An Adaptation and Validation Study of the Speech, Spatial, and Qualities of Hearing Scale (SSQ) in Italian Normal-Hearing Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Adaptation Procedure
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Participants
2.3.1. Population with Normal Hearing
2.3.2. Hearing-Impaired Population
2.4. Questionnaire Administration
2.4.1. SSQ for Parents
2.4.2. SSQ for Children
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Internal Consistency
3.2. Scale Reliability
3.3. Item Reliability
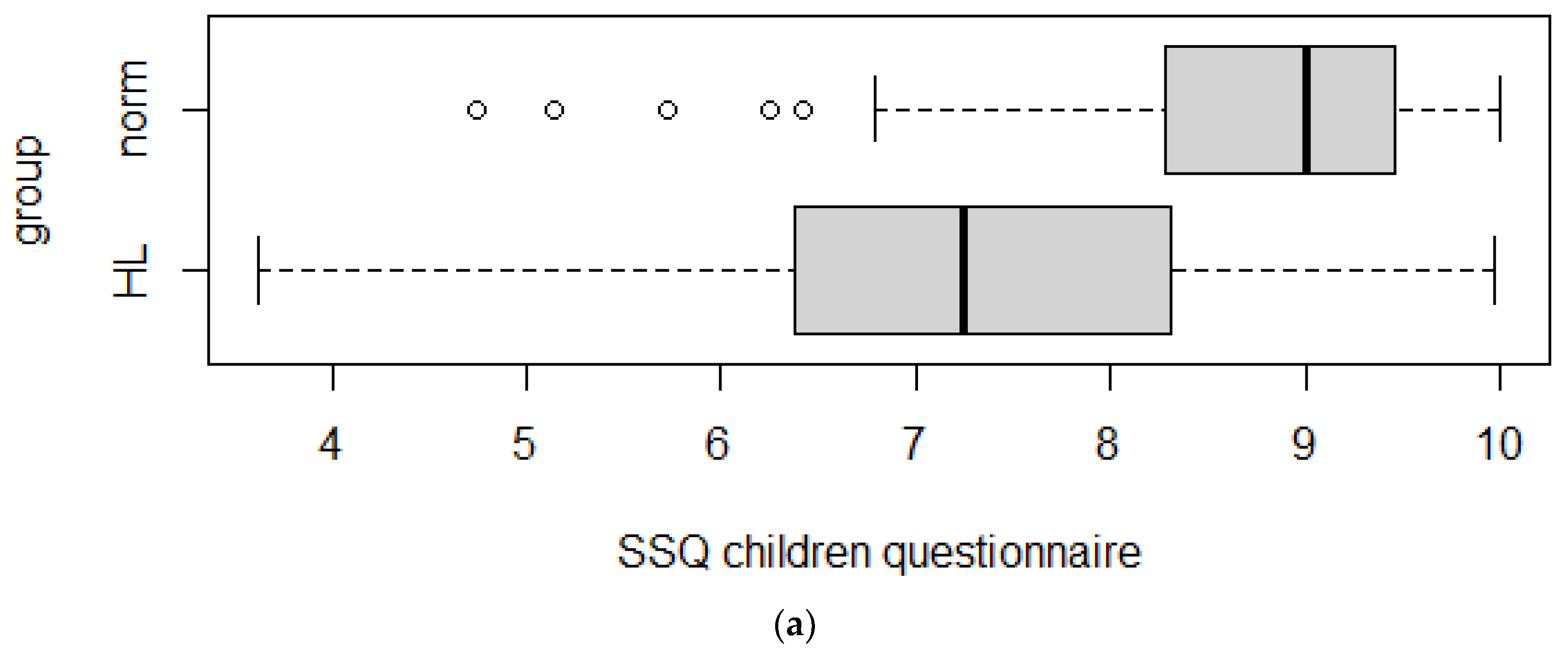
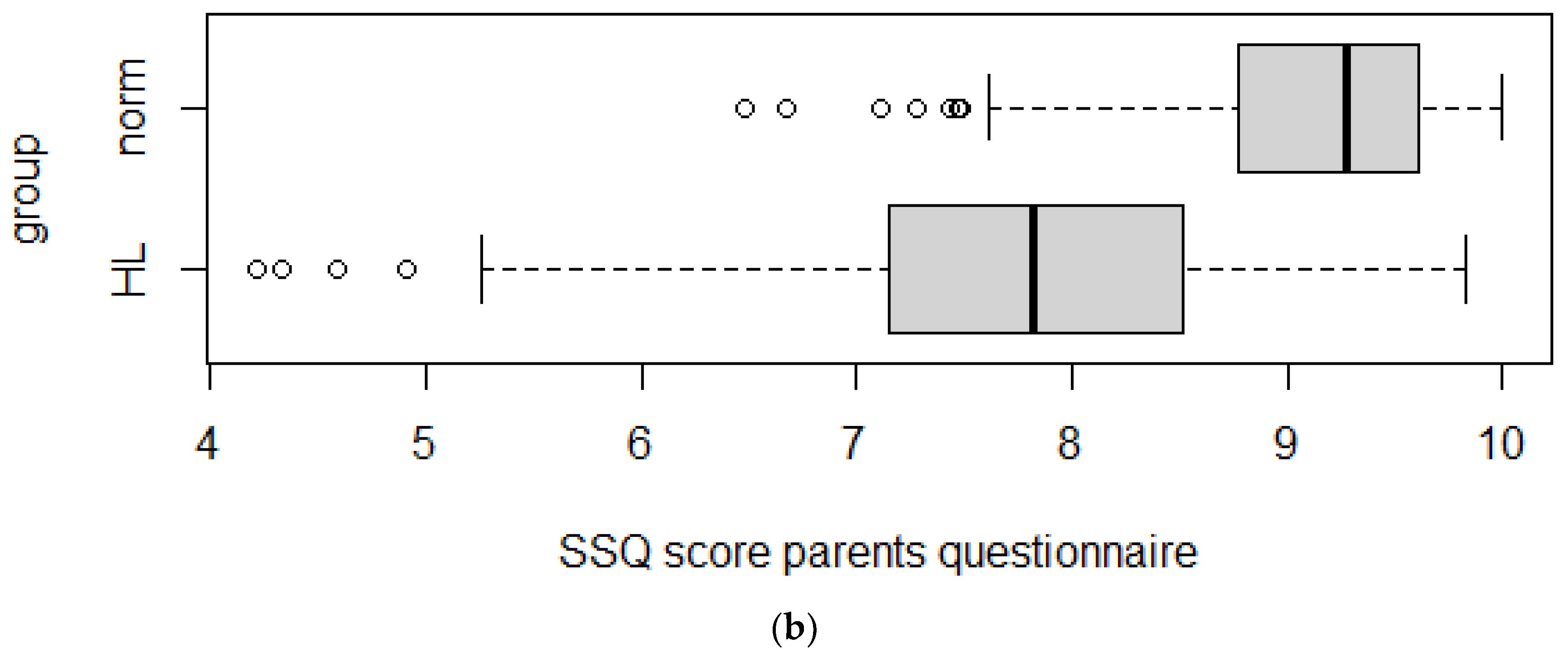
3.4. Discriminant Validity
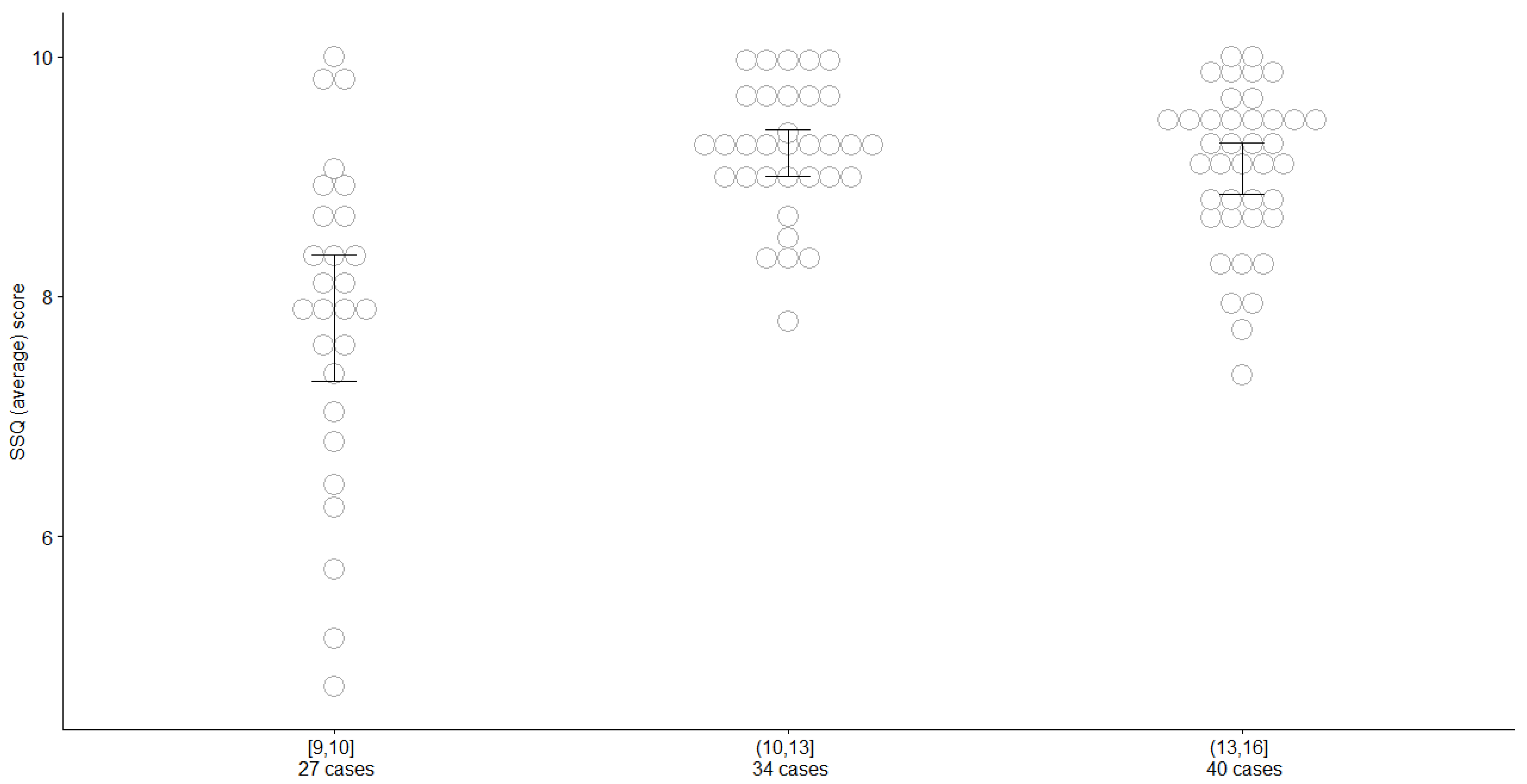
3.5. Analysis of the Impact of Age of Children on Answers
3.6. Correlations between the Children’s Scores and Their Parents’ Scores
- -
- Section A: 0.28 (p-value 0.03);
- -
- Section B: 0.38 (p-value < 0.001);
- -
- Section C: 0.22 (p-value 0.03).
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cox, R.M.; Geers, A.E.; Nicholas, J.G.; Sedey, A.L. Language skills of children with early cochlear implantation. Ear Hear. 2003, 24 (Suppl. S1), 46S–58S. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga-Itano, C.; Sedey, A.L.; Wiggin, M.; Mason, C.A. Language outcomes improved through early hearing detection and earlier cochlear implantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholas, J.G.; Geers, A.E. Effects of early auditory experience on the spoken language of deaf children at 3 years of age. Ear Hear. 2006, 27, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicholas, J.G.; Geers, A.E. Will they catch up? The role of age at cochlear implantation in the spoken language development of children with severe to profound hearing loss. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2007, 50, 1048–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.M. Assessment of subjective outcome of hearing aid fitting: Getting the client’s point of view. Int. J. Audiol. 2003, 42 (Suppl. S1), 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinger, S.D. How to assess outcome of hearing aid fitting in children. Scand. Audiol. 2001, 30 (Suppl. S53), 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagatto, M.P.; Moodie, S.T.; Seewald, R.C.; Bartlett, D.J.; Scollie, S.D. A critical review of audiological outcome measures for infants and children. Trends Amplif. 2011, 15, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MSTB. Minimum Speech Test Battery for Adult Cochlear Implant Users. 2011. Available online: http://www.auditorypotential.com/MSTBfiles/MSTBManual2011-06-20%20.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2019).
- Cavicchiolo, S.; Mozzanica, F.; Guerzoni, L.; Murri, A.; Dall’Ora, I.; Ambrogi, F.; Barozzi, S.; Cuda, D.; Schindler, A. Early prelingual auditory development in Italian infants and toddlers analysed through the Italian version of the Infant-Toddler Meaningful Auditory Integration Scale (IT-MAIS). Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2018, 275, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman-Phillips, S.; Osberger, M.J.; Robbins, A.M. Infant-toddler: Meaningful auditory integration scale (IT-MAIS). In Cochlear Implants for Kids; Estabrooks, W., Ed.; Alexander Graham Bell Association for the Deaf: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, A.M.; Osberger, M.J. Meaningful Use of Speech Scale (MUSS); Indianopolis: Indiana University School of Medicine press: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, A.M.; Renshaw, J.J.; Berry, S.W. Evaluating meaningful auditory integration in profoundly hearing impaired children. Am. J. Otol. 1991, 12, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, A.M.; Koch, D.B.; Osberger, M.J.; Zimmerman-Phillips, S.; Kishon-Rabin, L. Effect of Age at Implantation on Auditory-Skill Development in Infants and Toddlers. In Proceedings of the 9th Symposium on Cochlear Implants in Children, Washington, DC, USA, 24–26 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, R.M.; Alexander, G.C. The abbreviated profile of hearing aid benefit. Ear Hear. 1995, 16, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, S.C.; Farrington, D.R.; Moran, C.A.; Chard, L.L.; Hodgson, S.A. A parental questionnaire to evaluate children’s Auditory Behavior in Everyday Life (ABEL). Am. J. Audiol. 2002, 11, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.L.; Smaldino, J. Children’s home inventory for listening difficulties (CHILD). Educ. Audiol. Rev. 2000, 17, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, K.L.; Smaldino, J. Listening inventories for Education: A classroom measurement tool. Hear. J. 1999, 52, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, K.L.; Noble, W. Adaptation of the speech, spatial, and qualities of hearing scale for use with children, parents, and teachers. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2013, 14, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, W.; Gatehouse, S. Interaural asymmetry of hearing loss, Speech, Spatial and Qualities of Hearing Scale (SSQ) disabilities, and handicap. Int. J. Audiol. 2004, 43, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatehouse, S.; Noble, W. The speech, spatial and qualities of hearing scale (SSQ). Int. J. Audiol. 2004, 43, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, K.L.; Mok, M.; Dowell, R.C. Perceptual benefit and functional outcomes for children using sequential bilateral cochlear implants. Ear Hear. 2007, 28, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, K.L.; Mok, M.; Dowell, R.C.; Briggs, R.J. Speech detection and localization results and clinical outcomes for children receiving sequential bilateral cochlear implants before four years of age. Int. J. Audiol. 2008, 47, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2007 position statement: Principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics 2007, 120, 898–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaton, D.E.; Bombardier, C.; Guillemin, F.; Ferraz, M.B. Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine 2000, 25, 3186–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zijlmans, A.E.; van der Ark, A.L.; Tijmstra, J.; Sijtsma, K. Methods for estimating item-score reliability. Appl. Psychol. Meas. 2018, 42, 553–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual comparisons by ranking methods. Biometrics 1945, 1, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Revelle, W. Psych: Procedures for Personality and Psychological Research; Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 2021; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=psych (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Tavakol, M.; Dennick, R. Making sense of Cronbach’s alpha. Int. J. Med. Educ. 2011, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomczak, M.; Tomczak, E. The need to report effect size estimates revisited. An overview of some recommended measures of effect size. Trends Sport Sci. 2014, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Batthyany, C.; Schut, A.R.; Schroeff, M.; Vroegop, J. Translation and validation of the speech, spatial, and qualities of hearing scale (SSQ) and the hearing environments and reflection on quality of life (HEAR-QL) questionnaire for children and adolescents in Dutch. Int. J. Audiol. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killan, C.F.; Baxter, P.D.; Killan, E.C. Face and content validity of the Speech, Spatial and Qualities of Hearing Scale for Parents (SSQ-P) when used in a clinical service without interviews or week-long observation periods. Int. J. Pediatric Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 133, 109964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeroyd, M.A.; Guy, F.H.; Harrison, D.L.; Suller, S.L. A factor analysis of the SSQ (speech, spatial, and qualities of hearing scale). Int. J. Audiol. 2014, 53, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, A.; Pauzie, A.; Richard, C. Validation of a French translation of the Speech, Spatial, and Qualities of Hearing Scale (SSQ) and comparison with other language versions. Int. J. Audiol. 2015, 54, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangen, A.; Royackers, L.; Desloovere, C.; Wouters, J.; van Wieringen, A. Single-sided deafness affects language and auditory development- a case-control study. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2017, 42, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, A.K.; Arndt, S.; Aschendorff, A.; Beck, R.; Speck, I.; Ketterer, M.C.; Jakob, T.F.; Hassepass, F. Long-term results of cochlear implantation in children with congenital single-sided deafness. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021, 278, 3245–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macıas, A.R.; Borkoski-Barreiro, S.A.; Gonzalez, J.C.F.; Martınez, I.d.; de Miguel, A.R. Single-sided deafness and cochlear implantation in congenital and acquired hearing loss in children. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2019, 44, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canete, O.M.; Purdy, S.C.; Neeff, M.; Brown, C.R.S.; Thorne, P.R. Cortical auditory evoked potential (CAEP) and behavioural measures of auditory function in a child with a single-sided deafness. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2017, 18, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H.; Roh, J.M.; Choo, O.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Park, H.Y.; Choung, Y.H. Critical factors for binaural hearing in children with bilateral sequential cochlear implantation: First implant performance and inter-implant interval. Audiol. Neurotol. 2019, 24, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparreboom, M.; Snik, A.F.; Mylanus, E.A. Sequential bilateral cochlear implantation in children: Quality of life. Arch. Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 2012, 138, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beijen, J.W.; Snik, A.F.; Mylanus, E.A. Sound localization ability of young children with bilateral cochlear implants. Otol. Neurotol. 2007, 28, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Age of Children (Years) | Normal-Hearing Children (No.) | Hearing-Impaired Children (No.) |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | 7 | 12 |
| 7 | 12 | 4 |
| 8 | 12 | 7 |
| 9 | 14 | 3 |
| 10 | 14 | 9 |
| 11 | 11 | 11 |
| 12 | 15 | 8 |
| 13 | 9 | 6 |
| 14 | 17 | 10 |
| 15 | 11 | 3 |
| 16 | 11 | 4 |
| SSQ | Normal Hearing (Median) | Hearing Impaired (Median) | p-Value | Effect Size | Effect Size Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| For parents | 9.28 | 7.80 | <0.001 | 0.64 | Large |
| For children | 9.00 | 7.09 | <0.001 | 0.55 | Large |
| Scale | Normal Hearing (Median) | Hearing Impaired (Median) | p-Value | Effect Size | Effect Size Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Section A (parents) | 9.22 | 7.78 | <0.001 | 0.59 | Large |
| Section A (children) | 9.00 | 7.30 | <0.001 | 0.53 | Large |
| Section B (parents) | 9.17 | 7.33 | <0.001 | 0.58 | Large |
| Section B (children) | 8.85 | 6.89 | <0.001 | 0.47 | Moderate |
| Section C (parents) | 9.38 | 8.12 | <0.001 | 0.48 | Moderate |
| Section C (children) | 9.40 | 7.94 | <0.001 | 0.50 | Large |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Falzone, C.; Guerzoni, L.; Pizzol, E.; Fabrizi, E.; Cuda, D. An Adaptation and Validation Study of the Speech, Spatial, and Qualities of Hearing Scale (SSQ) in Italian Normal-Hearing Children. Audiol. Res. 2022, 12, 297-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres12030031
Falzone C, Guerzoni L, Pizzol E, Fabrizi E, Cuda D. An Adaptation and Validation Study of the Speech, Spatial, and Qualities of Hearing Scale (SSQ) in Italian Normal-Hearing Children. Audiology Research. 2022; 12(3):297-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres12030031
Chicago/Turabian StyleFalzone, Chiara, Letizia Guerzoni, Erica Pizzol, Enrico Fabrizi, and Domenico Cuda. 2022. "An Adaptation and Validation Study of the Speech, Spatial, and Qualities of Hearing Scale (SSQ) in Italian Normal-Hearing Children" Audiology Research 12, no. 3: 297-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres12030031
APA StyleFalzone, C., Guerzoni, L., Pizzol, E., Fabrizi, E., & Cuda, D. (2022). An Adaptation and Validation Study of the Speech, Spatial, and Qualities of Hearing Scale (SSQ) in Italian Normal-Hearing Children. Audiology Research, 12(3), 297-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres12030031







