Xenobiotics—Division and Methods of Detection: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Xenobiotics
3. Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, C. Urbanization: Processes and driving forces. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobierski, T. Harvard Business School. Available online: https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/globalization-effects-on-environment (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Ebele, A.J.; Abou-Elwafa Abdallah, M.; Harrad, S. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the freshwater aquatic environment. Emerg. Contam. 2017, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, A.; Meric, S.; Fatta, D. Occurrence patterns of pharmaceuticals in water and wastewater environments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embrandiri, A.; Kiyasudeen, S.K.; Rupani, P.F.; Ibrahim, M.H. Environmental Xenobiotics and Its Effects on Natural Ecosystem. In Plant Responses to Xenobiotics; Singh, A., Prasad, S., Singh, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. Biodegradation of xenobiotics–A way for environmental detoxification. Int. J. Dev. Res. 2017, 7, 14082–14087. [Google Scholar]
- Roccaro, P.; Sgroi, M.; Vagliasindi, F.G.A. Removal of xenobiotic compounds from wastewater for environment protection: Treatment processes and costs. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 32, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrity, D.W.; Benotti, M.J.; Reckhow, D.A.; Snyder, S.A. Pharmaceuticals and Endocrine-Disrupting Compounds in Drinking Water. In Biophysico-Chemical Processes of Anthropogenic Organic Compounds in Environmental Systems; Xing, B., Sensei, N., Huang, P.M., Eds.; 2011; Chapter 9; pp. 233–249. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9780470944479.ch9 (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Pedersen, J.A.; Yeager, M.A.; Suffet, I.H. Xenobiotic Organic Compounds in Runoff from Fields Irrigated with Treated Wastewater. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthigadevi, G.; Manikandan, S.; Karmegam, N.; Subbaiya, R.; Chozhavendhan, S.; Ravindran, B.; Chang, S.W.; Awasthi, M.K. Chemico-nanotreatment methods for the removal of persistent organic pollutants and xenobiotics in water—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 324, 124678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.; Frihling, B.E.F.; Velasques, J.; Filho, F.J.C.M.; Cavalheri, P.S.; Migliolo, L. Pharmaceuticals residues and xenobiotics contaminants: Occurrence, analytical techniques and sustainable alternatives for wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabet-Giraud, V.; Miège, C.; Choubert, J.M.; Ruel, S.M.; Coquery, M. Occurrence and removal of estrogens and beta blockers by various processes in wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4257–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieno, N.; Tuhkanen, T.; Kronberg, L. Elimination of pharmaceuticals in sewage treatment plants in Finland. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clara, M.; Strenn, B.; Gans, O.; Martinez, E.; Kreuzinger, N.; Kroiss, H. Removal of selected pharmaceuticals, fragrances and endocrine disrupting compounds in a membrane bioreactor and conventional wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4797–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Z.; Tang, Q.; Wu, M.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L.; Qu, Y. Performance and microbial community analysis of bioaugmented activated sludge for nitrogen-containing organic pollutants removal. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xiang, F.; Zhao, L.; Qiao, Z. Activated sludge microbial community and treatment performance of wastewater treatment plants in industrial and municipal zones. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.Y.C.; Yu, T.H.; Lateef, S.K. Removal of pharmaceuticals in secondary wastewater treatment processes in Taiwan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eur-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/homepage.html (accessed on 5 June 2021).
- European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en (accessed on 5 June 2021).
- Loos, R.; Carvalho, R.; Antonio, D.C.; Comero, S.; Locoro, G.; Tavazzi, S.; Paracchini, B.; Ghiani, M.; Lettieri, T.; Blaha, L.; et al. EU-wide monitoring survey on emerging polar organic contaminants in wastewater treatment plant effluents. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6475–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucek, P. Xenobiotics. In Encyclopedia of Cancer; Schwab, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Chopra, S. Xenobiotic Compounds in the Environment: Their Fate, Transport and Removal. In Proceedings of the 3rd National Conference on Medical Instrumentation, Biomaterials and Signal Processing (NCMBS-20), Sonepat, India, 26–27 February 2020; pp. 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, B.B.; Singh, H.; Biju, V.G.; Krishnamurthy, N.B. Classification, source, and effect of environmental pollutants and their biodegradation. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2017, 36, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noman, E.A.; Al-Gheethi, A.A.S.; Talip, B.A.; Radin Mohamed, R.M.S.; Nagao, H.; Mohd Kassim, A.H. Xenobiotic Organic Compounds in Greywater and Environmental Health Impacts. In Management of Greywater in Developing Countries; Radin Mohamed, R.M.S., Al-Gheethi, A.A.S., Mohd Kassim, A.H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 87, pp. 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO (World Helath Organization). Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/15-03-2016-an-estimated-12-6-million-deaths-each-year-are-attributable-to-unhealthy-environments (accessed on 3 June 2021).
- Narvaez, J.F.V.; Jimenez, C.C. Pharmaceutical Products in the Environment: Sources, Effects and Risks. Vitae 2012, 19, 93–108. [Google Scholar]
- Massanyi, P.; Lukac, N.; Massanyi, M.; Massanyi, P.; Stawarz, R.; Formicki, G.; Danko, J. Effects of Xenobiotics on Animal Reproduction in Vivo: Microscopical Examination. Microsc. Microanal. 2020, 26, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Boye, A.; Body-Malapel, M.; Herkovits, J. The Toxic Effects of Xenobiotics on the Health of Humans and Animals. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 4627872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluth, T.B.; Zanini, L.A.G.; Battisti, I.D.E. Pesticide exposure and cancer: An integrative literature review. Saúde Debate 2019, 43, 906–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, K.M.; Christy, J.M.; Cauvi, D.M.; Kono, D.H. Environmental Xenobiotic Exposure and Autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 10, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabrodskii, P.F. The Mechanisms of Formation of Immunodeficiency’s, Autoimmune Reactions and Hypersensitivity under the Influence of Xenobiotics. J. Immunol. Allergy 2020, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gaya, B.; Lopez-Herguedas, N.; Santamaria, A.; Mijangos, F.; Etxebarria, N.; Olivares, M.; Prieto, A.; Zuloaga, O. Suspect screening workflow comparison for the analysis of organic xenobiotics in environmental water samples. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzimski, T.; Sherma, J. Determination of Targe Xenobiotics and Unknown Compound Residues in Food, Environmental, and Biological Samples; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Policarpo Tonelli, F.C.; Policarpo Tonelli, F.M. Concerns and Threats of Xenobiotics on Aquatic Ecosystems. In Bioremediation and Biotechnology; Bhat, R.A., Hakeem, K.R., Saud Al-Saud, N.B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 3, pp. 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.; Lee, D.; Cho, H.-K.; Choi, S.-D. Review of the QuEChERS method for the analysis of organic pollutants: Persistent organic pollutants, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and pharmaceuticals. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 22, e00063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Kumar Kailasa, S.; Soo Lee, S.; Rascón, A.J.; Ballesteros, E.; Zhang, M.; Kim, K.H. Review of nanomaterials as sorbents in solid-phase extraction for environmental samples. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2018, 108, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashgari, M.; Singh, V.; Pawliszyn, J. A critical review on regulatory sample preparation methods: Validating solid-phase microextraction techniques. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2019, 119, 115618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, F.; Sandra, P. Stir bar sorptive extraction for trace analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1152, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.A.; Arain, M.B.; Yamini, Y.; Shah, N.; Kazi, T.G.; Pedersen-Bjergaard, S.; Tajik, M. Hollow fiber-based liquid phase microextraction followed by analytical instrumental techniques for quantitative analysis of heavy metal ions and pharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Grześkowiak, T. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2011, 30, 1382–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errekatxo, A.; Prieto, A.; Zuloaga, O.; Usobiaga, A.; Etxebarria, N.; Fernández, L.A. Simultaneous extraction of several persistent organic pollutants in sediment using focused ultrasonic solid-liquid extraction. Anal. Bioanal Chem. 2008, 392, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Moral, M.P.; Tena, M.T. Focused ultrasound solid–liquid extraction and selective pressurised liquid extraction to determine bisphenol A and alkylphenols in sewage sludge by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oros, G.; Cserháti, T.; Szőgyi, M. Chromatography of xenobiotics in biological and environmental matrices. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2012, 1, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, A.; Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Castaldo, L.; Izzo, L.; Ritieni, A. Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Quadrupole Orbitrap High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry for Multi-Residue Analysis of Mycotoxins and Pesticides in Botanical Nutraceuticals. Toxins 2020, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaria, G.; Calisto, V.; Otero, M.; Esteves, V.I. Monitoring pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)—A practical overview. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 3983–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, A.; Himmelsbach, M.; Zhu, Q.Z.; Frey, S.; Sengl, M.; Buchberger, W.; Niessner, R.; Knopp, D. Residue analysis of the pharmaceutical diclofenac in different water types using ELISA and GC-MS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3422–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estévez-Alberola, M.-C.; Marco, M.-P. Immunochemical determination of xenobiotics with endocreine disrupting effects. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mohamed, H.M. Sensors and Biosensors for Environment Contaminants. In Nanosensor Technology for Environmental Monitoring; Inamuddin, Asiri, A.M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, D.W.; LeBlanc, G.; Meschievitz, M.E.; Cliffel, D.E. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 685–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, A.; Oestreicher, V.; Perullini, M.; Bilmes, S.A.; Jobbágy, M.; Dulhoste, S.; Bayard, R.; Durrieu, C. Optimization of sensors based on encapsulated algae for pesticide detection in water. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 6193–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kim, H.; Kang, Y.; Lee, Y.; Yoon, Y. A biosensor platform for metal detection based on enhanced green fluorescent protein. Sensors 2019, 19, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliorini, F.L.; Sanfelice, R.C.; Mercante, L.A.; Facure, M.H.M.; Correa, D.S. Electrochemical sensor based on polyamide 6/polypyrrole electrospun nanofibers coated with reduced graphene oxide for malathion pesticide detection. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarante, A.M.; Oliveira, G.S.; Bueno, C.C.; Cunha, R.A.; Ierich, J.C.M.; Freitas, L.C.G.; Franca, E.F.; Oliveira, O.N., Jr.; Leite, F.L. Modeling the coverage of an AFM tip by enzymes and its application in nanobiosensors. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2014, 53, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, A.; Saraf, M.; Neha; Bharadwaj, S.K.; Sharma, A.L. Styrene Sulphonic Acid Doped Polyaniline Based Immunosensor for Highly Sensitive Impedimetric Sensing of Atrazine. Electrochim. Acta. 2014, 146, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Lin, Z.; Pang, S.; Zhang, W.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Recent Advanced Technologies for the Characterization of Xenobiotic-Degrading Microorganisms and Microbial Communities. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuerda-Correa, E.M.; Alexandre-Franco, M.F.; Fernández-González, C. Advanced oxidation processes for the removal of antibiotics from water. An overview. Water 2019, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Gangola, S.; Khati, P.; Kumar, G. Removal of Xenobiotics from environment using microbial metabolism. Sci. India Magzine 2017, 5, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathon, B.; Coquery, M.; Miege, C.; Penru, Y.; Choubert, J.M. Removal efficiencies and kinetic rate constants of xenobiotics by ozonation in tertiary treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2737–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özengin, N.; Elmaci, A. Removal of pharmaceutical products in a constructed wetland. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 14, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordio, A.V.; Carvalho, A.J.P. Organic xenobiotics removal in constructed wetlands, with emphasis on the importance of the support matrix. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 252–253, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahar, A.; Choubert, J.M.; Coquery, M. Xenobiotics removal by adsorption in the context of tertiary treatment: A mini review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5085–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapeshi, E.; Achilleos, A.; Vasquez, M.I.; Michael, C.; Xekoukoulotakis, N.P.; Mantzavinos, D.; Kassinos, D. Drugs degrading photocatalytically: Kinetics and mechanisms of ofloxacin and atenolol removal on titania suspensions. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timbrell, J.A.; Marrs, T.C. Biotransformation of Xenobiotics. In General, Applied and System Toxicology; Ballantyne, B., Marrs, T.C., Syversen, T., Casciano, D.A., Shau, S.C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsha, Y.M.; Deepthi, N.; Chenna, S. An Enphasis on Xenobiotic Degradation in Environmental Clean up. J. Bioremediat. Biodegrad. 2011, 2011, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornik, T.; Vozic, A.; Heath, E.; Trontelj, J.; Roskar, R.; Zigon, D.; Vione, D.; Kosjek, T. Determination and photodegradation of sertraline residues in aqueous environment. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 256, 113431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadzala-Kopciuch, R.M.; Berecka, B.; Bartoszewicz, J.; Buszewski, B. Some Considerations about Bioindicators in Environmental Monitoring. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2004, 13, 453–462. [Google Scholar]
- Bharadwaj, A. Bioremediation of Xenobiotics: An Eco-friendly Cleanup Approach. In Green Chemistry in Environmental Sustainability and Chemical Education, Proceedings of the ICGC 2016, New Delhi, India, 17–18 November 2016; Parmar, V.S., Malhotra, P., Mathur, D., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís-González, C.J.; Loza-Tavera, H. Alicycliphilus: Current knowledge and potential for bioremediation of xenobiotics. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1643–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Chen, X.; Tao, G.; Kekred, K. Fate of endocrine disrupting compounds in membrane bioreactor systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4097–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Hu, J.; Ong, S.L. Influence of dissolved organic matter on estrone removal by NF membranes and the role of their structures. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3077–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
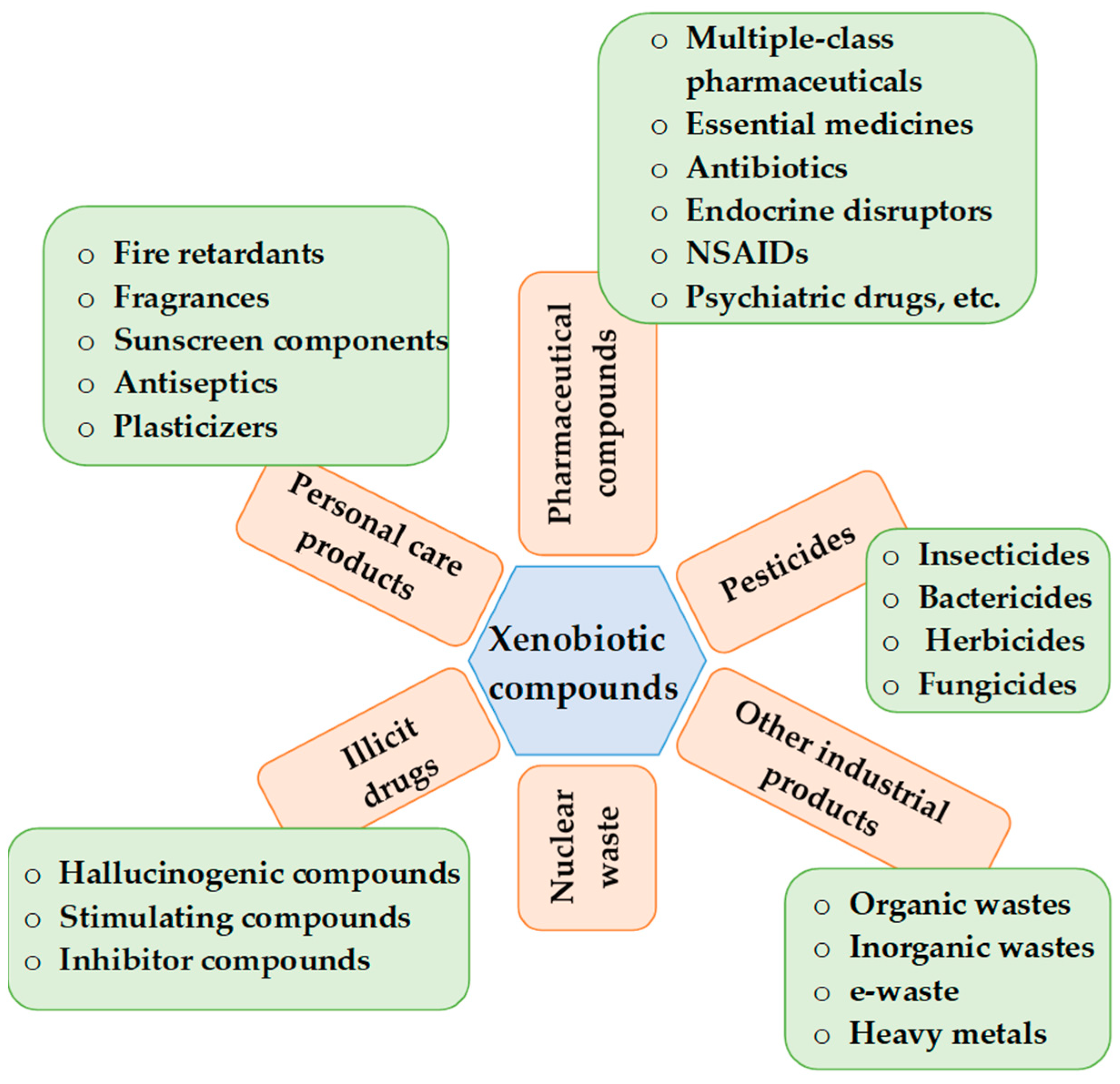
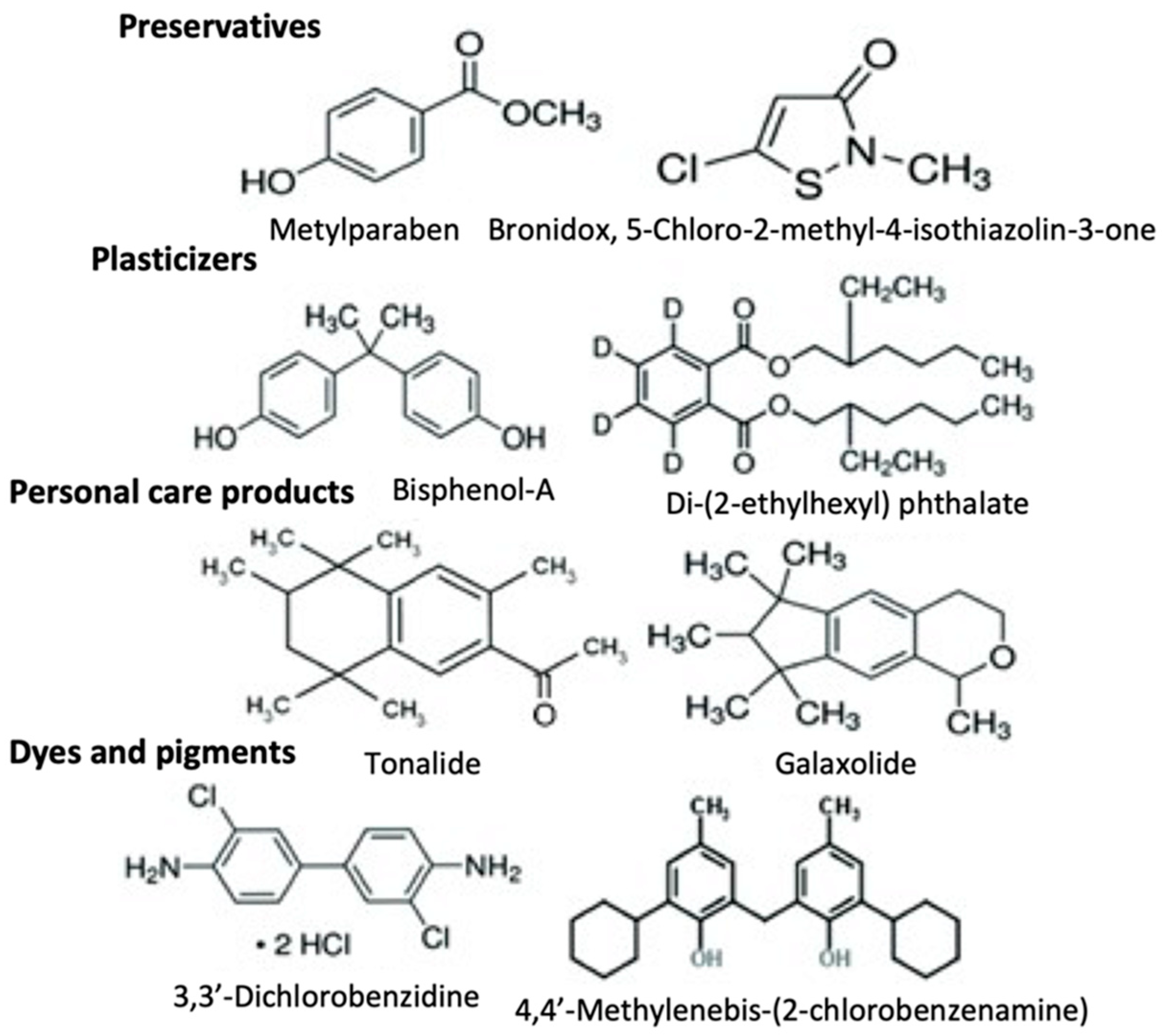
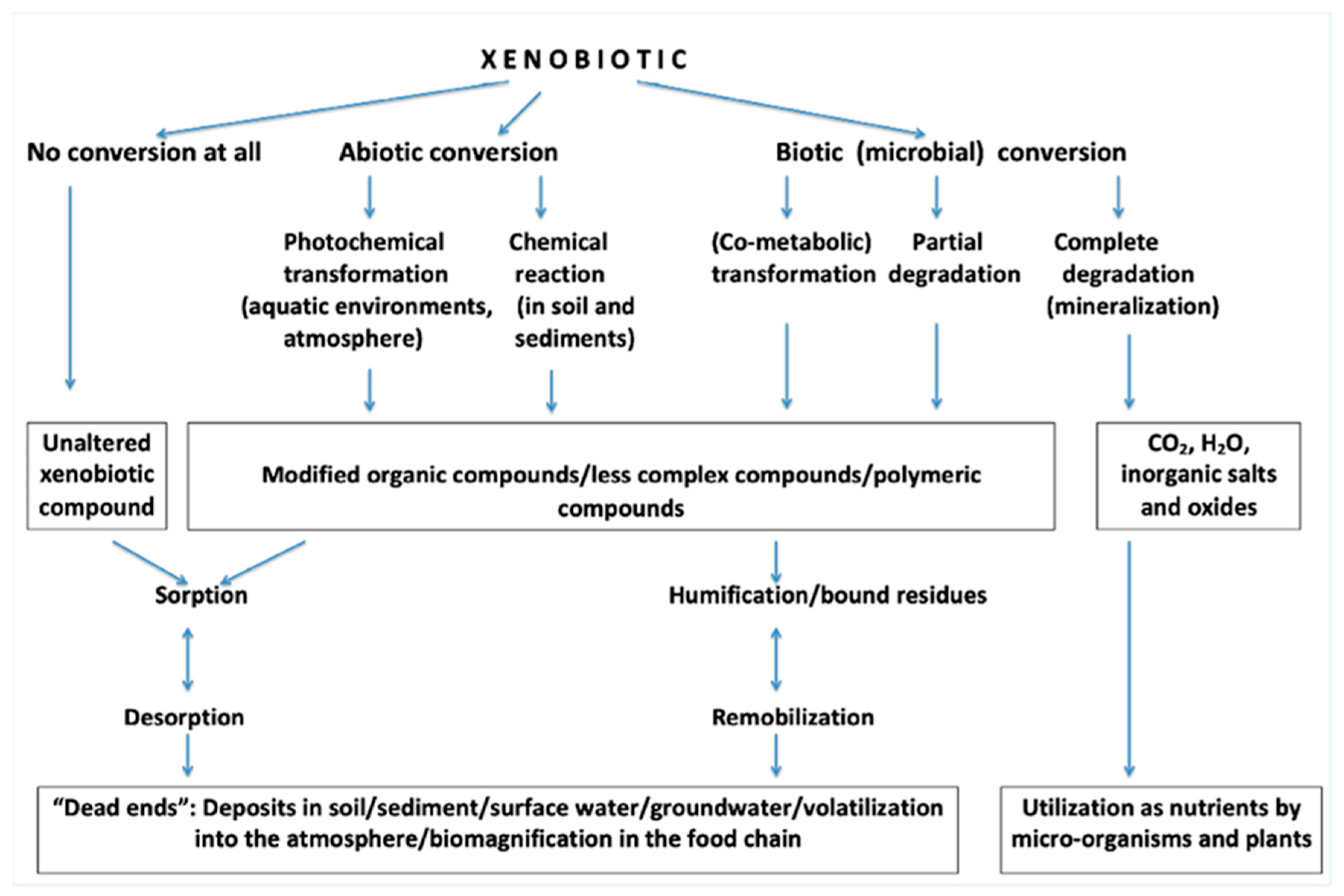
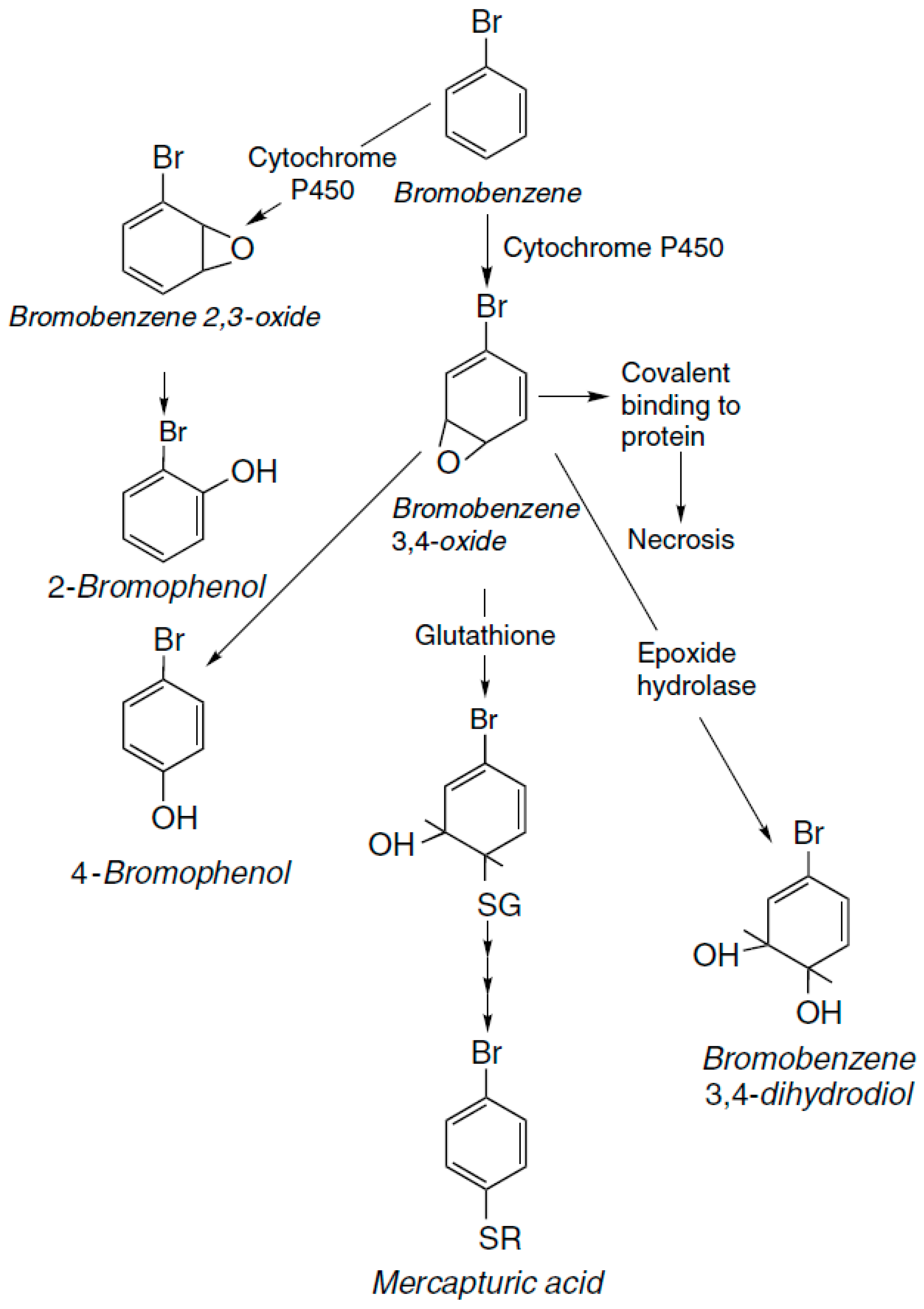
| Classification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Xenobiotic Substances | Xenobiotic Sources | ||
| characteristics | classification | example | Direct sources: pharma industries (phenols), petroleum effluent (hydrocarbons), plastics, paints, dyes, pesticides, insecticides, paper and pulp effluent Indirect sources: hospital discharge, pesticides or herbicide residues Product and processes: product of reaction of any processes–domestic or industrial scale Deliberate and accidental causes: chemicals used in paper and pulp industries; released into the environment due to accidents Moving and stationary: cars and industries Regulated and unregulated: large industries and automobiles household activity |
| nature | Natural | Bacteriotoxins, zootoxins, phytotoxins, serotonin | |
| Synthetic | Man-made substances, pesticides | ||
| uses | Active | Pesticides, dyes, paints | |
| Passive | Additives, carrier molecules | ||
| physical state | Gaseous | Benzene, aerosol form | |
| Dust-form | Asbestos powder | ||
| Liquid | Chemicals dissolved in water | ||
| pathophysiological effects | Tissue/organs | Kidney toxins | |
| Biochemical mechanism | Methemoglobin producing toxins | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Štefanac, T.; Grgas, D.; Landeka Dragičević, T. Xenobiotics—Division and Methods of Detection: A Review. J. Xenobiot. 2021, 11, 130-141. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox11040009
Štefanac T, Grgas D, Landeka Dragičević T. Xenobiotics—Division and Methods of Detection: A Review. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2021; 11(4):130-141. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox11040009
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠtefanac, Tea, Dijana Grgas, and Tibela Landeka Dragičević. 2021. "Xenobiotics—Division and Methods of Detection: A Review" Journal of Xenobiotics 11, no. 4: 130-141. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox11040009
APA StyleŠtefanac, T., Grgas, D., & Landeka Dragičević, T. (2021). Xenobiotics—Division and Methods of Detection: A Review. Journal of Xenobiotics, 11(4), 130-141. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox11040009






