Clinical Profile, Trends, and Management in Pediatric Patients with Audiovestibular Disorders: Can We Predict Emotional Disability in Pediatric Patients with Episodes of Vertigo and Dizziness?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Study Design
2.2. Patient Selection
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
- (1)
- Individuals under 18 years of age presenting to the Otolaryngology department with symptoms of vertigo or instability.
- (2)
- Patients with vestibular and auditory alterations, regardless of the involvement of other structures in the otolaryngological area.
- (3)
- Informed consent was obtained from their legal representatives, who agreed to participate in the study following the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki.
2.4. Medical and/or Surgical Treatment
2.5. Follow-Up
2.6. Measurement via Questionnaires
2.7. Representation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population
3.2. Symptoms and Diagnosis
3.3. Questionnaires
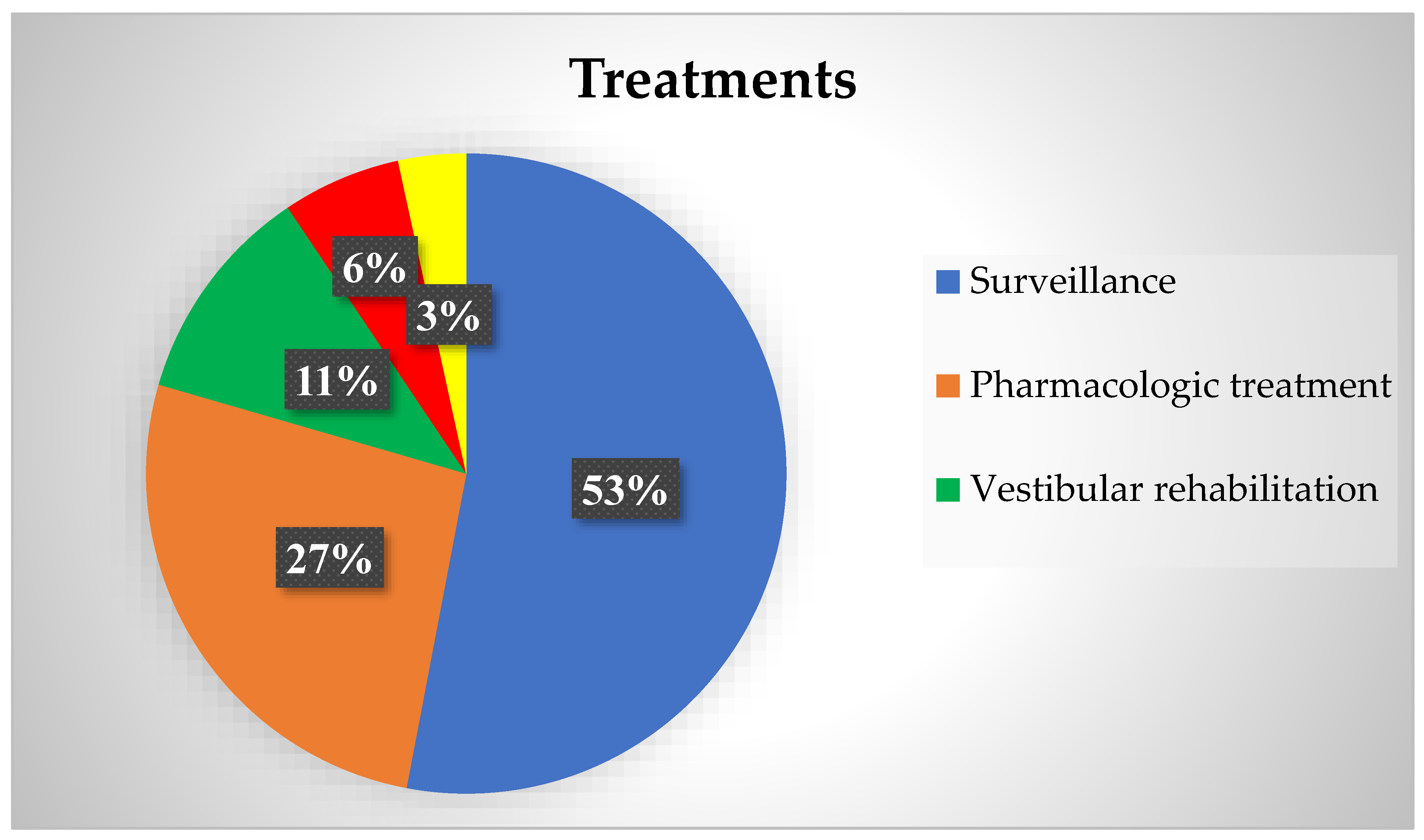
3.4. Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castillo-Bustamante, M.; Barona Cabrera, M.; Suárez Angulo, S.; García Campuzano, M.; García, A.; Madrigal, J. Facts of Vertigo in Adolescents: Controversies and Challenges—A Narrative Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e28294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-M.; Hoffman, H.J.; Ward, B.K.; Cohen, H.S.; Rine, R.M. Epidemiology of Dizziness and Balance Problems in Children in the United States: A Population-Based Study. J. Pediatr. 2016, 171, 240–247.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.; Goodkin, H.P. Dizziness and vertigo in the adolescent. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 44, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Toriyabe, I.; Takei, Y.; Kanzaki, J. Study on experimental motion sickness in children. Acta Otolaryngol. 1994, 114, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Femia, P.; González del Pino, B.; Pérez-Fernández, N. Exploración vestibular de niños con alteraciones del equilibrio (I): Métodos de la exploración clínica e instrumental. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2011, 62, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretti, T.; Desnous, B. Vertigo and dizziness in children: When to consider a neurological cause. Arch. Pédiatr. 2023, 30, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Oda, N.; Hatta, H. Behavioral genetic of early childhood: Fears, restlessness, motion sickness and enuresis. Acta Genet. Med. Gemellol. 1984, 33, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, A.J. Motion sickness. In Aviation Medicine; Nicholson, A.N., Rainford, D.S., Ernsting, J., Eds.; Butterworth Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1999; pp. 455–471. [Google Scholar]
- Balatsouras, D.G.; Kaberos, A.; Assimakopoulos, D.; Katotomichelakis, M.; Economou, N.C.; Korres, S.G. Etiology of vertigo in children. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2007, 71, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batuecas Caletrío, A.; Beltrán Mateos, L.D.; González Sánchez, M.; Santa Cruz Ruiz, S.; Benito González, F.; Serradilla López, J.M. Tortícolis y vértigo paroxístico. An. Pediatr. 2002, 57, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Erbek, S.H.; Erbek, S.S.; Yilmaz, I.; Topal, O.; Ozgirgin, N.; Ozluoglu, L.N.; Alehan, F. Vertigo in childhood: A clinical experience. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 70, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Newman-Toker, D.E.; Kerber, K.A.; Jahn, K.; Bertholon, P.; Waterston, J.; Lee, H.; Bisdorff, A.; Strupp, M. Vascular vertigo and dizziness: Diagnostic criteria. J. Vestib. Res. 2022, 32, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halmagyi, G.M.; Chen, L.; MacDougall, H.G.; Weber, K.P.; McGarvie, L.A.; Curthoys, I.S. The video head impulse test. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, J.; Manto, M. Pharmacotherapy of cerebellar and vestibular disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2021, 35, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golding, J.F.; Gresty, M.A. Pathophysiology and treatment of motion sickness. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2015, 28, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golding, J.F. Predicting individual differences in motion sickness susceptibility by questionnaire. Pers. Individ. Dif. 2006, 41, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, J.F. Motion sickness. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 137, pp. 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hromatka, B.S.; Tung, J.Y.; Kiefer, A.K.; Do, C.B.; Hinds, D.A.; Eriksson, N. Genetic variants associated with motion sickness point to roles for inner ear development, neurological processes and glucose homeostasis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 2700–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paillard, A.C.; Quarck, G.; Paolino, F.; Denise, P.; Paolino, M.; Golding, J.F.; Ghulyan-Bedikian, V. Motion sickness susceptibility in healthy subjects and vestibular patients: Effects of gender, age and trait-anxiety. J. Vestib. Res. 2013, 23, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golding, J.F.; Kadzere, P.; Gresty, M.A. Motion sickness susceptibility fluctuates through the menstrual cycle. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2005, 76, 970–973. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.; Griffin, M.J. Motion sickness incidence during a round-the-world yacht race. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1995, 66, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smitherman, T.A.; Burch, R.; Sheikh, H.; Loder, E. The prevalence, impact, and treatment of migraine and severe headaches in the United States: A review of statistics from national surveillance studies. Headache 2013, 53, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Sanchez, J.M.; Lopez-Escamez, J.A. New Insights into Pathophysiology of Vestibular Migraine. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Bustamante, M.; del Cid Chua, C.; Vázquez, M.; Bello Dotel, L.; Baez Recalde, M. Estrogen and neurotological diders in womenSexual hormones and neurotological disorders in women. Rev. Fac. Cienc. Med. Univ. Nac. Cordoba 2020, 77, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterich, M.; Obermann, M.; Celebisoy, N. Vestibular migraine: The most frequent entity of episodic vertigo. J. Neurol. 2016, 263 (Suppl. S1), 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, D.; Ashwal, S.; Hershey, A.; Hirtz, D.; Yonker, M.; Silberstein, S. Practice parameter: Pharmacological treatment of migraine headache in children and adolescents: Report of the American Academy of Neurology Quality Standards Subcommittee and the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology 2004, 63, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, M.; Grazzi, L.; La Mantia, L.; Bussone, G. Flunarizine in migraine: A minireview. Headache 1991, 31, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çelebisoy, N.; Gökçay, F.; Karahan, C.; Bilgen, C.; Kirazlı, T.; Karapolat, H.; Köse, T. Acetazolamide in vestibular migraine prophylaxis: A retrospective study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2016, 273, 2947–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reason, J.T. Motion sickness adaptation: A neural mismatch model. J. R. Soc. Med. 1978, 71, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdin, L.; Chamberlain, F.; Cheema, S.; Arshad, Q.; Gresty, M.A.; Golding, J.F.; Bronstein, A. Motion sickness in migraine and vestibular 45. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulmer, E.; Chays, A.; Brémond, G. Nystagmus induit par des vibrations: Physiopathogénie et intérêt en clinique. Ann. Otolaryngol. Chir. Cervicofac. 2004, 121, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, G.; Curthoys, I.S.; Lion, A.; Perrin, P.; Schmerber, S. The Skull Vibration-Induced Nystagmus Test of Vestibular Function—A Review. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batuecas-Caletrío, A.; Martínez-Carranza, R.; García Nuñez, G.M.; Fernández Nava, M.J.; Sánchez Gómez, H.; Santacruz Ruiz, S.; Pérez Guillén, V.; Pérez-Fernández, N. Skull vibration-induced nystagmus in vestibular neuritis. Acta Otolaryngol. 2020, 140, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynard, P.; Idriss, S.; Ltaief-Boudrigua, A.; Bertholon, P.; Pirvan, A.; Truy, E.; Thai-Van, H.; Ionescu, E.C. Proposal for a Unitary Anatomo-Clinical and Radiological Classification of Third Mobile Window Abnormalities. Front. Neurol. 2022, 12, 792545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Ratnayake, S.; Crunkhorn, R.; Iqbal, J.; Strachan, L.; Avula, S. Audiovestibular Quantification in Rare Third Window Disorders in Children. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choung, Y.H.; Park, K.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K. Rare cases of Ménière’s disease in children. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2006, 120, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brantberg, K.; Duan, M.; Falahat, B. Ménière’s disease in children aged 4–7 years. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2012, 132, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlugaiczyk, J.; Habs, M.; Dieterich, M. Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in vestibular migraine and Menière’s disease: cVEMPs make the difference. J. Neurol. 2020, 267 (Suppl. S1), 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Cheon, C. Epidemiology and Seasonal Variation of Ménière’s Disease: Data from a Population-Based Study. Audiol. Neurotol. 2020, 25, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente-Piera, J.; Prieto-Matos, C.; Manrique-Huarte, R.; Garaycochea, O.; Domínguez, P.; Manrique, M. Otic Capsule Dehiscences Simulating Other Inner Ear Diseases: Characterization, Clinical Profile, and Follow-Up—Is Ménière’s Disease the Sole Cause of Vertigo and Fluctuating Hearing Loss? Audiol. Res. 2024, 14, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, L.B. Clinical manifestations of superior semicircular canal dehiscence. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Demographic Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age At Diagnosis | 11.19 ± 5.61 (1–18) years | |
| Genre | 70 (59.82%) Women | 47 (40.17%) Men |
| Follow-Up | 4.33 ± 1.29 (1 month–6.23 years) | |
| Diagnostic | Patients | Spontaneous Nystagmus | SVIN | Altered vHIT | Altered VEMPS | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VM | 48 (41.03%) | n = 6 p value = 0.078 | n = 4 p value = 0.739 | n = 4 p value = 1.000 | n = 14 p value = 0.512 | n = 15 Definitive n = 33 Probable VM |
| RVC | 28 (23.93%) | n = 3 p value = 1.00 | n = 3 p value = 1.00 | n = 1 p value = 1.00 | n = 7 p value = 1.00 | - |
| Idiopathic | 9 (6.84%) | n = 0 p value = 0.571 | n = 0 p value = 0.529 | n = 0 p value = 1.00 | n = 0 p value = 1.00 | - |
| Otic capsule dehiscence | 8 (6.84%) | n = 3 p value = 0.072 | n = 4 p value = 0.051 | n = 4 p = 0.009 | n = 8 p value ≤ 0.001 | n = 4 SSCDS n = 2 EVA n = 1 Perilymphatic fistula and 1 PSC |
| BPPV | 6 (5.13%) | n = 0 p value = 1.00 | n = 1 p value = 1.00 | n = 0 p value = 1.00 | n = 2 p value = 1.00 | n = 2 HSC and 2 PSC n = 2 Multicanal |
| Endolymphatic hydrops | 6 (5.13%) | n = 3 p value = 0.072 | n = 3 p value = 0.153 | n = 3 p value = 0.153 | n = 6 p value ≤ 0.001 | n = 3 Autoimmune ear disease n = 3 definitive MD |
| Acute vestibular syndrome | 4 (3.42%) | n = 4 p = 0.072 | n = 2 p value = 0.003 | n = 3 p value = 0.003 | n = 3 p value = 0.194 | n = 2 Vestibular neuritis n = 2 Laberinthitis |
| Vestibular paroxysmia | 4 (3.42%) | n = 2 p = 0.001 | n = 0 p value = 0.286 | n = 0 p value = 1.00 | n = 2 p value = 1.00 | n = 2 Definitive and 2 Probable VP |
| Central vertigo | 3 (2.56%) | n = 2 p value = 0.070 | n = 2 p value = 0.076 | n = 2 p value = 0.286 | n = 3 p value = 1.00 | n = 1 Multiple sclerosis n = 1 Pilocytic astrocytoma n = 1 Rathke cleft cyst |
| Post cochear implantation | 1 (0.85%) | n = 1 p value = 0.019 | n = 1 p value = 0.033 | n = 0 p value = 0.033 | n = 1 p value = 1.00 | - |
| Diagnostic | Treatment |
|---|---|
| Vestibular migraine | Surveillance = 32 Calcium channel blockers = 6 Triptans = 5 Acetazolamide = 2 Tryptizol = 2 Topiramate = 1 |
| RVC | Surveillance = 17 Vestibular rehabilitation = 7 Antihistamines = 2 Calcium channel blockers = 2 |
| Idiopathic | Surveillance = 5 Vestibular rehabilitation = 4 |
| Otic capsule dehiscence | Surveillance = 4 Surgery for cochlear implantation = 3 Acetazolamide = 1 |
| BPPV | Lempert maneuver = 2 Epley maneuver = 2 Sulpiride = 1 Surveillance = 1 |
| Endolymphatic hydrops | Surgery for cochlear implantation = 3 Surveillance = 2 Acetazolamide = 1 |
| Acute vestibular syndrome | Steroids = 2 Vestibular rehabilitation = 1 Surveillance = 1 |
| Vestibular paroxysmia | Oxcarbazepine = 2 Calcium channel blockers = 2 |
| Central vertigo | Surgery and radiotherapy for astrocytoma = 1 Azetazolamide for IH due to Rathke cyst = 1 Natalizumab for multiple sclerosis = 1 |
| Post cochear implantation | Vestibular rehabilitation = 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorente-Piera, J.; Pérez-Fernández, N.; Blanco-Pareja, M.; Manrique-Huarte, R.; Michael Larenas, P.; Serra, V.; Manrique, M. Clinical Profile, Trends, and Management in Pediatric Patients with Audiovestibular Disorders: Can We Predict Emotional Disability in Pediatric Patients with Episodes of Vertigo and Dizziness? Audiol. Res. 2024, 14, 701-713. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14040059
Lorente-Piera J, Pérez-Fernández N, Blanco-Pareja M, Manrique-Huarte R, Michael Larenas P, Serra V, Manrique M. Clinical Profile, Trends, and Management in Pediatric Patients with Audiovestibular Disorders: Can We Predict Emotional Disability in Pediatric Patients with Episodes of Vertigo and Dizziness? Audiology Research. 2024; 14(4):701-713. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14040059
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorente-Piera, Joan, Nicolás Pérez-Fernández, Melissa Blanco-Pareja, Raquel Manrique-Huarte, Pia Michael Larenas, Valeria Serra, and Manuel Manrique. 2024. "Clinical Profile, Trends, and Management in Pediatric Patients with Audiovestibular Disorders: Can We Predict Emotional Disability in Pediatric Patients with Episodes of Vertigo and Dizziness?" Audiology Research 14, no. 4: 701-713. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14040059
APA StyleLorente-Piera, J., Pérez-Fernández, N., Blanco-Pareja, M., Manrique-Huarte, R., Michael Larenas, P., Serra, V., & Manrique, M. (2024). Clinical Profile, Trends, and Management in Pediatric Patients with Audiovestibular Disorders: Can We Predict Emotional Disability in Pediatric Patients with Episodes of Vertigo and Dizziness? Audiology Research, 14(4), 701-713. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14040059







