Tractionless Arthroscopic Treatment of Suspected Hip Septic Arthritis in Adults: A Single-Center Retrospective Case Series with Minimum One-Year Follow-Up
Highlights
- Tractionless arthroscopic treatment achieved significant improvements in pain scores and inflammatory markers with no perioperative complications and no infection recurrence at one-year follow-up.
- Tenosynovial giant cell tumor was identified in one-third of patients, all presenting with negative cultures and clinical features indistinguishable from septic arthritis.
- This technique provides effective infection control while avoiding traction-related complications and requiring only basic arthroscopic equipment.
- Tenosynovial giant cell tumor should be considered in culture-negative suspected hip septic arthritis to guide appropriate treatment decisions.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Pre-Operative Data
2.2.2. Intraoperative Data
2.2.3. Postoperative Outcomes
2.2.4. Antibiotic Protocol
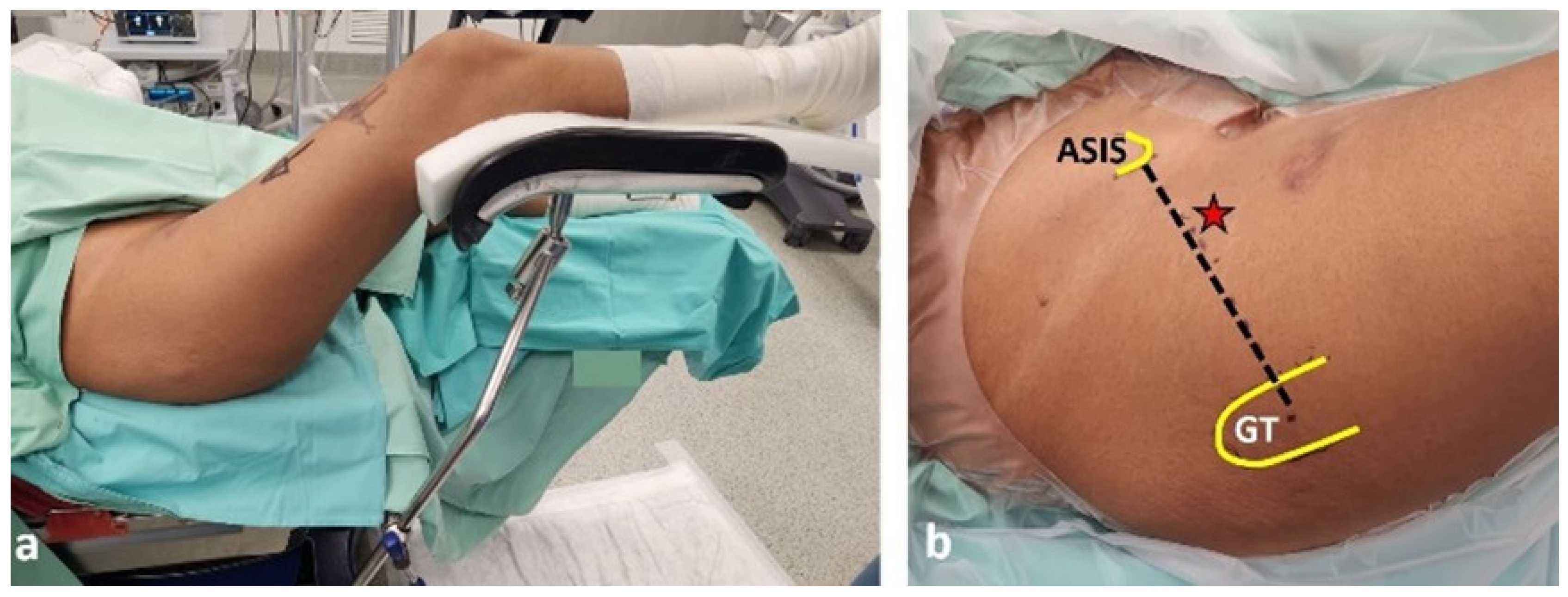
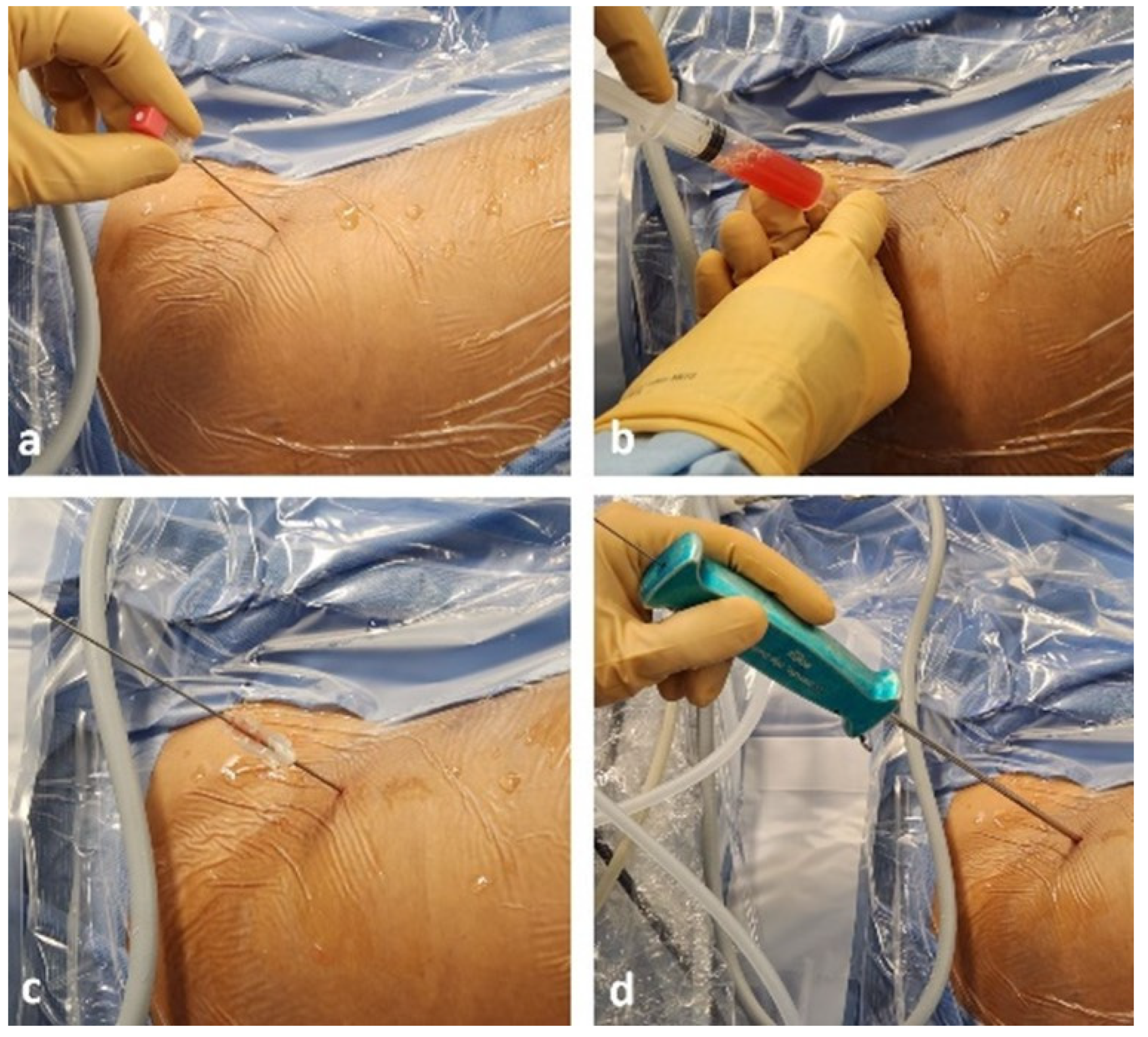
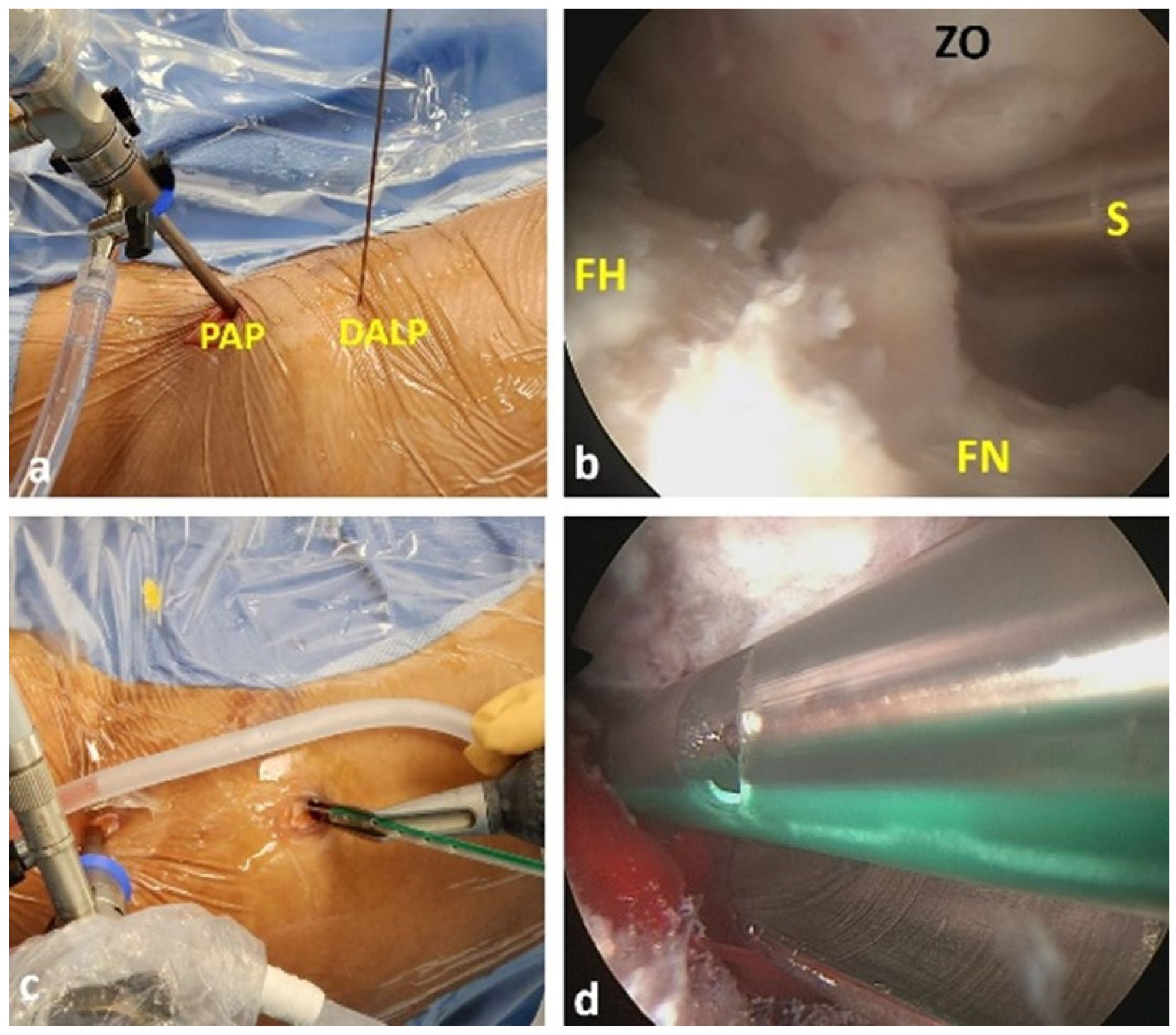
2.3. Surgical Technique
2.4. Adverse Events
2.5. Statistical Analysis
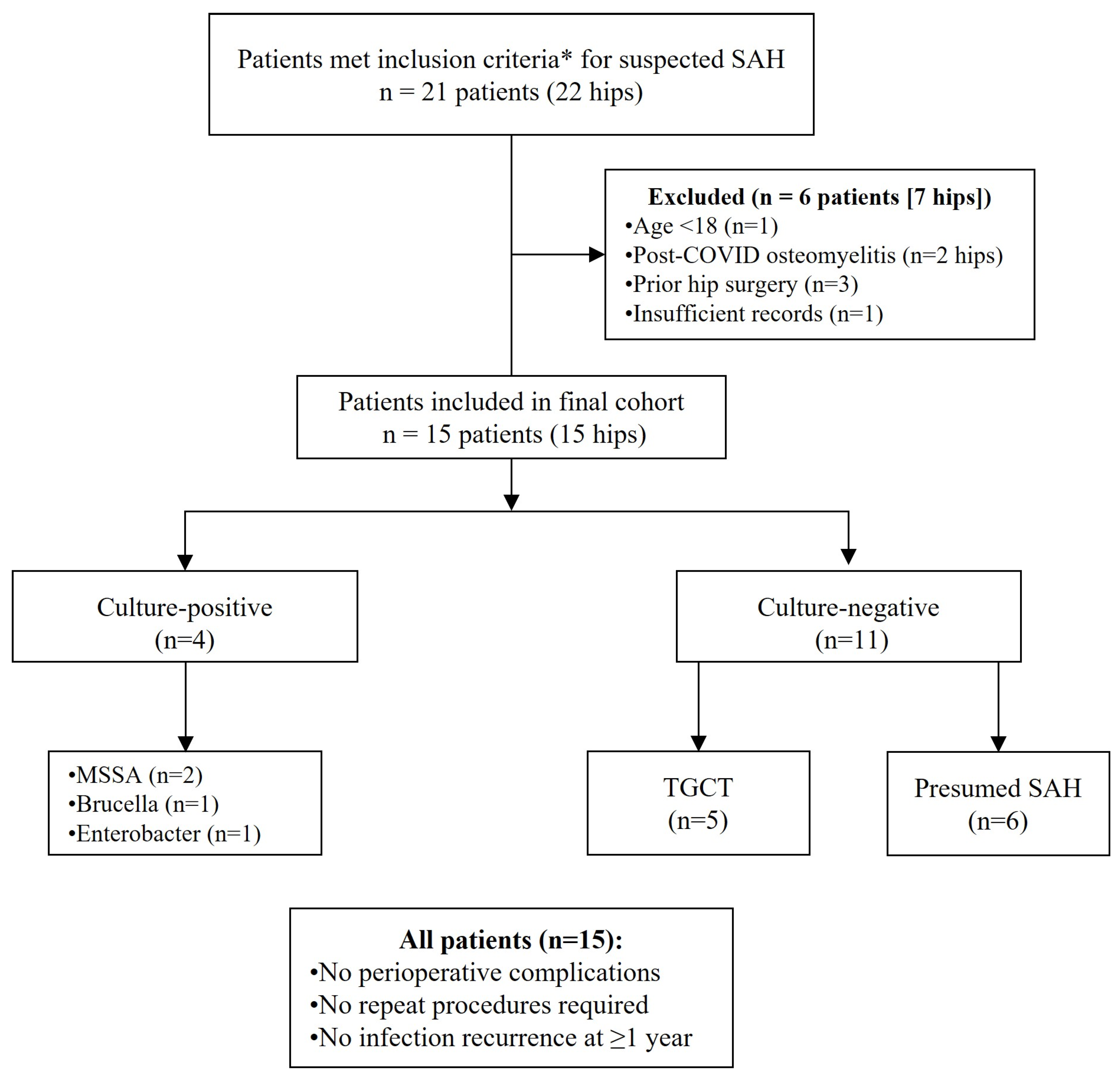
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Clinical Outcomes
3.3. Laboratory Findings
3.4. Microbiological Results
3.5. Treatment Outcomes and Follow-Up
3.6. Incidental Findings
3.7. Complications
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathews, C.J.; Weston, V.C.; Jones, A.; Field, M.; Coakley, G. Bacterial septic arthritis in adults. Lancet 2010, 375, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, F.C.; Hsu, Y.C.; Liu, P.H.; Tu, Y.K.; Jou, I.M. High 2-year mortality and recurrent infection rates after surgical treatment for primary septic arthritis of the hip in adult patients: An observational study. Medicine 2019, 98, e16765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.G.; Gross, J.M.; Dahl, J.D.; Amsdell, S.L.; Gorczyca, J.T. Risk Factors for Failure of a Single Surgical Debridement in Adults with Acute Septic Arthritis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2015, 97, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Miyahara, H.; Helito, C.P.; Oliva, G.B.; Aita, P.C.; Croci, A.T.; Vicente, J.R.N. Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of septic arthritis of the hip, 2006 to 2012, a seven-year review. Clinics 2014, 69, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, F.; Monestier, L.; Zagra, L. Active septic arthritis of the hip in adults: What’s new in the treatment? A systematic review. EFORT Open Rev. 2021, 6, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sa, D.; Cargnelli, S.; Catapano, M.; Peterson, D.; Simunovic, N.; Larson, C.M.; Ayeni, O.R. Efficacy of Hip Arthroscopy for the Management of Septic Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2015, 31, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lum, Z.C.; Shieh, A.K.; Meehan, J.P. Native Adult Hip with Bacterial Septic Arthritis. JBJS Rev. 2018, 6, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazi, Z.M.; Cates, W.T.; An, Q.; Duchman, K.R.; Wolf, B.R.; Westermann, R.W. Arthroscopy Versus Open Arthrotomy for Treatment of Native Hip Septic Arthritis: An Analysis of 30-Day Complications. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2020, 36, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Uekusa, Y.; Koyama, T.; Ohashi, Y.; Uchiyama, K.; Takahira, N.; Takaso, M. Efficacy and safety of arthroscopic treatment for native acute septic arthritis of the hip joint in adult patients. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavasiliou, A.V.; Bardakos, N.V. Complications of arthroscopic surgery of the hip. Bone Jt. Res. 2012, 1, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, L.R.; Oetgen, M.; Noonan, B.; Medvecky, M. Beginning Hip Arthroscopy: Indications, Positioning, Portals, Basic Techniques, and Complications. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2007, 23, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, N.; Lisenda, L.; Jones, T.L.; Loveday, D.T.; Khanduja, V. Complications following arthroscopic surgery of the hip: A systematic review of 36,761 cases. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 99, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei-Dan, O.; Kraeutler, M.J.; Garabekyan, T.; Goodrich, J.A.; Young, D.A. Hip Distraction Without a Perineal Post: A Prospective Study of 1000 Hip Arthroscopy Cases. Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraeutler, M.J.; Fasulo, S.M.; Dávila Castrodad, I.M.; Mei-Dan, O.; Scillia, A.J. A Prospective Comparison of Groin-Related Complications After Hip Arthroscopy With and Without a Perineal Post. Am. J. Sports Med. 2023, 51, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.M.; Zamora, R.A. Surgical Options and Approaches for Septic Arthritis of the Native Hip and Knee Joint. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, S14–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenberg, D.L. Septic arthritis. Lancet 1998, 351, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilizaliturri, V.M. Complications of Arthroscopic Femoroacetabular Impingement Treatment: A Review. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.M.M. Treatment of early septic arthritis of the hip in children: Comparison of results of open arthrotomy versus arthroscopic drainage. J. Child. Orthop. 2008, 2, 229–237. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, H.B.; Copley, L.; Pennock, A.; Nepple, J.J.; Willimon, C.; Mayer, S.W.; Yen, Y.M. Tractionless Hip Arthroscopy for Septic Arthritis in Children. Arthrosc. Tech. 2021, 10, e659–e667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Park, K.S.; Ha, Y.C.; Koo, K.H. Arthroscopic treatment for acute septic arthritis of the hip joint in adults. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.J. Septic Arthritis of Native Joints. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 31, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaretten, M.E.; Kohlwes, J.; Moore, D.; Bent, S. Does This Adult Patient Have Septic Arthritis? JAMA 2007, 297, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.H. Review of septic arthritis throughout the antibiotic era. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1976, 35, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, N.; Amit, S.; Geffen, Y.; Adler, A. Clinical utility of pan-microbial PCR assays in the routine diagnosis of infectious diseases. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 93, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wettstein, M.; Dienst, M. Arthroscopy of the Peripheral Compartment of the Hip. Oper. Tech. Orthop. 2005, 15, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornero, E.; Morata, L.; Martínez-Pastor, J.C.; Bori, G.; Climent, C.; García-Velez, D.M.; García-Ramiro, S.; Bosch, J.; Mensa, J.; Soriano, A. KLIC-score for predicting early failure in prosthetic joint infections treated with debridement, implant retention and antibiotics. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 786.e9–786.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovonratwet, P.; Nelson, S.J.; Bellamkonda, K.; Ondeck, N.T.; Shultz, B.N.; Medvecky, M.J.; Grauer, J.N. Similar 30-Day Complications for Septic Knee Arthritis Treated With Arthrotomy or Arthroscopy: An American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Analysis. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2018, 34, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, A.; Raza, A.; Jameson, S.; James, P.; Reed, M.R.; Partington, P.F. Complications and Survival Analyses of Hip Arthroscopies Performed in the National Health Service in England: A Review of 6,395 Cases. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2015, 31, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetanovich, G.L.; Chalmers, P.N.; Levy, D.M.; Mather, R.C.; Harris, J.D.; Bush-Joseph, C.A.; Nho, S.J. Hip Arthroscopy Surgical Volume Trends and 30-Day Postoperative Complications. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2016, 32, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.T.; Pugely, A.J.; Gao, Y.; Wolf, B.R. Risk Factors for Thirty-Day Morbidity and Mortality Following Knee Arthroscopy: A Review of 12,271 Patients from the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Database. JBJS 2013, 95, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.T.; Gao, Y.; Pugely, A.J.; Wolf, B.R. 30-day morbidity and mortality after elective shoulder arthroscopy: A review of 9410 cases. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2013, 22, 1667–1675.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, C.A.; Pugely, A.J.; Gao, Y.; Westermann, R.R.; Martin, C.T.; Wolf, B.R.; Amendola, A. Complications and Risk Factors for Morbidity in Elective Hip Arthroscopy: A Review of 1325 Cases. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2014, 32, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar]
- Domb, B.G.; Philippon, M.J.; Giordano, B.D. Arthroscopic Capsulotomy, Capsular Repair, and Capsular Plication of the Hip: Relation to Atraumatic Instability. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2013, 29, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhns, B.D.; Weber, A.E.; Levy, D.M.; Bedi, A.; Mather, R.C.; Salata, M.J.; Nho, S.J. Capsular Management in Hip Arthroscopy: An Anatomic, Biomechanical, and Technical Review. Available online: http://journal.frontiersin.org/Article/10.3389/fsurg.2016.00013/abstract (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- Schröder, J.H.; Krüger, D.; Perka, C.; Hufeland, M. Arthroscopic Treatment for Primary Septic Arthritis of the Hip in Adults. Adv. Orthop. 2016, 2016, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.; Beniwal, S.K.; Sinha, S. Outcome of arthroscopic drainage and debridement with continuous suction irrigation technique in acute septic arthritis. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma. 2014, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.D.; McCormick, F.M.; Abrams, G.D.; Gupta, A.K.; Ellis, T.J.; Bach, B.R.; Bush-Joseph, C.A.; Nho, S.J. Complications and Reoperations During and After Hip Arthroscopy: A Systematic Review of 92 Studies and More Than 6000 Patients. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2013, 29, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienst, M.; Seil, R.; Kohn, D.M. Safe Arthroscopic Access to the Central Compartment of the Hip. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2005, 21, 1510–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.W.T. Avoiding the labrum in hip arthroscopy. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2000, 16, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, L.; Lund, B.; Grønbech Nielsen, T.; Lind, M. Traction-related problems after hip arthroscopy. J. Hip Preserv. Surg. 2017, 4, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Redmond, J.M.; Hammarstedt, J.E.; Schwindel, L.; Domb, B.G. Safety Measures in Hip Arthroscopy and Their Efficacy in Minimizing Complications: A Systematic Review of the Evidence. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2014, 30, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, M.J.; Murray, R.S.; Sherman, T.I.; Postma, W.F. Incidence of Nerve Injury After Hip Arthroscopy. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2018, 26, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, H.D.; Palmer, I.J.; Champlin, K.; Kaiser, B.; Kelly, B.; Leunig, M. Physiological Changes as a Result of Hip Arthroscopy Performed With Traction. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2012, 28, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, D.J.; De Sa, D.; Simunovic, N.; Bhandari, M.; Safran, M.R.; Larson, C.M.; Ayeni, O.R. The Learning Curve for Hip Arthroscopy: A Systematic Review. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2014, 30, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.K.; Ha, Y.C.; Hwang, D.S.; Koo, K.H. Learning curve of basic hip arthroscopy technique: CUSUM analysis. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2013, 21, 1940–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Chamberlin, P.; Marx, R.G.; Hidaka, C.; Ge, Y.; Nawabi, D.H.; Lyman, S. Defining the Learning Curve for Hip Arthroscopy: A Threshold Analysis of the Volume-Outcomes Relationship. Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hip No. | Sex | Age (Years) | LOS (Days) | Relevant History | Days of Symp. Prior to Op | Fever at ER | WBC Syn. (Cells/µL) | Blood WBC (×103 Cells/µL) | Blood CRP (mg/L) | VAS Score | Pre-Op Syn. Culture | Bacteremia | Intra-Op Culture | Total Abx Tx (Wk) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Op | D/C * | Pre-Op | D/C * | Pre-Op | D/C * | ||||||||||||
| 1 (TGCT) | F | 28 | 19 | None | 9 | No | 38,000 | 8.2 | 8.5 | 35 | <5 | 6 | 0 | NI | - | NI (+ PM-PCR) | 2 |
| 2 (TGCT) | F | 20 | 7 | None | 2 | Yes | 50,500 | 15.2 | 10 | 49 | <5 | 8 | 0 | NI | - | NI (+ PM-PCR) | 1.3 |
| 3 (TGCT) | F | 34 | 10 | None | 3 | No | 82,500 | 14 | 8 | 65 | <5 | 8 | 0 | NI | - | NI | 2.5 |
| 4 | M | 25 | 10 | None | 3 | Yes | 8000 | 5.6 | 6.4 | 45 | 9 | 6 | 0 | B. melitensis | + | B. melitensis | 12 |
| 5 (TGCT) | F | 33 | 3 | None | 2 | No | 120,000 | 10.7 | 4.6 | 124 | <5 | 9 | 3 | NI | - | NI | 0.4 |
| 6 (TGCT) | F | 29 | 9 | None | 7 | No | 115,000 | 8.1 | 9 | 112 | 5 | 9 | 3 | NI | - | NI (+ PM-PCR) | 0.5 |
| 7 | M | 42 | 12 | None | 2 | No | 88,000 | 12.4 | 7.7 | 151 | 9 | 7 | 1 | NI | - | NI (+ PM-PCR) | 4 |
| 8 | F | 21 | 9 | IBD | 3 | No | 184,000 | 8.5 | 8 | 115 | <5 | 7 | 1 | NI | - | NI (+ PM-PCR) | 4 |
| 9 | F | 28 | 9 | RA | 1 | No | 164,000 | 11.4 | 8 | 170 | <5 | 6 | 1 | NI | - | NI (+ PM-PCR) | 4 |
| 10 | F | 56 | 10 | None | 3 | No | 54,000 | 15.3 | 8.7 | 100 | <5 | 7 | 3 | NI | - | NI (+ PM-PCR) | 1.3 |
| 11 | F | 37 | 32 | IVDU, HCV | 5 | Yes | 28,000 | 17.2 | 6 | 54 | <5 | 6 | 2 | NI | - | NI | 6 |
| 12 | M | 48 | 9 | TTP | 2 | No | 70,000 | 15 | 9.6 | 180 | 6 | 8 | 1 | Enterobacter spp. | - | NI | 6 |
| 13 | M | 26 | 8 | Psoriasis | 3 | No | 70,000 | 8.1 | 6.3 | 131 | <5 | 7 | 0 | NI | - | NI | 10 |
| 14 | M | 63 | 14 | Colonoscopy 1 day prior to onset of symp. | 7 | Yes | 53,000 | 12.3 | 9.1 | 152 | 6 | 6 | 2 | MSSA | + | MSSA | 6 |
| 15 | M | 76 | 14 | UTI prior to onset of symp.; DM, BPH | 2 | No | NS (Insufficient fluid) | 9.2 | 7.4 | 206 | <5 | 10 | 3 | MSSA | + | MSSA | 6 |
| Parameter | Pre-Operative | At Discharge * | p Value † |
|---|---|---|---|
| All patients (n = 15) | |||
| CRP (mg/L), median (range) | 115 (35–206) | <5 (<5–9) | <0.001 |
| VAS Score, median (range) | 7.0 (6–10) | 1.0 (0–3) | <0.001 |
| WBC > 11,000/µL, n (%) | 8 (53.3) | 0 (0.0) | NA ‡ |
| Fever > 38 °C, n (%) | 4 (26.7) | 0 (0.0) | NA ‡ |
| Septic patients (n = 10) | |||
| CRP (mg/L), median (range) | 141 (45–206) | <5 (<5–9) | <0.001 |
| VAS Score, median (range) | 7.0 (6–10) | 1.0 (0–3) | <0.001 |
| WBC > 11,000 Cells/µL, n (%) | 6 (60.0) | 0 (0.0) | NA ‡ |
| Fever > 38 °C, n (%) | 3 (30.0) | 0 (0.0) | NA ‡ |
| Parameter | Current Study—Septic Cases | Fukushima et al. [9] | Lee et al. [20] | Schröder et al. [35] | Shukla et al. [6,36] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Type | Case Series | Case Series | Case Series | Case Series | Case Series |
| Sample Size | 10 hips | 5 hips | 9 hips | 7 hips | 5 hips |
| Culture Positive Rate | 40% | 80% | 44.4% | 71.4% | 50% |
| Hospital Stay (days) | 8–32 | 20–56 | 7–34 | 7–16 | 9–24 |
| 30-day Complications | 0% | NR | No major complications | 0% | 0% |
| Additional Procedures | 0% | 0% | 10% | 0 | 0% |
| Follow-up (Months) | >12 | 40.2 (16–60) | Median, 18 (16–28) | 26.4 (13–66) | 3 (NR) |
| Tractionless Arthroscopy | Traditional Arthroscopy | Open Arthrotomy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical Aspects | |||
| Surgical approach | Minimally invasive | Minimally invasive | Open |
| Traction requirements | None | Required | None |
| Peripheral compartment access | Complete | Complete | Complete |
| Central compartment access | Limited | Complete | Limited |
| Visualization of articular surfaces | Limited | Comprehensive | Limited |
| Clinical Outcomes | |||
| Infection control rate | 100% | 90–100% | 85–95% |
| Return to OR rate | 0% | 0–10% | 5–15% |
| Risk Profile | |||
| Traction-related complications | None | 4–13% * | None |
| Iatrogenic chondral/labral injury | Not reported | 12–68% | Not reported |
| Capsular violation | Minimal | Minimal | Extensive |
| Practical Considerations | |||
| Learning curve † | Moderate [44] | Steep [44,45] | Standard [44,46] |
| Equipment requirements ‡ | Basic | Specialized | Standard surgical set |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Graif, N.; Atzmon, R.; Steen, A.; Factor, S.; Belmont, S.; Dekel, M.; Rath, E.; Amar, E. Tractionless Arthroscopic Treatment of Suspected Hip Septic Arthritis in Adults: A Single-Center Retrospective Case Series with Minimum One-Year Follow-Up. Surg. Tech. Dev. 2025, 14, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/std14040043
Graif N, Atzmon R, Steen A, Factor S, Belmont S, Dekel M, Rath E, Amar E. Tractionless Arthroscopic Treatment of Suspected Hip Septic Arthritis in Adults: A Single-Center Retrospective Case Series with Minimum One-Year Follow-Up. Surgical Techniques Development. 2025; 14(4):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/std14040043
Chicago/Turabian StyleGraif, Nadav, Ran Atzmon, Aimee Steen, Shai Factor, Samuel Belmont, Michal Dekel, Ehud Rath, and Eyal Amar. 2025. "Tractionless Arthroscopic Treatment of Suspected Hip Septic Arthritis in Adults: A Single-Center Retrospective Case Series with Minimum One-Year Follow-Up" Surgical Techniques Development 14, no. 4: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/std14040043
APA StyleGraif, N., Atzmon, R., Steen, A., Factor, S., Belmont, S., Dekel, M., Rath, E., & Amar, E. (2025). Tractionless Arthroscopic Treatment of Suspected Hip Septic Arthritis in Adults: A Single-Center Retrospective Case Series with Minimum One-Year Follow-Up. Surgical Techniques Development, 14(4), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/std14040043







