Hebrew Digits in Noise (DIN) Test in Cochlear Implant Users and Normal Hearing Listeners
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.1.1. CI Groups
2.1.2. NH Groups
2.2. Speech Perception Measures
2.2.1. Hebrew Digits in Noise (DIN) Test
2.2.2. HAB Words
2.2.3. HeBio Sentence in Quiet
2.2.4. Adaptive HeBio in Noise
2.2.5. Sentences for Children
2.3. Design and Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
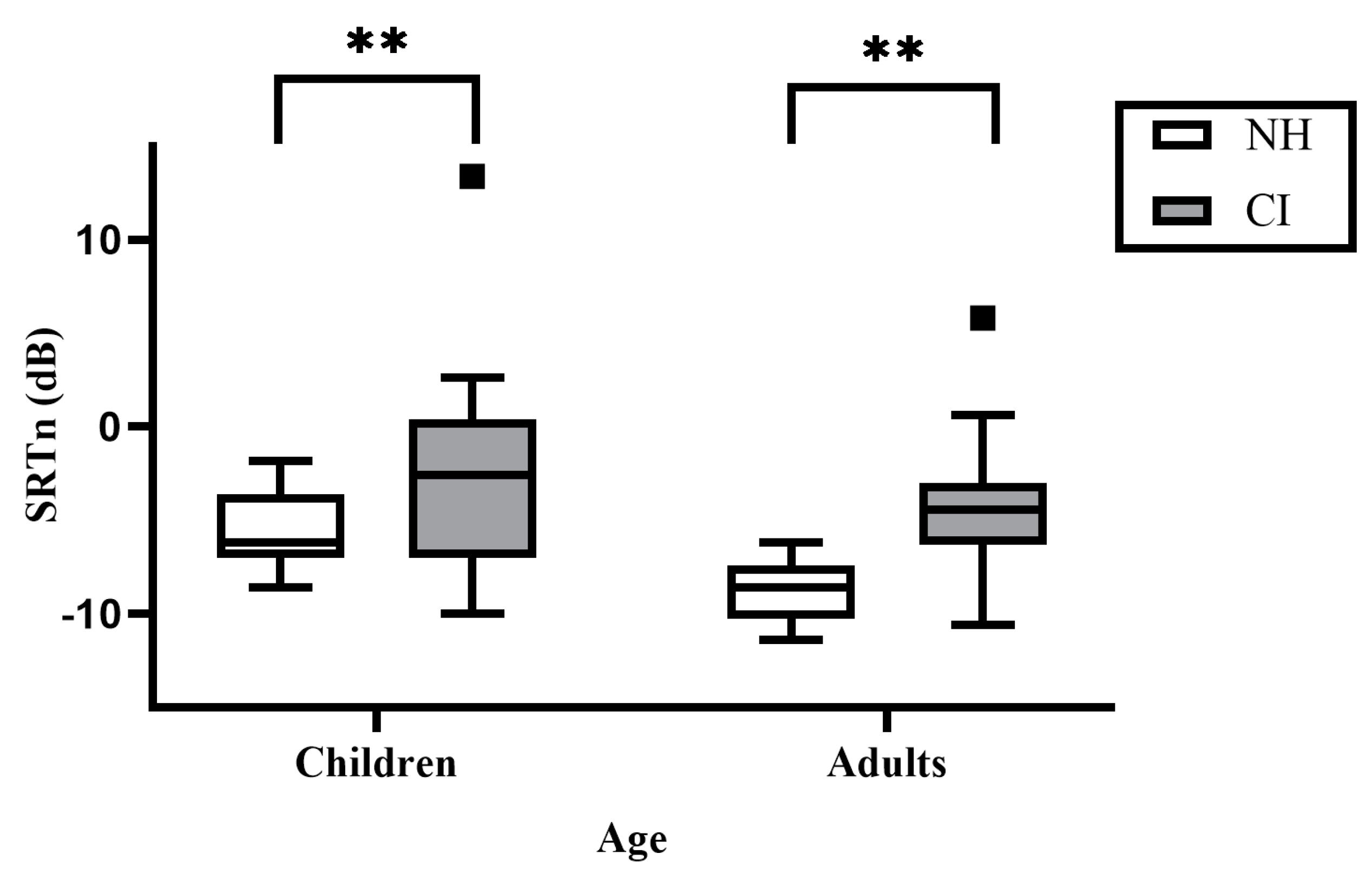
3.1. Hebrew DIN in CI Users and NH Aged-Matched Controls
3.1.1. Age and Hearing Status
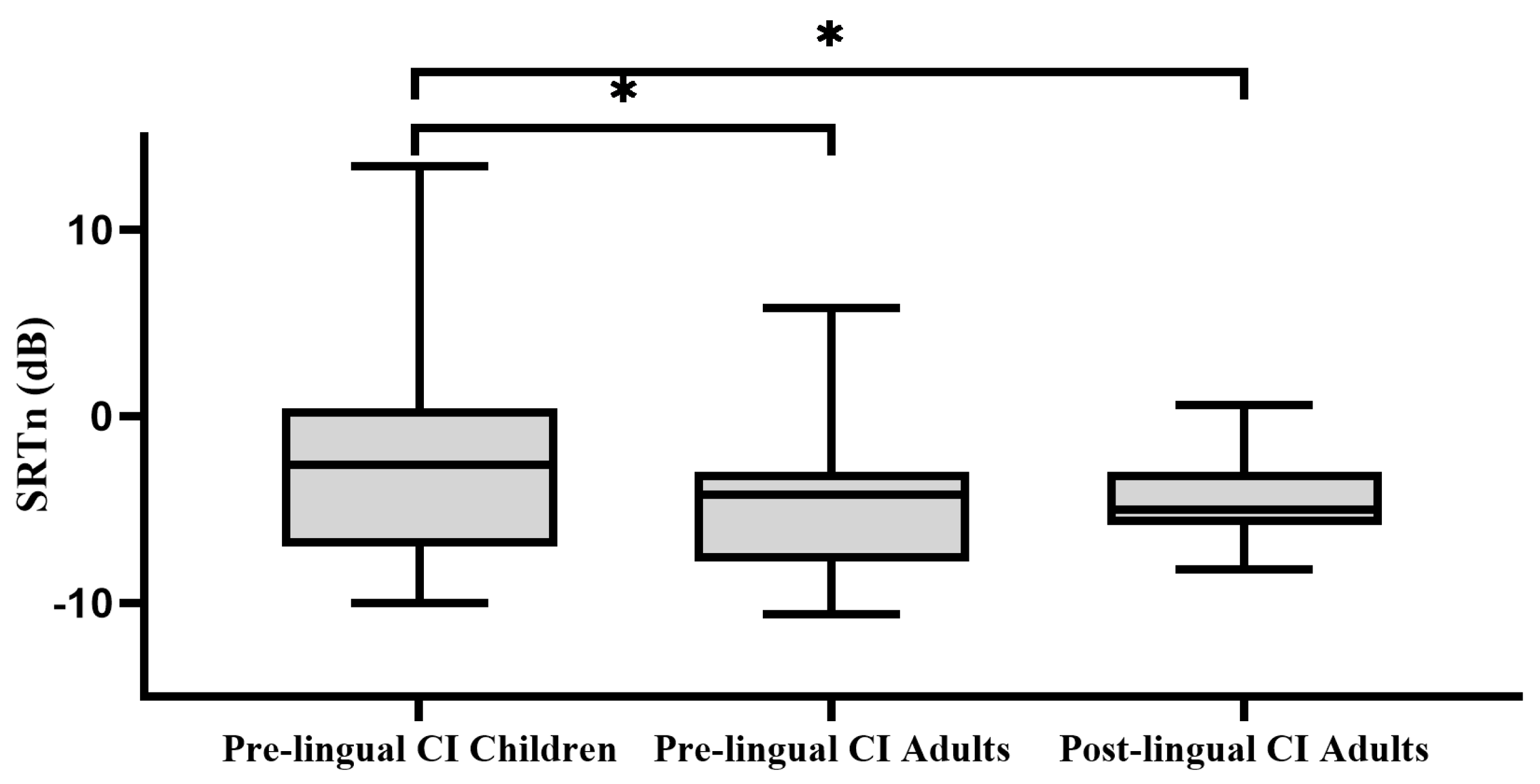
3.1.2. Age and Onset-of-Deafness
3.2. Hebrew DIN and Other Speech Perception Tests
3.2.1. Children
3.2.2. Pre-Lingual CI Users Adults
3.2.3. Post-Lingual CI Adults Users
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| No. | Age (y) | Gender | No. of CIs | Implanted Ear | Age at Onset | Age at 1st CI | Age at 2nd CI | Duration Implant Use (y) | HA Use | Type of CI | Etiology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-lingual CI Children | |||||||||||
| 1 | 7.8 | M | 1 | L | 2.5 | 6.5 | -- | 5.3 | Y | AB | Unknown |
| 2 | 5.9 | M | 1 | L | 1.2 | 1.5 | -- | 4.4 | Y | AB | Meningitis |
| 3 | 7.3 | F | 1 | L | 0 | 0.9 | -- | 6.4 | Y | C | CMV |
| 4 | 6.5 | F | 2 | R, L | 0 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 5.75 | AB | Genetic | |
| 5 | 6.5 | M | 2 | R, L | 0 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 5.1 | AB | Unknown | |
| 6 | 6.4 | F | 2 | R, L | 0 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 5.5 | C | Unknown | |
| 7 | 7.4 | F | 1 | R | 0 | 3.8 | -- | 3.6 | Y | AB | Unknown |
| 8 | 6.6 | M | 2 | R, L | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 5.1 | C | Infection | |
| 9 | 7.9 | M | 2 | R, L | 0 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 7 | C | Genetic | |
| 10 | 5.5 | M | 2 | R, L | 2.3 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 2.4 | C | Meningitis | |
| 11 | 10.5 | F | 2 | R, L | 0 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 9.4 | C | Unknown | |
| 12 | 9.6 | M | 1 | L | 0 | 4.5 | -- | 5.1 | Y | C | CMV |
| 13 | 11 | F | 2 | R, L | 0 | 1 | 4 | 7 | C | Unknown | |
| Pre-lingual CI adults users | |||||||||||
| 1 | 25.5 | F | 2 | R, L | 1.5 | 4 | 14 | 21.5 | C | CMV | |
| 2 | 23 | F | 2 | R, L | 0 | 2 | 13 | 21 | C | Familial | |
| 3 | 23 | F | 2 | R, L | 0 | 2 | 14 | 21 | C | Familial | |
| 4 | 28 | M | 1 | R | 0 | 6 | -- | 22 | C | Unknown | |
| 5 | 30 | F | 2 | R, L | 0 | 3 | 14 | 27 | C | Genetic | |
| 6 | 27 | M | 2 | R, L | 0 | 3 | 26 | 24 | C | Genetic | |
| 7 | 28.5 | F | 1 | R | 0 | 8 | -- | 20.5 | Y | AB | Genetic |
| 8 | 16 | F | 2 | R, L | 0 | 1 | 10 | 15 | C | Unknown | |
| 9 | 16 | M | 2 | R, L | 0 | 1 | 6 | 15 | C | Unknown | |
| 10 | 26 | M | 2 | R, L | 0 | 4 | 25 | 22 | C | Unknown | |
| 11 | 30 | F | 2 | R, L | 0 | 3 | 14 | 27 | C | Familial | |
| 12 | 20 | F | 2 | R, L | 0 | 3 | 7 | 17 | C | Unknown | |
| 13 | 23 | F | 2 | R, L | 0 | 2 | 11 | 21 | C | Unknown | |
| 14 | 15 | F | 2 | R, L | 0 | 1 | 4 | 14 | C | Genetic | |
| 15 | 14 | M | 2 | R, L | 0 | 1.25 | 1.25 | 12.55 | C | Genetic | |
| Post-lingual CI adults users | |||||||||||
| 1 | 36 | F | 1 | L | 15 | 31 | -- | 5 | AB | Unknown | |
| 2 | 49 | F | 1 | L | 32 | 40 | -- | 9 | Y | M | Otosclerosis |
| 3 | 60 | F | 1 | L | 10 | 45 | -- | 15 | C | Genetic | |
| 4 | 22 | F | 1 | R | 14 | 17 | -- | 3 | M | Unknown | |
| 5 | 24 | F | 2 | R, L | 8 | 19 | 21 | 5 | AB | Unknown | |
| 6 | 68 | F | 1 | R | 50 | 64 | -- | 4 | Y | C | Genetic |
| 7 | 55 | F | 1 | L | 35 | 45 | -- | 10 | Y | C | Meniere |
| 8 | 56 | F | 2 | R, L | 18 | 51 | 54 | 5 | M | Unknown | |
| 9 | 62 | M | 2 | R, L | 35 | 59 | 60 | 3 | M | Otosclerosis | |
| 10 | 29 | F | 1 | L | 10 | 28 | -- | 1 | Y | AB | Meningitis |
| 11 | 62 | M | 1 | L | 40 | 58 | -- | 4 | Y | M | Otosclerosis |
| 12 | 77 | F | 1 | R | 47 | 73 | -- | 4 | Y | C | Genetic |
| 13 | 74 | F | 1 | R | 57 | 72 | -- | 2 | Y | AB | Unknown |
| 14 | 60 | F | 1 | L | 38 | 58 | -- | 2 | Y | C | Autoimmune |
| 15 | 32 | F | 1 | R | 10 | 31 | -- | 1 | Y | C | Unknown |
References
- Wilson, B.S. Getting a decent (but sparse) signal to the brain for users of cochlear implants. Hear. Res. 2015, 322, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.G. Celebrating the one millionth cochlear implant. JASA Express Lett. 2022, 2, 077201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, M.L.; Sladen, D.P.; Haynes, D.S.; Driscoll, C.L.; DeJong, M.D.; Erickson, H.C.; Sunderhaus, L.W.; Hedley-Williams, A.; Rosenzweig, E.A.; Davis, T.J.; et al. Evidence for the expansion of pediatric cochlear implant candidacy. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, R.H.; Dorman, M.F.; Shallop, J.K.; Sydlowski, S.A. Evidence for the expansion of adult cochlear implant candidacy. Ear Hear. 2010, 31, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwolan, T.A.; Basura, G. Determining Cochlear Implant Candidacy in Adults: Limitations, Expansions, and Opportunities for Improvement. Semin. Hear. 2021, 42, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, A.; Nittrouer, S. Speech perception in noise by children with cochlear implants. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2013, 56, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, A.G.; Padilla, M.; Shannon, R.V.; Landsberger, D.M. Improving speech perception in noise with current focusing in cochlear implant users. Hear. Res. 2013, 299, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taitelbaum-Swead, R.; Fostick, L. The Effect of Age, Type of Noise, and Cochlear Implants on Adaptive Sentence-in-Noise Task. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taitelbaum-Swead, R.; Dahan, T.; Katzenel, U.; Dorman, M.F.; Litvak, L.M.; Fostick, L. AzBio Sentence test in Hebrew (HeBio): Development, preliminary validation, and the effect of noise. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2022, 23, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönnberg, J.; Lunner, T.; Zekveld, A.; Sörqvist, P.; Danielsson, H.; Lyxell, B.; Dahlström, O.; Signoret, C.; Stenfelt, S.; Pichora-Fuller, M.K.; et al. The Ease of Language Understanding (ELU) model: Theoretical, empirical, and clinical advances. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, C.; Theo Goverts, S.; Festen, J.M. The digits-in-noise test: Assessing auditory speech recognition abilities in noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 1693–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vroegop, J.; Rodenburg-Vlot, M.; Goedegebure, A.; Doorduin, A.; Homans, N.; van der Schroeff, M. The Feasibility and Reliability of a Digits-in-Noise Test in the Clinical Follow-Up of Children With Mild to Profound Hearing Loss. Ear Hear. 2021, 42, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaandorp, M.W.; Smits, C.; Merkus, P.; Goverts, S.T.; Festen, J.M. Assessing speech recognition abilities with digits in noise in cochlear implant and hearing aid users. Int. J. Audiol. 2015, 54, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willberg, T.; Sivonen, V.; Linder, P.; Dietz, A. Comparing the Speech Perception of Cochlear Implant Users with Three Different Finnish Speech Intelligibility Tests in Noise. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fostick, L.; Berlin, M.; Taitelbeum-Swead, R. Digit in Noise Test: Validation in Hebrew. Presented at the 56th Congress of the Israeli Speech, Hearing and Language Association, Tel Aviv, Israel, 12–13 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Boothroyd, A. Statistical theory of the speech discrimination score. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1968, 43, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taitelbaum-Swead, R.; Kishon-Rabin, L.; Kaplan-Neeman, R.; Muchnik, C.; Kronenberg, J.; Hildesheimer, M. Speech perception of children using Nucleus, Clarion or Med-El cochlear implants. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2005, 69, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.; Soli, S.D.; Sullivan, J.A. Development of the Hearing in Noise Test for the measurement of speech reception thresholds in quiet and in noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1994, 95, 1085–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crandell, C.C.; Smaldino, J.J. Classroom Acoustics for Children with Normal Hearing and with Hearing Impairment. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2000, 31, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trau-Margalit, A.; Fostick, L.; Harel-Arbeli, T.; Nissanholtz-Gannot, R.; Taitelbaum-Swead, R. Speech recognition in noise task among children and young-adults: A pupillometry study. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1188485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, C.; Kapteyn, T.S.; Houtgast, T. Development and validation of an automatic speech-in-noise screening test by telephone. Int. J. Audiol. 2004, 43, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullington, H.E.; Aidi, T. Is the digit triplet test an effective and acceptable way to assess speech recognition in adults using cochlear implants in a home environment? Cochlear Implant. Int. 2017, 18, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Graaff, F.; Huysmans, E.; Qazi, O.U.; Vanpoucke, F.J.; Merkus, P.; Goverts, S.T.; Smits, C. The Development of Remote Speech Recognition Tests for Adult Cochlear Implant Users: The Effect of Presentation Mode of the Noise and a Reliable Method to Deliver Sound in Home Environments. Audiol. Neurootol. 2016, 21 (Suppl. 1), 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| CI | NH | F (1,27) | p | Partial η2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Children | |||||
| DIN_SRTn | −1.75 (5.98) | −5.49 (2.18) | 5.08 | 0.033 | 0.17 |
| HAB_quiet | 0.78 (0.09) | 0.97 (0.04) | 52.87 | <0.001 | 0.68 |
| Sentences_quiet | 0.88 (0.10) | 0.97 (0.09) | 5.31 | 0.030 | 0.18 |
| B. Pre-lingual CI adult users | |||||
| DIN_SRTn | −5.15 (2.98) | −9.29 (1.37) | 23.44 | <0.001 | 0.47 |
| HeBio_SRTn | 12.88 (6.91) | −1.55 (1.68) | 61.47 | <0.001 | 0.70 |
| C. Post-lingual CI adult users | |||||
| DIN_SRTn | −4.44 (2.19) | −8.36 (1.53) | 32.26 | <0.001 | 0.54 |
| HeBio_SRTn | 12.03 (5.48) | −0.99 (2.24) | 72.53 | <0.001 | 0.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taitelbaum-Swead, R.; Fostick, L. Hebrew Digits in Noise (DIN) Test in Cochlear Implant Users and Normal Hearing Listeners. Audiol. Res. 2024, 14, 457-468. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14030038
Taitelbaum-Swead R, Fostick L. Hebrew Digits in Noise (DIN) Test in Cochlear Implant Users and Normal Hearing Listeners. Audiology Research. 2024; 14(3):457-468. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14030038
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaitelbaum-Swead, Riki, and Leah Fostick. 2024. "Hebrew Digits in Noise (DIN) Test in Cochlear Implant Users and Normal Hearing Listeners" Audiology Research 14, no. 3: 457-468. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14030038
APA StyleTaitelbaum-Swead, R., & Fostick, L. (2024). Hebrew Digits in Noise (DIN) Test in Cochlear Implant Users and Normal Hearing Listeners. Audiology Research, 14(3), 457-468. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres14030038







