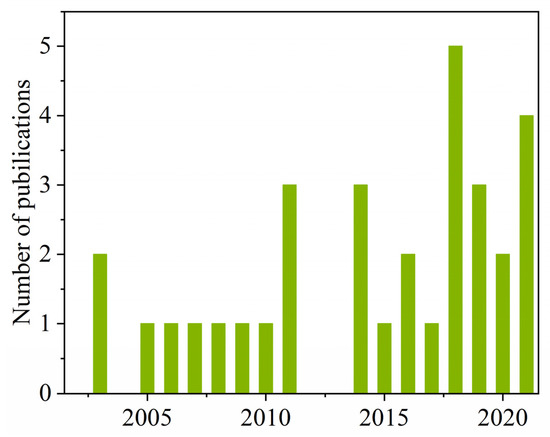
Figure 1.
The number of publications on endocrine-disrupting DBPs from 2000 to 2022.
3. Characterization of DBPs with Endocrine-Disrupting Data
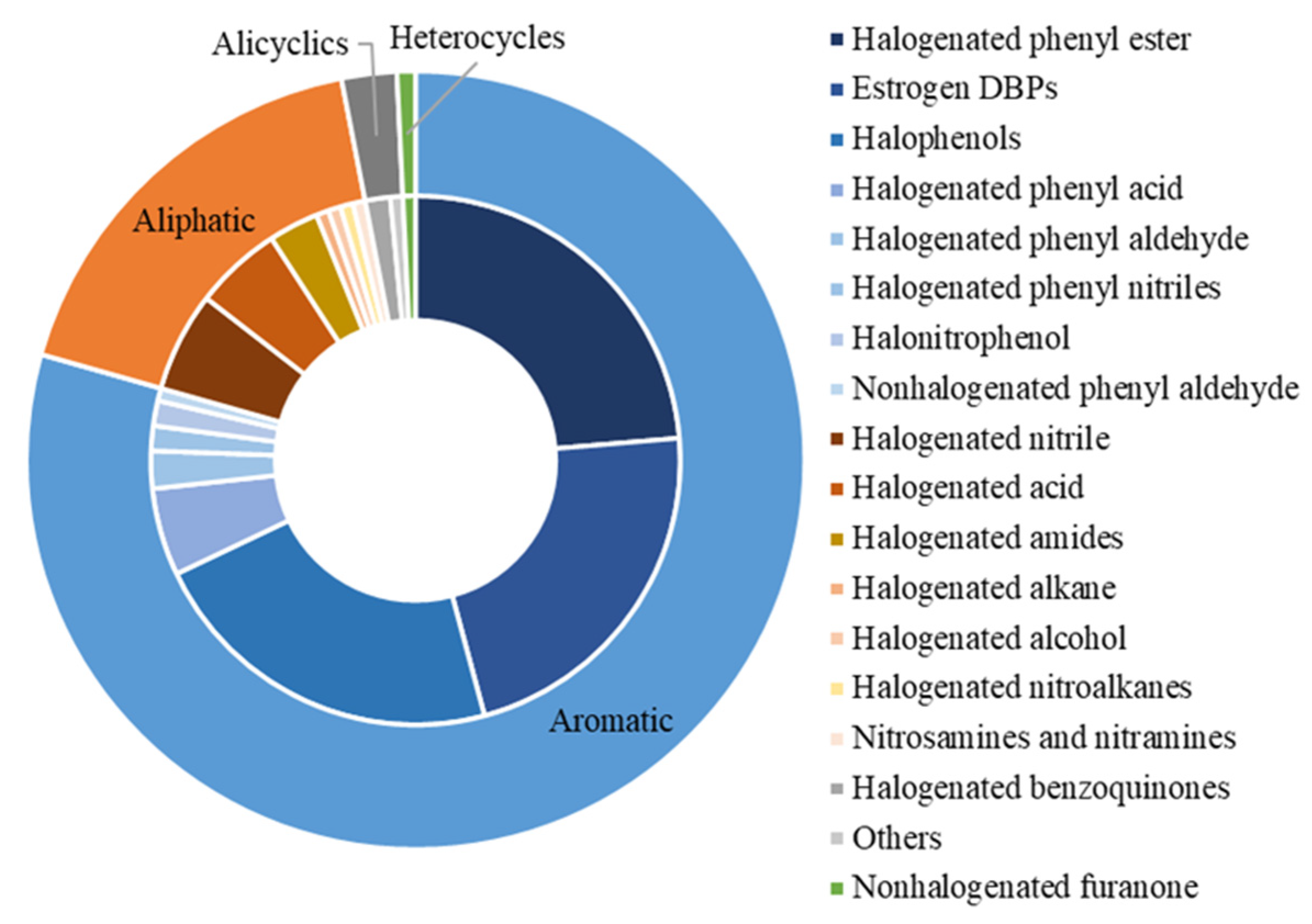
As shown in Figure 2, these 131 DBPs could be divided into four classes (i.e., aromatic, aliphatic, alicyclic, and heterocyclic DBPs) on the basis of their chemical structure. Aromatic DBPs could be further classified into eight subgroups (i.e., halogenated phenyl esters, estrogen DBPs, halophenols, halogenated phenyl acids, halogenated phenyl aldehydes, halogenated phenyl nitriles, halonitrophenols, and nonhalogenated phenyl aldehydes). Aliphatic DBPs included seven subgroups (i.e., halogenated nitriles, halogenated acids, halogenated amides, halogenated alkanes, halogenated alcohols, nitrosamines and nitramines, and halogenated nitroalkanes). Alicyclic DBPs contained two subgroups (halogenated benzoquinones and others). Heterocyclic DBPs were represented by nonhalogenated furanone.
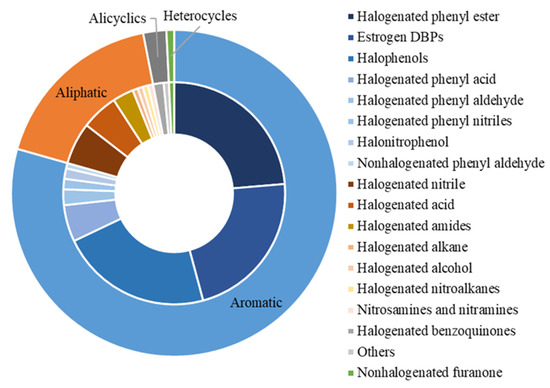
Figure 2.
Summary of DBPs identified with endocrine-disrupting potential.
The studied endocrine endpoints, as well as the corresponding DBP subgroups, are listed in Table 1. As shown, several DBPs in each studied subgroup except for halogenated phenyl esters and estrogen DBPs were investigated for their potential endocrine-disrupting effects. For halogenated phenyl esters and estrogen DBPs, however, more than 20 substances for each subgroup were tested for their potential activating/inhibiting potency toward human estrogen receptor α (hERα) and human aryl hydrocarbon receptor (hAhR). In addition, special attention was given to whether halophenols may pose a hazard to the endocrine system of organisms. For example, 12 out of 14 studied endocrine endpoints were tested using halophenols as model compounds. We also found that at least four subgroups of DBPs were evaluated for their potential interactions with hERα, human androgen receptor (hAR), and human transthyretin (hTTR).

Table 1.
Summary of all groups of DBPs focusing on endocrine activity.
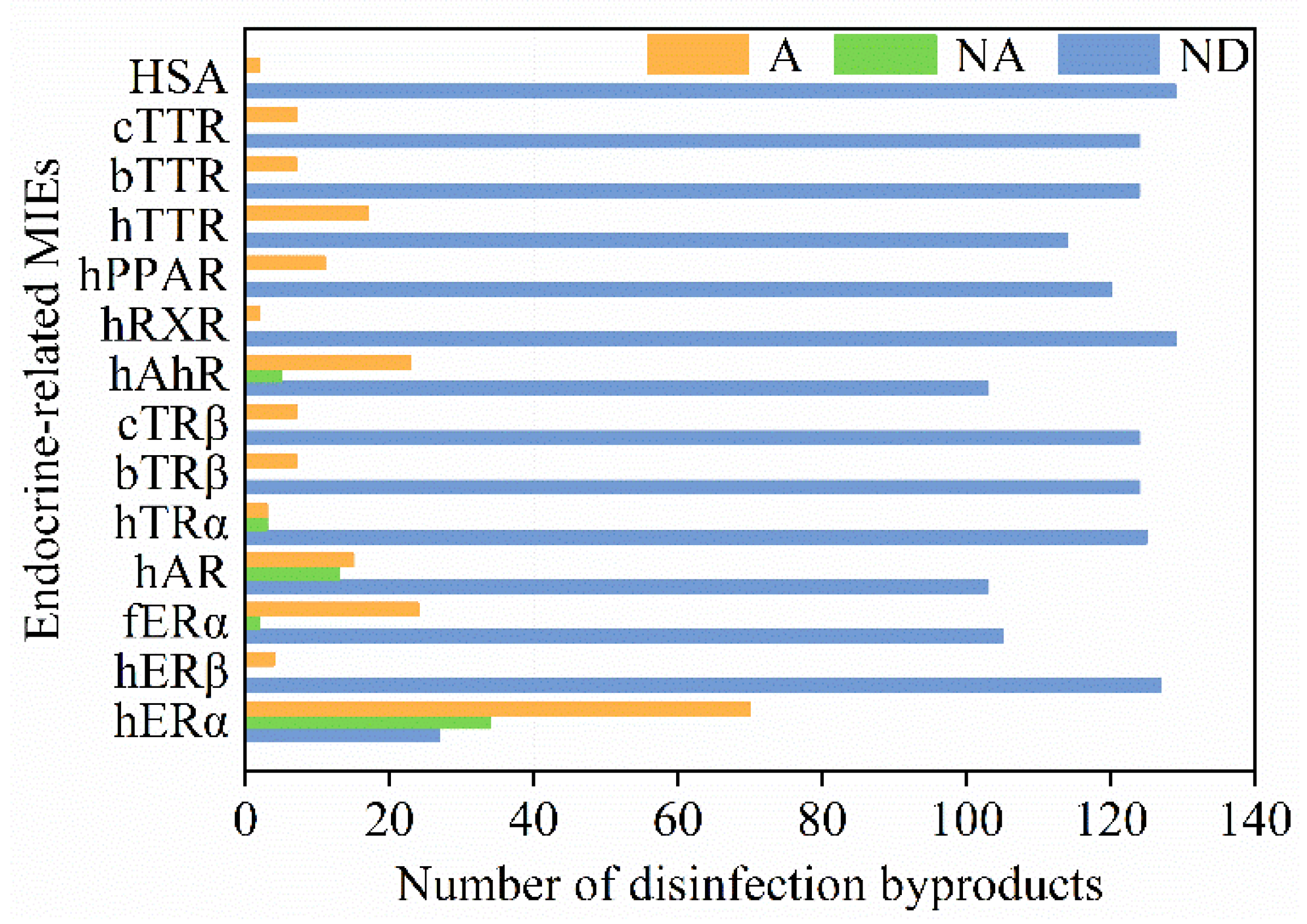
For each studied endocrine endpoint, we also summarized the number of active compounds, inactive compounds, and compounds without available data. As shown in Figure 3, the number of active compounds for hERα was more than that of other endpoints. For hERα, human aryl hydrocarbon receptor (hAhR), and human androgen receptor (hAR), the number of active compounds was greater than that of inactive compounds. On the other hand, all the tested DBPs were active compounds for human transthyretin (hTTR), bullfrog transthyretin (bTTR), chicken transthyretin (cTTR), human serum albumin (HSA), peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor (hPPAR), human retinoic X receptor (hRXR), bullfrog thyroid receptor β (bTRβ), chicken thyroid receptor β (cTRβ), and human estrogen receptor β (hERβ).
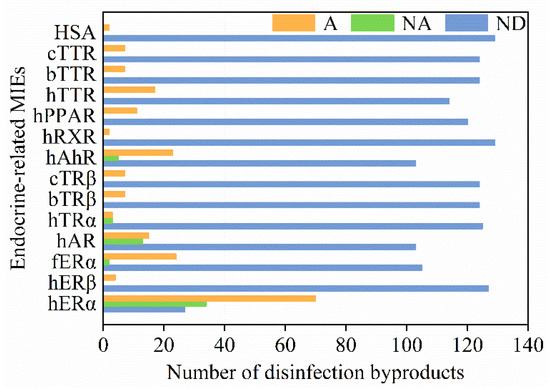
Figure 3.
Overview of DBPs and their associated endocrine-disrupting effects. Orange, the number of active compounds (A); green, the number of inactive compounds (NA); blue, the number of compounds without available data (ND). Abbreviations: hERα—human estrogen receptor α; hERβ—human estrogen receptor β; fERα—medaka fish estrogen receptor α; hAR—human androgen receptor; hTRα—human thyroid receptor α; bTRβ—bullfrog thyroid receptor β; cTRβ—chicken thyroid receptor β; hAhR—human aryl hydrocarbon receptor; hRXR—human retinoic X receptor; hPPAR—peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor; hTTR—human transthyretin; bTTR—bullfrog transthyretin; cTTR—chicken transthyretin; HSA—human serum albumin.
4. Endocrine-Related MIEs of DBPs
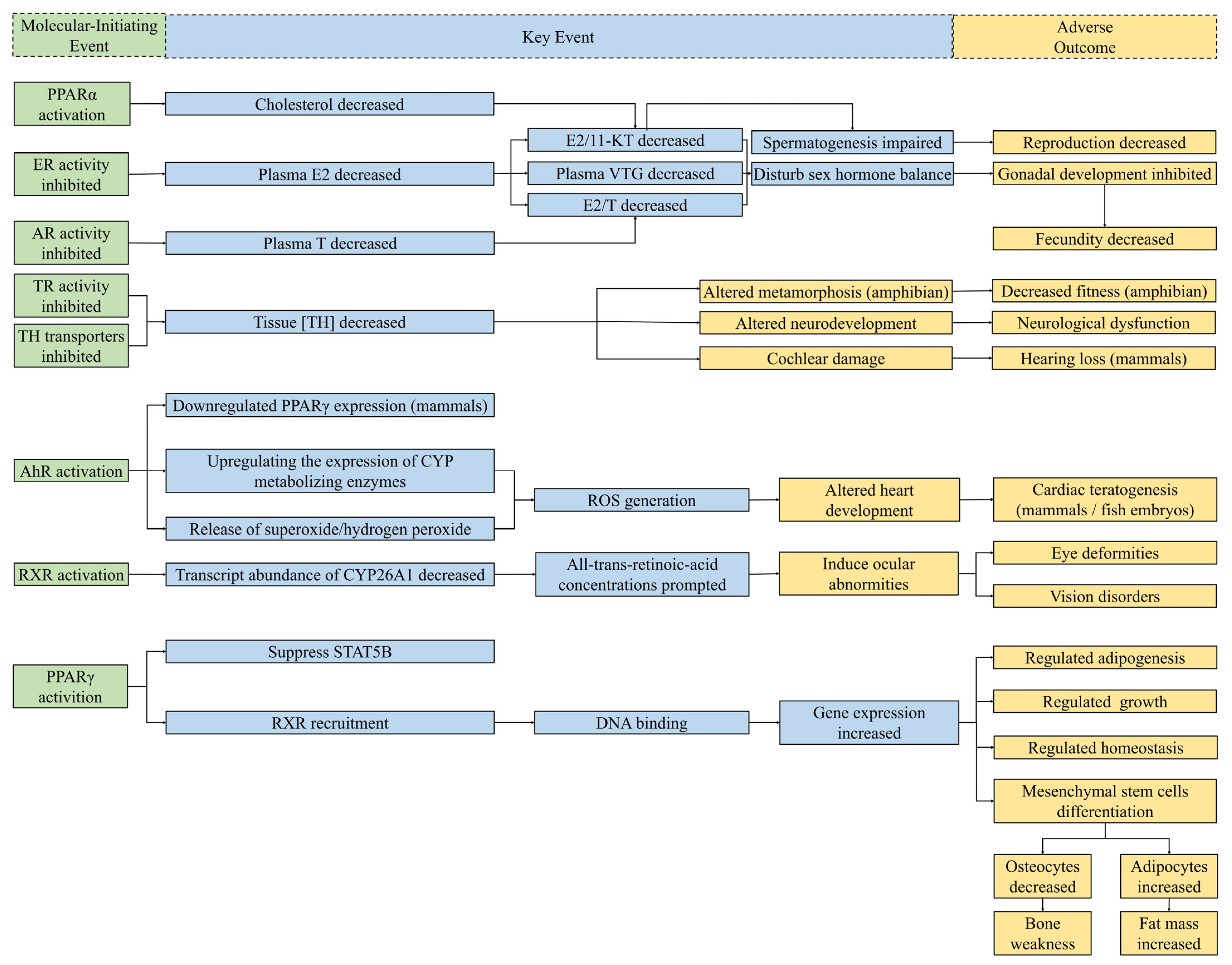
DBPs can disturb normal endocrine homeostasis by regulating the hormone system for fundamental physiological and developmental control [84]. The perturbing mechanisms of DBPs include activating/inhibiting nuclear receptors and interfering with non-receptor-mediated pathways. It is reported that most of adverse outcomes of endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) are attributed to the fact that they interfere with nuclear receptor (NR)-mediated hormone signals [60]. The substance structure of some DBPs is similar to that of natural hormones; thus, they can directly bind with receptors, interfere with the hormone pathway, and show distinct disrupting activities. The mediated physiological and biochemical pathways of several receptors on which the Guidance for the Identification of Endocrine Disruptors (EFSA/ECHA, 2018) focuses [85], including androgen receptor (AR), estrogen receptor (ER), and thyroid receptor (TR), are of critical importance in significant biological studies of endocrine disruption effects. All the tested molecular-initiating events related to DBPs are illustrated in Figure 4.
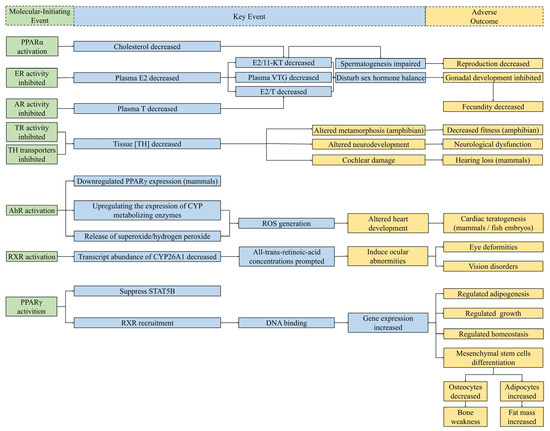
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of known MIEs for endocrine disruption of DBPs and several related potential KEs and AOs. The relationships between MIEs and potential KEs in this figure were collected from compounds other than DBPs [86,87,88,89,90,91]. Considering the significant relationships between each step, MIEs (left) bring about KEs (middle), and then lead to AOs (right). Green boxes, MIEs associated with endocrine perturbation of DBPs; blue boxes, KEs of endocrine disruptors collected from studies; yellow boxes, AOs for endocrine toxicity. Abbreviations: E2, estradiol; T, testosterone; 11-KT, 11-ketotestosterone; VTG, vitellogenin; TH, thyroid hormones; CYP, cytochrome P450; ROS, reactive oxygen species; STATSB, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5B.
4.1. Hormone Receptor-Mediated Mechanism of Endocrine Disruption
Estrogen receptors (ERs) have critical roles in the growth and development of organisms [53]. The recombinant yeast screening bioassay, the E-screen assay of MCF-7 and MVLN cell line, and the uterotrophic bioassay are usually adopted for identifying potential estrogenic disruptors [51,71,83]. Our analysis results indicated that 70 DBPs have been proven to have estrogenic activity, i.e., they can interfere with ER. There is evidence in toxicological and epidemiological research in cell cultures that haloacetonitriles (HANs), e.g., dibromoacetonitrile (DBAN) and 2,3-dibromopropionitrile (DBPN), can invoke adverse effects on the endocrine system by binding to the human estrogen receptor and androgen receptor [50,66]. Additionally, Nakamura et al. [58] reported that halogenated derivatives of E1, E2, E3, and EE2 showed estrogenic activity, interfering with estrogen receptor α, using yeast two-hybrid assays between human and medaka fish (Oryzias latipes), and the ER-binding potency of halogenated DBPs of estrogens substituted at the 2- and 4-positions displayed a similar trend.
The androgen hormone regulates the androgen signaling pathway via binding with the androgen receptor (AR), and it plays an essential role in the physiological processes of human development and reproduction [92]. Iodoacetic acid (IAA) was observed to show AR binding in vitro [50]. Despite the discrepancies between this result and others, studies have still demonstrated that IAA is a potential disruptor of human AR (hAR) [51]. The differences in research results may be due to factors such as the selection of species of cells and diverse endpoints. Additionally, among haloacetamide DBPs, bromoacetamide (BAM) exhibited slight androgenic activity according to a yeast-based reporter bioassay [69]. Notably, iodoacetonitrile (IAN) generated from water disinfection processes was found to have a weak androgenic effect (11.4% induction) at the highest concentration [71].
Thyroid hormones (THs), a series of essential endocrine hormones, are synthesized and secreted by thyroid follicular cells. They exist in many tissues in the brain, heart, liver, etc., where they regulate metabolism and development [82]. THs, especially triiodothyronine (T3), mainly moderate gene transcription or protein expression via binding to thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) [93]. Halogenated derivatives of bisphenol A (BPA) have been shown to act as agonists/antagonists for TH receptors, affecting the levels of THs and invoking thyroid system disruption in organisms. 3,3’,5,5’-Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA), 3,3’,5,5’-tetrachlorobisphenol A (TCBPA), and 3,3’,5-trichlorobisphenol A (3,3’,5-triClBPA) were proven to possess human TH agonist activity in a yeast two-hybrid assay incorporating hTRα [59]. In addition, Yamauchi et al. [56] investigated the influence of chlorinated compounds of BPA on T3 binding with the TR ligand-binding domains between chicken and bullfrog but demonstrated that they were unlikely to be TH system-disrupting compounds for these animals.
Some chemicals could bind to other receptors to indirectly participate in hormone regulation instead of acting directly on hormone receptors. For example, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), expressed in the fatty tissue, is a critical transcription element in the development and metabolism of adipocytes [65]. The imbalance of PPAR might be associated with diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and dysgenesis [94]. A previous 293T cell-based luciferase reporter bioassay indicated that chlorinated BPS analogs enhanced PPAR activities as opposed to the parent compound, and their activities were correlated to the values of logKow [65]. TBBPA and TCBPA could also activate PPAR through direct interaction with humans or animals, and the activation potential highly relied on the halogenation degree [60,61]. The results from in vitro experiments revealed that halogenated products of BPF were also potential disruptors of PPAR, similar to those of BPA and BPS [64]. Taken together, the presence of DBPs of BPA, BPS, and BPF in disinfected water should be of concern because they could pose a potential risk to mitigation of inflammation.
Furthermore, human retinoic X receptor (RXRs) have also been shown to be endocrine-related targets for DBPs action. RXRs are key partners for the nuclear receptor signaling pathways of cell growth, differentiation, and metabolism [95]. Chlorination byproducts of BPA have been identified as RXRβ antagonists, the antagonist activities of which are much higher than that of BPA according to a yeast assay [63]. Considering that previous studies documented that BPA could exhibit several detrimental effects (e.g., endocrine-related harmful effects) on organisms [96,97,98,99,100], those results indicate that both BPA and its halogenated DBPs are potential endocrine disruptors. Experimental evidence for DBPs with respect to their AhR binding affinities is rather limited. In terms of structure, halogenated parabens are similar to halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons, which were determined to possess AhR potency. Experimental values obtained via a yeast bioassay and HepG2 cells showed that the AhR activity of monochlorinated parabens was more effective than that of their unsubstituted or chlorinated counterparts [62]. Analogously, this regular pattern is also applicable to monobrominated by-products. Promisingly, it was noted that 3-BrBP, 3-BrBnP, and 3-BriBP, compared with their unsubstituted and brominated corresponding counterparts, were proven to have the highest AhR activity with EC50 values of 3.9 nM, 9.0 nM, and 9.6 nM, respectively [70].
4.2. Non-Receptor-Mediated Mechanism of Endocrine Disruption
It has been recognized that activation or inhibition of nuclear receptors is not the only endocrine-disrupting pathway for DBPs to exert endocrine-perturbing effects [85]. Another toxicity pathway leading to an endocrine-related detrimental influence is the non-receptor-mediated mechanism [69]. Instead of acting directly on nuclear receptors, the pathway of non-receptor-mediated activity interference comprises inhibition of protein synthesis, destruction of β-galactosidase gene transcription, and inhibition of enzyme activity [101]. Endocrine disruptors can affect some links of the hypothalamus–pituitary–thyroid (HPT), hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG), and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axes, and further disturb hormones biosynthesis, secretion, transport, metabolism, and feedback regulation [89,102]. There are three transporters in human blood that carry THs to target tissues: transthyretin (TTR), thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG), and albumin (ALB) [103].
The results from Yang et al. [67] revealed that 2,4,6-trihalo-phenols, 2,6-dihalo-4-nitrophenols, and 3,5-dihalo-4-hydroxybenzaldehydes, representing emerging polar phenolic DBPs, were identified as high-potency binders to compete with THs for binding to human TTR. Disrupting the transportation of TH might bring about DBPs being delivered to unexpected sites, which might further induce TH-related perturbing effects [102,104]. Previous evidence also showed that 2,6-dichloro-4-nonylphenol is a potent competitor of T3 interacting with chicken and bullfrog TTR, along with by-products of nonylphenol [56]. Furthermore, the comparison of TTR-binding activities among brominated derivatives of BPA indicated that the presence of a hydroxyl group at the para position and halogen substituents were conditions for TTR-binding effects [105]. These experimental results may confirm the conclusion that halogenated aromatic chemicals with phenol hydroxy groups can be considered as binders to TTR owing to their similar structure to the natural thyroxine (T4) [106]. ALB is also a potential endocrine-related target in the mechanism of TH transport disruption. According to competitive binding assays, 4-bromophenol and 2,4-dibromophenol were observed to interfere with human serum albumin (HSA) to form complexes [68]. Remarkably, 2,4-dibromophenol had a high binding affinity to HSA.
5. Potential Endocrine Adverse Outcome Pathways of DBPs
Compared with studies about molecular-initiating events, only a few studies focused on revealing the potential endocrine-related key events and adverse outcomes after DBP exposure. An in vivo experiment indicated that IAA, an aliphatic DBP, increased the weight of the testes of parental male rats and shortened the anorectal distance of male pups [51]. However, the specific toxicity mechanisms remain unclear and require to be further confirmed. Additionally, IAA exposure reduced the level of triiodothyronine (T3), but upregulated the thyrotropin-releasing hormone level and thyrotropin level, which could also result in changes in the thyroid follicles of Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats [82]. The possible molecular mechanism of thyroid gland function disruption might be associated with the binding potency of nuclear receptors. In vivo toxicity reports demonstrated that histopathological changes in both heart and brain induced by 2,6-dichloro-1, 4-benzoquinone exposure for adult zebrafish could be attributed to oxidative stress [107]. The results from in vivo experiences showed that bisphenol S disinfected derivatives could influence the mRNA expression level of TRβ in zebrafish larvae [49], which could further mediate the bioactivities of thyroid hormone. Additionally, limited toxicological reports in vivo revealed no significant indication for plasma VTG levels in adult Danio rerio during 21 day exposure to TBBPA and TCBPA disinfection derivatives [83]. The developmental toxicity induced by TCBPA and TBBPA disinfection derivatives might be irrelevant to their estrogenic activities. In vivo assays of estrogenic activity showed that 3-chlorobisphenol A and 3,3’-dichlorobisphenol A each evidently enlarged the uterine endometrial area in rats treated with 100 mg/kg/day of these substances [57]. Wang et al. [108] linked the developmental toxicity of halobenzoquinone to oxidative stress, but they did not link the ROS generation with MIEs of endocrine disruption. The relationship between endocrine-related MIEs and oxidative stress was revealed in animal toxicity studies showing that aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activation could increase ROS generation by regulating the expression of Cyp1b1, which led to cardiac malformation in zebrafish embryos [86].
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
With the development of analytical methods, a large number of DBPs are being continuously detected and identified in treated drinking water, purified swimming pool water, disinfected wastewater, etc. Here, we summarized the literature on the endocrine-disrupting effects of DBPs. The results from the limited studies suggested that exposure to some DBPs could elicit endocrine-related detrimental effects not only on humans, but also on other wildlife, e.g., aquatic vertebrates. Our analysis results also revealed that the available data related to the potential endocrine system-disrupting properties of DBPs are limited to molecular-initiating events, i.e., biomacromolecules in the endocrine system. The identified molecular-initiating events mainly involved receptor-mediated toxicity pathways.
The future directions are proposed below.
(1) Development of appropriate screening strategy for assessing the potential endocrine-disrupting effects of DBPs
It was reported that the cost to evaluate the potential endocrine-disrupting effects of one substance is about 1 million USD [109]. In this case, it is impossible to screen the potential EDCs from more than 800 identified DBPs using experimental assays only. Considering that computational models are cost-effective and rapid methods, a comprehensive screening strategy containing both computational models and experimental assays should be employed to identify the potential EDCs from analyzed DBPs. In this comprehensive screening strategy, the endocrine-related computational models can be firstly used to set the priority. Then, the limited test resources can be focused on verifying whether the DBPs with high priority are endocrine disruptors or not.
(2) Clarifying the potential endocrine-related adverse outcome after DBP exposure
In addition to revealing the endocrine-related molecular-initiating events influenced by DBP exposure, further biological studies are expected to illustrate the potential endocrine-related key events and adverse outcomes following DBP exposure, as well as confirm the detailed relationship of molecular-initiating events with key events and adverse outcomes.
(3) Attention to non-receptor-mediated toxicity pathways
In addition to the receptor-mediated model of action, EDCs may perturb the endocrine system via a non-receptor-mediated mode of action, such as by interfering with targets related to biosynthesis and metabolism and plasma binding. In future studies, we should pay more attention to testing the potential non-receptor-mediated toxicity pathways of DBPs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jox12030013/s1: Table S1. Available disinfection byproducts and endocrine-related targets.
Author Contributions
S.S., literature search, data analysis, and writing—original draft; H.L., writing—review and editing; X.Y., conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22176097), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2020T130301; No. 2020M671502), the Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds (No. 2020Z288), and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20190072).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wei, X.; Yang, M.; Zhu, Q.; Wagner, E.D.; Plewa, M.J. Comparative Quantitative Toxicology and QSAR Modeling of the Haloacetonitriles: Forcing Agents of Water Disinfection Byproduct Toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8909–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plewa, M.J.; Richardson, S.D. Disinfection By-Products in Drinking Water, Recycled Water and Wastewater: Formation, Detection, Toxicity and Health Effects: Preface. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 58, 1. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.D. Disinfection by-products and other emerging contaminants in drinking water. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2003, 22, 666–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D.; Plewa, M.J.; Wagner, E.D.; Schoeny, R.; Demarini, D.M. Occurrence, genotoxicity, and carcinogenicity of regulated and emerging disinfection by-products in drinking water: A review and roadmap for research. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2007, 636, 178–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Lin, Y.; Ruan, T.; Jiang, G. Identification of N-Nitrosamines and Nitrogenous Heterocyclic Byproducts during Chloramination of Aromatic Secondary Amine Precursors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12949–12958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellar, T.A.; Lichtenberg, J.J.; Kroner, R.C. The occurrence of organohalides in chlorinated drinking waters. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1974, 66, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čulin, J.; Mustać, B. Environmental risks associated with ballast water management systems that create disinfection by-products (DBPs). Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 105, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, X.; Liu, X.; Fang, C.; Chu, W.; Xu, Z. Ecotoxicological effects of disinfected wastewater effluents: A short review of in vivo toxicity bioassays on aquatic organisms. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 2275–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, D.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z. Formation of known and unknown disinfection by-products from natural organic matter fractions during chlorination, chloramination, and ozonation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.D.; DeMarini, D.M.; Kogevinas, M.; Fernandez, P.; Marco, E.; Lourencetti, C.; Ballesté, C.; Heederik, D.; Meliefste, K.; McKague, A.B.; et al. What’s in the pool? A comprehensive identification of disinfection by-products and assessment of mutagenicity of chlorinated and brominated swimming pool water. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhong, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Huo, Z.; Chu, W.; Xu, B. A New Group of Heterocyclic Nitrogenous Disinfection Byproducts (DBPs) in Drinking Water: Role of Extraction pH in Unknown DBP Exploration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 6764–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, A.; Shuang, C.; Xian, Q.; Xu, B.; Pan, Y. New phenolic halogenated disinfection byproducts in simulated chlorinated drinking water: Identification, decomposition, and control by ozone-activated carbon treatment. Water Res. 2018, 146, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Lu, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, W.L.; Yang, L.L.; Wu, Q.Y. Comprehensive GCxGC-qMS with a mass-to-charge ratio difference extraction method to identify new brominated byproducts during ozonation and their toxicity assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 124103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, R.S.; Guerreiro, C.S.; Cardoso, V.V.; Benoliel, M.J.; Santos, M.M. Toxicological assessment of seven unregulated drinking water Disinfection By-products (DBPs) using the zebrafish embryo bioassay. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Alhooshani, K.; Karanfil, T. Disinfection byproducts in swimming pool: Occurrences, implications and future needs. Water Res. 2014, 53, 68–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.H.; Lu, Z.W.; Wang, P.; He, M.J.; Huang, X.; Lu, W.Q. Temporal variability in urinary levels of drinking water disinfection byproducts dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid among men. Environ. Res. 2014, 135, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.C.; Zeng, Q.; Luo, Y.; Chen, H.X.; Miao, D.Y.; Li, L.; Cheng, Y.H.; Li, M.; Wang, F.; You, L.; et al. Blood Biomarkers of Late Pregnancy Exposure to Trihalomethanes in Drinking Water and Fetal Growth Measures and Gestational Age in a Chinese Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, E.D.; Plewa, M.J. CHO cell cytotoxicity and genotoxicity analyses of disinfection by-products: An updated review. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 58, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel, F.M.; Ternes, T.A.; Richardson, S.D.; Duirk, S.E.; Pals, J.A.; Wagner, E.D.; Plewa, M.J. Comparative Toxicity of High-Molecular Weight Iopamidol Disinfection Byproducts. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Rahman, S.M.; Gou, N.; Jiang, T.; Plewa, M.J.; Alshawabkeh, A.; Gu, A.Z. Genotoxicity Assessment of Drinking Water Disinfection Byproducts by DNA Damage and Repair Pathway Profiling Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6565–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kali, S.; Khan, M.; Ghaffar, M.S.; Rasheed, S.; Waseem, A.; Iqbal, M.M.; Bilal Khan Niazi, M.; Zafar, M.I. Occurrence, influencing factors, toxicity, regulations, and abatement approaches for disinfection by-products in chlorinated drinking water: A comprehensive review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 116950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Jin, J.; Gao, R.; Feng, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, A. Degradation of benzophenone-4 in a UV/chlorine disinfection process: Mechanism and toxicity evaluation. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberatore, H.K.; Plewa, M.J.; Wagner, E.D.; VanBriesen, J.M.; Burnett, D.B.; Cizmas, L.H.; Richardson, S.D. Identification and Comparative Mammalian Cell Cytotoxicity of New Iodo-Phenolic Disinfection Byproducts in Chloraminated Oil and Gas Wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, D.; Xu, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z. Spatial variations in the occurrence of potentially genotoxic disinfection by-products in drinking water distribution systems in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, C.; Yang, M.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhao, X. Comparative cytotoxicity of halogenated aromatic DBPs and implications of the corresponding developed QSAR model to toxicity mechanisms of those DBPs: Binding interactions between aromatic DBPs and catalase play an important role. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsioroski, A.; Mourikes, V.E.; Flaws, J.A. Endocrine Disruptors in Water and Their Effects on the Reproductive System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyak, V.; Koyuncu, I.; Oktem, I.; Cakmakci, M.; Toroz, I. Removal of trihalomethanes from drinking water by nanofiltration membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plattard, N.; Dupuis, A.; Migeot, V.; Haddad, S.; Venisse, N. An overview of the literature on emerging pollutants: Chlorinated derivatives of Bisphenol A (ClxBPA). Environ. Int. 2021, 153, 106547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, M.; Felipe-Sotelo, M.; Bond, T. Disinfection byproducts potentially responsible for the association between chlorinated drinking water and bladder cancer: A review. Water Res. 2019, 162, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, M.A.; Khan, N.A.; Ahmed, S.; Khan, A.H.; Hussain, A.; Rahisuddin; Changani, F.; Yousefi, M.; Ahmadi, S.; Vambol, V. Chlorination disinfection by-products in municipal drinking water—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 123159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. National Interim Primary Drinking Water Regulations. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1976, 68, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 307–434. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, J.; Li, W. How Much of the Total Organic Halogen and Developmental Toxicity of Chlorinated Drinking Water Might Be Attributed to Aromatic Halogenated DBPs? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5906–5916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, M.; Tan, C.; Chu, W. The occurrence, characteristics, transformation and control of aromatic disinfection by-products: A review. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.D.; Mitch, W.A. Halonitroalkanes, halonitriles, haloamides, and N-nitrosamines: A critical review of nitrogenous disinfection byproduct formation pathways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mian, H.R.; Hu, G.; Hewage, K.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Sadiq, R. Prioritization of unregulated disinfection by-products in drinking water distribution systems for human health risk mitigation: A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 147, 112–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Zhao, H.; Cao, H.; Huang, C.H.; Liu, W.; Li, Y. Transformation of halobenzoquinones with the presence of amino acids in water: Products, pathways and toxicity. Water Res. 2017, 122, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Qin, L.T.; Mo, L.Y.; Zhao, D.N.; Zeng, H.H.; Liang, Y.P. Synergetic effects of novel aromatic brominated and chlorinated disinfection byproducts on Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Chen, B.; Jiang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Cai, Z. Toxicity of 17 Disinfection By-products to Different Trophic Levels of Aquatic Organisms: Ecological Risks and Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10534–10541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacroix, S.; Vogelsang, C.; Tobiesen, A.; Liltved, H. Disinfection by-products and ecotoxicity of ballast water after oxidative treatment--results and experiences from seven years of full-scale testing of ballast water management systems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 73, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Dong, T.; Xia, Y.; Jiao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W. Developmental toxicity of disinfection by-product monohaloacetamides in embryo-larval stage of zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 110037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.; Yonkos, L.; Ziegler, G.; Friedel, E.; Burton, D. Acute and chronic toxicity of selected disinfection byproducts to Daphnia magna, Cyprinodon variegatus, and Isochrysis galbana. Water Res. 2014, 55, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanigan, D.; Truong, L.; Simonich, M.; Tanguay, R.; Westerhoff, P. Zebrafish embryo toxicity of 15 chlorinated, brominated, and iodinated disinfection by-products. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 58, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Zhou, D.; Yu, S.; Chen, W. The removal process of 2,2-dichloroacetamide (DCAcAm), a new disinfection by-product, in drinking water treatment process and its toxicity on zebrafish. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, A.; Ferreira, C.; Ferreira, I.; Mansilha, C. Acute and chronic toxicity assessment of haloacetic acids using Daphnia magna. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2019, 82, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixidó, E.; Piqué, E.; Gonzalez-Linares, J.; Llobet, J.M.; Gómez-Catalán, J. Developmental effects and genotoxicity of 10 water disinfection by-products in zebrafish. J. Water. Health. 2015, 13, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Lin, T.; Chen, W.; Tao, H. The toxicity of a new disinfection by-product, 2,2-dichloroacetamide (DCAcAm), on adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) and its occurrence in the chlorinated drinking water. Chemosphere 2015, 139, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, L. Aquatic toxicity and aquatic ecological risk assessment of wastewater-derived halogenated phenolic disinfection byproducts. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhan, T.; Ma, M.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, W.; Zhuang, S. Thyroid Disruption by Bisphenol S Analogues via Thyroid Hormone Receptor beta: In Vitro, in Vivo, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6617–6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, B.E.; Smeester, L.; Fry, R.C.; Weinberg, H.S. Identification of endocrine active disinfection by-products (DBPs) that bind to the androgen receptor. Chemosphere 2017, 187, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.; Sha, Y.; Mo, Y.; Wei, S.; Wu, H.; Lu, D.; Xia, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, W.; Wei, X. Androgenic and Teratogenic Effects of Iodoacetic Acid Drinking Water Disinfection Byproduct in Vitro and in Vivo. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3827–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Yin, C.; Wei, M.; He, X. Development of predictive models for predicting binding affinity of endocrine disrupting chemicals to fish sex hormone-binding globulin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 136, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Peng, T.; Yang, X.; Liu, H. Development of QSAR models for predicting the binding affinity of endocrine disrupting chemicals to eight fish estrogen receptor. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colborn, T.; vom Saal, F.S.; Soto, A.M. Developmental effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in wildlife and humans. Environ. Health Perspect. 1993, 101, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Ou, W.; Zhao, S.; Xi, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, H. Rapid Screening of Human Transthyretin Disruptors through a Tiered in Silico Approach. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 5661–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, K.; Ishihara, A.; Fukazawa, H.; Terao, Y. Competitive interactions of chlorinated phenol compounds with 3,3′,5-triiodothyronine binding to transthyretin: Detection of possible thyroid-disrupting chemicals in environmental waste water. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 187, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, H.; Ma, J.; Sayama, K.; Terao, Y.; Zhu, B.T.; Shimoi, K. In vitro and in vivo estrogenic activity of chlorinated derivatives of bisphenol A. Toxicology 2005, 207, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Shiozawa, T.; Terao, Y.; Shiraishi, F.; Fukazawa, H. By-products produced by the reaction of estrogens with hypochlorous acid and their estrogen activities. J. Health Sci. 2006, 52, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, M.; Kosaka, K.; Kunikane, S.; Makino, M.; Shiraishi, F. Assessment of thyroid hormone activity of halogenated bisphenol A using a yeast two-hybrid assay. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riu, A.; le Maire, A.; Grimaldi, M.; Audebert, M.; Hillenweck, A.; Bourguet, W.; Balaguer, P.; Zalko, D. Characterization of novel ligands of ERalpha, Erbeta, and PPARgamma: The case of halogenated bisphenol A and their conjugated metabolites. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 122, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riu, A.; Grimaldi, M.; le Maire, A.; Bey, G.; Phillips, K.; Boulahtouf, A.; Perdu, E.; Zalko, D.; Bourguet, W.; Balaguer, P. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is a target for halogenated analogs of bisphenol A. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, M.; Yasuda, M.; Makino, M.; Shimoi, K. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor potency of chlorinated parabens in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2015, 1, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Jiang, W.; Ma, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z. Chlorination by-products of bisphenol A enhanced retinoid X receptor disrupting effects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 320, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Shi, J.C.; Hu, J.Y.; Hu, W.X.; Zhang, J.; Shao, B. Chlorination of bisphenol F and the estrogenic and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma effects of its disinfection byproducts. Water Res. 2016, 107, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Hu, J.; Shao, B. Identification of the disinfection byproducts of bisphenol S and the disrupting effect on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) induced by chlorination. Water Res. 2018, 132, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, B.E.; Smeester, L.; Fry, R.C.; Weinberg, H.S. Disinfection Byproducts Bind Human Estrogen Receptor-alpha. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Ou, W.; Xi, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, H. Emerging Polar Phenolic Disinfection Byproducts Are High-Affinity Human Transthyretin Disruptors: An in Vitro and in Silico Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7019–7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, M.; Yi, J.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, B.; Zhao, X. Comprehensive Insights into the Interactions of Two Emerging Bromophenolic DBPs with Human Serum Albumin by Multispectroscopy and Molecular Docking. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, C.G.; Kim, Y.J. Characterizing the potential estrogenic and androgenic activities of two disinfection byproducts, mono-haloacetic acids and haloacetamides, using in vitro bioassays. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouukon, Y.; Yasuda, M.T.; Yasukawa, H.; Terasaki, M. Occurrence and AhR activity of brominated parabens in the Kitakami River, North Japan. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.G.; Jung, K.C.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, Y.J. Monohaloacetonitriles induce cytotoxicity and exhibit different mode of action in endocrine disruption. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Cheng, S.J.; Aizawa, T.; Terao, Y.; Kunikane, S. Products of aqueous chlorination of 17 beta-estradiol and their estrogenic activities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5665–5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bila, D.; Montalvão, A.F.; Azevedo Dde, A.; Dezotti, M. Estrogenic activity removal of 17beta-estradiol by ozonation and identification of by-products. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniero, M.G.; Bila, D.M.; Dezotti, M. Degradation and estrogenic activity removal of 17beta-estradiol and 17alpha-ethinylestradiol by ozonation and O3/H2O2. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 407, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.-Y.; Hu, H.-Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Y.-X. Effect of Chlorination on the Estrogenic/Antiestrogenic Activities of Biologically Treated Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4940–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Characterization and identification of antiestrogenic products of phenylalanine chlorination. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3625–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, G.; Xue, J.; Li, M.; Hu, H.Y.; Lu, Y. Estrogen receptor affinity chromatography: A new method for characterization of novel estrogenic disinfection by-products. Chemosphere 2014, 104, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.Y.; Tang, X.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Ding, Y.N.; Shao, Y.R. Antiestrogenic activity and related disinfection by-product formation induced by bromide during chlorine disinfection of sewage secondary effluent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 273, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, H.; An, W.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, J. Byproducts of aqueous chlorination of equol and their estrogenic potencies. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Terasaki, M. Estrogen agonistic/antagonistic activity of brominated parabens. Environ. Sci. Pollut Res. Int. 2018, 25, 21257–21266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakopin, Ž. Assessment of the endocrine-disrupting potential of halogenated parabens: An in silico approach. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Mo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Wei, S.; Lu, D.; Wu, H.; Lu, G.; Zou, Y.; et al. Iodoacetic Acid Disrupting the Thyroid Endocrine System in Vitro and in Vivo. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7545–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Liang, D.; Liang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Jiang, G. Assessing developmental toxicity and estrogenic activity of halogenated bisphenol A on zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2014, 112, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Bourguignon, J.P.; Giudice, L.C.; Hauser, R.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Zoeller, R.T.; Gore, A.C. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: An Endocrine Society scientific statement. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 293–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanojević, M.; Vračko Grobelšek, M.; Sollner Dolenc, M. Computational evaluation of endocrine activity of biocidal active substances. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Ji, C.; Ren, F.; Aniagu, S.; Tong, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, T. AHR-mediated oxidative stress contributes to the cardiac developmental toxicity of trichloroethylene in zebrafish embryos. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Chen, R.; Zhang, H.; Nakanishi, T.; Hu, J. Maternal Transfer of 2-Ethylhexyl Diphenyl Phosphate Leads to Developmental Toxicity Possibly by Blocking the Retinoic Acid Receptor and Retinoic X Receptor in Japanese Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5056–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, A.B.; Michelsen-Correa, S.; Rosen, C.; Martin, C.F.; Blumberg, B. PFAS and Potential Adverse Effects on Bone and Adipose Tissue Through Interactions with PPARgamma. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yang, J.; Chen, G.; Yi, S.; Liu, M.; Zhu, L. Thyroid-Disrupting Effects of 6:2 and 8:2 Polyfluoroalkyl Phosphate Diester (diPAPs) at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations from Integrated In Silico and In Vivo Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul Friedman, K.; Watt, E.D.; Hornung, M.W.; Hedge, J.M.; Judson, R.S.; Crofton, K.M.; Houck, K.A.; Simmons, S.O. Tiered High-Throughput Screening Approach to Identify Thyroperoxidase Inhibitors Within the ToxCast Phase I and II Chemical Libraries. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 151, 160–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.B.; Kim, G.E.; On, J.; Pyo, H.; Park, J.W.; Cho, S.H. Sex-specific effects of bisphenol S with tissue-specific responsiveness in adult zebrafish: The antiandrogenic and antiestrogenic effects. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 229, 113102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorn, K.M.; Foil, D.H.; Lane, T.R.; Hillwalker, W.; Feifarek, D.J.; Jones, F.; Klaren, W.D.; Brinkman, A.M.; Ekins, S. Comparison of Machine Learning Models for the Androgen Receptor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13690–13700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul-Friedman, K.; Martin, M.; Crofton, K.M.; Hsu, C.W.; Sakamuru, S.; Zhao, J.; Xia, M.; Huang, R.; Stavreva, D.A.; Soni, V.; et al. Limited Chemical Structural Diversity Found to Modulate Thyroid Hormone Receptor in the Tox21 Chemical Library. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 097009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swedenborg, E.; Rüegg, J.; Mäkelä, S.; Pongratz, I. Endocrine disruptive chemicals: Mechanisms of action and involvement in metabolic disorders. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; De Luca, L.M. Therapeutic Potential of "Rexinoids" in Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4945–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, A.D.; Andrade, A.; Harris, E.P.; Rissman, E.F.; Wolstenholme, J.T. Bisphenol A Exposure in Utero Disrupts Hypothalamic Gene Expression Particularly Genes Suspected in Autism Spectrum Disorders and Neuron and Hormone Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzi, D.; Gioiosa, L.; Parmigiani, S.; Palanza, P. Effects of Prenatal Exposure to a Low-Dose of Bisphenol A on Sex Differences in Emotional Behavior and Central Alpha2-Adrenergic Receptor Binding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, B.S. Bisphenol A: An endocrine disruptor with widespread exposure and multiple effects. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 127, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Maffini, M.V.; Sonnenschein, C.; Rubin, B.S.; Soto, A.M. Bisphenol-A and the Great Divide: A Review of Controversies in the Field of Endocrine Disruption. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochester, J.R. Bisphenol A and human health: A review of the literature. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 42, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fic, A.; Žegura, B.; Gramec, D.; Mašič, L.P. Estrogenic and androgenic activities of TBBA and TBMEPH, metabolites of novel brominated flame retardants, and selected bisphenols, using the XenoScreen XL YES/YAS assay. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Watson, P.; Yang, F. Binding interactions of halo-benzoic acids, halo-benzenesulfonic acids and halo-phenylboronic acids with human transthyretin. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kamstra, J.H.; Ghorbanzadeh, M.; Weiss, J.M.; Hamers, T.; Andersson, P.L. In Silico Approach to Identify Potential Thyroid Hormone Disruptors among Currently Known Dust Contaminants and Their Metabolites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10099–10107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, F.A.; Lehmler, H.J.; He, X.; Robertson, L.W.; Duffel, M.W. Sulfated metabolites of polychlorinated biphenyls are high-affinity ligands for the thyroid hormone transport protein transthyretin. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerts, I.; van Zanden, J.J.; Luijks, E.A.C.; van Leeuwen-Bol, I.; Marsh, G.; Jakobsson, E.; Bergman, A.; Brouwer, A. Potent competitive interactions of some brominated flame retardants and related compounds with human transthyretin in vitro. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 56, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, J.M.; Andersson, P.L.; Zhang, J.; Simon, E.; Leonards, P.E.; Hamers, T.; Lamoree, M.H. Tracing thyroid hormone-disrupting compounds: Database compilation and structure-activity evaluation for an effect-directed analysis of sediment. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 5625–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Huang, S.; Luo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, Q. Transcriptomic analysis of adult zebrafish heart and brain in response to 2, 6-dichloro-1, 4-benzoquinone exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 226, 112835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Moe, B.; Li, X.F. Halobenzoquinone-Induced Developmental Toxicity, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis in Zebrafish Embryos. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10590–10598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, K.; Kleinstreuer, N.; Abdelaziz, A.M.; Alberga, D.; Alves, V.M.; Andersson, P.L.; Andrade, C.H.; Bai, F.; Balabin, I.; Ballabio, D.; et al. CoMPARA: Collaborative Modeling Project for Androgen Receptor Activity. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 027002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).