Implementation of an Infection Prevention Care Bundle for Peripheral Intravenous Catheters (PIVCs): A Quality Improvement Study to Enhance PIVC Quality and Reduce Complications
Abstract
1. Introduction
Problem Description
2. Background
2.1. Healthcare-Associated Infections, Patient Safety, and Infection Prevention
2.2. Care Bundles
2.3. Specific Aims
2.4. Research Questions
- Prevalence of Phlebitis: What is the prevalence of phlebitis among patients with PIVCs, and does the prevalence decrease after the implementation of the care bundle?
- Predictive Factors for Phlebitis: Which factors are associated with and can predict phlebitis?
- Improvement in PIVC Dressing, IV Connection, and Documentation Quality: Has there been an improvement in the quality of the documentation, as well as the quality of the PIVC dressing and the IV connection, following the implementation of the care bundle?
- Comparison of PIVC-miniQ Scores: Is there a difference in the PIVC-miniQ sum score when comparing closed integrated PIVCs to ported PIVCs?
- Change in PIVC-miniQ Sum Score: Does the PIVC-miniQ sum score decrease after the implementation of the care bundle?
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Design
3.2. Quality Improvement
3.3. Sample
3.4. Setting
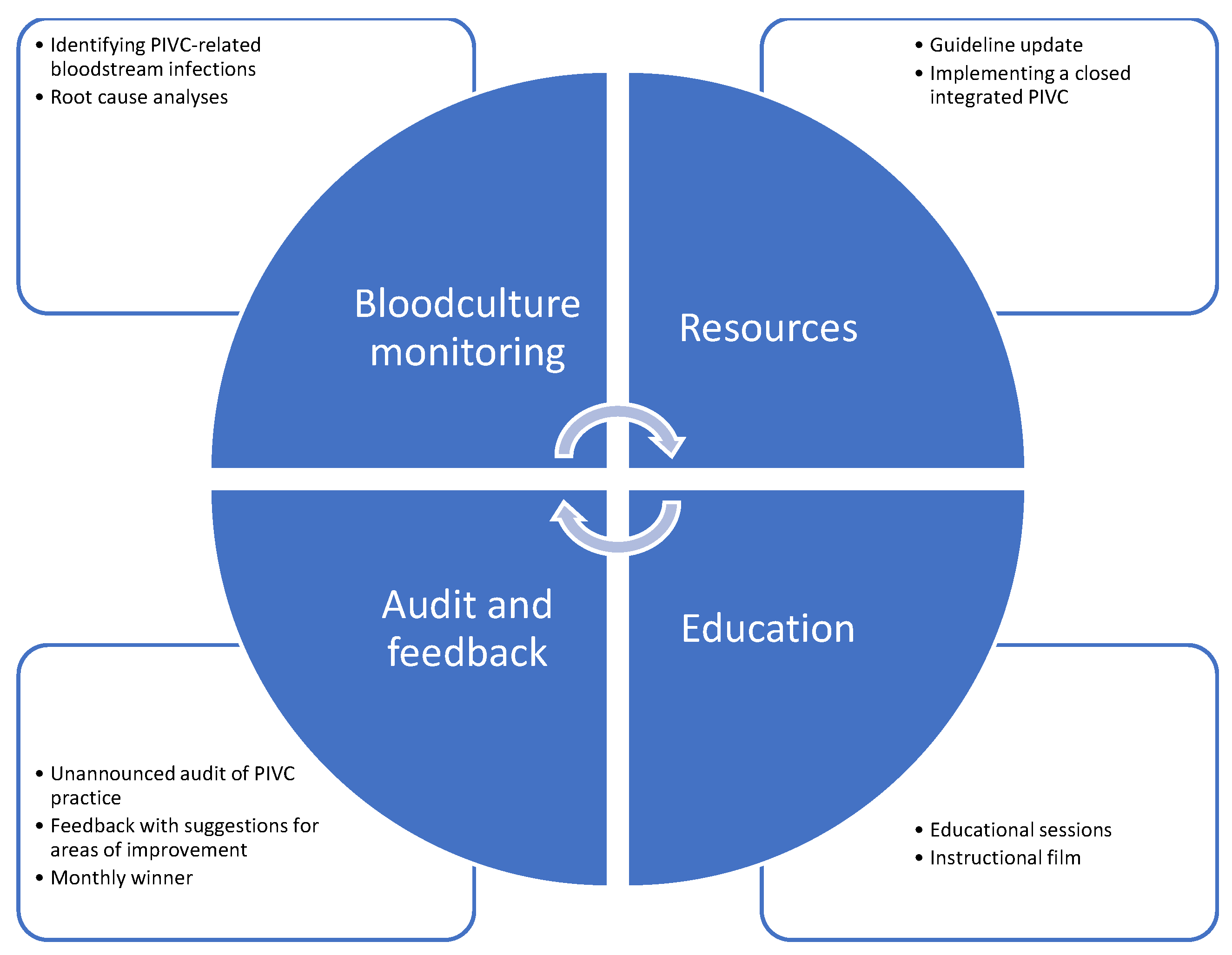
3.5. Care Bundle Interventions
3.6. Data Collection
3.7. Included Audit Tool and Variables
3.8. Statistical Analyses
3.9. Ethical Considerations
4. Results
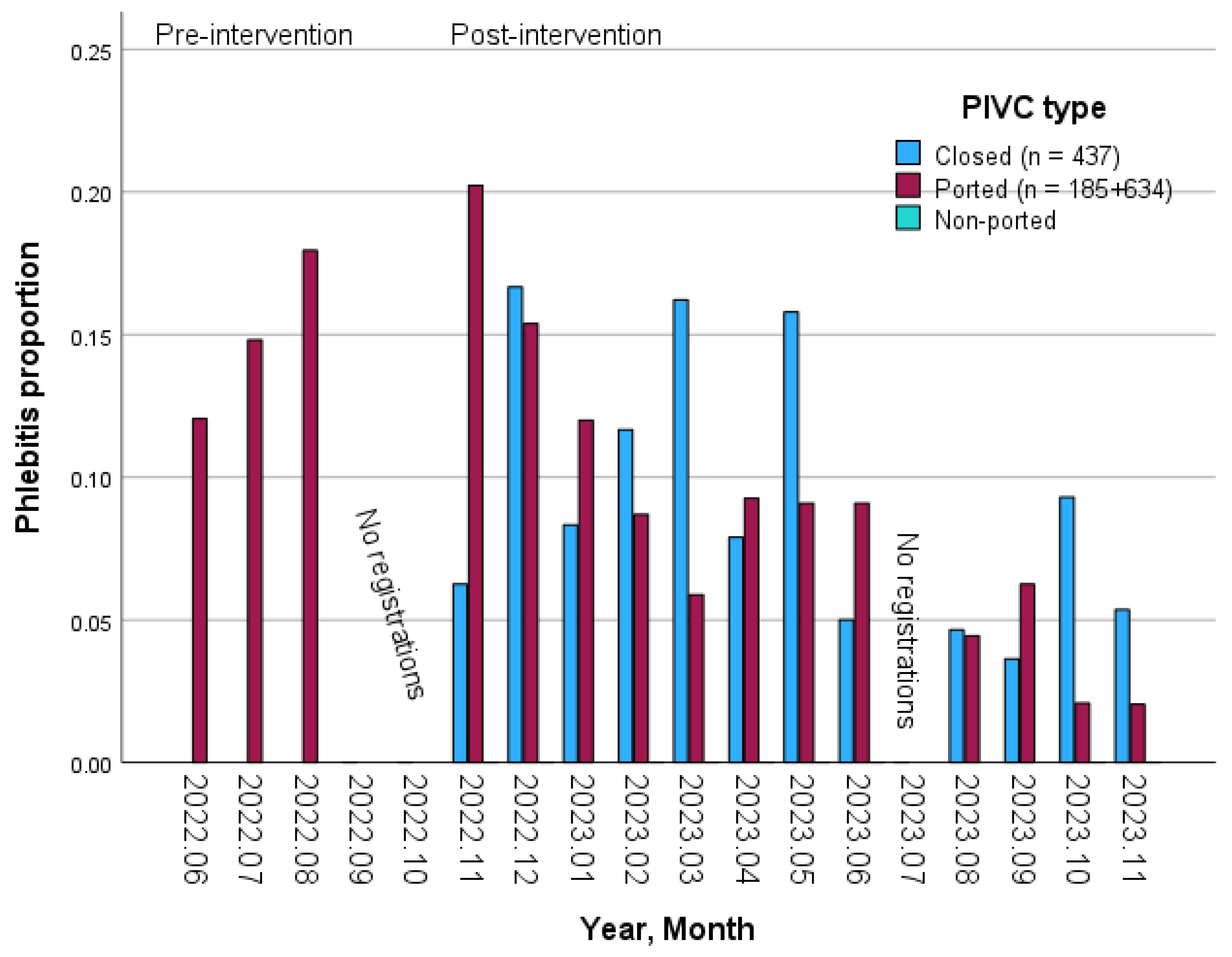
4.1. Prevalence of Phlebitis
4.2. Predictors of Phlebitis
4.3. Quality of the PIVC Dressing and IV Connection and the Documentation
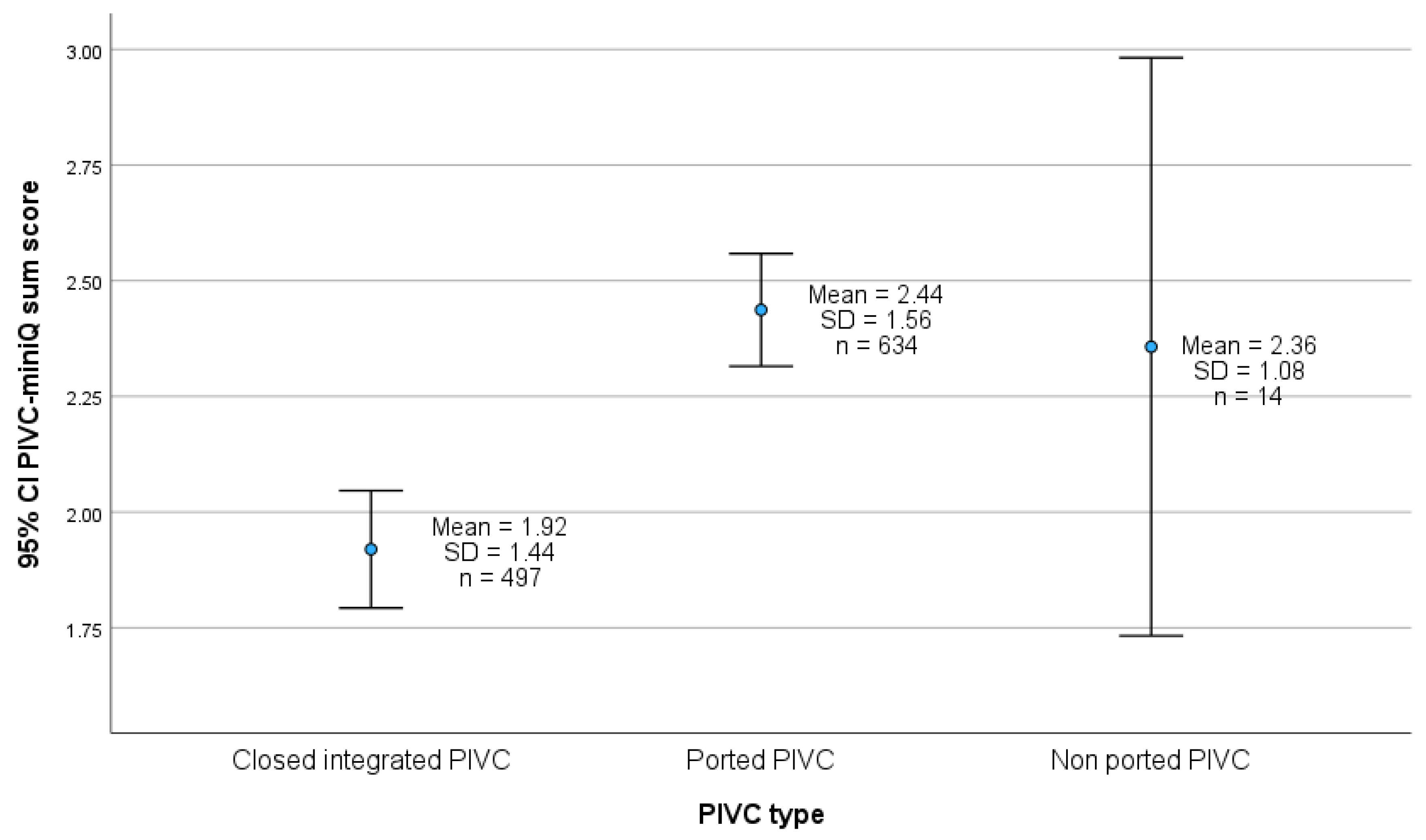
4.4. PIVC Type and PIVC-miniQ Sum Score
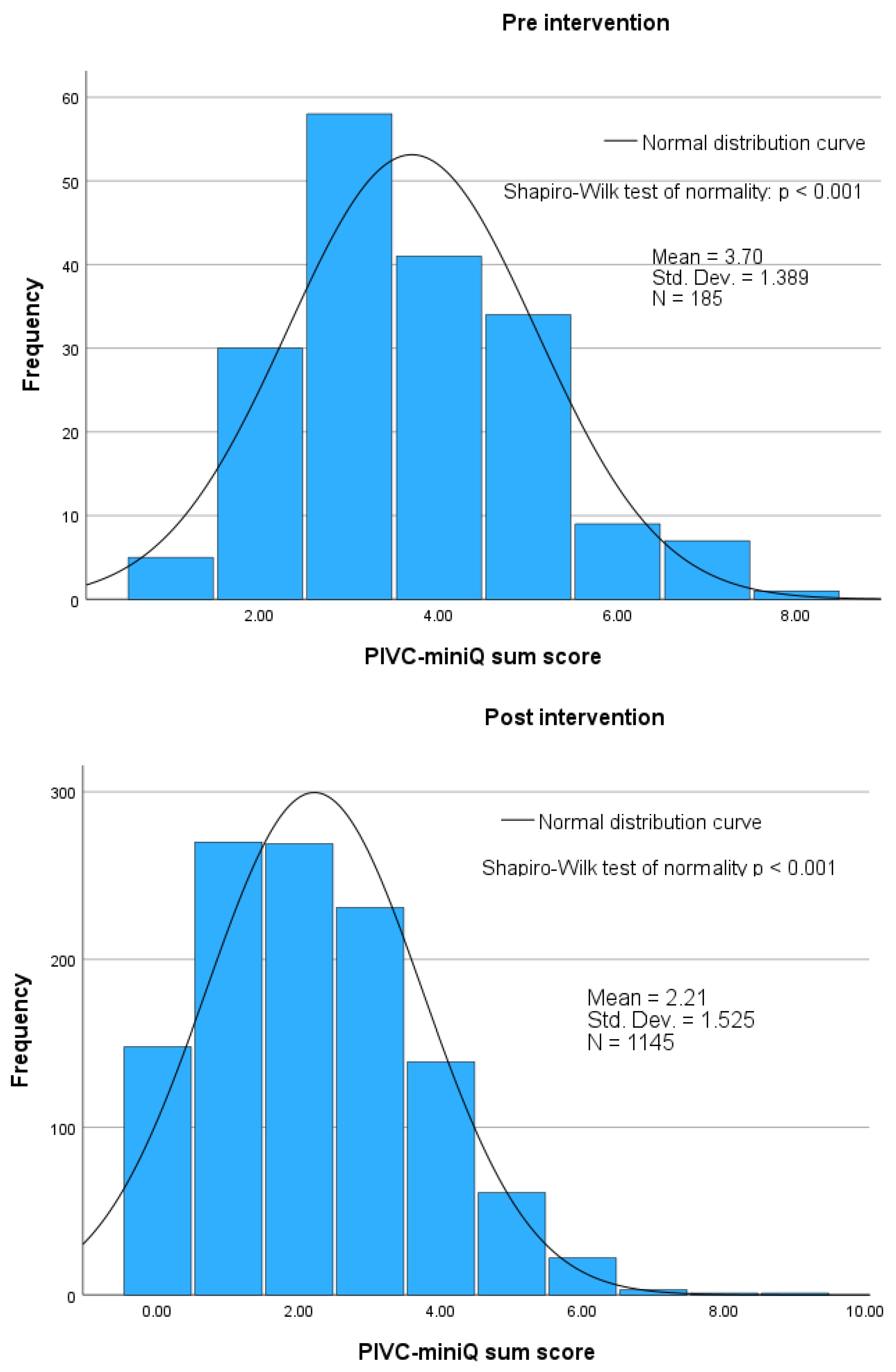
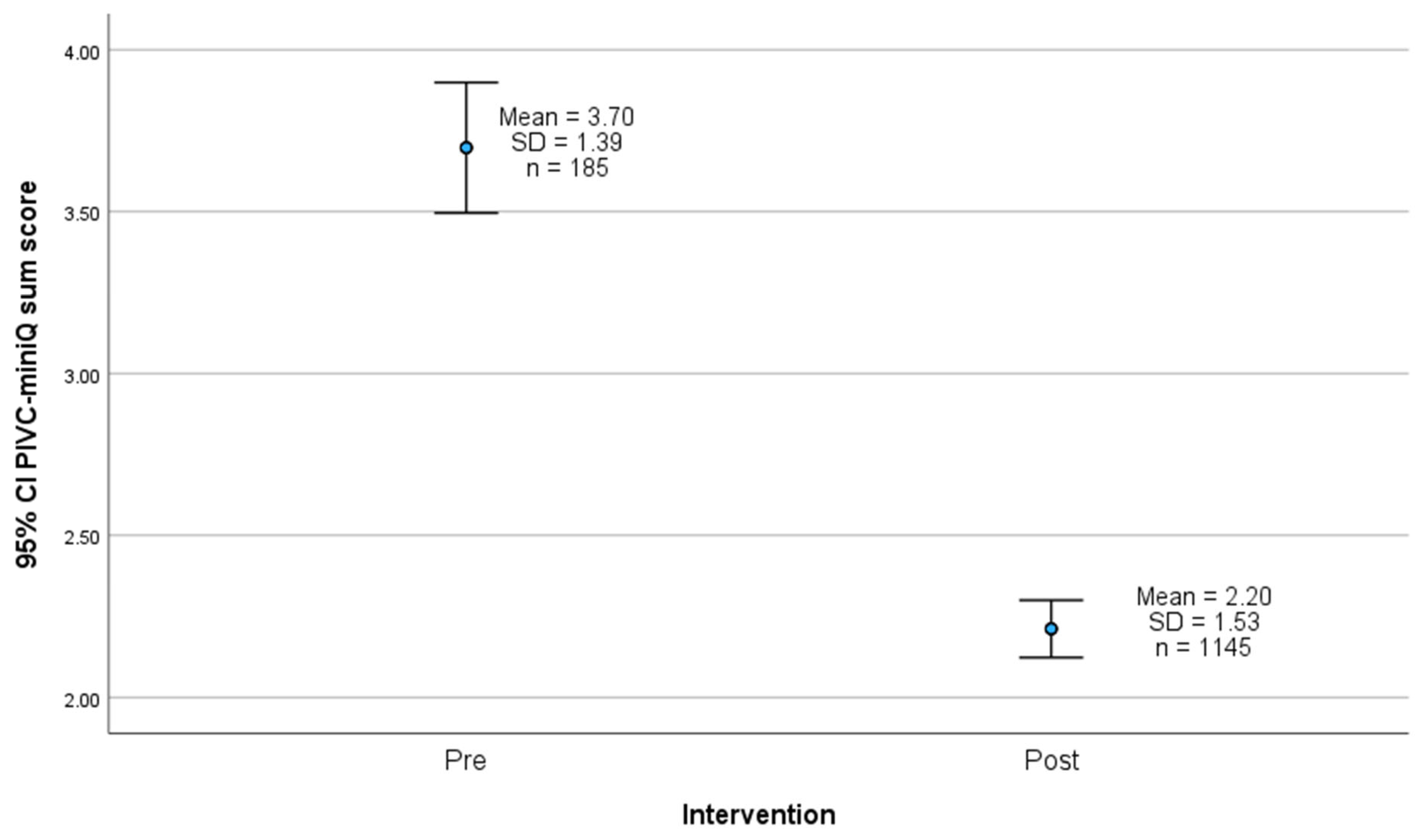
4.5. PIVC-miniQ Sum Score
5. Discussion
5.1. Prevalence of Signs and Symptoms of Phlebitis
5.2. Predictors of Phlebitis
5.3. Quality of the PIVC Dressing and IV Connection and Documentation
5.4. PIVC-miniQ Sum Score
5.5. Implications for Practice
6. Strengths and Limitations
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Public Involvement Statement
Guidelines and Standards Statement
Use of Artificial Intelligence
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PIVC | Peripheral Intravenous Catheter |
| IV | Intravenous |
| BSI | Bloodstream Infection |
| S. aureus | Staphylococcus aureus |
| HAI | Healthcare-Associated Infection |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| PIVC-miniQ | The Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Mini-Questionnaire |
| NIPH | Norwegian Institute of Public Health |
| SQUIRE 2.0 | Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence 2.0 |
| ICC | Intraclass Correlation Coefficient |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| REK | The Regional Committee for Medical and Health Research Ethics |
| G | Gauge |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| EMS | Emergency Medical Services |
| RR | Risk Ratio |
| PIVC mm | Peripheral Intravenous Catheter millimeters |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CC | Cannot Be Calculated |
| i.e. | That Is |
References
- Mermel, L.A. Short-Term Peripheral Venous Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infections: A Systematic Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray-Barruel, G.; Polit, D.F.; Murfield, J.E.; Rickard, C.M. Infusion Phlebitis Assessment Measures: A Systematic Review. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2014, 20, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, R.; Gavin, N.C.; Marsh, N.; Marquart-Wilson, L.; Keogh, S. Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Material and Design to Reduce Device Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Infect. Dis. Health 2023, 28, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittiruti, M.; Van Boxtel, T.; Scoppettuolo, G.; Carr, P.; Konstantinou, E.; Ortiz Miluy, G.; Lamperti, M.; Goossens, G.A.; Simcock, L.; Dupont, C.; et al. European Recommendations on the Proper Indication and Use of Peripheral Venous Access Devices (the ERPIUP Consensus): A WoCoVA Project. J. Vasc. Access 2023, 24, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Prevention of Bloodstream Infections and Other Infections Associated with the Use of Intravascular Catheters: Part 1: Peripheral Catheters. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240093829 (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Gabriel, J. Vascular Access Devices: Securement and Dressings. Nurs. Stand. 2010, 24, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, N.; Webster, J.; Mihala, G.; Rickard, C.M. Devices and Dressings to Secure Peripheral Venous Catheters to Prevent Complications. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD011070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrou, E.; Ray-Barruel, G.; Carr, P.J.; Frost, S.A.; Inwood, S.; Higgins, N.; Lin, F.; Alberto, L.; Mermel, L.; Rickard, C.M.; et al. Use of Short Peripheral Intravenous Catheters: Characteristics, Management, and Outcomes Worldwide. J. Hosp. Med. 2018, 13, E1–E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrou, E.; Ray-Barruel, G.; Carr, P.J.; Frost, S.; Inwood, S.; Higgins, N.; Lin, F.; Alberto, L.; Mermel, L.; Rickard, C.M. International Prevalence of the Use of Peripheral Intravenous Catheters. J. Hosp. Med. 2015, 10, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høvik, L.H.; Gjeilo, K.H.; Ray-Barruel, G.; Lydersen, S.; Børseth, A.W.; Gustad, L.T. Aligning Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Quality with Nursing Culture-A Mixed Method Study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2024, 33, 2593–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guembe, M.; Pérez-Granda, M.J.; Capdevila, J.A.; Barberán, J.; Pinilla, B.; Martín-Rabadán, P.; Bouza, E.; NUVE Study Group. Nationwide Study on Peripheral-Venous-Catheter-Associated-Bloodstream Infections in Internal Medicine Departments. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017, 97, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Doubrovsky, A.; Rickard, C.M.; Rockliff, L.; Tang, C.; Ullman, A.J. Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Care at Australian Emergency Departments: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. J. Adv. Nurs. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, B.; Gorski, L.; Kleidon, T.; Kyes, A.; Devries, M.; Keogh, S.; Meyer, B.; Sarver, M.J.; Crickman, R.; Ong, J.; et al. Infusion Therapy Standards of Practice, 9th Edition. J. Infus. Nurs. 2024, 47 (Suppl. S1), S1–S285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, N.; Webster, J.; Ullman, A.J.; Mihala, G.; Cooke, M.; Chopra, V.; Rickard, C.M. Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Non-infectious Complications in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 2020, 76, 3346–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, V. Catheter-Related Upper Extremity Venous Thrombosis in Adults. In UpToDate; Wolters Kluwer: Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zingg, W.; Pittet, D. Peripheral Venous Catheters: An under-Evaluated Problem. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, S38–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guanche-Sicilia, A.; Sánchez-Gómez, M.B.; Castro-Peraza, M.E.; Rodríguez-Gómez, J.Á.; Gómez-Salgado, J.; Duarte-Clíments, G. Prevention and Treatment of Phlebitis Secondary to the Insertion of a Peripheral Venous Catheter: A Scoping Review from a Nursing Perspective. Healthcare 2021, 9, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjade, T. Medisinsk mikrobiologi og infeksjonssykdommer; 4. utg.; Fagbokforl: Bergen, Norway, 2013; ISBN 978-82-450-1497-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, A.; Nakamura, I.; Fujita, H.; Tsukimori, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Fukushima, S.; Fujii, T.; Matsumoto, T. Peripheral Venous Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection Is Associated with Severe Complications and Potential Death: A Retrospective Observational Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, P.; Hornero, A.; Cuervo, G.; Grau, I.; Jimenez, E.; Berbel, D.; Martos, P.; Verge, J.M.; Tebe, C.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.M.; et al. Interventions to Decrease Short-Term Peripheral Venous Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infections: Impact on Incidence and Mortality. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 100, e178–e186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freixas, N.; Bella, F.; Limón, E.; Pujol, M.; Almirante, B.; Gudiol, F. Impact of a Multimodal Intervention to Reduce Bloodstream Infections Related to Vascular Catheters in Non-ICU Wards: A Multicentre Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, R.L.; Cameron, D.R.M.; Scott, C.; Kotsanas, D.; Grayson, M.L.; Korman, T.M.; Gillespie, E.E.; Johnson, P.D.R. Peripheral Intravenous Catheter-Associated Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteraemia: More than 5 Years of Prospective Data from Two Tertiary Health Services. Med. J. Aust. 2013, 198, 551–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.T.; Chan, P.A.; Edwards, O.; Hollenbeck, B.; Huang, B.; Burdick, N.; Jefferson, J.A.; Mermel, L.A. Peripheral Venous Catheter-Related Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteremia. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2011, 32, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwegian Institute of Public Health. Forebygging av Infeksjoner ved bruk av Intravaskulære Katetre. Available online: https://www.fhi.no/sm/smittevern-i-helsetjenesten/veileder-intravaskulare-katetre/ (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Hadaway, L. Short Peripheral Intravenous Catheters and Infections. J. Infus. Nurs. 2012, 35, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Healthcare-Associated Infections. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/healthcare-associated-infections (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- World Health Organization. The Burden of Health Care-Associated Infection Worldwide. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/the-burden-of-health-care-associated-infection-worldwide (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Statistisk Sentralbyrå. Pasienter på Sykehus. Available online: https://www.ssb.no/helse/helsetjenester/statistikk/pasienter-pa-sykehus (accessed on 18 April 2024).
- Helsedirektoratet. Sykehus—Forekomst av Helsetjenesteassosierte Infeksjoner (HAI). Available online: https://www.helsedirektoratet.no/statistikk/kvalitetsindikatorer/infeksjoner/forekomst-av-helsetjenesteassosierte-infeksjoner-i-sykehus (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Badia-Cebada, L.; Peñafiel, J.; Saliba, P.; Andrés, M.; Càmara, J.; Domenech, D.; Jiménez-Martínez, E.; Marrón, A.; Moreno, E.; Pomar, V.; et al. Trends in the Epidemiology of Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infections; towards a Paradigm Shift, Spain, 2007 to 2019. Euro Surveill 2022, 27, 2100610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasundram, S.; Tan, M.; Lim, K.Z.H.; Loh, V.M.P. Reducing the Incidence of Phlebitis in Medical Adult Inpatients with Peripheral Venous Catheter Care Bundle: A Best Practice Implementation Project. JBI Evid. Implement. 2021, 19, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hontoria-Alcoceba, R.; López-López, C.; Hontoria-Alcoceba, V.; Sánchez-Morgado, A.I. Implementation of Evidence-Based Practice in Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Care. J. Nurs. Care Qual. 2023, 38, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maura, Y.L.; Figuerola, M.L.B.; Moreno, M.J.R.; Garvi, V.L.; Felsner, E.E.S.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Almendral, A.; Limón, E.; Fuste, E. Care Bundle for the Prevention of Peripheral Venous Catheter Blood Stream Infections at a Secondary Care University Hospital: Implementation and Results. ScienceDirect 2023, 28, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray-Barruel, G.; Chopra, V.; Fulbrook, P.; Lovegrove, J.; Mihala, G.; Wishart, M.; Cooke, M.; Mitchell, M.; Rickard, C.M. The Impact of a Structured Assessment and Decision Tool (I-DECIDED®) on Improving Care of Peripheral Intravenous Catheters: A Multicenter, Interrupted Time-Series Study. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2023, 148, 104604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray-Barruel, G.; Xu, H.; Marsh, N.; Cooke, M.; Rickard, C.M. Effectiveness of Insertion and Maintenance Bundles in Preventing Peripheral Intravenous Catheter-Related Complications and Bloodstream Infection in Hospital Patients: A Systematic Review. Infect. Dis. Health 2019, 24, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, W.; Barton, A.; Bitmead, J.; Eggimann, P.; Pujol, M.; Simon, A.; Tatzel, J. Best Practice in the Use of Peripheral Venous Catheters: A Scoping Review and Expert Consensus. Infect. Prev. Pract. 2023, 5, 100271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, R.P.; Vincent, J.-L. The Surviving Sepsis Campaign Sepsis Change Bundles and Clinical Practice. Crit. Care 2005, 9, 653–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resar, R.; Griffin, F.A.; Haraden, C.; Nolan, T.W. Using Care Bundles to Improve Health Care Quality|Institute for Healthcare Improvement. Available online: https://www.ihi.org/resources/white-papers/using-care-bundles-improve-health-care-quality (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Høvik, L.H.; Gjeilo, K.H.; Lydersen, S.; Rickard, C.M.; Røtvold, B.; Damås, J.K.; Solligård, E.; Gustad, L.T. Monitoring Quality of Care for Peripheral Intravenous Catheters; Feasibility and Reliability of the Peripheral Intravenous Catheters Mini Questionnaire (PIVC-miniQ). BMC Health Serv. Res. 2019, 19, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brørs, G.; Gjeilo, K.H.; Lund, T.; Skevik, K.; Aa, E.; Høvik, L.H.; Skarsvaag, T.; Mjølstad, O.C. Amiodarone-Induced Phlebitis: Incidence and Adherence to a Clinical Practice Guideline. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2023, 22, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, N.T.; Linh, T.T.K.; Høvik, L.H. The preliminary approach to bundle insertion and maintenance in preventing peripheral intravenous catheter-related complications. J. Nurs. Sci. 2021, 4, 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Shaker, N. Monitoring Peripheral Intravenous Catheters Complications in Pediatric Patients in Erbil City/Iraq. Erbil J. Nurs. Midwifery 2023, 5, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Vieler, J.; Haug, N.J.; Afset, J.E.; Høvik, L.H.; Lydersen, S.; Gustad, L.T. Quality of Care for Peripheral Intravenous Catheters (PIVCs) in Nepal: A Cross-Sectional Study on Feasibility and Inter-Rater Agreement of the Peripheral Intravenous Catheters-Mini Questionnaire (PIVC-miniQ) in a Tertiary Care Hospital. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e048370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helland, E.L.; Høvik, L.H.; Gustad, L.T.; Gjeilo, K.H. COVID-19 og håndtering og stell av perifere venekatetre. Sykepleien 2024, 19, e-95645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polit, D.F.; Beck, C.T. Nursing Research: Generating and Assessing Evidence for Nursing Practice, 11th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-975154-14-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ogrinc, G.; Davies, L.; Goodman, D.; Batalden, P.; Davidoff, F.; Stevens, D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): Revised Publication Guidelines from a Detailed Consensus Process. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2016, 25, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Norwegian Electronic Health Library. Kvalitetsforbedring. Available online: https://www.helsebiblioteket.no/innhold/artikler/kvalitetsforbedring/kvalitetsforbedring (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Batalden, P.B.; Davidoff, F. What Is “Quality Improvement” and How Can It Transform Healthcare? BMJ Qual. Saf. 2007, 16, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, G.J.; Moen, R.D.; Nolan, K.M.; Nolan, T.W.; Norman, C.L.; Provost, L.P. The Improvement Guide; John Wiley Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-1-118-08341-3. [Google Scholar]
- Endalamaw, A.; Khatri, R.B.; Mengistu, T.S.; Erku, D.; Wolka, E.; Zewdie, A.; Assefa, Y. A Scoping Review of Continuous Quality Improvement in Healthcare System: Conceptualization, Models and Tools, Barriers and Facilitators, and Impact. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2024, 24, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onia, R.; Eshun-Wilson, I.; Arce, C.; Ellis, C.; Parvu, V.; Hassman, D.; Kassler-Taub, K. Evaluation of a New Safety Peripheral IV Catheter Designed to Reduce Mucocutaneous Blood Exposure. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2011, 27, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidaro, A.; Quici, M.; Giustivi, D.; Pinelli, F.; Samartin, F.; Casella, F.; Cogliati, C.; Rizzi, G.; Salvi, E.; Bartoli, A.; et al. Integrated Short Peripheral Intravenous Cannulas and Risk of Catheter Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Vasc. Access 2025, 26, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausone-Gazda, D.; Lefaiver, C.A.; Walters, S.-A. A Randomized Controlled Trial to Compare the Complications of 2 Peripheral Intravenous Catheter-Stabilization Systems. J. Infus. Nurs. 2010, 33, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rosenroll, A. Peripheral Intravenous Catheters: Improving Outcomes Through Change in Products, Clinical Practice and Education. Vasc. Access 2017, 11, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- DeVries, M.; Valentine, M.; Mancos, P. Protected Clinical Indication of Peripheral Intravenous Lines: Successful Implementation. J. Assoc. Vasc. Access 2016, 21, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterlow, D.; Hoddinott, P.; Harrison, S. Implementing and Standardising the Use of Peripheral Vascular Access Devices. J. Clin. Nurs. 2010, 19, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González López, J.L.; Arribi Vilela, A.; Fernández del Palacio, E.; Olivares Corral, J.; Benedicto Martí, C.; Herrera Portal, P. Indwell Times, Complications and Costs of Open vs Closed Safety Peripheral Intravenous Catheters: A Randomized Study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2014, 86, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, N.; Abe, S.; Hagimoto, K.; Kondo, A.; Matsuo, A.; Ozawa, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Yokokawa, S.; Kuri, J.; Tateno, H.; et al. Unfavorable Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Replacements Can Be Reduced Using an Integrated Closed Intravenous Catheter System. J. Vasc. Access 2014, 15, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronovost, P.J.; Berenholtz, S.M.; Needham, D.M. Translating Evidence into Practice: A Model for Large Scale Knowledge Translation. BMJ 2008, 337, 963–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovdata. Helsepersonelloven Lov Om Helsepersonell m.v.; LOV-1999-07-02-64; Lovdata: Oslo, Norway, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, B.; Grunow, A.; Park, S. Improvement Science at Your Fingertips: A Resource Guide for Coaches of Improvement, 2nd ed.; Improvement Collective: San Francisco, CA, USA; ISC LLC.: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, S.A.; Harel, Z.; McQuillan, R.; Weizman, A.V.; Thomas, A.; Chertow, G.M.; Nesrallah, G.; Bell, C.M.; Chan, C.T. How to Begin a Quality Improvement Project. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microsoft Microsoft 365. Excel. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/excel (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- Hernæs, N. Laget Verktøy for å Overvåke Perifere Venekatetre. Available online: https://sykepleien.no/2020/06/laget-verktoy-overvake-perifere-venekatetre (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM SPSS Statistics. IBM SPSS Statistics. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/products/spss-statistics (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Participants. JAMA 2024, 333, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenezan, J.; Marjanovic, N.; Drugeon, B.; Neill, R.O.; Liuu, E.; Roblot, F.; Palazzo, P.; Bironneau, V.; Prevost, F.; Paul, J.; et al. Chlorhexidine plus Alcohol versus Povidone Iodine plus Alcohol, Combined or Not with Innovative Devices, for Prevention of Short-Term Peripheral Venous Catheter Infection and Failure (CLEAN 3 Study): An Investigator-Initiated, Open-Label, Single Centre, Randomised-Controlled, Two-by-Two Factorial Trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, N.; Mihala, G.; Ray-Barruel, G.; Webster, J.; Wallis, M.C.; Rickard, C.M. Inter-Rater Agreement on PIVC-Associated Phlebitis Signs, Symptoms and Scales. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2015, 21, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torné-Ruiz, A.; Sanromà-Ortiz, M.; Corral-Nuñez, A.; Medel, D.; Roca, J.; García-Expósito, J. Management from a Multidisciplinary Perspective of Phlebitis Related to Peripheral Venous Catheter Insertion: An International Delphi Study. Nurs. Open 2024, 11, e2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlan, M.d.S.; Saba, A.; Lima, A.F.C. Risk Factors Associated with the Occurrence of the Adverse Event Phlebitis in Hospitalized Adult Patients. Rev. Bras. Enferm. 2024, 77, e20240162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidetu Bayeh, T.; Yirga Birhie, A.; Mesfin Alene, E. Time to Develop Phlebitis and Its Predictors Among Patients with Peripheral Intravenous Cannula at Public Hospitals of Bahir Dar City, Amhara, Ethiopia, 2022: A Prospective Observational Study. Nurs. Res. Rev. 2023, 13, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palese, A.; Ambrosi, E.; Fabris, F.; Guarnier, A.; Barelli, P.; Zambiasi, P.; Allegrini, E.; Bazoli, L.; Casson, P.; Marin, M.; et al. Nursing Care as a Predictor of Phlebitis Related to Insertion of a Peripheral Venous Cannula in Emergency Departments: Findings from a Prospective Study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2016, 92, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.-S. A Model of Phlebitis Associated with Peripheral Intravenous Catheters in Orthopedic Inpatients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicolini, G.; Bonghi, A.P.; Di Labio, L.; Di Mascio, R. Position of Peripheral Venous Cannulae and the Incidence of Thrombophlebitis: An Observational Study. J. Adv. Nurs. 2009, 65, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, M.C.; McGrail, M.; Webster, J.; Marsh, N.; Gowardman, J.; Playford, E.G.; Rickard, C.M. Risk Factors for Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Failure: A Multivariate Analysis of Data from a Randomized Controlled Trial. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2014, 35, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drugeon, B.; Marjanovic, N.; Boisson, M.; Buetti, N.; Mimoz, O.; Guenezan, J. Insertion Site and Risk of Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Colonization and/or Local Infection: A Post Hoc Analysis of the CLEAN 3 Study Including More than 800 Catheters. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2024, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.; Winchester, K.; Principe, R.B.; Culverwell, E. Prevalence of Peripheral Intravenous Catheters and Policy Adherence: A Point Prevalence in a Tertiary Care University Hospital. J. Clin. Nurs. 2022, 31, 2324–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynak, A.; Paquet, F.; Marchionni, C.; Lok, V.; Gauthier, M.; Frati, F. Nurses’ Knowledge on Routine Care and Maintenance of Adult Vascular Access Devices: A Scoping Review. J. Clin. Nurs. 2020, 29, 3905–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, N.; Larsen, E.N.; Takashima, M.; Kleidon, T.; Keogh, S.; Ullman, A.J.; Mihala, G.; Chopra, V.; Rickard, C.M. Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Failure: A Secondary Analysis of Risks from 11,830 Catheters. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2021, 124, 104095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Martínez, E.; Adamuz, J.; González-Samartino, M.; Muñoz-Carmona, M.A.; Hornero, A.; Martos-Martínez, M.P.; Membrive-Martínez, R.; Juvé-Udina, M.-E. Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Failure, Nurse Staffing Levels and Care Complexity Individual Factors: A Retrospective Multicentre Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0303152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Economic Co-Operation and Development. Patient Safety. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/topics/health.html (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Santos-Costa, P.; Paiva-Santos, F.; Sousa, L.B.; Bernardes, R.A.; Ventura, F.; Salgueiro-Oliveira, A.; Parreira, P.; Vieira, M.; Graveto, J. Evidence-Informed Development of a Bundle for Peripheral Intravenous Catheterization in Portugal: A Delphi Consensus Study. Nurs. Rep. 2022, 12, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Keogh, S.; Ullman, A.J.; Marsh, N.; Tobiano, G.; Rickard, C.M.; Clark, J.; Griffin, B. Implementation Frameworks, Strategies and Outcomes Used in Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Studies: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Nurs. 2023, 32, 6706–6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corley, A.; Ullman, A.J.; Mihala, G.; Ray-Barruel, G.; Alexandrou, E.; Rickard, C.M. Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Dressing and Securement Practice Is Associated with Site Complications and Suboptimal Dressing Integrity: A Secondary Analysis of 40,637 Catheters. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2019, 100, 103409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrescu, A.; Constantin, A.M.; Pinte, L.; Chapman, A.; Ratajczak, P.; Klerings, I.; Emprechtinger, R.; Allegranzi, B.; Zingg, W.; Grayson, M.L.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Measures to Prevent Infections and Other Complications Associated with Peripheral Intravenous Catheters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 78, 1640–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallant, J. SPSS Survival Manual: A Step by Step Guide to Data Analysis Using IBM SPSS, 7th ed.; Open University Press: London, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-0-335-24949-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rickard, C.M.; Ray-Barruel, G. Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Assessment: Beyond Phlebitis. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e402–e403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydersen, S. Statistical Review: Frequently given Comments. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammut, M.; Omarit, R.; Canning, M.; Cornford, C.; Monohan, J.; Wynne, R. Reducing Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Related Blood Stream Infections: Findings from a Quality Improvement Audit of Taskforce Strategies. Contemp. Nurse A J. Aust. Nurs. Prof. 2025, 61, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pre-Intervention (n = 185) | Post-Intervention (n = 1145) | Total (n = 1330) | Difference Pre-Post-Intervention | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Mean | (SD) | p-Value | ||||||||
| Age (years), n, mean (SD) | 185 | 71.6 | (16.8) | 1145 | 70.2 | (16.8) | 1330 | 1.5 | (1.3) | 0.266 a | |
| Gender, n (%) | 0.164 b | ||||||||||
| Female | 79 | (42.7) | 552 | (48.2) | 631 | (47.4) | |||||
| Male | 106 | (57.3) | 593 | (51.8) | 699 | (52.6) | |||||
| PIVC indwell days, n, mean (SD) | 172 | 1.88 | (1.3) | 1110 | 1.81 | (1.7) | 1282 | 0.08 | (0.1) | 0.506 a | |
| PIVC site, n (%) | 0.201 b | ||||||||||
| Hand | 38 | (20.5) | 269 | (23.5) | 307 | (23.1) | |||||
| Wrist | 11 | (5.9) | 84 | (7.3) | 95 | (7.1) | |||||
| Forearm | 86 | (46.5) | 475 | (41.5) | 561 | (42.2) | |||||
| Antecubital fossa | 39 | (21.1) | 284 | (24.8) | 323 | (24.3) | |||||
| Foot | 8 | (4.3) | 20 | (1.7) | 28 | (2.1) | |||||
| Upper arm | 3 | (1.6) | 12 | (1.0) | 15 | (1.1) | |||||
| Chest | 0 | (0.0) | 1 | (0.1) | 1 | (0.1) | |||||
| PIVC size (gauge), n (%) | 0.405 b | ||||||||||
| 22 G (blue) | 33 | (17.8) | 192 | (16.8) | 225 | (16.9) | |||||
| 20 G (pink) | 96 | (51.9) | 515 | (45.0) | 611 | (45.9) | |||||
| 18 G (green) | 55 | (29.7) | 427 | (37.3) | 482 | (36.2) | |||||
| 16 G (grey) | 1 | (0.5) | 3 | (0.3) | 4 | (0.3) | |||||
| Unknown | 8 | (0.6) | 8 | (0.6) | |||||||
| Insertion environment, n (%) | <0.001 b | ||||||||||
| Ambulance/EMS | 9 | (4.9) | 50 | (4.4) | 59 | (4.4) | |||||
| Emergency department | 73 | (39.5) | 434 | (37.9) | 507 | (38.1) | |||||
| Operating theatre | 19 | (10.3) | 170 | (14.8) | 189 | (14.2) | |||||
| Hospital ward/unit/ICU | 71 | (38.4) | 431 | (37.7) | 502 | (37.7) | |||||
| Radiology/procedure room | 1 | (0.5) | 1 | (0.1) | 2 | (0.2) | |||||
| Unknown | 12 | (6.5) | 59 | (5.2) | 71 | (5.3) | |||||
| Ward, n (%) | 0.010 b | ||||||||||
| Surgical ward | 40 | (21.6) | 275 | (24.0) | 315 | (23.7) | |||||
| Medical ward 2 | 60 | (32.4) | 289 | (25.2) | 349 | (26.2) | |||||
| Medical ward 1 | 58 | (31.4) | 296 | (25.9) | 354 | (26.6) | |||||
| Intensive care unit | 12 | (6.5) | 99 | (8.6) | 111 | (8.3) | |||||
| Observation unit | 15 | (8.1) | 186 | (16.2) | 201 | (15.1) | |||||
| PIVC, n (%) | <0.001 b | ||||||||||
| Closed integrated PIVC | 0 | (0.0) | 497 | (43.4) | 497 | (37.4) | |||||
| Ported PIVC | 185 | (100.0) | 634 | (55.4) | 819 | (61.6) | |||||
| Non ported PIVC | 0 | (0.0) | 14 | (1.2) | 14 | (1.1) | |||||
| Antibiotics, n (%) | 0.523 b | ||||||||||
| Yes | 59 | (31.9) | 372 | (32.5) | 431 | (32.4) | |||||
| No | 106 | (57.3) | 747 | (65.2) | 853 | (64.1) | |||||
| Unknown | 20 | (10.8) | 26 | (2.3) | 46 | (3.5) | |||||
| PIVC-miniQ Domain | Pre-Intervention (n = 185) | Post-Intervention (n = 1145) | Total (n = 1330) | Chi-Square Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Items | n | % | n | % | n | % | p-Value |
| Phlebitis-related signs and symptoms | |||||||
| Pain | 20 | 10.8 | 73 | 6.4 | 93 | 7.0 | 0.028 |
| Redness > 1 cm from insertion site | 9 | 4.9 | 30 | 2.6 | 39 | 2.9 | 0.093 |
| Swelling | 5 | 2.7 | 29 | 2.5 | 34 | 2.6 | 0.892 |
| Warmth at insertion site | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 |
| Purulence | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 |
| Streak/red line along the vein | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 |
| Induration, hardness of tissue > 1 cm from insertion site | 7 | 3.8 | 10 | 0.9 | 17 | 1.3 | <0.001 |
| Palpable hard vein beyond tip | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 1.000 |
| PIVC dressing and IV connection | |||||||
| Partial/complete dislodgement | 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 0.2 | 3 | 0.2 | 0.330 |
| Soiled with blood or fluids | 81 | 43.8 | 289 | 25.2 | 370 | 27.8 | <0.001 |
| Loose or lifting dressing edges | 40 | 21.6 | 168 | 14.7 | 208 | 15.6 | 0.016 |
| Sterile dressing missing | 0 | 0.0 | 4 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.3 | 0.421 |
| Blood in line | 73 | 39.5 | 216 | 18.9 | 289 | 21.7 | <0.001 |
| Documentation | |||||||
| Insertion date not documented on PIVC dressing | 124 | 67.0 | 511 | 44.6 | 635 | 47.7 | <0.001 |
| Documentation of indication in chart is missing | 185 | 100.0 | 595 | 52.0 | 780 | 58.7 | <0.001 |
| PIVC insertion date in chart is missing | 20 | 10.8 | 91 | 8.0 | 111 | 8.4 | 0.191 |
| Daily documentation of observation, care, and indication assessment in chart is missing | 119 | 64.3 | 514 | 44.9 | 633 | 47.6 | <0.001 |
| PIVC-miniQ | Pre-Intervention (n = 185) | Post-Intervention (n = 1145) | Total (n = 1330) | Chi-Square Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domains | n | % | n | % | n | % | p-Value | RR |
| Phlebitis | 28 | 15.1 | 108 | 9.4 | 136 | 10.2 | 0.018 | 1.61 |
| PIVC dressing and IV connection | 130 | 70.3 | 530 | 46.3 | 660 | 49.6 | <0.001 | 1.52 |
| Documentation | 185 | 100.0 | 901 | 78.7 | 1086 | 81.7 | <0.001 | 1.27 |
| Unadjusted Models | Fully Adjusted Model (n = 1276) | Final Model (n = 1276) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable (Predictors) | n | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | VIF | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Intervention | 1330 | 0.58 | (0.37, 0.91) | 0.024 | 1.0 | 0.51 | (0.30, 0.87) | 0.016 | 0.53 | (0.33, 0.86) | 0.014 |
| Ward | 1330 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||
| Medical ward 1 | 354 | 1.00 | (Reference) | - | 1.00 | (Reference) | 1.00 | (Reference) | |||
| Surgical ward | 315 | 1.74 | (1.05, 2.89) | 1.6 | 1.84 | (0.98, 3.45) | 1.63 | (0.96, 2.76) | |||
| Medical ward 2 | 349 | 1.51 | (0.91, 2.50) | 1.5 | 1.72 | (1.00, 2.95) | 1.56 | (0.92, 2.64) | |||
| Intensive care unit | 111 | 0.00 | cc | cc | 0.00 | cc | 0.00 | cc | |||
| Observation unit | 201 | 1.81 | (1.03, 3.16) | 1.3 | 1.66 | (0.92, 3.01) | 1.75 | (0.98, 3.13) | |||
| Gender | 1330 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.004 | |||||||
| Male | 699 | 1.00 | (Reference) | - | 1.00 | (Reference) | 1.00 | (Reference) | |||
| Female | 631 | 1.72 | (1.20, 2.47) | 1.0 | 1.70 | (1.16, 2.50) | 1.75 | (1.20, 2.55) | |||
| Insertion site | 1330 | 0.203 | 0.700 | ||||||||
| Forearm | 561 | 1.00 | (Reference) | - | 1.00 | (Reference) | |||||
| Antecubital fossa | 323 | 1.30 | (0.84, 2.00) | 1.0 | 1.13 | (0.68, 1.86) | |||||
| Chest | 1 | 0.00 | cc | 1.2 | 0.00 | cc | |||||
| Foot | 28 | 0.00 | cc | 1.8 | 0.00 | cc | |||||
| Hand | 307 | 1.07 | (0.68, 1.70) | 1.3 | 1.16 | (0.70, 1.90) | |||||
| Wrist | 95 | 0.85 | (0.39, 1.84) | 1.1 | 0.82 | (0.37, 1.83) | |||||
| Upper arm | 15 | 0.66 | (0.09, 5.09) | 1.8 | 1.02 | (0.12, 8.81) | |||||
| PIVC gauge (mm) | 1322 | 3.13 | (0.90, 10.90) | 0.071 | 1.4 | 4.62 | (0.92, 23.13) | 0.060 | 5.42 | (1.36, 21.56) | 0.016 |
| PIVC type | 1330 | 0.107 | 0.544 | ||||||||
| Ported PIVC | 819 | 1.00 | (Reference) | - | 1.00 | (Reference) | |||||
| Closed integrated PIVC | 497 | 0.80 | (0.55, 1.16) | 1.1 | 1.06 | (0.67, 1.69) | |||||
| Non ported PIVC | 14 | 0.00 | cc | - | 0.00 | cc | |||||
| Insertion environment | 1330 | 0.287 | 0.345 | ||||||||
| Emergency department | 507 | 1.00 | (Reference) | - | 1.00 | (Reference) | |||||
| Operating theatre | 189 | 0.97 | (0.57, 1.67) | 1.1 | 0.80 | (0.38, 1.72) | |||||
| Ambulance/EMS | 59 | 1.88 | (0.92, 3.84) | 1.0 | 1.74 | (0.80, 3.79) | |||||
| Radiology/procedure room | 2 | 0.00 | cc | 1.1 | 0.00 | cc | |||||
| Hospital ward/unit/ICU | 502 | 0.81 | (0.53, 1.23) | 0.97 | (0.62, 1.51) | ||||||
| Unknown | 71 | 0.62 | (0.24, 1.61) | 0.48 | (0.16, 1.39) | ||||||
| Antibiotics | 1284 | 0.62 | (0.41, 0.94) | 0.020 | 0.77 | (0.49, 1.21) | 0.246 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amble, K.; Skjelbreid, I.B.; Eide, G.E.; Muri, S.; Høvik, L.H.; Reime, M.H. Implementation of an Infection Prevention Care Bundle for Peripheral Intravenous Catheters (PIVCs): A Quality Improvement Study to Enhance PIVC Quality and Reduce Complications. Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15, 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15110379
Amble K, Skjelbreid IB, Eide GE, Muri S, Høvik LH, Reime MH. Implementation of an Infection Prevention Care Bundle for Peripheral Intravenous Catheters (PIVCs): A Quality Improvement Study to Enhance PIVC Quality and Reduce Complications. Nursing Reports. 2025; 15(11):379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15110379
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmble, Kristine, Ingun Børve Skjelbreid, Geir Egil Eide, Susann Muri, Lise Husby Høvik, and Marit Hegg Reime. 2025. "Implementation of an Infection Prevention Care Bundle for Peripheral Intravenous Catheters (PIVCs): A Quality Improvement Study to Enhance PIVC Quality and Reduce Complications" Nursing Reports 15, no. 11: 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15110379
APA StyleAmble, K., Skjelbreid, I. B., Eide, G. E., Muri, S., Høvik, L. H., & Reime, M. H. (2025). Implementation of an Infection Prevention Care Bundle for Peripheral Intravenous Catheters (PIVCs): A Quality Improvement Study to Enhance PIVC Quality and Reduce Complications. Nursing Reports, 15(11), 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nursrep15110379






