Cochlear and Bone Conduction Implants in Asymmetric Hearing Loss and Single-Sided Deafness: Effects on Localization, Speech in Noise, and Quality of Life
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Outcome Measures
- Audiological Evaluation and Hearing Thresholds
- Speech Perception in Noise Assessment
- Sound Localization Evaluation
- Speech, Spatial, and Qualities of Hearing Scale (SSQ12)
- Tinnitus Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. OUTCOMES
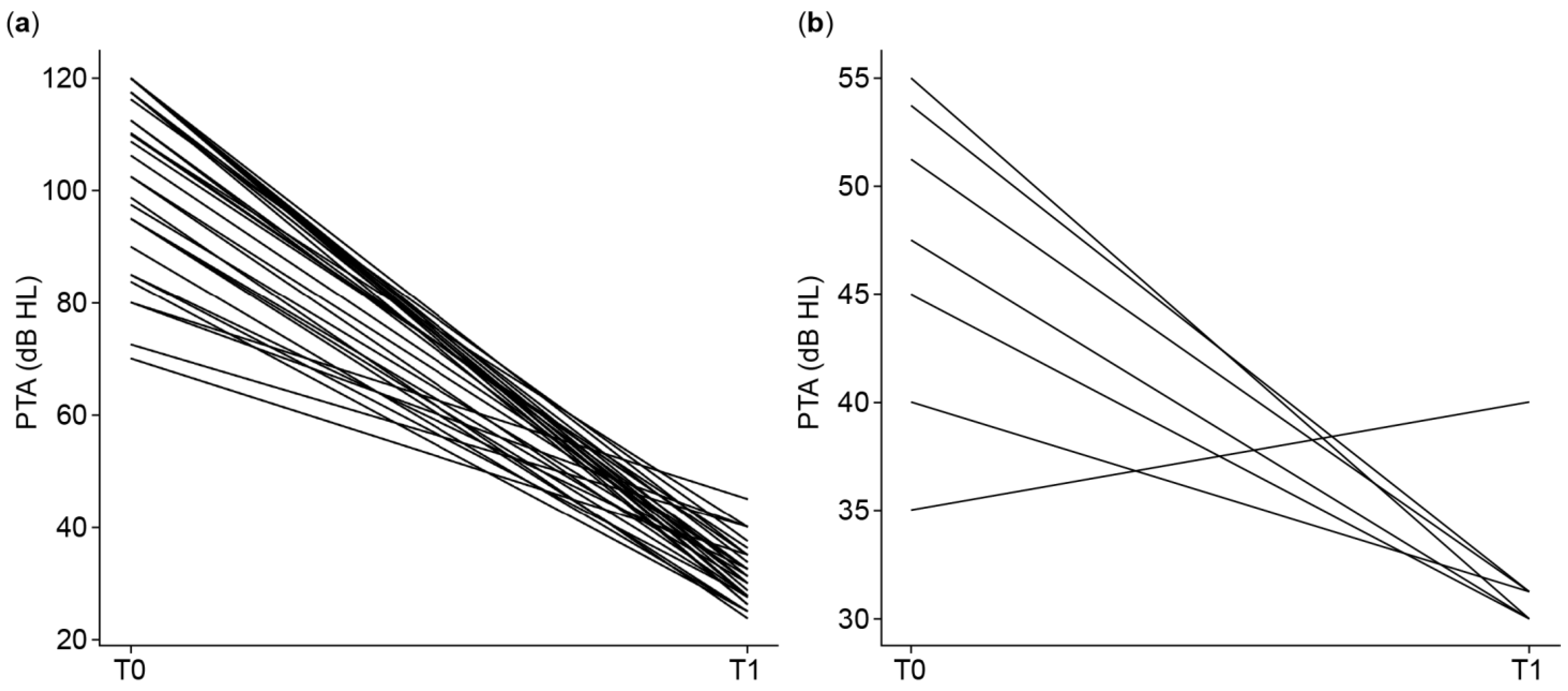
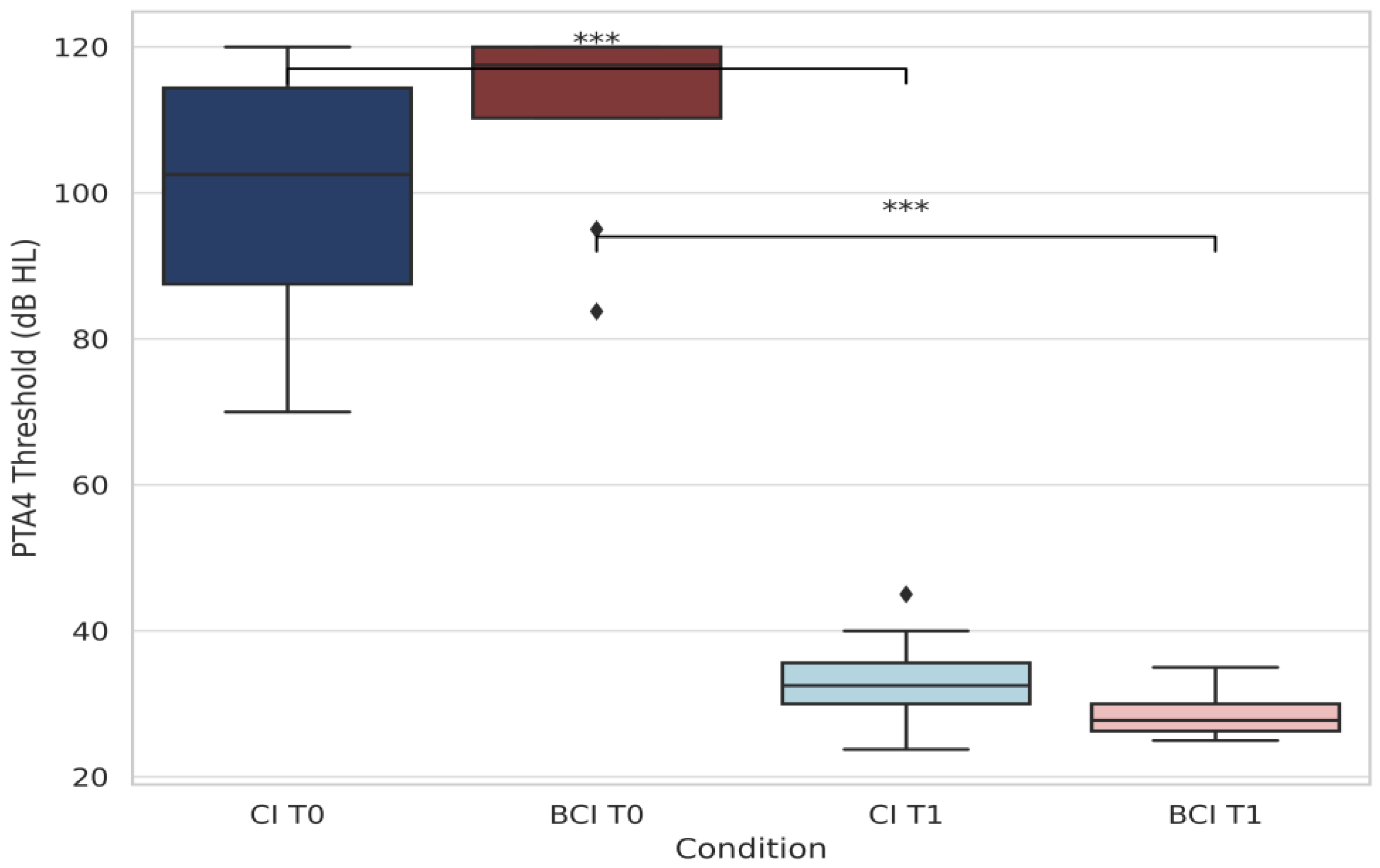
3.2.1. Pure-Tone Audiometry (PTA4)
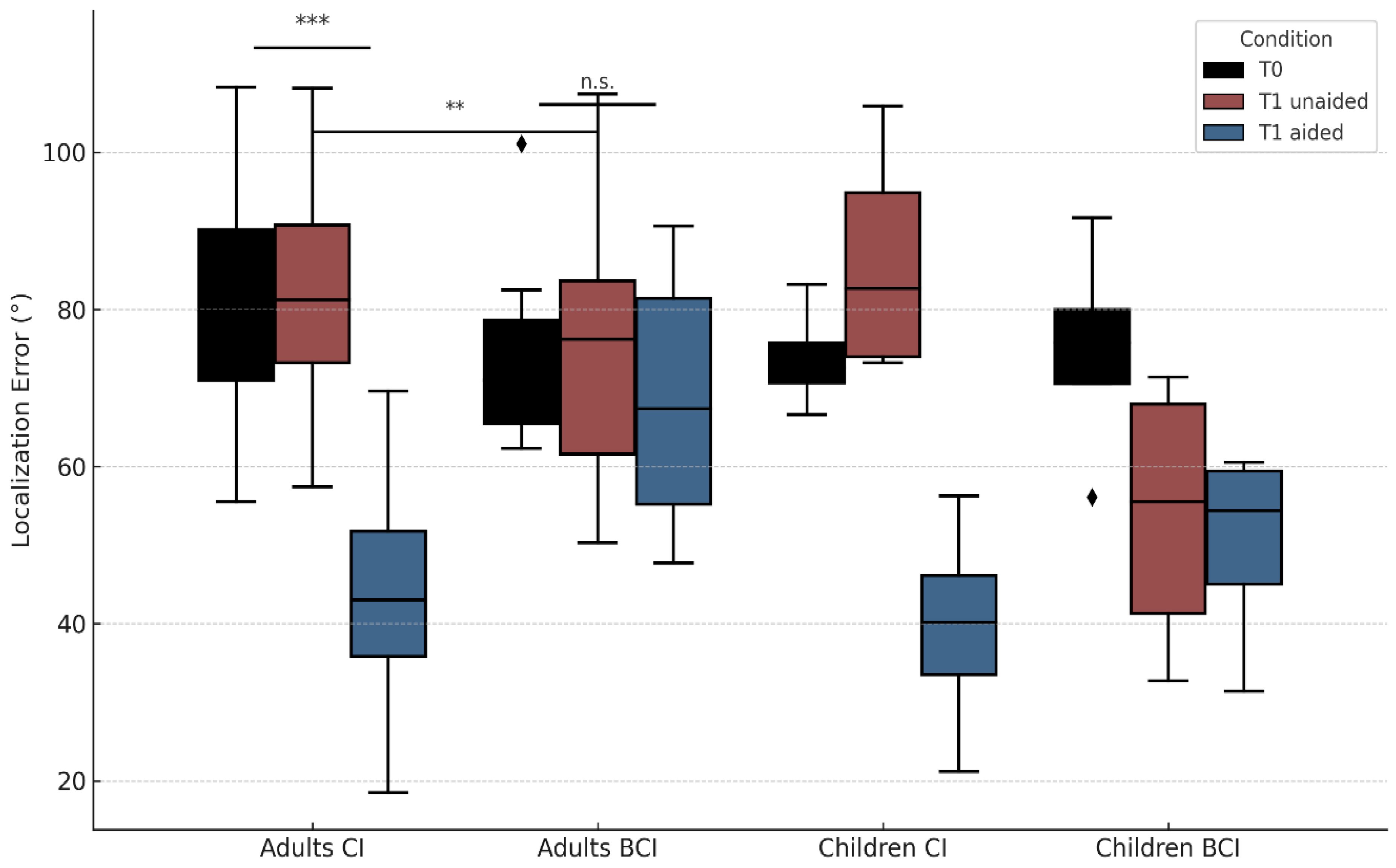
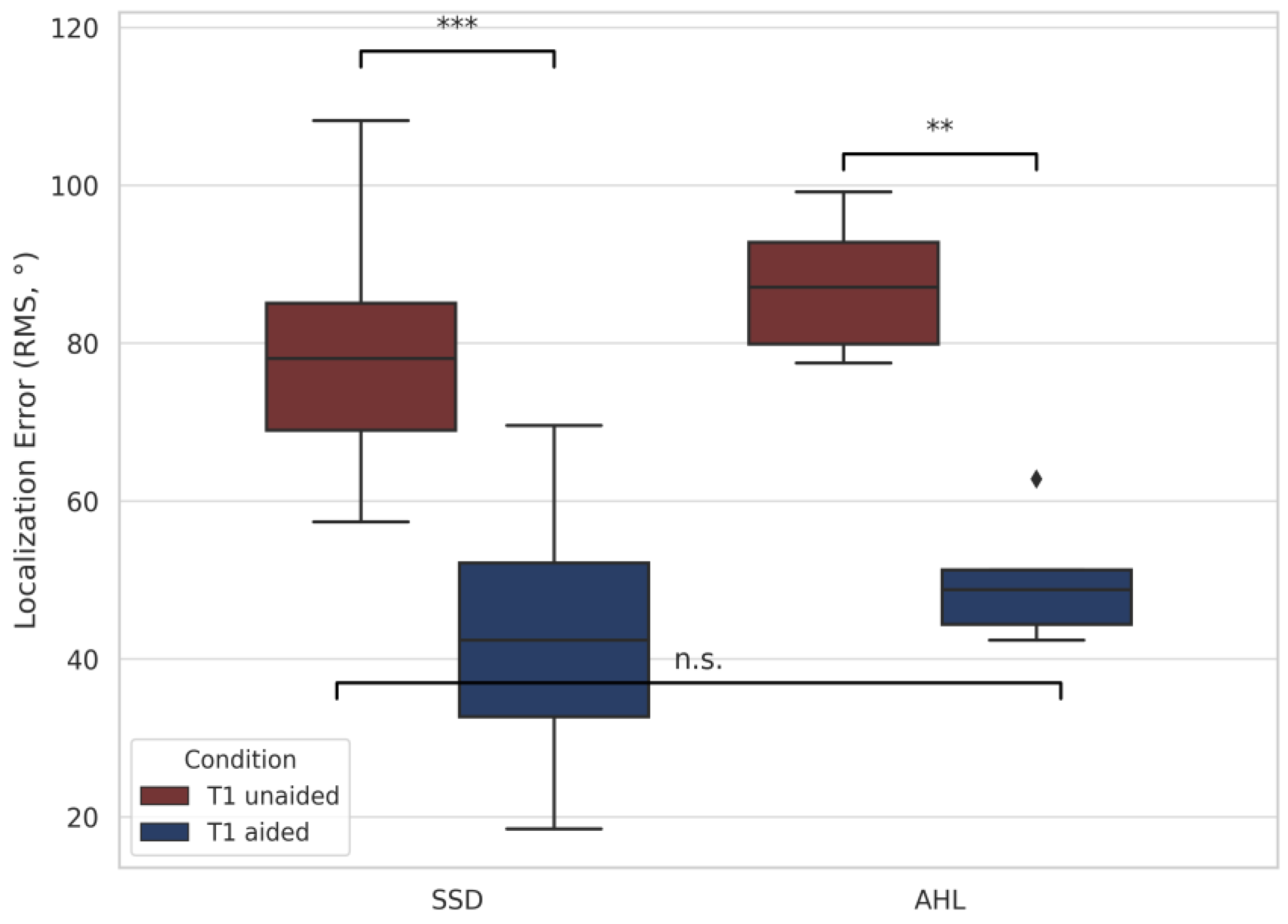
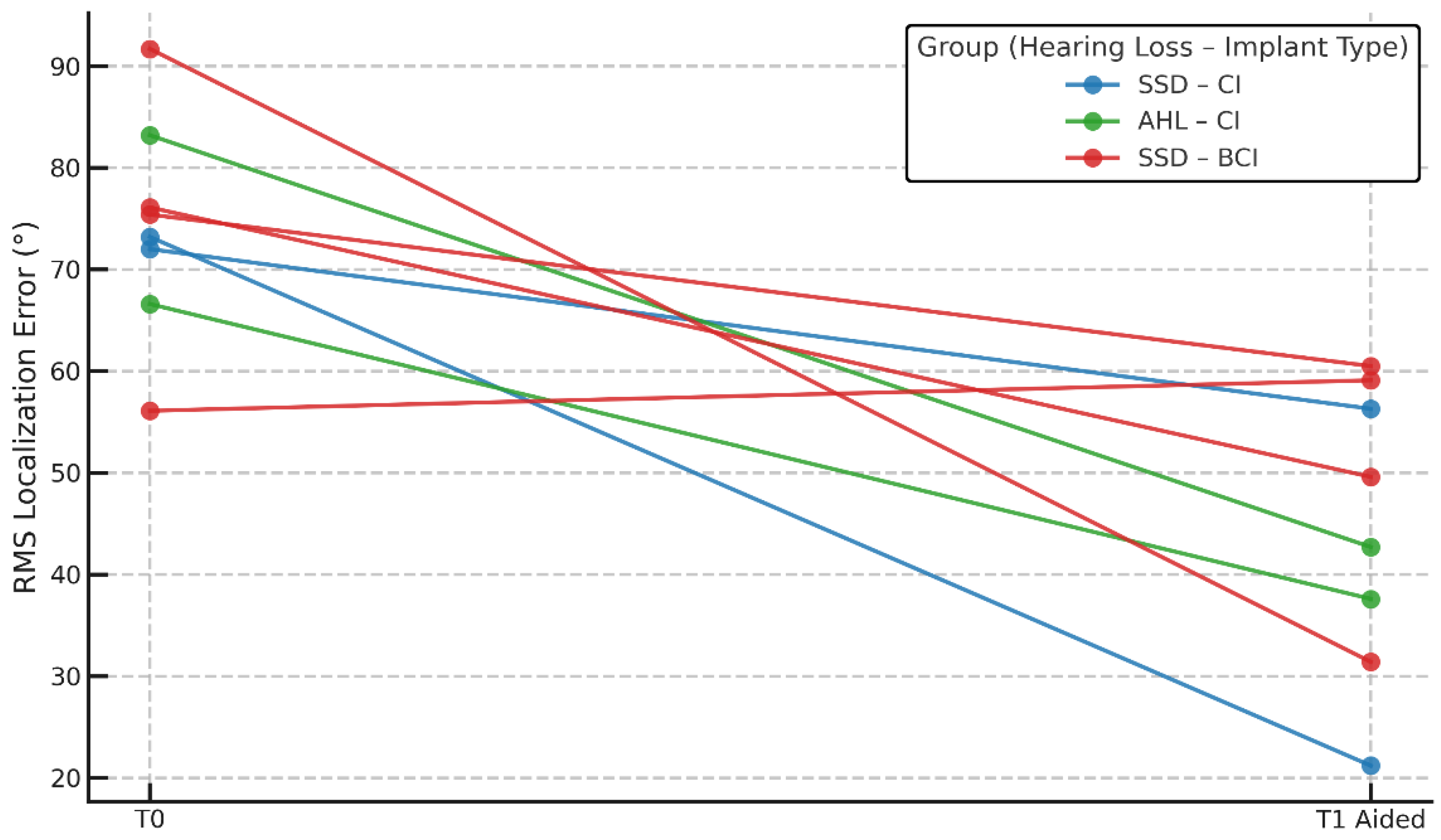
3.2.2. Localization Accuracy (RMS)
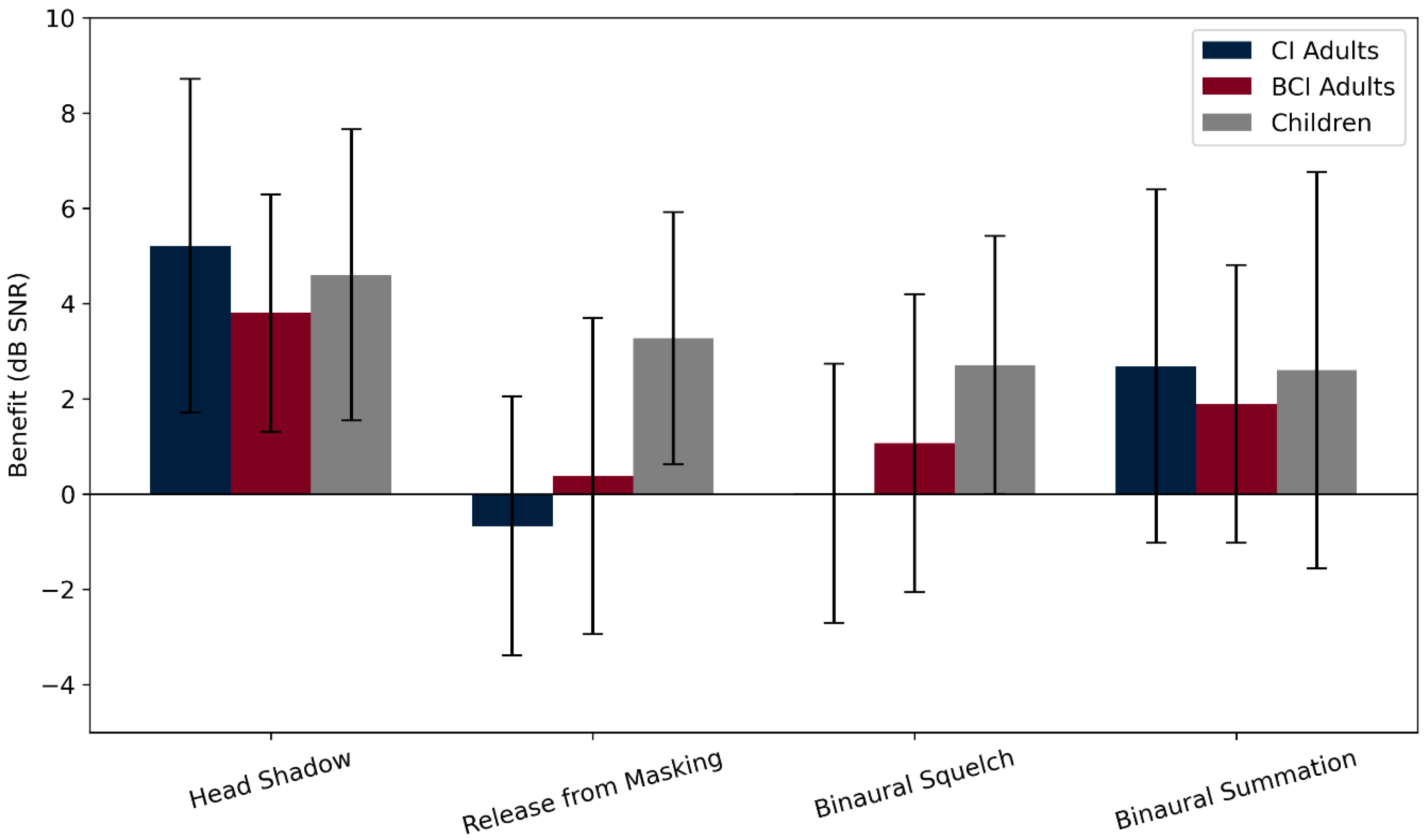
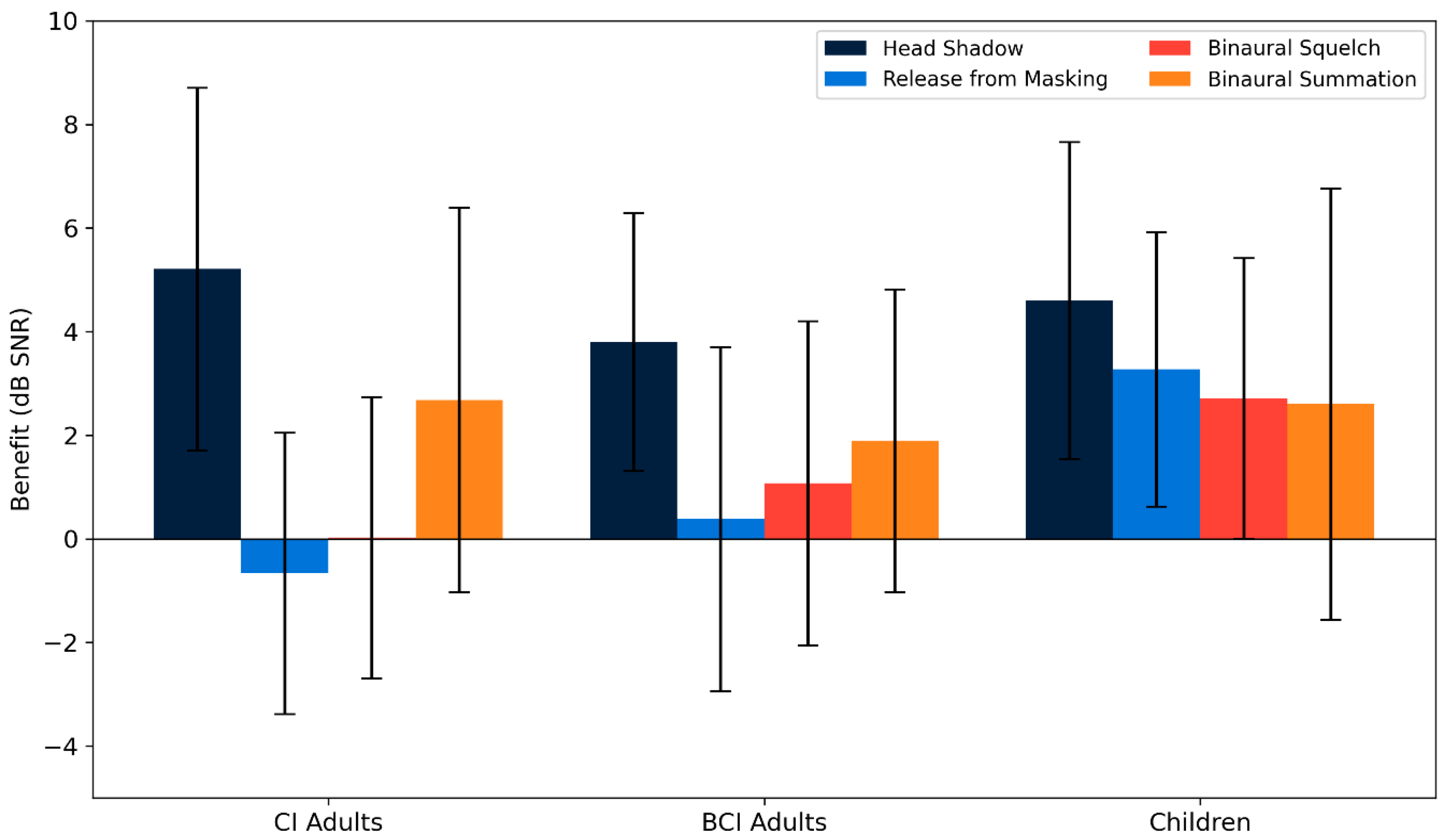
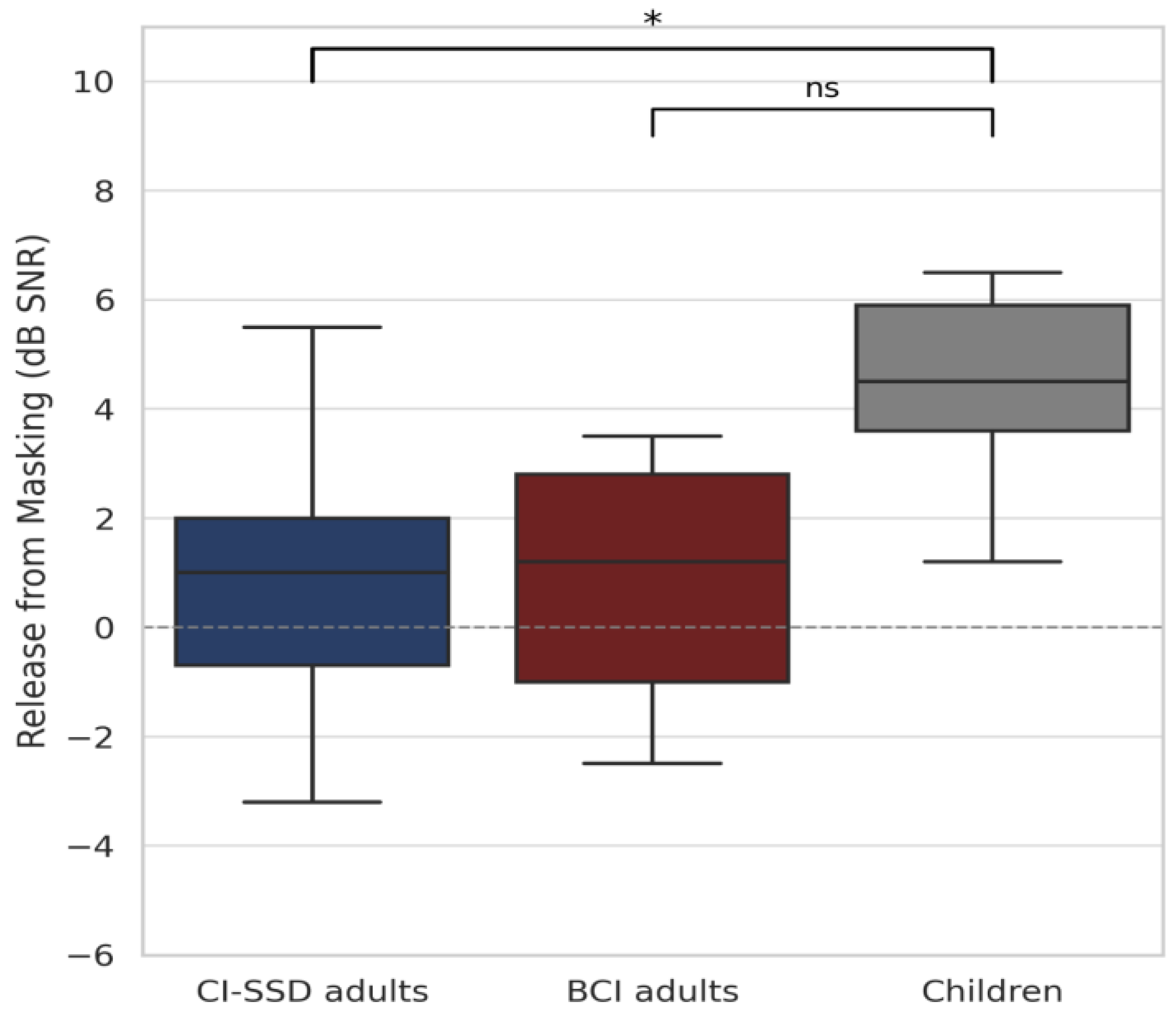
3.2.3. Speech Perception in Noise
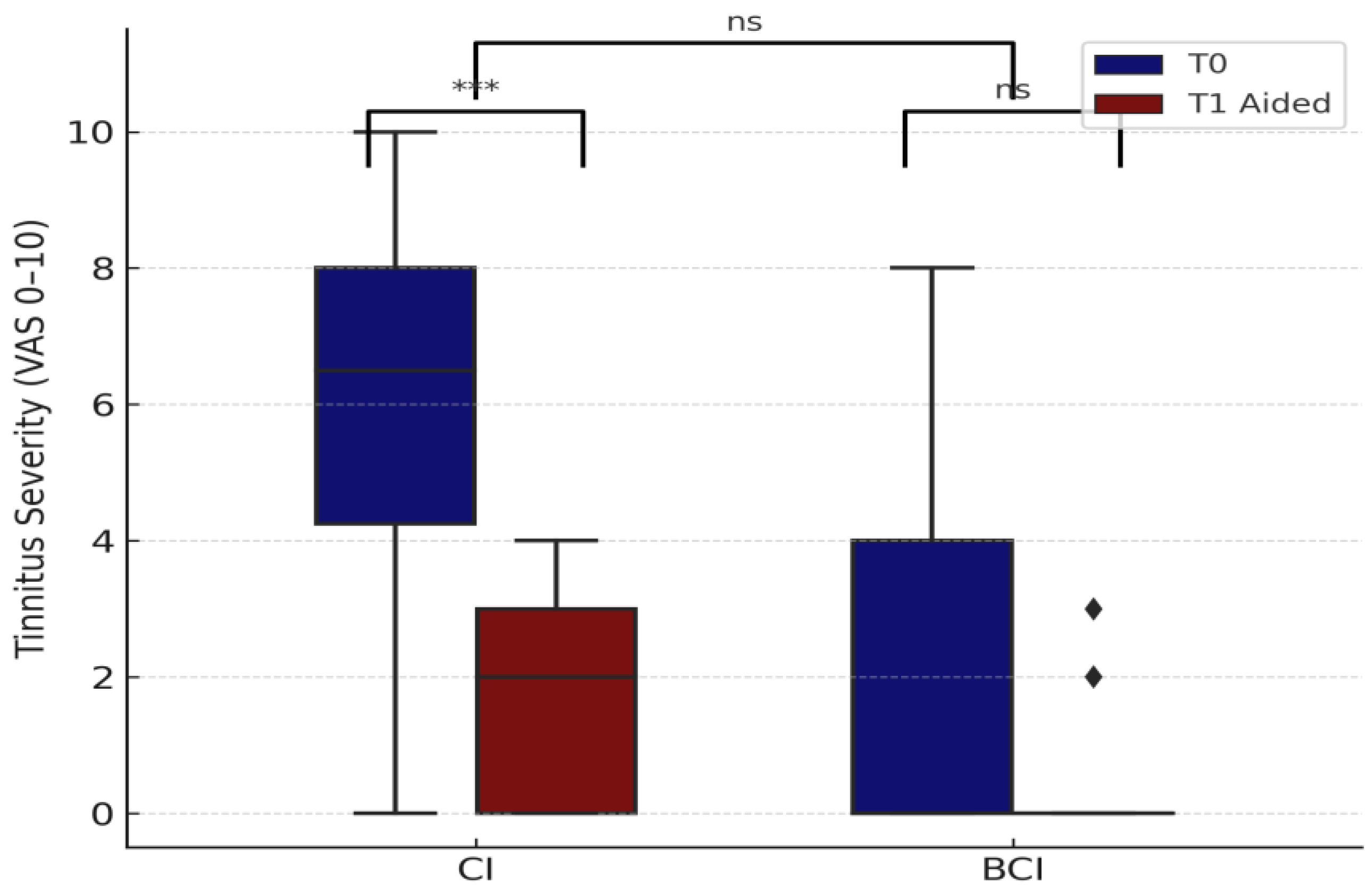
3.2.4. Tinnitus Severity
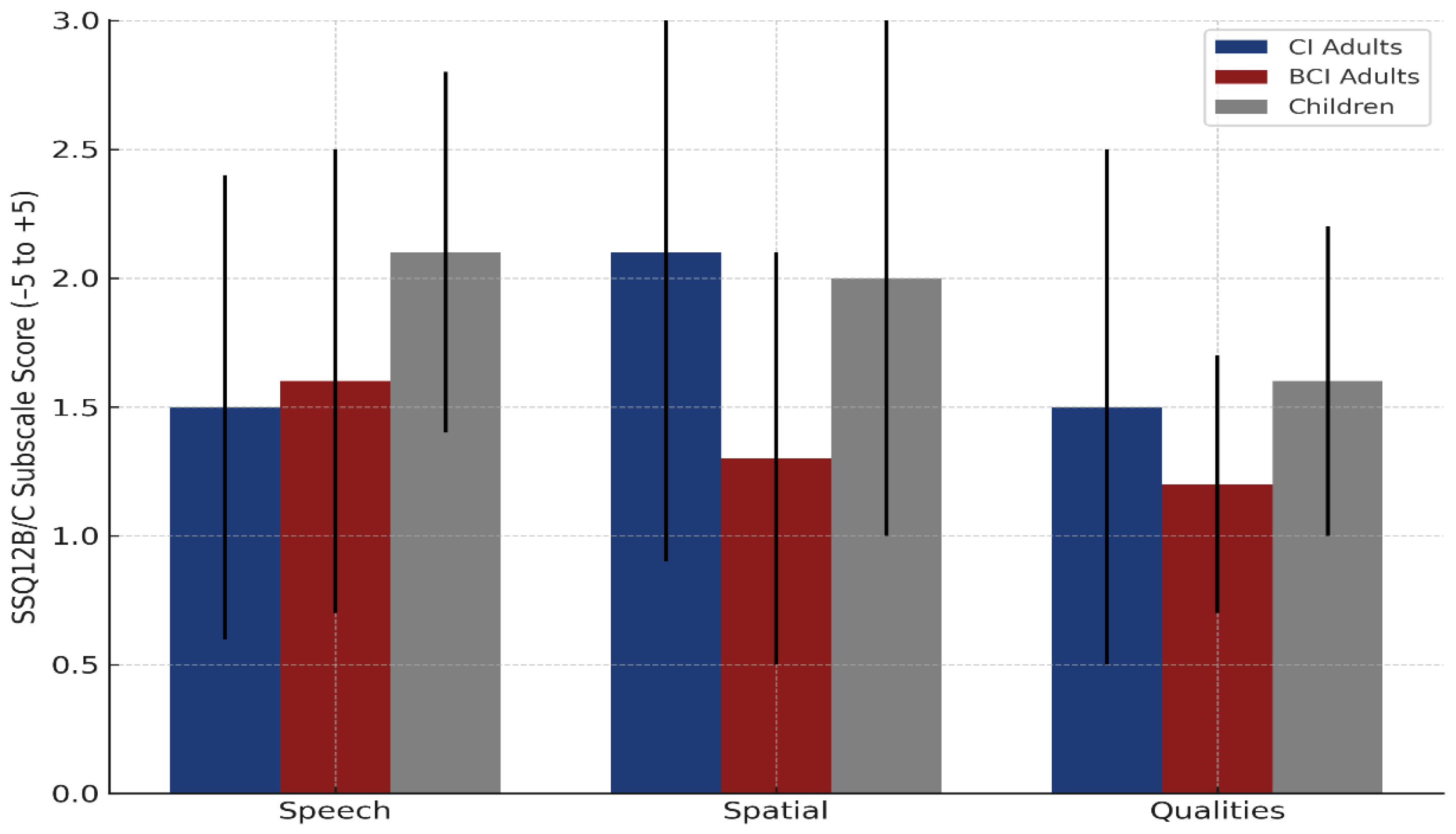
3.2.5. Self-Reported Hearing Outcomes—SSQ12
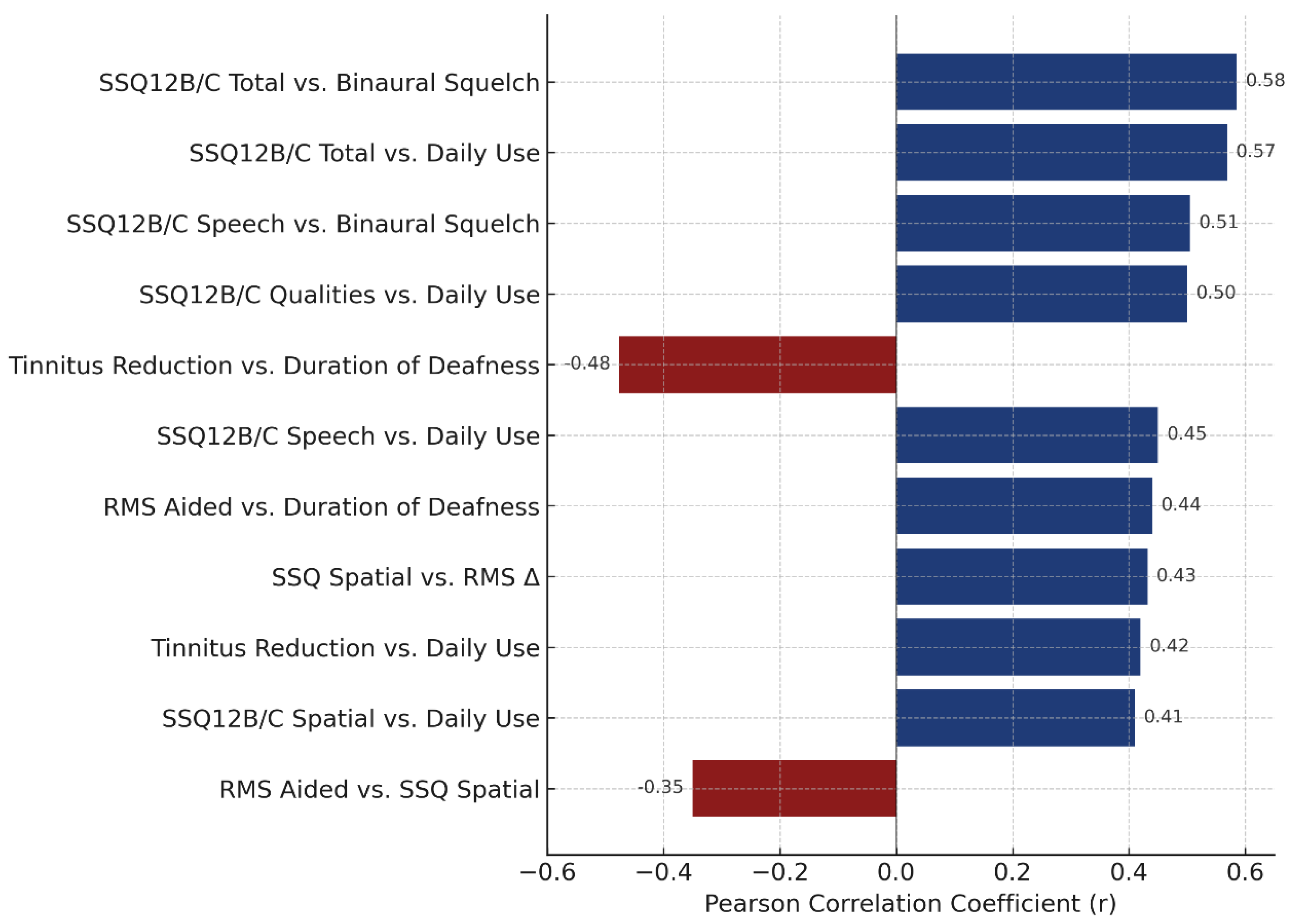
3.2.6. Correlations and Device Use
4. Discussion
4.1. Study Strengths
4.2. Limitations and Potential Biases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHL | Asymmetric hearing loss |
| BCI | Bone conduction implant |
| CI | Cochlear implant |
| CROS | Contralateral routing of signals |
| dB HL | Decibel hearing level |
| dB SNR | Decibel signal-to-noise ratio |
| eABR | Electrically evoked auditory brainstem response |
| eALR | Electrically evoked auditory late response |
| HL | Hearing loss |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| PTA | Pure-tone average |
| RMS | Root mean square (localization error) |
| SPN | Speech-in-noise |
| SRT | Speech reception threshold |
| SSD | Single-sided deafness |
| SSQ12 | Speech, Spatial, and Qualities of Hearing Scale–12-item version |
| TIN | Tinnitus score |
| VAS | Visual analog scale |
| S0N0 | Speech and noise presented frontally (0° azimuth) |
| S0N_AHL/SSD | Speech frontally, noise at impaired side (AHL/SSD) |
| S_AHL/SSD N0 | Speech at impaired side, noise frontally |
| S_AHL/SSD N_NH | Speech at impaired side, noise at normal-hearing ear |
| NAH | Normal-acoustic hearing ear (used in spatial test notation) |
References
- Van de Heyning, P.; Távora-Vieira, D.; Mertens, G. Towards a unified testing framework for single-sided deafness studies: A consensus paper. Audiol. Neurotol. 2017, 21, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, M.T.; Kocharyan, A.; Daher, G.S.; Carlson, M.L.; Shapiro, W.H.; Snapp, H.A.; Firszt, J.B. American Cochlear Implant Alliance Task Force Guidelines for Clinical Assessment and Management of Adult Cochlear Implantation for Single-Sided Deafness. Ear Hear. 2022, 43, 1605–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay-Rivest, E.; Irace, A.L.; Golub, J.S.; Svirsky, M.A. Prevalence of single-sided deafness in the United States. Laryngoscope 2022, 132, 1652–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasingh, A.; Hochmair, I. CI in single-sided deafness. Acta Otolaryngol. 2021, 141 (Suppl. S1), 82–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Swanson, J.; Koehnke, J.; Guan, J. Sound localization of listeners with normal hearing, impaired hearing, hearing aids, bone-anchored hearing instruments, and cochlear implants: A review. Am. J. Audiol. 2022, 31, 819–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snapp, H.A.; Ausili, S.A. Hearing with one ear: Consequences and treatments for profound unilateral hearing loss. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, L.; Katiri, R.; Kitterick, P.T. The psychological and social consequences of single-sided deafness in adulthood. Int. J. Audiol. 2017, 57, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitler, D.M.; Dorman, M.F. Cochlear implantation for single-sided deafness: A new treatment paradigm. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2019, 80, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, S.; Laszig, R.; Aschendorff, A.; Hassepass, F.; Beck, R.; Wesarg, T. Cochlear implant treatment of patients with single-sided deafness or asymmetric hearing loss. HNO 2017, 65 (Suppl. S2), 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firszt, J.B.; Reeder, R.M.; Holden, L.K.; Dwyer, N.Y. Results in adult cochlear implant recipients with varied asymmetric hearing: A prospective longitudinal study of speech recognition, localization, and participant report. Ear Hear. 2018, 39, 845–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantaleo, A.; Murri, A.; Cavallaro, G.; Pontillo, V.; Auricchio, D.; Quaranta, N. Single-sided deafness and hearing rehabilitation modalities: Contralateral routing of signal devices, bone conduction devices, and cochlear implants. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ontario Health (Quality). Implantable devices for single-sided deafness and conductive or mixed hearing loss: A health technology assessment. Ont. Health Technol. Assess. Ser. 2020, 20, 1–165. [Google Scholar]
- Donato, M.; Santos, R.; Correia, F.; Escada, P. Single-sided deafness: Bone conduction devices or cochlear implantation? A systematic review with meta-analysis. Acta Otorrinolaringol. 2020, 72, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitterick, P.T.; Smith, S.N.; Lucas, L. Hearing instruments for unilateral severe-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ear Hear. 2016, 37, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, N.J.; Dillon, M.T.; Buss, E.; Rooth, M.A.; Richter, M.E.; Pillsbury, H.C.; Brown, K.D. Long-term improvement in localization for cochlear implant users with single-sided deafness. Laryngoscope 2022, 132, 2453–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, C.B.; Al-Qurayshi, Z.; Zhu, V.; Liu, A.; Dunn, C.; Gantz, B.J.; Hansen, M.R. Long-term audiologic outcomes after cochlear implantation for single-sided deafness. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 1805–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speck, I.; Challier, P.; Wesarg, T.; Jakob, T.F.; Aschendorff, A.; Hassepass, F.; Arndt, S. Is the cochlear implant a successful long-term solution for single-sided deaf and asymmetric hearing-impaired patients? Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 278, 3257–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idriss, S.A.; Reynard, P.; Marx, M.; Mainguy, A.; Joly, C.-A.; Ionescu, E.C.; Assouly, K.K.S.; Thai-Van, H. Short- and long-term effect of cochlear implantation on disabling tinnitus in single-sided deafness patients: A systematic review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, G.; De Bodt, M.; Van de Heyning, P. Cochlear implantation as a long-term treatment for ipsilateral incapacitating tinnitus in subjects with unilateral hearing loss up to 10 years. Hear. Res. 2016, 331, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.J.; Mavrommatis, M.A.; Fan, C.J.; DiRisio, A.C.; Villavisanis, D.F.; Berson, E.R.; Schwam, Z.G.; Wanna, G.B.; Cosetti, M.K. Cochlear implantation in adults with single-sided deafness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 168, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, G.S.; Kocharyan, A.; Dillon, M.T.; Carlson, M.L. Cochlear implantation outcomes in adults with single-sided deafness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Otol. Neurotol. 2023, 44, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wazen, J.J.; Kim, C.S.; Ortega, C.; King, T.; Schwartz, S.R.; Zeitler, D.M. Benefits of unilateral cochlear implantation in adults with asymmetric hearing loss: Audiologic and patient-related outcome measures. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2024, 45, 104138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, L.; Fancello, V.; Gaino, F.; Cagliero, G.; Caruso, A.; Sanna, M. Cochlear implantation in single-sided deafness: A single-center experience of 138 cases. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 280, 4427–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Heteren, J.A.A.; Wendrich, A.W.; Peters, J.P.M.; Grolman, W.; Stokroos, R.J.; Smit, A.L. Speech perception in noise after cochlear implantation for single-sided deafness: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2025, 151, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sydlowski, S.A.; Farrokhian, N.; Carrozza, M.; Jamis, C.; Woodson, E. (Even off-label) cochlear implantation in single-sided deafness and asymmetric hearing loss results in measurable objective and subjective benefit. Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, e895–e902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, N.L.; Spitzer, E.R.; Shapiro, W.H.; Waltzman, S.B.; Roland, J.T., Jr.; Friedmann, D.R. Cochlear implantation in adults with single-sided deafness: Outcomes and device use. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesarg, T.; Kuntz, I.; Jung, L.; Wiebe, K.; Schatzer, R.; Brill, S.; Aschendorff, A.; Arndt, S. Masked speech perception with bone conduction device, contralateral routing of signals hearing aid, and cochlear implant use in adults with single-sided deafness: A prospective hearing device comparison using a unified testing framework. Audiol. Neurotol. 2024, 29, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, M.; Mosnier, I.; Venail, F.; Mondain, M.; Uziel, A.; Bakhos, D.; Lescanne, E.; N’Guyen, Y.; Bernardeschi, D.; Sterkers, O.; et al. Cochlear implantation and other treatments in single-sided deafness and asymmetric hearing loss: Results of a national multicenter study including a randomized controlled trial. Audiol. Neurotol. 2021, 26, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, S.; Ganaha, A.; Nakamura, T.; Kubuki, K.; Saruwatari, E.; Matsui, K.; Takahashi, K.; Tono, T. Pros and cons of a bone-conduction device implanted in the worse hearing ear of patients with asymmetric hearing loss. Front. Audiol. Otol. 2024, 2, 1362443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usami, S.-I.; Kitoh, R.; Moteki, H.; Nishio, S.-Y.; Kitano, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Watanabe, K. Etiology of single-sided deafness and asymmetrical hearing loss. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2017, 137 (Suppl. S565), S2–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, S.; Prosse, S.; Laszig, R.; Wesarg, T.; Aschendorff, A.; Hassepass, F. Cochlear implantation in children with single-sided deafness: Does aetiology and duration of deafness matter? Audiol. Neurotol. 2015, 20 (Suppl. S1), 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewyer, N.A.; Smith, S.; Herrmann, B.; Reinshagen, K.L.; Lee, D.J. Pediatric single-sided deafness: A review of prevalence, radiologic findings, and cochlear implant candidacy. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2022, 131, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santopietro, G.; Fancello, V.; Fancello, G.; Bianchini, C.; Pelucchi, S.; Ciorba, A. Cochlear implantation in children affected by single-sided deafness: A comprehensive review. Audiol. Res. 2024, 14, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benchetrit, L.; Ronner, E.A.; Anne, S.; Cohen, M.S. Cochlear implantation in children with single-sided deafness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 147, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, N.; Alajmi, N.; Alkoblan, F.I.; Alghtani, Y.A.; Abdelsamad, Y.; Alhussien, A.; Alhajress, R.I.; Alhabib, S.F. The chronological evolution of cochlear implant contraindications: A comprehensive review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, A.; Rak, K.; Hagen, R.; Ehrmann-Müller, D. Evaluating the decision for cochlear implantation in individuals with single-sided deafness (SSD): Implementing the SSD consensus protocol into clinical routine. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blamey, P.; Artieres, F.; Başkent, D.; Bergeron, F.; Beynon, A.; Burke, E.; Dillier, N.; Dowell, R.; Fraysse, B.; Gallégo, S.; et al. Factors affecting auditory performance of postlinguistically deaf adults using cochlear implants: An update with 2251 patients. Audiol Neurotol. 2013, 18, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.R.; Dillon, M.T.; Thompson, N.J.; Richter, M.E.; Overton, A.B.; Rooth, M.A.; Davis, A.G.; Dedmon, M.M.; Selleck, A.M.; Brown, K.D. Benefits of cochlear implantation for older adults with asymmetric hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2025, 135, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.P.M.; van Heteren, J.A.A.; Wendrich, A.W.; van Zanten, G.A.; Grolman, W.; Stokroos, R.J.; Smit, A.L. Short-term outcomes of cochlear implantation for single-sided deafness compared to bone conduction devices and contralateral routing of sound hearing aids: Results of a randomised controlled trial (CINGLE-trial). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Heteren, J.A.A.; van Oorschot, H.D.; Wendrich, A.W.; Peters, J.P.M.; Rhebergen, K.S.; Grolman, W.; Stokroos, R.J.; Smit, A.L. Sound localization in single-sided deafness: Outcomes of a randomized controlled trial on the comparison between cochlear implantation, bone conduction devices, and contralateral routing of signals hearing aids. Trends Hear. 2024, 28, 23312165241287092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, M.; Mounié, M.; Mosnier, I.; Venail, F.; Mondain, M.; Uziel, A.; Bakhos, D.; Lescanne, E.; N’guyen, Y.; Bernardeschi, D.; et al. Cost-utility of cochlear implantation in single-sided deafness and asymmetric hearing loss: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist, N.R.; Holder, J.T.; Patro, A.; Cass, N.D.; Tawfik, K.O.; O’Malley, M.R.; Bennett, M.L.; Haynes, D.S.; Gifford, R.H.; Perkins, E.L. Cochlear implants for single-sided deafness: Quality of life, daily usage, and duration of deafness. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 2362–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Yuen, H.W.; Low, D.; Kamath, S.; Chua, K.W.D. The functional impact of implantable hearing devices in patients with single-sided deafness. Proc. Singapore Healthc. 2023, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiri, R.; Hall, D.A.; Hoare, D.J.; Fackrell, K.; Horobin, A.; Hogan, N.; Buggy, N.; Van de Heyning, P.H.; Firszt, J.B.; Bruce, I.A.; et al. The Core Rehabilitation Outcome Set for Single-Sided Deafness (CROSSSD) study: International consensus on outcome measures for trials of interventions for adults with single-sided deafness. Trials 2022, 23, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Távora-Vieira, D.; Rajan, G.P.; Van de Heyning, P.; Mertens, G. Evaluating the long-term hearing outcomes of cochlear implant users with single-sided deafness. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, e575–e580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polterauer, D.; Mandruzzato, G.; Neuling, M.; Polak, M.; Müller, J.; Hempel, J.M. Evaluation of auditory pathway excitability using a pre-operative trans-tympanic electrically evoked auditory brainstem response under local anesthesia in cochlear implant candidates. Int. J. Audiol. 2023, 62, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radeloff, A.; Shehata-Dieler, W.; Rak, K.; Müller, L.; Schmidt, J.; Knorr, S.; Wagner, I.; Dietz, A.; Huber, A.; Fuchs, C.; et al. Intraoperative monitoring using electrically evoked auditory brainstem responses (eABR) in cochlear implant surgery: Clinical experience. Otol Neurotol. 2021, 42, e287–e293. [Google Scholar]
- Hempel, J.M.; Zimmermann, L.; Arnoldner, C.; Dhanasingh, A.; Polterauer, D.; Müller, J. Influence of cochlear coverage on speech perception in single sided deafness, bimodal, and bilateral implanted cochlear implant patients. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 281, 5197–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, E.; Smith, Z.; Tan, A.; Keller, M. Predicting hearing aid outcomes using machine learning. Audiol. Neurotol. 2025, 30, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, G.; Desloovere, C.; De Bodt, M.; Van de Heyning, P. Tinnitus and audiological outcomes after cochlear implantation in patients with single-sided deafness. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Han, J.J.; Hong, Y.T.; Chung, J.W. Impact of hearing aid use on cochlear implant outcomes in adults with asymmetric hearing loss. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 26, e541–e547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| (a) | |||||||
| Subject ID | Gender | Age at Implant (Years) | Etiology | Onset | Duration of Deafness (Years) | Electrode CI Type/BCI System | Follow-Up Period (Months) |
| S1 | F | 52.0 | trauma | postlingual | 1.0 | Cochlear Slim Straight | 16.0 |
| S2 | M | 18.0 | viral infection | postlingual | 8.0 | MED-EL FLEX 28 | 16.0 |
| S3 | F | 49.0 | Scohl-vest | postlingual | 2.0 | MED-EL FLEX 28 | 12.0 |
| S4 | F | 30.0 | Scohl-vest | postlingual | 4.0 | MED-EL FLEX 28 | 18.0 |
| S5 | M | 49.0 | trauma | postlingual | 15.0 | Cochlear Slim Straight | 16.0 |
| S6 | F | 52.0 | trauma | postlingual | 2.0 | Cochlear Slim Straight | 14.0 |
| S7 | F | 56.0 | Scohl-vest | postlingual | 8.0 | Cochlear Slim Straight | 14.0 |
| S8 | M | 50.0 | Scohl-vest | postlingual | 5.0 | Cochlear Slim Straight | 16.0 |
| S9 | M | 42.0 | trauma | postlingual | 2.0 | MED-EL FLEX 28 | 14.0 |
| S10 | F | 35.0 | Scohl-vest | postlingual | 4.0 | MED-EL FLEX 28 | 12.0 |
| S11 | M | 47.0 | viral infection | postlingual | 1.0 | MED-EL FLEX 28 | 12.0 |
| S12 | F | 33.0 | Scohl-vest | postlingual | 9.0 | Cochlear Slim Straight | 18.0 |
| S13 | M | 33.0 | schwannoma | postlingual | 2.0 | MED-EL FLEX 28 | 12.0 |
| S14 | F | 47.0 | Scohl-vest | postlingual | 9.0 | MED-EL FLEX 28 | 14.0 |
| S15 | F | 54.0 | otospongiozsis | postlingual | 7.0 | Cochlear Slim Straight | 16.0 |
| S16 | F | 45.0 | otospongiozsis | postlingual | 5.0 | MED-EL FLEX 28 | 16.0 |
| S17 | F | 52.0 | Scohl-vest | postlingual | 1.0 | Cochlear Slim Straight | 14.0 |
| S18 | F | 23.0 | ototoxicity | postlingual | 13.0 | Digisonic SP EVO | 24.0 |
| S19 | M | 63.0 | viral infection | postlingual | 25.0 | Cochlear Baha 5 | 14.0 |
| S20 | F | 37.0 | labyrinthitis | postlingual | 10.0 | Cochlear Baha 5 | 16.0 |
| S21 | M | 52.0 | labyrinthitis | postlingual | 3.0 | Cochlear Baha 5 | 14.0 |
| S22 | M | 51.0 | trauma | postlingual | 0.5 | MED-EL Bonebridge | 12.0 |
| S23 | M | 35.0 | unknown | perlingual | 35.0 | MED-EL Bonebridge | 12.0 |
| S24 | M | 54.0 | unknown | perlingual | 54.0 | MED-EL Bonebridge | 14.0 |
| S25 | F | 25.0 | unknown | perlingual | 25.0 | MED-EL Bonebridge | 12.0 |
| S26 | M | 30.0 | unknown | perilingual | 30.0 | MED-EL Bonebridge | 12.0 |
| S27 | F | 20.0 | unknown | perilingual | 20.0 | MED-EL Bonebridge | 12.0 |
| (b) | |||||||
| Subject ID | Gender | Age at Implant (Years) | Etiology | Onset | Duration of Deafness (Years) | Electrode Type CI/BCI System | Follow-Up Period (Months) |
| S1 | M | 16.0 | viral infection | postlingual | 8.0 | Cochlear Slim Straight | 16.0 |
| S2 | M | 13.0 | unknown | postlingual | 6.0 | MED-EL FLEX 28 | 12.0 |
| S3 | F | 12.0 | unknown | postlingual | 5.0 | Digisonic SP EVO | 24.0 |
| S4 | M | 9.0 | unknown | postlingual | 6.0 | MED-EL FLEX 28 | 12.0 |
| S5 | F | 13.0 | labyrinthitis | postlingual | 2.0 | MED-EL FLEX 28 | 16.0 |
| S6 | M | 10.0 | unknown | perilingual | 10.0 | MED-EL Bonebridge | 12.0 |
| S7 | F | 15.0 | unknown | perilingual | 15.0 | MED-EL Bonebridge | 12.0 |
| S8 | F | 15.0 | unknown | perilingual | 15.0 | MED-EL Bonebridge | 14.0 |
| S9 | M | 11.0 | unknown | perilingual | 11.0 | MED-EL Bonebridge | 14.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Astefanei, O.; Martu, C.; Cozma, S.; Radulescu, L. Cochlear and Bone Conduction Implants in Asymmetric Hearing Loss and Single-Sided Deafness: Effects on Localization, Speech in Noise, and Quality of Life. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030049
Astefanei O, Martu C, Cozma S, Radulescu L. Cochlear and Bone Conduction Implants in Asymmetric Hearing Loss and Single-Sided Deafness: Effects on Localization, Speech in Noise, and Quality of Life. Audiology Research. 2025; 15(3):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030049
Chicago/Turabian StyleAstefanei, Oana, Cristian Martu, Sebastian Cozma, and Luminita Radulescu. 2025. "Cochlear and Bone Conduction Implants in Asymmetric Hearing Loss and Single-Sided Deafness: Effects on Localization, Speech in Noise, and Quality of Life" Audiology Research 15, no. 3: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030049
APA StyleAstefanei, O., Martu, C., Cozma, S., & Radulescu, L. (2025). Cochlear and Bone Conduction Implants in Asymmetric Hearing Loss and Single-Sided Deafness: Effects on Localization, Speech in Noise, and Quality of Life. Audiology Research, 15(3), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres15030049








