HeGRI: A Novel Index of Serum Hepcidin Suppression in Relation to the Degree of Renal Dysfunction among β-Thalassemia Major Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Sampling, and Patients
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Diagnostic and Measurement Criteria
2.4. Laboratory Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffbrand, A.; Moss, P.; Pettit, I. Hypochromic anaemias. Esential Haematology, 6th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2011; pp. 34–49. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, R.; Sharma, S.; Chandra, J. What regulates hepcidin in poly-transfused β-Thalassemia Major: Erythroid drive or store drive? Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2014, 57, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdoukas, V.; Nord, A.; Carson, S.; Puliyel, M.; Hofstra, T.; Wood, J.; Coates, T.D. Tissue iron evaluation in chronically transfused children shows significant levels of iron loading at a very young age. Am. J. Hematol. 2013, 88, E283–E285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, B.; Rasool, S.; Jasim, S.; Abdulah, D. Hepcidin as a diagnostic biomarker of iron deficiency anemia during pregnancy. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019, 34, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Santen, S.; Kroot, J.J.; Zijderveld, G.; Wiegerinck, E.T.; Spaanderman, M.E.; Swinkels, D.W. The iron regulatory hormone hepcidin is decreased in pregnancy: A prospective longitudinal study. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2013, 51, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wray, K.; Allen, A.; Evans, E.; Fisher, C.; Premawardhena, A.; Perera, L.; Rodrigo, R.; Goonathilaka, G.; Ramees, L.; Webster, C. Hepcidin detects iron deficiency in S ri L ankan adolescents with a high burden of hemoglobinopathy: A diagnostic test accuracy study. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Tsuji, T.; Luo, J.; Sakao, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Hishida, A. Association of prohepcidin and hepcidin-25 with erythropoietin response and ferritin in hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, M.A.; Spinks, C.; Heath, A.L.; Harvey, L.J.; Foxall, R.; Wimperis, J.; Wolf, C.; Fairweather-Tait, S.J. Serum prohepcidin concentration: No association with iron absorption in healthy men; and no relationship with iron status in men carrying HFE mutations, hereditary haemochromatosis patients undergoing phlebotomy treatment, or pregnant women. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemna, E.H.; Kartikasari, A.E.; van Tits, L.J.; Pickkers, P.; Tjalsma, H.; Swinkels, D.W. Regulation of hepcidin: Insights from biochemical analyses on human serum samples. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2008, 40, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaritsky, J.; Young, B.; Wang, H.-J.; Westerman, M.; Olbina, G.; Nemeth, E.; Ganz, T.; Rivera, S.; Nissenson, A.R.; Salusky, I.B. Hepcidin—A potential novel biomarker for iron status in chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinkels, D.W.; Girelli, D.; Laarakkers, C.; Kroot, J.; Campostrini, N.; Kemna, E.H.; Tjalsma, H. Advances in quantitative hepcidin measurements by time-of-flight mass spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.; Haycock, G.; Edelmann, C.; Spitzer, A. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 1976, 58, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F.; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burtis, C.A.; Ashwood, E.R.; Bruns, D.E. Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics-e-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth, E. Hepcidin in β-thalassemia. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2010, 1202, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearney, S.L.; Nemeth, E.; Neufeld, E.J.; Thapa, D.; Ganz, T.; Weinstein, D.A.; Cunningham, M.J. Urinary hepcidin in congenital chronic anemias. Pediatric Blood Cancer 2007, 48, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardenghi, S.; Ramos, P.; Marongiu, M.F.; Melchiori, L.; Breda, L.; Guy, E.; Muirhead, K.; Rao, N.; Roy, C.N.; Andrews, N.C. Hepcidin as a therapeutic tool to limit iron overload and improve anemia in β-thalassemic mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4466–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, E. Hepcidin and β-thalassemia major. Blood 2013, 122, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagadishkumar, K.; Yerraguntla, N.; Vaddambal, M. Serum Hepcidin Levels in Children with Beta Thalassemia Major. Indian Pediatrics 2018, 55, 911–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaddah, A.M.; Abdel-Salam, A.; Farhan, M.S.; Ragab, R. Serum hepcidin as a diagnostic marker of severe iron overload in beta-thalassemia major. Indian J. Pediatrics 2017, 84, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashidy, F.H.; Elghar, H.M.A.; Eldin, S.M.K.; Taha, M.Z. Hepcidin and iron regulation in chronic hemolytic anemia. Menoufia Med. J. 2015, 28, 463. [Google Scholar]
- Paköz, Z.B.; Çekiç, C.; Arabul, M.; Sarıtaş Yüksel, E.; İpek, S.; Vatansever, S.; Ünsal, B. An evaluation of the correlation between hepcidin serum levels and disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 810942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolaou, G.; Tzilianos, M.; Christakis, J.I.; Bogdanos, D.; Tsimirika, K.; MacFarlane, J.; Goldberg, Y.P.; Sakellaropoulos, N.; Ganz, T.; Nemeth, E. Hepcidin in iron overload disorders. Blood 2005, 105, 4103–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Origa, R.; Galanello, R.; Ganz, T.; Giagu, N.; Maccioni, L.; Faa, G.; Nemeth, E. Liver iron concentrations and urinary hepcidin in β-thalassemia. Haematologica 2007, 92, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musallam, K.M.; Taher, A.T. Mechanisms of renal disease in β-thalassemia. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1299–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantiworawit, A.; Khemakapasiddhi, S.; Rattanathammethee, T.; Hantrakool, S.; Chai-Adisaksopha, C.; Rattarittamrong, E.; Norasetthada, L.; Charoenkwan, P.; Srichairatanakool, S.; Fanhchaksai, K. Correlation of hepcidin and serum ferritin levels in thalassemia patients at Chiang Mai University Hospital. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20203352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghpanah, S.; Esmaeilzadeh, M.; Honar, N.; Hassani, F.; Dehbozorgian, J.; Rezaei, N.; Abdollahi, M.; Bardestani, M.; Safaei, S.; Karimi, M. Relationship between serum hepcidin and ferritin levels in patients with thalassemia major and intermedia in Southern Iran. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2015, 17, e28343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ashby, D.R.; Gale, D.P.; Busbridge, M.; Murphy, K.G.; Duncan, N.D.; Cairns, T.D.; Taube, D.H.; Bloom, S.R.; Tam, F.W.; Chapman, R.S. Plasma hepcidin levels are elevated but responsive to erythropoietin therapy in renal disease. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyszko, J.; Malyszko, J.; Pawlak, K.; Mysliwiec, M. Hepcidin, an acute-phase protein and a marker of inflammation in kidney transplant recipients with and without coronary artery disease. Transplant. Proc. 2006, 38, 2895–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyszko, J.; Malyszko, J.S.; Pawlak, K.; Mysliwiec, M. Hepcidin, iron status, and renal function in chronic renal failure, kidney transplantation, and hemodialysis. Am. J. Hematol. 2006, 81, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longerfich, L. Predicting glomerular function from adjusted serum creatinine. Nephron 1992, 62, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Levey, A.S.; Bosch, J.P.; Lewis, J.B.; Greene, T.; Rogers, N.; Roth, D. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: A new prediction equation. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Hematological Parameters | Study Groups | Case–Control Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Controls (n = 61) | Cases (n = 60) | ||
| WBC (10⁹/L) | 7.61 (1.73) | 9.87 (3.56) | 2.26 (1.83) |
| RBC (1012/L) | 4.91 (0.53) | 3.02 (0.44) | −1.89 (−0.09) |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.53 (1.87) | 8.32 (1.20) | −5.21 (−0.67) |
| HCT (%) | 38.93 (5.54) | 21.82 (3.38) | −17.11 (−2.16) |
| MCV (fl) | 83.45 (5.46) | 71.96 (3.98) | −11.49 (−1.48) |
| MCH (pg) | 28.78 (1.03) | 27.51 (1.03) | −1.27 (0.00) |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 34.47 (0.80) | 38.10 (0.93) | 3.63 (0.13) |
| Iron (μg/dL) Normal/f (%) Abnormal | 106.80 (38.53) 42 (68.9) 19 (31.1) | 237.66 (45.50) 0 (0.0) 60 (100.0) | 130.86 (6.97) |
| TIBC (μg/dL) Normal/f (%) Abnormal | 429.85 (40.08 12 (19.7) 49 (80.3) | 280.48 (91.68) 27 (45.0) 33 (55.0) | −149.37 (51.60) |
| Transferrin saturation (%) | 26.52 (14.76) | 85.93 (38.42) | 59.41 (23.66) |
| Serum ferritin (ng/mL) Normal/f (%) Abnormal | 27.96 (17.29) 45 (73.8) 16 (26.2) | 3435.53 (1968.83) 0 (0.0) 60 (100.0) | 3407.57 (1951.54) |
| Parameters | Controls (n = 61) | Cases (n = 60) | Case–Control Difference | p-Value (Two-Tailed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepcidin | 9.941 (12.271) | 21.898 (30.087) | 11.96 (17.82) | <0.001 * |
| CRP | 0.11 (0.62) | 0.54 (2.04) | 0.43 (1.42) | <0.001 * |
| Blood urea (mg/dL) Normal Abnormal | 22 (36.1) 39 (63.9) | 8 (13.3) 52 (86.7) | 2.19 (−1.06) | 0.060 ** 0.004 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) Normal Abnormal | 36 (59.0) 25 (41.0) | 19 (31.7) 41 (68.3) | −0.12 (−0.04) | <0.001 ** 0.003 |
| eGFR Adult (>18 years) Pediatric (1–18 years) | 132.95 (24.31) 136.74 (16.03) 132.29 (25.53) | 179.71 (55.53) 162.08 (26.05) 182.83 (58.86) | 46.76 (31.22) 25.34 (10.02) 50.54 (33.33) | <0.001 ** 0.027 ** <0.001 ** |
| Dependent Variable: Serum Hepcidin (ng/mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controlling Factors (n = 60) | Standardized Coefficients | T | p-Value | 95.0% Confidence Interval for B | |
| Beta | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||
| Iron (μg/dL) | −0.101 | −0.596 | 0.554 | −0.174 | 0.095 |
| TIBC (μg/dL) | −0.442 | −2.346 | 0.024 | −0.159 | −0.012 |
| TS (%) | −0.343 | −2.353 | 0.023 | −0.481 | −0.037 |
| Serum ferritin (ng/mL) | 0.185 | 1.474 | 0.148 | −0.001 | 0.003 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 0.190 | 1.522 | 0.135 | −0.174 | 1.241 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | −0.625 | −3.185 | 0.003 | −141.672 | −31.764 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 0.039 | 0.281 | 0.780 | −3.068 | 4.060 |
| eGFR | −0.496 | −2.657 | 0.011 | −0.261 | −0.036 |
| Parameters | Controls (n = 61) | Cases (n = 60) | Case–Control Difference | p-Value (Two-Tailed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
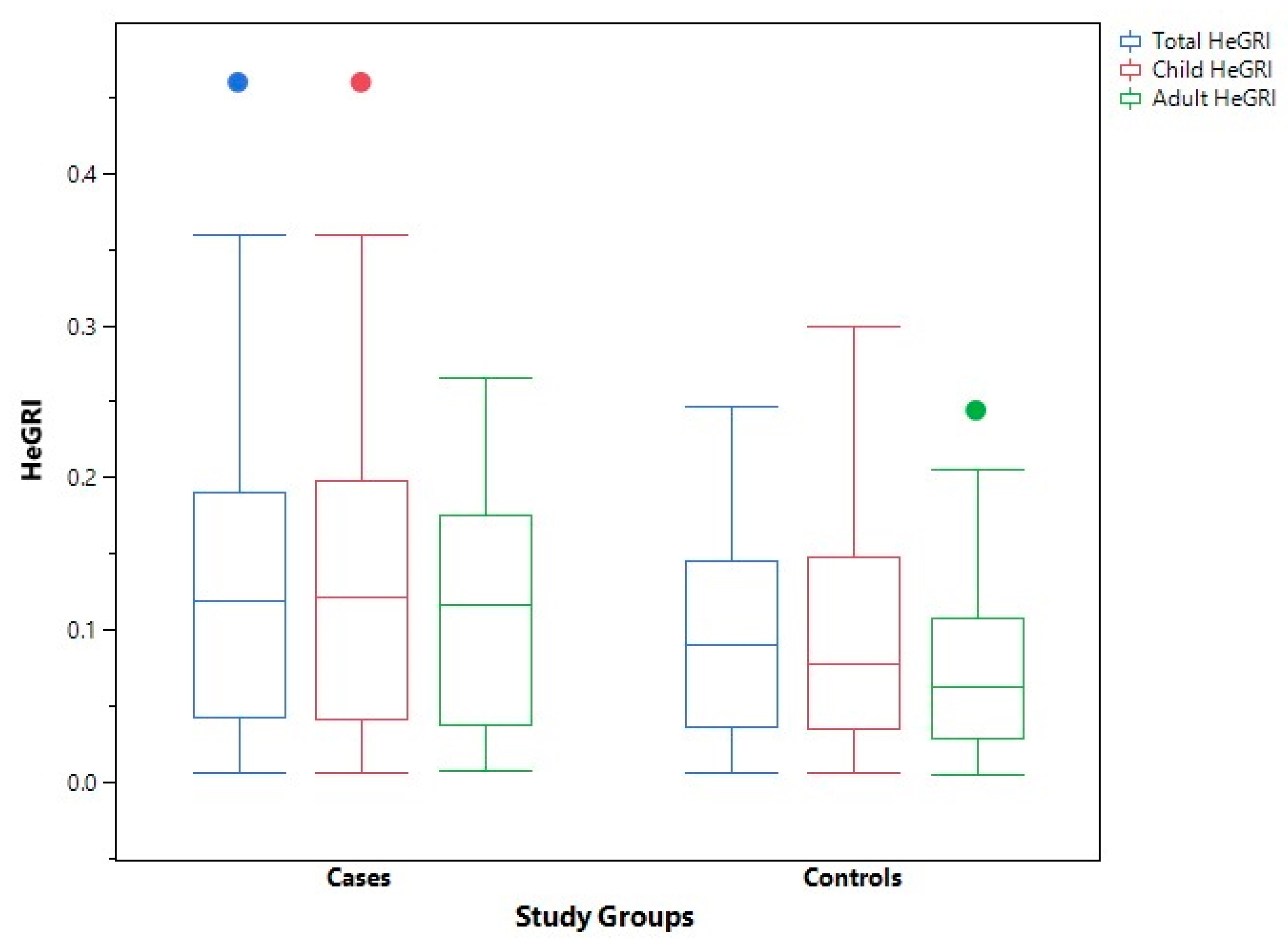
| Hepcidin/eGFR total Hepcidin/eGFR child Hepcidin/eGFR adult | 0.09 (0.11) 0.08 (0.11) 0.06 (0.08) | 0.12 (0.15) 0.12 (0.16) 0.12 (0.13) | 0.03 (0.04) −0.04 (0.05) −0.06 (0.05) | 0.031 0.023 0.001 |
| Hepcidin Hepcidin/ferritin ratio Min–max Mean (SD) | 9.941 (12.271) 0.088–3.826 0.3970 (0.1994) | 21.898 (30.087) 0.000–0.046 0.0069 (0.0047) | 11.96 (17.82) −0.3901 | <0.001 * <0.001 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaman, B.A.; Rasool, S.O.; Ibrahim, N.M.R.; Abdulah, D.M. HeGRI: A Novel Index of Serum Hepcidin Suppression in Relation to the Degree of Renal Dysfunction among β-Thalassemia Major Patients. Thalass. Rep. 2022, 12, 2-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/thalassrep12010002
Zaman BA, Rasool SO, Ibrahim NMR, Abdulah DM. HeGRI: A Novel Index of Serum Hepcidin Suppression in Relation to the Degree of Renal Dysfunction among β-Thalassemia Major Patients. Thalassemia Reports. 2022; 12(1):2-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/thalassrep12010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaman, Burhan A., Suzan O. Rasool, Nashwan M. R. Ibrahim, and Deldar M. Abdulah. 2022. "HeGRI: A Novel Index of Serum Hepcidin Suppression in Relation to the Degree of Renal Dysfunction among β-Thalassemia Major Patients" Thalassemia Reports 12, no. 1: 2-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/thalassrep12010002
APA StyleZaman, B. A., Rasool, S. O., Ibrahim, N. M. R., & Abdulah, D. M. (2022). HeGRI: A Novel Index of Serum Hepcidin Suppression in Relation to the Degree of Renal Dysfunction among β-Thalassemia Major Patients. Thalassemia Reports, 12(1), 2-11. https://doi.org/10.3390/thalassrep12010002








